## Practical Ultra Lightweight Classification scheme PULC
------
## Catalogue
- [1. Introduction of PULC solution](#1)
- [2. Data preparation](#2)
- [2.1 Dataset format description](#2.1)
- [2.2 Annotation file generation method](#2.2)
- [3. Training with standard classification configuration](#3)
- [3.1 PP-LCNet as backbone](#3.1)
- [3.2 SSLD pretrained model](#3.2)
- [3.3 EDA strategy](#3.3)
- [3.4 SKL-UGI knowledge distillation](#3.4)
- [3.5 Summary](#3.5)
- [4. Hyperparameters Searching](#4)
- [4.1 Search based on default configuration](#4.1)
- [4.2 Custom search configuration](#4.2)
### 1. Introduction of PULC solution
Image classification is one of the basic algorithms of computer vision, and it is also the most common algorithm in enterprise applications, and further, it is also an important part of many CV applications. In recent years, the backbone network model has developed rapidly, and the accuracy record of ImageNet has been continuously refreshed. However, the performance of these models in practical scenarios is sometimes unsatisfactory. On the one hand, models with high precision tend to have large storage and slow inference speed, which are often difficult to meet actual deployment requirements; on the other hand, after selecting a suitable model, experienced engineers are often required to adjust parameters, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. In order to solve the problems of enterprise application and make the training and parameter adjustment of classification models easier, PaddleClas summarized and launched a Practical Ultra Lightweight Classification (PULC) solution. PULC integrates various state-of-the-art algorithms such as backbone network, data augmentation and distillation, etc., and finally can automatically obtain a lightweight and high-precision image classification model.
The PULC solution has been verified to be effective in many scenarios, such as human-related scenarios, car-related scenarios, and OCR-related scenarios. With an ultra-lightweight model, the accuracy close to SwinTransformer can be achieved, and the inference speed can be 40+ times faster.
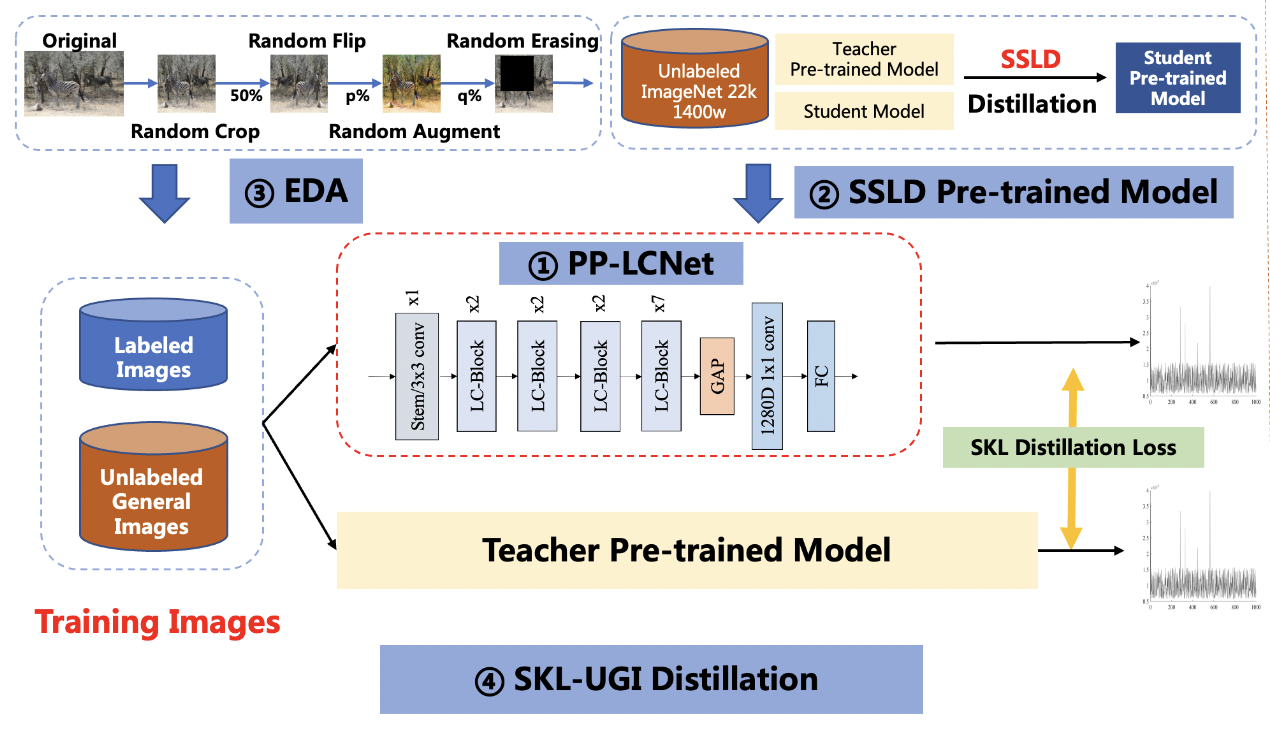
The solution mainly includes 4 parts, namely: PP-LCNet lightweight backbone network, SSLD pre-trained model, Ensemble Data Augmentation (EDA) and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation algorithm. In addition, we also adopt the method of hyperparameters searching to efficiently optimize the hyperparameters in training. Below, we take the person exists or not scene as an example to illustrate the solution.
**Note**:For some specific scenarios, we provide basic training documents for reference, such as [person exists or not classification model](PULC_person_exists_en.md), etc. You can find these documents [here](./PULC_model_list_en.md). If the methods in these documents do not meet your needs, or if you need a custom training task, you can refer to this document.
### 2. Data preparation
#### 2.1 Dataset format description
PaddleClas uses the `txt` format file to specify the training set and validation set. Take the person exists or not scene as an example, you need to specify `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` as the data labels of the training set and validation set. The format is in the form of as follows:
```
# Each line uses "space" to separate the image path and label
train/1.jpg 0
train/10.jpg 1
...
```
If you want to get more information about common classification datasets, you can refer to the document [PaddleClas Classification Dataset Format Description](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
#### 2.2 Annotation file generation method
If you already have the data in the actual scene, you can label it according to the format in the previous section. Here, we provide a script to quickly generate annotation files. You only need to put different categories of data in folders and run the script to generate annotation files.
First, assume that the path where you store the data is `./train`, `train/` contains the data of each category, the category number starts from 0, and the folder of each category contains specific image data.
```shell
train
├── 0
│ ├── 0.jpg
│ ├── 1.jpg
│ └── ...
└── 1
├── 0.jpg
├── 1.jpg
└── ...
└── ...
```
```shell
tree -r -i -f train | grep -E "jpg|JPG|jpeg|JPEG|png|PNG" | awk -F "/" '{print $0" "$2}' > train_list.txt
```
Among them, if more image name suffixes are involved, the content after `grep -E` can be added, and the `2` in `$2` is the level of the category number folder.
**Note:** The above is an introduction to the method of dataset acquisition and generation. Here you can directly download the person exists or not scene data to quickly start the experience.
Go to the PaddleClas directory.
```
cd path_to_PaddleClas
```
Go to the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the data.
```shell
cd dataset
wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/person_exists.tar
tar -xf person_exists.tar
cd ../
```
### 3. Training with standard classification configuration
#### 3.1 PP-LCNet as backbone
PULC adopts the lightweight backbone network PP-LCNet, which is 50% faster than other networks with the same accuracy. You can view the detailed introduction of the backbone network in [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md).
The command to train with PP-LCNet is:
```shell
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
--gpus="0,1,2,3" \
tools/train.py \
-c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0_search.yaml
```
For performance comparison, we also provide configuration files for the large model SwinTransformer_tiny and the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, which you can train with the command:
SwinTransformer_tiny:
```shell
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
--gpus="0,1,2,3" \
tools/train.py \
-c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/SwinTransformer_tiny_patch4_window7_224.yaml
```
MobileNetV3_small_x0_35:
```shell
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
--gpus="0,1,2,3" \
tools/train.py \
-c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/MobileNetV3_small_x0_35.yaml
```
The accuracy of the trained models is compared in the following table.
| Model | Tpr(%) | Latency(ms) | Storage Size(M) | Strategy |
|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
| SwinTranformer_tiny | 95.69 | 95.30 | 107 | Use ImageNet pretrained model|
| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 68.25 | 2.85 | 1.6 | Use ImageNet pretrained model |
| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 89.57 | 2.12 | 6.5 | Use ImageNet pretrained model |
It can be seen that PP-LCNet is much faster than SwinTransformer, but the accuracy is also slightly lower. Below we improve the accuracy of the PP-LCNet model through a series of optimizations.
#### 3.2 SSLD pretrained model
SSLD is a semi-supervised distillation algorithm developed by Baidu. On the ImageNet dataset, the model accuracy can be improved by 3-7 points. You can find a detailed introduction in [SSLD introduction](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md). We found that using SSLD pre-trained weights can effectively improve the accuracy of the applied classification model. In addition, using a smaller resolution in training can effectively improve model accuracy. At the same time, we also optimize the learning rate.
Based on the above three improvements, the accuracy of our trained model is 92.1%, an increase of 2.6%.
#### 3.3 EDA strategy
Data augmentation is a commonly used optimization strategy in vision algorithms, which can significantly improve the accuracy of the model. In addition to the traditional RandomCrop, RandomFlip, etc. methods, we also apply RandomAugment and RandomErasing. You can find a detailed introduction at [Data Augmentation Introduction](../advanced_tutorials/DataAugmentation_en.md).
Since these two kinds of data augmentation greatly modify the picture, making the classification task more difficult, it may lead to under-fitting of the model on some datasets. We will set the probability of enabling these two methods in advance.
Based on the above improvements, we obtained a model accuracy of 93.43%, an increase of 1.3%.
#### 3.4 SKL-UGI knowledge distillation
Knowledge distillation is a method that can effectively improve the accuracy of small models. You can find a detailed introduction in [Introduction to Knowledge Distillation](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md). We choose ResNet101_vd as the teacher model for distillation. In order to adapt to the distillation process, we also adjust the learning rate of different stages of the network here. Based on the above improvements, we trained the model to get a model accuracy of 95.6%, an increase of 1.4%.
#### 3.5 Summary
After the optimization of the above methods, the final accuracy of PP-LCNet reaches 95.6%, reaching the accuracy level of the large model. We summarize the experimental results in the following table:
| Model | Tpr(%) | Latency(ms) | Storage Size(M) | Strategy |
|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
| SwinTranformer_tiny | 95.69 | 95.30 | 107 | Use ImageNet pretrained model |
| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 68.25 | 2.85 | 1.6 | Use ImageNet pretrained model |
| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 89.57 | 2.12 | 6.5 | Use ImageNet pretrained model |
| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 92.10 | 2.12 | 6.5 | Use SSLD pretrained model |
| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 93.43 | 2.12 | 6.5 | Use SSLD pretrained model + EDA Strategy|
| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 95.60 | 2.12 | 6.5 | Use SSLD pretrained model + EDA Strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation |
We also used the same optimization strategy in the other 8 scenarios and got the following results:
| scenarios | large model | large model metrics(%) | small model | small model metrics(%) |
|----------|----------|----------|----------|----------|
| Pedestrian Attribute Classification | Res2Net200_vd | 81.25 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 78.59 |
| Classification of Wheather Wearing Safety Helmet | Res2Net200_vd| 98.92 | PPLCNet_x1_0 |99.38 |
| Traffic Sign Classification | SwinTransformer_tiny | 98.11 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.35 |
| Vehicle Attribute Classification | Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s | 91.36 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 90.81 |
| Car Exists Classification | SwinTransformer_tiny | 97.71 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 95.92 |
| Text Image Orientation Classification | SwinTransformer_tiny |99.12 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 99.06 |
| Text-line Orientation Classification | SwinTransformer_tiny | 93.61 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 96.01 |
| Language Classification | SwinTransformer_tiny | 98.12 | PPLCNet_x1_0 | 99.26 |
It can be seen from the results that the PULC scheme can improve the model accuracy in multiple application scenarios. Using the PULC scheme can greatly reduce the workload of model optimization and quickly obtain models with higher accuracy.
### 4. Hyperparameters Searching
In the above training process, we adjusted parameters such as learning rate, data augmentation probability, and stage learning rate mult list. The optimal values of these parameters may not be the same in different scenarios. We provide a quick hyperparameters searching script to automate the process of hyperparameter tuning. This script traverses the parameters in the search value list to replace the parameters in the default configuration, then trains in sequence, and finally selects the parameters corresponding to the model with the highest accuracy as the search result.
#### 4.1 Search based on default configuration
The configuration file [search.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/search.yaml) defines the configuration of hyperparameters searching in person exists or not scenarios. Use the following commands to complete hyperparameters searching.
```bash
python3 tools/search_strategy.py -c ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/search.yaml
```
**Note**:Regarding the search part, we are also constantly improving, so stay tuned.
#### 4.2 Custom search configuration
You can also modify the configuration of hyperparameters searching based on training results or your parameter tuning experience.
Modify the `search_values` field in `lrs` to modify the list of learning rate search values;
Modify the `search_values` field in `resolutions` to modify the search value list of resolutions;
Modify the `search_values` field in `ra_probs` to modify the search value list of RandAugment activation probability;
Modify the `search_values` field in `re_probs` to modify the search value list of RnadomErasing on probability;
Modify the `search_values` field in `lr_mult_list` to modify the lr_mult search value list;
Modify the `search_values` field in `teacher` to modify the search list of the teacher model.
After the search is completed, the final results will be generated in `output/search_person_exists`, where, except for `search_res`, the directories in `output/search_person_exists` are the weights and training log files of the results of the corresponding hyperparameters of each search training, ` search_res` corresponds to the result of knowledge distillation, that is, the final model. The weights of the model are stored in `output/output_dir/search_person_exists/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.

