
@@ -111,6 +135,11 @@ PP-ShiTu图像识别快速体验:[点击这里](./docs/zh_CN/quick_start/quick
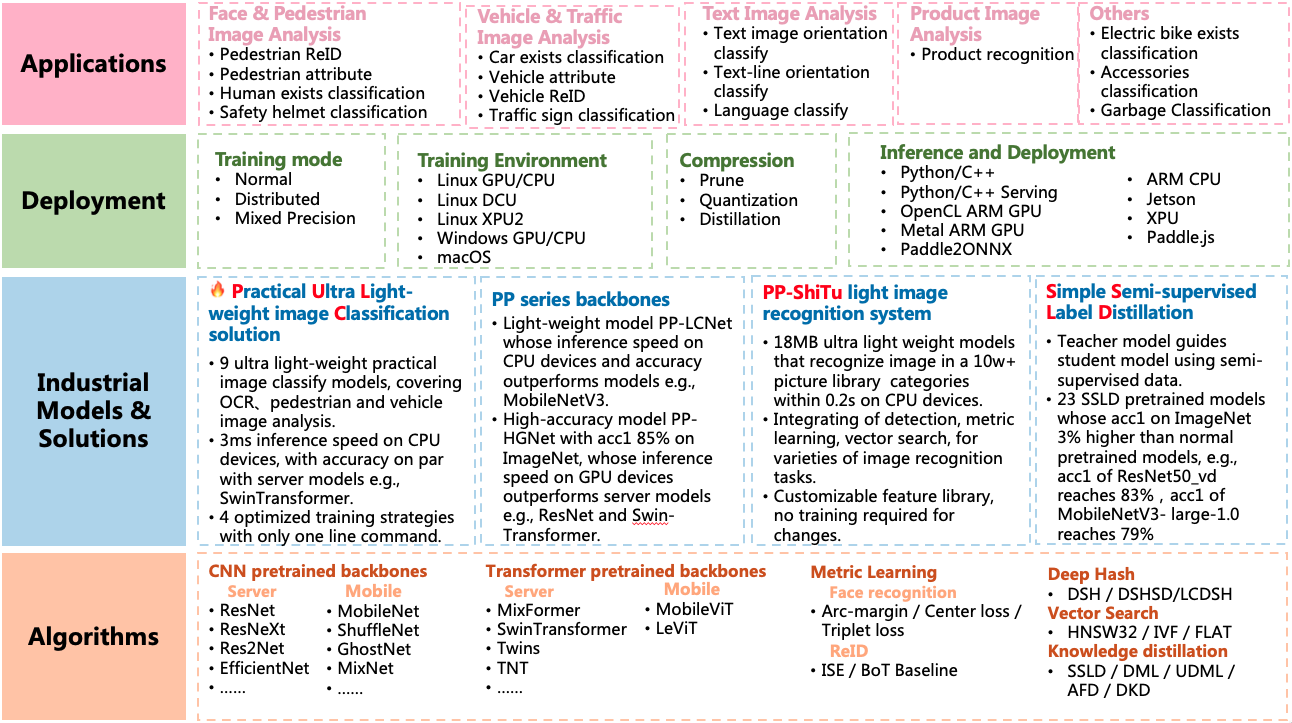
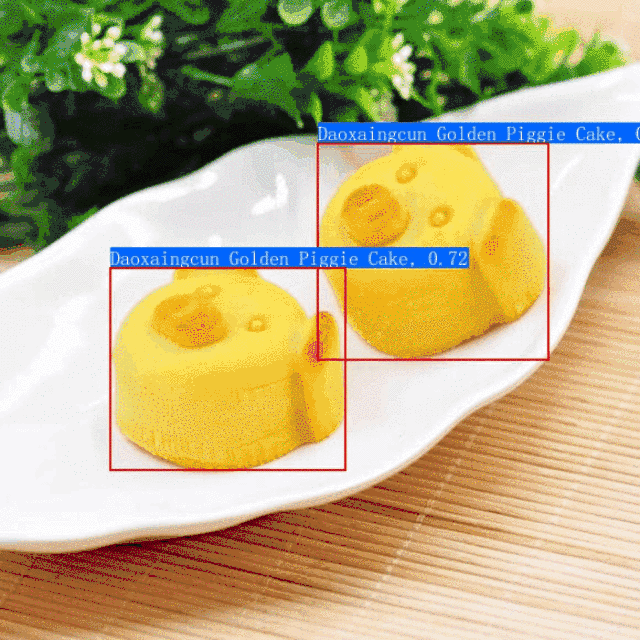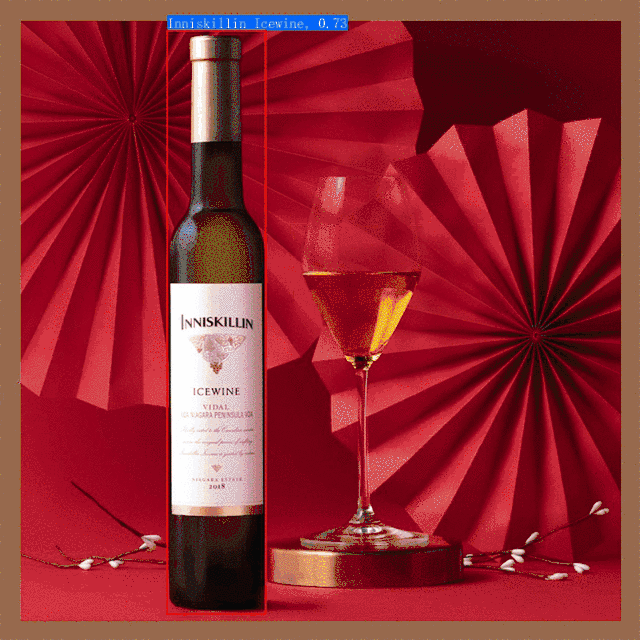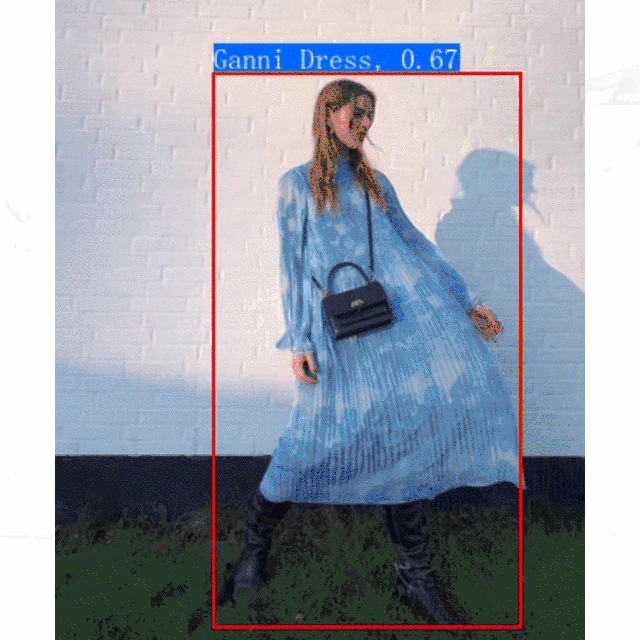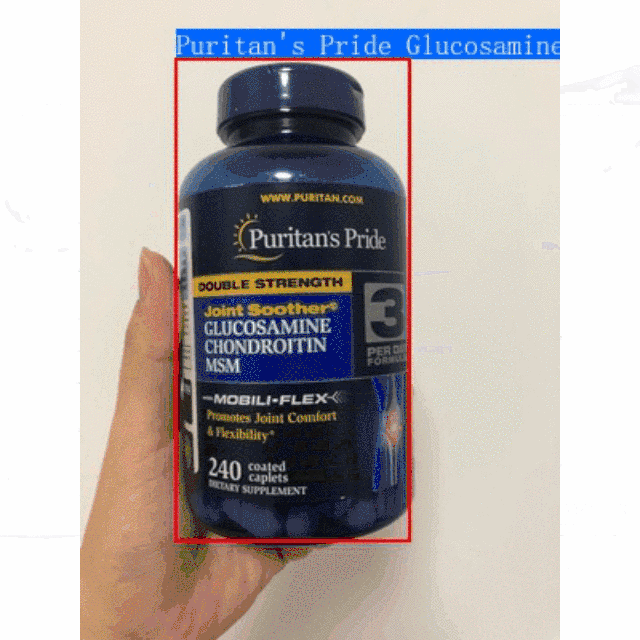
PP-ShiTu是一个实用的轻量级通用图像识别系统,主要由主体检测、特征学习和向量检索三个模块组成。该系统从骨干网络选择和调整、损失函数的选择、数据增强、学习率变换策略、正则化参数选择、预训练模型使用以及模型裁剪量化8个方面,采用多种策略,对各个模块的模型进行优化,最终得到在CPU上仅0.2s即可完成10w+库的图像识别的系统。更多细节请参考[PP-ShiTu技术方案](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.00775.pdf)。
+
+## PULC实用图像分类模型效果展示
+
+

+
## PP-ShiTu图像识别系统效果展示
diff --git a/README_en.md b/README_en.md
index 9b0d7c85d76cf06eac8fb265abb85c3bb98a275f..4bf960e57f2e56972f889c4bcf6a6d715b903477 100644
--- a/README_en.md
+++ b/README_en.md
@@ -4,39 +4,41 @@
## Introduction
-PaddleClas is an image recognition toolset for industry and academia, helping users train better computer vision models and apply them in real scenarios.
+PaddleClas is an image classification and image recognition toolset for industry and academia, helping users train better computer vision models and apply them in real scenarios.
-**Recent updates**
-
-- 2022.4.21 Added the related [code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/pull/1820/files) of the CVPR2022 oral paper [MixFormer](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2204.02557.pdf).
-
-- 2021.09.17 Add PP-LCNet series model developed by PaddleClas, these models show strong competitiveness on Intel CPUs.
-For the introduction of PP-LCNet, please refer to [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.15099.pdf) or [PP-LCNet model introduction](docs/en/models/PP-LCNet_en.md). The metrics and pretrained model are available [here](docs/en/ImageNet_models_en.md).
-
-- 2021.06.29 Add Swin-transformer series model,Highest top1 acc on ImageNet1k dataset reaches 87.2%, training, evaluation and inference are all supported. Pretrained models can be downloaded [here](docs/en/models/models_intro_en.md).
-- 2021.06.16 PaddleClas release/2.2. Add metric learning and vector search modules. Add product recognition, animation character recognition, vehicle recognition and logo recognition. Added 30 pretrained models of LeViT, Twins, TNT, DLA, HarDNet, and RedNet, and the accuracy is roughly the same as that of the paper.
-- [more](./docs/en/update_history_en.md)
+
+

-## Features
+PULC demo images
+
+
-- A practical image recognition system consist of detection, feature learning and retrieval modules, widely applicable to all types of image recognition tasks.
-Four sample solutions are provided, including product recognition, vehicle recognition, logo recognition and animation character recognition.
-- Rich library of pre-trained models: Provide a total of 164 ImageNet pre-trained models in 35 series, among which 6 selected series of models support fast structural modification.
+
+

-- Comprehensive and easy-to-use feature learning components: 12 metric learning methods are integrated and can be combined and switched at will through configuration files.
+PP-ShiTu demo images
+
-- SSLD knowledge distillation: The 14 classification pre-training models generally improved their accuracy by more than 3%; among them, the ResNet50_vd model achieved a Top-1 accuracy of 84.0% on the Image-Net-1k dataset and the Res2Net200_vd pre-training model achieved a Top-1 accuracy of 85.1%.
+**Recent updates**
+- 2022.6.15 Release [**P**ractical **U**ltra **L**ight-weight image **C**lassification solutions](./docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md). PULC models inference within 3ms on CPU devices, with accuracy on par with SwinTransformer. We also release 9 practical classification models covering pedestrian, vehicle and OCR scenario.
+- 2022.4.21 Added the related [code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/pull/1820/files) of the CVPR2022 oral paper [MixFormer](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2204.02557.pdf).
-- Data augmentation: Provide 8 data augmentation algorithms such as AutoAugment, Cutout, Cutmix, etc. with detailed introduction, code replication and evaluation of effectiveness in a unified experimental environment.
+- 2021.09.17 Add PP-LCNet series model developed by PaddleClas, these models show strong competitiveness on Intel CPUs.
+For the introduction of PP-LCNet, please refer to [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.15099.pdf) or [PP-LCNet model introduction](docs/en/models/PP-LCNet_en.md). The metrics and pretrained model are available [here](docs/en/algorithm_introduction/ImageNet_models_en.md).
+- 2021.06.29 Add [Swin-transformer](docs/en/models/SwinTransformer_en.md)) series model,Highest top1 acc on ImageNet1k dataset reaches 87.2%, training, evaluation and inference are all supported. Pretrained models can be downloaded [here](docs/en/algorithm_introduction/ImageNet_models_en.md#16).
+- 2021.06.16 PaddleClas release/2.2. Add metric learning and vector search modules. Add product recognition, animation character recognition, vehicle recognition and logo recognition. Added 30 pretrained models of LeViT, Twins, TNT, DLA, HarDNet, and RedNet, and the accuracy is roughly the same as that of the paper.
+- [more](./docs/en/others/update_history_en.md)
+## Features
+PaddleClas release PP-HGNet、PP-LCNetv2、 PP-LCNet and **S**imple **S**emi-supervised **L**abel **D**istillation algorithms, and support plenty of
+image classification and image recognition algorithms.
+Based on th algorithms above, PaddleClas release PP-ShiTu image recognition system and [**P**ractical **U**ltra **L**ight-weight image **C**lassification solutions](docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md).
-
-

-
+
## Welcome to Join the Technical Exchange Group
@@ -48,41 +50,57 @@ Four sample solutions are provided, including product recognition, vehicle recog
## Quick Start
-Quick experience of image recognition:[Link](./docs/en/tutorials/quick_start_recognition_en.md)
+Quick experience of PP-ShiTu image recognition system:[Link](./docs/en/quick_start/quick_start_recognition_en.md)
+
+Quick experience of **P**ractical **U**ltra **L**ight-weight image **C**lassification models:[Link](docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md)
## Tutorials
-- [Quick Installation](./docs/en/tutorials/install_en.md)
-- [Quick Start of Recognition](./docs/en/tutorials/quick_start_recognition_en.md)
+- [Install Paddle](./docs/en/installation/install_paddle_en.md)
+- [Install PaddleClas Environment](./docs/en/installation/install_paddleclas_en.md)
+- [Practical Ultra Light-weight image Classification solutions](./docs/en/PULC/PULC_train_en.md)
+ - [PULC Quick Start](docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md)
+ - [PULC Model Zoo](docs/en/PULC/PULC_model_list_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Someone or Nobody](docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_exists_en.md)
+ - [PULC Recognition Model of Person Attribute](docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_attribute_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Wearing or Unwearing Safety Helmet](docs/en/PULC/PULC_safety_helmet_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Traffic Sign](docs/en/PULC/PULC_traffic_sign_en.md)
+ - [PULC Recognition Model of Vehicle Attribute](docs/en/PULC/PULC_vehicle_attribute_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Containing or Uncontaining Car](docs/en/PULC/PULC_car_exists_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Text Image Orientation](docs/en/PULC/PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Textline Orientation](docs/en/PULC/PULC_textline_orientation_en.md)
+ - [PULC Classification Model of Language](docs/en/PULC/PULC_language_classification_en.md)
+- [Quick Start of Recognition](./docs/en/quick_start/quick_start_recognition_en.md)
- [Introduction to Image Recognition Systems](#Introduction_to_Image_Recognition_Systems)
-- [Demo images](#Demo_images)
+- [Image Recognition Demo images](#Rec_Demo_images)
+- [PULC demo images](#Clas_Demo_images)
- Algorithms Introduction
- - [Backbone Network and Pre-trained Model Library](./docs/en/ImageNet_models_en.md)
- - [Mainbody Detection](./docs/en/application/mainbody_detection_en.md)
- - [Image Classification](./docs/en/tutorials/image_classification_en.md)
- - [Feature Learning](./docs/en/application/feature_learning_en.md)
- - [Product Recognition](./docs/en/application/product_recognition_en.md)
- - [Vehicle Recognition](./docs/en/application/vehicle_recognition_en.md)
- - [Logo Recognition](./docs/en/application/logo_recognition_en.md)
- - [Animation Character Recognition](./docs/en/application/cartoon_character_recognition_en.md)
+ - [Backbone Network and Pre-trained Model Library](./docs/en/algorithm_introduction/ImageNet_models_en.md)
+ - [Mainbody Detection](./docs/en/image_recognition_pipeline/mainbody_detection_en.md)
+ - [Feature Learning](./docs/en/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction_en.md)
- [Vector Search](./deploy/vector_search/README.md)
-- Models Training/Evaluation
- - [Image Classification](./docs/en/tutorials/getting_started_en.md)
- - [Feature Learning](./docs/en/tutorials/getting_started_retrieval_en.md)
- Inference Model Prediction
- - [Python Inference](./docs/en/inference.md)
+ - [Python Inference](./docs/en/inference_deployment/python_deploy_en.md)
- [C++ Classfication Inference](./deploy/cpp/readme_en.md), [C++ PP-ShiTu Inference](deploy/cpp_shitu/readme_en.md)
- Model Deploy (only support classification for now, recognition coming soon)
- [Hub Serving Deployment](./deploy/hubserving/readme_en.md)
- [Mobile Deployment](./deploy/lite/readme_en.md)
- - [Inference Using whl](./docs/en/whl_en.md)
+ - [Inference Using whl](./docs/en/inference_deployment/whl_deploy_en.md)
- Advanced Tutorial
- [Knowledge Distillation](./docs/en/advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md)
- - [Model Quantization](./docs/en/extension/paddle_quantization_en.md)
- - [Data Augmentation](./docs/en/advanced_tutorials/image_augmentation/ImageAugment_en.md)
+ - [Model Quantization](./docs/en/algorithm_introduction/model_prune_quantization_en.md)
+ - [Data Augmentation](./docs/en/advanced_tutorials/DataAugmentation_en.md)
- [License](#License)
- [Contribution](#Contribution)
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b6733069d99b5622c83321bc628f3d70274ce8d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/car_exists_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: no_car
+ label_1: contains_car
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fb9fb6b6631e774e7486bcdb31c25621e2b7d790
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/language_classification_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/language_classification_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d5be2a3568291d0a31a7026974fc22ecf54a8f4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
similarity index 81%
rename from deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
rename to deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
index a70f663a792fcdcab3b7d45059f2afe0b1efbf07..3df94a80c7c75814e778e5320a31b20a8a7eb742 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg"
- inference_model_dir: "./models/person_cls_infer"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_exists_infer"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
enable_mkldnn: False
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ PreProcess:
PostProcess:
main_indicator: ThreshOutput
ThreshOutput:
- threshold: 0.9
+ threshold: 0.5
label_0: nobody
label_1: someone
SavePreLabel:
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..66a4cebb359a9b1f03a205ee6a031ca6464cffa8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/safety_helmet_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: wearing_helmet
+ label_1: unwearing_helmet
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c6c3969ffa627288fe58fab28b3fe1cbffe9dd03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/text_image_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/text_image_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..108b3dd53a95c06345bdd7ccd34b2e5252d2df19
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/textline_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 1
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/textline_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..53699718b4fdd38da86eaee4cccc584dcc87d2b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/traffic_sign_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 5
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/traffic_sign_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..14ae348d09faca113d5863fbb57f066675b3f447
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/vehicle_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [256, 192]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: VehicleAttribute
+ VehicleAttribute:
+ color_threshold: 0.5
+ type_threshold: 0.5
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..88f73db5419414812450b768ac783982386f0a78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "../inference/"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
index fc0f0fe67aa628e504bb6fcb743f29fd020548cc..d9181278cc617822f98e4966abf0d12ceca498a4 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
index 9b740ed8293c3d66a325682cafc42e2b1415df4d..85f9acb29a88772da63abe302354f5e17a9c3e59 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9959954b6b8bf27589e1d2081f86c6078d16e2c1
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea65b3108ec0476ce952b3221c31ac54fcef161d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c0cd74632460e01676fbc5a43b220c0a7f7d0474
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9149670e8a2aa086c91451442f63a727661fd7d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9e1789ab47aefecac8eaf1121decfc6a8cfb1e8b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..140694eeec3d2925303e8c0d544ef5979cd78219
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9fea2e7c9e0047a8b59606877ad41fe24bf2e24c
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c28f54f77d54df6e68e471538846b01db4387e08
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8e784af808afb58d67fdb3e277dfeebd134ee846
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..412d41956ba48c8e3243bdeff746d389be7e762b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f4725b96698e2ac222ae9d4830d8f29a33322443
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4b8d24d29ff0f8b4befff6bf943d506c36061d4d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..42ad5234973679e65be6054f90c1cc7c0f989bd2
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ac2447842dd0fac260c0d3c6e0d156dda9890923
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7d5b75f7e5bbeabded56eba1b4b566c4ca019590
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6f32ed5ae2d8483d29986e3a45db1789da2a4d43
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c792fdf6eb64395fffaf8289a1ec14d47279860e
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bb5de9fc6ff99550bf9bff8d4a9f0d0e0fe18c06
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76207d43ce597a1079c523dca0c32923bf15db19
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6a87e856af8c17a3b93617b93ea517b91c508619
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
index d1307ea84e3d7a1465c7c464d3b41dfa7613a046..bacc202806bf1a60e85790969edcb70f1489f7df 100644
--- a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
@@ -1,53 +1,59 @@
# paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测
-本章节介绍 ResNet50_vd 模型如何转化为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
+## 目录
+
+- [paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测](#paddle2onnx-模型转化与预测)
+ - [1. 环境准备](#1-环境准备)
+ - [2. 模型转换](#2-模型转换)
+ - [3. onnx 预测](#3-onnx-预测)
## 1. 环境准备
需要准备 Paddle2ONNX 模型转化环境,和 ONNX 模型预测环境。
-Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11,部分Paddle算子支持更低的ONNX Opset转换。
-更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_zh.md)
+Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11。
+更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX#paddle2onnx)
- 安装 Paddle2ONNX
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
-```
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+ ```
-- 安装 ONNX 运行时
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
-```
+- 安装 ONNX 推理引擎
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+ ```
+下面以 ResNet50_vd 为例,介绍如何将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型转换为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
## 2. 模型转换
- ResNet50_vd inference模型下载
-```
-cd deploy
-mkdir models && cd models
-wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
-cd ..
-```
+ ```shell
+ cd deploy
+ mkdir models && cd models
+ wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+ cd ..
+ ```
- 模型转换
-使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
-```
-paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
---model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
---params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
---save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
---opset_version=10 \
---enable_onnx_checker=True
-```
+ 使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
+ ```shell
+ paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+ --model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+ --params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+ --save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+ --opset_version=10 \
+ --enable_onnx_checker=True
+ ```
-执行完毕后,ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
+转换完毕后,生成的ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
## 3. onnx 预测
执行如下命令:
-```
+```shell
python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
-o Global.use_onnx=True \
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6df13e5fe31805d642432dea8526661e82b6e95b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+# Paddle2ONNX: Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+This section introduce that how to convert the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd to ONNX model and deployment based on ONNX engine.
+
+## 1. Installation
+
+First, you need to install Paddle2ONNX and onnxruntime. Paddle2ONNX is a toolkit to convert Paddle Inference Model to ONNX model. Please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_en.md) for more information.
+
+- Paddle2ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+```
+
+- ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+```
+
+## 2. Converting to ONNX
+
+Download the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd:
+
+```
+cd deploy
+mkdir models && cd models
+wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+cd ..
+```
+
+Converting to ONNX model:
+
+```
+paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+--model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+--params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+--save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+--opset_version=10 \
+--enable_onnx_checker=True
+```
+
+After running the above command, the ONNX model file converted would be save in `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/`.
+
+## 3. Deployment
+
+Deployment with ONNX model, command is as shown below.
+
+```
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
+-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
+-o Global.use_onnx=True \
+-o Global.use_gpu=False \
+-o Global.inference_model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg: class id(s): [153, 204, 229, 332, 155], score(s): [0.69, 0.10, 0.02, 0.01, 0.01], label_name(s): ['Maltese dog, Maltese terrier, Maltese', 'Lhasa, Lhasa apso', 'Old English sheepdog, bobtail', 'Angora, Angora rabbit', 'Shih-Tzu']
+```
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1329a3684ff72862858ee25c0a938bd61ff654ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+# 使用镜像:
+# registry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:latest-dev-cuda10.1-cudnn7-gcc82
+
+# 编译Serving Server:
+
+# client和app可以直接使用release版本
+
+# server因为加入了自定义OP,需要重新编译
+
+# 默认编译时的${PWD}=PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/
+
+python_name=${1:-'python'}
+
+apt-get update
+apt install -y libcurl4-openssl-dev libbz2-dev
+wget -nc https://paddle-serving.bj.bcebos.com/others/centos_ssl.tar
+tar xf centos_ssl.tar
+rm -rf centos_ssl.tar
+mv libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k
+mv libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10 /usr/lib/libcrypto.so
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.10 /usr/lib/libssl.so
+
+# 安装go依赖
+rm -rf /usr/local/go
+wget -qO- https://paddle-ci.cdn.bcebos.com/go1.17.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz | tar -xz -C /usr/local
+export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
+export GOPATH=/root/gopath
+export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin:$GOROOT/bin
+go env -w GO111MODULE=on
+go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go@v1.4.3
+go install google.golang.org/grpc@v1.33.0
+go env -w GO111MODULE=auto
+
+# 下载opencv库
+wget https://paddle-qa.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleServing/opencv3.tar.gz
+tar -xvf opencv3.tar.gz
+rm -rf opencv3.tar.gz
+export OPENCV_DIR=$PWD/opencv3
+
+# clone Serving
+git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving.git -b develop --depth=1
+
+cd Serving # PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/Serving
+export Serving_repo_path=$PWD
+git submodule update --init --recursive
+${python_name} -m pip install -r python/requirements.txt
+
+# set env
+export PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$(${python_name} -c "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_inc; print(get_python_inc())")
+export PYTHON_LIBRARIES=$(${python_name} -c "import distutils.sysconfig as sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var('LIBDIR'))")
+export PYTHON_EXECUTABLE=`which ${python_name}`
+
+export CUDA_PATH='/usr/local/cuda'
+export CUDNN_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH='/usr/local/TensorRT6-cuda10.1-cudnn7/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/'
+
+# cp 自定义OP代码
+\cp ../preprocess/general_clas_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/general-server/op
+\cp ../preprocess/preprocess_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/predictor/tools/pp_shitu_tools
+
+# 编译Server
+mkdir server-build-gpu-opencv
+cd server-build-gpu-opencv
+cmake -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR \
+-DPYTHON_LIBRARIES=$PYTHON_LIBRARIES \
+-DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$PYTHON_EXECUTABLE \
+-DCUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR=${CUDA_PATH} \
+-DCUDNN_LIBRARY=${CUDNN_LIBRARY} \
+-DCUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY=${CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY} \
+-DTENSORRT_ROOT=${TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH} \
+-DOPENCV_DIR=${OPENCV_DIR} \
+-DWITH_OPENCV=ON \
+-DSERVER=ON \
+-DWITH_GPU=ON ..
+make -j32
+
+${python_name} -m pip install python/dist/paddle*
+
+# export SERVING_BIN
+export SERVING_BIN=$PWD/core/general-server/serving
+cd ../../
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
index d9f464dd093d5a3d0ac34a61f4af17e3792fcd86..92d8297f9f23a4082cb0a499ca4c172e71d79caf 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
@@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ op:
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
- fetch_list: ["prediction"]
+ fetch_list: ["prediction"]
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e0ab48fa52da70a558b34e7ab1deda52675e99bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#include "core/general-server/op/general_clas_op.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/infer.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/memory.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/resource.h"
+#include "core/util/include/timer.h"
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+namespace baidu {
+namespace paddle_serving {
+namespace serving {
+
+using baidu::paddle_serving::Timer;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::MempoolWrapper;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::general_model::Tensor;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::general_model::Response;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::general_model::Request;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::InferManager;
+using baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::PaddleGeneralModelConfig;
+
+int GeneralClasOp::inference() {
+ VLOG(2) << "Going to run inference";
+ const std::vector pre_node_names = pre_names();
+ if (pre_node_names.size() != 1) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "This op(" << op_name()
+ << ") can only have one predecessor op, but received "
+ << pre_node_names.size();
+ return -1;
+ }
+ const std::string pre_name = pre_node_names[0];
+
+ const GeneralBlob *input_blob = get_depend_argument(pre_name);
+ if (!input_blob) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "input_blob is nullptr,error";
+ return -1;
+ }
+ uint64_t log_id = input_blob->GetLogId();
+ VLOG(2) << "(logid=" << log_id << ") Get precedent op name: " << pre_name;
+
+ GeneralBlob *output_blob = mutable_data();
+ if (!output_blob) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "output_blob is nullptr,error";
+ return -1;
+ }
+ output_blob->SetLogId(log_id);
+
+ if (!input_blob) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "(logid=" << log_id
+ << ") Failed mutable depended argument, op:" << pre_name;
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ const TensorVector *in = &input_blob->tensor_vector;
+ TensorVector *out = &output_blob->tensor_vector;
+
+ int batch_size = input_blob->_batch_size;
+ output_blob->_batch_size = batch_size;
+ VLOG(2) << "(logid=" << log_id << ") infer batch size: " << batch_size;
+
+ Timer timeline;
+ int64_t start = timeline.TimeStampUS();
+ timeline.Start();
+
+ // only support string type
+
+ char *total_input_ptr = static_cast(in->at(0).data.data());
+ std::string base64str = total_input_ptr;
+
+ cv::Mat img = Base2Mat(base64str);
+
+ // RGB2BGR
+ cv::cvtColor(img, img, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
+
+ // Resize
+ cv::Mat resize_img;
+ resize_op_.Run(img, resize_img, resize_short_size_);
+
+ // CenterCrop
+ crop_op_.Run(resize_img, crop_size_);
+
+ // Normalize
+ normalize_op_.Run(&resize_img, mean_, scale_, is_scale_);
+
+ // Permute
+ std::vector input(1 * 3 * resize_img.rows * resize_img.cols, 0.0f);
+ permute_op_.Run(&resize_img, input.data());
+ float maxValue = *max_element(input.begin(), input.end());
+ float minValue = *min_element(input.begin(), input.end());
+
+ TensorVector *real_in = new TensorVector();
+ if (!real_in) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "real_in is nullptr,error";
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ std::vector input_shape;
+ int in_num = 0;
+ void *databuf_data = NULL;
+ char *databuf_char = NULL;
+ size_t databuf_size = 0;
+
+ input_shape = {1, 3, resize_img.rows, resize_img.cols};
+ in_num = std::accumulate(input_shape.begin(), input_shape.end(), 1,
+ std::multiplies());
+
+ databuf_size = in_num * sizeof(float);
+ databuf_data = MempoolWrapper::instance().malloc(databuf_size);
+ if (!databuf_data) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "Malloc failed, size: " << databuf_size;
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ memcpy(databuf_data, input.data(), databuf_size);
+ databuf_char = reinterpret_cast(databuf_data);
+ paddle::PaddleBuf paddleBuf(databuf_char, databuf_size);
+ paddle::PaddleTensor tensor_in;
+ tensor_in.name = in->at(0).name;
+ tensor_in.dtype = paddle::PaddleDType::FLOAT32;
+ tensor_in.shape = {1, 3, resize_img.rows, resize_img.cols};
+ tensor_in.lod = in->at(0).lod;
+ tensor_in.data = paddleBuf;
+ real_in->push_back(tensor_in);
+
+ if (InferManager::instance().infer(engine_name().c_str(), real_in, out,
+ batch_size)) {
+ LOG(ERROR) << "(logid=" << log_id
+ << ") Failed do infer in fluid model: " << engine_name().c_str();
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ int64_t end = timeline.TimeStampUS();
+ CopyBlobInfo(input_blob, output_blob);
+ AddBlobInfo(output_blob, start);
+ AddBlobInfo(output_blob, end);
+ return 0;
+}
+
+cv::Mat GeneralClasOp::Base2Mat(std::string &base64_data) {
+ cv::Mat img;
+ std::string s_mat;
+ s_mat = base64Decode(base64_data.data(), base64_data.size());
+ std::vector base64_img(s_mat.begin(), s_mat.end());
+ img = cv::imdecode(base64_img, cv::IMREAD_COLOR); // CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR
+ return img;
+}
+
+std::string GeneralClasOp::base64Decode(const char *Data, int DataByte) {
+ const char DecodeTable[] = {
+ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
+ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
+ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
+ 62, // '+'
+ 0, 0, 0,
+ 63, // '/'
+ 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, // '0'-'9'
+ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
+ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, // 'A'-'Z'
+ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36,
+ 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, // 'a'-'z'
+ };
+
+ std::string strDecode;
+ int nValue;
+ int i = 0;
+ while (i < DataByte) {
+ if (*Data != '\r' && *Data != '\n') {
+ nValue = DecodeTable[*Data++] << 18;
+ nValue += DecodeTable[*Data++] << 12;
+ strDecode += (nValue & 0x00FF0000) >> 16;
+ if (*Data != '=') {
+ nValue += DecodeTable[*Data++] << 6;
+ strDecode += (nValue & 0x0000FF00) >> 8;
+ if (*Data != '=') {
+ nValue += DecodeTable[*Data++];
+ strDecode += nValue & 0x000000FF;
+ }
+ }
+ i += 4;
+ } else // 回车换行,跳过
+ {
+ Data++;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return strDecode;
+}
+DEFINE_OP(GeneralClasOp);
+} // namespace serving
+} // namespace paddle_serving
+} // namespace baidu
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.h b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.h
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..69b7a8e005872d7b66b9a61265ca5798b4ac8bab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.h
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#pragma once
+#include "core/general-server/general_model_service.pb.h"
+#include "core/general-server/op/general_infer_helper.h"
+#include "core/predictor/tools/pp_shitu_tools/preprocess_op.h"
+#include "paddle_inference_api.h" // NOLINT
+#include
+#include
+
+#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+namespace baidu {
+namespace paddle_serving {
+namespace serving {
+
+class GeneralClasOp
+ : public baidu::paddle_serving::predictor::OpWithChannel {
+public:
+ typedef std::vector TensorVector;
+
+ DECLARE_OP(GeneralClasOp);
+
+ int inference();
+
+private:
+ // clas preprocess
+ std::vector mean_ = {0.485f, 0.456f, 0.406f};
+ std::vector scale_ = {0.229f, 0.224f, 0.225f};
+ bool is_scale_ = true;
+
+ int resize_short_size_ = 256;
+ int crop_size_ = 224;
+
+ PaddleClas::ResizeImg resize_op_;
+ PaddleClas::Normalize normalize_op_;
+ PaddleClas::Permute permute_op_;
+ PaddleClas::CenterCropImg crop_op_;
+
+ // read pics
+ cv::Mat Base2Mat(std::string &base64_data);
+ std::string base64Decode(const char *Data, int DataByte);
+};
+
+} // namespace serving
+} // namespace paddle_serving
+} // namespace baidu
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.cpp b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9c79342ceda115fe3c213bb6f5d32c6e56f2380a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
+#include "paddle_api.h"
+#include "paddle_inference_api.h"
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+#include "preprocess_op.h"
+
+namespace Feature {
+
+void Permute::Run(const cv::Mat *im, float *data) {
+ int rh = im->rows;
+ int rw = im->cols;
+ int rc = im->channels();
+ for (int i = 0; i < rc; ++i) {
+ cv::extractChannel(*im, cv::Mat(rh, rw, CV_32FC1, data + i * rh * rw), i);
+ }
+}
+
+void Normalize::Run(cv::Mat *im, const std::vector &mean,
+ const std::vector &std, float scale) {
+ (*im).convertTo(*im, CV_32FC3, scale);
+ for (int h = 0; h < im->rows; h++) {
+ for (int w = 0; w < im->cols; w++) {
+ im->at(h, w)[0] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[0] - mean[0]) / std[0];
+ im->at(h, w)[1] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[1] - mean[1]) / std[1];
+ im->at(h, w)[2] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[2] - mean[2]) / std[2];
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+void CenterCropImg::Run(cv::Mat &img, const int crop_size) {
+ int resize_w = img.cols;
+ int resize_h = img.rows;
+ int w_start = int((resize_w - crop_size) / 2);
+ int h_start = int((resize_h - crop_size) / 2);
+ cv::Rect rect(w_start, h_start, crop_size, crop_size);
+ img = img(rect);
+}
+
+void ResizeImg::Run(const cv::Mat &img, cv::Mat &resize_img,
+ int resize_short_size, int size) {
+ int resize_h = 0;
+ int resize_w = 0;
+ if (size > 0) {
+ resize_h = size;
+ resize_w = size;
+ } else {
+ int w = img.cols;
+ int h = img.rows;
+
+ float ratio = 1.f;
+ if (h < w) {
+ ratio = float(resize_short_size) / float(h);
+ } else {
+ ratio = float(resize_short_size) / float(w);
+ }
+ resize_h = round(float(h) * ratio);
+ resize_w = round(float(w) * ratio);
+ }
+ cv::resize(img, resize_img, cv::Size(resize_w, resize_h));
+}
+
+} // namespace Feature
+
+namespace PaddleClas {
+void Permute::Run(const cv::Mat *im, float *data) {
+ int rh = im->rows;
+ int rw = im->cols;
+ int rc = im->channels();
+ for (int i = 0; i < rc; ++i) {
+ cv::extractChannel(*im, cv::Mat(rh, rw, CV_32FC1, data + i * rh * rw), i);
+ }
+}
+
+void Normalize::Run(cv::Mat *im, const std::vector &mean,
+ const std::vector &scale, const bool is_scale) {
+ double e = 1.0;
+ if (is_scale) {
+ e /= 255.0;
+ }
+ (*im).convertTo(*im, CV_32FC3, e);
+ for (int h = 0; h < im->rows; h++) {
+ for (int w = 0; w < im->cols; w++) {
+ im->at(h, w)[0] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[0] - mean[0]) / scale[0];
+ im->at(h, w)[1] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[1] - mean[1]) / scale[1];
+ im->at(h, w)[2] =
+ (im->at(h, w)[2] - mean[2]) / scale[2];
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+void CenterCropImg::Run(cv::Mat &img, const int crop_size) {
+ int resize_w = img.cols;
+ int resize_h = img.rows;
+ int w_start = int((resize_w - crop_size) / 2);
+ int h_start = int((resize_h - crop_size) / 2);
+ cv::Rect rect(w_start, h_start, crop_size, crop_size);
+ img = img(rect);
+}
+
+void ResizeImg::Run(const cv::Mat &img, cv::Mat &resize_img,
+ int resize_short_size) {
+ int w = img.cols;
+ int h = img.rows;
+
+ float ratio = 1.f;
+ if (h < w) {
+ ratio = float(resize_short_size) / float(h);
+ } else {
+ ratio = float(resize_short_size) / float(w);
+ }
+
+ int resize_h = round(float(h) * ratio);
+ int resize_w = round(float(w) * ratio);
+
+ cv::resize(img, resize_img, cv::Size(resize_w, resize_h));
+}
+
+} // namespace PaddleClas
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.h b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.h
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0ea9d2e14a525365bb049a13358660a2567dadc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/preprocess_op.h
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#pragma once
+
+#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+namespace Feature {
+
+class Normalize {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(cv::Mat *im, const std::vector &mean,
+ const std::vector &std, float scale);
+};
+
+// RGB -> CHW
+class Permute {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(const cv::Mat *im, float *data);
+};
+
+class CenterCropImg {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(cv::Mat &im, const int crop_size = 224);
+};
+
+class ResizeImg {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(const cv::Mat &img, cv::Mat &resize_img, int max_size_len,
+ int size = 0);
+};
+
+} // namespace Feature
+
+namespace PaddleClas {
+
+class Normalize {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(cv::Mat *im, const std::vector &mean,
+ const std::vector &scale, const bool is_scale = true);
+};
+
+// RGB -> CHW
+class Permute {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(const cv::Mat *im, float *data);
+};
+
+class CenterCropImg {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(cv::Mat &im, const int crop_size = 224);
+};
+
+class ResizeImg {
+public:
+ virtual void Run(const cv::Mat &img, cv::Mat &resize_img, int max_size_len);
+};
+
+} // namespace PaddleClas
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/config.yml b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/config.yml
index 6ecc32e22435f07a549ffcdeb6a435b33c4901f1..e4108006e6f2ea1a3698e4fdf9c32f25dcbfbeb0 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/config.yml
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/config.yml
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ op:
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["features"]
-
+
det:
concurrency: 1
local_service_conf:
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c781eb6f449fe06afbba7f96e01798c974bccf54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+feed_var {
+ name: "x"
+ alias_name: "x"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 3
+ shape: 224
+ shape: 224
+}
+feed_var {
+ name: "boxes"
+ alias_name: "boxes"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 6
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "features"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: 512
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "boxes"
+ alias_name: "boxes"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: 6
+}
+
+
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..04812f42ed90fbbd47c73b9ec706d57c04b4c571
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+feed_var {
+ name: "x"
+ alias_name: "x"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 3
+ shape: 224
+ shape: 224
+}
+feed_var {
+ name: "boxes"
+ alias_name: "boxes"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 6
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "features"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: 512
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "boxes"
+ alias_name: "boxes"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: 6
+}
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d9ab81a8b3c275f638f314489a84deef46011d73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+feed_var {
+ name: "im_shape"
+ alias_name: "im_shape"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 2
+}
+feed_var {
+ name: "image"
+ alias_name: "image"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 7
+ shape: -1
+ shape: -1
+ shape: 3
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ is_lod_tensor: true
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: -1
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_1.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "save_infer_model/scale_1.tmp_1"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 2
+}
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d9ab81a8b3c275f638f314489a84deef46011d73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/preprocess/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+feed_var {
+ name: "im_shape"
+ alias_name: "im_shape"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 1
+ shape: 2
+}
+feed_var {
+ name: "image"
+ alias_name: "image"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ feed_type: 7
+ shape: -1
+ shape: -1
+ shape: 3
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"
+ is_lod_tensor: true
+ fetch_type: 1
+ shape: -1
+}
+fetch_var {
+ name: "save_infer_model/scale_1.tmp_1"
+ alias_name: "save_infer_model/scale_1.tmp_1"
+ is_lod_tensor: false
+ fetch_type: 2
+}
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/test_cpp_serving_client.py b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/test_cpp_serving_client.py
index a2bf1ae3e9d0a69628319b9f845a1e6f7701b391..e2cd17e855ebfe8fb286ebaeff8ab63874e2e972 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/test_cpp_serving_client.py
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/recognition/test_cpp_serving_client.py
@@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
-import sys
import numpy as np
from paddle_serving_client import Client
@@ -22,181 +21,101 @@ import faiss
import os
import pickle
-
-class MainbodyDetect():
- """
- pp-shitu mainbody detect.
- include preprocess, process, postprocess
- return detect results
- Attention: Postprocess include num limit and box filter; no nms
- """
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.preprocess = DetectionSequential([
- DetectionFile2Image(), DetectionNormalize(
- [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225], True),
- DetectionResize(
- (640, 640), False, interpolation=2), DetectionTranspose(
- (2, 0, 1))
- ])
-
- self.client = Client()
- self.client.load_client_config(
- "../../models/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt"
- )
- self.client.connect(['127.0.0.1:9293'])
-
- self.max_det_result = 5
- self.conf_threshold = 0.2
-
- def predict(self, imgpath):
- im, im_info = self.preprocess(imgpath)
- im_shape = np.array(im.shape[1:]).reshape(-1)
- scale_factor = np.array(list(im_info['scale_factor'])).reshape(-1)
-
- fetch_map = self.client.predict(
- feed={
- "image": im,
- "im_shape": im_shape,
- "scale_factor": scale_factor,
- },
- fetch=["save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"],
- batch=False)
- return self.postprocess(fetch_map, imgpath)
-
- def postprocess(self, fetch_map, imgpath):
- #1. get top max_det_result
- det_results = fetch_map["save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"]
- if len(det_results) > self.max_det_result:
- boxes_reserved = fetch_map[
- "save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1"][:self.max_det_result]
- else:
- boxes_reserved = det_results
-
- #2. do conf threshold
- boxes_list = []
- for i in range(boxes_reserved.shape[0]):
- if (boxes_reserved[i, 1]) > self.conf_threshold:
- boxes_list.append(boxes_reserved[i, :])
-
- #3. add origin image box
- origin_img = cv2.imread(imgpath)
- boxes_list.append(
- np.array([0, 1.0, 0, 0, origin_img.shape[1], origin_img.shape[0]]))
- return np.array(boxes_list)
-
-
-class ObjectRecognition():
- """
- pp-shitu object recognion for all objects detected by MainbodyDetect.
- include preprocess, process, postprocess
- preprocess include preprocess for each image and batching.
- Batch process
- postprocess include retrieval and nms
- """
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.client = Client()
- self.client.load_client_config(
- "../../models/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt"
- )
- self.client.connect(["127.0.0.1:9294"])
-
- self.seq = Sequential([
- BGR2RGB(), Resize((224, 224)), Div(255),
- Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225],
- False), Transpose((2, 0, 1))
- ])
-
- self.searcher, self.id_map = self.init_index()
-
- self.rec_nms_thresold = 0.05
- self.rec_score_thres = 0.5
- self.feature_normalize = True
- self.return_k = 1
-
- def init_index(self):
- index_dir = "../../drink_dataset_v1.0/index"
- assert os.path.exists(os.path.join(
- index_dir, "vector.index")), "vector.index not found ..."
- assert os.path.exists(os.path.join(
- index_dir, "id_map.pkl")), "id_map.pkl not found ... "
-
- searcher = faiss.read_index(os.path.join(index_dir, "vector.index"))
-
- with open(os.path.join(index_dir, "id_map.pkl"), "rb") as fd:
- id_map = pickle.load(fd)
- return searcher, id_map
-
- def predict(self, det_boxes, imgpath):
- #1. preprocess
- batch_imgs = []
- origin_img = cv2.imread(imgpath)
- for i in range(det_boxes.shape[0]):
- box = det_boxes[i]
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(x) for x in box[2:]]
- cropped_img = origin_img[y1:y2, x1:x2, :].copy()
- tmp = self.seq(cropped_img)
- batch_imgs.append(tmp)
- batch_imgs = np.array(batch_imgs)
-
- #2. process
- fetch_map = self.client.predict(
- feed={"x": batch_imgs}, fetch=["features"], batch=True)
- batch_features = fetch_map["features"]
-
- #3. postprocess
- if self.feature_normalize:
- feas_norm = np.sqrt(
- np.sum(np.square(batch_features), axis=1, keepdims=True))
- batch_features = np.divide(batch_features, feas_norm)
- scores, docs = self.searcher.search(batch_features, self.return_k)
-
- results = []
- for i in range(scores.shape[0]):
- pred = {}
- if scores[i][0] >= self.rec_score_thres:
- pred["bbox"] = [int(x) for x in det_boxes[i, 2:]]
- pred["rec_docs"] = self.id_map[docs[i][0]].split()[1]
- pred["rec_scores"] = scores[i][0]
- results.append(pred)
- return self.nms_to_rec_results(results)
-
- def nms_to_rec_results(self, results):
- filtered_results = []
- x1 = np.array([r["bbox"][0] for r in results]).astype("float32")
- y1 = np.array([r["bbox"][1] for r in results]).astype("float32")
- x2 = np.array([r["bbox"][2] for r in results]).astype("float32")
- y2 = np.array([r["bbox"][3] for r in results]).astype("float32")
- scores = np.array([r["rec_scores"] for r in results])
-
- areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
- order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
- while order.size > 0:
- i = order[0]
- xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
- yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
- xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
- yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
-
- w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
- h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
- inter = w * h
- ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
- inds = np.where(ovr <= self.rec_nms_thresold)[0]
- order = order[inds + 1]
- filtered_results.append(results[i])
- return filtered_results
-
-
+rec_nms_thresold = 0.05
+rec_score_thres = 0.5
+feature_normalize = True
+return_k = 1
+index_dir = "../../drink_dataset_v1.0/index"
+
+
+def init_index(index_dir):
+ assert os.path.exists(os.path.join(
+ index_dir, "vector.index")), "vector.index not found ..."
+ assert os.path.exists(os.path.join(
+ index_dir, "id_map.pkl")), "id_map.pkl not found ... "
+
+ searcher = faiss.read_index(os.path.join(index_dir, "vector.index"))
+
+ with open(os.path.join(index_dir, "id_map.pkl"), "rb") as fd:
+ id_map = pickle.load(fd)
+ return searcher, id_map
+
+
+#get box
+def nms_to_rec_results(results, thresh=0.1):
+ filtered_results = []
+
+ x1 = np.array([r["bbox"][0] for r in results]).astype("float32")
+ y1 = np.array([r["bbox"][1] for r in results]).astype("float32")
+ x2 = np.array([r["bbox"][2] for r in results]).astype("float32")
+ y2 = np.array([r["bbox"][3] for r in results]).astype("float32")
+ scores = np.array([r["rec_scores"] for r in results])
+
+ areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
+ order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
+ while order.size > 0:
+ i = order[0]
+ xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
+ yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
+ xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
+ yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
+
+ w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
+ h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
+ inter = w * h
+ ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
+ inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
+ order = order[inds + 1]
+ filtered_results.append(results[i])
+ return filtered_results
+
+
+def postprocess(fetch_dict, feature_normalize, det_boxes, searcher, id_map,
+ return_k, rec_score_thres, rec_nms_thresold):
+ batch_features = fetch_dict["features"]
+
+ #do feature norm
+ if feature_normalize:
+ feas_norm = np.sqrt(
+ np.sum(np.square(batch_features), axis=1, keepdims=True))
+ batch_features = np.divide(batch_features, feas_norm)
+
+ scores, docs = searcher.search(batch_features, return_k)
+
+ results = []
+ for i in range(scores.shape[0]):
+ pred = {}
+ if scores[i][0] >= rec_score_thres:
+ pred["bbox"] = [int(x) for x in det_boxes[i, 2:]]
+ pred["rec_docs"] = id_map[docs[i][0]].split()[1]
+ pred["rec_scores"] = scores[i][0]
+ results.append(pred)
+
+ #do nms
+ results = nms_to_rec_results(results, rec_nms_thresold)
+ return results
+
+
+#do client
if __name__ == "__main__":
- det = MainbodyDetect()
- rec = ObjectRecognition()
-
- #1. get det_results
- imgpath = "../../drink_dataset_v1.0/test_images/001.jpeg"
- det_results = det.predict(imgpath)
-
- #2. get rec_results
- rec_results = rec.predict(det_results, imgpath)
- print(rec_results)
+ client = Client()
+ client.load_client_config([
+ "../../models/picodet_PPLCNet_x2_5_mainbody_lite_v1.0_client",
+ "../../models/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_lite_v1.0_client"
+ ])
+ client.connect(['127.0.0.1:9400'])
+
+ im = cv2.imread("../../drink_dataset_v1.0/test_images/001.jpeg")
+ im_shape = np.array(im.shape[:2]).reshape(-1)
+ fetch_map = client.predict(
+ feed={"image": im,
+ "im_shape": im_shape},
+ fetch=["features", "boxes"],
+ batch=False)
+
+ #add retrieval procedure
+ det_boxes = fetch_map["boxes"]
+ searcher, id_map = init_index(index_dir)
+ results = postprocess(fetch_map, feature_normalize, det_boxes, searcher,
+ id_map, return_k, rec_score_thres, rec_nms_thresold)
+ print(results)
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/test_cpp_serving_client.py b/deploy/paddleserving/test_cpp_serving_client.py
index 50794b363767c8236ccca1001a441b535a9f9db3..ba5399c90dcd5e0701df26e2d2f8337a4105ab51 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/test_cpp_serving_client.py
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/test_cpp_serving_client.py
@@ -12,16 +12,20 @@
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
-import sys
+import base64
+import time
+
from paddle_serving_client import Client
-#app
-from paddle_serving_app.reader import Sequential, URL2Image, Resize
-from paddle_serving_app.reader import CenterCrop, RGB2BGR, Transpose, Div, Normalize
-import time
+
+def bytes_to_base64(image: bytes) -> str:
+ """encode bytes into base64 string
+ """
+ return base64.b64encode(image).decode('utf8')
+
client = Client()
-client.load_client_config("./ResNet50_vd_serving/serving_server_conf.prototxt")
+client.load_client_config("./ResNet50_client/serving_client_conf.prototxt")
client.connect(["127.0.0.1:9292"])
label_dict = {}
@@ -31,22 +35,17 @@ with open("imagenet.label") as fin:
label_dict[label_idx] = line.strip()
label_idx += 1
-#preprocess
-seq = Sequential([
- URL2Image(), Resize(256), CenterCrop(224), RGB2BGR(), Transpose((2, 0, 1)),
- Div(255), Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225], True)
-])
-
-start = time.time()
-image_file = "https://paddle-serving.bj.bcebos.com/imagenet-example/daisy.jpg"
+image_file = "./daisy.jpg"
for i in range(1):
- img = seq(image_file)
- fetch_map = client.predict(
- feed={"inputs": img}, fetch=["prediction"], batch=False)
-
- prob = max(fetch_map["prediction"][0])
- label = label_dict[fetch_map["prediction"][0].tolist().index(prob)].strip(
- ).replace(",", "")
- print("prediction: {}, probability: {}".format(label, prob))
-end = time.time()
-print(end - start)
+ start = time.time()
+ with open(image_file, 'rb') as img_file:
+ image_data = img_file.read()
+ image = bytes_to_base64(image_data)
+ fetch_dict = client.predict(
+ feed={"inputs": image}, fetch=["prediction"], batch=False)
+ prob = max(fetch_dict["prediction"][0])
+ label = label_dict[fetch_dict["prediction"][0].tolist().index(
+ prob)].strip().replace(",", "")
+ print("prediction: {}, probability: {}".format(label, prob))
+ end = time.time()
+ print(end - start)
diff --git a/deploy/python/postprocess.py b/deploy/python/postprocess.py
index 4f4d005fdff2bf17e04265e136443d0cd837f10e..23a803e284361e98b60f193c450318536d992937 100644
--- a/deploy/python/postprocess.py
+++ b/deploy/python/postprocess.py
@@ -64,9 +64,17 @@ class ThreshOutput(object):
for idx, probs in enumerate(x):
score = probs[1]
if score < self.threshold:
- result = {"class_ids": [0], "scores": [1 - score], "label_names": [self.label_0]}
+ result = {
+ "class_ids": [0],
+ "scores": [1 - score],
+ "label_names": [self.label_0]
+ }
else:
- result = {"class_ids": [1], "scores": [score], "label_names": [self.label_1]}
+ result = {
+ "class_ids": [1],
+ "scores": [score],
+ "label_names": [self.label_1]
+ }
if file_names is not None:
result["file_name"] = file_names[idx]
y.append(result)
@@ -179,3 +187,136 @@ class Binarize(object):
byte[:, i:i + 1] = np.dot(x[:, i * 8:(i + 1) * 8], self.unit)
return byte
+
+
+class PersonAttribute(object):
+ def __init__(self,
+ threshold=0.5,
+ glasses_threshold=0.3,
+ hold_threshold=0.6):
+ self.threshold = threshold
+ self.glasses_threshold = glasses_threshold
+ self.hold_threshold = hold_threshold
+
+ def __call__(self, batch_preds, file_names=None):
+ # postprocess output of predictor
+ age_list = ['AgeLess18', 'Age18-60', 'AgeOver60']
+ direct_list = ['Front', 'Side', 'Back']
+ bag_list = ['HandBag', 'ShoulderBag', 'Backpack']
+ upper_list = ['UpperStride', 'UpperLogo', 'UpperPlaid', 'UpperSplice']
+ lower_list = [
+ 'LowerStripe', 'LowerPattern', 'LongCoat', 'Trousers', 'Shorts',
+ 'Skirt&Dress'
+ ]
+ batch_res = []
+ for res in batch_preds:
+ res = res.tolist()
+ label_res = []
+ # gender
+ gender = 'Female' if res[22] > self.threshold else 'Male'
+ label_res.append(gender)
+ # age
+ age = age_list[np.argmax(res[19:22])]
+ label_res.append(age)
+ # direction
+ direction = direct_list[np.argmax(res[23:])]
+ label_res.append(direction)
+ # glasses
+ glasses = 'Glasses: '
+ if res[1] > self.glasses_threshold:
+ glasses += 'True'
+ else:
+ glasses += 'False'
+ label_res.append(glasses)
+ # hat
+ hat = 'Hat: '
+ if res[0] > self.threshold:
+ hat += 'True'
+ else:
+ hat += 'False'
+ label_res.append(hat)
+ # hold obj
+ hold_obj = 'HoldObjectsInFront: '
+ if res[18] > self.hold_threshold:
+ hold_obj += 'True'
+ else:
+ hold_obj += 'False'
+ label_res.append(hold_obj)
+ # bag
+ bag = bag_list[np.argmax(res[15:18])]
+ bag_score = res[15 + np.argmax(res[15:18])]
+ bag_label = bag if bag_score > self.threshold else 'No bag'
+ label_res.append(bag_label)
+ # upper
+ upper_res = res[4:8]
+ upper_label = 'Upper:'
+ sleeve = 'LongSleeve' if res[3] > res[2] else 'ShortSleeve'
+ upper_label += ' {}'.format(sleeve)
+ for i, r in enumerate(upper_res):
+ if r > self.threshold:
+ upper_label += ' {}'.format(upper_list[i])
+ label_res.append(upper_label)
+ # lower
+ lower_res = res[8:14]
+ lower_label = 'Lower: '
+ has_lower = False
+ for i, l in enumerate(lower_res):
+ if l > self.threshold:
+ lower_label += ' {}'.format(lower_list[i])
+ has_lower = True
+ if not has_lower:
+ lower_label += ' {}'.format(lower_list[np.argmax(lower_res)])
+
+ label_res.append(lower_label)
+ # shoe
+ shoe = 'Boots' if res[14] > self.threshold else 'No boots'
+ label_res.append(shoe)
+
+ threshold_list = [0.5] * len(res)
+ threshold_list[1] = self.glasses_threshold
+ threshold_list[18] = self.hold_threshold
+ pred_res = (np.array(res) > np.array(threshold_list)
+ ).astype(np.int8).tolist()
+ batch_res.append({"attributes": label_res, "output": pred_res})
+ return batch_res
+
+
+class VehicleAttribute(object):
+ def __init__(self, color_threshold=0.5, type_threshold=0.5):
+ self.color_threshold = color_threshold
+ self.type_threshold = type_threshold
+ self.color_list = [
+ "yellow", "orange", "green", "gray", "red", "blue", "white",
+ "golden", "brown", "black"
+ ]
+ self.type_list = [
+ "sedan", "suv", "van", "hatchback", "mpv", "pickup", "bus",
+ "truck", "estate"
+ ]
+
+ def __call__(self, batch_preds, file_names=None):
+ # postprocess output of predictor
+ batch_res = []
+ for res in batch_preds:
+ res = res.tolist()
+ label_res = []
+ color_idx = np.argmax(res[:10])
+ type_idx = np.argmax(res[10:])
+ if res[color_idx] >= self.color_threshold:
+ color_info = f"Color: ({self.color_list[color_idx]}, prob: {res[color_idx]})"
+ else:
+ color_info = "Color unknown"
+
+ if res[type_idx + 10] >= self.type_threshold:
+ type_info = f"Type: ({self.type_list[type_idx]}, prob: {res[type_idx + 10]})"
+ else:
+ type_info = "Type unknown"
+
+ label_res = f"{color_info}, {type_info}"
+
+ threshold_list = [self.color_threshold
+ ] * 10 + [self.type_threshold] * 9
+ pred_res = (np.array(res) > np.array(threshold_list)
+ ).astype(np.int8).tolist()
+ batch_res.append({"attributes": label_res, "output": pred_res})
+ return batch_res
diff --git a/deploy/python/predict_cls.py b/deploy/python/predict_cls.py
index 64c07ea875eaa2c456393328183b7270080a64d1..49bf62fa3060b9336a3438b2ee5c25b2bac49667 100644
--- a/deploy/python/predict_cls.py
+++ b/deploy/python/predict_cls.py
@@ -138,13 +138,20 @@ def main(config):
continue
batch_results = cls_predictor.predict(batch_imgs)
for number, result_dict in enumerate(batch_results):
- filename = batch_names[number]
- clas_ids = result_dict["class_ids"]
- scores_str = "[{}]".format(", ".join("{:.2f}".format(
- r) for r in result_dict["scores"]))
- label_names = result_dict["label_names"]
- print("{}:\tclass id(s): {}, score(s): {}, label_name(s): {}".
- format(filename, clas_ids, scores_str, label_names))
+ if "PersonAttribute" in config[
+ "PostProcess"] or "VehicleAttribute" in config[
+ "PostProcess"]:
+ filename = batch_names[number]
+ print("{}:\t {}".format(filename, result_dict))
+ else:
+ filename = batch_names[number]
+ clas_ids = result_dict["class_ids"]
+ scores_str = "[{}]".format(", ".join("{:.2f}".format(
+ r) for r in result_dict["scores"]))
+ label_names = result_dict["label_names"]
+ print(
+ "{}:\tclass id(s): {}, score(s): {}, label_name(s): {}".
+ format(filename, clas_ids, scores_str, label_names))
batch_imgs = []
batch_names = []
if cls_predictor.benchmark:
diff --git a/deploy/slim/quant_post_static.py b/deploy/slim/quant_post_static.py
index 5c8469794ad29e18dad15f985b611e423fd4b474..20507c66ad1ed583c2baf1bae7e812e0364e015e 100644
--- a/deploy/slim/quant_post_static.py
+++ b/deploy/slim/quant_post_static.py
@@ -43,6 +43,7 @@ def main():
'inference.pdiparams'))
config["DataLoader"]["Eval"]["sampler"]["batch_size"] = 1
config["DataLoader"]["Eval"]["loader"]["num_workers"] = 0
+
init_logger()
device = paddle.set_device("cpu")
train_dataloader = build_dataloader(config["DataLoader"], "Eval", device,
@@ -67,6 +68,7 @@ def main():
quantize_model_path=os.path.join(
config["Global"]["save_inference_dir"], "quant_post_static_model"),
sample_generator=sample_generator(train_dataloader),
+ batch_size=config["DataLoader"]["Eval"]["sampler"]["batch_size"],
batch_nums=10)
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_car_exists_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_car_exists_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..33c0932e6f118d7f9e31650e7d1e9754af19ec17
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_car_exists_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,457 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Containing or Uncontaining Car
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of car exists using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in monitoring scenarios, massive data filtering scenarios, etc.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to sixth lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Tpr(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+|-------|----------------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 97.71 | 95.30 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 81.23 | 2.85 | 2.7 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 94.72 | 2.12 | 7.1 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 95.48 | 2.12 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 95.48 | 2.12 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 95.92 | 2.12 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high Tpr can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the Tpr will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the Tpr is higher more 13 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 20% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the Tpr can be improved by about 0.7 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Finally, after additional using the SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, the Tpr can be further improved by 0.44 percentage points. At this point, the Tpr is close to that of SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is more than 40 times faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About `Tpr` metric, please refer to [3.2 section](#3.2) for more information .
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=car_exists --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [1], scores: [0.9871138], label_names: ['contains_car'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="car_exists")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="car_exists", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [1], 'scores': [0.9871138], 'label_names': ['contains_car'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+All datasets used in this case are open source data. Train and validation data are the subset of [Object365](https://www.objects365.org/overview.html) data. ImageNet_val is [ImageNet-1k](https://www.image-net.org/) validation data.
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The data used in this case can be getted by processing the open source data. The detailed processes are as follows:
+
+- Training data. This case deals with the annotation file of Objects365 data training data. If a certain image contains the label of "car" and the area of this box is greater than 10% in the whole image, it is considered that the image contains car. If there is no label of any vehicle in a certain image, such as car, bus and so on, it is considered that the image does not contain car. After processing, 108629 images were obtained, including 27422 images containing car and 81207 images uncontaining car.
+- Validation data: Same as Training data, but checked manually to remove some labeled wrong images.
+
+**Note**: the labels of objects365 are not completely mutually exclusive. For example, F1 racing cars may be "F1 formula" or "car". In order to reduce the interference, we only keep the "car" label as containing car, and the figure without any vehicle as uncontaining car.
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/car_exists.tar
+tar -xf car_exists.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `car_exists` directory:
+
+```
+
+├── objects365_car
+│ ├── objects365_00000039.jpg
+│ ├── objects365_00000099.jpg
+├── ImageNet_val
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000001.JPEG
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000002.JPEG
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+├── train_list.txt.debug
+├── train_list_for_distill.txt
+├── val_list.txt
+└── val_list.txt.debug
+```
+
+Where `train/` and `val/` are training set and validation set respectively. The `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively. The file `train_list.txt.debug` and `val_list.txt.debug` are subset of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` respectively. `ImageNet_val/` is the validation data of ImageNet-1k, which will be used for SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, and its label file is `train_list_for_distill.txt`.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+* About the `train_list_for_distill.txt`, please refer to [Knowledge Distillation Label](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.95` and `0.96`. There would be fluctuations because the data size is small.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The metric Tpr, that describe the True Positive Rate when False Positive Rate is less than a certain threshold(1/100 used in this case), is one of the commonly used metric for binary classification. About the details of Fpr and Tpr, please refer [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receiver_operating_characteristic).
+* When evaluation, the best metric TprAtFpr will be printed that include `Fpr`, `Tpr` and the current `threshold`. The `Tpr` means the Recall rate under the current `Fpr`. The `Tpr` higher, the model better. The `threshold` would be used in deployment, which means the classification threshold under best `Fpr` metric.
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [1], 'scores': [0.9871138], 'label_names': ['contains_car'], 'filename': 'deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg'}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+* The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9794`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9794` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/100` in this valuation dataset.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.96` and `0.98`. The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd`, the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0` and the additional unlabeled training data is validation data of ImageNet1k. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model
+```
+
+The best metric is between `0.95` and `0.97`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/car_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_car_exists_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_car_exists_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_car_exists_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/car_exists_infer.tar && tar -xf car_exists_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── car_exists_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify whether there are cars in the image `./images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+objects365_00001507.jpeg: class id(s): [1], score(s): [0.99], label_name(s): ['contains_car']
+```
+
+**Note**: The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9794`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9794` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/100` in this valuation dataset. Please refer to [3.3 section](#3.3) for details.
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/car_exists/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+objects365_00001507.jpeg: class id(s): [1], score(s): [0.99], label_name(s): ['contains_car']
+objects365_00001521.jpeg: class id(s): [0], score(s): [0.99], label_name(s): ['no_car']
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `contains_car` means that there is a car in the image, `no_car` means that there is no car in the image.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_language_classification_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_language_classification_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c7cd5f5db9c01f01c4fbb2299086bc1adcfc98d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_language_classification_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,470 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Language
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of language in the image using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in various scenarios involving multilingual OCR processing, such as finance and government affairs.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to sixth lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy. When replacing the backbone with PPLCNet_x1_0, the input shape of model is changed to [192, 48], and the stride of the network is changed to [2, [2, 1], [2, 1], [2, 1]].
+
+| Backbone | Top1-Acc(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+| ----------------------- | --------- | -------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 98.12 | 89.09 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 95.92 | 2.98 | 3.7 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.35 | 2.58 | 7.1 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.7 | 2.58 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 99.12 | 2.58 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| **PPLCNet_x1_0** | **99.26** | **2.58** | **7.1** | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high accuracy can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the accuracy will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0 and changing the input shape and stride of network, the accuracy is higher more 2.43 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 20% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the accuracy can be improved by about 0.35 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Further, additional using the EDA strategy, the accuracy can be increased by 0.42 percentage points. Finally, after additional using the SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, the accuracy can be further improved by 0.14 percentage points. At this point, the accuracy is higher than that of SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is more faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=language_classification --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/language_classification/word_35404.png
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [4, 6], scores: [0.88672, 0.01434], label_names: ['japan', 'korean'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/language_classification/word_35404.png
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="language_classification")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/language_classification/word_35404.png")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="language_classification", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [4, 6], 'scores': [0.88672, 0.01434], 'label_names': ['japan', 'korean'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/language_classification/word_35404.png'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+The models wo provided are trained with internal data, which is not open source yet. So it is suggested that constructing dataset based on open source dataset [Multi-lingual scene text detection and recognition](https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=15&com=downloads) to experience the this case.
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The models provided support to classcify 10 languages, which as shown in the following list:
+
+`0` : means Arabic
+`1` : means chinese_cht
+`2` : means cyrillic
+`3` : means devanagari
+`4` : means Japanese
+`5` : means ka
+`6` : means Korean
+`7` : means ta
+`8` : means te
+`9` : means Latin
+
+In the `Multi-lingual scene text detection and recognition`, only Arabic, Japanese, Korean and Latin data are included. 1600 images from each of the four languages are taken as the training data of this case, 300 images as the evaluation data, and 400 images as the supplementary data is used for the `SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation`.
+
+Therefore, for the demo dataset in this case, the language categories are shown in following list:
+`0` : means arabic
+`4` : means japan
+`6` : means korean
+`9` : means latin
+
+**Note**: The images used in this task should be cropped by text from original image. Only the text line part is used as the image data.
+
+If you want to create your own dataset, you can collect and sort out the data of the required languages in your task as required. And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/language_classification.tar
+tar -xf language_classification.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `language_classification` directory:
+
+```
+├── img
+│ ├── word_1.png
+│ ├── word_2.png
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+├── train_list_for_distill.txt
+├── test_list.txt
+└── label_list.txt
+```
+
+Where `img/` is the directory including 9200 images in 4 languages. The `train_list.txt` and `test_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively. `label_list.txt` is the mapping file corresponding to the four languages. `train_list_for_distill.txt` is the label list of images used for `SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation`.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+* About the `train_list_for_distill.txt`, please refer to [Knowledge Distillation Label](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.class_num=4
+```
+
+**Note**: Because the class num of demo dataset is 4, the argument `-o Arch.class_num=4` should be specifed to change the prediction class num of model to 4.
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model" \
+ -o Arch.class_num=4
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model" \
+ -o Arch.class_num=4
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [4, 9], 'scores': [0.96809, 0.01001], 'file_name': 'deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png', 'label_names': ['japan', 'latin']}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+* Among the prediction results, `japan` means japanese and `korean` means korean.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd \
+ -o Arch.class_num=4
+```
+
+The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+**Note**: Training the ResNet101_vd model requires more GPU memory. If the memory is not enough, you can reduce the learning rate and batch size in the same proportion.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd`, the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model \
+ -o Arch.class_num=4
+```
+
+The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/language_classification/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_language_classification_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_language_classification_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_language_classification_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/language_classification_infer.tar && tar -xf language_classification_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── language_classification_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify language about the image `./images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+word_35404.png: class id(s): [4, 6], score(s): [0.89, 0.01], label_name(s): ['japan', 'korean']
+```
+
+**Note**: Among the prediction results, `japan` means japanese and `korean` means korean.
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/language_classification/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+word_17.png: class id(s): [9, 4], score(s): [0.80, 0.09], label_name(s): ['latin', 'japan']
+word_20.png: class id(s): [0, 4], score(s): [0.91, 0.02], label_name(s): ['arabic', 'japan']
+word_35404.png: class id(s): [4, 6], score(s): [0.89, 0.01], label_name(s): ['japan', 'korean']
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `japan` means japanese, `latin` means latin, `arabic` means arabic and `korean` means korean.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_model_list_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_model_list_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a7de0ce2c996132e6c882a10f5fcecd22398cc22
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_model_list_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+# PULC Model Zoo
+
+------
+
+The PULC model zoo is provided here, mainly providing indicators, model storage size, and download links of the model. The pre-trained model can be used for fine-tuning training, and the inference model can be directly used for prediction and deployment.
+
+
+|Model name| Model Description | Metrics |Storage Size| Latency| Download Address|
+| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| person_exists |[Human Exists Classification](PULC_person_exists_en.md)| 96.23 |7.0M|2.58ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/person_exists_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/person_exists_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| person_attribute |[Pedestrian Attribute Classification](PULC_person_attribute_en.md)| 78.59 |7.2M|2.01ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/person_attribute_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/person_attribute_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| safety_helmet |[Classification of Wheather Wearing Safety Helmet](PULC_safety_helmet_en.md)| 99.38 |7.1M|2.03ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/safety_helmet_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/safety_helmet_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| traffic_sign |[Traffic Sign Classification](PULC_traffic_sign_en.md)| 98.35 |8.2M|2.10ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/traffic_sign_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/traffic_sign_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| vehicle_attribute |[Vehicle Attribute Classification](PULC_vehicle_attribute_en.md)| 90.81 |7.2M|2.36ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/vehicle_attribute_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/vehicle_attribute_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| car_exists |[Car Exists Classification](PULC_car_exists_en.md) | 95.92 | 7.1M | 2.38ms |[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/car_exists_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/car_exists_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| text_image_orientation |[Text Image Orientation Classification](PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md)| 99.06 | 7.1M | 2.16ms |[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/text_image_orientation_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/text_image_orientation_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| textline_orientation |[Text-line Orientation Classification](PULC_textline_orientation_en.md)| 96.01 |7.0M|2.72ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/textline_orientation_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/textline_orientation_pretrained.pdparams)|
+| language_classification |[Language Classification](PULC_language_classification_en.md)| 99.26 |7.1M|2.58ms|[inference model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/inference/language_classification_infer.tar) / [pretrained model](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/pretrained/language_classification_pretrained.pdparams)|
+
+
+**Note:**
+
+* The backbone of all the above models is PPLCNet_x1_0. The different sizes of some models are caused by the different output sizes of the classification layer. The inference time is tested on the Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. During the test process, the MKLDNN acceleration strategy is turned on, and the number of threads is 10. There will be slight fluctuations during the speed test process.
+
+* The evaluation indicators of person_exists, safety_helmet, and car_exists are TprAtFpr. The evaluation indicators of person_attribute and vehicle_attribute are ma. The evaluation indicators of traffic_sign, text_image_orientation, textline_orientation and language_classification are Top-1 Acc.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_attribute_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_attribute_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..173313aad1a684289f3a6825cdf73ea01493847d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_attribute_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,448 @@
+# PULC Recognition Model of Person Attribute
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of person attribute using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in
+Pedestrian analysis scenarios, pedestrian tracking scenarios, etc.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first three lines means that using Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s, SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The fourth to seventh lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+
+| Backbone | ma(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M) | Training Strategy |
+|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s | 81.25 | 77.51 | 293 | using ImageNet pretrained |
+| SwinTransformer_tiny | 80.17 | 89.51 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 70.79 | 2.90 | 1.7 | using ImageNet pretrained |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 76.31 | 2.01 | 7.1 | using ImageNet pretrained |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 77.31 | 2.01 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 77.71 | 2.01 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained + EDA strategy|
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 78.59 | 2.01 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high ma metric can be getted when backbone are Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s and SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the ma metric will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the ma metric is higher more 5.5 percentage points higher than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 20% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the ma metric can be improved by about 1 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Further, additional using the EDA strategy, the ma metric can be increased by 0.4 percentage points. Finally, after additional using the SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, the ma matric can be further improved by 0.88 percentage points. At this time, the ma metric of PPLCNet_x1_0 is only 1.58% different from SwinTransformer_tiny, but the speed is more than 44 times faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=person_attribute --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/person_attribute/090004.jpg
+```
+
+Results:
+```
+>>> result
+attributes: ['Male', 'Age18-60', 'Back', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'Backpack', 'Upper: LongSleeve UpperPlaid', 'Lower: Trousers', 'No boots'], output: [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/person_attribute/090004.jpg
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_attribute")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/person_attribute/090004.jpg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_attribute", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'attributes': ['Male', 'Age18-60', 'Back', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'Backpack', 'Upper: LongSleeve UpperPlaid', 'Lower: Trousers', 'No boots'], 'output': [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/person_attribute/090004.jpg'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+The data used in this case is the [pa100k dataset](https://www.v7labs.com/open-datasets/pa-100k).
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+
+We converted the data into a PaddleClas multi-label readable data format that can be downloaded directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pa100k.tar
+tar -xf pa100k.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `pa100k` directory:
+
+```
+pa100k
+├── train
+│ ├── 000001.jpg
+│ ├── 000002.jpg
+...
+├── val
+│ ├── 080001.jpg
+│ ├── 080002.jpg
+...
+├── test
+│ ├── 090001.jpg
+│ ├── 090002.jpg
+...
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+├── train_val_list.txt
+├── val_list.txt
+├── test_list.txt
+```
+
+Where `train/`, `val/`, `test/` are training set, validation set and test set respectively. `train_list.txt`, `val_list.txt`, `test_list.txt` are the label files of the training set, validation set, and test set, respectively. In this example, `test_list.txt` is not used for now.
+
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric for the validation set is around `77.71%` (the dataset is small and generally fluctuates around 0.3%).
+
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'attributes': ['Male', 'Age18-60', 'Back', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'Backpack', 'Upper: LongSleeve UpperPlaid', 'Lower: Trousers', 'No boots'], 'output': [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd
+```
+
+The best metric for the validation set is around `80.10%`. The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0_Distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd`, the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0_Distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model
+```
+
+The best metric for the validation set is around `78.5%`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_person_attribute_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `PPLCNet_x1_0_person_attribute_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_person_attribute_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/person_attribute_infer.tar && tar -xf person_attribute_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── person_attribute_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify whether there are human in the image `./images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=True
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+090004.jpg: {'attributes': ['Male', 'Age18-60', 'Back', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'Backpack', 'Upper: LongSleeve UpperPlaid', 'Lower: Trousers', 'No boots'], 'output': [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]}
+```
+
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/person_attribute/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+090004.jpg: {'attributes': ['Male', 'Age18-60', 'Back', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'Backpack', 'Upper: LongSleeve UpperPlaid', 'Lower: Trousers', 'No boots'], 'output': [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]}
+090007.jpg: {'attributes': ['Female', 'Age18-60', 'Side', 'Glasses: False', 'Hat: False', 'HoldObjectsInFront: False', 'No bag', 'Upper: ShortSleeve', 'Lower: Skirt&Dress', 'No boots'], 'output': [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]}
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `someone` means that there is a human in the image, `nobody` means that there is no human in the image.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_exists_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_exists_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..baf5ce3e4c295a57d928853f5a0b3da1d3c7b366
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_person_exists_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,458 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Someone or Nobody
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of human exists using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in monitoring scenarios, personnel access control scenarios, massive data filtering scenarios, etc.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to sixth lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Tpr(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 95.69 | 95.30 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 68.25 | 2.85 | 2.6 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 89.57 | 2.12 | 7.0 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 92.10 | 2.12 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 93.43 | 2.12 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 96.23 | 2.12 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high Tpr can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the Tpr will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the Tpr is higher more 20 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 20% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the Tpr can be improved by about 2.6 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Further, additional using the EDA strategy, the Tpr can be increased by 1.3 percentage points. Finally, after additional using the SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, the Tpr can be further improved by 2.8 percentage points. At this point, the Tpr is close to that of SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is more than 40 times faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About `Tpr` metric, please refer to [3.2 section](#3.2) for more information .
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=person_exists --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
+```
+
+Results:
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [0], scores: [0.9955421453341842], label_names: ['nobody'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_exists")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_exists", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [0], 'scores': [0.9955421453341842], 'label_names': ['nobody'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+All datasets used in this case are open source data. Train data is the subset of [MS-COCO](https://cocodataset.org/#overview) training data. And the validation data is the subset of [Object365](https://www.objects365.org/overview.html) training data. ImageNet_val is [ImageNet-1k](https://www.image-net.org/) validation data.
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The data used in this case can be getted by processing the open source data. The detailed processes are as follows:
+
+- Training data. This case deals with the annotation file of MS-COCO data training data. If a certain image contains the label of "person" and the area of this box is greater than 10% in the whole image, it is considered that the image contains human. If there is no label of "person" in a certain image, It is considered that the image does not contain human. After processing, 92964 pieces of available data were obtained, including 39813 images containing human and 53151 images without containing human.
+- Validation data: randomly select a small part of data from object365 data, use the better model trained on MS-COCO to predict these data, take the intersection between the prediction results and the data annotation file, and filter the intersection results into the validation set according to the method of obtaining the training set. After processing, 27820 pieces of available data were obtained. There are 2255 pieces of data with human and 25565 pieces of data without human. The data visualization of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/person_exists.tar
+tar -xf person_exists.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `person_exists` directory:
+
+```
+├── train
+│ ├── 000000000009.jpg
+│ ├── 000000000025.jpg
+...
+├── val
+│ ├── objects365_01780637.jpg
+│ ├── objects365_01780640.jpg
+...
+├── ImageNet_val
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000001.JPEG
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000002.JPEG
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+├── train_list.txt.debug
+├── train_list_for_distill.txt
+├── val_list.txt
+└── val_list.txt.debug
+```
+
+Where `train/` and `val/` are training set and validation set respectively. The `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively. The file `train_list.txt.debug` and `val_list.txt.debug` are subset of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` respectively. `ImageNet_val/` is the validation data of ImageNet-1k, which will be used for SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, and its label file is `train_list_for_distill.txt`.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+* About the `train_list_for_distill.txt`, please refer to [Knowledge Distillation Label](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.94` and `0.95`. There would be fluctuations because the data size is small.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The metric Tpr, that describe the True Positive Rate when False Positive Rate is less than a certain threshold(1/1000 used in this case), is one of the commonly used metric for binary classification. About the details of Fpr and Tpr, please refer [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receiver_operating_characteristic).
+* When evaluation, the best metric TprAtFpr will be printed that include `Fpr`, `Tpr` and the current `threshold`. The `Tpr` means the Recall rate under the current `Fpr`. The `Tpr` higher, the model better. The `threshold` would be used in deployment, which means the classification threshold under best `Fpr` metric.
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [1], 'scores': [0.9999976], 'label_names': ['someone'], 'file_name': 'deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg'}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+* The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9794`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9794` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/1000` in this valuation dataset.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.96` and `0.98`. The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd`, the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0` and the additional unlabeled training data is validation data of ImageNet1k. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model
+```
+
+The best metric is between `0.95` and `0.97`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_person_exists_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_person_exists_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_person_exists_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/person_exists_infer.tar && tar -xf person_exists_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── person_exists_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify whether there are humans in the image `./images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+objects365_02035329.jpg: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['someone']
+```
+
+**Note**: The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9794`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9794` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/1000` in this valuation dataset. Please refer to [3.3 section](#3.3) for details.
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/person_exists/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+objects365_01780782.jpg: class id(s): [0], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['nobody']
+objects365_02035329.jpg: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['someone']
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `someone` means that there is a human in the image, `nobody` means that there is no human in the image.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..087c359283c0e288db91bc80774163eda336853b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_quickstart_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+# PULC Quick Start
+
+------
+
+This document introduces the prediction using PULC series model based on PaddleClas wheel.
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Installation](#1)
+ - [1.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#11)
+ - [1.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation](#12)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 Predicion with Command Line](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 Predicion with Python](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Supported Model List](#2.3)
+- [3. Summary](#3)
+
+
+
+## 1. Installation
+
+
+
+### 1.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 1.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+PaddleClas provides a series of test cases, which contain demos of different scenes about people, cars, OCR, etc. Click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download the data.
+
+
+
+### 2.1 Predicion with Command Line
+
+```
+cd /path/to/pulc_demo_imgs
+```
+
+The prediction command:
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=person_exists --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
+```
+
+Result:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [0], scores: [0.9955421453341842], label_names: ['nobody'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
+Predict complete!
+```
+`Nobody` means there is no one in the image, `someone` means there is someone in the image. Therefore, the prediction result indicates that there is no one in the figure.
+
+**Note**: The "--infer_imgs" argument specify the image(s) to be predict, and you can also specify a directoy contains images. If use other model, you can specify the `--model_name` argument. Please refer to [2.3 Supported Model List](#2.3) for the supported model list.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 Predicion with Python
+
+You can also use in Python:
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_exists")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+The printed result information:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [0], 'scores': [0.9955421453341842], 'label_names': ['nobody'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg'}]
+```
+
+**Note**: `model.predict()` is a generator, so `next()` or `for` is needed to call it. This would to predict by batch that length is `batch_size`, default by 1. You can specify the argument `batch_size` and `model_name` when instantiating PaddleClas object, for example: `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="person_exists", batch_size=2)`. Please refer to [2.3 Supported Model List](#2.3) for the supported model list.
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Supported Model List
+
+The name of PULC series models are as follows:
+
+| Name | Intro |
+| --- | --- |
+| person_exists | Human Exists Classification |
+| person_attribute | Pedestrian Attribute Classification |
+| safety_helmet | Classification of Wheather Wearing Safety Helmet |
+| traffic_sign | Traffic Sign Classification |
+| vehicle_attribute | Vehicle Attribute Classification |
+| car_exists | Car Exists Classification |
+| text_image_orientation | Text Image Orientation Classification |
+| textline_orientation | Text-line Orientation Classification |
+| language_classification | Language Classification |
+
+
+
+## 3. Summary
+
+The PULC series models have been verified to be effective in different scenarios about people, vehicles, OCR, etc. The ultra lightweight model can achieve the accuracy close to SwinTransformer model, and the speed is increased by 40+ times. And PULC also provides the whole process of dataset getting, model training, model compression and deployment. Please refer to [Human Exists Classification](PULC_person_exists_en.md)、[Pedestrian Attribute Classification](PULC_person_attribute_en.md)、[Classification of Wheather Wearing Safety Helmet](PULC_safety_helmet_en.md)、[Traffic Sign Classification](PULC_traffic_sign_en.md)、[Vehicle Attribute Classification](PULC_vehicle_attribute_en.md)、[Car Exists Classification](PULC_car_exists_en.md)、[Text Image Orientation Classification](PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md)、[Text-line Orientation Classification](PULC_textline_orientation_en.md)、[Language Classification](PULC_language_classification_en.md) for more information about different scenarios.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_safety_helmet_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_safety_helmet_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d2e5cb32931cdc98b0776f4692e6162e907aa6fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_safety_helmet_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,432 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Wheather Wearing Safety Helmet or Not
+
+-----
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of wheather wearing safety helmet using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in construction scenes, factory workshop scenes, traffic scenes and so on.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first three lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny, Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The fourth to seventh lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Tpr(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 93.57 | 91.32 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s | 98.92 | 80.99 | 284 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 84.83 | 2.85 | 2.6 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 93.27 | 2.03 | 7.1 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.16 | 2.03 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 99.30 | 2.03 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 99.38 | 2.03 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high Tpr can be getted when backbone is Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the Tpr will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the Tpr is higher more 8.5 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 20% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the Tpr can be improved by about 4.9 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Further, additional using the EDA strategy, the Tpr can be increased by 1.1 percentage points. Finally, after additional using the UDML knowledge distillation, the Tpr can be further improved by 2.2 percentage points. At this point, the Tpr is higher than that of Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s, but the speed is more than 70 times faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About `Tpr` metric, please refer to [3.2 section](#3.2) for more information .
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=safety_helmet --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [1], scores: [0.9986255], label_names: ['unwearing_helmet'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png
+Predict complete!
+```
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="safety_helmet")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="safety_helmet", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [1], 'scores': [0.9986255], 'label_names': ['unwearing_helmet'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+All datasets used in this case are open source data. Train data is the subset of [Safety-Helmet-Wearing-Dataset](https://github.com/njvisionpower/Safety-Helmet-Wearing-Dataset), [hard-hat-detection](https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/andrewmvd/hard-hat-detection) and [Large-scale CelebFaces Attributes (CelebA) Dataset](https://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/CelebA.html).
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The data used in this case can be getted by processing the open source data. The detailed processes are as follows:
+
+* `Safety-Helmet-Wearing-Dataset`: according to the bbox label data, the image is cropped by enlarging width and height of bbox by 3 times. The label is 0 if wearing safety helmet in the image, and the label is 1 if not;
+* `hard-hat-detection`: Only use the image that labeled "hat" and crop it with bbox. The label is 0;
+* `CelebA`: Only use the image labeled "wearing_hat" and crop it with bbox. The label is 0;
+
+After processing, the dataset totals about 150000 images, of which the number of images with and without wearing safety helmet is about 28000 and 121000 respectively. Then 5600 images are randomly selected in the two labels as the valuation data, a total of about 11200 images, and about 138000 other images as the training data.
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/safety_helmet.tar
+tar -xf safety_helmet.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `safety_helmet` directory:
+
+```
+├── images
+│ ├── VOC2028_part2_001209_1.jpg
+│ ├── HHD_hard_hat_workers23_1.jpg
+│ ├── CelebA_077809.jpg
+│ ├── ...
+│ └── ...
+├── train_list.txt
+└── val_list.txt
+```
+
+The `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively. All images in `images/` directory.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/person_exists/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.985` and `0.993`. There would be fluctuations because the data size is small.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The metric Tpr, that describe the True Positive Rate when False Positive Rate is less than a certain threshold(1/10000 used in this case), is one of the commonly used metric for binary classification. About the details of Fpr and Tpr, please refer [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receiver_operating_characteristic).
+* When evaluation, the best metric TprAtFpr will be printed that include `Fpr`, `Tpr` and the current `threshold`. The `Tpr` means the Recall rate under the current `Fpr`. The `Tpr` higher, the model better. The `threshold` would be used in deployment, which means the classification threshold under best `Fpr` metric.
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [1], 'scores': [0.9524797], 'label_names': ['unwearing_helmet'], 'file_name': 'deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png'}]
+```
+
+**备注:**
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+* The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9167`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9167` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/10000` in this valuation dataset.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 UDML Knowledge Distillation
+
+UDML is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas. Please refer to [UDML 知识蒸馏](../advanced_tutorials/knowledge_distillation_en.md#1.2.3) for more details.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+Training with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric is between `0.990` and `0.993`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_safety_helmet_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_safety_helmet_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_safety_helmet_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/safety_helmet_infer.tar && tar -xf safety_helmet_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── safety_helmet_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify whether wearing safety helmet about the image `./images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+safety_helmet_test_1.png: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['unwearing_helmet']
+```
+
+**Note**: The default threshold is `0.5`. If needed, you can specify the argument `Infer.PostProcess.threshold`, such as: `-o Infer.PostProcess.threshold=0.9167`. And the argument `threshold` is needed to be specified according by specific case. The `0.9167` is the best threshold when `Fpr` is less than `1/10000` in this valuation dataset. Please refer to [3.3 section](#3.3) for details.
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/safety_helmet/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+safety_helmet_test_1.png: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['unwearing_helmet']
+safety_helmet_test_2.png: class id(s): [0], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['wearing_helmet']
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `wearing_helmet` means that wearing safety helmet about the image, `unwearing_helmet` means not.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1d3cc41f992adff90f396463205cd060147023c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_text_image_orientation_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,466 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Text Image Orientation
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+In the process of document scanning, license shooting and so on, sometimes in order to shoot more clearly, the camera device will be rotated, resulting in photo in different directions. At this time, the standard OCR process cannot cope with these issues well. Using the text image orientation classification technology, the direction of the text image can be predicted and adjusted, so as to improve the accuracy of OCR processing. This case provides a way for users to use PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification) to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision, practical classification model of text image orientation. This model can be widely used in OCR processing scenarios of rotating pictures in financial, government and other industries.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to fifth lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of SSLD pretrained model and additional use of hyperparameters searching strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Top1-Acc(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+| ----------------------- | --------- | ---------- | --------- | ------------------------------------- |
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 99.12 | 89.65 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 83.61 | 2.95 | 2.6 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 97.85 | 2.16 | 7.1 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.02 | 2.16 | 7.1 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| **PPLCNet_x1_0** | **99.06** | **2.16** | **7.1** | using SSLD pretrained model + hyperparameters searching strategy |
+
+It can be seen that high accuracy can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the accuracy will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the accuracy is higher more 14 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the accuracy can be improved by about 0.17 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Finally, after additional using the hyperparameters searching strategy, the accuracy can be further improved by 1.04 percentage points. At this point, the accuracy is close to that of SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is more faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=text_image_orientation --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [0, 2], scores: [0.85615, 0.05046], label_names: ['0', '180'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="text_image_orientation")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="text_image_orientation", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [0, 2], 'scores': [0.85615, 0.05046], 'label_names': ['0', '180'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+The model provided in [1 section](#1) is trained using internal data, which has not been open source. So we provide a dataset with [ICDAR2019-ArT](https://ai.baidu.com/broad/introduction?dataset=art), [XFUND](https://github.com/doc-analysis/XFUND) and [ICDAR2015](https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=4&com=introduction) to experience.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The data used in this case can be getted by processing the open source data. The detailed processes are as follows:
+
+Considering the resolution of original image is too high to need long training time, all the data are scaled in advance. Keeping image aspect ratio, the short edge is scaled to 384. Then rotate the data clockwise to generate composite data of 90 degrees, 180 degrees and 270 degrees respectively. Among them, 41460 images generated by ICDAR2019-ArT and XFUND are randomly divided into training set and verification set according to the ratio of 9:1. 6000 images generated by ICDAR2015 are used as supplementary data in the experiment of `SKL-UGI knowledge distillation`.
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/text_image_orientation.tar
+tar -xf text_image_orientation.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `text_image_orientation` directory:
+
+```
+├── img_0
+│ ├── img_rot0_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_rot0_1.png
+...
+├── img_90
+│ ├── img_rot90_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_rot90_1.png
+...
+├── img_180
+│ ├── img_rot180_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_rot180_1.png
+...
+├── img_270
+│ ├── img_rot270_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_rot270_1.png
+...
+├── distill_data
+│ ├── gt_7060_0.jpg
+│ ├── gt_7060_90.jpg
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+├── train_list.txt.debug
+├── train_list_for_distill.txt
+├── test_list.txt
+├── test_list.txt.debug
+└── label_list.txt
+```
+
+Where `img_0/`, `img_90/`, `img_180/` and `img_270/` are data of 4 angles respectively. The `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively. The file `train_list.txt.debug` and `val_list.txt.debug` are subset of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` respectively. `distill_data/` is the supplementary data, which will be used for SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, and its label file is `train_list_for_distill.txt`.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+* About the `train_list_for_distill.txt`, please refer to [Knowledge Distillation Label](../advanced_tutorials/distillation/distillation_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is about `0.99`.
+
+
+**Note**:
+* The metric mentioned in this document are training on large-scale internal dataset. When using demo data to train, this metric cannot be achieved because the dataset is small and the distribution is different from large-scale internal data. You can further expand your own data and use the optimization method described in this case to achieve higher accuracy.
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [0, 2], 'scores': [0.85615, 0.05046], 'file_name': 'deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg', 'label_names': ['0', '180']}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+* The Top2 result would be printed. `0` means that the text direction of the drawing is 0 degrees, `90` means that 90 degrees clockwise, `180` means that 180 degrees clockwise, `270` means that 270 degrees clockwise.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is about `0.996`. The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+**Note**: Training ResNet101_vd need more GPU memory. So you can reduce `batch_size` and `learning rate` at the same time, such as: `-o DataLoader.Train.sampler.batch_size=64`, `Optimizer.lr.learning_rate=0.1`.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd` and the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0`.
+
+The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model
+```
+
+The best metric is about `0.99`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model_student \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_text_image_orientation_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_text_image_orientation_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_text_image_orientation_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# download the inference model and decompression
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/text_image_orientation_infer.tar && tar -xf text_image_orientation_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── text_image_orientation_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify text image orientation about image `./images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.png`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+img_rot0_demo.jpg: class id(s): [0, 2], score(s): [0.86, 0.05], label_name(s): ['0', '180']
+```
+
+Among the results, `0` means that the text direction of the drawing is 0 degrees, `90` means that 90 degrees clockwise, `180` means that 180 degrees clockwise, `270` means that 270 degrees clockwise.
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/text_image_orientation/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+img_rot0_demo.jpg: class id(s): [0, 2], score(s): [0.86, 0.05], label_name(s): ['0', '180']
+img_rot180_demo.jpg: class id(s): [2, 1], score(s): [0.88, 0.04], label_name(s): ['180', '90']
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_textline_orientation_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_textline_orientation_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d11307d0b5aafe056c1f1e53a85882d2449ac277
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_textline_orientation_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,450 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Textline Orientation
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of textline orientation using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in character correction, character recognition, etc.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to seventh lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Top-1 Acc(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 93.61 | 89.64 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 81.40 | 2.96 | 2.6 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 89.99 | 2.11 | 7.0 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0* | 94.06 | 2.68 | 7.0 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0* | 94.11 | 2.68 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0** | 96.01 | 2.72 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0** | 95.86 | 2.72 | 7.0 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high accuracy can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the accuracy will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the accuracy is higher more 8.6 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 10% faster. On this basis, by changing the resolution and stripe (refer to [PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)), the speed becomes 27% slower, but the accuracy can be improved by 4.5 percentage points. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the accuracy can be improved by about 0.05 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Finally, additional using the EDA strategy, the accuracy can be increased by 1.9 percentage points. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+* Backbone name without \* means the resolution is 224x224, and with \* means the resolution is 48x192 (h\*w). The stride of the network is changed to `[2, [2, 1], [2, 1], [2, 1]`. Please refer to [PaddleOCR]( https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)for more details.
+* Backbone name with \*\* means that the resolution is 80x160 (h\*w), and the stride of the network is changed to `[2, [2, 1], [2, 1], [2, 1]]`. This resolution is searched by [Hyperparameter Searching](pulc_train_en.md#4).
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=textline_orientation --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [0], scores: [1.0], label_names: ['0_degree'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="textline_orientation")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="textline_orientation", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [0], 'scores': [1.0], 'label_names': ['0_degree'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+The data used in this case come from internal data. If you want to experience the training process, you can use open source data, such as [ICDAR2019-LSVT](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/8429).
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+Take ICDAR2019-LSVT for example, images with ID numbers from 0 to 1999 would be processed and used. After rotation, it is divided into class 0 or class 1. Class 0 means that the textline rotation angle is 0 degrees, and class 1 means 180 degrees.
+
+- Training data: The images with ID number from 0 to 1799 are used as the training set. 3600 images in total.
+- Evaluation data: The images with ID number from 1800 to 1999 are used as the evaluation set. 400 images in total.
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+
+And you can also download the data processed directly.
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+Enter the `dataset/` directory, download and unzip the dataset.
+
+```shell
+cd dataset
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/textline_orientation.tar
+tar -xf textline_orientation.tar
+cd ../
+```
+
+The datas under `textline_orientation` directory:
+
+```
+├── 0
+│ ├── img_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_1.jpg
+...
+├── 1
+│ ├── img_0.jpg
+│ ├── img_1.jpg
+...
+├── train_list.txt
+└── val_list.txt
+```
+
+其中 `0/` 和 `1/` 分别存放 0 类和 1 类的数据。`train_list.txt` 和 `val_list.txt` 分别为训练集和验证集的标签文件。
+
+Where `0/` and `1/` are class 0 and class 1 data respectively. The `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt` are label files of training data and validation data respectively.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* About the contents format of `train_list.txt` and `val_list.txt`, please refer to [Description about Classification Dataset in PaddleClas](../data_preparation/classification_dataset_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 3.3 Training
+
+The details of training config in `ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command about training as follows:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Because the ICDAR2019-LSVT data set is different from the dataset used in the provided pretrained model. If you want to get higher accuracy, you can process [ICDAR2019-LSVT](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/8429).
+
+
+
+### 3.4 Evaluation
+
+After training, you can use the following commands to evaluate the model.
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"
+```
+
+Among the above command, the argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+
+
+
+### 3.5 Inference
+
+After training, you can use the model that trained to infer. Command is as follow:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+The results:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [0], 'scores': [1.0], 'file_name': 'deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png', 'label_names': ['0_degree']}]
+```
+
+**Note**:
+
+* Among the above command, argument `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model"` specify the path of the best model weight file. You can specify other path if needed.
+* The default test image is `deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png`. And you can test other image, only need to specify the argument `-o Infer.infer_imgs=path_to_test_image`.
+
+
+
+## 4. Model Compression
+
+
+
+### 4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation
+
+SKL-UGI is a simple but effective knowledge distillation algrithem proposed by PaddleClas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.1 Teacher Model Training
+
+Training the teacher model with hyperparameters specified in `ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Arch.name=ResNet101_vd
+```
+
+The best metric of validation data is between `0.96` and `0.98`. The best teacher model weight would be saved in file `output/ResNet101_vd/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training
+
+The training strategy, specified in training config file `ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml`, the teacher model is `ResNet101_vd` and the student model is `PPLCNet_x1_0`. The command is as follow:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
+ tools/train.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0_distillation.yaml \
+ -o Arch.models.0.Teacher.pretrained=output/ResNet101_vd/best_model
+```
+
+The best metric is between `0.95` and `0.97`. The best student model weight would be saved in file `output/DistillationModel/best_model_student.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+## 5. Hyperparameters Searching
+
+The hyperparameters used by [3.2 section](#3.2) and [4.1 section](#4.1) are according by `Hyperparameters Searching` in PaddleClas. If you want to get better results on your own dataset, you can refer to [Hyperparameters Searching](PULC_train_en.md#4) to get better hyperparameters.
+
+**Note**: This section is optional. Because the search process will take a long time, you can selectively run according to your specific. If not replace the dataset, you can ignore this section.
+
+
+
+## 6. Inference Deployment
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model
+
+Paddle Inference is the original Inference Library of the PaddlePaddle, provides high-performance inference for server deployment. And compared with directly based on the pretrained model, Paddle Inference can use tools to accelerate prediction, so as to achieve better inference performance. Please refer to [Paddle Inference](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html) for more information.
+
+Paddle Inference need Paddle Inference Model to predict. Two process provided to get Paddle Inference Model. If want to use the provided by PaddleClas, you can download directly, click [Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2).
+
+
+
+### 6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model
+
+The command about exporting Paddle Inference Model is as follow:
+
+```bash
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model \
+ -o Global.save_inference_dir=deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_textline_orientation_infer
+```
+
+After running above command, the inference model files would be saved in `deploy/models/PPLCNet_x1_0_textline_orientation_infer`, as shown below:
+
+```
+├── PPLCNet_x1_0_textline_orientation_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+**Note**: The best model is from knowledge distillation training. If knowledge distillation training is not used, the best model would be saved in `output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model.pdparams`.
+
+
+
+### 6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model
+
+You can also download directly.
+
+```
+cd deploy/models
+# 下载 inference 模型并解压
+wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/models/PULC/textline_orientation_infer.tar && tar -xf textline_orientation_infer.tar
+```
+
+After decompression, the directory `models` should be shown below.
+
+```
+├── textline_orientation_infer
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams
+│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
+│ └── inference.pdmodel
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Prediction with Python
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.1 Image Prediction
+
+Return the directory `deploy`:
+
+```
+cd ../
+```
+
+Run the following command to classify the rotation of image `./images/PULC/textline_orientation/objects365_02035329.jpg`.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
+# Use the following command to predict with CPU.
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml -o Global.use_gpu=False
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+textline_orientation_test_0_0.png: class id(s): [0], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['0_degree']
+```
+
+
+
+#### 6.2.2 Images Prediction
+
+If you want to predict images in directory, please specify the argument `Global.infer_imgs` as directory path by `-o Global.infer_imgs`. The command is as follow.
+
+```shell
+# Use the following command to predict with GPU. If want to replace with CPU, you can add argument -o Global.use_gpu=False
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml -o Global.infer_imgs="./images/PULC/textline_orientation/"
+```
+
+All prediction results will be printed, as shown below.
+
+```
+textline_orientation_test_0_0.png: class id(s): [0], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['0_degree']
+textline_orientation_test_0_1.png: class id(s): [0], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['0_degree']
+textline_orientation_test_1_0.png: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['180_degree']
+textline_orientation_test_1_1.png: class id(s): [1], score(s): [1.00], label_name(s): ['180_degree']
+```
+
+Among the prediction results above, `0_degree` means that the rotation angle of the textline image is 0, and `180_degree` means that 180.
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Deployment with C++
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy with C++. Please refer to [Deployment with C++](../inference_deployment/cpp_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.4 Deployment as Service
+
+Paddle Serving is a flexible, high-performance carrier for machine learning models, and supports different protocol, such as RESTful, gRPC, bRPC and so on, which provides different deployment solutions for a variety of heterogeneous hardware and operating system environments. Please refer [Paddle Serving](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example about how to deploy as service by Paddle Serving. Please refer to [Paddle Serving Deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_serving_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.5 Deployment on Mobile
+
+Paddle-Lite is an open source deep learning framework that designed to make easy to perform inference on mobile, embeded, and IoT devices. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite) for more information.
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to deploy on mobile by Paddle-Lite. Please refer to [Paddle-Lite deployment](../inference_deployment/paddle_lite_deploy_en.md).
+
+
+
+### 6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+Paddle2ONNX support convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model. And you can deploy with ONNX model on different inference engine, such as TensorRT, OpenVINO, MNN/TNN, NCNN and so on. About Paddle2ONNX details, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
+
+PaddleClas provides an example of how to convert Paddle Inference model to ONNX model by paddle2onnx toolkit and predict by ONNX model. You can refer to [paddle2onnx](../../../deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md) for deployment details.
diff --git a/docs/en/PULC/PULC_traffic_sign_en.md b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_traffic_sign_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..baa0faf4828a6c7acc16f8c12587a2af58c04f99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/PULC/PULC_traffic_sign_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,475 @@
+# PULC Classification Model of Traffic Sign
+
+------
+
+## Catalogue
+
+- [1. Introduction](#1)
+- [2. Quick Start](#2)
+ - [2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 PaddleClas Installation](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 Prediction](#2.3)
+- [3. Training, Evaluation and Inference](#3)
+ - [3.1 Installation](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 Dataset](#3.2)
+ - [3.2.1 Dataset Introduction](#3.2.1)
+ - [3.2.2 Getting Dataset](#3.2.2)
+ - [3.3 Training](#3.3)
+ - [3.4 Evaluation](#3.4)
+ - [3.5 Inference](#3.5)
+- [4. Model Compression](#4)
+ - [4.1 SKL-UGI Knowledge Distillation](#4.1)
+ - [4.1.1 Teacher Model Training](#4.1.1)
+ - [4.1.2 Knowledge Distillation Training](#4.1.2)
+- [5. SHAS](#5)
+- [6. Inference Deployment](#6)
+ - [6.1 Getting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1)
+ - [6.1.1 Exporting Paddle Inference Model](#6.1.1)
+ - [6.1.2 Downloading Inference Model](#6.1.2)
+ - [6.2 Prediction with Python](#6.2)
+ - [6.2.1 Image Prediction](#6.2.1)
+ - [6.2.2 Images Prediction](#6.2.2)
+ - [6.3 Deployment with C++](#6.3)
+ - [6.4 Deployment as Service](#6.4)
+ - [6.5 Deployment on Mobile](#6.5)
+ - [6.6 Converting To ONNX and Deployment](#6.6)
+
+
+
+## 1. Introduction
+
+This case provides a way for users to quickly build a lightweight, high-precision and practical classification model of traffic sign using PaddleClas PULC (Practical Ultra Lightweight image Classification). The model can be widely used in automatic driving, road monitoring, etc.
+
+The following table lists the relevant indicators of the model. The first two lines means that using SwinTransformer_tiny and MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 as the backbone to training. The third to sixth lines means that the backbone is replaced by PPLCNet, additional use of EDA strategy and additional use of EDA strategy and SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy.
+
+| Backbone | Top-1 Acc(%) | Latency(ms) | Size(M)| Training Strategy |
+|-------|-----------|----------|---------------|---------------|
+| SwinTranformer_tiny | 98.11 | 89.45 | 111 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 | 93.88 | 3.01 | 3.9 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 97.78 | 2.10 | 8.2 | using ImageNet pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 97.84 | 2.10 | 8.2 | using SSLD pretrained model |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.14 | 2.10 | 8.2 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy |
+| PPLCNet_x1_0 | 98.35 | 2.10 | 8.2 | using SSLD pretrained model + EDA strategy + SKL-UGI knowledge distillation strategy|
+
+It can be seen that high accuracy can be getted when backbone is SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is slow. Replacing backbone with the lightweight model MobileNetV3_small_x0_35, the speed can be greatly improved, but the accuracy will be greatly reduced. Replacing backbone with faster backbone PPLCNet_x1_0, the accuracy is lower 3.9 percentage points than MobileNetv3_small_x0_35. At the same time, the speed can be more than 43% faster. After additional using the SSLD pretrained model, the accuracy can be improved by about 0.06 percentage points without affecting the inference speed. Further, additional using the EDA strategy, the accuracy can be increased by 0.3 percentage points. Finally, after additional using the SKL-UGI knowledge distillation, the accuracy can be further improved by 0.21 percentage points. At this point, the accuracy exceeds that of SwinTranformer_tiny, but the speed is more than 41 times faster. The training method and deployment instructions of PULC will be introduced in detail below.
+
+**Note**:
+
+* The Latency is tested on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz. The MKLDNN is enabled and the number of threads is 10.
+* About PP-LCNet, please refer to [PP-LCNet Introduction](../models/PP-LCNet_en.md) and [PP-LCNet Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.15099).
+
+
+
+## 2. Quick Start
+
+
+
+### 2.1 PaddlePaddle Installation
+
+- Run the following command to install if CUDA9 or CUDA10 is available.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+- Run the following command to install if GPU device is unavailable.
+
+```bash
+python3 -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+```
+
+Please refer to [PaddlePaddle Installation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html) for more information about installation, for examples other versions.
+
+
+
+### 2.2 PaddleClas wheel Installation
+
+The command of PaddleClas installation as bellow:
+
+```bash
+pip3 install paddleclas
+```
+
+
+
+### 2.3 Prediction
+
+First, please click [here](https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/pulc_demo_imgs.zip) to download and unzip to get the test demo images.
+
+* Prediction with CLI
+
+```bash
+paddleclas --model_name=traffic_sign --infer_imgs=pulc_demo_imgs/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg
+```
+
+Results:
+
+```
+>>> result
+class_ids: [182, 179, 162, 128, 24], scores: [0.98623, 0.01255, 0.00022, 0.00021, 0.00012], label_names: ['pl110', 'pl100', 'pl120', 'p26', 'pm10'], filename: pulc_demo_imgs/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg
+Predict complete!
+```
+
+**Note**: If you want to test other images, only need to specify the `--infer_imgs` argument, and the directory containing images is also supported.
+
+* Prediction in Python
+
+```python
+import paddleclas
+model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="traffic_sign")
+result = model.predict(input_data="pulc_demo_imgs/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg")
+print(next(result))
+```
+
+**Note**: The `result` returned by `model.predict()` is a generator, so you need to use the `next()` function to call it or `for` loop to loop it. And it will predict with `batch_size` size batch and return the prediction results when called. The default `batch_size` is 1, and you also specify the `batch_size` when instantiating, such as `model = paddleclas.PaddleClas(model_name="traffic_sign", batch_size=2)`. The result of demo above:
+
+```
+>>> result
+[{'class_ids': [182, 179, 162, 128, 24], 'scores': [0.98623, 0.01255, 0.00022, 0.00021, 0.00012], 'label_names': ['pl110', 'pl100', 'pl120', 'p26', 'pm10'], 'filename': 'pulc_demo_imgs/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg'}]
+```
+
+
+
+## 3. Training, Evaluation and Inference
+
+
+
+### 3.1 Installation
+
+Please refer to [Installation](../installation/install_paddleclas_en.md) to get the description about installation.
+
+
+
+### 3.2 Dataset
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.1 Dataset Introduction
+
+All datasets used in this case are open source data. Train data is the subset of [MS-COCO](https://cocodataset.org/#overview) training data. And the validation data is the subset of [Object365](https://www.objects365.org/overview.html) training data. ImageNet_val is [ImageNet-1k](https://www.image-net.org/) validation data.
+
+The dataset used in this case is based on the [Tsinghua-Tencent 100K dataset (CC-BY-NC license), TT100K](https://cg.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/traffic-sign/) randomly expanded and cropped according to the bounding box.
+
+
+
+#### 3.2.2 Getting Dataset
+
+The processing to `TT00K` includes randomly expansion and cropping, details are shown below.
+
+```python
+def get_random_crop_box(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, img_height, img_width, ratio=1.0):
+ h = ymax - ymin
+ w = ymax - ymin
+
+ xmin_diff = random.random() * ratio * min(w, xmin/ratio)
+ ymin_diff = random.random() * ratio * min(h, ymin/ratio)
+ xmax_diff = random.random() * ratio * min(w, (img_width-xmin-1)/ratio)
+ ymax_diff = random.random() * ratio * min(h, (img_height-ymin-1)/ratio)
+
+ new_xmin = round(xmin - xmin_diff)
+ new_ymin = round(ymin - ymin_diff)
+ new_xmax = round(xmax + xmax_diff)
+ new_ymax = round(ymax + ymax_diff)
+
+ return new_xmin, new_ymin, new_xmax, new_ymax
+```
+
+Some image of the processed dataset is as follows:
+
+
+

+
+
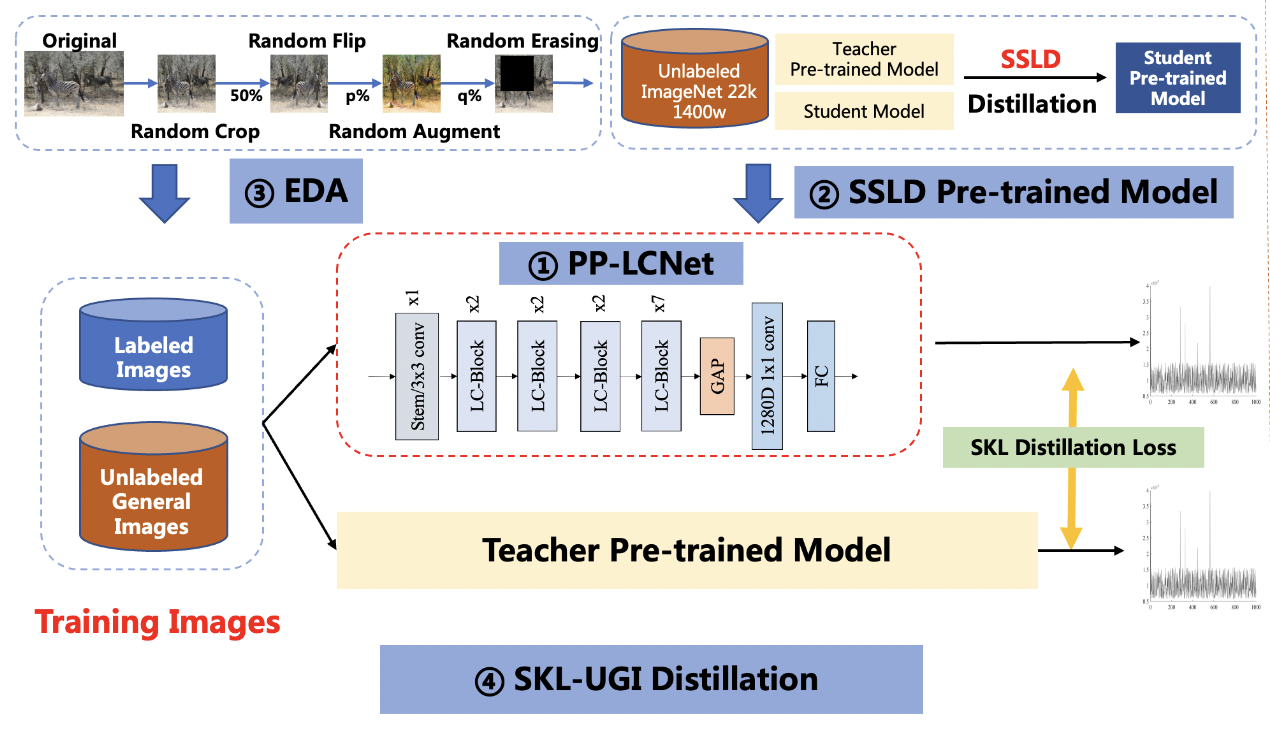
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
Augment\[1\] | Rand-
Augment\[2\] | CutOut\[3\] | Rand
Erasing\[4\] | HideAnd-
Seek\[5\] | GridMask\[6\] | Mixup\[7\] | Cutmix\[8\] |
+|-------------|---------------------------|---------------------------|------------------|------------------|-------------|------------------|------------------|---------------|------------|------------|
+| Image
Decode | Binary | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| RandCrop | (:, :, 3)
uint8 | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| **Process** | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | Y | Y | \- | \- | \- | \- | \- | \- |
+| RandFlip | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | (224, 224, 3)
float32 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| Normalize | (224, 224, 3)
uint8 | (3, 224, 224)
float32 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| Transpose | (224, 224, 3)
float32 | (3, 224, 224)
float32 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| **Process** | (3, 224, 224)
float32 | (3, 224, 224)
float32 | \- | \- | Y | Y | Y | Y | \- | \- |
+| Batch | (3, 224, 224)
float32 | (N, 3, 224, 224)
float32 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
+| **Process** | (N, 3, 224, 224)
float32 | (N, 3, 224, 224)
float32 | \- | \- | \- | \- | \- | \- | Y | Y |
+
+
+PaddleClas 中集成了上述所有的数据增强策略,每种数据增强策略的参考论文与参考开源代码均在下面的介绍中列出。下文将介绍这些策略的原理与使用方法,并以下图为例,对变换后的效果进行可视化。为了说明问题,本章节中将 `RandCrop` 替换为 `Resize`。
+
+![][test_baseline]
+
+
+
+### 1.2 图像变换类
+
+图像变换类指的是对 `RandCrop` 后的 224 的图像进行一些变换,主要包括
+
++ AutoAugment
++ RandAugment
++ TimmAutoAugment
+
+
+
+#### 1.2.1 AutoAugment
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.1.1 AutoAugment 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.09501v1](https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.09501v1)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/DeepVoltaire/AutoAugment](https://github.com/DeepVoltaire/AutoAugment)
+
+不同于常规的人工设计图像增广方式,AutoAugment 是在一系列图像增广子策略的搜索空间中通过搜索算法找到的适合特定数据集的图像增广方案。针对 ImageNet 数据集,最终搜索出来的数据增强方案包含 25 个子策略组合,每个子策略中都包含两种变换,针对每幅图像都随机的挑选一个子策略组合,然后以一定的概率来决定是否执行子策略中的每种变换。
+
+经过 AutoAugment 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_autoaugment]
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.1.2 AutoAugment 配置
`AotoAugment` 的图像增广方式的配置如下。`AutoAugment` 是在 uint8 的数据格式上转换的,所以其处理过程应该放在归一化操作(`NormalizeImage`)之前。
@@ -48,8 +164,31 @@
order: ''
```
-
-### 1.2 RandAugment
+
+
+#### 1.2.2 RandAugment
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.2.1 RandAugment 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.13719.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.13719.pdf)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/heartInsert/randaugment](https://github.com/heartInsert/randaugment)
+
+
+`AutoAugment` 的搜索方法比较暴力,直接在数据集上搜索针对该数据集的最优策略,其计算量很大。在 `RandAugment` 文章中作者发现,一方面,针对越大的模型,越大的数据集,使用 `AutoAugment` 方式搜索到的增广方式产生的收益也就越小;另一方面,这种搜索出的最优策略是针对该数据集的,其迁移能力较差,并不太适合迁移到其他数据集上。
+
+在 `RandAugment` 中,作者提出了一种随机增广的方式,不再像 `AutoAugment` 中那样使用特定的概率确定是否使用某种子策略,而是所有的子策略都会以同样的概率被选择到,论文中的实验也表明这种数据增强方式即使在大模型的训练中也具有很好的效果。
+
+
+经过 RandAugment 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_randaugment]
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.2.2 RandAugment 配置
`RandAugment` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `num_layers` 与 `magnitude`,默认的数值分别是 `2` 和 `5`。`RandAugment` 是在 uint8 的数据格式上转换的,所以其处理过程应该放在归一化操作(`NormalizeImage`)之前。
@@ -72,8 +211,21 @@
order: ''
```
-
-### 1.3 TimmAutoAugment
+
+
+#### 1.2.3 TimmAutoAugment
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.3.1 TimmAutoAugment 算法介绍
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/data/auto_augment.py](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/data/auto_augment.py)
+
+`TimmAutoAugment` 是开源作者对 AutoAugment 和 RandAugment 的改进,事实证明,其在很多视觉任务上有更好的表现,目前绝大多数 VisionTransformer 模型都是基于 TimmAutoAugment 去实现的。
+
+
+
+##### 1.2.3.2 TimmAutoAugment 配置
`TimmAutoAugment` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `config_str`、`interpolation`、`img_size`,默认的数值分别是 `rand-m9-mstd0.5-inc1`、`bicubic`、`224`。`TimmAutoAugment` 是在 uint8 的数据格式上转换的,所以其处理过程应该放在归一化操作(`NormalizeImage`)之前。
@@ -97,8 +249,43 @@
order: ''
```
-
-### 1.4 Cutout
+
+
+### 1.3 图像裁剪类
+
+图像裁剪类主要是对 `Transpose` 后的 224 的图像进行一些裁剪,并将裁剪区域的像素值置为特定的常数(默认为 0),主要包括:
+
++ CutOut
++ RandErasing
++ HideAndSeek
++ GridMask
+
+图像裁剪的这些增广并非一定要放在归一化之后,也有不少实现是放在归一化之前的,也就是直接对 uint8 的图像进行操作,两种方式的差别是:如果直接对 uint8 的图像进行操作,那么再经过归一化之后被裁剪的区域将不再是纯黑或纯白(减均值除方差之后像素值不为 0)。而对归一后之后的数据进行操作,裁剪的区域会是纯黑或纯白。
+
+上述的裁剪变换思路是相同的,都是为了解决训练出的模型在有遮挡数据上泛化能力较差的问题,不同的是他们的裁剪方式、区域不太一样。
+
+
+
+#### 1.3.1 Cutout
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.1.1 Cutout 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552](https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/uoguelph-mlrg/Cutout](https://github.com/uoguelph-mlrg/Cutout)
+
+Cutout 可以理解为 Dropout 的一种扩展操作,不同的是 Dropout 是对图像经过网络后生成的特征进行遮挡,而 Cutout 是直接对输入的图像进行遮挡,相对于 Dropout 对噪声的鲁棒性更好。作者在论文中也进行了说明,这样做法有以下两点优势:(1)通过 Cutout 可以模拟真实场景中主体被部分遮挡时的分类场景;(2)可以促进模型充分利用图像中更多的内容来进行分类,防止网络只关注显著性的图像区域,从而发生过拟合。
+
+
+经过 RandAugment 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_cutout]
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.1.2 Cutout 配置
`Cutout` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `n_holes` 与 `length`,默认的数值分别是 `1` 和 `112`。类似其他图像裁剪类的数据增强方式,`Cutout` 既可以在 uint8 格式的数据上操作,也可以在归一化)(`NormalizeImage`)后的数据上操作,此处给出的是在归一化后的操作。
@@ -121,8 +308,31 @@
length: 112
```
-
-### 1.5 RandomErasing
+
+
+
+#### 1.3.2 RandomErasing
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.2.1 RandomErasing 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.04896.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.04896.pdf)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/zhunzhong07/Random-Erasing](https://github.com/zhunzhong07/Random-Erasing)
+
+`RandomErasing` 与 `Cutout` 方法类似,同样是为了解决训练出的模型在有遮挡数据上泛化能力较差的问题,作者在论文中也指出,随机裁剪的方式与随机水平翻转具有一定的互补性。作者也在行人再识别(REID)上验证了该方法的有效性。与 `Cutout` 不同的是,在 `RandomErasing` 中,图片以一定的概率接受该种预处理方法,生成掩码的尺寸大小与长宽比也是根据预设的超参数随机生成。
+
+
+PaddleClas 中 `RandomErasing` 的使用方法如下所示。
+
+经过 RandomErasing 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_randomerassing]
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.2.2 RandomErasing 配置
`RandomErasing` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `EPSILON`、`sl`、`sh`、`r1`、`attempt`、`use_log_aspect`、`mode`,默认的数值分别是 `0.25`、`0.02`、`1.0/3.0`、`0.3`、`10`、`True`、`pixel`。类似其他图像裁剪类的数据增强方式,`RandomErasing` 既可以在 uint8 格式的数据上操作,也可以在归一化(`NormalizeImage`)后的数据上操作,此处给出的是在归一化后的操作。
@@ -150,8 +360,35 @@
mode: pixel
```
-
-### 1.6 HideAndSeek
+
+
+#### 1.3.3 HideAndSeek
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.3.1 HideAndSeek 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.02545.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.02545.pdf)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/kkanshul/Hide-and-Seek](https://github.com/kkanshul/Hide-and-Seek)
+
+
+`HideAndSeek` 论文将图像分为若干块区域(patch),对于每块区域,都以一定的概率生成掩码,不同区域的掩码含义如下图所示。
+
+
+![][hide_and_seek_mask_expanation]
+
+
+PaddleClas 中 `HideAndSeek` 的使用方法如下所示。
+
+
+经过 HideAndSeek 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_hideandseek]
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.3.2 HideAndSeek 配置
`HideAndSeek` 的图像增广方式的配置如下。类似其他图像裁剪类的数据增强方式,`HideAndSeek` 既可以在 uint8 格式的数据上操作,也可以在归一化(`NormalizeImage`)后的数据上操作,此处给出的是在归一化后的操作。
@@ -172,9 +409,43 @@
- HideAndSeek:
```
-
+
+
+#### 1.3.4 GridMask
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.4.1 GridMask 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04086](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04086)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/akuxcw/GridMask](https://github.com/akuxcw/GridMask)
-### 1.7 GridMask
+
+作者在论文中指出,此前存在的基于对图像 crop 的方法存在两个问题,如下图所示:
+
+1. 过度删除区域可能造成目标主体大部分甚至全部被删除,或者导致上下文信息的丢失,导致增广后的数据成为噪声数据;
+2. 保留过多的区域,对目标主体及上下文基本产生不了什么影响,失去增广的意义。
+
+![][gridmask-0]
+
+因此如果避免过度删除或过度保留成为需要解决的核心问题。
+
+
+`GridMask` 是通过生成一个与原图分辨率相同的掩码,并将掩码进行随机翻转,与原图相乘,从而得到增广后的图像,通过超参数控制生成的掩码网格的大小。
+
+
+在训练过程中,有两种以下使用方法:
+1. 设置一个概率 p,从训练开始就对图片以概率 p 使用 `GridMask` 进行增广。
+2. 一开始设置增广概率为 0,随着迭代轮数增加,对训练图片进行 `GridMask` 增广的概率逐渐增大,最后变为 p。
+
+论文中验证上述第二种方法的训练效果更好一些。
+
+经过 GridMask 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+
+
+##### 1.3.4.2 GridMask 配置
`GridMask` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `d1`、`d2`、`rotate`、`ratio`、`mode`, 默认的数值分别是 `96`、`224`、`1`、`0.5`、`0`。类似其他图像裁剪类的数据增强方式,`GridMask` 既可以在 uint8 格式的数据上操作,也可以在归一化(`NormalizeImage`)后的数据上操作,此处给出的是在归一化后的操作。
@@ -200,8 +471,43 @@
mode: 0
```
-
-### 1.8 Mixup
+![][test_gridmask]
+
+
+
+### 1.4 图像混叠类
+
+图像混叠主要对 `Batch` 后的数据进行混合,包括:
+
++ Mixup
++ Cutmix
+
+前文所述的图像变换与图像裁剪都是针对单幅图像进行的操作,而图像混叠是对两幅图像进行融合,生成一幅图像,两种方法的主要区别为混叠的方式不太一样。
+
+
+
+#### 1.4.1 Mixup
+
+
+
+##### 1.4.1.1 Mixup 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/facebookresearch/mixup-cifar10](https://github.com/facebookresearch/mixup-cifar10)
+
+Mixup 是最先提出的图像混叠增广方案,其原理简单、方便实现,不仅在图像分类上,在目标检测上也取得了不错的效果。为了便于实现,通常只对一个 batch 内的数据进行混叠,在 `Cutmix` 中也是如此。
+
+如下是 `imaug` 中的实现,需要指出的是,下述实现会出现对同一幅进行相加的情况,也就是最终得到的图和原图一样,随着 `batch-size` 的增加这种情况出现的概率也会逐渐减小。
+
+
+经过 Mixup 数据增强结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_mixup]
+
+
+
+##### 1.4.1.2 Mixup 配置
`Mixup` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `alpha`,默认的数值是 `0.2`。类似其他图像混合类的数据增强方式,`Mixup` 是在图像做完数据处理后将每个 batch 内的数据做图像混叠,将混叠后的图像和标签输入网络中训练,所以其是在图像数据处理(图像变换、图像裁剪)后操作。
@@ -224,8 +530,26 @@
alpha: 0.2
```
-
-### 1.9 Cutmix
+
+#### 1.4.2 Cutmix
+
+
+
+##### 1.4.2.1 Cutmix 算法介绍
+
+论文地址:[https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.04899v2.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.04899v2.pdf)
+
+开源代码 github 地址:[https://github.com/clovaai/CutMix-PyTorch](https://github.com/clovaai/CutMix-PyTorch)
+
+与 `Mixup` 直接对两幅图进行相加不一样,`Cutmix` 是从一幅图中随机裁剪出一个 `ROI`,然后覆盖当前图像中对应的区域,代码实现如下所示:
+
+经过 Cutmix 数据增强后结果如下图所示。
+
+![][test_cutmix]
+
+
+
+##### 1.4.2.2 Cutmix 配置
`Cutmix` 的图像增广方式的配置如下,其中用户需要指定其中的参数 `alpha`,默认的数值是 `0.2`。类似其他图像混合类的数据增强方式,`Cutmix` 是在图像做完数据处理后将每个 batch 内的数据做图像混叠,将混叠后的图像和标签输入网络中训练,所以其是在图像数据处理(图像变换、图像裁剪)后操作。
@@ -248,8 +572,9 @@
alpha: 0.2
```
-
-### 1.10 Mixup 与 Cutmix 同时使用
+
+
+##### 1.4.2.3 Mixup 和 Cutmix 混合使用配置
`Mixup` 与 `Cutmix` 同时使用的配置如下,其中用户需要指定额外的参数 `prob`,该参数控制不同数据增强的概率,默认为 `0.5`。
@@ -277,55 +602,149 @@
```
-## 2. 启动命令
-当用户配置完训练环境后,类似于训练其他分类任务,只需要将 `tools/train.sh` 中的配置文件替换成为相应的数据增强方式的配置文件即可。
+## 2. 模型训练、评估和预测
+
+
-其中 `train.sh` 中的内容如下:
+### 2.1 环境配置
-```bash
+* 安装:请先参考 [Paddle 安装教程](../installation/install_paddle.md) 以及 [PaddleClas 安装教程](../installation/install_paddleclas.md) 配置 PaddleClas 运行环境。
+
+
+
+### 2.2 数据准备
+
+请在[ImageNet 官网](https://www.image-net.org/)准备 ImageNet-1k 相关的数据。
+
+
+进入 PaddleClas 目录。
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+进入 `dataset/` 目录,将下载好的数据命名为 `ILSVRC2012` ,存放于此。 `ILSVRC2012` 目录中具有以下数据:
+
+```
+├── train
+│ ├── n01440764
+│ │ ├── n01440764_10026.JPEG
+│ │ ├── n01440764_10027.JPEG
+├── train_list.txt
+...
+├── val
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000001.JPEG
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000002.JPEG
+├── val_list.txt
+```
+
+其中 `train/` 和 `val/` 分别为训练集和验证集。`train_list.txt` 和 `val_list.txt` 分别为训练集和验证集的标签文件。
+
+**备注:**
+* 关于 `train_list.txt`、`val_list.txt`的格式说明,可以参考[PaddleClas分类数据集格式说明](../data_preparation/classification_dataset.md#1-数据集格式说明) 。
+
+
+
+
+### 2.3 模型训练
+
+
+在 `ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment` 中提供了基于 ResNet50 的不同的数据增强的训练配置,这里以使用 `AutoAugment` 为例,介绍数据增强的使用方法。可以通过如下脚本启动训练:
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
- --selected_gpus="0,1,2,3" \
- --log_dir=ResNet50_Cutout \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
tools/train.py \
- -c ./ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment/ResNet50_Cutout.yaml
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment/ResNet50_AutoAugment.yaml
```
-运行 `train.sh`:
+
+**备注:**
+
+* 1.当前精度最佳的模型会保存在 `output/ResNet50/best_model.pdparams`。
+* 2.如需更改数据增强类型,只需要替换`ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment`中的其他的配置文件即可。
+* 3.如果希望多种数据增强混合使用,请参考[第 2 节](#2)中的相关配置更改配置文件中的数据增强即可。
+* 4.由于图像混叠时需对 label 进行混叠,无法计算训练数据的准确率,所以在训练过程中没有打印训练准确率。
+* 5.在使用数据增强后,由于训练数据更难,所以训练损失函数可能较大,训练集的准确率相对较低,但其有拥更好的泛化能力,所以验证集的准确率相对较高。
+* 6.在使用数据增强后,模型可能会趋于欠拟合状态,建议可以适当的调小 `l2_decay` 的值来获得更高的验证集准确率。
+* 7.几乎每一类图像增强均含有超参数,我们只提供了基于 ImageNet-1k 的超参数,其他数据集需要用户自己调试超参数,具体超参数的含义用户可以阅读相关的论文,调试方法也可以参考[训练技巧](../models_training/train_strategy.md)。
+
+
+
+### 2.4 模型评估
+
+训练好模型之后,可以通过以下命令实现对模型指标的评估。
```bash
-sh tools/train.sh
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment/ResNet50_AutoAugment.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/ResNet50/best_model
```
+其中 `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/ResNet50/best_model"` 指定了当前最佳权重所在的路径,如果指定其他权重,只需替换对应的路径即可。
+
+
+
+### 2.5 模型预测
+
+模型训练完成之后,可以加载训练得到的预训练模型,进行模型预测。在模型库的 `tools/infer.py` 中提供了完整的示例,只需执行下述命令即可完成模型预测:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/DataAugment/ResNet50_AutoAugment.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/ResNet50/best_model
+```
+
+输出结果如下:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [8, 7, 86, 81, 85], 'scores': [0.91347, 0.03779, 0.0036, 0.00117, 0.00112], 'file_name': 'docs/images/inference_deployment/whl_demo.jpg', 'label_names': ['hen', 'cock', 'partridge', 'ptarmigan', 'quail']}]
+```
+
+**备注:**
+
+* 这里`-o Global.pretrained_model="output/ResNet50/best_model"` 指定了当前最佳权重所在的路径,如果指定其他权重,只需替换对应的路径即可。
+
+* 默认是对 `docs/images/inference_deployment/whl_demo.jpg` 进行预测,此处也可以通过增加字段 `-o Infer.infer_imgs=xxx` 对其他图片预测。
+
+* 默认输出的是 Top-5 的值,如果希望输出 Top-k 的值,可以指定`-o Infer.PostProcess.topk=k`,其中,`k` 为您指定的值。
+
+
+
-## 3. 注意事项
-* 由于图像混叠时需对 label 进行混叠,无法计算训练数据的准确率,所以在训练过程中没有打印训练准确率。
+## 3.参考文献
-* 在使用数据增强后,由于训练数据更难,所以训练损失函数可能较大,训练集的准确率相对较低,但其有拥更好的泛化能力,所以验证集的准确率相对较高。
+[1] Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Mane D, et al. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation strategies from data[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019: 113-123.
-* 在使用数据增强后,模型可能会趋于欠拟合状态,建议可以适当的调小 `l2_decay` 的值来获得更高的验证集准确率。
-* 几乎每一类图像增强均含有超参数,我们只提供了基于 ImageNet-1k 的超参数,其他数据集需要用户自己调试超参数,具体超参数的含义用户可以阅读相关的论文,调试方法也可以参考[训练技巧](../models_training/train_strategy.md)。
+[2] Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Shlens J, et al. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.13719, 2019.
-
-## 4. 实验结果
+[3] DeVries T, Taylor G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04552, 2017.
+
+[4] Zhong Z, Zheng L, Kang G, et al. Random erasing data augmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04896, 2017.
+
+[5] Singh K K, Lee Y J. Hide-and-seek: Forcing a network to be meticulous for weakly-supervised object and action localization[C]//2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, 2017: 3544-3553.
+
+[6] Chen P. GridMask Data Augmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04086, 2020.
+
+[7] Zhang H, Cisse M, Dauphin Y N, et al. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09412, 2017.
+
+[8] Yun S, Han D, Oh S J, et al. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 6023-6032.
-基于 PaddleClas,在 ImageNet1k 数据集上的分类精度如下。
-| 模型 | 初始学习率策略 | l2 decay | batch size | epoch | 数据变化策略 | Top1 Acc | 论文中结论 |
-|-------------|------------------|--------------|------------|-------|----------------|------------|----|
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | 标准变换 | 0.7731 | - |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | AutoAugment | 0.7795 | 0.7763 |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | mixup | 0.7828 | 0.7790 |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | cutmix | 0.7839 | 0.7860 |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | cutout | 0.7801 | - |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | gridmask | 0.7785 | 0.7790 |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | random-augment | 0.7770 | 0.7760 |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | random erasing | 0.7791 | - |
-| ResNet50 | 0.1/cosine_decay | 0.0001 | 256 | 300 | hide and seek | 0.7743 | 0.7720 |
-**注意**:
-* 在这里的实验中,为了便于对比,我们将 l2 decay 固定设置为 1e-4,在实际使用中,我们推荐尝试使用更小的 l2 decay。结合数据增强,我们发现将 l2 decay 由 1e-4 减小为 7e-5 均能带来至少 0.3~0.5% 的精度提升。
-* 我们目前尚未对不同策略进行组合并验证效果,这一块后续我们会开展更多的对比实验,敬请期待。
+[test_baseline]: ../../images/image_aug/test_baseline.jpeg
+[test_autoaugment]: ../../images/image_aug/test_autoaugment.jpeg
+[test_cutout]: ../../images/image_aug/test_cutout.jpeg
+[test_gridmask]: ../../images/image_aug/test_gridmask.jpeg
+[gridmask-0]: ../../images/image_aug/gridmask-0.png
+[test_hideandseek]: ../../images/image_aug/test_hideandseek.jpeg
+[test_randaugment]: ../../images/image_aug/test_randaugment.jpeg
+[test_randomerassing]: ../../images/image_aug/test_randomerassing.jpeg
+[hide_and_seek_mask_expanation]: ../../images/image_aug/hide-and-seek-visual.png
+[test_mixup]: ../../images/image_aug/test_mixup.png
+[test_cutmix]: ../../images/image_aug/test_cutmix.png
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/knowledge_distillation.md b/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/knowledge_distillation.md
index d3e6d77cf254a933fd6e6776e361f2c499b5c14d..6224e82a79eb39cc62641c66acd8bbc0133070ce 100644
--- a/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/knowledge_distillation.md
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/knowledge_distillation.md
@@ -1,209 +1,411 @@
-# 知识蒸馏
+# 知识蒸馏实战
## 目录
- - [1. 模型压缩与知识蒸馏方法简介](#1)
- - [2. SSLD 蒸馏策略](#2)
- - [2.1 简介](#2.1)
- - [2.2 数据选择](#2.2)
- - [3. 实验](#3)
- - [3.1 教师模型的选择](#3.1)
- - [3.2 大数据蒸馏](#3.2)
- - [3.3 ImageNet1k 训练集 finetune](#3.3)
- - [3.4 数据增广以及基于 Fix 策略的微调](#3.4)
- - [3.5 实验过程中的一些问题](#3.5)
- - [4. 蒸馏模型的应用](#4)
- - [4.1 使用方法](#4.1)
- - [4.2 迁移学习 finetune](#4.2)
- - [4.3 目标检测](#4.3)
- - [5. SSLD 实战](#5)
- - [5.1 参数配置](#5.1)
- - [5.2 启动命令](#5.2)
- - [5.3 注意事项](#5.3)
- - [6. 参考文献](#6)
+
+- [1. 算法介绍](#1)
+ - [1.1 知识蒸馏简介](#1.1)
+ - [1.1.1 Response based distillation](#1.1.1)
+ - [1.1.2 Feature based distillation](#1.1.2)
+ - [1.1.3 Relation based distillation](#1.1.3)
+ - [1.2 PaddleClas支持的知识蒸馏算法](#1.2)
+ - [1.2.1 SSLD](#1.2.1)
+ - [1.2.2 DML](#1.2.2)
+ - [1.2.3 UDML](#1.2.3)
+ - [1.2.4 AFD](#1.2.4)
+ - [1.2.5 DKD](#1.2.5)
+- [2. 使用方法](#2)
+ - [2.1 环境配置](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 数据准备](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 模型训练](#2.3)
+ - [2.4 模型评估](#2.4)
+ - [2.5 模型预测](#2.5)
+ - [2.6 模型导出与推理](#2.6)
+- [3. 参考文献](#3)
+
+
-## 1. 模型压缩与知识蒸馏方法简介
+
+## 1. 算法介绍
+
+
+
+### 1.1 知识蒸馏简介
近年来,深度神经网络在计算机视觉、自然语言处理等领域被验证是一种极其有效的解决问题的方法。通过构建合适的神经网络,加以训练,最终网络模型的性能指标基本上都会超过传统算法。
在数据量足够大的情况下,通过合理构建网络模型的方式增加其参数量,可以显著改善模型性能,但是这又带来了模型复杂度急剧提升的问题。大模型在实际场景中使用的成本较高。
-深度神经网络一般有较多的参数冗余,目前有几种主要的方法对模型进行压缩,减小其参数量。如裁剪、量化、知识蒸馏等,其中知识蒸馏是指使用教师模型(teacher model)去指导学生模型(student model)学习特定任务,保证小模型在参数量不变的情况下,得到比较大的性能提升,甚至获得与大模型相似的精度指标 [1]。 PaddleClas 融合已有的蒸馏方法 [2,3],提供了一种简单的半监督标签知识蒸馏方案(SSLD,Simple Semi-supervised Label Distillation),基于 ImageNet1k 分类数据集,在 ResNet_vd 以及 MobileNet 系列上的精度均有超过 3% 的绝对精度提升,具体指标如下图所示。
+深度神经网络一般有较多的参数冗余,目前有几种主要的方法对模型进行压缩,减小其参数量。如裁剪、量化、知识蒸馏等,其中知识蒸馏是指使用教师模型(teacher model)去指导学生模型(student model)学习特定任务,保证小模型在参数量不变的情况下,得到比较大的性能提升,甚至获得与大模型相似的精度指标 [1]。
-
-
-## 2. SSLD 蒸馏策略
+根据蒸馏方式的不同,可以将知识蒸馏方法分为3个不同的类别:Response based distillation、Feature based distillation、Relation based distillation。下面进行详细介绍。
-
-### 2.1 简介
+
-SSLD 的流程图如下图所示。
+#### 1.1.1 Response based distillation
-
-首先,我们从 ImageNet22k 中挖掘出了近 400 万张图片,同时与 ImageNet-1k 训练集整合在一起,得到了一个新的包含 500 万张图片的数据集。然后,我们将学生模型与教师模型组合成一个新的网络,该网络分别输出学生模型和教师模型的预测分布,与此同时,固定教师模型整个网络的梯度,而学生模型可以做正常的反向传播。最后,我们将两个模型的 logits 经过 softmax 激活函数转换为 soft label,并将二者的 soft label 做 JS 散度作为损失函数,用于蒸馏模型训练。下面以 MobileNetV3(该模型直接训练,精度为 75.3%)的知识蒸馏为例,介绍该方案的核心关键点(baseline 为 79.12% 的 ResNet50_vd 模型蒸馏 MobileNetV3,训练集为 ImageNet1k 训练集,loss 为 cross entropy loss,迭代轮数为 120epoch,精度指标为 75.6%)。
+最早的知识蒸馏算法 KD,由 Hinton 提出,训练的损失函数中除了 gt loss 之外,还引入了学生模型与教师模型输出的 KL 散度,最终精度超过单纯使用 gt loss 训练的精度。这里需要注意的是,在训练的时候,需要首先训练得到一个更大的教师模型,来指导学生模型的训练过程。
-* 教师模型的选择。在进行知识蒸馏时,如果教师模型与学生模型的结构差异太大,蒸馏得到的结果反而不会有太大收益。相同结构下,精度更高的教师模型对结果也有很大影响。相比于 79.12% 的 ResNet50_vd 教师模型,使用 82.4% 的 ResNet50_vd 教师模型可以带来 0.4% 的绝对精度收益(`75.6%->76.0%`)。
+PaddleClas 中提出了一种简单使用的 SSLD 知识蒸馏算法 [6],在训练的时候去除了对 gt label 的依赖,结合大量无标注数据,最终蒸馏训练得到的预训练模型在 15 个模型上的精度提升平均高达 3%。
-* 改进 loss 计算方法。分类 loss 计算最常用的方法就是 cross entropy loss,我们经过实验发现,在使用 soft label 进行训练时,相对于 cross entropy loss,KL div loss 对模型性能提升几乎无帮助,但是使用具有对称特性的 JS div loss 时,在多个蒸馏任务上相比 cross entropy loss 均有 0.2% 左右的收益(`76.0%->76.2%`),SSLD 中也基于 JS div loss 展开实验。
+上述标准的蒸馏方法是通过一个大模型作为教师模型来指导学生模型提升效果,而后来又发展出 DML(Deep Mutual Learning)互学习蒸馏方法 [7],即通过两个结构相同的模型互相学习。具体的。相比于 KD 等依赖于大的教师模型的知识蒸馏算法,DML 脱离了对大的教师模型的依赖,蒸馏训练的流程更加简单,模型产出效率也要更高一些。
-* 更多的迭代轮数。蒸馏的 baseline 实验只迭代了 120 个 epoch 。实验发现,迭代轮数越多,蒸馏效果越好,最终我们迭代了 360 epoch,精度指标可以达到 77.1%(`76.2%->77.1%`)。
+
-* 无需数据集的真值标签,很容易扩展训练集。 SSLD 的 loss 在计算过程中,仅涉及到教师和学生模型对于相同图片的处理结果(经过 softmax 激活函数处理之后的 soft label),因此即使图片数据不包含真值标签,也可以用来进行训练并提升模型性能。该蒸馏方案的无标签蒸馏策略也大大提升了学生模型的性能上限(`77.1%->78.5%`)。
+#### 1.1.2 Feature based distillation
-* ImageNet1k 蒸馏 finetune 。 我们仅使用 ImageNet1k 数据,使用蒸馏方法对上述模型进行 finetune,最终仍然可以获得 0.4% 的性能提升(`78.5%->78.9%`)。
+Heo 等人提出了 OverHaul [8], 计算学生模型与教师模型的 feature map distance,作为蒸馏的 loss,在这里使用了学生模型、教师模型的转移,来保证二者的 feature map 可以正常地进行 distance 的计算。
+基于 feature map distance 的知识蒸馏方法也能够和 `3.1 章节` 中的基于 response 的知识蒸馏算法融合在一起,同时对学生模型的输出结果和中间层 feature map 进行监督。而对于 DML 方法来说,这种融合过程更为简单,因为不需要对学生和教师模型的 feature map 进行转换,便可以完成对齐(alignment)过程。PP-OCRv2 系统中便使用了这种方法,最终大幅提升了 OCR 文字识别模型的精度。
-
-### 2.2 数据选择
+
-* SSLD 蒸馏方案的一大特色就是无需使用图像的真值标签,因此可以任意扩展数据集的大小,考虑到计算资源的限制,我们在这里仅基于 ImageNet22k 数据集对蒸馏任务的训练集进行扩充。在 SSLD 蒸馏任务中,我们使用了 `Top-k per class` 的数据采样方案 [3] 。具体步骤如下。
- * 训练集去重。我们首先基于 SIFT 特征相似度匹配的方式对 ImageNet22k 数据集与 ImageNet1k 验证集进行去重,防止添加的 ImageNet22k 训练集中包含 ImageNet1k 验证集图像,最终去除了 4511 张相似图片。部分过滤的相似图片如下所示。
+#### 1.1.3 Relation based distillation
- 
+[1.1.1](#1.1.1) 和 [1.1.2](#1.1.2) 章节中的论文中主要是考虑到学生模型与教师模型的输出或者中间层 feature map,这些知识蒸馏算法只关注个体的输出结果,没有考虑到个体之间的输出关系。
- * 大数据集 soft label 获取,对于去重后的 ImageNet22k 数据集,我们使用 `ResNeXt101_32x16d_wsl` 模型进行预测,得到每张图片的 soft label 。
- * Top-k 数据选择,ImageNet1k 数据共有 1000 类,对于每一类,找出属于该类并且得分最高的 `k` 张图片,最终得到一个数据量不超过 `1000*k` 的数据集(某些类上得到的图片数量可能少于 `k` 张)。
- * 将该数据集与 ImageNet1k 的训练集融合组成最终蒸馏模型所使用的数据集,数据量为 500 万。
+Park 等人提出了 RKD [10],基于关系的知识蒸馏算法,RKD 中进一步考虑个体输出之间的关系,使用 2 种损失函数,二阶的距离损失(distance-wise)和三阶的角度损失(angle-wise)
-
-## 3. 实验
-* PaddleClas 的蒸馏策略为`大数据集训练 + ImageNet1k 蒸馏 finetune` 的策略。选择合适的教师模型,首先在挑选得到的 500 万数据集上进行训练,然后在 ImageNet1k 训练集上进行 finetune,最终得到蒸馏后的学生模型。
+本论文提出的算法关系知识蒸馏(RKD)迁移教师模型得到的输出结果间的结构化关系给学生模型,不同于之前的只关注个体输出结果,RKD 算法使用两种损失函数:二阶的距离损失(distance-wise)和三阶的角度损失(angle-wise)。在最终计算蒸馏损失函数的时候,同时考虑 KD loss 和 RKD loss。最终精度优于单独使用 KD loss 蒸馏得到的模型精度。
+
+
+
+### 1.2 PaddleClas支持的知识蒸馏算法
+
+
+
+#### 1.2.1 SSLD
+
+##### 1.2.1.1 SSLD 算法介绍
+
+论文信息:
+
+> [Beyond Self-Supervision: A Simple Yet Effective Network Distillation Alternative to Improve Backbones
+](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.05959)
+>
+> Cheng Cui, Ruoyu Guo, Yuning Du, Dongliang He, Fu Li, Zewu Wu, Qiwen Liu, Shilei Wen, Jizhou Huang, Xiaoguang Hu, Dianhai Yu, Errui Ding, Yanjun Ma
+>
+> arxiv, 2021
+
+SSLD是百度于2021年提出的一种简单的半监督知识蒸馏方案,通过设计一种改进的JS散度作为损失函数,结合基于ImageNet22k数据集的数据挖掘策略,最终帮助15个骨干网络模型的精度平均提升超过3%。
-
-### 3.1 教师模型的选择
+更多关于SSLD的原理、模型库与使用介绍,请参考:[SSLD知识蒸馏算法介绍](./ssld.md)。
-为了验证教师模型和学生模型的模型大小差异和教师模型的模型精度对蒸馏结果的影响,我们做了几组实验验证。训练策略统一为:`cosine_decay_warmup,lr=1.3, epoch=120, bs=2048`,学生模型均为从头训练。
-|Teacher Model | Teacher Top1 | Student Model | Student Top1|
-|- |:-: |:-: | :-: |
-| ResNeXt101_32x16d_wsl | 84.2% | MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 75.78% |
-| ResNet50_vd | 79.12% | MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 75.60% |
-| ResNet50_vd | 82.35% | MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 76.00% |
+##### 1.2.1.2 SSLD 配置
+SSLD配置如下所示。在模型构建Arch字段中,需要同时定义学生模型与教师模型,教师模型固定梯度,并且加载预训练参数。在损失函数Loss字段中,需要定义`DistillationDMLLoss`,作为训练的损失函数。
-从表中可以看出
+```yaml
+# model architecture
+Arch:
+ name: "DistillationModel" # 模型名称,这里使用的是蒸馏模型,
+ class_num: &class_num 1000 # 类别数量,对于ImageNet1k数据集来说,类别数为1000
+ pretrained_list: # 预训练模型列表,因为在下面的子网络中指定了预训练模型,这里无需指定
+ freeze_params_list: # 固定网络参数列表,为True时,表示固定该index对应的网络
+ - True
+ - False
+ infer_model_name: "Student" # 在模型导出的时候,会导出Student子网络
+ models: # 子网络列表
+ - Teacher: # 教师模型
+ name: ResNet50_vd # 模型名称
+ class_num: *class_num # 类别数
+ pretrained: True # 预训练模型路径,如果为True,则会从官网下载默认的预训练模型
+ use_ssld: True # 是否使用SSLD蒸馏得到的预训练模型,精度会更高一些
+ - Student: # 学生模型
+ name: PPLCNet_x2_5 # 模型名称
+ class_num: *class_num # 类别数
+ pretrained: False # 预训练模型路径,可以指定为bool值或者字符串,这里为False,表示学生模型默认不加载预训练模型
+
+# loss function config for traing/eval process
+Loss: # 定义损失函数
+ Train: # 定义训练的损失函数,为列表形式
+ - DistillationDMLLoss: # 蒸馏的DMLLoss,对DMLLoss进行封装,支持蒸馏结果(dict形式)的损失函数计算
+ weight: 1.0 # loss权重
+ model_name_pairs: # 用于计算的模型对,这里表示计算Student和Teacher输出的损失函数
+ - ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ Eval: # 定义评估时的损失函数
+ - CELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+```
-> 教师模型结构相同时,其精度越高,最终的蒸馏效果也会更好一些。
+
+
+#### 1.2.2 DML
+
+##### 1.2.2.1 DML 算法介绍
+
+论文信息:
+
+> [Deep Mutual Learning](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/html/Zhang_Deep_Mutual_Learning_CVPR_2018_paper.html)
+>
+> Ying Zhang, Tao Xiang, Timothy M. Hospedales, Huchuan Lu
>
-> 教师模型与学生模型的模型大小差异不宜过大,否则反而会影响蒸馏结果的精度。
+> CVPR, 2018
+
+DML论文中,在蒸馏的过程中,不依赖于教师模型,两个结构相同的模型互相学习,计算彼此输出(logits)的KL散度,最终完成训练过程。
+
+
+在ImageNet1k公开数据集上,效果如下所示。
+
+| 策略 | 骨干网络 | 配置文件 | Top-1 acc | 下载链接 |
+| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| baseline | PPLCNet_x2_5 | [PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml) | 74.93% | - |
+| DML | PPLCNet_x2_5 | [PPLCNet_x2_5_dml.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_dml.yaml) | 76.68%(**+1.75%**) | - |
+
+
+* 注:完整的PPLCNet_x2_5模型训练了360epoch,这里为了方便对比,baseline和DML均训练了100epoch,因此指标比官网最终开源出来的模型精度(76.60%)低一些。
+
+
+##### 1.2.2.2 DML 配置
+
+DML配置如下所示。在模型构建Arch字段中,需要同时定义学生模型与教师模型,教师模型与学生模型均保持梯度更新状态。在损失函数Loss字段中,需要定义`DistillationDMLLoss`(学生与教师之间的JS-Div loss)以及`DistillationGTCELoss`(学生与教师关于真值标签的CE loss),作为训练的损失函数。
+
+```yaml
+Arch:
+ name: "DistillationModel"
+ class_num: &class_num 1000
+ pretrained_list:
+ freeze_params_list: # 两个模型互相学习,因此这里两个子网络的参数均不能固定
+ - False
+ - False
+ models:
+ - Teacher:
+ name: PPLCNet_x2_5 # 两个模型互学习,因此均没有加载预训练模型
+ class_num: *class_num
+ pretrained: False
+ - Student:
+ name: PPLCNet_x2_5
+ class_num: *class_num
+ pretrained: False
+
+Loss:
+ Train:
+ - DistillationGTCELoss: # 因为2个子网络均没有加载预训练模型,这里需要同时计算不同子网络的输出与真值标签之间的CE loss
+ weight: 1.0
+ model_names: ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ - DistillationDMLLoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ model_name_pairs:
+ - ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ Eval:
+ - CELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+```
+
+
+
+#### 1.2.3 UDML
+
+##### 1.2.3.1 UDML 算法介绍
+
+论文信息:
+
+UDML 是百度飞桨视觉团队提出的无需依赖教师模型的知识蒸馏算法,它基于DML进行改进,在蒸馏的过程中,除了考虑两个模型的输出信息,也考虑两个模型的中间层特征信息,从而进一步提升知识蒸馏的精度。更多关于UDML的说明与应用,请参考[PP-ShiTu论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00775)以及[PP-OCRv3论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144)。
-因此最终在蒸馏实验中,对于 ResNet 系列学生模型,我们使用 `ResNeXt101_32x16d_wsl` 作为教师模型;对于 MobileNet 系列学生模型,我们使用蒸馏得到的 `ResNet50_vd` 作为教师模型。
-
-### 3.2 大数据蒸馏
+在ImageNet1k公开数据集上,效果如下所示。
-基于 PaddleClas 的蒸馏策略为`大数据集训练 + imagenet1k finetune` 的策略。
+| 策略 | 骨干网络 | 配置文件 | Top-1 acc | 下载链接 |
+| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| baseline | PPLCNet_x2_5 | [PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/PPLCNet/PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml) | 74.93% | - |
+| UDML | PPLCNet_x2_5 | [PPLCNet_x2_5_dml.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_udml.yaml) | 76.74%(**+1.81%**) | - |
+
+
+##### 1.2.3.2 UDML 配置
+
+
+```yaml
+Arch:
+ name: "DistillationModel"
+ class_num: &class_num 1000
+ # if not null, its lengths should be same as models
+ pretrained_list:
+ # if not null, its lengths should be same as models
+ freeze_params_list:
+ - False
+ - False
+ models:
+ - Teacher:
+ name: PPLCNet_x2_5
+ class_num: *class_num
+ pretrained: False
+ # return_patterns表示除了返回输出的logits,也会返回对应名称的中间层feature map
+ return_patterns: ["blocks3", "blocks4", "blocks5", "blocks6"]
+ - Student:
+ name: PPLCNet_x2_5
+ class_num: *class_num
+ pretrained: False
+ return_patterns: ["blocks3", "blocks4", "blocks5", "blocks6"]
+
+# loss function config for traing/eval process
+Loss:
+ Train:
+ - DistillationGTCELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ key: logits
+ model_names: ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ - DistillationDMLLoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ key: logits
+ model_name_pairs:
+ - ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ - DistillationDistanceLoss: # 基于蒸馏结果的距离loss,这里默认使用l2 loss计算block5之间的损失函数
+ weight: 1.0
+ key: "blocks5"
+ model_name_pairs:
+ - ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ Eval:
+ - CELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+```
-针对从 ImageNet22k 挑选出的 400 万数据,融合 imagenet1k 训练集,组成共 500 万的训练集进行训练,具体地,在不同模型上的训练超参及效果如下。
+**注意(:** 上述在网络中指定`return_patterns`,返回中间层特征的功能是基于TheseusLayer,更多关于TheseusLayer的使用说明,请参考:[TheseusLayer 使用说明](./theseus_layer.md)。
-|Student Model | num_epoch | l2_ecay | batch size/gpu cards | base lr | learning rate decay | top1 acc |
-| - |:-: |:-: | :-: |:-: |:-: |:-: |
-| MobileNetV1 | 360 | 3e-5 | 4096/8 | 1.6 | cosine_decay_warmup | 77.65% |
-| MobileNetV2 | 360 | 1e-5 | 3072/8 | 0.54 | cosine_decay_warmup | 76.34% |
-| MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 360 | 1e-5 | 5760/24 | 3.65625 | cosine_decay_warmup | 78.54% |
-| MobileNetV3_small_x1_0 | 360 | 1e-5 | 5760/24 | 3.65625 | cosine_decay_warmup | 70.11% |
-| ResNet50_vd | 360 | 7e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.4 | cosine_decay_warmup | 82.07% |
-| ResNet101_vd | 360 | 7e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.4 | cosine_decay_warmup | 83.41% |
-| Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s | 360 | 4e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.4 | cosine_decay_warmup | 84.82% |
+
-
-### 3.3 ImageNet1k 训练集 finetune
+#### 1.2.4 AFD
-对于在大数据集上训练的模型,其学习到的特征可能与 ImageNet1k 数据特征有偏,因此在这里使用 ImageNet1k 数据集对模型进行 finetune。 finetune 的超参和 finetune 的精度收益如下。
+##### 1.2.4.1 AFD 算法介绍
+论文信息:
-|Student Model | num_epoch | l2_ecay | batch size/gpu cards | base lr | learning rate decay | top1 acc |
-| - |:-: |:-: | :-: |:-: |:-: |:-: |
-| MobileNetV1 | 30 | 3e-5 | 4096/8 | 0.016 | cosine_decay_warmup | 77.89% |
-| MobileNetV2 | 30 | 1e-5 | 3072/8 | 0.0054 | cosine_decay_warmup | 76.73% |
-| MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 30 | 1e-5 | 2048/8 | 0.008 | cosine_decay_warmup | 78.96% |
-| MobileNetV3_small_x1_0 | 30 | 1e-5 | 6400/32 | 0.025 | cosine_decay_warmup | 71.28% |
-| ResNet50_vd | 60 | 7e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.004 | cosine_decay_warmup | 82.39% |
-| ResNet101_vd | 30 | 7e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.004 | cosine_decay_warmup | 83.73% |
-| Res2Net200_vd_26w_4s | 360 | 4e-5 | 1024/32 | 0.004 | cosine_decay_warmup | 85.13% |
-
-### 3.4 数据增广以及基于 Fix 策略的微调
+> [Show, attend and distill: Knowledge distillation via attention-based feature matching](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.02973)
+>
+> Mingi Ji, Byeongho Heo, Sungrae Park
+>
+> AAAI, 2018
-* 基于前文所述的实验结论,我们在训练的过程中加入自动增广(AutoAugment)[4],同时进一步减小了 l2_decay(4e-5->2e-5),最终 ResNet50_vd 经过 SSLD 蒸馏策略,在 ImageNet1k 上的精度可以达到 82.99%,相比之前不加数据增广的蒸馏策略再次增加了 0.6% 。
+AFD提出在蒸馏的过程中,利用基于注意力的元网络学习特征之间的相对相似性,并应用识别的相似关系来控制所有可能的特征图pair的蒸馏强度。
+在ImageNet1k公开数据集上,效果如下所示。
-* 对于图像分类任务,在测试的时候,测试尺度为训练尺度的 1.15 倍左右时,往往在不需要重新训练模型的情况下,模型的精度指标就可以进一步提升 [5],对于 82.99% 的 ResNet50_vd 在 320x320 的尺度下测试,精度可达 83.7%,我们进一步使用 Fix 策略,即在 320x320 的尺度下进行训练,使用与预测时相同的数据预处理方法,同时固定除 FC 层以外的所有参数,最终在 320x320 的预测尺度下,精度可以达到 **84.0%**。
+| 策略 | 骨干网络 | 配置文件 | Top-1 acc | 下载链接 |
+| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| baseline | ResNet18 | [ResNet18.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/ResNet/ResNet18.yaml) | 70.8% | - |
+| AFD | ResNet18 | [resnet34_distill_resnet18_afd.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/resnet34_distill_resnet18_afd.yaml) | 71.68%(**+0.88%**) | - |
-
-### 3.5 实验过程中的一些问题
+注意:这里为了与论文的训练配置保持对齐,设置训练的迭代轮数为100epoch,因此baseline精度低于PaddleClas中开源出的模型精度(71.0%)
-* 在预测过程中,batch norm 的平均值与方差是通过加载预训练模型得到(设其模式为 test mode)。在训练过程中,batch norm 是通过统计当前 batch 的信息(设其模式为 train mode),与历史保存信息进行滑动平均计算得到,在蒸馏任务中,我们发现通过 train mode,即教师模型的均值与方差实时变化的模式,去指导学生模型,比通过 test mode 蒸馏,得到的学生模型性能更好一些,下面是一组实验结果。因此我们在该蒸馏方案中,均使用 train mode 去得到教师模型的 soft label 。
+##### 1.2.4.2 AFD 配置
-|Teacher Model | Teacher Top1 | Student Model | Student Top1|
-|- |:-: |:-: | :-: |
-| ResNet50_vd | 82.35% | MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 76.00% |
-| ResNet50_vd | 82.35% | MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 | 75.84% |
+AFD配置如下所示。在模型构建Arch字段中,需要同时定义学生模型与教师模型,固定教师模型的权重。这里需要对从教师模型获取的特征进行变换,进而与学生模型进行损失函数的计算。在损失函数Loss字段中,需要定义`DistillationKLDivLoss`(学生与教师之间的KL-Div loss)、`AFDLoss`(学生与教师之间的AFD loss)以及`DistillationGTCELoss`(学生与教师关于真值标签的CE loss),作为训练的损失函数。
-
-## 4. 蒸馏模型的应用
+```yaml
+Arch:
+ name: "DistillationModel"
+ pretrained_list:
+ freeze_params_list:
+ models:
+ - Teacher:
+ name: AttentionModel # 包含若干个串行的网络,后面的网络会将前面的网络输出作为输入并进行处理
+ pretrained_list:
+ freeze_params_list:
+ - True
+ - False
+ models:
+ # AttentionModel 的基础网络
+ - ResNet34:
+ name: ResNet34
+ pretrained: True
+ # return_patterns表示除了返回输出的logits,也会返回对应名称的中间层feature map
+ return_patterns: &t_keys ["blocks[0]", "blocks[1]", "blocks[2]", "blocks[3]",
+ "blocks[4]", "blocks[5]", "blocks[6]", "blocks[7]",
+ "blocks[8]", "blocks[9]", "blocks[10]", "blocks[11]",
+ "blocks[12]", "blocks[13]", "blocks[14]", "blocks[15]"]
+ # AttentionModel的变换网络,会对基础子网络的特征进行变换
+ - LinearTransformTeacher:
+ name: LinearTransformTeacher
+ qk_dim: 128
+ keys: *t_keys
+ t_shapes: &t_shapes [[64, 56, 56], [64, 56, 56], [64, 56, 56], [128, 28, 28],
+ [128, 28, 28], [128, 28, 28], [128, 28, 28], [256, 14, 14],
+ [256, 14, 14], [256, 14, 14], [256, 14, 14], [256, 14, 14],
+ [256, 14, 14], [512, 7, 7], [512, 7, 7], [512, 7, 7]]
-
-### 4.1 使用方法
+ - Student:
+ name: AttentionModel
+ pretrained_list:
+ freeze_params_list:
+ - False
+ - False
+ models:
+ - ResNet18:
+ name: ResNet18
+ pretrained: False
+ return_patterns: &s_keys ["blocks[0]", "blocks[1]", "blocks[2]", "blocks[3]",
+ "blocks[4]", "blocks[5]", "blocks[6]", "blocks[7]"]
+ - LinearTransformStudent:
+ name: LinearTransformStudent
+ qk_dim: 128
+ keys: *s_keys
+ s_shapes: &s_shapes [[64, 56, 56], [64, 56, 56], [128, 28, 28], [128, 28, 28],
+ [256, 14, 14], [256, 14, 14], [512, 7, 7], [512, 7, 7]]
+ t_shapes: *t_shapes
-* 中间层学习率调整。蒸馏得到的模型的中间层特征图更加精细化,因此将蒸馏模型预训练应用到其他任务中时,如果采取和之前相同的学习率,容易破坏中间层特征。而如果降低整体模型训练的学习率,则会带来训练收敛速度慢的问题。因此我们使用了中间层学习率调整的策略。具体地:
- * 针对 ResNet50_vd,我们设置一个学习率倍数列表,res block 之前的 3 个 conv2d 卷积参数具有统一的学习率倍数,4 个 res block 的 conv2d 分别有一个学习率参数,共需设置 5 个学习率倍数的超参。在实验中发现。用于迁移学习 finetune 分类模型时,`[0.1,0.1,0.2,0.2,0.3]` 的中间层学习率倍数设置在绝大多数的任务中都性能更好;而在目标检测任务中,`[0.05,0.05,0.05,0.1,0.15]` 的中间层学习率倍数设置能够带来更大的精度收益。
- * 对于 MoblileNetV3_large_x1_0,由于其包含 15 个 block,我们设置每 3 个 block 共享一个学习率倍数参数,因此需要共 5 个学习率倍数的参数,最终发现在分类和检测任务中,`[0.25,0.25,0.5,0.5,0.75]` 的中间层学习率倍数能够带来更大的精度收益。
+ infer_model_name: "Student"
-* 适当的 l2 decay 。不同分类模型在训练的时候一般都会根据模型设置不同的 l2 decay,大模型为了防止过拟合,往往会设置更大的 l2 decay,如 ResNet50 等模型,一般设置为 `1e-4` ;而如 MobileNet 系列模型,在训练时往往都会设置为 `1e-5~4e-5`,防止模型过度欠拟合,在蒸馏时亦是如此。在将蒸馏模型应用到目标检测任务中时,我们发现也需要调节 backbone 甚至特定任务模型模型的 l2 decay,和预训练蒸馏时的 l2 decay 尽可能保持一致。以 Faster RCNN MobiletNetV3 FPN 为例,我们发现仅修改该参数,在 COCO2017 数据集上就可以带来最多 0.5% 左右的精度(mAP)提升(默认 Faster RCNN l2 decay 为 1e-4,我们修改为 1e-5~4e-5 均有 0.3%~0.5% 的提升)。
+# loss function config for traing/eval process
+Loss:
+ Train:
+ - DistillationGTCELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ model_names: ["Student"]
+ key: logits
+ - DistillationKLDivLoss: # 蒸馏的KL-Div loss,会根据model_name_pairs中的模型名称去提取对应模型的输出特征,计算loss
+ weight: 0.9 # 该loss的权重
+ model_name_pairs: [["Student", "Teacher"]]
+ temperature: 4
+ key: logits
+ - AFDLoss: # AFD loss
+ weight: 50.0
+ model_name_pair: ["Student", "Teacher"]
+ student_keys: ["bilinear_key", "value"]
+ teacher_keys: ["query", "value"]
+ s_shapes: *s_shapes
+ t_shapes: *t_shapes
+ Eval:
+ - CELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+```
-
-### 4.2 迁移学习 finetune
-* 为验证迁移学习的效果,我们在 10 个小的数据集上验证其效果。在这里为了保证实验的可对比性,我们均使用 ImageNet1k 数据集训练的标准预处理过程,对于蒸馏模型我们也添加了蒸馏模型中间层学习率的搜索。
-* 对于 ResNet50_vd, baseline 为 Top1 Acc 79.12% 的预训练模型基于 grid search 搜索得到的最佳精度,对比实验则为基于该精度对预训练和中间层学习率进一步搜索得到的最佳精度。下面给出 10 个数据集上所有 baseline 和蒸馏模型的精度对比。
+**注意(:** 上述在网络中指定`return_patterns`,返回中间层特征的功能是基于TheseusLayer,更多关于TheseusLayer的使用说明,请参考:[TheseusLayer 使用说明](./theseus_layer.md)。
+
-| Dataset | Model | Baseline Top1 Acc | Distillation Model Finetune |
-|- |:-: |:-: | :-: |
-| Oxford102 flowers | ResNete50_vd | 97.18% | 97.41% |
-| caltech-101 | ResNete50_vd | 92.57% | 93.21% |
-| Oxford-IIIT-Pets | ResNete50_vd | 94.30% | 94.76% |
-| DTD | ResNete50_vd | 76.48% | 77.71% |
-| fgvc-aircraft-2013b | ResNete50_vd | 88.98% | 90.00% |
-| Stanford-Cars | ResNete50_vd | 92.65% | 92.76% |
-| SUN397 | ResNete50_vd | 64.02% | 68.36% |
-| cifar100 | ResNete50_vd | 86.50% | 87.58% |
-| cifar10 | ResNete50_vd | 97.72% | 97.94% |
-| Food-101 | ResNete50_vd | 89.58% | 89.99% |
+#### 1.2.5 DKD
-* 可以看出在上面 10 个数据集上,结合适当的中间层学习率倍数设置,蒸馏模型平均能够带来 1% 以上的精度提升。
+##### 1.2.5.1 DKD 算法介绍
-
-### 4.3 目标检测
+论文信息:
-我们基于两阶段目标检测 Faster/Cascade RCNN 模型验证蒸馏得到的预训练模型的效果。
-* ResNet50_vd
+> [Decoupled Knowledge Distillation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.08679)
+>
+> Borui Zhao, Quan Cui, Renjie Song, Yiyu Qiu, Jiajun Liang
+>
+> CVPR, 2022
-设置训练与评测的尺度均为 640x640,最终 COCO 上检测指标如下。
+DKD将蒸馏中常用的 KD Loss 进行了解耦成为Target Class Knowledge Distillation(TCKD,目标类知识蒸馏)以及Non-target Class Knowledge Distillation(NCKD,非目标类知识蒸馏)两个部分,对两个部分的作用分别研究,并使它们各自的权重可以独立调节,提升了蒸馏的精度和灵活性。
-| Model | train/test scale | pretrain top1 acc | feature map lr | coco mAP |
-|- |:-: |:-: | :-: | :-: |
-| Faster RCNN R50_vd FPN | 640/640 | 79.12% | [1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0] | 34.8% |
-| Faster RCNN R50_vd FPN | 640/640 | 79.12% | [0.05,0.05,0.1,0.1,0.15] | 34.3% |
-| Faster RCNN R50_vd FPN | 640/640 | 82.18% | [0.05,0.05,0.1,0.1,0.15] | 36.3% |
+在ImageNet1k公开数据集上,效果如下所示。
-在这里可以看出,对于未蒸馏模型,过度调整中间层学习率反而降低最终检测模型的性能指标。基于该蒸馏模型,我们也提供了领先的服务端实用目标检测方案,详细的配置与训练代码均已开源,可以参考 [PaddleDetection](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/tree/master/configs/rcnn_enhance)。
+| 策略 | 骨干网络 | 配置文件 | Top-1 acc | 下载链接 |
+| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
+| baseline | ResNet18 | [ResNet18.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/ResNet/ResNet18.yaml) | 70.8% | - |
+| AFD | ResNet18 | [resnet34_distill_resnet18_dkd.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/resnet34_distill_resnet18_dkd.yaml) | 72.59%(**+1.79%**) | - |
-
-## 5. SSLD 实战
-本节将基于 ImageNet-1K 的数据集详细介绍 SSLD 蒸馏实验,如果想快速体验此方法,可以参考 [**30 分钟玩转 PaddleClas(进阶版)**](../quick_start/quick_start_classification_professional.md)中基于 CIFAR100 的 SSLD 蒸馏实验。
+##### 1.2.5.2 DKD 配置
-
-### 5.1 参数配置
+DKD 配置如下所示。在模型构建Arch字段中,需要同时定义学生模型与教师模型,教师模型固定参数,且需要加载预训练模型。在损失函数Loss字段中,需要定义`DistillationDKDLoss`(学生与教师之间的DKD loss)以及`DistillationGTCELoss`(学生与教师关于真值标签的CE loss),作为训练的损失函数。
-实战部分提供了 SSLD 蒸馏的示例,在 `ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/mv3_large_x1_0_distill_mv3_small_x1_0.yaml` 中提供了 `MobileNetV3_large_x1_0` 蒸馏 `MobileNetV3_small_x1_0` 的配置文件,用户可以在 `tools/train.sh` 里直接替换配置文件的路径即可使用。
```yaml
Arch:
@@ -216,53 +418,165 @@ Arch:
- False
models:
- Teacher:
- name: MobileNetV3_large_x1_0
+ name: ResNet34
pretrained: True
- use_ssld: True
+
- Student:
- name: MobileNetV3_small_x1_0
+ name: ResNet18
pretrained: False
infer_model_name: "Student"
+
+
+# loss function config for traing/eval process
+Loss:
+ Train:
+ - DistillationGTCELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ model_names: ["Student"]
+ - DistillationDKDLoss:
+ weight: 1.0
+ model_name_pairs: [["Student", "Teacher"]]
+ temperature: 1
+ alpha: 1.0
+ beta: 1.0
+ Eval:
+ - CELoss:
+ weight: 1.0
```
+
-在参数配置中,`freeze_params_list` 中需要指定模型是否需要冻结参数,`models` 中需要指定 Teacher 模型和 Student 模型,其中 Teacher 模型需要加载预训练模型。用户可以直接在此处更改模型。
+## 2. 模型训练、评估和预测
-
-### 5.2 启动命令
+
-当用户配置完训练环境后,类似于训练其他分类任务,只需要将 `tools/train.sh` 中的配置文件替换成为相应的蒸馏配置文件即可。
+### 2.1 环境配置
-其中 `train.sh` 中的内容如下:
+* 安装:请先参考 [Paddle 安装教程](../installation/install_paddle.md) 以及 [PaddleClas 安装教程](../installation/install_paddleclas.md) 配置 PaddleClas 运行环境。
-```bash
+
+
+### 2.2 数据准备
+
+请在[ImageNet 官网](https://www.image-net.org/)准备 ImageNet-1k 相关的数据。
+
+
+进入 PaddleClas 目录。
+
+```
+cd path_to_PaddleClas
+```
+
+进入 `dataset/` 目录,将下载好的数据命名为 `ILSVRC2012` ,存放于此。 `ILSVRC2012` 目录中具有以下数据:
+
+```
+├── train
+│ ├── n01440764
+│ │ ├── n01440764_10026.JPEG
+│ │ ├── n01440764_10027.JPEG
+├── train_list.txt
+...
+├── val
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000001.JPEG
+│ ├── ILSVRC2012_val_00000002.JPEG
+├── val_list.txt
+```
+
+其中 `train/` 和 `val/` 分别为训练集和验证集。`train_list.txt` 和 `val_list.txt` 分别为训练集和验证集的标签文件。
+
+
+如果包含与训练集场景相似的无标注数据,则也可以按照与训练集标注完全相同的方式进行整理,将文件与当前有标注的数据集放在相同目录下,将其标签值记为0,假设整理的标签文件名为`train_list_unlabel.txt`,则可以通过下面的命令生成用于SSLD训练的标签文件。
+
+```shell
+cat train_list.txt train_list_unlabel.txt > train_list_all.txt
+```
+
+
+**备注:**
-python -m paddle.distributed.launch \
- --selected_gpus="0,1,2,3" \
- --log_dir=mv3_large_x1_0_distill_mv3_small_x1_0 \
+* 关于 `train_list.txt`、`val_list.txt`的格式说明,可以参考[PaddleClas分类数据集格式说明](../data_preparation/classification_dataset.md#1-数据集格式说明) 。
+
+
+
+
+### 2.3 模型训练
+
+
+以SSLD知识蒸馏算法为例,介绍知识蒸馏算法的模型训练、评估、预测等过程。配置文件为 [PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml](../../../ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml) ,使用下面的命令可以完成模型训练。
+
+
+```shell
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" \
tools/train.py \
- -c ./ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/mv3_large_x1_0_distill_mv3_small_x1_0.yaml
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml
```
-运行 `train.sh` :
+
+
+### 2.4 模型评估
+
+训练好模型之后,可以通过以下命令实现对模型指标的评估。
```bash
-sh tools/train.sh
+python3 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model
+```
+
+其中 `-o Global.pretrained_model="output/DistillationModel/best_model"` 指定了当前最佳权重所在的路径,如果指定其他权重,只需替换对应的路径即可。
+
+
+
+### 2.5 模型预测
+
+模型训练完成之后,可以加载训练得到的预训练模型,进行模型预测。在模型库的 `tools/infer.py` 中提供了完整的示例,只需执行下述命令即可完成模型预测:
+
+```python
+python3 tools/infer.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=output/DistillationModel/best_model
+```
+
+输出结果如下:
+
+```
+[{'class_ids': [8, 7, 86, 82, 21], 'scores': [0.87908, 0.12091, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 'file_name': 'docs/images/inference_deployment/whl_demo.jpg', 'label_names': ['hen', 'cock', 'partridge', 'ruffed grouse, partridge, Bonasa umbellus', 'kite']}]
```
-
-### 5.3 注意事项
-* 用户在使用 SSLD 蒸馏之前,首先需要在目标数据集上训练一个教师模型,该教师模型用于指导学生模型在该数据集上的训练。
+**备注:**
-* 如果学生模型没有加载预训练模型,训练的其他超参数可以参考该学生模型在 ImageNet-1k 上训练的超参数,如果学生模型加载了预训练模型,学习率可以调整到原来的 1/10 或者 1/100 。
+* 这里`-o Global.pretrained_model="output/ResNet50/best_model"` 指定了当前最佳权重所在的路径,如果指定其他权重,只需替换对应的路径即可。
-* 在 SSLD 蒸馏的过程中,学生模型只学习 soft-label 导致训练目标变的更加复杂,建议可以适当的调小 `l2_decay` 的值来获得更高的验证集准确率。
+* 默认是对 `docs/images/inference_deployment/whl_demo.jpg` 进行预测,此处也可以通过增加字段 `-o Infer.infer_imgs=xxx` 对其他图片预测。
-* 若用户准备添加无标签的训练数据,只需要将新的训练数据放置在原本训练数据的路径下,生成新的数据 list 即可,另外,新生成的数据 list 需要将无标签的数据添加伪标签(只是为了统一读数据)。
-
-## 6. 参考文献
+
+
+### 2.6 模型导出与推理
+
+
+Paddle Inference 是飞桨的原生推理库, 作用于服务器端和云端,提供高性能的推理能力。相比于直接基于预训练模型进行预测,Paddle Inference可使用MKLDNN、CUDNN、TensorRT 进行预测加速,从而实现更优的推理性能。更多关于Paddle Inference推理引擎的介绍,可以参考[Paddle Inference官网教程](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/guides/infer/inference/inference_cn.html)。
+
+在模型推理之前需要先导出模型。对于知识蒸馏训练得到的模型,在导出时需要指定`-o Global.infer_model_name=Student`,来表示导出的模型为学生模型。具体命令如下所示。
+
+```shell
+python3 tools/export_model.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/ImageNet/Distillation/PPLCNet_x2_5_ssld.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model=./output/DistillationModel/best_model \
+ -o Arch.infer_model_name=Student
+```
+
+最终在`inference`目录下会产生`inference.pdiparams`、`inference.pdiparams.info`、`inference.pdmodel` 3个文件。
+
+关于更多模型推理相关的教程,请参考:[Python 预测推理](../inference_deployment/python_deploy.md)。
+
+
+
+
+## 3. 参考文献
[1] Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.02531, 2015.
@@ -273,3 +587,17 @@ sh tools/train.sh
[4] Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Mane D, et al. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation strategies from data[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019: 113-123.
[5] Touvron H, Vedaldi A, Douze M, et al. Fixing the train-test resolution discrepancy[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2019: 8250-8260.
+
+[6] Cui C, Guo R, Du Y, et al. Beyond Self-Supervision: A Simple Yet Effective Network Distillation Alternative to Improve Backbones[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.05959, 2021.
+
+[7] Zhang Y, Xiang T, Hospedales T M, et al. Deep mutual learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 4320-4328.
+
+[8] Heo B, Kim J, Yun S, et al. A comprehensive overhaul of feature distillation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 1921-1930.
+
+[9] Du Y, Li C, Guo R, et al. PP-OCRv2: Bag of Tricks for Ultra Lightweight OCR System[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.03144, 2021.
+
+[10] Park W, Kim D, Lu Y, et al. Relational knowledge distillation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 3967-3976.
+
+[11] Zhao B, Cui Q, Song R, et al. Decoupled Knowledge Distillation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.08679, 2022.
+
+[12] Ji M, Heo B, Park S. Show, attend and distill: Knowledge distillation via attention-based feature matching[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2021, 35(9): 7945-7952.
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/ssld.md b/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/ssld.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e19a98cbc866bc02f0ca9df6d8e939b3342663f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/advanced_tutorials/ssld.md
@@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
+
+# SSLD 知识蒸馏实战
+
+## 目录
+
+- [1. 算法介绍](#1)
+ - [1.1 知识蒸馏简介](#1.1)
+ - [1.2 SSLD蒸馏策略](#1.2)
+ - [1.3 SKL-UGI蒸馏策略](#1.3)
+- [2. SSLD预训练模型库](#2)
+- [3. SSLD使用](#3)
+ - [3.1 加载SSLD模型进行微调](#3.1)
+ - [3.2 使用SSLD方案进行知识蒸馏](#3.2)
+- [4. 参考文献](#4)
+
+
+
+
+
+## 1. 算法介绍
+
+
+
+### 1.1 简介
+
+PaddleClas 融合已有的知识蒸馏方法 [2,3],提供了一种简单的半监督标签知识蒸馏方案(SSLD,Simple Semi-supervised Label Distillation),基于 ImageNet1k 分类数据集,在 ResNet_vd 以及 MobileNet 系列上的精度均有超过 3% 的绝对精度提升,具体指标如下图所示。
+
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
bs=1 | time(ms)
bs=4 | time(ms)
bs=8 | FLOPs(G) | Params(M) | 预训练模型下载地址 | inference模型下载地址 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| PPHGNet_tiny | 0.7983 | 0.9504 | 1.77 | - | - | 4.54 | 14.75 | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/legendary_models/PPHGNet_tiny_pretrained.pdparams) | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPHGNet_tiny_infer.tar) |
+| PPHGNet_tiny_ssld | 0.8195 | 0.9612 | 1.77 | - | - | 4.54 | 14.75 | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/legendary_models/PPHGNet_tiny_ssld_pretrained.pdparams) | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPHGNet_tiny_ssld_infer.tar) |
| PPHGNet_small | 0.8151 | 0.9582 | 2.52 | - | - | 8.53 | 24.38 | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/legendary_models/PPHGNet_small_pretrained.pdparams) | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPHGNet_small_infer.tar) |
+| PPHGNet_small_ssld | 0.8382 | 0.9681 | 2.52 | - | - | 8.53 | 24.38 | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/legendary_models/PPHGNet_small_ssld_pretrained.pdparams) | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPHGNet_small_ssld_infer.tar) |
+| PPHGNet_base_ssld | 0.8500 | 0.9735 | 5.97 | - | - | 25.14 | 71.62 | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/legendary_models/PPHGNet_base_ssld_pretrained.pdparams) | [下载链接](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPHGNet_base_ssld_infer.tar) |
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/algorithm_introduction/knowledge_distillation.md b/docs/zh_CN/algorithm_introduction/knowledge_distillation.md
index 58092195956119416277e62ec225318373a2bfa3..afedce7f07117c857717575ca063bab8a5decc66 100644
--- a/docs/zh_CN/algorithm_introduction/knowledge_distillation.md
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/algorithm_introduction/knowledge_distillation.md
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@
PaddleClas 中提出了一种简单使用的 SSLD 知识蒸馏算法 [6],在训练的时候去除了对 gt label 的依赖,结合大量无标注数据,最终蒸馏训练得到的预训练模型在 15 个模型上的精度提升平均高达 3%。
-上述标准的蒸馏方法是通过一个大模型作为教师模型来指导学生模型提升效果,而后来又发展出 DML(Deep Mutual Learning)互学习蒸馏方法 [7],即通过两个结构相同的模型互相学习。具体的。相比于 KD 等依赖于大的教师模型的知识蒸馏算法,DML 脱离了对大的教师模型的依赖,蒸馏训练的流程更加简单,模型产出效率也要更高一些。�
+上述标准的蒸馏方法是通过一个大模型作为教师模型来指导学生模型提升效果,而后来又发展出 DML(Deep Mutual Learning)互学习蒸馏方法 [7],即通过两个结构相同的模型互相学习。具体的。相比于 KD 等依赖于大的教师模型的知识蒸馏算法,DML 脱离了对大的教师模型的依赖,蒸馏训练的流程更加简单,模型产出效率也要更高一些。
### 3.2 Feature based distillation
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction.md b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction.md
index 1438e9661200ede1adf67cf6813f763c3a13c095..368abc3da9856c8d9232819aef3b43f0ef66735d 100644
--- a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction.md
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction.md
@@ -1,182 +1,247 @@
+简体中文|[English](../../en/image_recognition_pipeline/feature_extraction_en.md)
# 特征提取
## 目录
-- [1. 简介](#1)
-- [2. 网络结构](#2)
-- [3. 通用识别模型](#3)
-- [4. 自定义特征提取](#4)
- - [4.1 数据准备](#4.1)
- - [4.2 模型训练](#4.2)
- - [4.3 模型评估](#4.3)
- - [4.4 模型推理](#4.4)
- - [4.4.1 导出推理模型](#4.4.1)
- - [4.4.2 获取特征向量](#4.4.2)
+- [1. 摘要](#1-摘要)
+- [2. 介绍](#2-介绍)
+- [3. 方法](#3-方法)
+ - [3.1 Backbone](#31-backbone)
+ - [3.2 Neck](#32-neck)
+ - [3.3 Head](#33-head)
+ - [3.4 Loss](#34-loss)
+- [4. 实验部分](#4-实验部分)
+- [5. 自定义特征提取](#5-自定义特征提取)
+ - [5.1 数据准备](#51-数据准备)
+ - [5.2 模型训练](#52-模型训练)
+ - [5.3 模型评估](#53-模型评估)
+ - [5.4 模型推理](#54-模型推理)
+ - [5.4.1 导出推理模型](#541-导出推理模型)
+ - [5.4.2 获取特征向量](#542-获取特征向量)
+- [6. 总结](#6-总结)
+- [7. 参考文献](#7-参考文献)
-## 1. 简介
+## 1. 摘要
-特征提取是图像识别中的关键一环,它的作用是将输入的图片转化为固定维度的特征向量,用于后续的[向量检索](./vector_search.md)。好的特征需要具备相似度保持性,即在特征空间中,相似度高的图片对其特征相似度要比较高(距离比较近),相似度低的图片对,其特征相似度要比较小(距离比较远)。[Deep Metric Learning](../algorithm_introduction/metric_learning.md)用以研究如何通过深度学习的方法获得具有强表征能力的特征。
+特征提取是图像识别中的关键一环,它的作用是将输入的图片转化为固定维度的特征向量,用于后续的[向量检索](./vector_search.md)。一个好的特征需要具备“相似度保持性”,即相似度高的图片对,其特征的相似度也比较高(特征空间中的距离比较近),相似度低的图片对,其特征相似度要比较低(特征空间中的距离比较远)。为此[Deep Metric Learning](../algorithm_introduction/metric_learning.md)领域内提出了不少方法用以研究如何通过深度学习来获得具有强表征能力的特征。
-## 2. 网络结构
+## 2. 介绍
+
为了图像识别任务的灵活定制,我们将整个网络分为 Backbone、 Neck、 Head 以及 Loss 部分,整体结构如下图所示:

图中各个模块的功能为:
-- **Backbone**: 指定所使用的骨干网络。 值得注意的是,PaddleClas 提供的基于 ImageNet 的预训练模型,最后一层的输出为 1000,我们需要依据所需的特征维度定制最后一层的输出。
-- **Neck**: 用以特征增强及特征维度变换。这儿的 Neck,可以是一个简单的 Linear Layer,用来做特征维度变换;也可以是较复杂的 FPN 结构,用以做特征增强。
-- **Head**: 用来将 feature 转化为 logits。除了常用的 Fc Layer 外,还可以替换为 cosmargin, arcmargin, circlemargin 等模块。
-- **Loss**: 指定所使用的 Loss 函数。我们将 Loss 设计为组合 loss 的形式,可以方便地将 Classification Loss 和 Pair_wise Loss 组合在一起。
+- **Backbone**: 用于提取输入图像初步特征的骨干网络,一般由配置文件中的 [`Backbone`](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml#L26-L29) 以及 [`BackboneStopLayer`](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml#L30-L31) 字段共同指定。
+- **Neck**: 用以特征增强及特征维度变换。可以是一个简单的 FC Layer,用来做特征维度变换;也可以是较复杂的 FPN 结构,用以做特征增强,一般由配置文件中的 [`Neck`](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml#L32-L35)字段指定。
+- **Head**: 用来将 feature 转化为 logits,让模型在训练阶段能以分类任务的形式进行训练。除了常用的 FC Layer 外,还可以替换为 cosmargin, arcmargin, circlemargin 等模块,一般由配置文件中的 [`Head`](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml#L36-L41)字段指定。
+- **Loss**: 指定所使用的 Loss 函数。我们将 Loss 设计为组合 loss 的形式,可以方便地将 Classification Loss 和 Metric learning Loss 组合在一起,一般由配置文件中的 [`Loss`](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml#L44-L50)字段指定。
-## 3. 通用识别模型
+## 3. 方法
+
+### 3.1 Backbone
+
+Backbone 部分采用了 [PP_LCNet_x2_5](../models/PP-LCNet.md),其针对Intel CPU端的性能优化探索了多个有效的结构设计方案,最终实现了在不增加推理时间的情况下,进一步提升模型的性能,最终大幅度超越现有的 SOTA 模型。
+
+### 3.2 Neck
+
+Neck 部分采用了 [FC Layer](../../../ppcls/arch/gears/fc.py),对 Backbone 抽取得到的特征进行降维,减少了特征存储的成本与计算量。
+
+### 3.3 Head
+
+Head 部分选用 [ArcMargin](../../../ppcls/arch/gears/arcmargin.py),在训练时通过指定margin,增大同类特征之间的角度差异再进行分类,进一步提升抽取特征的表征能力。
-在 PP-Shitu 中, 我们采用 [PP_LCNet_x2_5](../models/PP-LCNet.md) 作为骨干网络 Neck 部分选用 Linear Layer, Head 部分选用 [ArcMargin](../../../ppcls/arch/gears/arcmargin.py),Loss 部分选用 CELoss,详细的配置文件见[通用识别配置文件](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml)。其中,训练数据为如下 7 个公开数据集的汇总:
+### 3.4 Loss
-| 数据集 | 数据量 | 类别数 | 场景 | 数据集地址 |
-| :------------: | :-------------: | :-------: | :-------: | :--------: |
-| Aliproduct | 2498771 | 50030 | 商品 | [地址](https://retailvisionworkshop.github.io/recognition_challenge_2020/) |
-| GLDv2 | 1580470 | 81313 | 地标 | [地址](https://github.com/cvdfoundation/google-landmark) |
-| VeRI-Wild | 277797 | 30671 | 车辆 | [地址](https://github.com/PKU-IMRE/VERI-Wild)|
-| LogoDet-3K | 155427 | 3000 | Logo | [地址](https://github.com/Wangjing1551/LogoDet-3K-Dataset) |
-| iCartoonFace | 389678 | 5013 | 动漫人物 | [地址](http://challenge.ai.iqiyi.com/detail?raceId=5def69ace9fcf68aef76a75d) |
-| SOP | 59551 | 11318 | 商品 | [地址](https://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/lifted_struct/) |
-| Inshop | 25882 | 3997 | 商品 | [地址](http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/DeepFashion.html) |
-| **Total** | **5M** | **185K** | ---- | ---- |
+Loss 部分选用 [Cross entropy loss](../../../ppcls/loss/celoss.py),在训练时以分类任务的损失函数来指导网络进行优化。详细的配置文件见[通用识别配置文件](../../../ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml)。
+
+
+
+## 4. 实验部分
+
+训练数据为如下 7 个公开数据集的汇总:
+
+| 数据集 | 数据量 | 类别数 | 场景 | 数据集地址 |
+| :----------: | :-----: | :------: | :------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+| Aliproduct | 2498771 | 50030 | 商品 | [地址](https://retailvisionworkshop.github.io/recognition_challenge_2020/) |
+| GLDv2 | 1580470 | 81313 | 地标 | [地址](https://github.com/cvdfoundation/google-landmark) |
+| VeRI-Wild | 277797 | 30671 | 车辆 | [地址](https://github.com/PKU-IMRE/VERI-Wild) |
+| LogoDet-3K | 155427 | 3000 | Logo | [地址](https://github.com/Wangjing1551/LogoDet-3K-Dataset) |
+| iCartoonFace | 389678 | 5013 | 动漫人物 | [地址](http://challenge.ai.iqiyi.com/detail?raceId=5def69ace9fcf68aef76a75d) |
+| SOP | 59551 | 11318 | 商品 | [地址](https://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/lifted_struct/) |
+| Inshop | 25882 | 3997 | 商品 | [地址](http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/DeepFashion.html) |
+| **Total** | **5M** | **185K** | ---- | ---- |
最终的模型效果如下表所示:
-| 模型 | Aliproduct | VeRI-Wild | LogoDet-3K | iCartoonFace | SOP | Inshop | Latency(ms) |
-| :----------: | :---------: | :-------: | :-------: | :--------: | :--------: | :--------: | :--------: |
-PP-LCNet-2.5x | 0.839 | 0.888 | 0.861 | 0.841 | 0.793 | 0.892 | 5.0
+| 模型 | Aliproduct | VeRI-Wild | LogoDet-3K | iCartoonFace | SOP | Inshop | Latency(ms) |
+| :-----------------------------: | :--------: | :-------: | :--------: | :----------: | :---: | :----: | :---------: |
+| GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5 | 0.839 | 0.888 | 0.861 | 0.841 | 0.793 | 0.892 | 5.0 |
+* 预训练模型地址:[通用识别预训练模型](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/rec/models/pretrain/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_pretrained_v1.0.pdparams)
* 采用的评测指标为:`Recall@1`
* 速度评测机器的 CPU 具体信息为:`Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz`
* 速度指标的评测条件为: 开启 MKLDNN, 线程数设置为 10
-* 预训练模型地址:[通用识别预训练模型](https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/rec/models/pretrain/general_PPLCNet_x2_5_pretrained_v1.0.pdparams)
-
+
-## 4. 自定义特征提取
+## 5. 自定义特征提取
-自定义特征提取,是指依据自己的任务,重新训练特征提取模型。主要包含四个步骤:1)数据准备;2)模型训练;3)模型评估;4)模型推理。
+自定义特征提取,是指依据自己的任务,重新训练特征提取模型。
-
+下面基于`GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml`配置文件,介绍主要的四个步骤:1)数据准备;2)模型训练;3)模型评估;4)模型推理
-### 4.1 数据准备
-首先,需要基于任务定制自己的数据集。数据集格式参见[格式说明](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/develop/docs/zh_CN/data_preparation/recognition_dataset.md#%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E9%9B%86%E6%A0%BC%E5%BC%8F%E8%AF%B4%E6%98%8E)。在启动模型训练之前,需要在配置文件中修改数据配置相关的内容, 主要包括数据集的地址以及类别数量。对应到配置文件中的位置如下所示:
-```
- Head:
- name: ArcMargin
- embedding_size: 512
- class_num: 185341 #此处表示类别数
-```
-```
- Train:
- dataset:
- name: ImageNetDataset
- image_root: ./dataset/ #此处表示train数据所在的目录
- cls_label_path: ./dataset/train_reg_all_data.txt #此处表示train数据集label文件的地址
-```
-```
- Query:
- dataset:
- name: VeriWild
- image_root: ./dataset/Aliproduct/. #此处表示query数据集所在的目录
- cls_label_path: ./dataset/Aliproduct/val_list.txt. #此处表示query数据集label文件的地址
-```
-```
- Gallery:
- dataset:
- name: VeriWild
- image_root: ./dataset/Aliproduct/ #此处表示gallery数据集所在的目录
- cls_label_path: ./dataset/Aliproduct/val_list.txt. #此处表示gallery数据集label文件的地址
-```
-
-
+
-### 4.2 模型训练
+### 5.1 数据准备
-- 单机单卡训练
-```shell
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
-python tools/train.py -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml
-```
-- 单机多卡训练
-```shell
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
-python -m paddle.distributed.launch \
- --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/train.py \
- -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml
-```
-**注意:**
-配置文件中默认采用`在线评估`的方式,如果你想加快训练速度,去除`在线评估`,只需要在上述命令后面,增加 `-o eval_during_train=False`。训练完毕后,在 output 目录下会生成最终模型文件 `latest`,`best_model` 和训练日志文件 `train.log`。其中,`best_model` 用来存储当前评测指标下的最佳模型;`latest` 用来存储最新生成的模型, 方便在任务中断的情况下从断点位置启动训练。
+首先需要基于任务定制自己的数据集。数据集格式与文件结构详见[数据集格式说明](../data_preparation/recognition_dataset.md)。
-- 断点续训:
-```shell
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
-python -m paddle.distributed.launch \
- --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/train.py \
- -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
- -o Global.checkpoint="output/RecModel/latest"
-```
+准备完毕之后还需要在配置文件中修改数据配置相关的内容, 主要包括数据集的地址以及类别数量。对应到配置文件中的位置如下所示:
-
+- 修改类别数:
+ ```yaml
+ Head:
+ name: ArcMargin
+ embedding_size: 512
+ class_num: 185341 # 此处表示类别数
+ ```
+- 修改训练数据集配置:
+ ```yaml
+ Train:
+ dataset:
+ name: ImageNetDataset
+ image_root: ./dataset/ # 此处表示train数据所在的目录
+ cls_label_path: ./dataset/train_reg_all_data.txt # 此处表示train数据集label文件的地址
+ ```
+- 修改评估数据集中query数据配置:
+ ```yaml
+ Query:
+ dataset:
+ name: VeriWild
+ image_root: ./dataset/Aliproduct/ # 此处表示query数据集所在的目录
+ cls_label_path: ./dataset/Aliproduct/val_list.txt # 此处表示query数据集label文件的地址
+ ```
+- 修改评估数据集中gallery数据配置:
+ ```yaml
+ Gallery:
+ dataset:
+ name: VeriWild
+ image_root: ./dataset/Aliproduct/ # 此处表示gallery数据集所在的目录
+ cls_label_path: ./dataset/Aliproduct/val_list.txt # 此处表示gallery数据集label文件的地址
+ ```
+
+
+
+### 5.2 模型训练
+
+模型训练主要包括启动训练和断点恢复训练的功能
-### 4.3 模型评估
+- 单机单卡训练
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+ python3.7 tools/train.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml
+ ```
+- 单机多卡训练
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+ python3.7 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/train.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml
+ ```
+**注意:**
+配置文件中默认采用`在线评估`的方式,如果你想加快训练速度,可以关闭`在线评估`功能,只需要在上述命令的后面,增加 `-o Global.eval_during_train=False`。
+
+训练完毕后,在 output 目录下会生成最终模型文件 `latest.pdparams`,`best_model.pdarams` 和训练日志文件 `train.log`。其中,`best_model` 保存了当前评测指标下的最佳模型,`latest` 用来保存最新生成的模型, 方便在任务中断的情况下从断点位置恢复训练。通过在上述训练命令的末尾加上`-o Global.checkpoint="path_to_resume_checkpoint"`即可从断点恢复训练,示例如下。
+
+- 单机单卡断点恢复训练
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+ python3.7 tools/train.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
+ -o Global.checkpoint="output/RecModel/latest"
+ ```
+- 单机多卡断点恢复训练
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+ python3.7 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/train.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
+ -o Global.checkpoint="output/RecModel/latest"
+ ```
+
+
+
+### 5.3 模型评估
+
+除了训练过程中对模型进行的在线评估,也可以手动启动评估程序来获得指定的模型的精度指标。
- 单卡评估
-```shell
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
-python tools/eval.py \
--c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
--o Global.pretrained_model="output/RecModel/best_model"
-```
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+ python3.7 tools/eval.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/RecModel/best_model"
+ ```
- 多卡评估
-```shell
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
-python -m paddle.distributed.launch \
- --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/eval.py \
- -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
- -o Global.pretrained_model="output/RecModel/best_model"
-```
-**推荐:** 建议使用多卡评估。多卡评估方式可以利用多卡并行计算快速得到整体数据集的特征集合,能够加速评估的过程。
+ ```shell
+ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
+ python3.7 -m paddle.distributed.launch \
+ --gpus="0,1,2,3" tools/eval.py \
+ -c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
+ -o Global.pretrained_model="output/RecModel/best_model"
+ ```
+**注:** 建议使用多卡评估。该方式可以利用多卡并行计算快速得到全部数据的特征,能够加速评估的过程。
-
+
-### 4.4 模型推理
+### 5.4 模型推理
-推理过程包括两个步骤: 1)导出推理模型; 2)获取特征向量
+推理过程包括两个步骤: 1)导出推理模型;2)模型推理以获取特征向量
-
+#### 5.4.1 导出推理模型
-#### 4.4.1 导出推理模型
-
-```
-python tools/export_model.py \
+首先需要将 `*.pdparams` 模型文件转换成 inference 格式,转换命令如下。
+```shell
+python3.7 tools/export_model.py \
-c ppcls/configs/GeneralRecognition/GeneralRecognition_PPLCNet_x2_5.yaml \
-o Global.pretrained_model="output/RecModel/best_model"
```
-生成的推理模型位于 `inference` 目录,里面包含三个文件,分别为 `inference.pdmodel`、`inference.pdiparams`、`inference.pdiparams.info`。
-其中: `inference.pdmodel` 用来存储推理模型的结构, `inference.pdiparams` 和 `inference.pdiparams.info` 用来存储推理模型相关的参数信息。
+生成的推理模型默认位于 `PaddleClas/inference` 目录,里面包含三个文件,分别为 `inference.pdmodel`、`inference.pdiparams`、`inference.pdiparams.info`。
+其中`inference.pdmodel` 用来存储推理模型的结构, `inference.pdiparams` 和 `inference.pdiparams.info` 用来存储推理模型相关的参数信息。
-
+#### 5.4.2 获取特征向量
-#### 4.4.2 获取特征向量
+使用上一步转换得到的 inference 格式模型,将输入图片转换为对应的特征向量,推理命令如下。
-```
+```shell
cd deploy
-python python/predict_rec.py \
+python3.7 python/predict_rec.py \
-c configs/inference_rec.yaml \
-o Global.rec_inference_model_dir="../inference"
```
得到的特征输出格式如下图所示:

-在实际使用过程中,单纯得到特征往往并不能够满足业务的需求。如果想进一步通过特征检索来进行图像识别,可以参照文档[向量检索](./vector_search.md)。
+在实际使用过程中,仅仅得到特征可能并不能满足业务需求。如果想进一步通过特征检索来进行图像识别,可以参照文档[向量检索](./vector_search.md)。
+
+
+
+## 6. 总结
+
+特征提取模块作为图像识别中的关键一环,在网络结构的设计,损失函数的选取上有很大的改进空间。不同的数据集类型有各自不同的特点,如行人重识别、商品识别、人脸识别数据集的分布、图片内容都不尽相同。学术界根据这些特点提出了各种各样的方法,如PCB、MGN、ArcFace、CircleLoss、TripletLoss等,围绕的还是增大类间差异、减少类内差异的最终目标,从而有效地应对各种真实场景数据。
+
+
+
+## 7. 参考文献
+
+1. [PP-LCNet: A Lightweight CPU Convolutional Neural Network](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.15099.pdf)
+2. [ArcFace: Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.07698)
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/mainbody_detection.md b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/mainbody_detection.md
index f3d7989029ae763523cebf3d504920863b356adc..828fdf4f1f017d524aa9ebea1f1a409dee0eaf43 100644
--- a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/mainbody_detection.md
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/mainbody_detection.md
@@ -19,9 +19,13 @@
- [3.3 配置文件改动和说明](#3.3)
- [3.4 启动训练](#3.4)
- [3.5 模型预测与调试](#3.5)
- - [3.6 模型导出与预测部署](#3.6)
+- [4. 模型推理部署](#4)
+ - [4.1 推理模型准备](#4.1)
+ - [4.2 基于python预测引擎推理](#4.2)
+ - [4.3 其他推理方式](#4.3)
-
+
+
## 1. 数据集
@@ -37,7 +41,7 @@
在实际训练的过程中,将所有数据集混合在一起。由于是主体检测,这里将所有标注出的检测框对应的类别都修改为 `前景` 的类别,最终融合的数据集中只包含 1 个类别,即前景。
-
+
## 2. 模型选择
@@ -55,7 +59,7 @@
* 速度评测机器的 CPU 具体信息为:`Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz`,速度指标为开启 mkldnn,线程数设置为 10 测试得到。
* 主体检测的预处理过程较为耗时,平均每张图在上述机器上的时间在 40~55 ms 左右,没有包含在上述的预测耗时统计中。
-
+
### 2.1 轻量级主体检测模型
@@ -72,7 +76,7 @@ PicoDet 由 [PaddleDetection](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection)
在轻量级主体检测任务中,为了更好地兼顾检测速度与效果,我们使用 PPLCNet_x2_5 作为主体检测模型的骨干网络,同时将训练与预测的图像尺度修改为了 640x640,其余配置与 [picodet_lcnet_1_5x_416_coco.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/develop/configs/picodet/more_config/picodet_lcnet_1_5x_416_coco.yml) 完全一致。将数据集更换为自定义的主体检测数据集,进行训练,最终得到检测模型。
-
+
### 2.2 服务端主体检测模型
@@ -93,13 +97,13 @@ PP-YOLO 由 [PaddleDetection](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection)
在服务端主体检测任务中,为了保证检测效果,我们使用 ResNet50vd-DCN 作为检测模型的骨干网络,使用配置文件 [ppyolov2_r50vd_dcn_365e_coco.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.1/configs/ppyolo/ppyolov2_r50vd_dcn_365e_coco.yml),更换为自定义的主体检测数据集,进行训练,最终得到检测模型。
-
+
## 3. 模型训练
本节主要介绍怎样基于 PaddleDetection,基于自己的数据集,训练主体检测模型。
-
+
### 3.1 环境准备
@@ -116,7 +120,7 @@ pip install -r requirements.txt
更多安装教程,请参考: [安装文档](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.1/docs/tutorials/INSTALL_cn.md)
-
+
### 3.2 数据准备
@@ -128,7 +132,7 @@ pip install -r requirements.txt
[{u'id': 1, u'name': u'foreground', u'supercategory': u'foreground'}]
```
-
+
### 3.3 配置文件改动和说明
@@ -154,7 +158,7 @@ ppyolov2_reader.yml:主要说明数据读取器配置,如 batch size,并
此外,也可以根据实际情况,修改上述文件,比如,如果显存溢出,可以将 batch size 和学习率等比缩小等。
-
+
### 3.4 启动训练
@@ -198,7 +202,7 @@ python -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus 0,1,2,3 tools/train.py -c configs/ppy
注意:如果遇到 "`Out of memory error`" 问题, 尝试在 `ppyolov2_reader.yml` 文件中调小 `batch_size`,同时等比例调小学习率。
-
+
### 3.5 模型预测与调试
@@ -211,9 +215,11 @@ python tools/infer.py -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolov2_r50vd_dcn_365e_coco.yml --infer
`--draw_threshold` 是个可选参数. 根据 [NMS](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1699659) 的计算,不同阈值会产生不同的结果 `keep_top_k` 表示设置输出目标的最大数量,默认值为 100,用户可以根据自己的实际情况进行设定。
-
+
+## 4. 模型推理部署
-### 3.6 模型导出与预测部署。
+
+### 4.1 推理模型准备
执行导出模型脚本:
@@ -225,15 +231,21 @@ python tools/export_model.py -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolov2_r50vd_dcn_365e_coco.yml
注意: `PaddleDetection` 导出的 inference 模型的文件格式为 `model.xxx`,这里如果希望与 PaddleClas 的 inference 模型文件格式保持一致,需要将其 `model.xxx` 文件修改为 `inference.xxx` 文件,用于后续主体检测的预测部署。
-更多模型导出教程,请参考: [EXPORT_MODEL](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.1/deploy/EXPORT_MODEL.md)
+更多模型导出教程,请参考: [EXPORT_MODEL](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/deploy/EXPORT_MODEL.md)
最终,目录 `inference/ppyolov2_r50vd_dcn_365e_coco` 中包含 `inference.pdiparams`, `inference.pdiparams.info` 以及 `inference.pdmodel` 文件,其中 `inference.pdiparams` 为保存的 inference 模型权重文件,`inference.pdmodel` 为保存的 inference 模型结构文件。
+
+### 4.2 基于python预测引擎推理
导出模型之后,在主体检测与识别任务中,就可以将检测模型的路径更改为该 inference 模型路径,完成预测。
以商品识别为例,其配置文件为 [inference_product.yaml](../../../deploy/configs/inference_product.yaml),修改其中的 `Global.det_inference_model_dir` 字段为导出的主体检测 inference 模型目录,参考[图像识别快速开始教程](../quick_start/quick_start_recognition.md),即可完成商品检测与识别过程。
+
+### 4.3 其他推理方式
+其他推理方法,如C++推理部署、PaddleServing部署等请参考[检测模型推理部署](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/blob/release/2.4/deploy/README.md)。
+
### FAQ
diff --git a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/vector_search.md b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/vector_search.md
index 6cf4d207ddfa5f3cade2ac727b12df2038f3943c..be0bf785c9b4844a9e6d2ae744ceb37c5ddbfed7 100644
--- a/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/vector_search.md
+++ b/docs/zh_CN/image_recognition_pipeline/vector_search.md
@@ -1,5 +1,21 @@
# 向量检索
+## 目录
+
+- [1. 向量检索应用场景介绍](#1)
+- [2. 向量检索算法介绍](#2)
+ - [2.1 HNSW](#2.1)
+ - [2.2 IVF](#2.2)
+ - [2.3 FLAT](#2.3)
+- [3. 检索库安装](#3)
+- [4. 使用及配置文档介绍](#4)
+ - [4.1 建库及配置文件参数](#4.1)
+ - [4.2 检索配置文件参数](#4.2)
+
+
+
+## 1. 向量检索应用场景介绍
+
向量检索技术在图像识别、图像检索中应用比较广泛。其主要目标是,对于给定的查询向量,在已经建立好的向量库中,与库中所有的待查询向量,进行特征向量的相似度或距离计算,得到相似度排序。在图像识别系统中,我们使用 [Faiss](https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss) 对此部分进行支持,具体信息请详查 [Faiss 官网](https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss)。`Faiss` 主要有以下优势
- 适配性好:支持 Windos、Linux、MacOS 系统
@@ -20,17 +36,33 @@
--------------------------
-## 目录
+
+## 2. 使用的检索算法
+
+目前 `PaddleClas` 中检索模块,支持三种检索算法**HNSW32**、**IVF**、**FLAT**。每种检索算法,满足不同场景。其中 `HNSW32` 为默认方法,此方法的检索精度、检索速度可以取得一个较好的平衡,具体算法介绍可以查看[官方文档](https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss/wiki)。
+
+
+### 2.1 HNSW方法
+
+此方法为图索引方法,如下图所示,在建立索引的时候,分为不同的层,所以检索精度较高,速度较快,但是特征库只支持添加图像功能,不支持删除图像特征功能。基于图的向量检索算法在向量检索的评测中性能都是比较优异的。如果比较在乎检索算法的效率,而且可以容忍一定的空间成本,多数场景下比较推荐基于图的检索算法。而HNSW是一种典型的,应用广泛的图算法,很多分布式检索引擎都对HNSW算法进行了分布式改造,以应用于高并发,大数据量的线上查询。此方法为默认方法。
+
+

+
 -
-  -
-  +
+ +
+ +
+

 +
+
 +
+ @@ -111,6 +135,11 @@ PP-ShiTu图像识别快速体验:[点击这里](./docs/zh_CN/quick_start/quick
PP-ShiTu是一个实用的轻量级通用图像识别系统,主要由主体检测、特征学习和向量检索三个模块组成。该系统从骨干网络选择和调整、损失函数的选择、数据增强、学习率变换策略、正则化参数选择、预训练模型使用以及模型裁剪量化8个方面,采用多种策略,对各个模块的模型进行优化,最终得到在CPU上仅0.2s即可完成10w+库的图像识别的系统。更多细节请参考[PP-ShiTu技术方案](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.00775.pdf)。
+
+## PULC实用图像分类模型效果展示
+
@@ -111,6 +135,11 @@ PP-ShiTu图像识别快速体验:[点击这里](./docs/zh_CN/quick_start/quick
PP-ShiTu是一个实用的轻量级通用图像识别系统,主要由主体检测、特征学习和向量检索三个模块组成。该系统从骨干网络选择和调整、损失函数的选择、数据增强、学习率变换策略、正则化参数选择、预训练模型使用以及模型裁剪量化8个方面,采用多种策略,对各个模块的模型进行优化,最终得到在CPU上仅0.2s即可完成10w+库的图像识别的系统。更多细节请参考[PP-ShiTu技术方案](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.00775.pdf)。
+
+## PULC实用图像分类模型效果展示
+ +
+ -## Features
+PULC demo images
+
-## Features
+PULC demo images
+ -- Comprehensive and easy-to-use feature learning components: 12 metric learning methods are integrated and can be combined and switched at will through configuration files.
+PP-ShiTu demo images
+
-- Comprehensive and easy-to-use feature learning components: 12 metric learning methods are integrated and can be combined and switched at will through configuration files.
+PP-ShiTu demo images
+ -
- +
+ +
+ diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b6733069d99b5622c83321bc628f3d70274ce8d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/car_exists_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: no_car
+ label_1: contains_car
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fb9fb6b6631e774e7486bcdb31c25621e2b7d790
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/language_classification_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/language_classification_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d5be2a3568291d0a31a7026974fc22ecf54a8f4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
similarity index 81%
rename from deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
rename to deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
index a70f663a792fcdcab3b7d45059f2afe0b1efbf07..3df94a80c7c75814e778e5320a31b20a8a7eb742 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg"
- inference_model_dir: "./models/person_cls_infer"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_exists_infer"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
enable_mkldnn: False
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ PreProcess:
PostProcess:
main_indicator: ThreshOutput
ThreshOutput:
- threshold: 0.9
+ threshold: 0.5
label_0: nobody
label_1: someone
SavePreLabel:
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..66a4cebb359a9b1f03a205ee6a031ca6464cffa8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/safety_helmet_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: wearing_helmet
+ label_1: unwearing_helmet
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c6c3969ffa627288fe58fab28b3fe1cbffe9dd03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/text_image_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/text_image_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..108b3dd53a95c06345bdd7ccd34b2e5252d2df19
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/textline_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 1
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/textline_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..53699718b4fdd38da86eaee4cccc584dcc87d2b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/traffic_sign_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 5
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/traffic_sign_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..14ae348d09faca113d5863fbb57f066675b3f447
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/vehicle_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [256, 192]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: VehicleAttribute
+ VehicleAttribute:
+ color_threshold: 0.5
+ type_threshold: 0.5
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..88f73db5419414812450b768ac783982386f0a78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "../inference/"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
index fc0f0fe67aa628e504bb6fcb743f29fd020548cc..d9181278cc617822f98e4966abf0d12ceca498a4 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
index 9b740ed8293c3d66a325682cafc42e2b1415df4d..85f9acb29a88772da63abe302354f5e17a9c3e59 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9959954b6b8bf27589e1d2081f86c6078d16e2c1
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea65b3108ec0476ce952b3221c31ac54fcef161d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c0cd74632460e01676fbc5a43b220c0a7f7d0474
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9149670e8a2aa086c91451442f63a727661fd7d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9e1789ab47aefecac8eaf1121decfc6a8cfb1e8b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..140694eeec3d2925303e8c0d544ef5979cd78219
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9fea2e7c9e0047a8b59606877ad41fe24bf2e24c
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c28f54f77d54df6e68e471538846b01db4387e08
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8e784af808afb58d67fdb3e277dfeebd134ee846
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..412d41956ba48c8e3243bdeff746d389be7e762b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f4725b96698e2ac222ae9d4830d8f29a33322443
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4b8d24d29ff0f8b4befff6bf943d506c36061d4d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..42ad5234973679e65be6054f90c1cc7c0f989bd2
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ac2447842dd0fac260c0d3c6e0d156dda9890923
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7d5b75f7e5bbeabded56eba1b4b566c4ca019590
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6f32ed5ae2d8483d29986e3a45db1789da2a4d43
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c792fdf6eb64395fffaf8289a1ec14d47279860e
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bb5de9fc6ff99550bf9bff8d4a9f0d0e0fe18c06
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76207d43ce597a1079c523dca0c32923bf15db19
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6a87e856af8c17a3b93617b93ea517b91c508619
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
index d1307ea84e3d7a1465c7c464d3b41dfa7613a046..bacc202806bf1a60e85790969edcb70f1489f7df 100644
--- a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
@@ -1,53 +1,59 @@
# paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测
-本章节介绍 ResNet50_vd 模型如何转化为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
+## 目录
+
+- [paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测](#paddle2onnx-模型转化与预测)
+ - [1. 环境准备](#1-环境准备)
+ - [2. 模型转换](#2-模型转换)
+ - [3. onnx 预测](#3-onnx-预测)
## 1. 环境准备
需要准备 Paddle2ONNX 模型转化环境,和 ONNX 模型预测环境。
-Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11,部分Paddle算子支持更低的ONNX Opset转换。
-更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_zh.md)
+Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11。
+更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX#paddle2onnx)
- 安装 Paddle2ONNX
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
-```
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+ ```
-- 安装 ONNX 运行时
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
-```
+- 安装 ONNX 推理引擎
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+ ```
+下面以 ResNet50_vd 为例,介绍如何将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型转换为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
## 2. 模型转换
- ResNet50_vd inference模型下载
-```
-cd deploy
-mkdir models && cd models
-wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
-cd ..
-```
+ ```shell
+ cd deploy
+ mkdir models && cd models
+ wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+ cd ..
+ ```
- 模型转换
-使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
-```
-paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
---model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
---params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
---save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
---opset_version=10 \
---enable_onnx_checker=True
-```
+ 使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
+ ```shell
+ paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+ --model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+ --params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+ --save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+ --opset_version=10 \
+ --enable_onnx_checker=True
+ ```
-执行完毕后,ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
+转换完毕后,生成的ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
## 3. onnx 预测
执行如下命令:
-```
+```shell
python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
-o Global.use_onnx=True \
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6df13e5fe31805d642432dea8526661e82b6e95b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+# Paddle2ONNX: Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+This section introduce that how to convert the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd to ONNX model and deployment based on ONNX engine.
+
+## 1. Installation
+
+First, you need to install Paddle2ONNX and onnxruntime. Paddle2ONNX is a toolkit to convert Paddle Inference Model to ONNX model. Please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_en.md) for more information.
+
+- Paddle2ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+```
+
+- ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+```
+
+## 2. Converting to ONNX
+
+Download the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd:
+
+```
+cd deploy
+mkdir models && cd models
+wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+cd ..
+```
+
+Converting to ONNX model:
+
+```
+paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+--model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+--params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+--save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+--opset_version=10 \
+--enable_onnx_checker=True
+```
+
+After running the above command, the ONNX model file converted would be save in `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/`.
+
+## 3. Deployment
+
+Deployment with ONNX model, command is as shown below.
+
+```
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
+-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
+-o Global.use_onnx=True \
+-o Global.use_gpu=False \
+-o Global.inference_model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg: class id(s): [153, 204, 229, 332, 155], score(s): [0.69, 0.10, 0.02, 0.01, 0.01], label_name(s): ['Maltese dog, Maltese terrier, Maltese', 'Lhasa, Lhasa apso', 'Old English sheepdog, bobtail', 'Angora, Angora rabbit', 'Shih-Tzu']
+```
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1329a3684ff72862858ee25c0a938bd61ff654ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+# 使用镜像:
+# registry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:latest-dev-cuda10.1-cudnn7-gcc82
+
+# 编译Serving Server:
+
+# client和app可以直接使用release版本
+
+# server因为加入了自定义OP,需要重新编译
+
+# 默认编译时的${PWD}=PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/
+
+python_name=${1:-'python'}
+
+apt-get update
+apt install -y libcurl4-openssl-dev libbz2-dev
+wget -nc https://paddle-serving.bj.bcebos.com/others/centos_ssl.tar
+tar xf centos_ssl.tar
+rm -rf centos_ssl.tar
+mv libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k
+mv libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10 /usr/lib/libcrypto.so
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.10 /usr/lib/libssl.so
+
+# 安装go依赖
+rm -rf /usr/local/go
+wget -qO- https://paddle-ci.cdn.bcebos.com/go1.17.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz | tar -xz -C /usr/local
+export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
+export GOPATH=/root/gopath
+export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin:$GOROOT/bin
+go env -w GO111MODULE=on
+go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go@v1.4.3
+go install google.golang.org/grpc@v1.33.0
+go env -w GO111MODULE=auto
+
+# 下载opencv库
+wget https://paddle-qa.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleServing/opencv3.tar.gz
+tar -xvf opencv3.tar.gz
+rm -rf opencv3.tar.gz
+export OPENCV_DIR=$PWD/opencv3
+
+# clone Serving
+git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving.git -b develop --depth=1
+
+cd Serving # PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/Serving
+export Serving_repo_path=$PWD
+git submodule update --init --recursive
+${python_name} -m pip install -r python/requirements.txt
+
+# set env
+export PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$(${python_name} -c "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_inc; print(get_python_inc())")
+export PYTHON_LIBRARIES=$(${python_name} -c "import distutils.sysconfig as sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var('LIBDIR'))")
+export PYTHON_EXECUTABLE=`which ${python_name}`
+
+export CUDA_PATH='/usr/local/cuda'
+export CUDNN_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH='/usr/local/TensorRT6-cuda10.1-cudnn7/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/'
+
+# cp 自定义OP代码
+\cp ../preprocess/general_clas_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/general-server/op
+\cp ../preprocess/preprocess_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/predictor/tools/pp_shitu_tools
+
+# 编译Server
+mkdir server-build-gpu-opencv
+cd server-build-gpu-opencv
+cmake -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR \
+-DPYTHON_LIBRARIES=$PYTHON_LIBRARIES \
+-DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$PYTHON_EXECUTABLE \
+-DCUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR=${CUDA_PATH} \
+-DCUDNN_LIBRARY=${CUDNN_LIBRARY} \
+-DCUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY=${CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY} \
+-DTENSORRT_ROOT=${TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH} \
+-DOPENCV_DIR=${OPENCV_DIR} \
+-DWITH_OPENCV=ON \
+-DSERVER=ON \
+-DWITH_GPU=ON ..
+make -j32
+
+${python_name} -m pip install python/dist/paddle*
+
+# export SERVING_BIN
+export SERVING_BIN=$PWD/core/general-server/serving
+cd ../../
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
index d9f464dd093d5a3d0ac34a61f4af17e3792fcd86..92d8297f9f23a4082cb0a499ca4c172e71d79caf 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
@@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ op:
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
- fetch_list: ["prediction"]
+ fetch_list: ["prediction"]
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e0ab48fa52da70a558b34e7ab1deda52675e99bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#include "core/general-server/op/general_clas_op.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/infer.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/memory.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/resource.h"
+#include "core/util/include/timer.h"
+#include
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b6733069d99b5622c83321bc628f3d70274ce8d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/car_exists/inference_car_exists.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/car_exists_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: no_car
+ label_1: contains_car
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fb9fb6b6631e774e7486bcdb31c25621e2b7d790
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/language_classification/inference_language_classification.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/language_classification_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/language_classification_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d5be2a3568291d0a31a7026974fc22ecf54a8f4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_attribute/inference_person_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
similarity index 81%
rename from deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
rename to deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
index a70f663a792fcdcab3b7d45059f2afe0b1efbf07..3df94a80c7c75814e778e5320a31b20a8a7eb742 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/PULC/person/inference_person_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/person_exists/inference_person_exists.yaml
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg"
- inference_model_dir: "./models/person_cls_infer"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/person_exists_infer"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
enable_mkldnn: False
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ PreProcess:
PostProcess:
main_indicator: ThreshOutput
ThreshOutput:
- threshold: 0.9
+ threshold: 0.5
label_0: nobody
label_1: someone
SavePreLabel:
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..66a4cebb359a9b1f03a205ee6a031ca6464cffa8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/safety_helmet/inference_safety_helmet.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/safety_helmet_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: ThreshOutput
+ ThreshOutput:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ label_0: wearing_helmet
+ label_1: unwearing_helmet
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c6c3969ffa627288fe58fab28b3fe1cbffe9dd03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/inference_text_image_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/text_image_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 2
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/text_image_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..108b3dd53a95c06345bdd7ccd34b2e5252d2df19
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/textline_orientation/inference_textline_orientation.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/textline_orientation_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [160, 80]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 1
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/textline_orientation_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..53699718b4fdd38da86eaee4cccc584dcc87d2b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/traffic_sign/inference_traffic_sign.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/traffic_sign_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ resize_short: 256
+ - CropImage:
+ size: 224
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 0.00392157
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: Topk
+ Topk:
+ topk: 5
+ class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/PULC_label_list/traffic_sign_label_list.txt"
+ SavePreLabel:
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..14ae348d09faca113d5863fbb57f066675b3f447
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/PULC/vehicle_attribute/inference_vehicle_attribute.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "./models/vehicle_attribute_infer"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: True
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ benchmark: False
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [256, 192]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: VehicleAttribute
+ VehicleAttribute:
+ color_threshold: 0.5
+ type_threshold: 0.5
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..88f73db5419414812450b768ac783982386f0a78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_attr.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Global:
+ infer_imgs: "./images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg"
+ inference_model_dir: "../inference/"
+ batch_size: 1
+ use_gpu: True
+ enable_mkldnn: False
+ cpu_num_threads: 10
+ enable_benchmark: True
+ use_fp16: False
+ ir_optim: True
+ use_tensorrt: False
+ gpu_mem: 8000
+ enable_profile: False
+
+PreProcess:
+ transform_ops:
+ - ResizeImage:
+ size: [192, 256]
+ - NormalizeImage:
+ scale: 1.0/255.0
+ mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
+ std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
+ order: ''
+ channel_num: 3
+ - ToCHWImage:
+
+PostProcess:
+ main_indicator: PersonAttribute
+ PersonAttribute:
+ threshold: 0.5 #default threshold
+ glasses_threshold: 0.3 #threshold only for glasses
+ hold_threshold: 0.6 #threshold only for hold
+
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
index fc0f0fe67aa628e504bb6fcb743f29fd020548cc..d9181278cc617822f98e4966abf0d12ceca498a4 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
index 9b740ed8293c3d66a325682cafc42e2b1415df4d..85f9acb29a88772da63abe302354f5e17a9c3e59 100644
--- a/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
+++ b/deploy/configs/inference_cls_ch4.yaml
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
Global:
- infer_imgs: "./images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
+ infer_imgs: "./images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg"
inference_model_dir: "./models"
batch_size: 1
use_gpu: True
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ PostProcess:
topk: 5
class_id_map_file: "../ppcls/utils/imagenet1k_label_list.txt"
SavePreLabel:
- save_dir: ./pre_label/
\ No newline at end of file
+ save_dir: ./pre_label/
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00010010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00020010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg b/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
rename to deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00030010.jpeg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9959954b6b8bf27589e1d2081f86c6078d16e2c1
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001507.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea65b3108ec0476ce952b3221c31ac54fcef161d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/car_exists/objects365_00001521.jpeg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c0cd74632460e01676fbc5a43b220c0a7f7d0474
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_17.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9149670e8a2aa086c91451442f63a727661fd7d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_20.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9e1789ab47aefecac8eaf1121decfc6a8cfb1e8b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/language_classification/word_35404.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..140694eeec3d2925303e8c0d544ef5979cd78219
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090004.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9fea2e7c9e0047a8b59606877ad41fe24bf2e24c
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/person_attribute/090007.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_01780782.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_01780782.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
similarity index 100%
rename from deploy/images/PULC/person/objects365_02035329.jpg
rename to deploy/images/PULC/person_exists/objects365_02035329.jpg
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c28f54f77d54df6e68e471538846b01db4387e08
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8e784af808afb58d67fdb3e277dfeebd134ee846
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/safety_helmet/safety_helmet_test_2.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..412d41956ba48c8e3243bdeff746d389be7e762b
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot0_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f4725b96698e2ac222ae9d4830d8f29a33322443
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/text_image_orientation/img_rot180_demo.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4b8d24d29ff0f8b4befff6bf943d506c36061d4d
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..42ad5234973679e65be6054f90c1cc7c0f989bd2
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_0_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ac2447842dd0fac260c0d3c6e0d156dda9890923
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_0.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7d5b75f7e5bbeabded56eba1b4b566c4ca019590
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/textline_orientation/textline_orientation_test_1_1.png differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6f32ed5ae2d8483d29986e3a45db1789da2a4d43
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/100999_83928.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c792fdf6eb64395fffaf8289a1ec14d47279860e
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/traffic_sign/99603_17806.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bb5de9fc6ff99550bf9bff8d4a9f0d0e0fe18c06
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0002_c002_00030670_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76207d43ce597a1079c523dca0c32923bf15db19
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/PULC/vehicle_attribute/0014_c012_00040750_0.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6a87e856af8c17a3b93617b93ea517b91c508619
Binary files /dev/null and b/deploy/images/Pedestrain_Attr.jpg differ
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
index d1307ea84e3d7a1465c7c464d3b41dfa7613a046..bacc202806bf1a60e85790969edcb70f1489f7df 100644
--- a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md
@@ -1,53 +1,59 @@
# paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测
-本章节介绍 ResNet50_vd 模型如何转化为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
+## 目录
+
+- [paddle2onnx 模型转化与预测](#paddle2onnx-模型转化与预测)
+ - [1. 环境准备](#1-环境准备)
+ - [2. 模型转换](#2-模型转换)
+ - [3. onnx 预测](#3-onnx-预测)
## 1. 环境准备
需要准备 Paddle2ONNX 模型转化环境,和 ONNX 模型预测环境。
-Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11,部分Paddle算子支持更低的ONNX Opset转换。
-更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_zh.md)
+Paddle2ONNX 支持将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型格式转化到 ONNX 模型格式,算子目前稳定支持导出 ONNX Opset 9~11。
+更多细节可参考 [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX#paddle2onnx)
- 安装 Paddle2ONNX
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
-```
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+ ```
-- 安装 ONNX 运行时
-```
-python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
-```
+- 安装 ONNX 推理引擎
+ ```shell
+ python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+ ```
+下面以 ResNet50_vd 为例,介绍如何将 PaddlePaddle inference 模型转换为 ONNX 模型,并基于 ONNX 引擎预测。
## 2. 模型转换
- ResNet50_vd inference模型下载
-```
-cd deploy
-mkdir models && cd models
-wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
-cd ..
-```
+ ```shell
+ cd deploy
+ mkdir models && cd models
+ wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+ cd ..
+ ```
- 模型转换
-使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
-```
-paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
---model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
---params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
---save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
---opset_version=10 \
---enable_onnx_checker=True
-```
+ 使用 Paddle2ONNX 将 Paddle 静态图模型转换为 ONNX 模型格式:
+ ```shell
+ paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+ --model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+ --params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+ --save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+ --opset_version=10 \
+ --enable_onnx_checker=True
+ ```
-执行完毕后,ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
+转换完毕后,生成的ONNX 模型 `inference.onnx` 会被保存在 `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/` 路径下
## 3. onnx 预测
执行如下命令:
-```
+```shell
python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
-o Global.use_onnx=True \
diff --git a/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6df13e5fe31805d642432dea8526661e82b6e95b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+# Paddle2ONNX: Converting To ONNX and Deployment
+
+This section introduce that how to convert the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd to ONNX model and deployment based on ONNX engine.
+
+## 1. Installation
+
+First, you need to install Paddle2ONNX and onnxruntime. Paddle2ONNX is a toolkit to convert Paddle Inference Model to ONNX model. Please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/blob/develop/README_en.md) for more information.
+
+- Paddle2ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install paddle2onnx
+```
+
+- ONNX Installation
+```
+python3.7 -m pip install onnxruntime
+```
+
+## 2. Converting to ONNX
+
+Download the Paddle Inference Model ResNet50_vd:
+
+```
+cd deploy
+mkdir models && cd models
+wget -nc https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/ResNet50_vd_infer.tar && tar xf ResNet50_vd_infer.tar
+cd ..
+```
+
+Converting to ONNX model:
+
+```
+paddle2onnx --model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/ \
+--model_filename=inference.pdmodel \
+--params_filename=inference.pdiparams \
+--save_file=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/inference.onnx \
+--opset_version=10 \
+--enable_onnx_checker=True
+```
+
+After running the above command, the ONNX model file converted would be save in `./models/ResNet50_vd_infer/`.
+
+## 3. Deployment
+
+Deployment with ONNX model, command is as shown below.
+
+```
+python3.7 python/predict_cls.py \
+-c configs/inference_cls.yaml \
+-o Global.use_onnx=True \
+-o Global.use_gpu=False \
+-o Global.inference_model_dir=./models/ResNet50_vd_infer
+```
+
+The prediction results:
+
+```
+ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg: class id(s): [153, 204, 229, 332, 155], score(s): [0.69, 0.10, 0.02, 0.01, 0.01], label_name(s): ['Maltese dog, Maltese terrier, Maltese', 'Lhasa, Lhasa apso', 'Old English sheepdog, bobtail', 'Angora, Angora rabbit', 'Shih-Tzu']
+```
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1329a3684ff72862858ee25c0a938bd61ff654ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/build_server.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+# 使用镜像:
+# registry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:latest-dev-cuda10.1-cudnn7-gcc82
+
+# 编译Serving Server:
+
+# client和app可以直接使用release版本
+
+# server因为加入了自定义OP,需要重新编译
+
+# 默认编译时的${PWD}=PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/
+
+python_name=${1:-'python'}
+
+apt-get update
+apt install -y libcurl4-openssl-dev libbz2-dev
+wget -nc https://paddle-serving.bj.bcebos.com/others/centos_ssl.tar
+tar xf centos_ssl.tar
+rm -rf centos_ssl.tar
+mv libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k
+mv libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.1.0.2k /usr/lib/libssl.so.10
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libcrypto.so.10 /usr/lib/libcrypto.so
+ln -sf /usr/lib/libssl.so.10 /usr/lib/libssl.so
+
+# 安装go依赖
+rm -rf /usr/local/go
+wget -qO- https://paddle-ci.cdn.bcebos.com/go1.17.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz | tar -xz -C /usr/local
+export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
+export GOPATH=/root/gopath
+export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin:$GOROOT/bin
+go env -w GO111MODULE=on
+go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger@v1.15.2
+go install github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go@v1.4.3
+go install google.golang.org/grpc@v1.33.0
+go env -w GO111MODULE=auto
+
+# 下载opencv库
+wget https://paddle-qa.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleServing/opencv3.tar.gz
+tar -xvf opencv3.tar.gz
+rm -rf opencv3.tar.gz
+export OPENCV_DIR=$PWD/opencv3
+
+# clone Serving
+git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving.git -b develop --depth=1
+
+cd Serving # PaddleClas/deploy/paddleserving/Serving
+export Serving_repo_path=$PWD
+git submodule update --init --recursive
+${python_name} -m pip install -r python/requirements.txt
+
+# set env
+export PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$(${python_name} -c "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_inc; print(get_python_inc())")
+export PYTHON_LIBRARIES=$(${python_name} -c "import distutils.sysconfig as sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var('LIBDIR'))")
+export PYTHON_EXECUTABLE=`which ${python_name}`
+
+export CUDA_PATH='/usr/local/cuda'
+export CUDNN_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY='/usr/local/cuda/lib64/'
+export TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH='/usr/local/TensorRT6-cuda10.1-cudnn7/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/'
+
+# cp 自定义OP代码
+\cp ../preprocess/general_clas_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/general-server/op
+\cp ../preprocess/preprocess_op.* ${Serving_repo_path}/core/predictor/tools/pp_shitu_tools
+
+# 编译Server
+mkdir server-build-gpu-opencv
+cd server-build-gpu-opencv
+cmake -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=$PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR \
+-DPYTHON_LIBRARIES=$PYTHON_LIBRARIES \
+-DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$PYTHON_EXECUTABLE \
+-DCUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR=${CUDA_PATH} \
+-DCUDNN_LIBRARY=${CUDNN_LIBRARY} \
+-DCUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY=${CUDA_CUDART_LIBRARY} \
+-DTENSORRT_ROOT=${TENSORRT_LIBRARY_PATH} \
+-DOPENCV_DIR=${OPENCV_DIR} \
+-DWITH_OPENCV=ON \
+-DSERVER=ON \
+-DWITH_GPU=ON ..
+make -j32
+
+${python_name} -m pip install python/dist/paddle*
+
+# export SERVING_BIN
+export SERVING_BIN=$PWD/core/general-server/serving
+cd ../../
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
index d9f464dd093d5a3d0ac34a61f4af17e3792fcd86..92d8297f9f23a4082cb0a499ca4c172e71d79caf 100644
--- a/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
@@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ op:
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
- fetch_list: ["prediction"]
+ fetch_list: ["prediction"]
diff --git a/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e0ab48fa52da70a558b34e7ab1deda52675e99bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deploy/paddleserving/preprocess/general_clas_op.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
+// Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+//
+// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+// You may obtain a copy of the License at
+//
+// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+//
+// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+// limitations under the License.
+
+#include "core/general-server/op/general_clas_op.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/infer.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/memory.h"
+#include "core/predictor/framework/resource.h"
+#include "core/util/include/timer.h"
+#include  +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+