RNN Configuration¶
This tutorial will guide you how to configure recurrent neural network in PaddlePaddle. PaddlePaddle supports highly flexible and efficient recurrent neural network configuration. In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
- prepare sequence data for learning recurrent neural networks.
- configure recurrent neural network architecture.
- generate sequence with learned recurrent neural network models.
We will use vanilla recurrent neural network, and sequence to sequence model to guide you through these steps. The code of sequence to sequence model can be found at demo/seqToseq.
Prepare Sequence Data¶
PaddlePaddle does not need any preprocessing to sequence data, such as padding. The only thing that needs to be done is to set the type of the corresponding type to input. For example, the following code snippets defines three input. All of them are sequences, and the size of them are src_dict, trg_dict, and trg_dict:
settings.input_types = [
integer_value_sequence(len(settings.src_dict)),
integer_value_sequence(len(settings.trg_dict)),
integer_value_sequence(len(settings.trg_dict))]
Then at the process function, each yield function will return three integer lists. Each integer list is treated as a sequence of integers:
yield src_ids, trg_ids, trg_ids_next
For more details description of how to write a data provider, please refer to PyDataProvider2 . The full data provider file is located at demo/seqToseq/dataprovider.py.
Configure Recurrent Neural Network Architecture¶
Simple Gated Recurrent Neural Network¶
Recurrent neural network process a sequence at each time step sequentially. An example of the architecture of LSTM is listed below.
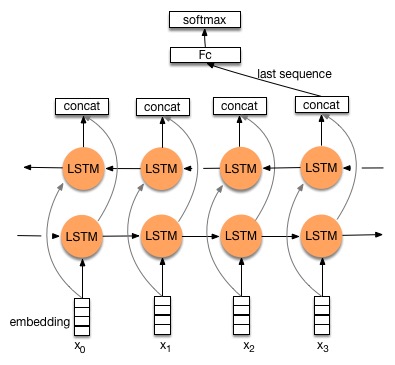
Generally speaking, a recurrent network perform the following operations from \(t=1\) to \(t=T\), or reversely from \(t=T\) to \(t=1\).
where \(f_x(.)\) is called step function, and \(f_y(.)\) is called output function. In vanilla recurrent neural network, both of the step function and output function are very simple. However, PaddlePaddle supports the configuration of very complex architectures by modifying these two functions. We will use the sequence to sequence model with attention as an example to demonstrate how you can configure complex recurrent neural network models. In this section, we will use a simple vanilla recurrent neural network as an example of configuring simple recurrent neural network using recurrent_group. Notice that if you only need to use simple RNN, GRU, or LSTM, then grumemory and lstmemory is recommended because they are more computationally efficient than recurrent_group.
For vanilla RNN, at each time step, the step function is:
where \(x_t\) is the RNN state, and \(I_t\) is the input, \(W_x\) and \(W_i\) are transformation matrices for RNN states and inputs, respectively. \(b\) is the bias. Its output function simply takes \(x_t\) as the output.
recurrent_group is the most important tools for constructing recurrent neural networks. It defines the step function, output function and the inputs of the recurrent neural network. Notice that the step argument of this function implements both the step function and the output function:
def simple_rnn(input,
size=None,
name=None,
reverse=False,
rnn_bias_attr=None,
act=None,
rnn_layer_attr=None):
def __rnn_step__(ipt):
out_mem = memory(name=name, size=size)
rnn_out = mixed_layer(input = [full_matrix_projection(ipt),
full_matrix_projection(out_mem)],
name = name,
bias_attr = rnn_bias_attr,
act = act,
layer_attr = rnn_layer_attr,
size = size)
return rnn_out
return recurrent_group(name='%s_recurrent_group' % name,
step=__rnn_step__,
reverse=reverse,
input=input)
PaddlePaddle uses memory to construct step function. Memory is the most important concept when constructing recurrent neural networks in PaddlePaddle. A memory is a state that is used recurrently in step functions, such as \(x_{t+1} = f_x(x_t)\). One memory contains an output and a input. The output of memory at the current time step is utilized as the input of the memory at the next time step. A memory can also has a boot layer, whose output is utilized as the initial value of the memory. In our case, the output of the gated recurrent unit is employed as the output memory. Notice that the name of the layer rnn_out is the same as the name of out_mem. This means the output of the layer rnn_out (\(x_{t+1}\)) is utilized as the output of out_mem memory.
A memory can also be a sequence. In this case, at each time step, we have a sequence as the state of the recurrent neural network. This can be useful when constructing very complex recurrent neural network. Other advanced functions include defining multiple memories, and defining hierarchical recurrent neural network architecture using sub-sequence.
We return rnn_out at the end of the function. It means that the output of the layer rnn_out is utilized as the output function of the gated recurrent neural network.
Sequence to Sequence Model with Attention¶
We will use the sequence to sequence model with attention as an example to demonstrate how you can configure complex recurrent neural network models. An illustration of the sequence to sequence model with attention is shown in the following figure.
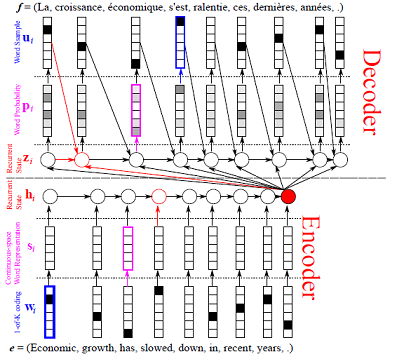
In this model, the source sequence \(S = \{s_1, \dots, s_T\}\) is encoded with a bidirectional gated recurrent neural networks. The hidden states of the bidirectional gated recurrent neural network \(H_S = \{H_1, \dots, H_T\}\) is called encoder vector The decoder is a gated recurrent neural network. When decoding each token \(y_t\), the gated recurrent neural network generates a set of weights \(W_S^t = \{W_1^t, \dots, W_T^t\}\), which are used to compute a weighted sum of the encoder vector. The weighted sum of the encoder vector is utilized to condition the generation of the token \(y_t\).
The encoder part of the model is listed below. It calls grumemory to represent gated recurrent neural network. It is the recommended way of using recurrent neural network if the network architecture is simple, because it is faster than recurrent_group. We have implemented most of the commonly used recurrent neural network architectures, you can refer to Layers for more details.
We also project the encoder vector to decoder_size dimensional space, get the first instance of the backward recurrent network, and project it to decoder_size dimensional space:
# Define the data layer of the source sentence.
src_word_id = data_layer(name='source_language_word', size=source_dict_dim)
# Calculate the word embedding of each word.
src_embedding = embedding_layer(
input=src_word_id,
size=word_vector_dim,
param_attr=ParamAttr(name='_source_language_embedding'))
# Apply forward recurrent neural network.
src_forward = grumemory(input=src_embedding, size=encoder_size)
# Apply backward recurrent neural network. reverse=True means backward recurrent neural network.
src_backward = grumemory(input=src_embedding,
size=encoder_size,
reverse=True)
# Mix the forward and backward parts of the recurrent neural network together.
encoded_vector = concat_layer(input=[src_forward, src_backward])
# Project encoding vector to decoder_size.
encoder_proj = mixed_layer(input = [full_matrix_projection(encoded_vector)],
size = decoder_size)
# Compute the first instance of the backward RNN.
backward_first = first_seq(input=src_backward)
# Project the first instance of backward RNN to decoder size.
decoder_boot = mixed_layer(input=[full_matrix_projection(backward_first)], size=decoder_size, act=TanhActivation())
The decoder uses recurrent_group to define the recurrent neural network. The step and output functions are defined in gru_decoder_with_attention:
group_inputs=[StaticInput(input=encoded_vector,is_seq=True),
StaticInput(input=encoded_proj,is_seq=True)]
trg_embedding = embedding_layer(
input=data_layer(name='target_language_word',
size=target_dict_dim),
size=word_vector_dim,
param_attr=ParamAttr(name='_target_language_embedding'))
group_inputs.append(trg_embedding)
# For decoder equipped with attention mechanism, in training,
# target embedding (the groudtruth) is the data input,
# while encoded source sequence is accessed to as an unbounded memory.
# StaticInput means the same value is utilized at different time steps.
# Otherwise, it is a sequence input. Inputs at different time steps are different.
# All sequence inputs should have the same length.
decoder = recurrent_group(name=decoder_group_name,
step=gru_decoder_with_attention,
input=group_inputs)
The implementation of the step function is listed as below. First, it defines the memory of the decoder network. Then it defines attention, gated recurrent unit step function, and the output function:
def gru_decoder_with_attention(enc_vec, enc_proj, current_word):
# Defines the memory of the decoder.
# The output of this memory is defined in gru_step.
# Notice that the name of gru_step should be the same as the name of this memory.
decoder_mem = memory(name='gru_decoder',
size=decoder_size,
boot_layer=decoder_boot)
# Compute attention weighted encoder vector.
context = simple_attention(encoded_sequence=enc_vec,
encoded_proj=enc_proj,
decoder_state=decoder_mem)
# Mix the current word embedding and the attention weighted encoder vector.
decoder_inputs = mixed_layer(inputs = [full_matrix_projection(context),
full_matrix_projection(current_word)],
size = decoder_size * 3)
# Define Gated recurrent unit recurrent neural network step function.
gru_step = gru_step_layer(name='gru_decoder',
input=decoder_inputs,
output_mem=decoder_mem,
size=decoder_size)
# Defines the output function.
out = mixed_layer(input=[full_matrix_projection(input=gru_step)],
size=target_dict_dim,
bias_attr=True,
act=SoftmaxActivation())
return out
Generate Sequence¶
After training the model, we can use it to generate sequences. A common practice is to use beam search to generate sequences. The following code snippets defines a beam search algorithm. Notice that beam_search function assumes the output function of the step returns a softmax normalized probability vector of the next token. We made the following changes to the model.
- use
GeneratedInputfor trg_embedding.GeneratedInputcomputes the embedding of the generated token at the last time step for the input at the current time step. - use
beam_searchfunction. This function needs to set:bos_id: the start token. Every sentence starts with the start token.eos_id: the end token. Every sentence ends with the end token.beam_size: the beam size used in beam search.max_length: the maximum length of the generated sentences.
- use
seqtext_printer_evaluatorto print text according to index matrix and dictionary. This function needs to set:id_input: the integer ID of the data, used to identify the corresponding output in the generated files.dict_file: the dictionary file for converting word id to word.result_file: the path of the generation result file.
The code is listed below:
group_inputs=[StaticInput(input=encoded_vector,is_seq=True),
StaticInput(input=encoded_proj,is_seq=True)]
# In generation, decoder predicts a next target word based on
# the encoded source sequence and the last generated target word.
# The encoded source sequence (encoder's output) must be specified by
# StaticInput which is a read-only memory.
# Here, GeneratedInputs automatically fetchs the last generated word,
# which is initialized by a start mark, such as <s>.
trg_embedding = GeneratedInput(
size=target_dict_dim,
embedding_name='_target_language_embedding',
embedding_size=word_vector_dim)
group_inputs.append(trg_embedding)
beam_gen = beam_search(name=decoder_group_name,
step=gru_decoder_with_attention,
input=group_inputs,
bos_id=0, # Beginnning token.
eos_id=1, # End of sentence token.
beam_size=beam_size,
max_length=max_length)
seqtext_printer_evaluator(input=beam_gen,
id_input=data_layer(name="sent_id", size=1),
dict_file=trg_dict_path,
result_file=gen_trans_file)
outputs(beam_gen)
Notice that this generation technique is only useful for decoder like generation process. If you are working on sequence tagging tasks, please refer to Semantic Role labeling Tutorial for more details.
The full configuration file is located at demo/seqToseq/seqToseq_net.py.
