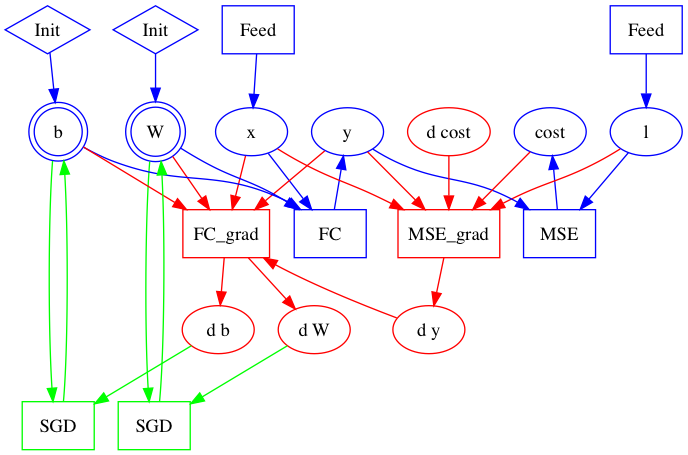
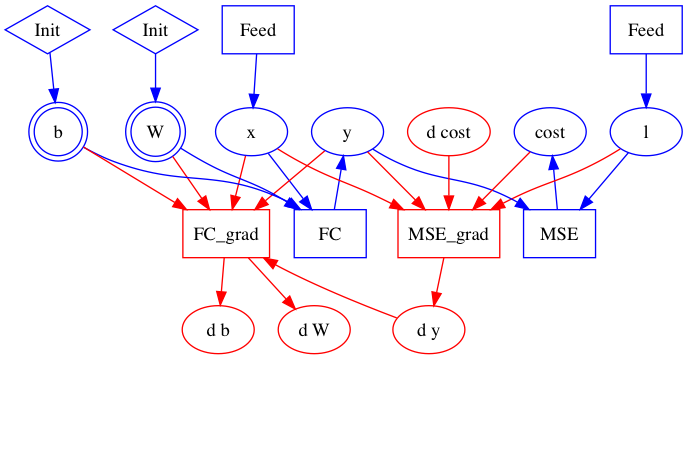
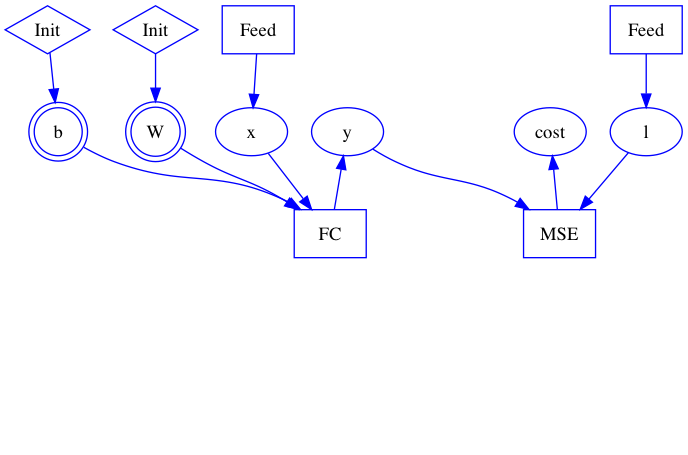
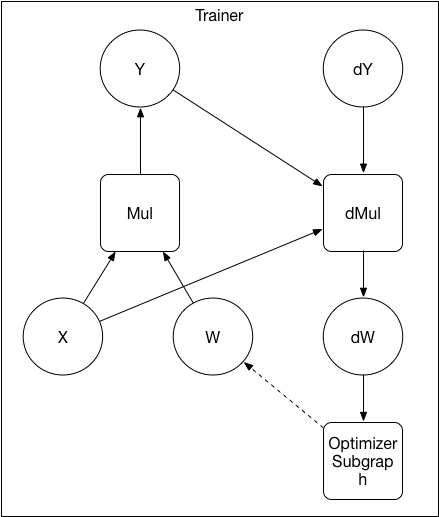
Merge branch 'develop' into build_ios
Showing
doc/design/graph.md
0 → 100644
58.3 KB
50.2 KB
31.5 KB
doc/design/ops/dist_train.md
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/design/ops/src/dist-graph.png
0 → 100644
222.2 KB
文件已添加
27.9 KB
doc/design/var_desc.md
0 → 100644
doc/howto/dev/use_eigen_cn.md
0 → 100644
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


paddle/function/GruFunctor.h
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOp.cpp
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOp.h
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOpGpu.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOpTest.cpp
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/concat_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/concat_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/cos_sim_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/cos_sim_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/identity_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/im2col.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/im2col.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/im2col.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/reshape_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/reshape_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/reshape_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/sum_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/sum_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/sum_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/top_k_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/top_k_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/top_k_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/platform/cudnn_helper.h
0 → 100644
paddle/platform/macros.h
0 → 100644
文件已移动