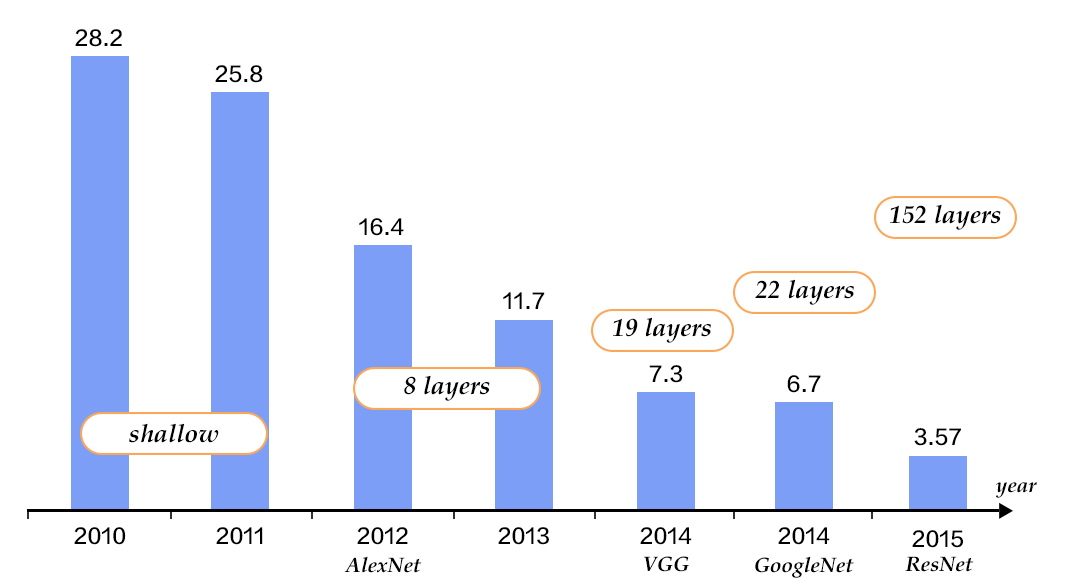
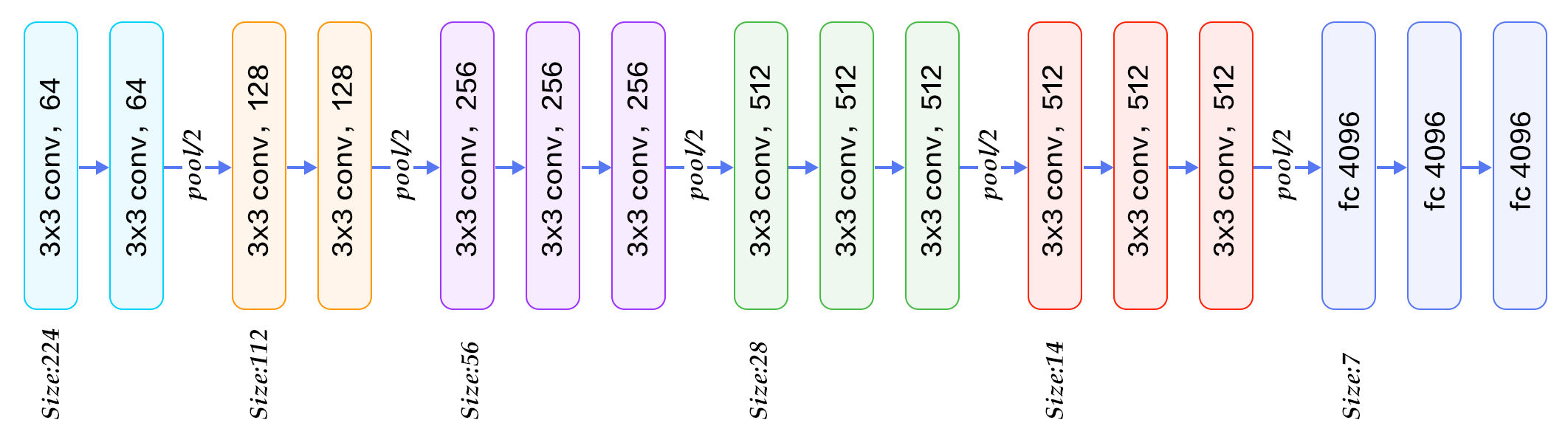
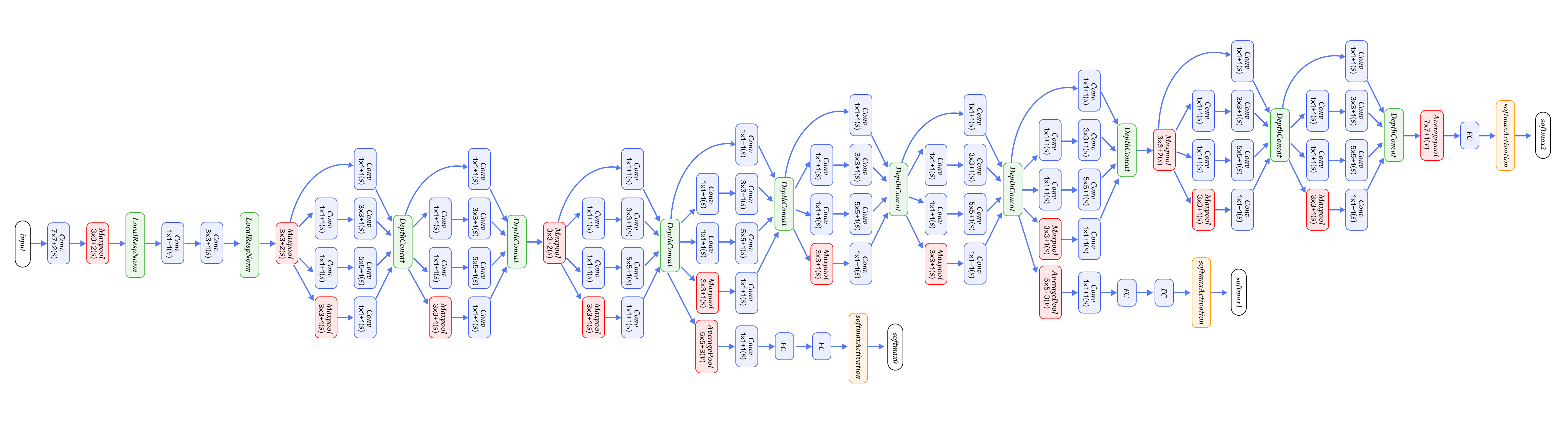
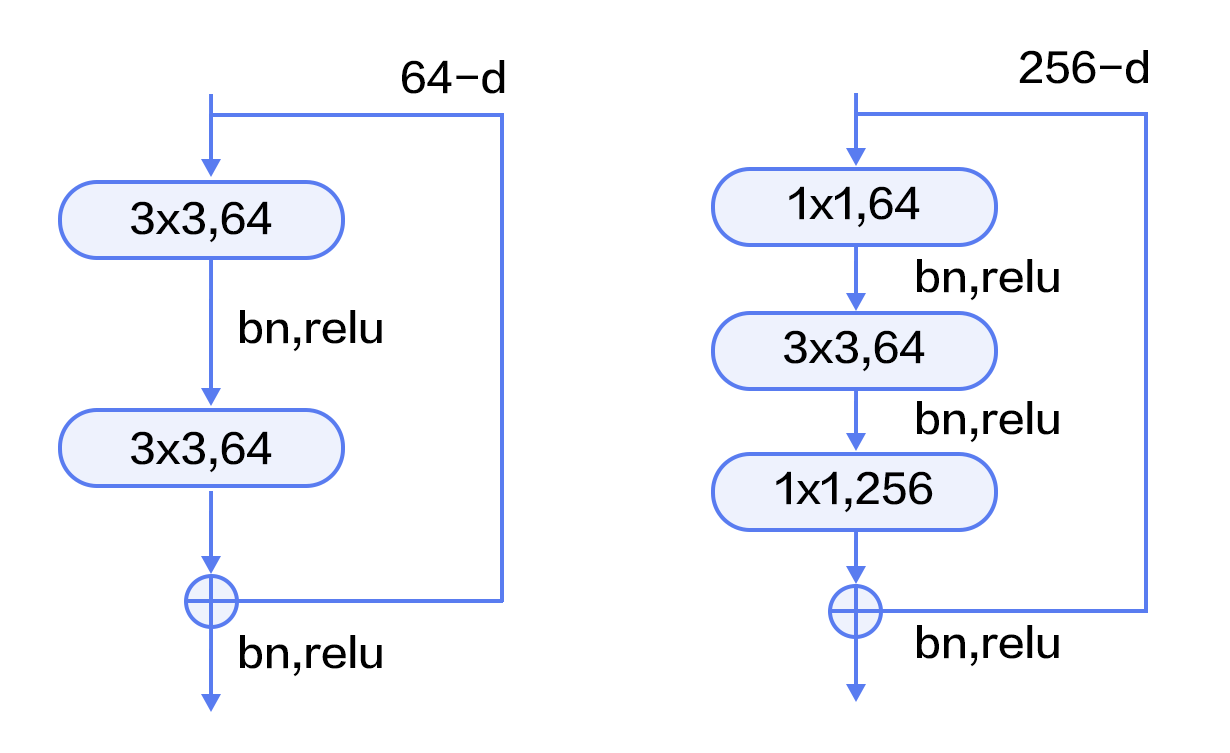
-图12. CIFAR10数据集上VGG模型的分类错误率
+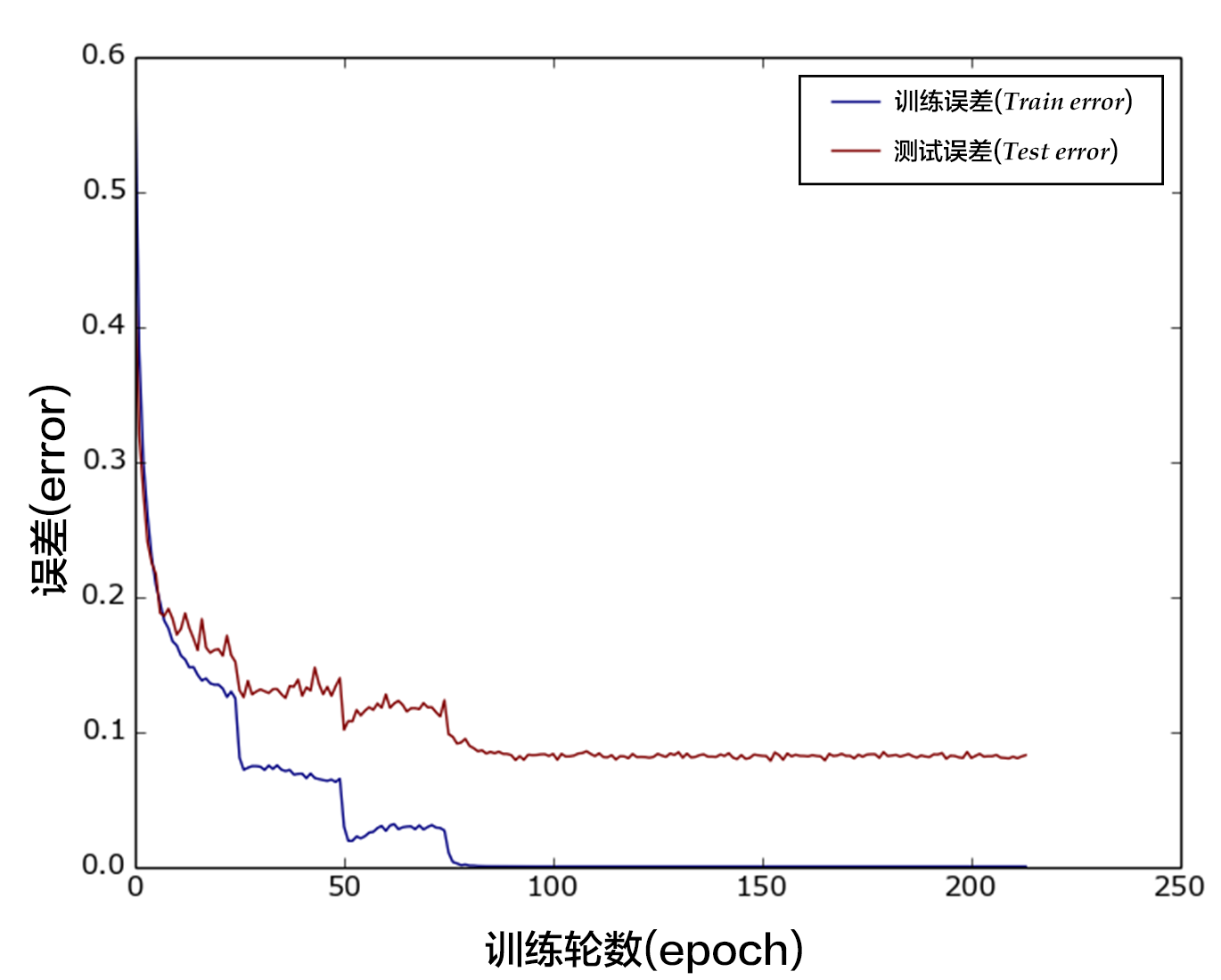
+图13. CIFAR10数据集上VGG模型的分类错误率
## 应用模型
@@ -471,19 +488,19 @@ import numpy as np
import os
def load_image(file):
-im = Image.open(file)
-im = im.resize((32, 32), Image.ANTIALIAS)
+ im = Image.open(file)
+ im = im.resize((32, 32), Image.ANTIALIAS)
-im = np.array(im).astype(np.float32)
-# The storage order of the loaded image is W(width),
-# H(height), C(channel). PaddlePaddle requires
-# the CHW order, so transpose them.
-im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # CHW
-im = im / 255.0
+ im = np.array(im).astype(np.float32)
+ # The storage order of the loaded image is W(width),
+ # H(height), C(channel). PaddlePaddle requires
+ # the CHW order, so transpose them.
+ im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # CHW
+ im = im / 255.0
-# Add one dimension to mimic the list format.
-im = numpy.expand_dims(im, axis=0)
-return im
+ # Add one dimension to mimic the list format.
+ im = numpy.expand_dims(im, axis=0)
+ return im
cur_dir = os.getcwd()
img = load_image(cur_dir + '/image/dog.png')
@@ -497,11 +514,11 @@ img = load_image(cur_dir + '/image/dog.png')
```python
inferencer = fluid.Inferencer(
-infer_func=inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
-
+ infer_func=inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
+label_list = ["airplane", "automobile", "bird", "cat", "deer", "dog", "frog", "horse", "ship", "truck"]
# inference
results = inferencer.infer({'pixel': img})
-print("infer results: ", results)
+print("infer results: %s" % label_list[np.argmax(results[0])])
```
## 总结
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ca8f858a902ea723d886d2b88c2c0a1005301c50..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog_cat.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog_cat.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 38b21f21604b1bb84fc3f6aa96bd5fce45d15a55..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/dog_cat.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/fea_conv0.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/fea_conv0.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 647c822e52cd55d50e5f207978f5e6ada86cf34c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/fea_conv0.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/flowers.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/flowers.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 04245cef60fe7126ae4c92ba8085273965078bee..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/flowers.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/googlenet.jpeg b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/googlenet.jpeg
deleted file mode 100644
index 249dbf96df61c3352ea5bd80470f6c4a1e03ff10..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/googlenet.jpeg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/ilsvrc.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/ilsvrc.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4660ac122e9d533023a21154d35eee29e3b08d27..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/ilsvrc.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/inception.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/inception.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 9591a0c1e8c0165c40ca560be35a7b9a91cd5027..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/inception.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/lenet.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/lenet.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 77f785e03bacd38c4c64a817874a58ff3298d2f3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/lenet.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/plot.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/plot.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 57e45cc0c27dd99b9918de2ff1228bc6b65f7424..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/plot.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0aeb4f254639fdbf18e916dc219ca61602596d85..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet_block.jpg b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet_block.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index c500eb01a90190ff66150871fe83ec275e2de8d7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/resnet_block.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/train_and_test.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/train_and_test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c6336a9a69b95dc978719ce68896e3e752e67fed..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/train_and_test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/vgg16.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/vgg16.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6270eefcfd7071bc1643ee06567e5b81aaf4c177..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/image_classification/image/vgg16.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/index.rst b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/index.rst
index d16f8b947253a535567ddc8d7b227dd153d9b154..0fcb008e0a7773e81e5124da09fe07366130b924 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/index.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/index.rst
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- image_classification/index.md
- word2vec/index.md
- recommender_system/index.md
- understand_sentiment/index.md
- label_semantic_roles/index.md
- machine_translation/index.md
+ image_classification/README.cn.md
+ word2vec/README.cn.md
+ recommender_system/README.cn.md
+ understand_sentiment/README.cn.md
+ label_semantic_roles/README.cn.md
+ machine_translation/README.cn.md
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/index.md b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/README.cn.md
similarity index 54%
rename from doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/index.md
rename to doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/README.cn.md
index 828ca738317992270487647e66b08b6d2f80e209..545f6002f23c1c698bd0d77fb39a8797ff7f5bde 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/index.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/README.cn.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# 语义角色标注
-本教程源代码目录在[book/label_semantic_roles](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/07.label_semantic_roles), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书)。
+本教程源代码目录在[book/label_semantic_roles](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/07.label_semantic_roles), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书),更多内容请参考本教程的[视频课堂](http://bit.baidu.com/course/detail/id/178.html)。
## 背景介绍
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
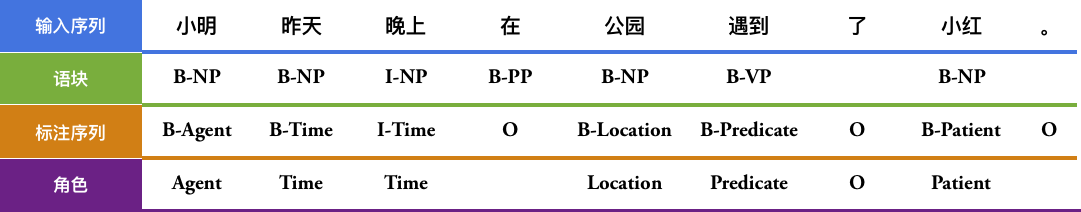
请看下面的例子,“遇到” 是谓词(Predicate,通常简写为“Pred”),“小明”是施事者(Agent),“小红”是受事者(Patient),“昨天” 是事件发生的时间(Time),“公园”是事情发生的地点(Location)。
-$$\mbox{[小明]}_{\mbox{Agent}}\mbox{[昨天]}_{\mbox{Time}}\mbox{[晚上]}_{\mbox{Time}}\mbox{在[公园]}_{\mbox{Location}}\mbox{[遇到]}_{\mbox{Predicate}}\mbox{了[小红]}_{\mbox{Patient}}\mbox{。}$$
+$$\mbox{[小明]}_{\mbox{Agent}}\mbox{[昨天]}_{\mbox{Time}}\mbox{[晚上]}_\mbox{Time}\mbox{在[公园]}_{\mbox{Location}}\mbox{[遇到]}_{\mbox{Predicate}}\mbox{了[小红]}_{\mbox{Patient}}\mbox{。}$$
语义角色标注(Semantic Role Labeling,SRL)以句子的谓词为中心,不对句子所包含的语义信息进行深入分析,只分析句子中各成分与谓词之间的关系,即句子的谓词(Predicate)- 论元(Argument)结构,并用语义角色来描述这些结构关系,是许多自然语言理解任务(如信息抽取,篇章分析,深度问答等)的一个重要中间步骤。在研究中一般都假定谓词是给定的,所要做的就是找出给定谓词的各个论元和它们的语义角色。
@@ -20,17 +20,17 @@ $$\mbox{[小明]}_{\mbox{Agent}}\mbox{[昨天]}_{\mbox{Time}}\mbox{[晚上]}_{\m
4. 论元识别:这个过程是从上一步剪除之后的候选中判断哪些是真正的论元,通常当做一个二分类问题来解决。
5. 对第4步的结果,通过多分类得到论元的语义角色标签。可以看到,句法分析是基础,并且后续步骤常常会构造的一些人工特征,这些特征往往也来自句法分析。
-
+
+

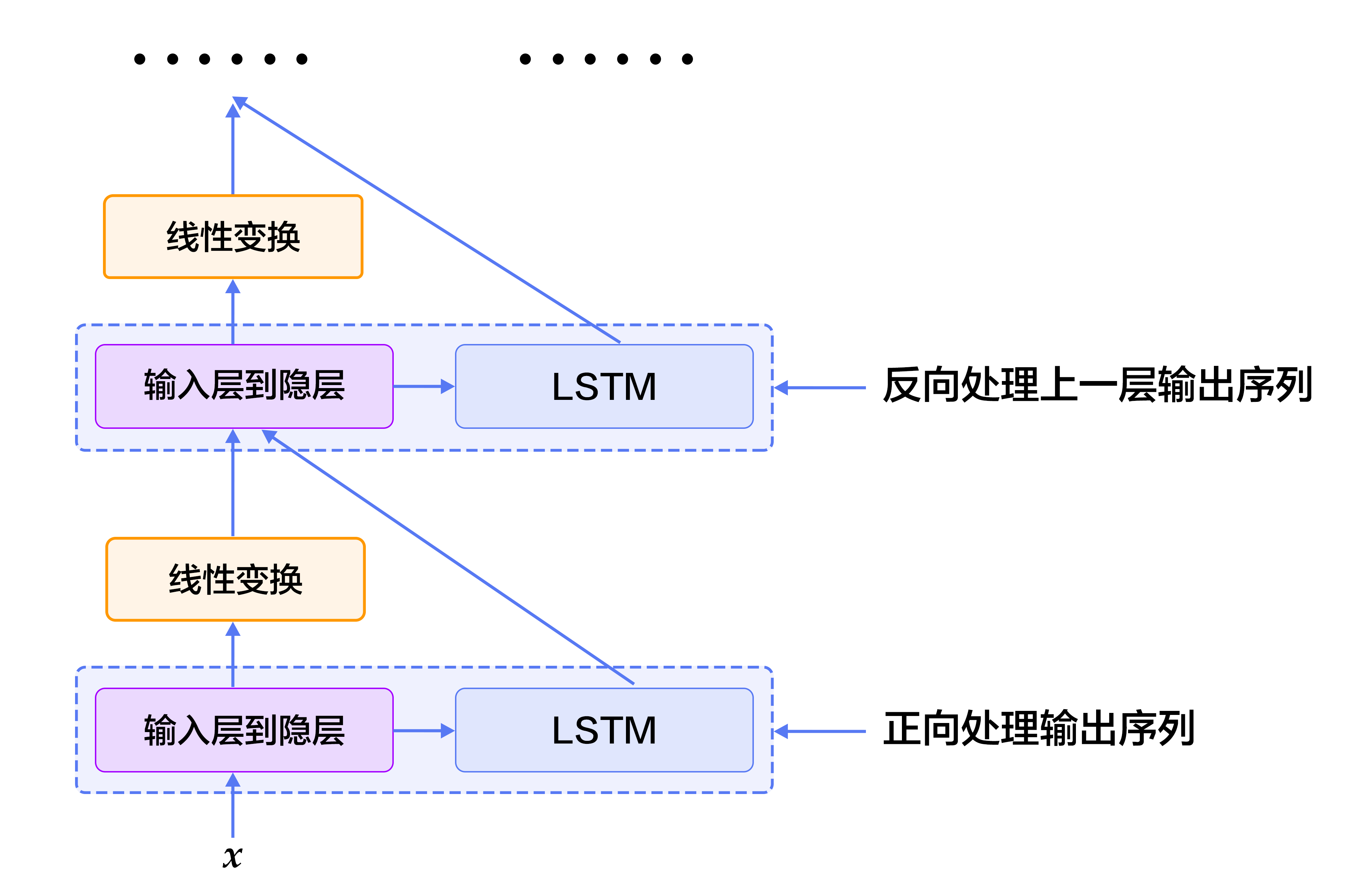
图6. SRL任务上的深层双向LSTM模型
@@ -137,8 +137,8 @@ $$\DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{arg\,max} L(\lambda, D) = - \text{log}\left(\pr
```text
conll05st-release/
└── test.wsj
-├── props # 标注结果
-└── words # 输入文本序列
+ ├── props # 标注结果
+ └── words # 输入文本序列
```
标注信息源自Penn TreeBank\[[7](#参考文献)\]和PropBank\[[8](#参考文献)\]的标注结果。PropBank标注结果的标签和我们在文章一开始示例中使用的标注结果标签不同,但原理是相同的,关于标注结果标签含义的说明,请参考论文\[[9](#参考文献)\]。
@@ -146,19 +146,11 @@ conll05st-release/
原始数据需要进行数据预处理才能被PaddlePaddle处理,预处理包括下面几个步骤:
1. 将文本序列和标记序列其合并到一条记录中;
-2. 一个句子如果含有`$n$`个谓词,这个句子会被处理`$n$`次,变成`$n$`条独立的训练样本,每个样本一个不同的谓词;
+2. 一个句子如果含有$n$个谓词,这个句子会被处理$n$次,变成$n$条独立的训练样本,每个样本一个不同的谓词;
3. 抽取谓词上下文和构造谓词上下文区域标记;
4. 构造以BIO法表示的标记;
5. 依据词典获取词对应的整数索引。
-
-```python
-# import paddle.v2.dataset.conll05 as conll05
-# conll05.corpus_reader函数完成上面第1步和第2步.
-# conll05.reader_creator函数完成上面第3步到第5步.
-# conll05.test函数可以获取处理之后的每条样本来供PaddlePaddle训练.
-```
-
预处理完成之后一条训练样本包含9个特征,分别是:句子序列、谓词、谓词上下文(占 5 列)、谓词上下区域标志、标注序列。下表是一条训练样本的示例。
| 句子序列 | 谓词 | 谓词上下文(窗口 = 5) | 谓词上下文区域标记 | 标注序列 |
@@ -187,6 +179,8 @@ conll05st-release/
获取词典,打印词典大小:
```python
+from __future__ import print_function
+
import math, os
import numpy as np
import paddle
@@ -201,9 +195,9 @@ word_dict_len = len(word_dict)
label_dict_len = len(label_dict)
pred_dict_len = len(verb_dict)
-print word_dict_len
-print label_dict_len
-print pred_dict_len
+print('word_dict_len: ', word_dict_len)
+print('label_dict_len: ', label_dict_len)
+print('pred_dict_len: ', pred_dict_len)
```
## 模型配置说明
@@ -232,96 +226,96 @@ embedding_name = 'emb'
```python
# 这里加载PaddlePaddle上版保存的二进制模型
def load_parameter(file_name, h, w):
-with open(file_name, 'rb') as f:
-f.read(16) # skip header.
-return np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.float32).reshape(h, w)
+ with open(file_name, 'rb') as f:
+ f.read(16) # skip header.
+ return np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.float32).reshape(h, w)
```
- 8个LSTM单元以“正向/反向”的顺序对所有输入序列进行学习。
-```python
+```python
def db_lstm(word, predicate, ctx_n2, ctx_n1, ctx_0, ctx_p1, ctx_p2, mark,
-**ignored):
-# 8 features
-predicate_embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=predicate,
-size=[pred_dict_len, word_dim],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=IS_SPARSE,
-param_attr='vemb')
-
-mark_embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=mark,
-size=[mark_dict_len, mark_dim],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=IS_SPARSE)
-
-word_input = [word, ctx_n2, ctx_n1, ctx_0, ctx_p1, ctx_p2]
-# Since word vector lookup table is pre-trained, we won't update it this time.
-# trainable being False prevents updating the lookup table during training.
-emb_layers = [
-fluid.layers.embedding(
-size=[word_dict_len, word_dim],
-input=x,
-param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(
-name=embedding_name, trainable=False)) for x in word_input
-]
-emb_layers.append(predicate_embedding)
-emb_layers.append(mark_embedding)
-
-# 8 LSTM units are trained through alternating left-to-right / right-to-left order
-# denoted by the variable `reverse`.
-hidden_0_layers = [
-fluid.layers.fc(input=emb, size=hidden_dim, act='tanh')
-for emb in emb_layers
-]
-
-hidden_0 = fluid.layers.sums(input=hidden_0_layers)
-
-lstm_0 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
-input=hidden_0,
-size=hidden_dim,
-candidate_activation='relu',
-gate_activation='sigmoid',
-cell_activation='sigmoid')
-
-# stack L-LSTM and R-LSTM with direct edges
-input_tmp = [hidden_0, lstm_0]
-
-# In PaddlePaddle, state features and transition features of a CRF are implemented
-# by a fully connected layer and a CRF layer seperately. The fully connected layer
-# with linear activation learns the state features, here we use fluid.layers.sums
-# (fluid.layers.fc can be uesed as well), and the CRF layer in PaddlePaddle:
-# fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf only
-# learns the transition features, which is a cost layer and is the last layer of the network.
-# fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf outputs the log probability of true tag sequence
-# as the cost by given the input sequence and it requires the true tag sequence
-# as target in the learning process.
-
-for i in range(1, depth):
-mix_hidden = fluid.layers.sums(input=[
-fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[0], size=hidden_dim, act='tanh'),
-fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[1], size=hidden_dim, act='tanh')
-])
-
-lstm = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
-input=mix_hidden,
-size=hidden_dim,
-candidate_activation='relu',
-gate_activation='sigmoid',
-cell_activation='sigmoid',
-is_reverse=((i % 2) == 1))
-
-input_tmp = [mix_hidden, lstm]
-
-# 取最后一个栈式LSTM的输出和这个LSTM单元的输入到隐层映射,
-# 经过一个全连接层映射到标记字典的维度,来学习 CRF 的状态特征
-feature_out = fluid.layers.sums(input=[
-fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[0], size=label_dict_len, act='tanh'),
-fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[1], size=label_dict_len, act='tanh')
-])
-
-return feature_out
+ **ignored):
+ # 8 features
+ predicate_embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=predicate,
+ size=[pred_dict_len, word_dim],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=IS_SPARSE,
+ param_attr='vemb')
+
+ mark_embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=mark,
+ size=[mark_dict_len, mark_dim],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=IS_SPARSE)
+
+ word_input = [word, ctx_n2, ctx_n1, ctx_0, ctx_p1, ctx_p2]
+ # Since word vector lookup table is pre-trained, we won't update it this time.
+ # trainable being False prevents updating the lookup table during training.
+ emb_layers = [
+ fluid.layers.embedding(
+ size=[word_dict_len, word_dim],
+ input=x,
+ param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(
+ name=embedding_name, trainable=False)) for x in word_input
+ ]
+ emb_layers.append(predicate_embedding)
+ emb_layers.append(mark_embedding)
+
+ # 8 LSTM units are trained through alternating left-to-right / right-to-left order
+ # denoted by the variable `reverse`.
+ hidden_0_layers = [
+ fluid.layers.fc(input=emb, size=hidden_dim, act='tanh')
+ for emb in emb_layers
+ ]
+
+ hidden_0 = fluid.layers.sums(input=hidden_0_layers)
+
+ lstm_0 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
+ input=hidden_0,
+ size=hidden_dim,
+ candidate_activation='relu',
+ gate_activation='sigmoid',
+ cell_activation='sigmoid')
+
+ # stack L-LSTM and R-LSTM with direct edges
+ input_tmp = [hidden_0, lstm_0]
+
+ # In PaddlePaddle, state features and transition features of a CRF are implemented
+ # by a fully connected layer and a CRF layer seperately. The fully connected layer
+ # with linear activation learns the state features, here we use fluid.layers.sums
+ # (fluid.layers.fc can be uesed as well), and the CRF layer in PaddlePaddle:
+ # fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf only
+ # learns the transition features, which is a cost layer and is the last layer of the network.
+ # fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf outputs the log probability of true tag sequence
+ # as the cost by given the input sequence and it requires the true tag sequence
+ # as target in the learning process.
+
+ for i in range(1, depth):
+ mix_hidden = fluid.layers.sums(input=[
+ fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[0], size=hidden_dim, act='tanh'),
+ fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[1], size=hidden_dim, act='tanh')
+ ])
+
+ lstm = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
+ input=mix_hidden,
+ size=hidden_dim,
+ candidate_activation='relu',
+ gate_activation='sigmoid',
+ cell_activation='sigmoid',
+ is_reverse=((i % 2) == 1))
+
+ input_tmp = [mix_hidden, lstm]
+
+ # 取最后一个栈式LSTM的输出和这个LSTM单元的输入到隐层映射,
+ # 经过一个全连接层映射到标记字典的维度,来学习 CRF 的状态特征
+ feature_out = fluid.layers.sums(input=[
+ fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[0], size=label_dict_len, act='tanh'),
+ fluid.layers.fc(input=input_tmp[1], size=label_dict_len, act='tanh')
+ ])
+
+ return feature_out
```
## 训练模型
@@ -338,116 +332,116 @@ return feature_out
```python
def train(use_cuda, save_dirname=None, is_local=True):
-# define network topology
-
-# 句子序列
-word = fluid.layers.data(
-name='word_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-
-# 谓词
-predicate = fluid.layers.data(
-name='verb_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-
-# 谓词上下文5个特征
-ctx_n2 = fluid.layers.data(
-name='ctx_n2_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-ctx_n1 = fluid.layers.data(
-name='ctx_n1_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-ctx_0 = fluid.layers.data(
-name='ctx_0_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-ctx_p1 = fluid.layers.data(
-name='ctx_p1_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-ctx_p2 = fluid.layers.data(
-name='ctx_p2_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-
-# 谓词上下区域标志
-mark = fluid.layers.data(
-name='mark_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-
-# define network topology
-feature_out = db_lstm(**locals())
-
-# 标注序列
-target = fluid.layers.data(
-name='target', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-
-# 学习 CRF 的转移特征
-crf_cost = fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf(
-input=feature_out,
-label=target,
-param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(
-name='crfw', learning_rate=mix_hidden_lr))
-
-avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(crf_cost)
-
-sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(
-learning_rate=fluid.layers.exponential_decay(
-learning_rate=0.01,
-decay_steps=100000,
-decay_rate=0.5,
-staircase=True))
-
-sgd_optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
-
-# The CRF decoding layer is used for evaluation and inference.
-# It shares weights with CRF layer. The sharing of parameters among multiple layers
-# is specified by using the same parameter name in these layers. If true tag sequence
-# is provided in training process, `fluid.layers.crf_decoding` calculates labelling error
-# for each input token and sums the error over the entire sequence.
-# Otherwise, `fluid.layers.crf_decoding` generates the labelling tags.
-crf_decode = fluid.layers.crf_decoding(
-input=feature_out, param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='crfw'))
-
-train_data = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.conll05.test(), buf_size=8192),
-batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
-
-place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
-
-
-feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(
-feed_list=[
-word, ctx_n2, ctx_n1, ctx_0, ctx_p1, ctx_p2, predicate, mark, target
-],
-place=place)
-exe = fluid.Executor(place)
-
-def train_loop(main_program):
-exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-embedding_param = fluid.global_scope().find_var(
-embedding_name).get_tensor()
-embedding_param.set(
-load_parameter(conll05.get_embedding(), word_dict_len, word_dim),
-place)
-
-start_time = time.time()
-batch_id = 0
-for pass_id in xrange(PASS_NUM):
-for data in train_data():
-cost = exe.run(main_program,
-feed=feeder.feed(data),
-fetch_list=[avg_cost])
-cost = cost[0]
-
-if batch_id % 10 == 0:
-print("avg_cost:" + str(cost))
-if batch_id != 0:
-print("second per batch: " + str((time.time(
-) - start_time) / batch_id))
-# Set the threshold low to speed up the CI test
-if float(cost) < 60.0:
-if save_dirname is not None:
-fluid.io.save_inference_model(save_dirname, [
-'word_data', 'verb_data', 'ctx_n2_data',
-'ctx_n1_data', 'ctx_0_data', 'ctx_p1_data',
-'ctx_p2_data', 'mark_data'
-], [feature_out], exe)
-return
-
-batch_id = batch_id + 1
-
-train_loop(fluid.default_main_program())
+ # define network topology
+
+ # 句子序列
+ word = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='word_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+
+ # 谓词
+ predicate = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='verb_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+
+ # 谓词上下文5个特征
+ ctx_n2 = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='ctx_n2_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ ctx_n1 = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='ctx_n1_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ ctx_0 = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='ctx_0_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ ctx_p1 = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='ctx_p1_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ ctx_p2 = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='ctx_p2_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+
+ # 谓词上下区域标志
+ mark = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='mark_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+
+ # define network topology
+ feature_out = db_lstm(**locals())
+
+ # 标注序列
+ target = fluid.layers.data(
+ name='target', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+
+ # 学习 CRF 的转移特征
+ crf_cost = fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf(
+ input=feature_out,
+ label=target,
+ param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(
+ name='crfw', learning_rate=mix_hidden_lr))
+
+ avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(crf_cost)
+
+ sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(
+ learning_rate=fluid.layers.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.01,
+ decay_steps=100000,
+ decay_rate=0.5,
+ staircase=True))
+
+ sgd_optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
+
+ # The CRF decoding layer is used for evaluation and inference.
+ # It shares weights with CRF layer. The sharing of parameters among multiple layers
+ # is specified by using the same parameter name in these layers. If true tag sequence
+ # is provided in training process, `fluid.layers.crf_decoding` calculates labelling error
+ # for each input token and sums the error over the entire sequence.
+ # Otherwise, `fluid.layers.crf_decoding` generates the labelling tags.
+ crf_decode = fluid.layers.crf_decoding(
+ input=feature_out, param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='crfw'))
+
+ train_data = paddle.batch(
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.conll05.test(), buf_size=8192),
+ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
+
+ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
+
+
+ feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(
+ feed_list=[
+ word, ctx_n2, ctx_n1, ctx_0, ctx_p1, ctx_p2, predicate, mark, target
+ ],
+ place=place)
+ exe = fluid.Executor(place)
+
+ def train_loop(main_program):
+ exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+ embedding_param = fluid.global_scope().find_var(
+ embedding_name).get_tensor()
+ embedding_param.set(
+ load_parameter(conll05.get_embedding(), word_dict_len, word_dim),
+ place)
+
+ start_time = time.time()
+ batch_id = 0
+ for pass_id in xrange(PASS_NUM):
+ for data in train_data():
+ cost = exe.run(main_program,
+ feed=feeder.feed(data),
+ fetch_list=[avg_cost])
+ cost = cost[0]
+
+ if batch_id % 10 == 0:
+ print("avg_cost: " + str(cost))
+ if batch_id != 0:
+ print("second per batch: " + str((time.time(
+ ) - start_time) / batch_id))
+ # Set the threshold low to speed up the CI test
+ if float(cost) < 60.0:
+ if save_dirname is not None:
+ fluid.io.save_inference_model(save_dirname, [
+ 'word_data', 'verb_data', 'ctx_n2_data',
+ 'ctx_n1_data', 'ctx_0_data', 'ctx_p1_data',
+ 'ctx_p2_data', 'mark_data'
+ ], [feature_out], exe)
+ return
+
+ batch_id = batch_id + 1
+
+ train_loop(fluid.default_main_program())
```
@@ -457,92 +451,92 @@ train_loop(fluid.default_main_program())
```python
def infer(use_cuda, save_dirname=None):
-if save_dirname is None:
-return
-
-place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
-exe = fluid.Executor(place)
-
-inference_scope = fluid.core.Scope()
-with fluid.scope_guard(inference_scope):
-# Use fluid.io.load_inference_model to obtain the inference program desc,
-# the feed_target_names (the names of variables that will be fed
-# data using feed operators), and the fetch_targets (variables that
-# we want to obtain data from using fetch operators).
-[inference_program, feed_target_names,
-fetch_targets] = fluid.io.load_inference_model(save_dirname, exe)
-
-# Setup inputs by creating LoDTensors to represent sequences of words.
-# Here each word is the basic element of these LoDTensors and the shape of
-# each word (base_shape) should be [1] since it is simply an index to
-# look up for the corresponding word vector.
-# Suppose the length_based level of detail (lod) info is set to [[3, 4, 2]],
-# which has only one lod level. Then the created LoDTensors will have only
-# one higher level structure (sequence of words, or sentence) than the basic
-# element (word). Hence the LoDTensor will hold data for three sentences of
-# length 3, 4 and 2, respectively.
-# Note that lod info should be a list of lists.
-lod = [[3, 4, 2]]
-base_shape = [1]
-# The range of random integers is [low, high]
-word = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-pred = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=pred_dict_len - 1)
-ctx_n2 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-ctx_n1 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-ctx_0 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-ctx_p1 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-ctx_p2 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
-mark = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
-lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=mark_dict_len - 1)
-
-# Construct feed as a dictionary of {feed_target_name: feed_target_data}
-# and results will contain a list of data corresponding to fetch_targets.
-assert feed_target_names[0] == 'word_data'
-assert feed_target_names[1] == 'verb_data'
-assert feed_target_names[2] == 'ctx_n2_data'
-assert feed_target_names[3] == 'ctx_n1_data'
-assert feed_target_names[4] == 'ctx_0_data'
-assert feed_target_names[5] == 'ctx_p1_data'
-assert feed_target_names[6] == 'ctx_p2_data'
-assert feed_target_names[7] == 'mark_data'
-
-results = exe.run(inference_program,
-feed={
-feed_target_names[0]: word,
-feed_target_names[1]: pred,
-feed_target_names[2]: ctx_n2,
-feed_target_names[3]: ctx_n1,
-feed_target_names[4]: ctx_0,
-feed_target_names[5]: ctx_p1,
-feed_target_names[6]: ctx_p2,
-feed_target_names[7]: mark
-},
-fetch_list=fetch_targets,
-return_numpy=False)
-print(results[0].lod())
-np_data = np.array(results[0])
-print("Inference Shape: ", np_data.shape)
+ if save_dirname is None:
+ return
+
+ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
+ exe = fluid.Executor(place)
+
+ inference_scope = fluid.core.Scope()
+ with fluid.scope_guard(inference_scope):
+ # Use fluid.io.load_inference_model to obtain the inference program desc,
+ # the feed_target_names (the names of variables that will be fed
+ # data using feed operators), and the fetch_targets (variables that
+ # we want to obtain data from using fetch operators).
+ [inference_program, feed_target_names,
+ fetch_targets] = fluid.io.load_inference_model(save_dirname, exe)
+
+ # Setup inputs by creating LoDTensors to represent sequences of words.
+ # Here each word is the basic element of these LoDTensors and the shape of
+ # each word (base_shape) should be [1] since it is simply an index to
+ # look up for the corresponding word vector.
+ # Suppose the length_based level of detail (lod) info is set to [[3, 4, 2]],
+ # which has only one lod level. Then the created LoDTensors will have only
+ # one higher level structure (sequence of words, or sentence) than the basic
+ # element (word). Hence the LoDTensor will hold data for three sentences of
+ # length 3, 4 and 2, respectively.
+ # Note that lod info should be a list of lists.
+ lod = [[3, 4, 2]]
+ base_shape = [1]
+ # The range of random integers is [low, high]
+ word = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ pred = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=pred_dict_len - 1)
+ ctx_n2 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ ctx_n1 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ ctx_0 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ ctx_p1 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ ctx_p2 = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=word_dict_len - 1)
+ mark = fluid.create_random_int_lodtensor(
+ lod, base_shape, place, low=0, high=mark_dict_len - 1)
+
+ # Construct feed as a dictionary of {feed_target_name: feed_target_data}
+ # and results will contain a list of data corresponding to fetch_targets.
+ assert feed_target_names[0] == 'word_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[1] == 'verb_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[2] == 'ctx_n2_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[3] == 'ctx_n1_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[4] == 'ctx_0_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[5] == 'ctx_p1_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[6] == 'ctx_p2_data'
+ assert feed_target_names[7] == 'mark_data'
+
+ results = exe.run(inference_program,
+ feed={
+ feed_target_names[0]: word,
+ feed_target_names[1]: pred,
+ feed_target_names[2]: ctx_n2,
+ feed_target_names[3]: ctx_n1,
+ feed_target_names[4]: ctx_0,
+ feed_target_names[5]: ctx_p1,
+ feed_target_names[6]: ctx_p2,
+ feed_target_names[7]: mark
+ },
+ fetch_list=fetch_targets,
+ return_numpy=False)
+ print(results[0].lod())
+ np_data = np.array(results[0])
+ print("Inference Shape: ", np_data.shape)
```
整个程序的入口如下:
```python
def main(use_cuda, is_local=True):
-if use_cuda and not fluid.core.is_compiled_with_cuda():
-return
+ if use_cuda and not fluid.core.is_compiled_with_cuda():
+ return
-# Directory for saving the trained model
-save_dirname = "label_semantic_roles.inference.model"
+ # Directory for saving the trained model
+ save_dirname = "label_semantic_roles.inference.model"
-train(use_cuda, save_dirname, is_local)
-infer(use_cuda, save_dirname)
+ train(use_cuda, save_dirname, is_local)
+ infer(use_cuda, save_dirname)
main(use_cuda=False)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e63f5ebd6d00f2e4ecf97b9ab2027e74683013f2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index f0a195c24d9ee493f96bb93c28a99e70566be7a4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bidirectional_stacked_lstm_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example.png
deleted file mode 100755
index e5f7151c9fcc50a7cf7af485cbbc7e4fccab0c20..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 93b44dd4874402ef29ad7bd7d94147609b92e309..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/bio_example_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 592f7ee23bdc88a9a35059612e5ab880bbc9d34b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index c3646312e48db977402fb353dc0c9b4d02269bf4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/db_lstm_network_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 9265b671735940ed6549e2980064d2ce08baae64..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 23f4f45b603e3d60702af2b2464d10fc8deed061..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/dependency_parsing_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/linear_chain_crf.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/linear_chain_crf.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0778fda74b2ad22ce4b631791a7b028cdef780a5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/linear_chain_crf.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d2914c726b5f4c46e66dfa85d4e88649fede6b3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 0b944ef91e8b5ba4b14d2a35bd8879f261cf8f61..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/label_semantic_roles/image/stacked_lstm_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/index.md b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/README.cn.md
similarity index 70%
rename from doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/index.md
rename to doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/README.cn.md
index fc161aaae9c37b0e1a596204e7138025a98adb1d..3f6efec8841a608638389331152a720cbb3d9735 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/index.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/README.cn.md
@@ -11,10 +11,10 @@
为解决以上问题,统计机器翻译(Statistical Machine Translation, SMT)技术应运而生。在统计机器翻译技术中,转化规则是由机器自动从大规模的语料中学习得到的,而非我们人主动提供规则。因此,它克服了基于规则的翻译系统所面临的知识获取瓶颈的问题,但仍然存在许多挑战:1)人为设计许多特征(feature),但永远无法覆盖所有的语言现象;2)难以利用全局的特征;3)依赖于许多预处理环节,如词语对齐、分词或符号化(tokenization)、规则抽取、句法分析等,而每个环节的错误会逐步累积,对翻译的影响也越来越大。
近年来,深度学习技术的发展为解决上述挑战提供了新的思路。将深度学习应用于机器翻译任务的方法大致分为两类:1)仍以统计机器翻译系统为框架,只是利用神经网络来改进其中的关键模块,如语言模型、调序模型等(见图1的左半部分);2)不再以统计机器翻译系统为框架,而是直接用神经网络将源语言映射到目标语言,即端到端的神经网络机器翻译(End-to-End Neural Machine Translation, End-to-End NMT)(见图1的右半部分),简称为NMT模型。
-
-
+
+

图1. 基于神经网络的机器翻译系统
-
+
本教程主要介绍NMT模型,以及如何用PaddlePaddle来训练一个NMT模型。
@@ -30,7 +30,9 @@
1 -6.23177 These are the light of hope and relief .
2 -7.7914 These are the light of hope and the relief of hope .
```
+
- 左起第一列是生成句子的序号;左起第二列是该条句子的得分(从大到小),分值越高越好;左起第三列是生成的英语句子。
+
- 另外有两个特殊标志:``表示句子的结尾,``表示未登录词(unknown word),即未在训练字典中出现的词。
## 模型概览
@@ -43,18 +45,20 @@
具体来说,该双向循环神经网络分别在时间维以顺序和逆序——即前向(forward)和后向(backward)——依次处理输入序列,并将每个时间步RNN的输出拼接成为最终的输出层。这样每个时间步的输出节点,都包含了输入序列中当前时刻完整的过去和未来的上下文信息。下图展示的是一个按时间步展开的双向循环神经网络。该网络包含一个前向和一个后向RNN,其中有六个权重矩阵:输入到前向隐层和后向隐层的权重矩阵(`$W_1, W_3$`),隐层到隐层自己的权重矩阵(`$W_2,W_5$`),前向隐层和后向隐层到输出层的权重矩阵(`$W_4, W_6$`)。注意,该网络的前向隐层和后向隐层之间没有连接。
-
-
-图3. 按时间步展开的双向循环神经网络
-
+
+
+
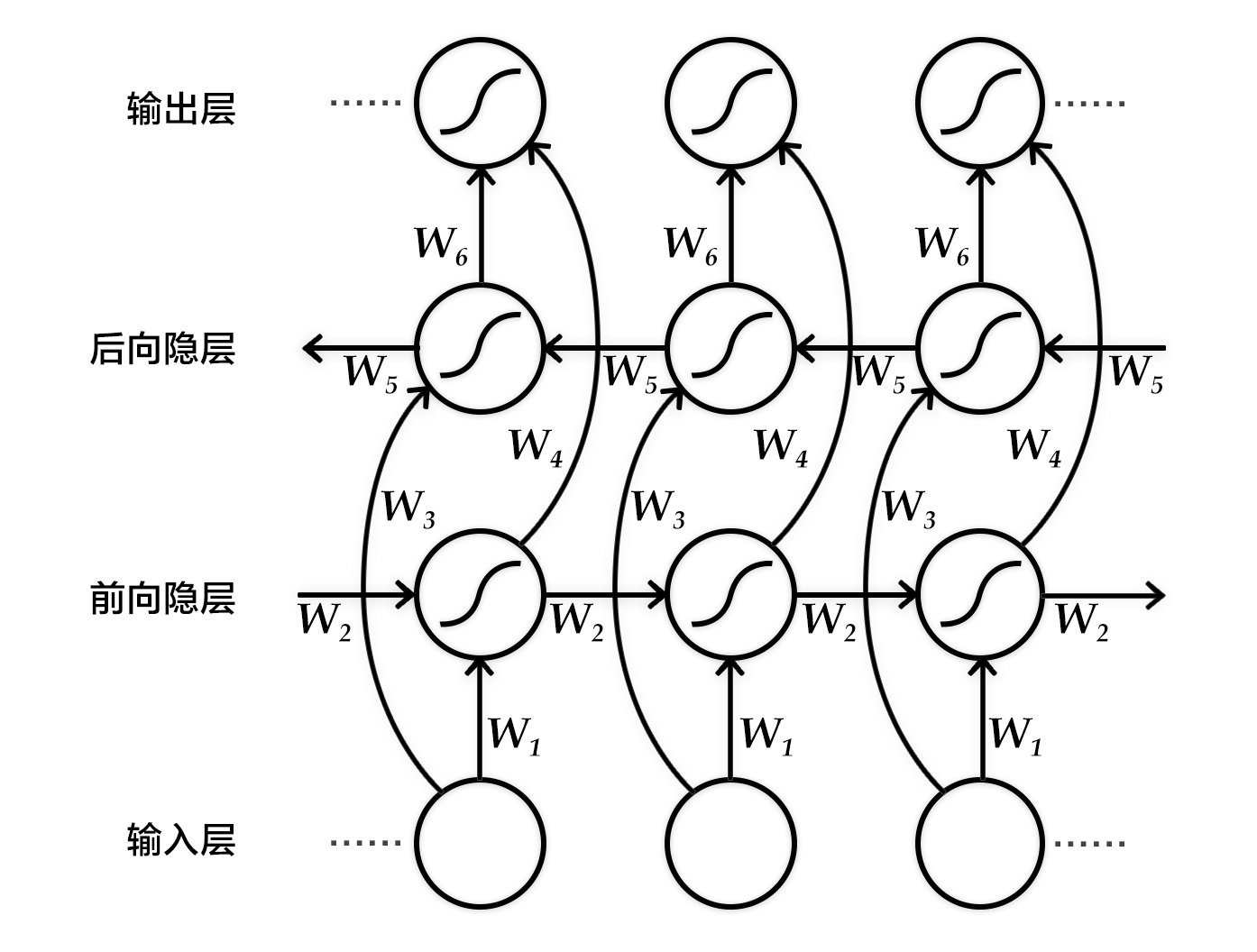
+图2. 按时间步展开的双向循环神经网络
+
-图4. 编码器-解码器框架
-
+
+

+图3. 编码器-解码器框架
+
-图5. 使用双向GRU的编码器
-
+
+
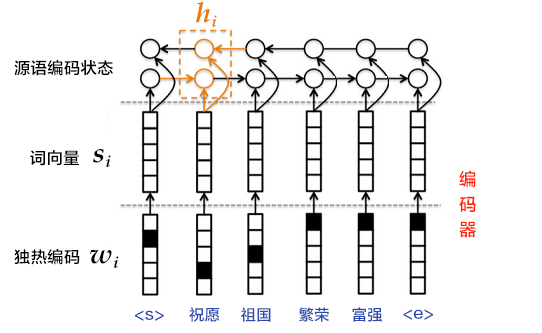
+图4. 使用双向GRU的编码器
+
`,表示解码开始;`$z_i$`是`$i$`时刻解码RNN的隐层状态,`$z_0$`是一个全零的向量。
2. 将`$z_{i+1}$`通过`softmax`归一化,得到目标语言序列的第`$i+1$`个单词的概率分布`$p_{i+1}$`。概率分布公式如下:
-
$$p\left ( u_{i+1}|u_{<i+1},\mathbf{x} \right )=softmax(W_sz_{i+1}+b_z)$$
-
其中`$W_sz_{i+1}+b_z$`是对每个可能的输出单词进行打分,再用softmax归一化就可以得到第`$i+1$`个词的概率`$p_{i+1}$`。
3. 根据`$p_{i+1}$`和`$u_{i+1}$`计算代价。
+
4. 重复步骤1~3,直到目标语言序列中的所有词处理完毕。
机器翻译任务的生成过程,通俗来讲就是根据预先训练的模型来翻译源语言句子。生成过程中的解码阶段和上述训练过程的有所差异,具体介绍请见[柱搜索算法](#柱搜索算法)。
@@ -101,10 +100,12 @@ $$p\left ( u_{i+1}|u_{<i+1},\mathbf{x} \right )=softmax(W_sz_{i+1}+b_z)$$
柱搜索算法使用广度优先策略建立搜索树,在树的每一层,按照启发代价(heuristic cost)(本教程中,为生成词的log概率之和)对节点进行排序,然后仅留下预先确定的个数(文献中通常称为beam width、beam size、柱宽度等)的节点。只有这些节点会在下一层继续扩展,其他节点就被剪掉了,也就是说保留了质量较高的节点,剪枝了质量较差的节点。因此,搜索所占用的空间和时间大幅减少,但缺点是无法保证一定获得最优解。
使用柱搜索算法的解码阶段,目标是最大化生成序列的概率。思路是:
-
1. 每一个时刻,根据源语言句子的编码信息`$c$`、生成的第`$i$`个目标语言序列单词`$u_i$`和`$i$`时刻RNN的隐层状态`$z_i$`,计算出下一个隐层状态`$z_{i+1}$`。
+
2. 将`$z_{i+1}$`通过`softmax`归一化,得到目标语言序列的第`$i+1$`个单词的概率分布`$p_{i+1}$`。
+
3. 根据`$p_{i+1}$`采样出单词`$u_{i+1}$`。
+
4. 重复步骤1~3,直到获得句子结束标记``或超过句子的最大生成长度为止。
注意:`$z_{i+1}$`和`$p_{i+1}$`的计算公式同[解码器](#解码器)中的一样。且由于生成时的每一步都是通过贪心法实现的,因此并不能保证得到全局最优解。
@@ -116,9 +117,13 @@ $$p\left ( u_{i+1}|u_{<i+1},\mathbf{x} \right )=softmax(W_sz_{i+1}+b_z)$$
### 数据预处理
我们的预处理流程包括两步:
+
- 将每个源语言到目标语言的平行语料库文件合并为一个文件:
+
- 合并每个`XXX.src`和`XXX.trg`文件为`XXX`。
+
- `XXX`中的第`$i$`行内容为`XXX.src`中的第`$i$`行和`XXX.trg`中的第`$i$`行连接,用'\t'分隔。
+
- 创建训练数据的“源字典”和“目标字典”。每个字典都有**DICTSIZE**个单词,包括:语料中词频最高的(DICTSIZE - 3)个单词,和3个特殊符号``(序列的开始)、``(序列的结束)和``(未登录词)。
### 示例数据
@@ -132,6 +137,7 @@ $$p\left ( u_{i+1}|u_{<i+1},\mathbf{x} \right )=softmax(W_sz_{i+1}+b_z)$$
下面我们开始根据输入数据的形式配置模型。首先引入所需的库函数以及定义全局变量。
```python
+from __future__ import print_function
import contextlib
import numpy as np
@@ -157,139 +163,152 @@ decoder_size = hidden_dim
然后如下实现编码器框架:
-```python
-def encoder(is_sparse):
-src_word_id = pd.data(
-name="src_word_id", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-src_embedding = pd.embedding(
-input=src_word_id,
-size=[dict_size, word_dim],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='vemb'))
-
-fc1 = pd.fc(input=src_embedding, size=hidden_dim * 4, act='tanh')
-lstm_hidden0, lstm_0 = pd.dynamic_lstm(input=fc1, size=hidden_dim * 4)
-encoder_out = pd.sequence_last_step(input=lstm_hidden0)
-return encoder_out
-```
+ ```python
+ def encoder(is_sparse):
+ src_word_id = pd.data(
+ name="src_word_id", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ src_embedding = pd.embedding(
+ input=src_word_id,
+ size=[dict_size, word_dim],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='vemb'))
+
+ fc1 = pd.fc(input=src_embedding, size=hidden_dim * 4, act='tanh')
+ lstm_hidden0, lstm_0 = pd.dynamic_lstm(input=fc1, size=hidden_dim * 4)
+ encoder_out = pd.sequence_last_step(input=lstm_hidden0)
+ return encoder_out
+ ```
再实现训练模式下的解码器:
```python
-def train_decoder(context, is_sparse):
-trg_language_word = pd.data(
-name="target_language_word", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-trg_embedding = pd.embedding(
-input=trg_language_word,
-size=[dict_size, word_dim],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='vemb'))
-
-rnn = pd.DynamicRNN()
-with rnn.block():
-current_word = rnn.step_input(trg_embedding)
-pre_state = rnn.memory(init=context)
-current_state = pd.fc(input=[current_word, pre_state],
-size=decoder_size,
-act='tanh')
-
-current_score = pd.fc(input=current_state,
-size=target_dict_dim,
-act='softmax')
-rnn.update_memory(pre_state, current_state)
-rnn.output(current_score)
-
-return rnn()
+ def train_decoder(context, is_sparse):
+ trg_language_word = pd.data(
+ name="target_language_word", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ trg_embedding = pd.embedding(
+ input=trg_language_word,
+ size=[dict_size, word_dim],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='vemb'))
+
+ rnn = pd.DynamicRNN()
+ with rnn.block():
+ current_word = rnn.step_input(trg_embedding)
+ pre_state = rnn.memory(init=context)
+ current_state = pd.fc(input=[current_word, pre_state],
+ size=decoder_size,
+ act='tanh')
+
+ current_score = pd.fc(input=current_state,
+ size=target_dict_dim,
+ act='softmax')
+ rnn.update_memory(pre_state, current_state)
+ rnn.output(current_score)
+
+ return rnn()
```
实现推测模式下的解码器:
```python
def decode(context, is_sparse):
-init_state = context
-array_len = pd.fill_constant(shape=[1], dtype='int64', value=max_length)
-counter = pd.zeros(shape=[1], dtype='int64', force_cpu=True)
-
-# fill the first element with init_state
-state_array = pd.create_array('float32')
-pd.array_write(init_state, array=state_array, i=counter)
-
-# ids, scores as memory
-ids_array = pd.create_array('int64')
-scores_array = pd.create_array('float32')
-
-init_ids = pd.data(name="init_ids", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=2)
-init_scores = pd.data(
-name="init_scores", shape=[1], dtype="float32", lod_level=2)
-
-pd.array_write(init_ids, array=ids_array, i=counter)
-pd.array_write(init_scores, array=scores_array, i=counter)
-
-cond = pd.less_than(x=counter, y=array_len)
-
-while_op = pd.While(cond=cond)
-with while_op.block():
-pre_ids = pd.array_read(array=ids_array, i=counter)
-pre_state = pd.array_read(array=state_array, i=counter)
-pre_score = pd.array_read(array=scores_array, i=counter)
-
-# expand the lod of pre_state to be the same with pre_score
-pre_state_expanded = pd.sequence_expand(pre_state, pre_score)
-
-pre_ids_emb = pd.embedding(
-input=pre_ids,
-size=[dict_size, word_dim],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse)
-
-# use rnn unit to update rnn
-current_state = pd.fc(input=[pre_state_expanded, pre_ids_emb],
-size=decoder_size,
-act='tanh')
-current_state_with_lod = pd.lod_reset(x=current_state, y=pre_score)
-# use score to do beam search
-current_score = pd.fc(input=current_state_with_lod,
-size=target_dict_dim,
-act='softmax')
-topk_scores, topk_indices = pd.topk(current_score, k=topk_size)
-selected_ids, selected_scores = pd.beam_search(
-pre_ids, topk_indices, topk_scores, beam_size, end_id=10, level=0)
-
-pd.increment(x=counter, value=1, in_place=True)
-
-# update the memories
-pd.array_write(current_state, array=state_array, i=counter)
-pd.array_write(selected_ids, array=ids_array, i=counter)
-pd.array_write(selected_scores, array=scores_array, i=counter)
-
-pd.less_than(x=counter, y=array_len, cond=cond)
-
-translation_ids, translation_scores = pd.beam_search_decode(
-ids=ids_array, scores=scores_array)
-
-return translation_ids, translation_scores
+ init_state = context
+ array_len = pd.fill_constant(shape=[1], dtype='int64', value=max_length)
+ counter = pd.zeros(shape=[1], dtype='int64', force_cpu=True)
+
+ # fill the first element with init_state
+ state_array = pd.create_array('float32')
+ pd.array_write(init_state, array=state_array, i=counter)
+
+ # ids, scores as memory
+ ids_array = pd.create_array('int64')
+ scores_array = pd.create_array('float32')
+
+ init_ids = pd.data(name="init_ids", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=2)
+ init_scores = pd.data(
+ name="init_scores", shape=[1], dtype="float32", lod_level=2)
+
+ pd.array_write(init_ids, array=ids_array, i=counter)
+ pd.array_write(init_scores, array=scores_array, i=counter)
+
+ cond = pd.less_than(x=counter, y=array_len)
+
+ while_op = pd.While(cond=cond)
+ with while_op.block():
+ pre_ids = pd.array_read(array=ids_array, i=counter)
+ pre_state = pd.array_read(array=state_array, i=counter)
+ pre_score = pd.array_read(array=scores_array, i=counter)
+
+ # expand the lod of pre_state to be the same with pre_score
+ pre_state_expanded = pd.sequence_expand(pre_state, pre_score)
+
+ pre_ids_emb = pd.embedding(
+ input=pre_ids,
+ size=[dict_size, word_dim],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse)
+
+ # use rnn unit to update rnn
+ current_state = pd.fc(input=[pre_state_expanded, pre_ids_emb],
+ size=decoder_size,
+ act='tanh')
+ current_state_with_lod = pd.lod_reset(x=current_state, y=pre_score)
+ # use score to do beam search
+ current_score = pd.fc(input=current_state_with_lod,
+ size=target_dict_dim,
+ act='softmax')
+ topk_scores, topk_indices = pd.topk(current_score, k=beam_size)
+ # calculate accumulated scores after topk to reduce computation cost
+ accu_scores = pd.elementwise_add(
+ x=pd.log(topk_scores), y=pd.reshape(pre_score, shape=[-1]), axis=0)
+ selected_ids, selected_scores = pd.beam_search(
+ pre_ids,
+ pre_score,
+ topk_indices,
+ accu_scores,
+ beam_size,
+ end_id=10,
+ level=0)
+
+ pd.increment(x=counter, value=1, in_place=True)
+
+ # update the memories
+ pd.array_write(current_state, array=state_array, i=counter)
+ pd.array_write(selected_ids, array=ids_array, i=counter)
+ pd.array_write(selected_scores, array=scores_array, i=counter)
+
+ # update the break condition: up to the max length or all candidates of
+ # source sentences have ended.
+ length_cond = pd.less_than(x=counter, y=array_len)
+ finish_cond = pd.logical_not(pd.is_empty(x=selected_ids))
+ pd.logical_and(x=length_cond, y=finish_cond, out=cond)
+
+ translation_ids, translation_scores = pd.beam_search_decode(
+ ids=ids_array, scores=scores_array, beam_size=beam_size, end_id=10)
+
+ return translation_ids, translation_scores
```
进而,我们定义一个`train_program`来使用`inference_program`计算出的结果,在标记数据的帮助下来计算误差。我们还定义了一个`optimizer_func`来定义优化器。
```python
def train_program(is_sparse):
-context = encoder(is_sparse)
-rnn_out = train_decoder(context, is_sparse)
-label = pd.data(
-name="target_language_next_word", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
-cost = pd.cross_entropy(input=rnn_out, label=label)
-avg_cost = pd.mean(cost)
-return avg_cost
+ context = encoder(is_sparse)
+ rnn_out = train_decoder(context, is_sparse)
+ label = pd.data(
+ name="target_language_next_word", shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
+ cost = pd.cross_entropy(input=rnn_out, label=label)
+ avg_cost = pd.mean(cost)
+ return avg_cost
def optimizer_func():
-return fluid.optimizer.Adagrad(
-learning_rate=1e-4,
-regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2DecayRegularizer(
-regularization_coeff=0.1))
+ return fluid.optimizer.Adagrad(
+ learning_rate=1e-4,
+ regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2DecayRegularizer(
+ regularization_coeff=0.1))
```
## 训练模型
@@ -307,9 +326,9 @@ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
```python
train_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.wmt14.train(dict_size), buf_size=1000),
-batch_size=batch_size)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.wmt14.train(dict_size), buf_size=1000),
+ batch_size=batch_size)
```
### 构造训练器(trainer)
@@ -318,9 +337,9 @@ batch_size=batch_size)
```python
is_sparse = False
trainer = fluid.Trainer(
-train_func=partial(train_program, is_sparse),
-place=place,
-optimizer_func=optimizer_func)
+ train_func=partial(train_program, is_sparse),
+ place=place,
+ optimizer_func=optimizer_func)
```
### 提供数据
@@ -329,8 +348,8 @@ optimizer_func=optimizer_func)
```python
feed_order = [
-'src_word_id', 'target_language_word', 'target_language_next_word'
-]
+ 'src_word_id', 'target_language_word', 'target_language_next_word'
+ ]
```
### 事件处理器
@@ -338,12 +357,12 @@ feed_order = [
```python
def event_handler(event):
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
-if event.step % 10 == 0:
-print('pass_id=' + str(event.epoch) + ' batch=' + str(event.step))
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
+ if event.step % 10 == 0:
+ print('pass_id=' + str(event.epoch) + ' batch=' + str(event.step))
-if event.step == 20:
-trainer.stop()
+ if event.step == 20:
+ trainer.stop()
```
### 开始训练
@@ -353,10 +372,10 @@ trainer.stop()
EPOCH_NUM = 1
trainer.train(
-reader=train_reader,
-num_epochs=EPOCH_NUM,
-event_handler=event_handler,
-feed_order=feed_order)
+ reader=train_reader,
+ num_epochs=EPOCH_NUM,
+ event_handler=event_handler,
+ feed_order=feed_order)
```
## 应用模型
@@ -377,7 +396,7 @@ translation_ids, translation_scores = decode(context, is_sparse)
```python
init_ids_data = np.array([1 for _ in range(batch_size)], dtype='int64')
init_scores_data = np.array(
-[1. for _ in range(batch_size)], dtype='float32')
+ [1. for _ in range(batch_size)], dtype='float32')
init_ids_data = init_ids_data.reshape((batch_size, 1))
init_scores_data = init_scores_data.reshape((batch_size, 1))
init_lod = [1] * batch_size
@@ -387,14 +406,14 @@ init_ids = fluid.create_lod_tensor(init_ids_data, init_lod, place)
init_scores = fluid.create_lod_tensor(init_scores_data, init_lod, place)
test_data = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.wmt14.test(dict_size), buf_size=1000),
-batch_size=batch_size)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.wmt14.test(dict_size), buf_size=1000),
+ batch_size=batch_size)
feed_order = ['src_word_id']
feed_list = [
-framework.default_main_program().global_block().var(var_name)
-for var_name in feed_order
+ framework.default_main_program().global_block().var(var_name)
+ for var_name in feed_order
]
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list, place)
@@ -409,27 +428,30 @@ exe = Executor(place)
exe.run(framework.default_startup_program())
for data in test_data():
-feed_data = map(lambda x: [x[0]], data)
-feed_dict = feeder.feed(feed_data)
-feed_dict['init_ids'] = init_ids
-feed_dict['init_scores'] = init_scores
-
-results = exe.run(
-framework.default_main_program(),
-feed=feed_dict,
-fetch_list=[translation_ids, translation_scores],
-return_numpy=False)
-
-result_ids = np.array(results[0])
-result_scores = np.array(results[1])
-
-print("Original sentence:")
-print(" ".join([src_dict[w] for w in feed_data[0][0]]))
-print("Translated sentence:")
-print(" ".join([trg_dict[w] for w in result_ids]))
-print("Corresponding score: ", result_scores)
-
-break
+ feed_data = map(lambda x: [x[0]], data)
+ feed_dict = feeder.feed(feed_data)
+ feed_dict['init_ids'] = init_ids
+ feed_dict['init_scores'] = init_scores
+
+ results = exe.run(
+ framework.default_main_program(),
+ feed=feed_dict,
+ fetch_list=[translation_ids, translation_scores],
+ return_numpy=False)
+
+ result_ids = np.array(results[0])
+ result_scores = np.array(results[1])
+
+ print("Original sentence:")
+ print(" ".join([src_dict[w] for w in feed_data[0][0][1:-1]]))
+ print("Translated score and sentence:")
+ for i in xrange(beam_size):
+ start_pos = result_ids_lod[1][i] + 1
+ end_pos = result_ids_lod[1][i+1]
+ print("%d\t%.4f\t%s\n" % (i+1, result_scores[end_pos-1],
+ " ".join([trg_dict[w] for w in result_ids[start_pos:end_pos]])))
+
+ break
```
## 总结
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d8efd50a49d0305586f550344472ab94c93bed3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 4b35c88fc8ea2c503473c0c15711744e784d6af6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/bi_rnn_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b355e7786d25487a3f564af758c2c52c43b4690..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 3728f782ee09d9308d02b42305027b2735467ead..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/decoder_attention_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 28d7a15a3bd65262bde22a3f41b5aa78b46b368a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index ea8585565da1ecaf241654c278c6f9b15e283286..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_attention_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 60aee0017de73f462e35708b1055aff8992c03e1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 6b73798fe632e0873b35c117b86f347c8cf3116a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/encoder_decoder_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0cde685b84106650a4df18ce335a23e6338d3d11..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index a6af429f23f0f7e82650139bbd8dcbef27a34abe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/gru_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bf56d73ebf297fadf522389c7b6836dd379aa097..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 557310e044b2b6687e5ea6895417ed946ac7bc11..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/machine_translation/image/nmt_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/index.md b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/README.cn.md
similarity index 67%
rename from doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/index.md
rename to doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/README.cn.md
index 09a07f3dc30abc57ab3731af054dd83491acc9a6..3174a8c6d70166619306c784db9126f20a85f4c8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/index.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/recommender_system/README.cn.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# 个性化推荐
-本教程源代码目录在[book/recommender_system](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/05.recommender_system), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书)。
+本教程源代码目录在[book/recommender_system](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/05.recommender_system), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书),更多内容请参考本教程的[视频课堂](http://bit.baidu.com/course/detail/id/176.html)。
## 背景介绍
@@ -36,8 +36,8 @@ Prediction Score is 4.25
YouTube是世界上最大的视频上传、分享和发现网站,YouTube推荐系统为超过10亿用户从不断增长的视频库中推荐个性化的内容。整个系统由两个神经网络组成:候选生成网络和排序网络。候选生成网络从百万量级的视频库中生成上百个候选,排序网络对候选进行打分排序,输出排名最高的数十个结果。系统结构如图1所示:
-
+
图1. YouTube 推荐系统结构
@@ -45,20 +45,20 @@ YouTube是世界上最大的视频上传、分享和发现网站,YouTube推荐
候选生成网络将推荐问题建模为一个类别数极大的多类分类问题:对于一个Youtube用户,使用其观看历史(视频ID)、搜索词记录(search tokens)、人口学信息(如地理位置、用户登录设备)、二值特征(如性别,是否登录)和连续特征(如用户年龄)等,对视频库中所有视频进行多分类,得到每一类别的分类结果(即每一个视频的推荐概率),最终输出概率较高的几百个视频。
-首先,将观看历史及搜索词记录这类历史信息,映射为向量后取平均值得到定长表示;同时,输入人口学特征以优化新用户的推荐效果,并将二值特征和连续特征归一化处理到[0, 1]范围。接下来,将所有特征表示拼接为一个向量,并输入给非线形多层感知器(MLP,详见[识别数字](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/02.recognize_digits/README.cn.md)教程)处理。最后,训练时将MLP的输出给softmax做分类,预测时计算用户的综合特征(MLP的输出)与所有视频的相似度,取得分最高的`$k$`个作为候选生成网络的筛选结果。图2显示了候选生成网络结构。
+首先,将观看历史及搜索词记录这类历史信息,映射为向量后取平均值得到定长表示;同时,输入人口学特征以优化新用户的推荐效果,并将二值特征和连续特征归一化处理到[0, 1]范围。接下来,将所有特征表示拼接为一个向量,并输入给非线形多层感知器(MLP,详见[识别数字](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/02.recognize_digits/README.cn.md)教程)处理。最后,训练时将MLP的输出给softmax做分类,预测时计算用户的综合特征(MLP的输出)与所有视频的相似度,取得分最高的$k$个作为候选生成网络的筛选结果。图2显示了候选生成网络结构。
-
+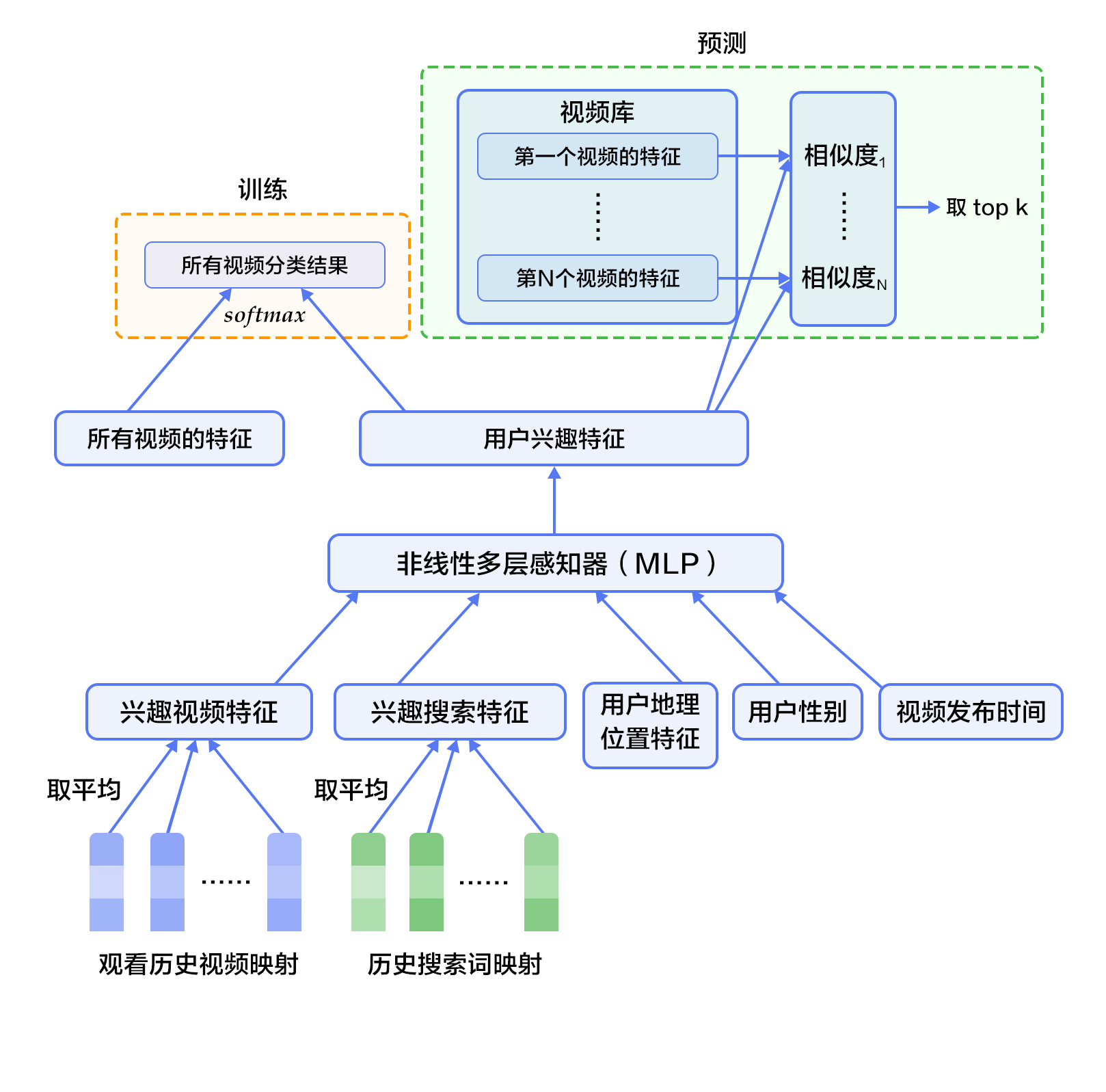
图2. 候选生成网络结构
-对于一个用户`$U$`,预测此刻用户要观看的视频`$\omega$`为视频`$i$`的概率公式为:
+对于一个用户$U$,预测此刻用户要观看的视频$\omega$为视频$i$的概率公式为:
$$P(\omega=i|u)=\frac{e^{v_{i}u}}{\sum_{j \in V}e^{v_{j}u}}$$
-其中`$u$`为用户`$U$`的特征表示,`$V$`为视频库集合,`$v_i$`为视频库中第`$i$`个视频的特征表示。`$u$`和`$v_i$`为长度相等的向量,两者点积可以通过全连接层实现。
+其中$u$为用户$U$的特征表示,$V$为视频库集合,$v_i$为视频库中第$i$个视频的特征表示。$u$和$v_i$为长度相等的向量,两者点积可以通过全连接层实现。
-考虑到softmax分类的类别数非常多,为了保证一定的计算效率:1)训练阶段,使用负样本类别采样将实际计算的类别数缩小至数千;2)推荐(预测)阶段,忽略softmax的归一化计算(不影响结果),将类别打分问题简化为点积(dot product)空间中的最近邻(nearest neighbor)搜索问题,取与`$u$`最近的`$k$`个视频作为生成的候选。
+考虑到softmax分类的类别数非常多,为了保证一定的计算效率:1)训练阶段,使用负样本类别采样将实际计算的类别数缩小至数千;2)推荐(预测)阶段,忽略softmax的归一化计算(不影响结果),将类别打分问题简化为点积(dot product)空间中的最近邻(nearest neighbor)搜索问题,取与$u$最近的$k$个视频作为生成的候选。
#### 排序网络(Ranking Network)
排序网络的结构类似于候选生成网络,但是它的目标是对候选进行更细致的打分排序。和传统广告排序中的特征抽取方法类似,这里也构造了大量的用于视频排序的相关特征(如视频 ID、上次观看时间等)。这些特征的处理方式和候选生成网络类似,不同之处是排序网络的顶部是一个加权逻辑回归(weighted logistic regression),它对所有候选视频进行打分,从高到底排序后将分数较高的一些视频返回给用户。
@@ -72,20 +72,20 @@ $$P(\omega=i|u)=\frac{e^{v_{i}u}}{\sum_{j \in V}e^{v_{j}u}}$$
卷积神经网络主要由卷积(convolution)和池化(pooling)操作构成,其应用及组合方式灵活多变,种类繁多。本小结我们以如图3所示的网络进行讲解:
-
+
图3. 卷积神经网络文本分类模型
-假设待处理句子的长度为`$n$`,其中第`$i$`个词的词向量(word embedding)为`$x_i\in\mathbb{R}^k$`,`$k$`为维度大小。
+假设待处理句子的长度为$n$,其中第$i$个词的词向量(word embedding)为$x_i\in\mathbb{R}^k$,$k$为维度大小。
-首先,进行词向量的拼接操作:将每`$h$`个词拼接起来形成一个大小为`$h$`的词窗口,记为`$x_{i:i+h-1}$`,它表示词序列`$x_{i},x_{i+1},\ldots,x_{i+h-1}$`的拼接,其中,`$i$`表示词窗口中第一个词在整个句子中的位置,取值范围从`$1$`到`$n-h+1$`,`$x_{i:i+h-1}\in\mathbb{R}^{hk}$`。
+首先,进行词向量的拼接操作:将每$h$个词拼接起来形成一个大小为$h$的词窗口,记为$x_{i:i+h-1}$,它表示词序列$x_{i},x_{i+1},\ldots,x_{i+h-1}$的拼接,其中,$i$表示词窗口中第一个词在整个句子中的位置,取值范围从$1$到$n-h+1$,$x_{i:i+h-1}\in\mathbb{R}^{hk}$。
-其次,进行卷积操作:把卷积核(kernel)`$w\in\mathbb{R}^{hk}$`应用于包含`$h$`个词的窗口`$x_{i:i+h-1}$`,得到特征`$c_i=f(w\cdot x_{i:i+h-1}+b)$`,其中`$b\in\mathbb{R}$`为偏置项(bias),`$f$`为非线性激活函数,如`$sigmoid$`。将卷积核应用于句子中所有的词窗口`${x_{1:h},x_{2:h+1},\ldots,x_{n-h+1:n}}$`,产生一个特征图(feature map):
+其次,进行卷积操作:把卷积核(kernel)$w\in\mathbb{R}^{hk}$应用于包含$h$个词的窗口$x_{i:i+h-1}$,得到特征$c_i=f(w\cdot x_{i:i+h-1}+b)$,其中$b\in\mathbb{R}$为偏置项(bias),$f$为非线性激活函数,如$sigmoid$。将卷积核应用于句子中所有的词窗口${x_{1:h},x_{2:h+1},\ldots,x_{n-h+1:n}}$,产生一个特征图(feature map):
$$c=[c_1,c_2,\ldots,c_{n-h+1}], c \in \mathbb{R}^{n-h+1}$$
-接下来,对特征图采用时间维度上的最大池化(max pooling over time)操作得到此卷积核对应的整句话的特征`$\hat c$`,它是特征图中所有元素的最大值:
+接下来,对特征图采用时间维度上的最大池化(max pooling over time)操作得到此卷积核对应的整句话的特征$\hat c$,它是特征图中所有元素的最大值:
$$\hat c=max(c)$$
@@ -95,9 +95,9 @@ $$\hat c=max(c)$$
1. 首先,使用用户特征和电影特征作为神经网络的输入,其中:
-- 用户特征融合了四个属性信息,分别是用户ID、性别、职业和年龄。
+ - 用户特征融合了四个属性信息,分别是用户ID、性别、职业和年龄。
-- 电影特征融合了三个属性信息,分别是电影ID、电影类型ID和电影名称。
+ - 电影特征融合了三个属性信息,分别是电影ID、电影类型ID和电影名称。
2. 对用户特征,将用户ID映射为维度大小为256的向量表示,输入全连接层,并对其他三个属性也做类似的处理。然后将四个属性的特征表示分别全连接并相加。
@@ -105,8 +105,9 @@ $$\hat c=max(c)$$
4. 得到用户和电影的向量表示后,计算二者的余弦相似度作为推荐系统的打分。最后,用该相似度打分和用户真实打分的差异的平方作为该回归模型的损失函数。
-
+
+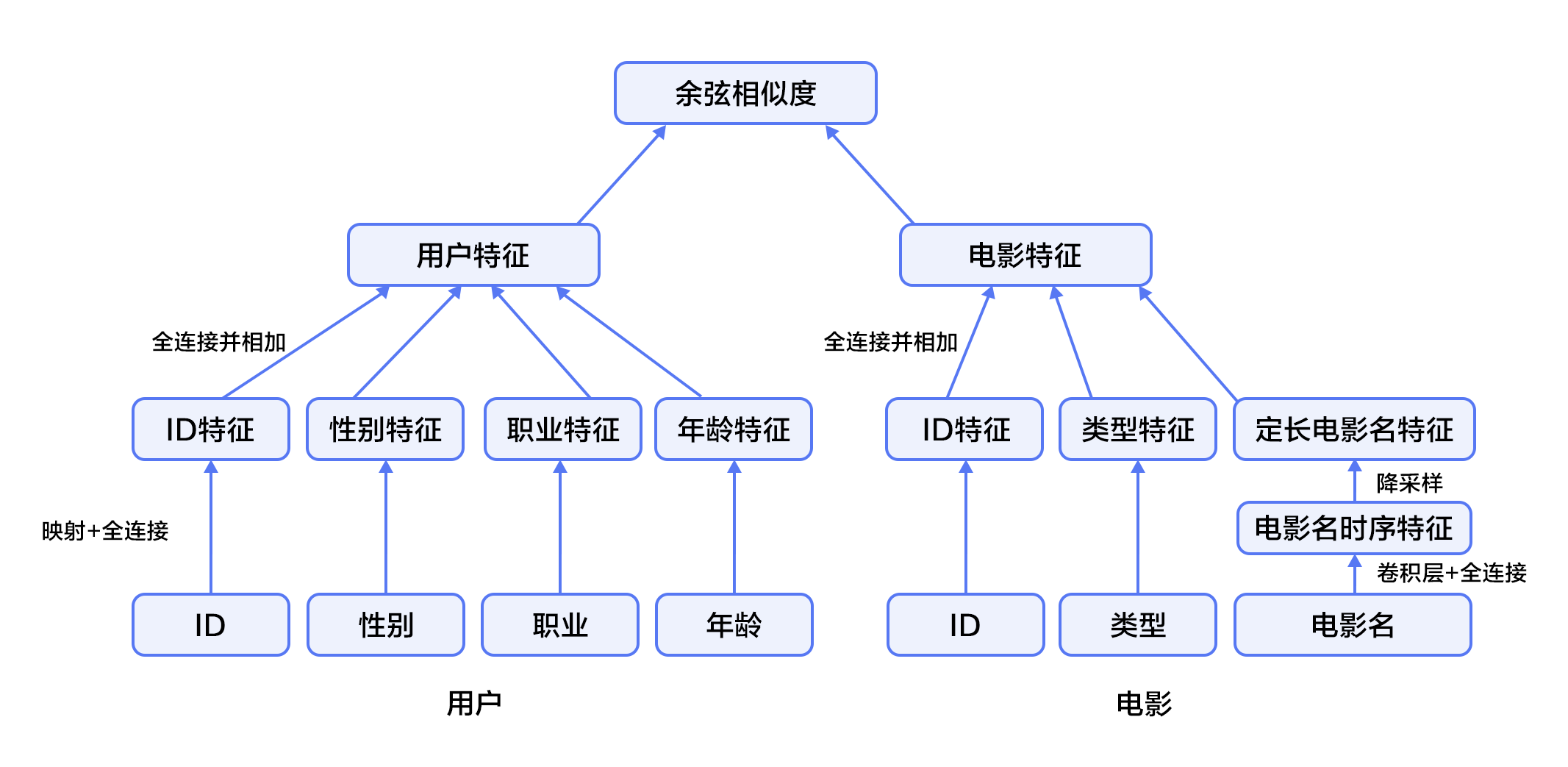
图4. 融合推荐模型
@@ -141,7 +142,7 @@ movie_info = paddle.dataset.movielens.movie_info()
print movie_info.values()[0]
```
-
+
这表示,电影的id是1,标题是《Toy Story》,该电影被分为到三个类别中。这三个类别是动画,儿童,喜剧。
@@ -152,13 +153,14 @@ user_info = paddle.dataset.movielens.user_info()
print user_info.values()[0]
```
-
+
这表示,该用户ID是1,女性,年龄比18岁还年轻。职业ID是10。
其中,年龄使用下列分布
+
* 1: "Under 18"
* 18: "18-24"
* 25: "25-34"
@@ -168,6 +170,7 @@ print user_info.values()[0]
* 56: "56+"
职业是从下面几种选项里面选则得出:
+
* 0: "other" or not specified
* 1: "academic/educator"
* 2: "artist"
@@ -203,7 +206,7 @@ mov_id = train_sample[len(user_info[uid].value())]
print "User %s rates Movie %s with Score %s"%(user_info[uid], movie_info[mov_id], train_sample[-1])
```
-User rates Movie with Score [5.0]
+ User rates Movie with Score [5.0]
即用户1对电影1193的评价为5分。
@@ -214,6 +217,7 @@ User rates Movie 表格 1 电影评论情感分析
-在自然语言处理中,情感分析属于典型的**文本分类**问题,即把需要进行情感分析的文本划分为其所属类别。文本分类涉及文本表示和分类方法两个问题。在深度学习的方法出现之前,主流的文本表示方法为词袋模型BOW(bag of words),话题模型等等;分类方法有SVM(support vector machine), LR(logistic regression)等等。
+在自然语言处理中,情感分析属于典型的**文本分类**问题,即把需要进行情感分析的文本划分为其所属类别。文本分类涉及文本表示和分类方法两个问题。在深度学习的方法出现之前,主流的文本表示方法为词袋模型BOW(bag of words),话题模型等等;分类方法有SVM(support vector machine), LR(logistic regression)等等。
-对于一段文本,BOW表示会忽略其词顺序、语法和句法,将这段文本仅仅看做是一个词集合,因此BOW方法并不能充分表示文本的语义信息。例如,句子“这部电影糟糕透了”和“一个乏味,空洞,没有内涵的作品”在情感分析中具有很高的语义相似度,但是它们的BOW表示的相似度为0。又如,句子“一个空洞,没有内涵的作品”和“一个不空洞而且有内涵的作品”的BOW相似度很高,但实际上它们的意思很不一样。
+对于一段文本,BOW表示会忽略其词顺序、语法和句法,将这段文本仅仅看做是一个词集合,因此BOW方法并不能充分表示文本的语义信息。例如,句子“这部电影糟糕透了”和“一个乏味,空洞,没有内涵的作品”在情感分析中具有很高的语义相似度,但是它们的BOW表示的相似度为0。又如,句子“一个空洞,没有内涵的作品”和“一个不空洞而且有内涵的作品”的BOW相似度很高,但实际上它们的意思很不一样。
本章我们所要介绍的深度学习模型克服了BOW表示的上述缺陷,它在考虑词顺序的基础上把文本映射到低维度的语义空间,并且以端对端(end to end)的方式进行文本表示及分类,其性能相对于传统方法有显著的提升\[[1](#参考文献)\]。
@@ -36,54 +36,54 @@
循环神经网络是一种能对序列数据进行精确建模的有力工具。实际上,循环神经网络的理论计算能力是图灵完备的\[[4](#参考文献)\]。自然语言是一种典型的序列数据(词序列),近年来,循环神经网络及其变体(如long short term memory\[[5](#参考文献)\]等)在自然语言处理的多个领域,如语言模型、句法解析、语义角色标注(或一般的序列标注)、语义表示、图文生成、对话、机器翻译等任务上均表现优异甚至成为目前效果最好的方法。
-
+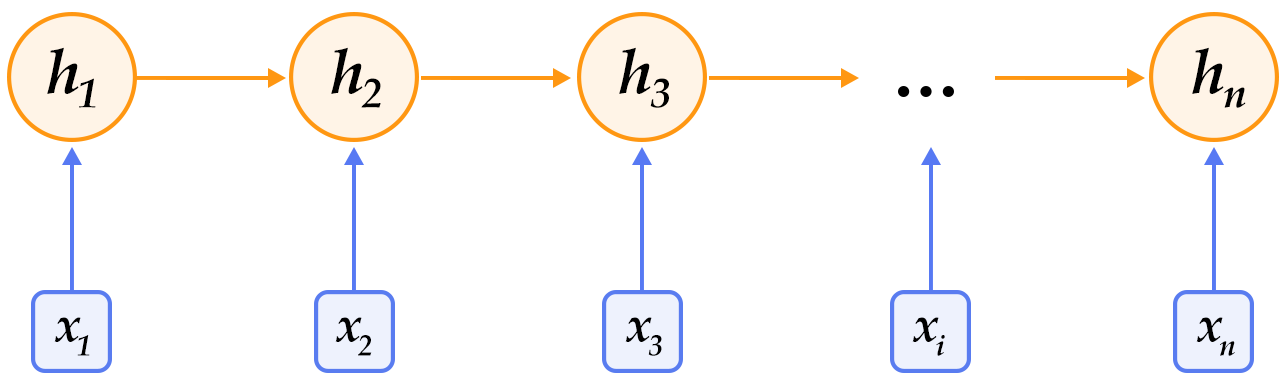
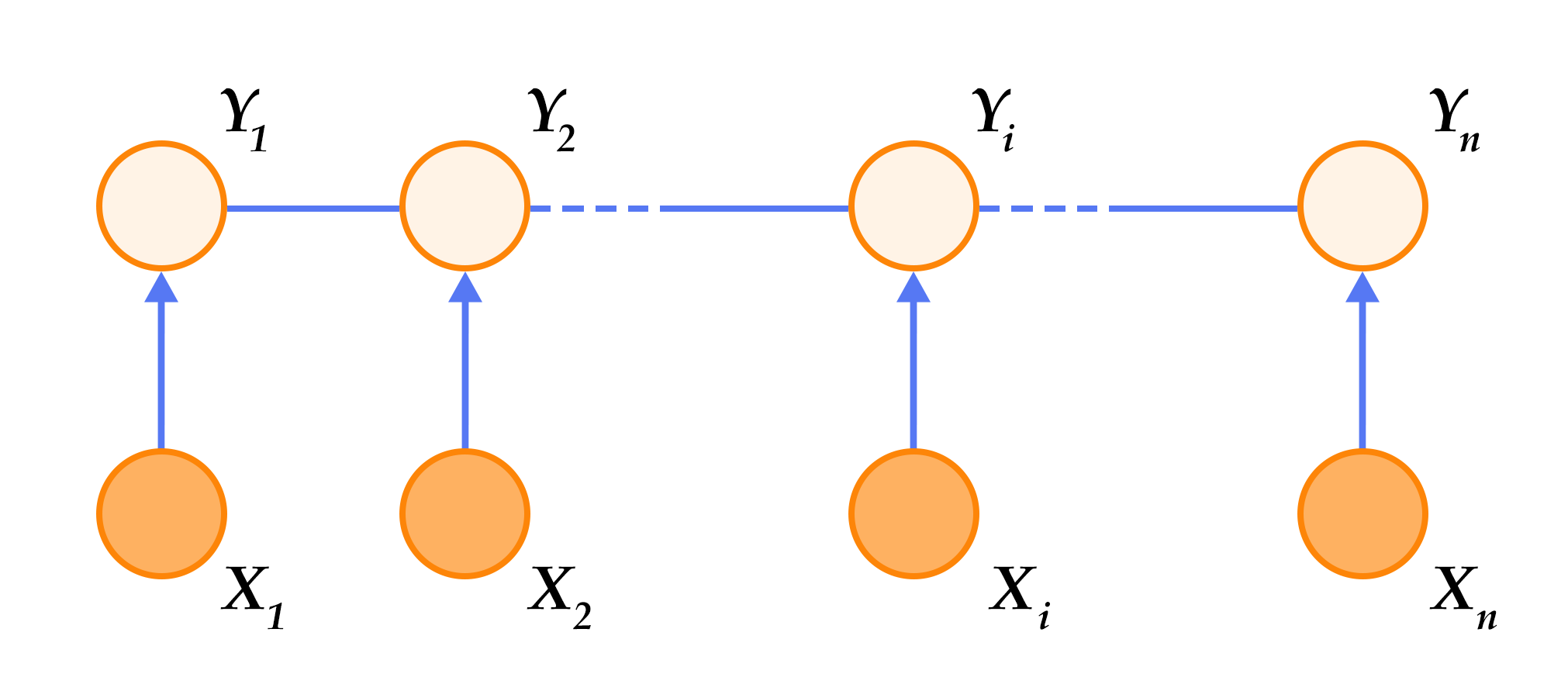
图1. 循环神经网络按时间展开的示意图
-循环神经网络按时间展开后如图1所示:在第`$t$`时刻,网络读入第`$t$`个输入`$x_t$`(向量表示)及前一时刻隐层的状态值`$h_{t-1}$`(向量表示,`$h_0$`一般初始化为`$0$`向量),计算得出本时刻隐层的状态值`$h_t$`,重复这一步骤直至读完所有输入。如果将循环神经网络所表示的函数记为`$f$`,则其公式可表示为:
+循环神经网络按时间展开后如图1所示:在第$t$时刻,网络读入第$t$个输入$x_t$(向量表示)及前一时刻隐层的状态值$h_{t-1}$(向量表示,$h_0$一般初始化为$0$向量),计算得出本时刻隐层的状态值$h_t$,重复这一步骤直至读完所有输入。如果将循环神经网络所表示的函数记为$f$,则其公式可表示为:
$$h_t=f(x_t,h_{t-1})=\sigma(W_{xh}x_t+W_{hh}h_{t-1}+b_h)$$
-其中`$W_{xh}$`是输入到隐层的矩阵参数,`$W_{hh}$`是隐层到隐层的矩阵参数,`$b_h$`为隐层的偏置向量(bias)参数,`$\sigma$`为`$sigmoid$`函数。
+其中$W_{xh}$是输入到隐层的矩阵参数,$W_{hh}$是隐层到隐层的矩阵参数,$b_h$为隐层的偏置向量(bias)参数,$\sigma$为$sigmoid$函数。
-在处理自然语言时,一般会先将词(one-hot表示)映射为其词向量(word embedding)表示,然后再作为循环神经网络每一时刻的输入`$x_t$`。此外,可以根据实际需要的不同在循环神经网络的隐层上连接其它层。如,可以把一个循环神经网络的隐层输出连接至下一个循环神经网络的输入构建深层(deep or stacked)循环神经网络,或者提取最后一个时刻的隐层状态作为句子表示进而使用分类模型等等。
+在处理自然语言时,一般会先将词(one-hot表示)映射为其词向量(word embedding)表示,然后再作为循环神经网络每一时刻的输入$x_t$。此外,可以根据实际需要的不同在循环神经网络的隐层上连接其它层。如,可以把一个循环神经网络的隐层输出连接至下一个循环神经网络的输入构建深层(deep or stacked)循环神经网络,或者提取最后一个时刻的隐层状态作为句子表示进而使用分类模型等等。
### 长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
-对于较长的序列数据,循环神经网络的训练过程中容易出现梯度消失或爆炸现象\[[6](#参考文献)\]。为了解决这一问题,Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. (1997)提出了LSTM(long short term memory\[[5](#参考文献)\])。
+对于较长的序列数据,循环神经网络的训练过程中容易出现梯度消失或爆炸现象\[[6](#参考文献)\]。为了解决这一问题,Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. (1997)提出了LSTM(long short term memory\[[5](#参考文献)\])。
-相比于简单的循环神经网络,LSTM增加了记忆单元`$c$`、输入门`$i$`、遗忘门`$f$`及输出门`$o$`。这些门及记忆单元组合起来大大提升了循环神经网络处理长序列数据的能力。若将基于LSTM的循环神经网络表示的函数记为`$F$`,则其公式为:
+相比于简单的循环神经网络,LSTM增加了记忆单元$c$、输入门$i$、遗忘门$f$及输出门$o$。这些门及记忆单元组合起来大大提升了循环神经网络处理长序列数据的能力。若将基于LSTM的循环神经网络表示的函数记为$F$,则其公式为:
$$ h_t=F(x_t,h_{t-1})$$
-`$F$`由下列公式组合而成\[[7](#参考文献)\]:
+$F$由下列公式组合而成\[[7](#参考文献)\]:
$$ i_t = \sigma{(W_{xi}x_t+W_{hi}h_{t-1}+W_{ci}c_{t-1}+b_i)} $$
$$ f_t = \sigma(W_{xf}x_t+W_{hf}h_{t-1}+W_{cf}c_{t-1}+b_f) $$
$$ c_t = f_t\odot c_{t-1}+i_t\odot tanh(W_{xc}x_t+W_{hc}h_{t-1}+b_c) $$
$$ o_t = \sigma(W_{xo}x_t+W_{ho}h_{t-1}+W_{co}c_{t}+b_o) $$
$$ h_t = o_t\odot tanh(c_t) $$
-其中,`$i_t, f_t, c_t, o_t$`分别表示输入门,遗忘门,记忆单元及输出门的向量值,带角标的`$W$`及`$b$`为模型参数,`$tanh$`为双曲正切函数,`$\odot$`表示逐元素(elementwise)的乘法操作。输入门控制着新输入进入记忆单元`$c$`的强度,遗忘门控制着记忆单元维持上一时刻值的强度,输出门控制着输出记忆单元的强度。三种门的计算方式类似,但有着完全不同的参数,它们各自以不同的方式控制着记忆单元`$c$`,如图2所示:
+其中,$i_t, f_t, c_t, o_t$分别表示输入门,遗忘门,记忆单元及输出门的向量值,带角标的$W$及$b$为模型参数,$tanh$为双曲正切函数,$\odot$表示逐元素(elementwise)的乘法操作。输入门控制着新输入进入记忆单元$c$的强度,遗忘门控制着记忆单元维持上一时刻值的强度,输出门控制着输出记忆单元的强度。三种门的计算方式类似,但有着完全不同的参数,它们各自以不同的方式控制着记忆单元$c$,如图2所示:
-
-图2. 时刻`$t$`的LSTM [7]
+
+图2. 时刻$t$的LSTM [7]
LSTM通过给简单的循环神经网络增加记忆及控制门的方式,增强了其处理远距离依赖问题的能力。类似原理的改进还有Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)\[[8](#参考文献)\],其设计更为简洁一些。**这些改进虽然各有不同,但是它们的宏观描述却与简单的循环神经网络一样(如图2所示),即隐状态依据当前输入及前一时刻的隐状态来改变,不断地循环这一过程直至输入处理完毕:**
$$ h_t=Recrurent(x_t,h_{t-1})$$
-其中,`$Recrurent$`可以表示简单的循环神经网络、GRU或LSTM。
+其中,$Recrurent$可以表示简单的循环神经网络、GRU或LSTM。
### 栈式双向LSTM(Stacked Bidirectional LSTM)
-对于正常顺序的循环神经网络,`$h_t$`包含了`$t$`时刻之前的输入信息,也就是上文信息。同样,为了得到下文信息,我们可以使用反方向(将输入逆序处理)的循环神经网络。结合构建深层循环神经网络的方法(深层神经网络往往能得到更抽象和高级的特征表示),我们可以通过构建更加强有力的基于LSTM的栈式双向循环神经网络\[[9](#参考文献)\],来对时序数据进行建模。
+对于正常顺序的循环神经网络,$h_t$包含了$t$时刻之前的输入信息,也就是上文信息。同样,为了得到下文信息,我们可以使用反方向(将输入逆序处理)的循环神经网络。结合构建深层循环神经网络的方法(深层神经网络往往能得到更抽象和高级的特征表示),我们可以通过构建更加强有力的基于LSTM的栈式双向循环神经网络\[[9](#参考文献)\],来对时序数据进行建模。
如图3所示(以三层为例),奇数层LSTM正向,偶数层LSTM反向,高一层的LSTM使用低一层LSTM及之前所有层的信息作为输入,对最高层LSTM序列使用时间维度上的最大池化即可得到文本的定长向量表示(这一表示充分融合了文本的上下文信息,并且对文本进行了深层次抽象),最后我们将文本表示连接至softmax构建分类模型。
-
+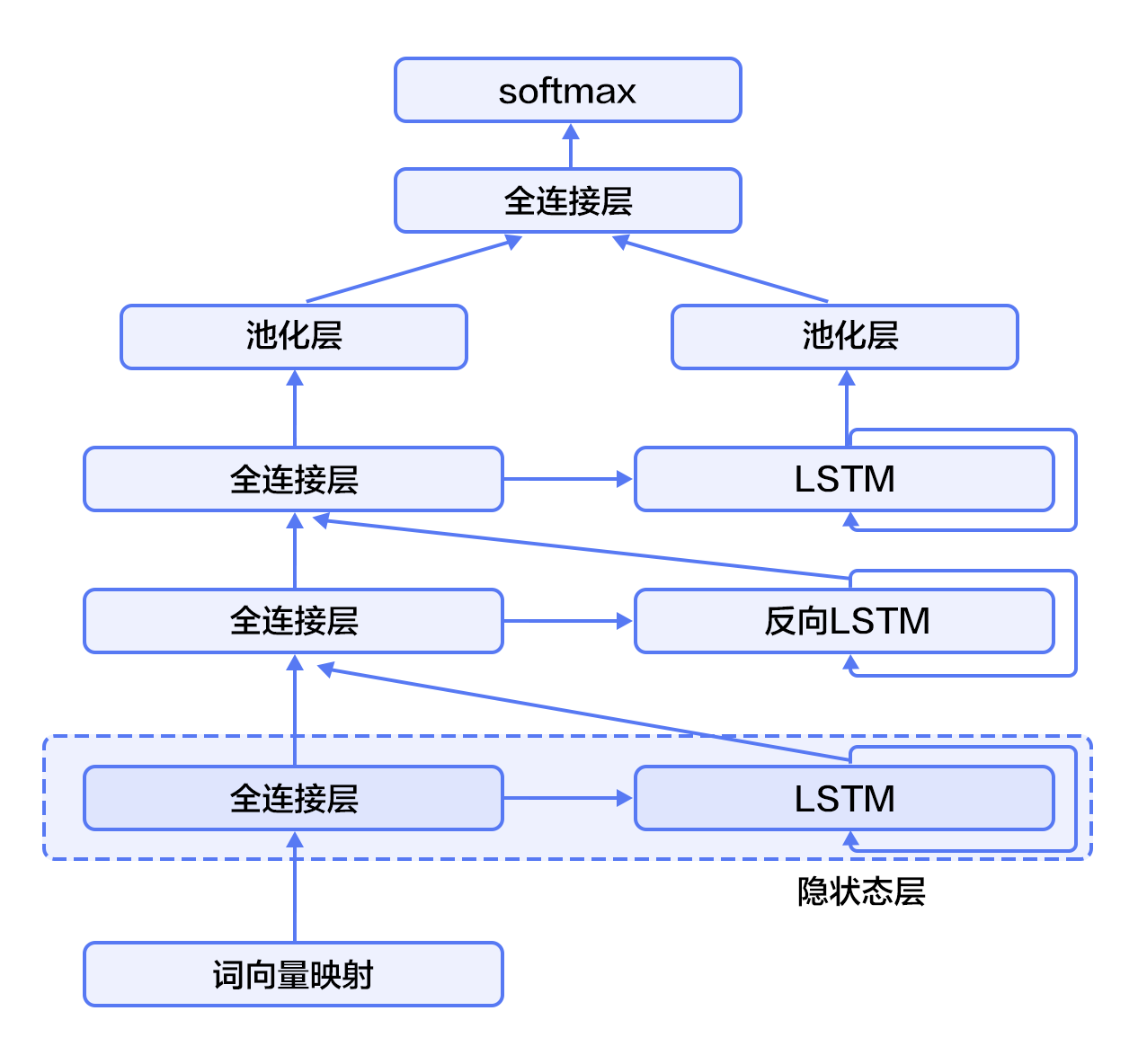
图3. 栈式双向LSTM用于文本分类
@@ -94,11 +94,11 @@ $$ h_t=Recrurent(x_t,h_{t-1})$$
```text
aclImdb
|- test
-|-- neg
-|-- pos
+ |-- neg
+ |-- pos
|- train
-|-- neg
-|-- pos
+ |-- neg
+ |-- pos
```
Paddle在`dataset/imdb.py`中提实现了imdb数据集的自动下载和读取,并提供了读取字典、训练数据、测试数据等API。
@@ -107,6 +107,7 @@ Paddle在`dataset/imdb.py`中提实现了imdb数据集的自动下载和读取
在该示例中,我们实现了两种文本分类算法,分别基于[推荐系统](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/05.recommender_system)一节介绍过的文本卷积神经网络,以及[栈式双向LSTM](#栈式双向LSTM(Stacked Bidirectional LSTM))。我们首先引入要用到的库和定义全局变量:
```python
+from __future__ import print_function
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from functools import partial
@@ -115,6 +116,7 @@ import numpy as np
CLASS_DIM = 2
EMB_DIM = 128
HID_DIM = 512
+STACKED_NUM = 3
BATCH_SIZE = 128
USE_GPU = False
```
@@ -126,23 +128,23 @@ USE_GPU = False
```python
def convolution_net(data, input_dim, class_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim):
-emb = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=data, size=[input_dim, emb_dim], is_sparse=True)
-conv_3 = fluid.nets.sequence_conv_pool(
-input=emb,
-num_filters=hid_dim,
-filter_size=3,
-act="tanh",
-pool_type="sqrt")
-conv_4 = fluid.nets.sequence_conv_pool(
-input=emb,
-num_filters=hid_dim,
-filter_size=4,
-act="tanh",
-pool_type="sqrt")
-prediction = fluid.layers.fc(
-input=[conv_3, conv_4], size=class_dim, act="softmax")
-return prediction
+ emb = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=data, size=[input_dim, emb_dim], is_sparse=True)
+ conv_3 = fluid.nets.sequence_conv_pool(
+ input=emb,
+ num_filters=hid_dim,
+ filter_size=3,
+ act="tanh",
+ pool_type="sqrt")
+ conv_4 = fluid.nets.sequence_conv_pool(
+ input=emb,
+ num_filters=hid_dim,
+ filter_size=4,
+ act="tanh",
+ pool_type="sqrt")
+ prediction = fluid.layers.fc(
+ input=[conv_3, conv_4], size=class_dim, act="softmax")
+ return prediction
```
网络的输入`input_dim`表示的是词典的大小,`class_dim`表示类别数。这里,我们使用[`sequence_conv_pool`](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/python/paddle/trainer_config_helpers/networks.py) API实现了卷积和池化操作。
@@ -154,27 +156,26 @@ return prediction
```python
def stacked_lstm_net(data, input_dim, class_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, stacked_num):
-emb = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=data, size=[input_dim, emb_dim], is_sparse=True)
+ emb = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=data, size=[input_dim, emb_dim], is_sparse=True)
-fc1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=emb, size=hid_dim)
-lstm1, cell1 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(input=fc1, size=hid_dim)
+ fc1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=emb, size=hid_dim)
+ lstm1, cell1 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(input=fc1, size=hid_dim)
-inputs = [fc1, lstm1]
+ inputs = [fc1, lstm1]
-for i in range(2, stacked_num + 1):
-fc = fluid.layers.fc(input=inputs, size=hid_dim)
-lstm, cell = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
-input=fc, size=hid_dim, is_reverse=(i % 2) == 0)
-inputs = [fc, lstm]
+ for i in range(2, stacked_num + 1):
+ fc = fluid.layers.fc(input=inputs, size=hid_dim)
+ lstm, cell = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
+ input=fc, size=hid_dim, is_reverse=(i % 2) == 0)
+ inputs = [fc, lstm]
-fc_last = fluid.layers.sequence_pool(input=inputs[0], pool_type='max')
-lstm_last = fluid.layers.sequence_pool(input=inputs[1], pool_type='max')
+ fc_last = fluid.layers.sequence_pool(input=inputs[0], pool_type='max')
+ lstm_last = fluid.layers.sequence_pool(input=inputs[1], pool_type='max')
-prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=[fc_last, lstm_last],
-size=class_dim,
-act='softmax')
-return prediction
+ prediction = fluid.layers.fc(
+ input=[fc_last, lstm_last], size=class_dim, act='softmax')
+ return prediction
```
以上的栈式双向LSTM抽象出了高级特征并把其映射到和分类类别数同样大小的向量上。`paddle.activation.Softmax`函数用来计算分类属于某个类别的概率。
@@ -184,12 +185,13 @@ return prediction
```python
def inference_program(word_dict):
-data = fluid.layers.data(
-name="words", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
+ data = fluid.layers.data(
+ name="words", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
-dict_dim = len(word_dict)
-net = convolution_net(data, dict_dim, CLASS_DIM, EMB_DIM, HID_DIM)
-return net
+ dict_dim = len(word_dict)
+ net = convolution_net(data, dict_dim, CLASS_DIM, EMB_DIM, HID_DIM)
+ # net = stacked_lstm_net(data, dict_dim, CLASS_DIM, EMB_DIM, HID_DIM, STACKED_NUM)
+ return net
```
我们这里定义了`training_program`。它使用了从`inference_program`返回的结果来计算误差。我们同时定义了优化函数`optimizer_func`。
@@ -200,16 +202,16 @@ return net
```python
def train_program(word_dict):
-prediction = inference_program(word_dict)
-label = fluid.layers.data(name="label", shape=[1], dtype="int64")
-cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=prediction, label=label)
-avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
-accuracy = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=prediction, label=label)
-return [avg_cost, accuracy]
+ prediction = inference_program(word_dict)
+ label = fluid.layers.data(name="label", shape=[1], dtype="int64")
+ cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=prediction, label=label)
+ avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
+ accuracy = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=prediction, label=label)
+ return [avg_cost, accuracy]
def optimizer_func():
-return fluid.optimizer.Adagrad(learning_rate=0.002)
+ return fluid.optimizer.Adagrad(learning_rate=0.002)
```
## 训练模型
@@ -236,9 +238,9 @@ word_dict = paddle.dataset.imdb.word_dict()
print ("Reading training data....")
train_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.imdb.train(word_dict), buf_size=25000),
-batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.imdb.train(word_dict), buf_size=25000),
+ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
```
### 构造训练器(trainer)
@@ -246,9 +248,9 @@ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
```python
trainer = fluid.Trainer(
-train_func=partial(train_program, word_dict),
-place=place,
-optimizer_func=optimizer_func)
+ train_func=partial(train_program, word_dict),
+ place=place,
+ optimizer_func=optimizer_func)
```
### 提供数据
@@ -268,13 +270,13 @@ feed_order = ['words', 'label']
params_dirname = "understand_sentiment_conv.inference.model"
def event_handler(event):
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
-print("Step {0}, Epoch {1} Metrics {2}".format(
-event.step, event.epoch, map(np.array, event.metrics)))
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
+ print("Step {0}, Epoch {1} Metrics {2}".format(
+ event.step, event.epoch, map(np.array, event.metrics)))
-if event.step == 10:
-trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
-trainer.stop()
+ if event.step == 10:
+ trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
+ trainer.stop()
```
### 开始训练
@@ -283,10 +285,10 @@ trainer.stop()
```python
trainer.train(
-num_epochs=1,
-event_handler=event_handler,
-reader=train_reader,
-feed_order=feed_order)
+ num_epochs=1,
+ event_handler=event_handler,
+ reader=train_reader,
+ feed_order=feed_order)
```
## 应用模型
@@ -297,7 +299,7 @@ feed_order=feed_order)
```python
inferencer = fluid.Inferencer(
-inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
+ infer_func=partial(inference_program, word_dict), param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
```
### 生成测试用输入数据
@@ -307,14 +309,14 @@ inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
```python
reviews_str = [
-'read the book forget the movie', 'this is a great movie', 'this is very bad'
+ 'read the book forget the movie', 'this is a great movie', 'this is very bad'
]
reviews = [c.split() for c in reviews_str]
UNK = word_dict['']
lod = []
for c in reviews:
-lod.append([word_dict.get(words, UNK) for words in c])
+ lod.append([word_dict.get(words, UNK) for words in c])
base_shape = [[len(c) for c in lod]]
@@ -329,7 +331,7 @@ tensor_words = fluid.create_lod_tensor(lod, base_shape, place)
results = inferencer.infer({'words': tensor_words})
for i, r in enumerate(results[0]):
-print("Predict probability of ", r[0], " to be positive and ", r[1], " to be negative for review \'", reviews_str[i], "\'")
+ print("Predict probability of ", r[0], " to be positive and ", r[1], " to be negative for review \'", reviews_str[i], "\'")
```
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 98fbea413a98a619004ca669c67f5f867fe974c9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index d73a00bf2c1fca2f9b8c26bccf5ea844fa1db50b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/lstm_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/rnn.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/rnn.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 26c904102a6e6c4e30f0048b81373ae8c148b355..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/rnn.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm.jpg b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 6b2adf70f2b5112a2e82505da5cff9f5fd0c6298..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 8b5dbd726178b5555c513294e7b10a81acc96ff5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/understand_sentiment/image/stacked_lstm_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/index.md b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/README.cn.md
similarity index 56%
rename from doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/index.md
rename to doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/README.cn.md
index e73a6334ca1acd49379604f24d3d4e463192a902..0d2d4dbc2caf8f5163d6401b6eec1a7f26e2a12e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/index.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/README.cn.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
# 词向量
-本教程源代码目录在[book/word2vec](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/04.word2vec), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书)。
+本教程源代码目录在[book/word2vec](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/04.word2vec), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书),更多内容请参考本教程的[视频课堂](http://bit.baidu.com/course/detail/id/175.html)。
## 背景介绍
@@ -12,17 +12,19 @@
One-hot vector虽然自然,但是用处有限。比如,在互联网广告系统里,如果用户输入的query是“母亲节”,而有一个广告的关键词是“康乃馨”。虽然按照常理,我们知道这两个词之间是有联系的——母亲节通常应该送给母亲一束康乃馨;但是这两个词对应的one-hot vectors之间的距离度量,无论是欧氏距离还是余弦相似度(cosine similarity),由于其向量正交,都认为这两个词毫无相关性。 得出这种与我们相悖的结论的根本原因是:每个词本身的信息量都太小。所以,仅仅给定两个词,不足以让我们准确判别它们是否相关。要想精确计算相关性,我们还需要更多的信息——从大量数据里通过机器学习方法归纳出来的知识。
-在机器学习领域里,各种“知识”被各种模型表示,词向量模型(word embedding model)就是其中的一类。通过词向量模型可将一个 one-hot vector映射到一个维度更低的实数向量(embedding vector),如`$embedding(Mother's\ Day) = [0.3, 4.2, -1.5, ...], embedding(Carnation) = [0.2, 5.6, -2.3, ...]$`。在这个映射到的实数向量表示中,希望两个语义(或用法)上相似的词对应的词向量“更像”,这样如“母亲节”和“康乃馨”的对应词向量的余弦相似度就不再为零了。
+在机器学习领域里,各种“知识”被各种模型表示,词向量模型(word embedding model)就是其中的一类。通过词向量模型可将一个 one-hot vector映射到一个维度更低的实数向量(embedding vector),如$embedding(母亲节) = [0.3, 4.2, -1.5, ...], embedding(康乃馨) = [0.2, 5.6, -2.3, ...]$。在这个映射到的实数向量表示中,希望两个语义(或用法)上相似的词对应的词向量“更像”,这样如“母亲节”和“康乃馨”的对应词向量的余弦相似度就不再为零了。
-词向量模型可以是概率模型、共生矩阵(co-occurrence matrix)模型或神经元网络模型。在用神经网络求词向量之前,传统做法是统计一个词语的共生矩阵`$X$`。`$X$`是一个`$|V| \times |V|$` 大小的矩阵,`$X_{ij}$`表示在所有语料中,词汇表`V`(vocabulary)中第i个词和第j个词同时出现的词数,`$|V|$`为词汇表的大小。对`$X$`做矩阵分解(如奇异值分解,Singular Value Decomposition \[[5](#参考文献)\]),得到的`$U$`即视为所有词的词向量:
+词向量模型可以是概率模型、共生矩阵(co-occurrence matrix)模型或神经元网络模型。在用神经网络求词向量之前,传统做法是统计一个词语的共生矩阵$X$。$X$是一个$|V| \times |V|$ 大小的矩阵,$X_{ij}$表示在所有语料中,词汇表`V`(vocabulary)中第i个词和第j个词同时出现的词数,$|V|$为词汇表的大小。对$X$做矩阵分解(如奇异值分解,Singular Value Decomposition \[[5](#参考文献)\]),得到的$U$即视为所有词的词向量:
$$X = USV^T$$
-但这样的传统做法有很多问题:
-1) 由于很多词没有出现,导致矩阵极其稀疏,因此需要对词频做额外处理来达到好的矩阵分解效果;
-2) 矩阵非常大,维度太高(通常达到`$10^6*10^6$`的数量级);
-3) 需要手动去掉停用词(如although, a,...),不然这些频繁出现的词也会影响矩阵分解的效果。
+但这样的传统做法有很多问题:
+
+1) 由于很多词没有出现,导致矩阵极其稀疏,因此需要对词频做额外处理来达到好的矩阵分解效果;
+2) 矩阵非常大,维度太高(通常达到$10^6 \times 10^6$的数量级);
+
+3) 需要手动去掉停用词(如although, a,...),不然这些频繁出现的词也会影响矩阵分解的效果。
基于神经网络的模型不需要计算存储一个在全语料上统计的大表,而是通过学习语义信息得到词向量,因此能很好地解决以上问题。在本章里,我们将展示基于神经网络训练词向量的细节,以及如何用PaddlePaddle训练一个词向量模型。
@@ -31,19 +33,21 @@ $$X = USV^T$$
本章中,当词向量训练好后,我们可以用数据可视化算法t-SNE\[[4](#参考文献)\]画出词语特征在二维上的投影(如下图所示)。从图中可以看出,语义相关的词语(如a, the, these; big, huge)在投影上距离很近,语意无关的词(如say, business; decision, japan)在投影上的距离很远。
-
-图1. 词向量的二维投影
+ 
+ 图1. 词向量的二维投影
-另一方面,我们知道两个向量的余弦值在`$[-1,1]$`的区间内:两个完全相同的向量余弦值为1, 两个相互垂直的向量之间余弦值为0,两个方向完全相反的向量余弦值为-1,即相关性和余弦值大小成正比。因此我们还可以计算两个词向量的余弦相似度:
+另一方面,我们知道两个向量的余弦值在$[-1,1]$的区间内:两个完全相同的向量余弦值为1, 两个相互垂直的向量之间余弦值为0,两个方向完全相反的向量余弦值为-1,即相关性和余弦值大小成正比。因此我们还可以计算两个词向量的余弦相似度:
```
-similarity: 0.899180685161
+
please input two words: big huge
+similarity: 0.899180685161
please input two words: from company
similarity: -0.0997506977351
+
```
以上结果可以通过运行`calculate_dis.py`, 加载字典里的单词和对应训练特征结果得到,我们将在[应用模型](#应用模型)中详细描述用法。
@@ -56,10 +60,10 @@ similarity: -0.0997506977351
### 语言模型
在介绍词向量模型之前,我们先来引入一个概念:语言模型。
-语言模型旨在为语句的联合概率函数`$P(w_1, ..., w_T)$`建模, 其中`$w_i$`表示句子中的第i个词。语言模型的目标是,希望模型对有意义的句子赋予大概率,对没意义的句子赋予小概率。
+语言模型旨在为语句的联合概率函数$P(w_1, ..., w_T)$建模, 其中$w_i$表示句子中的第i个词。语言模型的目标是,希望模型对有意义的句子赋予大概率,对没意义的句子赋予小概率。
这样的模型可以应用于很多领域,如机器翻译、语音识别、信息检索、词性标注、手写识别等,它们都希望能得到一个连续序列的概率。 以信息检索为例,当你在搜索“how long is a football bame”时(bame是一个医学名词),搜索引擎会提示你是否希望搜索"how long is a football game", 这是因为根据语言模型计算出“how long is a football bame”的概率很低,而与bame近似的,可能引起错误的词中,game会使该句生成的概率最大。
-对语言模型的目标概率`$P(w_1, ..., w_T)$`,如果假设文本中每个词都是相互独立的,则整句话的联合概率可以表示为其中所有词语条件概率的乘积,即:
+对语言模型的目标概率$P(w_1, ..., w_T)$,如果假设文本中每个词都是相互独立的,则整句话的联合概率可以表示为其中所有词语条件概率的乘积,即:
$$P(w_1, ..., w_T) = \prod_{t=1}^TP(w_t)$$
@@ -75,7 +79,7 @@ $$P(w_1, ..., w_T) = \prod_{t=1}^TP(w_t | w_1, ... , w_{t-1})$$
Yoshua Bengio等科学家就于2003年在著名论文 Neural Probabilistic Language Models \[[1](#参考文献)\] 中介绍如何学习一个神经元网络表示的词向量模型。文中的神经概率语言模型(Neural Network Language Model,NNLM)通过一个线性映射和一个非线性隐层连接,同时学习了语言模型和词向量,即通过学习大量语料得到词语的向量表达,通过这些向量得到整个句子的概率。用这种方法学习语言模型可以克服维度灾难(curse of dimensionality),即训练和测试数据不同导致的模型不准。注意:由于“神经概率语言模型”说法较为泛泛,我们在这里不用其NNLM的本名,考虑到其具体做法,本文中称该模型为N-gram neural model。
-我们在上文中已经讲到用条件概率建模语言模型,即一句话中第`$t$`个词的概率和该句话的前`$t-1$`个词相关。可实际上越远的词语其实对该词的影响越小,那么如果考虑一个n-gram, 每个词都只受其前面`n-1`个词的影响,则有:
+我们在上文中已经讲到用条件概率建模语言模型,即一句话中第$t$个词的概率和该句话的前$t-1$个词相关。可实际上越远的词语其实对该词的影响越小,那么如果考虑一个n-gram, 每个词都只受其前面`n-1`个词的影响,则有:
$$P(w_1, ..., w_T) = \prod_{t=n}^TP(w_t|w_{t-1}, w_{t-2}, ..., w_{t-n+1})$$
@@ -83,33 +87,33 @@ $$P(w_1, ..., w_T) = \prod_{t=n}^TP(w_t|w_{t-1}, w_{t-2}, ..., w_{t-n+1})$$
$$\frac{1}{T}\sum_t f(w_t, w_{t-1}, ..., w_{t-n+1};\theta) + R(\theta)$$
-其中`$f(w_t, w_{t-1}, ..., w_{t-n+1})$`表示根据历史n-1个词得到当前词`$w_t$`的条件概率,`$R(\theta)$`表示参数正则项。
+其中$f(w_t, w_{t-1}, ..., w_{t-n+1})$表示根据历史n-1个词得到当前词$w_t$的条件概率,$R(\theta)$表示参数正则项。
-
-图2. N-gram神经网络模型
+ 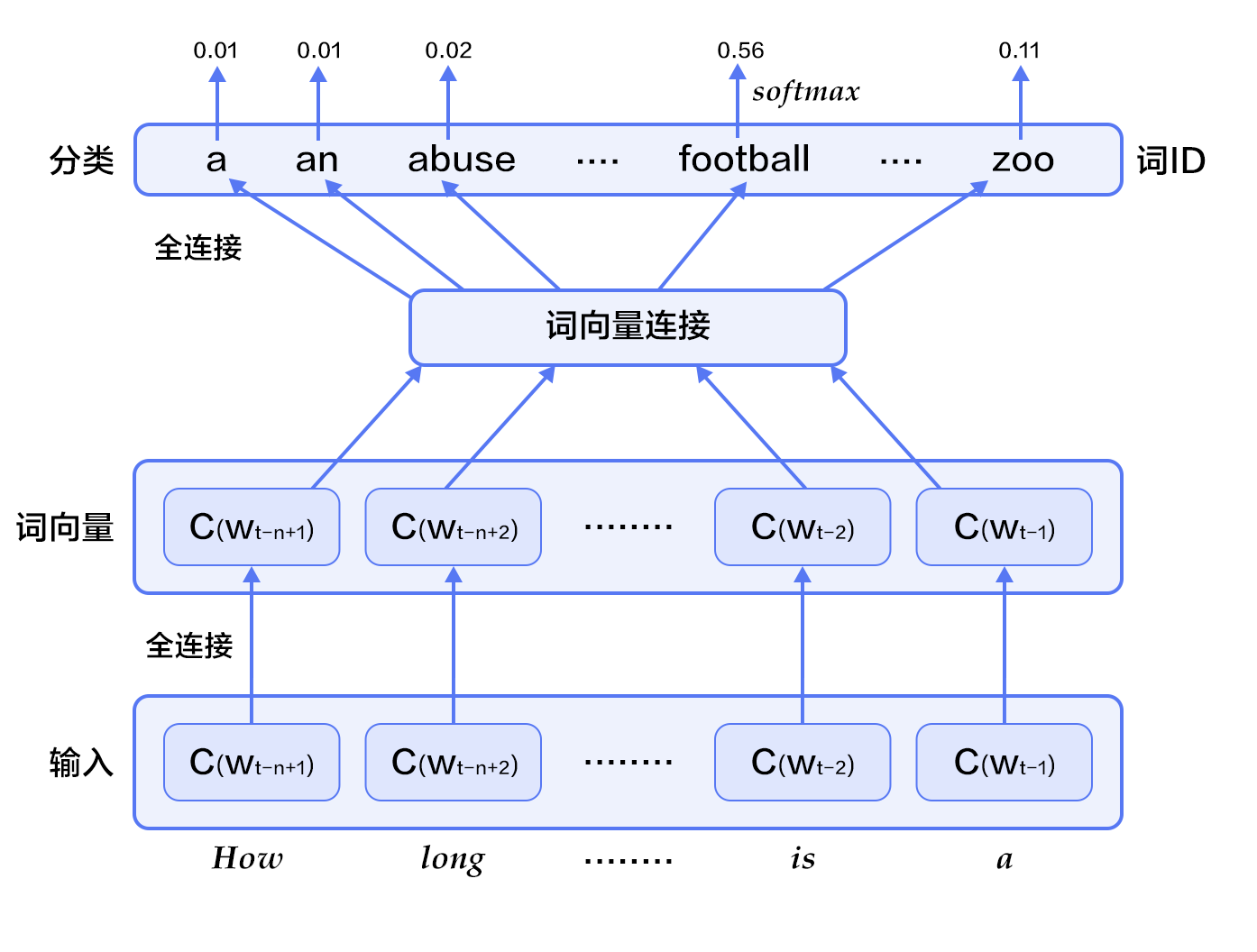
+ 图2. N-gram神经网络模型
图2展示了N-gram神经网络模型,从下往上看,该模型分为以下几个部分:
-- 对于每个样本,模型输入`$w_{t-n+1},...w_{t-1}$`, 输出句子第t个词为字典中`|V|`个词的概率。
+ - 对于每个样本,模型输入$w_{t-n+1},...w_{t-1}$, 输出句子第t个词为字典中`|V|`个词的概率。
-每个输入词`$w_{t-n+1},...w_{t-1}$`首先通过映射矩阵映射到词向量`$C(w_{t-n+1}),...C(w_{t-1})$`。
+ 每个输入词$w_{t-n+1},...w_{t-1}$首先通过映射矩阵映射到词向量$C(w_{t-n+1}),...C(w_{t-1})$。
-- 然后所有词语的词向量连接成一个大向量,并经过一个非线性映射得到历史词语的隐层表示:
+ - 然后所有词语的词向量连接成一个大向量,并经过一个非线性映射得到历史词语的隐层表示:
-$$g=Utanh(\theta^Tx + b_1) + Wx + b_2$$
+ $$g=Utanh(\theta^Tx + b_1) + Wx + b_2$$
-其中,`$x$`为所有词语的词向量连接成的大向量,表示文本历史特征;`$\theta$`、`$U$`、`$b_1$`、`$b_2$`和`$W$`分别为词向量层到隐层连接的参数。`$g$`表示未经归一化的所有输出单词概率,`$g_i$`表示未经归一化的字典中第`$i$`个单词的输出概率。
+ 其中,$x$为所有词语的词向量连接成的大向量,表示文本历史特征;$\theta$、$U$、$b_1$、$b_2$和$W$分别为词向量层到隐层连接的参数。$g$表示未经归一化的所有输出单词概率,$g_i$表示未经归一化的字典中第$i$个单词的输出概率。
-- 根据softmax的定义,通过归一化`$g_i$`, 生成目标词`$w_t$`的概率为:
+ - 根据softmax的定义,通过归一化$g_i$, 生成目标词$w_t$的概率为:
-$$P(w_t | w_1, ..., w_{t-n+1}) = \frac{e^{g_{w_t}}}{\sum_i^{|V|} e^{g_i}}$$
+ $$P(w_t | w_1, ..., w_{t-n+1}) = \frac{e^{g_{w_t}}}{\sum_i^{|V|} e^{g_i}}$$
-- 整个网络的损失值(cost)为多类分类交叉熵,用公式表示为
+ - 整个网络的损失值(cost)为多类分类交叉熵,用公式表示为
-$$J(\theta) = -\sum_{i=1}^N\sum_{c=1}^{|V|}y_k^{i}log(softmax(g_k^i))$$
+ $$J(\theta) = -\sum_{i=1}^N\sum_{c=1}^{|V|}y_k^{i}log(softmax(g_k^i))$$
-其中`$y_k^i$`表示第`$i$`个样本第`$k$`类的真实标签(0或1),`$softmax(g_k^i)$`表示第i个样本第k类softmax输出的概率。
+ 其中$y_k^i$表示第$i$个样本第$k$类的真实标签(0或1),$softmax(g_k^i)$表示第i个样本第k类softmax输出的概率。
@@ -117,27 +121,27 @@ $$J(\theta) = -\sum_{i=1}^N\sum_{c=1}^{|V|}y_k^{i}log(softmax(g_k^i))$$
CBOW模型通过一个词的上下文(各N个词)预测当前词。当N=2时,模型如下图所示:
-
-图3. CBOW模型
+ 
+ 图3. CBOW模型
具体来说,不考虑上下文的词语输入顺序,CBOW是用上下文词语的词向量的均值来预测当前词。即:
$$context = \frac{x_{t-1} + x_{t-2} + x_{t+1} + x_{t+2}}{4}$$
-其中`$x_t$`为第`$t$`个词的词向量,分类分数(score)向量 `$z=U*context$`,最终的分类`$y$`采用softmax,损失函数采用多类分类交叉熵。
+其中$x_t$为第$t$个词的词向量,分类分数(score)向量 $z=U*context$,最终的分类$y$采用softmax,损失函数采用多类分类交叉熵。
### Skip-gram model
CBOW的好处是对上下文词语的分布在词向量上进行了平滑,去掉了噪声,因此在小数据集上很有效。而Skip-gram的方法中,用一个词预测其上下文,得到了当前词上下文的很多样本,因此可用于更大的数据集。
-
-图4. Skip-gram模型
+ 
+ 图4. Skip-gram模型
-如上图所示,Skip-gram模型的具体做法是,将一个词的词向量映射到`$2n$`个词的词向量(`$2n$`表示当前输入词的前后各`$n$`个词),然后分别通过softmax得到这`$2n$`个词的分类损失值之和。
+如上图所示,Skip-gram模型的具体做法是,将一个词的词向量映射到$2n$个词的词向量($2n$表示当前输入词的前后各$n$个词),然后分别通过softmax得到这$2n$个词的分类损失值之和。
## 数据准备
@@ -148,21 +152,21 @@ CBOW的好处是对上下文词语的分布在词向量上进行了平滑,去
-
-| 训练数据 |
-验证数据 |
-测试数据 |
-
-
-| ptb.train.txt |
-ptb.valid.txt |
-ptb.test.txt |
-
-
-| 42068句 |
-3370句 |
-3761句 |
-
+
+ | 训练数据 |
+ 验证数据 |
+ 测试数据 |
+
+
+ | ptb.train.txt |
+ ptb.valid.txt |
+ ptb.test.txt |
+
+
+ | 42068句 |
+ 3370句 |
+ 3761句 |
+
@@ -189,9 +193,9 @@ dream that one day
本配置的模型结构如下图所示:
-
-图5. 模型配置中的N-gram神经网络模型
+ 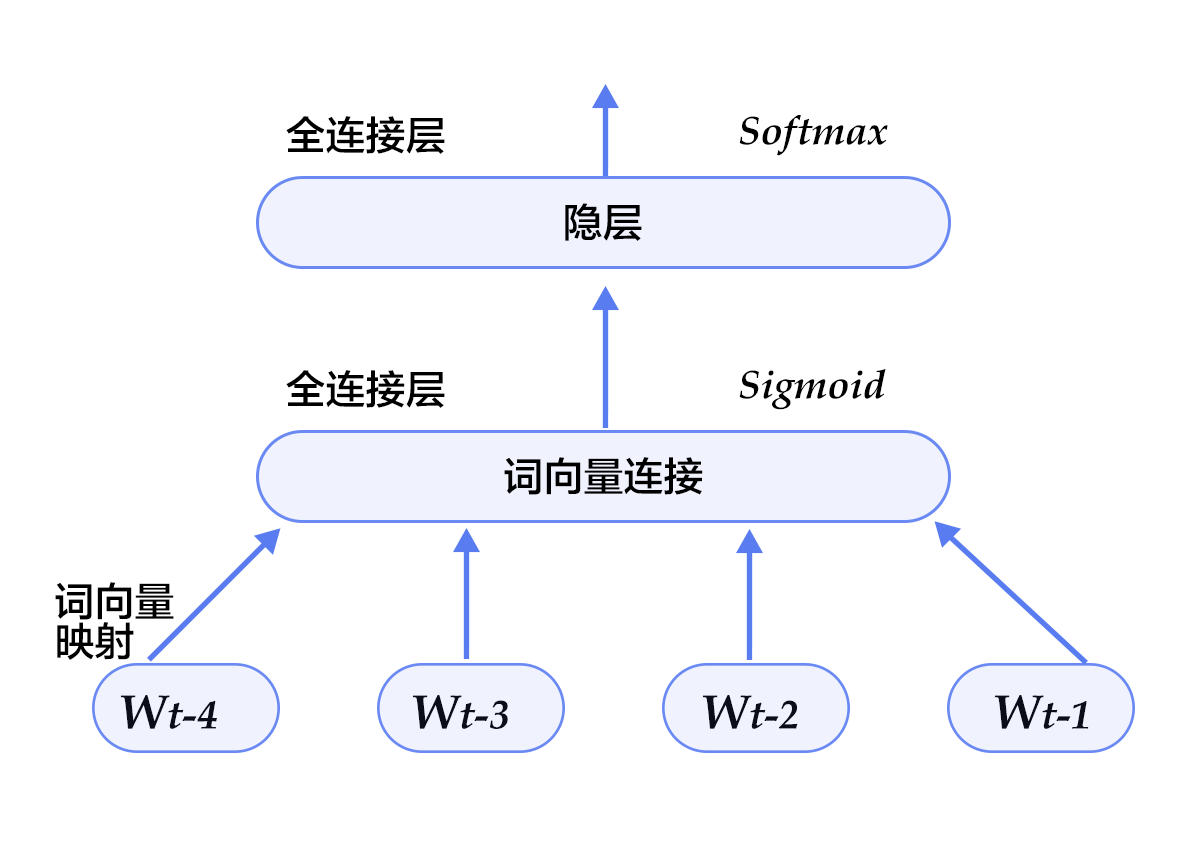
+ 图5. 模型配置中的N-gram神经网络模型
首先,加载所需要的包:
@@ -204,6 +208,7 @@ from functools import partial
import math
import os
import sys
+from __future__ import print_function
```
然后,定义参数:
@@ -226,57 +231,57 @@ dict_size = len(word_dict)
```python
def inference_program(is_sparse):
-first_word = fluid.layers.data(name='firstw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-second_word = fluid.layers.data(name='secondw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-third_word = fluid.layers.data(name='thirdw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-fourth_word = fluid.layers.data(name='fourthw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-
-embed_first = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=first_word,
-size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr='shared_w')
-embed_second = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=second_word,
-size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr='shared_w')
-embed_third = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=third_word,
-size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr='shared_w')
-embed_fourth = fluid.layers.embedding(
-input=fourth_word,
-size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
-dtype='float32',
-is_sparse=is_sparse,
-param_attr='shared_w')
-
-concat_embed = fluid.layers.concat(
-input=[embed_first, embed_second, embed_third, embed_fourth], axis=1)
-hidden1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=concat_embed,
-size=HIDDEN_SIZE,
-act='sigmoid')
-predict_word = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden1, size=dict_size, act='softmax')
-return predict_word
+ first_word = fluid.layers.data(name='firstw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+ second_word = fluid.layers.data(name='secondw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+ third_word = fluid.layers.data(name='thirdw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+ fourth_word = fluid.layers.data(name='fourthw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+
+ embed_first = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=first_word,
+ size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr='shared_w')
+ embed_second = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=second_word,
+ size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr='shared_w')
+ embed_third = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=third_word,
+ size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr='shared_w')
+ embed_fourth = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=fourth_word,
+ size=[dict_size, EMBED_SIZE],
+ dtype='float32',
+ is_sparse=is_sparse,
+ param_attr='shared_w')
+
+ concat_embed = fluid.layers.concat(
+ input=[embed_first, embed_second, embed_third, embed_fourth], axis=1)
+ hidden1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=concat_embed,
+ size=HIDDEN_SIZE,
+ act='sigmoid')
+ predict_word = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden1, size=dict_size, act='softmax')
+ return predict_word
```
- 基于以上的神经网络结构,我们可以如下定义我们的`训练`方法
```python
def train_program(is_sparse):
-# The declaration of 'next_word' must be after the invoking of inference_program,
-# or the data input order of train program would be [next_word, firstw, secondw,
-# thirdw, fourthw], which is not correct.
-predict_word = inference_program(is_sparse)
-next_word = fluid.layers.data(name='nextw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict_word, label=next_word)
-avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
-return avg_cost
+ # The declaration of 'next_word' must be after the invoking of inference_program,
+ # or the data input order of train program would be [next_word, firstw, secondw,
+ # thirdw, fourthw], which is not correct.
+ predict_word = inference_program(is_sparse)
+ next_word = fluid.layers.data(name='nextw', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+ cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict_word, label=next_word)
+ avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
+ return avg_cost
```
- 现在我们可以开始训练啦。如今的版本较之以前就简单了许多。我们有现成的训练和测试集:`paddle.dataset.imikolov.train()`和`paddle.dataset.imikolov.test()`。两者都会返回一个读取器。在PaddlePaddle中,读取器是一个Python的函数,每次调用,会读取下一条数据。它是一个Python的generator。
@@ -285,59 +290,59 @@ return avg_cost
```python
def optimizer_func():
-# Note here we need to choose more sophisticated optimizers
-# such as AdaGrad with a decay rate. The normal SGD converges
-# very slowly.
-# optimizer=fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001),
-return fluid.optimizer.AdagradOptimizer(
-learning_rate=3e-3,
-regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2DecayRegularizer(8e-4))
+ # Note here we need to choose more sophisticated optimizers
+ # such as AdaGrad with a decay rate. The normal SGD converges
+ # very slowly.
+ # optimizer=fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001),
+ return fluid.optimizer.AdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=3e-3,
+ regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2DecayRegularizer(8e-4))
def train(use_cuda, train_program, params_dirname):
-train_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.dataset.imikolov.train(word_dict, N), BATCH_SIZE)
-test_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.dataset.imikolov.test(word_dict, N), BATCH_SIZE)
-
-place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
-
-def event_handler(event):
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
-# We output cost every 10 steps.
-if event.step % 10 == 0:
-outs = trainer.test(
-reader=test_reader,
-feed_order=['firstw', 'secondw', 'thirdw', 'fourthw', 'nextw'])
-avg_cost = outs[0]
-
-print "Step %d: Average Cost %f" % (event.step, avg_cost)
-
-# If average cost is lower than 5.8, we consider the model good enough to stop.
-# Note 5.8 is a relatively high value. In order to get a better model, one should
-# aim for avg_cost lower than 3.5. But the training could take longer time.
-if avg_cost < 5.8:
-trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
-trainer.stop()
-
-if math.isnan(avg_cost):
-sys.exit("got NaN loss, training failed.")
-
-trainer = fluid.Trainer(
-train_func=train_program,
-optimizer_func=optimizer_func,
-place=place)
-
-trainer.train(
-reader=train_reader,
-num_epochs=1,
-event_handler=event_handler,
-feed_order=['firstw', 'secondw', 'thirdw', 'fourthw', 'nextw'])
+ train_reader = paddle.batch(
+ paddle.dataset.imikolov.train(word_dict, N), BATCH_SIZE)
+ test_reader = paddle.batch(
+ paddle.dataset.imikolov.test(word_dict, N), BATCH_SIZE)
+
+ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
+
+ def event_handler(event):
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
+ # We output cost every 10 steps.
+ if event.step % 10 == 0:
+ outs = trainer.test(
+ reader=test_reader,
+ feed_order=['firstw', 'secondw', 'thirdw', 'fourthw', 'nextw'])
+ avg_cost = outs[0]
+
+ print("Step %d: Average Cost %f" % (event.step, avg_cost))
+
+ # If average cost is lower than 5.8, we consider the model good enough to stop.
+ # Note 5.8 is a relatively high value. In order to get a better model, one should
+ # aim for avg_cost lower than 3.5. But the training could take longer time.
+ if avg_cost < 5.8:
+ trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
+ trainer.stop()
+
+ if math.isnan(avg_cost):
+ sys.exit("got NaN loss, training failed.")
+
+ trainer = fluid.Trainer(
+ train_func=train_program,
+ optimizer_func=optimizer_func,
+ place=place)
+
+ trainer.train(
+ reader=train_reader,
+ num_epochs=1,
+ event_handler=event_handler,
+ feed_order=['firstw', 'secondw', 'thirdw', 'fourthw', 'nextw'])
```
- `trainer.train`将会开始训练。从`event_handler`返回的监控情况如下:
-```python
+```text
Step 0: Average Cost 7.337213
Step 10: Average Cost 6.136128
Step 20: Average Cost 5.766995
@@ -352,50 +357,49 @@ Step 20: Average Cost 5.766995
```python
def infer(use_cuda, inference_program, params_dirname=None):
-place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
-inferencer = fluid.Inferencer(
-infer_func=inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
-
-# Setup inputs by creating 4 LoDTensors representing 4 words. Here each word
-# is simply an index to look up for the corresponding word vector and hence
-# the shape of word (base_shape) should be [1]. The length-based level of
-# detail (lod) info of each LoDtensor should be [[1]] meaning there is only
-# one lod_level and there is only one sequence of one word on this level.
-# Note that lod info should be a list of lists.
-
-data1 = [[211]] # 'among'
-data2 = [[6]] # 'a'
-data3 = [[96]] # 'group'
-data4 = [[4]] # 'of'
-lod = [[1]]
-
-first_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data1, lod, place)
-second_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data2, lod, place)
-third_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data3, lod, place)
-fourth_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data4, lod, place)
-
-result = inferencer.infer(
-{
-'firstw': first_word,
-'secondw': second_word,
-'thirdw': third_word,
-'fourthw': fourth_word
-},
-return_numpy=False)
-
-print(numpy.array(result[0]))
-most_possible_word_index = numpy.argmax(result[0])
-print(most_possible_word_index)
-print([
-key for key, value in word_dict.iteritems()
-if value == most_possible_word_index
-][0])
+ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
+ inferencer = fluid.Inferencer(
+ infer_func=inference_program, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
+
+ # Setup inputs by creating 4 LoDTensors representing 4 words. Here each word
+ # is simply an index to look up for the corresponding word vector and hence
+ # the shape of word (base_shape) should be [1]. The length-based level of
+ # detail (lod) info of each LoDtensor should be [[1]] meaning there is only
+ # one lod_level and there is only one sequence of one word on this level.
+ # Note that lod info should be a list of lists.
+
+ data1 = [[211]] # 'among'
+ data2 = [[6]] # 'a'
+ data3 = [[96]] # 'group'
+ data4 = [[4]] # 'of'
+ lod = [[1]]
+
+ first_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data1, lod, place)
+ second_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data2, lod, place)
+ third_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data3, lod, place)
+ fourth_word = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data4, lod, place)
+
+ result = inferencer.infer(
+ {
+ 'firstw': first_word,
+ 'secondw': second_word,
+ 'thirdw': third_word,
+ 'fourthw': fourth_word
+ },
+ return_numpy=False)
+
+ print(numpy.array(result[0]))
+ most_possible_word_index = numpy.argmax(result[0])
+ print(most_possible_word_index)
+ print([
+ key for key, value in word_dict.iteritems()
+ if value == most_possible_word_index
+ ][0])
```
在经历3分钟的短暂训练后,我们得到如下的预测。我们的模型预测 `among a group of` 的下一个词是`a`。这比较符合文法规律。如果我们训练时间更长,比如几个小时,那么我们会得到的下一个预测是 `workers`。
-
-```python
+```text
[[0.00106646 0.0007907 0.00072041 ... 0.00049024 0.00041355 0.00084464]]
6
a
@@ -405,20 +409,20 @@ a
```python
def main(use_cuda, is_sparse):
-if use_cuda and not fluid.core.is_compiled_with_cuda():
-return
+ if use_cuda and not fluid.core.is_compiled_with_cuda():
+ return
-params_dirname = "word2vec.inference.model"
+ params_dirname = "word2vec.inference.model"
-train(
-use_cuda=use_cuda,
-train_program=partial(train_program, is_sparse),
-params_dirname=params_dirname)
+ train(
+ use_cuda=use_cuda,
+ train_program=partial(train_program, is_sparse),
+ params_dirname=params_dirname)
-infer(
-use_cuda=use_cuda,
-inference_program=partial(inference_program, is_sparse),
-params_dirname=params_dirname)
+ infer(
+ use_cuda=use_cuda,
+ inference_program=partial(inference_program, is_sparse),
+ params_dirname=params_dirname)
main(use_cuda=use_cuda, is_sparse=True)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/2d_similarity.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/2d_similarity.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 384f59919a2c8dedb198e97d51434616648932e1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/2d_similarity.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 76b7d4bc0f99372465bd9aa34721513d39ad0776..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index d985c393e618e9b79df05e4ff0ae57ccc93744d0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/cbow_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 2e16ab2f443732b8ef5404a8e7cd2457bc5eee23..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2449dce6a86b43b1b997ff418ed0dba56848463f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/ngram.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1e0b40a8f7aefdf46d42761305511f281c08e595..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 158bd64b8f8729dea67834a8d591d21bce8b8564..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/nnlm_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/sentence_emb.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/sentence_emb.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ce4a8bf4769183cbaff91793753d2350a3ce936c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/sentence_emb.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a3ab385845d3dc8b5c670bae91225bc8dd47a8bb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram_en.png b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram_en.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 3c36c6d1f66eb98ea78c0673965d02a4ee3aa288..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/basics/word2vec/image/skipgram_en.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/quick_start/fit_a_line/README.cn.md b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/quick_start/fit_a_line/README.cn.md
index ba43ada5100ed1db7192de9c795b4b8a6596d705..84d971a458038080e3f3883ac35e57059be2786d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/quick_start/fit_a_line/README.cn.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/new_docs/beginners_guide/quick_start/fit_a_line/README.cn.md
@@ -1,144 +1,75 @@
-```eval_rst
-.. _quick_start_fit_a_line:
-```
# 线性回归
让我们从经典的线性回归(Linear Regression \[[1](#参考文献)\])模型开始这份教程。在这一章里,你将使用真实的数据集建立起一个房价预测模型,并且了解到机器学习中的若干重要概念。
-本教程源代码目录在[book/fit_a_line](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/01.fit_a_line), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书)。
+本教程源代码目录在[book/fit_a_line](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/tree/develop/01.fit_a_line), 初次使用请参考PaddlePaddle[安装教程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/README.cn.md#运行这本书),更多内容请参考本教程的[视频课堂](http://bit.baidu.com/course/detail/id/137.html)。
## 背景介绍
-给定一个大小为`$n$`的数据集 `${\{y_{i}, x_{i1}, ..., x_{id}\}}_{i=1}^{n}$`,其中`$x_{i1}, \ldots, x_{id}$`是第`$i$`个样本`$d$`个属性上的取值,`$y_i$`是该样本待预测的目标。线性回归模型假设目标`$y_i$`可以被属性间的线性组合描述,即
+给定一个大小为$n$的数据集 ${\{y_{i}, x_{i1}, ..., x_{id}\}}_{i=1}^{n}$,其中$x_{i1}, \ldots, x_{id}$是第$i$个样本$d$个属性上的取值,$y_i$是该样本待预测的目标。线性回归模型假设目标$y_i$可以被属性间的线性组合描述,即
$$y_i = \omega_1x_{i1} + \omega_2x_{i2} + \ldots + \omega_dx_{id} + b, i=1,\ldots,n$$
-例如,在我们将要建模的房价预测问题里,`$x_{ij}$`是描述房子`$i$`的各种属性(比如房间的个数、周围学校和医院的个数、交通状况等),而 `$y_i$`是房屋的价格。
+例如,在我们将要建模的房价预测问题里,$x_{ij}$是描述房子$i$的各种属性(比如房间的个数、周围学校和医院的个数、交通状况等),而 $y_i$是房屋的价格。
初看起来,这个假设实在过于简单了,变量间的真实关系很难是线性的。但由于线性回归模型有形式简单和易于建模分析的优点,它在实际问题中得到了大量的应用。很多经典的统计学习、机器学习书籍\[[2,3,4](#参考文献)\]也选择对线性模型独立成章重点讲解。
## 效果展示
我们使用从[UCI Housing Data Set](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Housing)获得的波士顿房价数据集进行模型的训练和预测。下面的散点图展示了使用模型对部分房屋价格进行的预测。其中,每个点的横坐标表示同一类房屋真实价格的中位数,纵坐标表示线性回归模型根据特征预测的结果,当二者值完全相等的时候就会落在虚线上。所以模型预测得越准确,则点离虚线越近。
-
-
-图1. 预测值 V.S. 真实值
+
+ 
+ 图1. 预测值 V.S. 真实值
+
## 模型概览
### 模型定义
-在波士顿房价数据集中,和房屋相关的值共有14个:前13个用来描述房屋相关的各种信息,即模型中的 `$x_i$`;最后一个值为我们要预测的该类房屋价格的中位数,即模型中的 `$y_i$`。因此,我们的模型就可以表示成:
+在波士顿房价数据集中,和房屋相关的值共有14个:前13个用来描述房屋相关的各种信息,即模型中的 $x_i$;最后一个值为我们要预测的该类房屋价格的中位数,即模型中的 $y_i$。因此,我们的模型就可以表示成:
$$\hat{Y} = \omega_1X_{1} + \omega_2X_{2} + \ldots + \omega_{13}X_{13} + b$$
-`$\hat{Y}$` 表示模型的预测结果,用来和真实值`$Y$`区分。模型要学习的参数即:`$\omega_1, \ldots, \omega_{13}, b$`。
+$\hat{Y}$ 表示模型的预测结果,用来和真实值$Y$区分。模型要学习的参数即:$\omega_1, \ldots, \omega_{13}, b$。
-建立模型后,我们需要给模型一个优化目标,使得学到的参数能够让预测值`$\hat{Y}$`尽可能地接近真实值`$Y$`。这里我们引入损失函数([Loss Function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Loss_function),或Cost Function)这个概念。 输入任意一个数据样本的目标值`$y_{i}$`和模型给出的预测值`$\hat{y_{i}}$`,损失函数输出一个非负的实值。这个实值通常用来反映模型误差的大小。
+建立模型后,我们需要给模型一个优化目标,使得学到的参数能够让预测值$\hat{Y}$尽可能地接近真实值$Y$。这里我们引入损失函数([Loss Function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Loss_function),或Cost Function)这个概念。 输入任意一个数据样本的目标值$y_{i}$和模型给出的预测值$\hat{y_{i}}$,损失函数输出一个非负的实值。这个实值通常用来反映模型误差的大小。
对于线性回归模型来讲,最常见的损失函数就是均方误差(Mean Squared Error, [MSE](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mean_squared_error))了,它的形式是:
$$MSE=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}{(\hat{Y_i}-Y_i)}^2$$
-即对于一个大小为`$n$`的测试集,`$MSE$`是`$n$`个数据预测结果误差平方的均值。
+即对于一个大小为$n$的测试集,$MSE$是$n$个数据预测结果误差平方的均值。
### 训练过程
定义好模型结构之后,我们要通过以下几个步骤进行模型训练
-1. 初始化参数,其中包括权重`$\omega_i$`和偏置`$b$`,对其进行初始化(如0均值,1方差)。
-2. 网络正向传播计算网络输出和损失函数。
-3. 根据损失函数进行反向误差传播 ([backpropagation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backpropagation)),将网络误差从输出层依次向前传递, 并更新网络中的参数。
-4. 重复2~3步骤,直至网络训练误差达到规定的程度或训练轮次达到设定值。
+ 1. 初始化参数,其中包括权重$\omega_i$和偏置$b$,对其进行初始化(如0均值,1方差)。
+ 2. 网络正向传播计算网络输出和损失函数。
+ 3. 根据损失函数进行反向误差传播 ([backpropagation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backpropagation)),将网络误差从输出层依次向前传递, 并更新网络中的参数。
+ 4. 重复2~3步骤,直至网络训练误差达到规定的程度或训练轮次达到设定值。
## 数据集
### 数据集介绍
这份数据集共506行,每行包含了波士顿郊区的一类房屋的相关信息及该类房屋价格的中位数。其各维属性的意义如下:
-
-
-
-
- | 属性名 |
- 解释 |
- 类型 |
-
-
-
-
- | CRIM |
- 该镇的人均犯罪率 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | ZN |
- 占地面积超过25,000平方呎的住宅用地比例 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | INDUS |
- 非零售商业用地比例 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | CHAS |
- 是否邻近 Charles River |
- 离散值,1=邻近;0=不邻近 |
-
-
- | NOX |
- 一氧化氮浓度 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | RM |
- 每栋房屋的平均客房数 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | AGE |
- 1940年之前建成的自用单位比例 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | DIS |
- 到波士顿5个就业中心的加权距离 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | RAD |
- 到径向公路的可达性指数 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | TAX |
- 全值财产税率 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | PTRATIO |
- 学生与教师的比例 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | B |
- 1000(BK - 0.63)^2,其中BK为黑人占比 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | LSTAT |
- 低收入人群占比 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
- | MEDV |
- 同类房屋价格的中位数 |
- 连续值 |
-
-
-
-
+| 属性名 | 解释 | 类型 |
+| ------| ------ | ------ |
+| CRIM | 该镇的人均犯罪率 | 连续值 |
+| ZN | 占地面积超过25,000平方呎的住宅用地比例 | 连续值 |
+| INDUS | 非零售商业用地比例 | 连续值 |
+| CHAS | 是否邻近 Charles River | 离散值,1=邻近;0=不邻近 |
+| NOX | 一氧化氮浓度 | 连续值 |
+| RM | 每栋房屋的平均客房数 | 连续值 |
+| AGE | 1940年之前建成的自用单位比例 | 连续值 |
+| DIS | 到波士顿5个就业中心的加权距离 | 连续值 |
+| RAD | 到径向公路的可达性指数 | 连续值 |
+| TAX | 全值财产税率 | 连续值 |
+| PTRATIO | 学生与教师的比例 | 连续值 |
+| B | 1000(BK - 0.63)^2,其中BK为黑人占比 | 连续值 |
+| LSTAT | 低收入人群占比 | 连续值 |
+| MEDV | 同类房屋价格的中位数 | 连续值 |
### 数据预处理
#### 连续值与离散值
-观察一下数据,我们的第一个发现是:所有的13维属性中,有12维的连续值和1维的离散值(CHAS)。离散值虽然也常使用类似0、1、2这样的数字表示,但是其含义与连续值是不同的,因为这里的差值没有实际意义。例如,我们用0、1、2来分别表示红色、绿色和蓝色的话,我们并不能因此说“蓝色和红色”比“绿色和红色”的距离更远。所以通常对一个有`$d$`个可能取值的离散属性,我们会将它们转为`$d$`个取值为0或1的二值属性或者将每个可能取值映射为一个多维向量。不过就这里而言,因为CHAS本身就是一个二值属性,就省去了这个麻烦。
+观察一下数据,我们的第一个发现是:所有的13维属性中,有12维的连续值和1维的离散值(CHAS)。离散值虽然也常使用类似0、1、2这样的数字表示,但是其含义与连续值是不同的,因为这里的差值没有实际意义。例如,我们用0、1、2来分别表示红色、绿色和蓝色的话,我们并不能因此说“蓝色和红色”比“绿色和红色”的距离更远。所以通常对一个有$d$个可能取值的离散属性,我们会将它们转为$d$个取值为0或1的二值属性或者将每个可能取值映射为一个多维向量。不过就这里而言,因为CHAS本身就是一个二值属性,就省去了这个麻烦。
#### 属性的归一化
另外一个稍加观察即可发现的事实是,各维属性的取值范围差别很大(如图2所示)。例如,属性B的取值范围是[0.32, 396.90],而属性NOX的取值范围是[0.3850, 0.8170]。这里就要用到一个常见的操作-归一化(normalization)了。归一化的目标是把各位属性的取值范围放缩到差不多的区间,例如[-0.5,0.5]。这里我们使用一种很常见的操作方法:减掉均值,然后除以原取值范围。
@@ -148,11 +79,13 @@ $$MSE=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}{(\hat{Y_i}-Y_i)}^2$$
- 不同的数值范围会导致不同属性对模型的重要性不同(至少在训练的初始阶段如此),而这个隐含的假设常常是不合理的。这会对优化的过程造成困难,使训练时间大大的加长。
- 很多的机器学习技巧/模型(例如L1,L2正则项,向量空间模型-Vector Space Model)都基于这样的假设:所有的属性取值都差不多是以0为均值且取值范围相近的。
-
-图2. 各维属性的取值范围
+
+ 
+ 图2. 各维属性的取值范围
+
#### 整理训练集与测试集
-我们将数据集分割为两份:一份用于调整模型的参数,即进行模型的训练,模型在这份数据集上的误差被称为**训练误差**;另外一份被用来测试,模型在这份数据集上的误差被称为**测试误差**。我们训练模型的目的是为了通过从训练数据中找到规律来预测未知的新数据,所以测试误差是更能反映模型表现的指标。分割数据的比例要考虑到两个因素:更多的训练数据会降低参数估计的方差,从而得到更可信的模型;而更多的测试数据会降低测试误差的方差,从而得到更可信的测试误差。我们这个例子中设置的分割比例为`$8:2$`
+我们将数据集分割为两份:一份用于调整模型的参数,即进行模型的训练,模型在这份数据集上的误差被称为**训练误差**;另外一份被用来测试,模型在这份数据集上的误差被称为**测试误差**。我们训练模型的目的是为了通过从训练数据中找到规律来预测未知的新数据,所以测试误差是更能反映模型表现的指标。分割数据的比例要考虑到两个因素:更多的训练数据会降低参数估计的方差,从而得到更可信的模型;而更多的测试数据会降低测试误差的方差,从而得到更可信的测试误差。我们这个例子中设置的分割比例为$8:2$
在更复杂的模型训练过程中,我们往往还会多使用一种数据集:验证集。因为复杂的模型中常常还有一些超参数([Hyperparameter](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperparameter_optimization))需要调节,所以我们会尝试多种超参数的组合来分别训练多个模型,然后对比它们在验证集上的表现选择相对最好的一组超参数,最后才使用这组参数下训练的模型在测试集上评估测试误差。由于本章训练的模型比较简单,我们暂且忽略掉这个过程。
@@ -167,6 +100,7 @@ $$MSE=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}{(\hat{Y_i}-Y_i)}^2$$
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy
+from __future__ import print_function
```
我们通过uci_housing模块引入了数据集合[UCI Housing Data Set](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Housing)
@@ -182,14 +116,14 @@ import numpy
BATCH_SIZE = 20
train_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.uci_housing.train(), buf_size=500),
-batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.uci_housing.train(), buf_size=500),
+ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
test_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.uci_housing.test(), buf_size=500),
-batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.uci_housing.test(), buf_size=500),
+ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
```
### 配置训练程序
@@ -197,16 +131,25 @@ batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
```python
def train_program():
-y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[1], dtype='float32')
+ y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[1], dtype='float32')
-# feature vector of length 13
-x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[13], dtype='float32')
-y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
+ # feature vector of length 13
+ x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[13], dtype='float32')
+ y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
-loss = fluid.layers.square_error_cost(input=y_predict, label=y)
-avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ loss = fluid.layers.square_error_cost(input=y_predict, label=y)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
-return avg_loss
+ return avg_loss
+```
+
+### Optimizer Function 配置
+
+在下面的 `SGD optimizer`,`learning_rate` 是训练的速度,与网络的训练收敛速度有关系。
+
+```python
+def optimizer_program():
+ return fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001)
```
### 定义运算场所
@@ -222,9 +165,9 @@ place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
```python
trainer = fluid.Trainer(
-train_func=train_program,
-place=place,
-optimizer_func=fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001))
+ train_func=train_program,
+ place=place,
+ optimizer_func=optimizer_program)
```
### 开始提供数据
@@ -237,7 +180,7 @@ feed_order=['x', 'y']
除此之外,可以定义一个事件相应器来处理类似`打印训练进程`的事件:
```python
-# Specify the directory path to save the parameters
+# Specify the directory to save the parameters
params_dirname = "fit_a_line.inference.model"
# Plot data
@@ -248,27 +191,30 @@ plot_cost = Ploter(train_title, test_title)
step = 0
-# event_handler to print training and testing info
+# event_handler prints training and testing info
def event_handler_plot(event):
-global step
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
-if event.step % 10 == 0: # every 10 batches, record a test cost
-test_metrics = trainer.test(
-reader=test_reader, feed_order=feed_order)
-
-plot_cost.append(test_title, step, test_metrics[0])
-plot_cost.plot()
-
-if test_metrics[0] < 10.0:
-# If the accuracy is good enough, we can stop the training.
-print('loss is less than 10.0, stop')
-trainer.stop()
-
-# We can save the trained parameters for the inferences later
-if params_dirname is not None:
-trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
-
-step += 1
+ global step
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
+ if step % 10 == 0: # record a train cost every 10 batches
+ plot_cost.append(train_title, step, event.metrics[0])
+
+ if step % 100 == 0: # record a test cost every 100 batches
+ test_metrics = trainer.test(
+ reader=test_reader, feed_order=feed_order)
+ plot_cost.append(test_title, step, test_metrics[0])
+ plot_cost.plot()
+
+ if test_metrics[0] < 10.0:
+ # If the accuracy is good enough, we can stop the training.
+ print('loss is less than 10.0, stop')
+ trainer.stop()
+ step += 1
+
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndEpochEvent):
+ if event.epoch % 10 == 0:
+ # We can save the trained parameters for the inferences later
+ if params_dirname is not None:
+ trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
```
### 开始训练
@@ -279,13 +225,16 @@ step += 1
# The training could take up to a few minutes.
trainer.train(
-reader=train_reader,
-num_epochs=100,
-event_handler=event_handler_plot,
-feed_order=feed_order)
+ reader=train_reader,
+ num_epochs=100,
+ event_handler=event_handler_plot,
+ feed_order=feed_order)
```
+
+

+图3 训练结果
+
图1. MNIST图片示例
+
+
+图1. MNIST图片示例
+
MNIST数据集是从 [NIST](https://www.nist.gov/srd/nist-special-database-19) 的Special Database 3(SD-3)和Special Database 1(SD-1)构建而来。由于SD-3是由美国人口调查局的员工进行标注,SD-1是由美国高中生进行标注,因此SD-3比SD-1更干净也更容易识别。Yann LeCun等人从SD-1和SD-3中各取一半作为MNIST的训练集(60000条数据)和测试集(10000条数据),其中训练集来自250位不同的标注员,此外还保证了训练集和测试集的标注员是不完全相同的。
@@ -20,86 +22,96 @@ Yann LeCun早先在手写字符识别上做了很多研究,并在研究过程
## 模型概览
基于MNIST数据训练一个分类器,在介绍本教程使用的三个基本图像分类网络前,我们先给出一些定义:
-- `$X$`是输入:MNIST图片是`$28\times28$` 的二维图像,为了进行计算,我们将其转化为`$784$`维向量,即`$X=\left ( x_0, x_1, \dots, x_{783} \right )$`。
-- `$Y$`是输出:分类器的输出是10类数字(0-9),即`$Y=\left ( y_0, y_1, \dots, y_9 \right )$`,每一维`$y_i$`代表图片分类为第`$i$`类数字的概率。
-- `$L$`是图片的真实标签:`$L=\left ( l_0, l_1, \dots, l_9 \right )$`也是10维,但只有一维为1,其他都为0。
+- $X$是输入:MNIST图片是$28\times28$ 的二维图像,为了进行计算,我们将其转化为$784$维向量,即$X=\left ( x_0, x_1, \dots, x_{783} \right )$。
+- $Y$是输出:分类器的输出是10类数字(0-9),即$Y=\left ( y_0, y_1, \dots, y_9 \right )$,每一维$y_i$代表图片分类为第$i$类数字的概率。
+- $L$是图片的真实标签:$L=\left ( l_0, l_1, \dots, l_9 \right )$也是10维,但只有一维为1,其他都为0。
### Softmax回归(Softmax Regression)
最简单的Softmax回归模型是先将输入层经过一个全连接层得到的特征,然后直接通过softmax 函数进行多分类\[[9](#参考文献)\]。
-输入层的数据`$X$`传到输出层,在激活操作之前,会乘以相应的权重 `$W$` ,并加上偏置变量 `$b$` ,具体如下:
+输入层的数据$X$传到输出层,在激活操作之前,会乘以相应的权重 $W$ ,并加上偏置变量 $b$ ,具体如下:
$$ y_i = \text{softmax}(\sum_j W_{i,j}x_j + b_i) $$
-其中 `$ \text{softmax}(x_i) = \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_j e^{x_j}} $`
+其中 $ \text{softmax}(x_i) = \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_j e^{x_j}} $
-对于有 `$N$` 个类别的多分类问题,指定 `$N$` 个输出节点,`$N$` 维结果向量经过softmax将归一化为 `$N$` 个[0,1]范围内的实数值,分别表示该样本属于这 `$N$` 个类别的概率。此处的 `$y_i$` 即对应该图片为数字 `$i$` 的预测概率。
+对于有 $N$ 个类别的多分类问题,指定 $N$ 个输出节点,$N$ 维结果向量经过softmax将归一化为 $N$ 个[0,1]范围内的实数值,分别表示该样本属于这 $N$ 个类别的概率。此处的 $y_i$ 即对应该图片为数字 $i$ 的预测概率。
-在分类问题中,我们一般采用交叉熵代价损失函数(cross entropy),公式如下:
+在分类问题中,我们一般采用交叉熵代价损失函数(cross entropy loss),公式如下:
-$$ \text{crossentropy}(label, y) = -\sum_i label_ilog(y_i) $$
+$$ L_{cross-entropy}(label, y) = -\sum_i label_ilog(y_i) $$
图2为softmax回归的网络图,图中权重用蓝线表示、偏置用红线表示、+1代表偏置参数的系数为1。
-
-图2. softmax回归网络结构图
+
+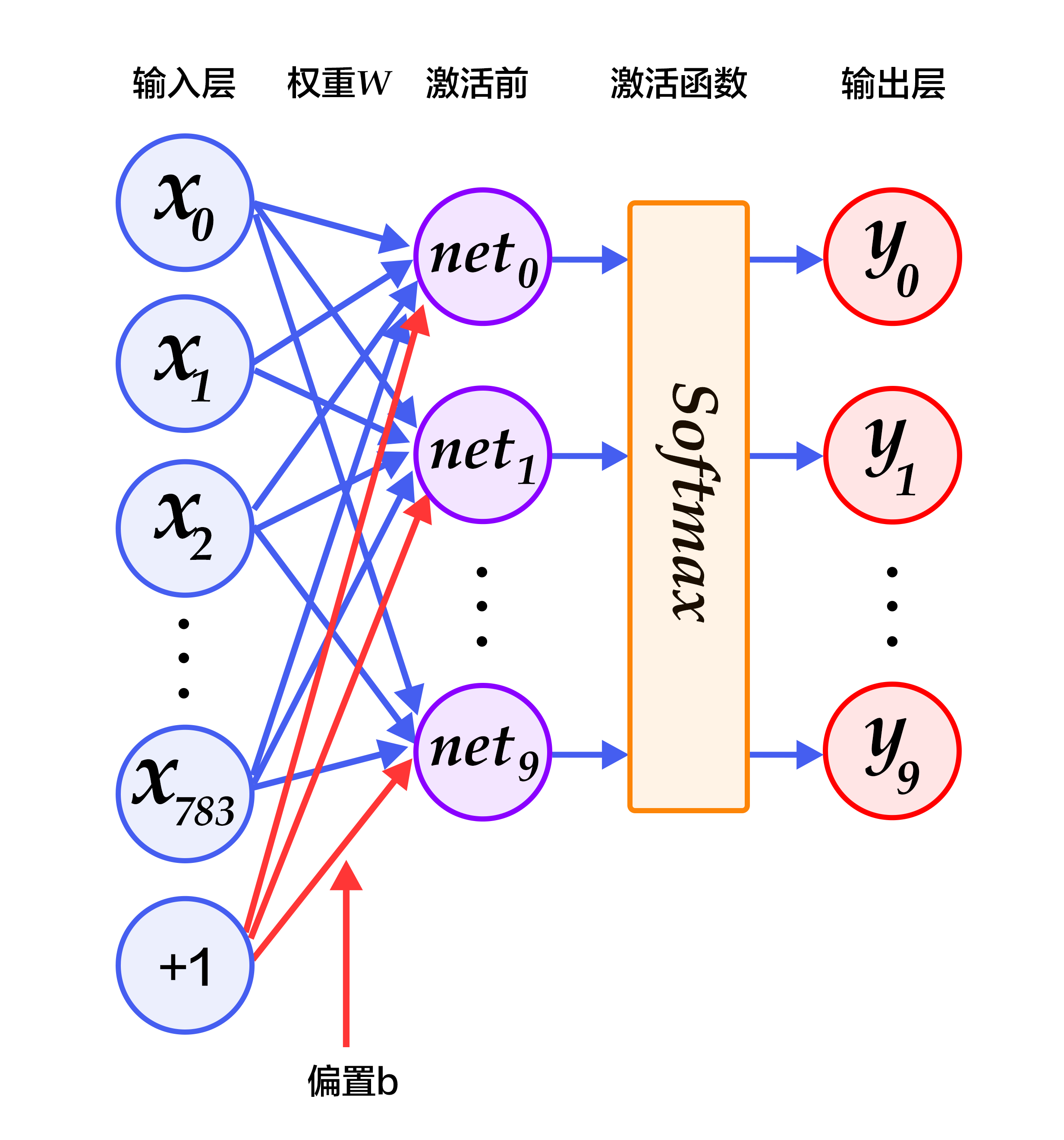
+图2. softmax回归网络结构图
+
### 多层感知器(Multilayer Perceptron, MLP)
Softmax回归模型采用了最简单的两层神经网络,即只有输入层和输出层,因此其拟合能力有限。为了达到更好的识别效果,我们考虑在输入层和输出层中间加上若干个隐藏层\[[10](#参考文献)\]。
-1. 经过第一个隐藏层,可以得到 `$ H_1 = \phi(W_1X + b_1) $`,其中`$\phi$`代表激活函数,常见的有sigmoid、tanh或ReLU等函数。
-2. 经过第二个隐藏层,可以得到 `$ H_2 = \phi(W_2H_1 + b_2) $`。
-3. 最后,再经过输出层,得到的`$Y=\text{softmax}(W_3H_2 + b_3)$`,即为最后的分类结果向量。
+1. 经过第一个隐藏层,可以得到 $ H_1 = \phi(W_1X + b_1) $,其中$\phi$代表激活函数,常见的有sigmoid、tanh或ReLU等函数。
+2. 经过第二个隐藏层,可以得到 $ H_2 = \phi(W_2H_1 + b_2) $。
+3. 最后,再经过输出层,得到的$Y=\text{softmax}(W_3H_2 + b_3)$,即为最后的分类结果向量。
图3为多层感知器的网络结构图,图中权重用蓝线表示、偏置用红线表示、+1代表偏置参数的系数为1。
-
-图3. 多层感知器网络结构图
+
+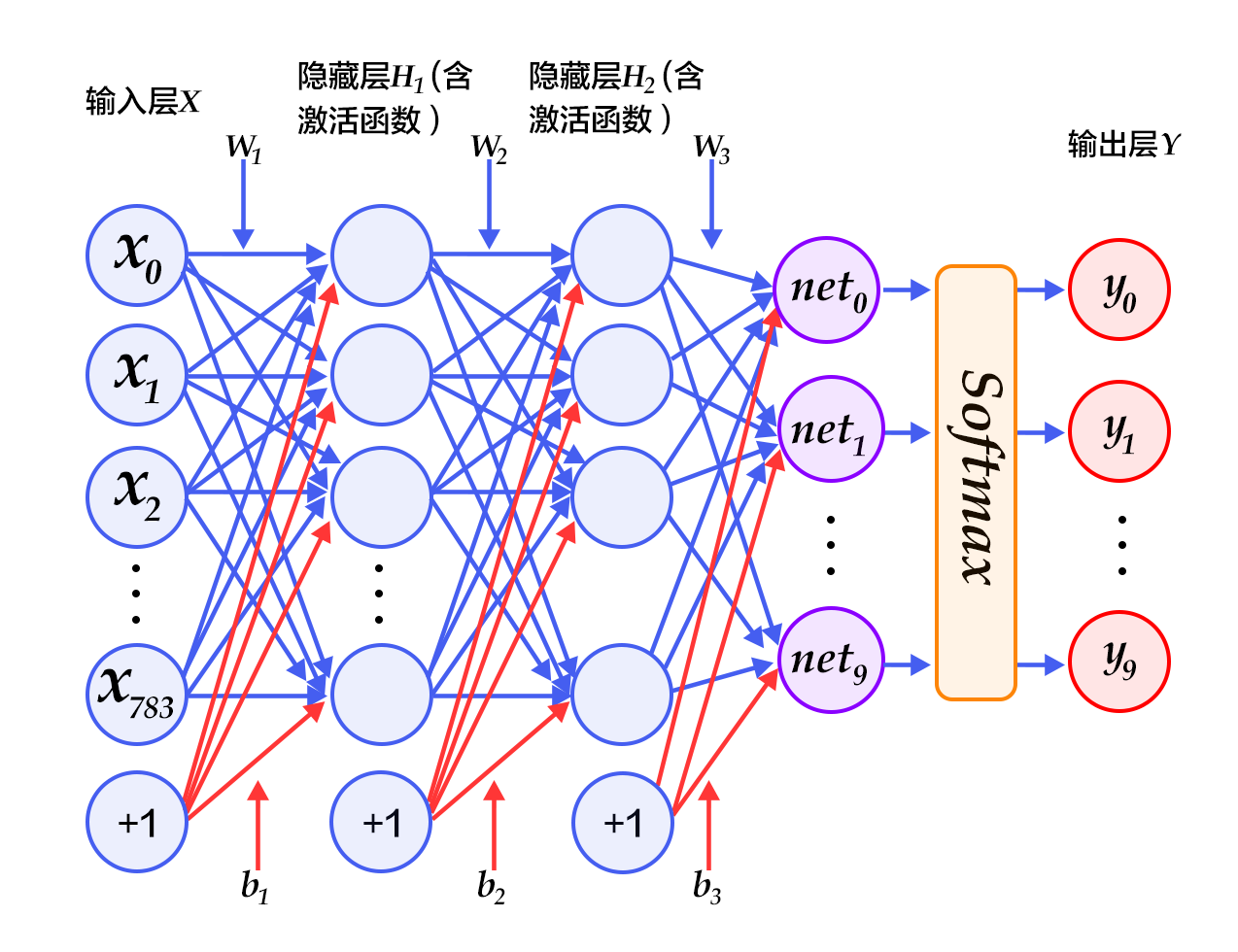
+图3. 多层感知器网络结构图
+
### 卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)
在多层感知器模型中,将图像展开成一维向量输入到网络中,忽略了图像的位置和结构信息,而卷积神经网络能够更好的利用图像的结构信息。[LeNet-5](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/lenet/)是一个较简单的卷积神经网络。图4显示了其结构:输入的二维图像,先经过两次卷积层到池化层,再经过全连接层,最后使用softmax分类作为输出层。下面我们主要介绍卷积层和池化层。
-
-图4. LeNet-5卷积神经网络结构
+
+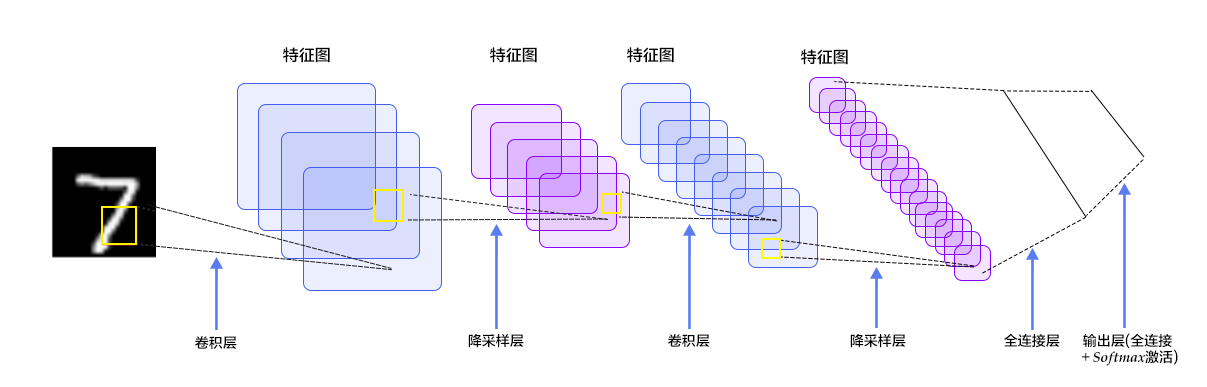
+图4. LeNet-5卷积神经网络结构
+
#### 卷积层
卷积层是卷积神经网络的核心基石。在图像识别里我们提到的卷积是二维卷积,即离散二维滤波器(也称作卷积核)与二维图像做卷积操作,简单的讲是二维滤波器滑动到二维图像上所有位置,并在每个位置上与该像素点及其领域像素点做内积。卷积操作被广泛应用与图像处理领域,不同卷积核可以提取不同的特征,例如边沿、线性、角等特征。在深层卷积神经网络中,通过卷积操作可以提取出图像低级到复杂的特征。
-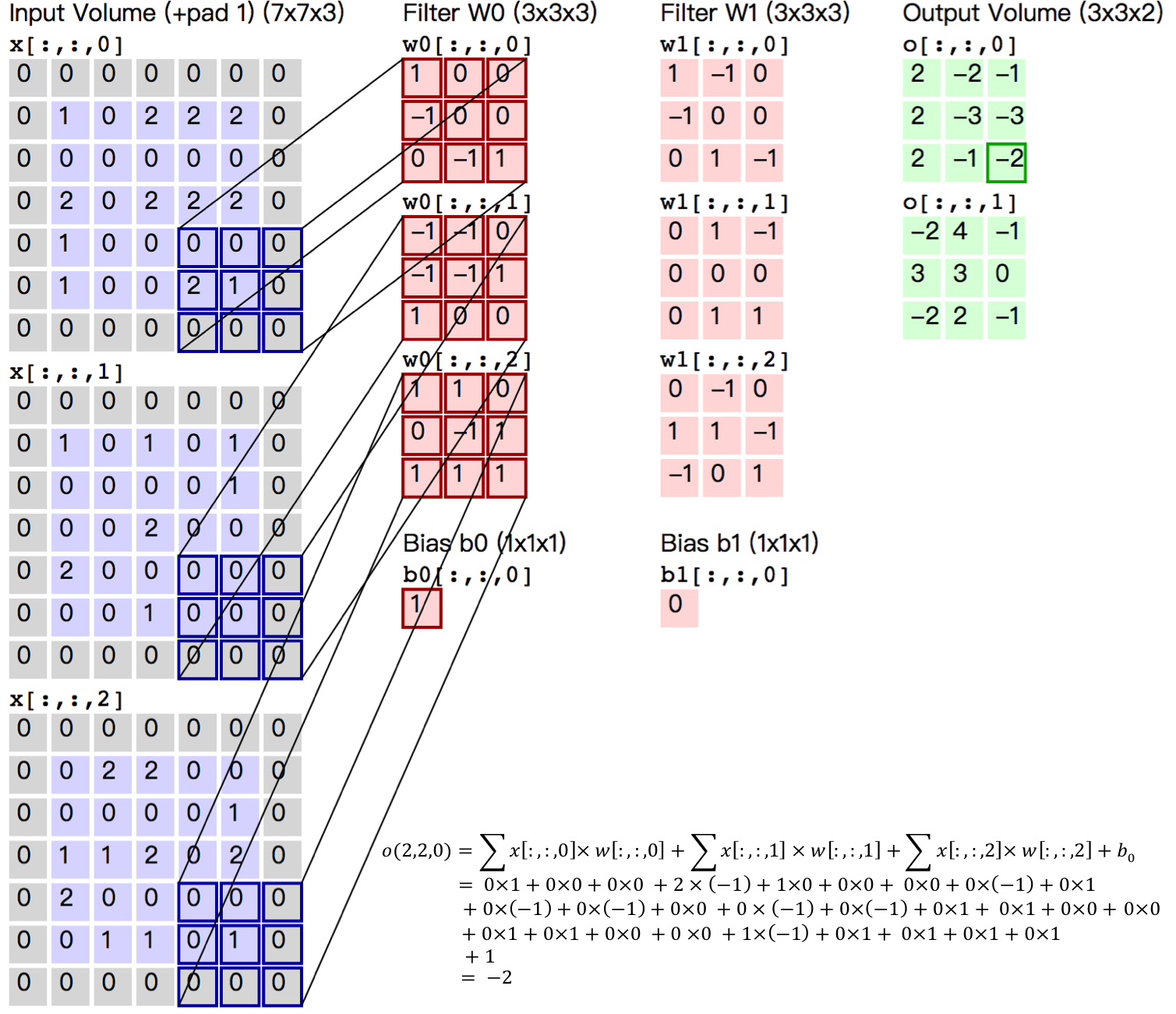
-图5. 卷积层图片
+
+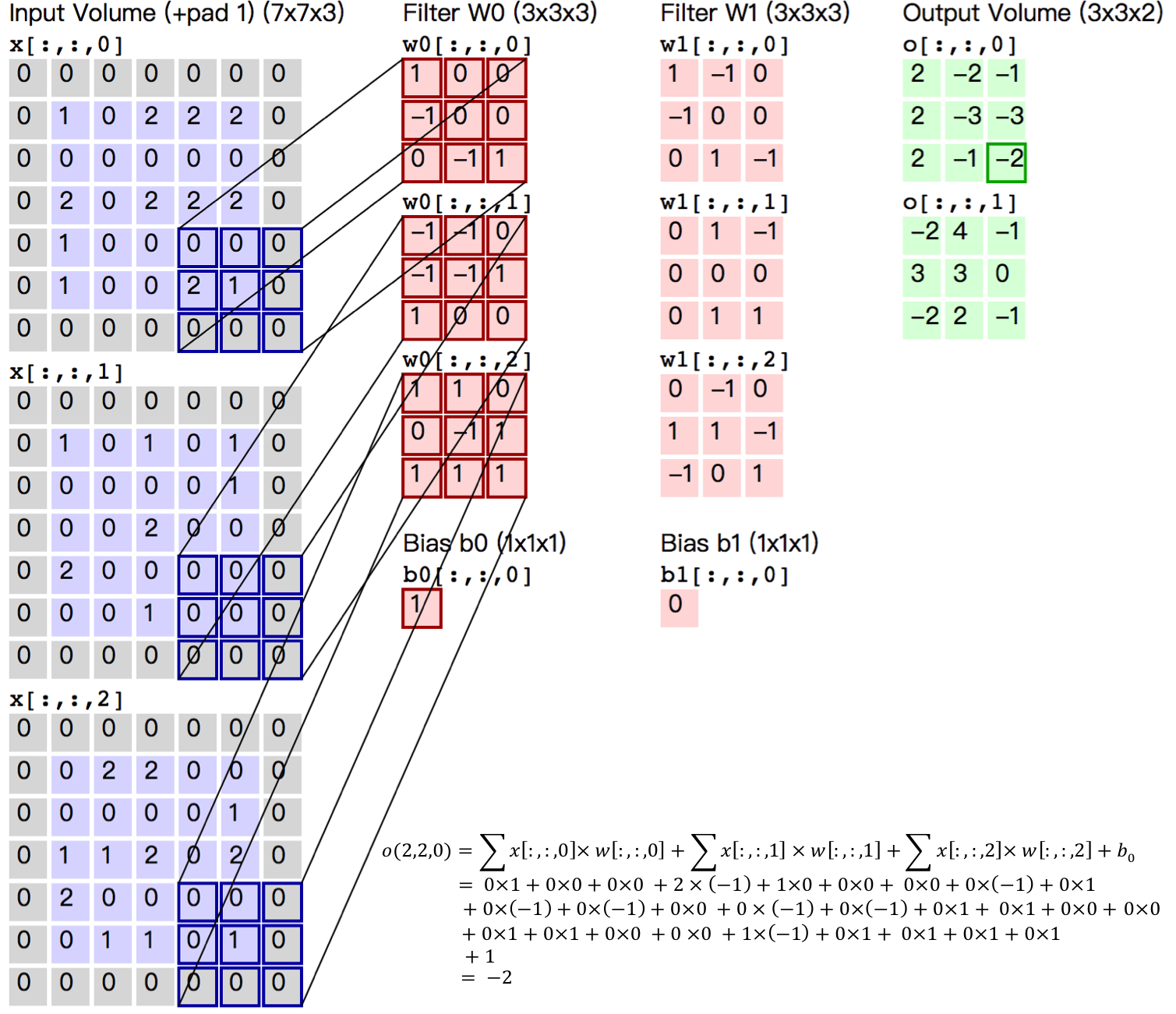
+图5. 卷积层图片
+
-图5给出一个卷积计算过程的示例图,输入图像大小为`$H=5,W=5,D=3$`,即`$5 \times 5$`大小的3通道(RGB,也称作深度)彩色图像。这个示例图中包含两(用`$K$`表示)组卷积核,即图中滤波器`$W_0$`和`$W_1$`。在卷积计算中,通常对不同的输入通道采用不同的卷积核,如图示例中每组卷积核包含(`$D=3$`)个`$3 \times 3$`(用`$F \times F$`表示)大小的卷积核。另外,这个示例中卷积核在图像的水平方向(`$W$`方向)和垂直方向(`$H$`方向)的滑动步长为2(用`$S$`表示);对输入图像周围各填充1(用`$P$`表示)个0,即图中输入层原始数据为蓝色部分,灰色部分是进行了大小为1的扩展,用0来进行扩展。经过卷积操作得到输出为`$3 \times 3 \times 2$`(用`$H_{o} \times W_{o} \times K$`表示)大小的特征图,即`$3 \times 3$`大小的2通道特征图,其中`$H_o$`计算公式为:`$H_o = (H - F + 2 \times P)/S + 1$`,`$W_o$`同理。 而输出特征图中的每个像素,是每组滤波器与输入图像每个特征图的内积再求和,再加上偏置`$b_o$`,偏置通常对于每个输出特征图是共享的。输出特征图`$o[:,:,0]$`中的最后一个`$-2$`计算如图5右下角公式所示。
+图5给出一个卷积计算过程的示例图,输入图像大小为$H=5,W=5,D=3$,即$5 \times 5$大小的3通道(RGB,也称作深度)彩色图像。这个示例图中包含两(用$K$表示)组卷积核,即图中滤波器$W_0$和$W_1$。在卷积计算中,通常对不同的输入通道采用不同的卷积核,如图示例中每组卷积核包含($D=3)$个$3 \times 3$(用$F \times F$表示)大小的卷积核。另外,这个示例中卷积核在图像的水平方向($W$方向)和垂直方向($H$方向)的滑动步长为2(用$S$表示);对输入图像周围各填充1(用$P$表示)个0,即图中输入层原始数据为蓝色部分,灰色部分是进行了大小为1的扩展,用0来进行扩展。经过卷积操作得到输出为$3 \times 3 \times 2$(用$H_{o} \times W_{o} \times K$表示)大小的特征图,即$3 \times 3$大小的2通道特征图,其中$H_o$计算公式为:$H_o = (H - F + 2 \times P)/S + 1$,$W_o$同理。 而输出特征图中的每个像素,是每组滤波器与输入图像每个特征图的内积再求和,再加上偏置$b_o$,偏置通常对于每个输出特征图是共享的。输出特征图$o[:,:,0]$中的最后一个$-2$计算如图5右下角公式所示。
-在卷积操作中卷积核是可学习的参数,经过上面示例介绍,每层卷积的参数大小为`$D \times F \times F \times K$`。在多层感知器模型中,神经元通常是全部连接,参数较多。而卷积层的参数较少,这也是由卷积层的主要特性即局部连接和共享权重所决定。
+在卷积操作中卷积核是可学习的参数,经过上面示例介绍,每层卷积的参数大小为$D \times F \times F \times K$。在多层感知器模型中,神经元通常是全部连接,参数较多。而卷积层的参数较少,这也是由卷积层的主要特性即局部连接和共享权重所决定。
- 局部连接:每个神经元仅与输入神经元的一块区域连接,这块局部区域称作感受野(receptive field)。在图像卷积操作中,即神经元在空间维度(spatial dimension,即上图示例H和W所在的平面)是局部连接,但在深度上是全部连接。对于二维图像本身而言,也是局部像素关联较强。这种局部连接保证了学习后的过滤器能够对于局部的输入特征有最强的响应。局部连接的思想,也是受启发于生物学里面的视觉系统结构,视觉皮层的神经元就是局部接受信息的。
-- 权重共享:计算同一个深度切片的神经元时采用的滤波器是共享的。例如图4中计算`$o[:,:,0]$`的每个每个神经元的滤波器均相同,都为`$W_0$`,这样可以很大程度上减少参数。共享权重在一定程度上讲是有意义的,例如图片的底层边缘特征与特征在图中的具体位置无关。但是在一些场景中是无意的,比如输入的图片是人脸,眼睛和头发位于不同的位置,希望在不同的位置学到不同的特征 (参考[斯坦福大学公开课]( http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/))。请注意权重只是对于同一深度切片的神经元是共享的,在卷积层,通常采用多组卷积核提取不同特征,即对应不同深度切片的特征,不同深度切片的神经元权重是不共享。另外,偏重对同一深度切片的所有神经元都是共享的。
+- 权重共享:计算同一个深度切片的神经元时采用的滤波器是共享的。例如图4中计算$o[:,:,0]$的每个每个神经元的滤波器均相同,都为$W_0$,这样可以很大程度上减少参数。共享权重在一定程度上讲是有意义的,例如图片的底层边缘特征与特征在图中的具体位置无关。但是在一些场景中是无意的,比如输入的图片是人脸,眼睛和头发位于不同的位置,希望在不同的位置学到不同的特征 (参考[斯坦福大学公开课]( http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/))。请注意权重只是对于同一深度切片的神经元是共享的,在卷积层,通常采用多组卷积核提取不同特征,即对应不同深度切片的特征,不同深度切片的神经元权重是不共享。另外,偏重对同一深度切片的所有神经元都是共享的。
通过介绍卷积计算过程及其特性,可以看出卷积是线性操作,并具有平移不变性(shift-invariant),平移不变性即在图像每个位置执行相同的操作。卷积层的局部连接和权重共享使得需要学习的参数大大减小,这样也有利于训练较大卷积神经网络。
#### 池化层
-
-图6. 池化层图片
+
+
+图6. 池化层图片
+
池化是非线性下采样的一种形式,主要作用是通过减少网络的参数来减小计算量,并且能够在一定程度上控制过拟合。通常在卷积层的后面会加上一个池化层。池化包括最大池化、平均池化等。其中最大池化是用不重叠的矩形框将输入层分成不同的区域,对于每个矩形框的数取最大值作为输出层,如图6所示。
更详细的关于卷积神经网络的具体知识可以参考[斯坦福大学公开课]( http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/ )和[图像分类](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book/blob/develop/image_classification/README.md)教程。
-### 常见激活函数介绍
-- sigmoid激活函数: `$ f(x) = sigmoid(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} $`
+### 常见激活函数介绍
+- sigmoid激活函数: $ f(x) = sigmoid(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} $
-- tanh激活函数: `$ f(x) = tanh(x) = \frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} $`
+- tanh激活函数: $ f(x) = tanh(x) = \frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} $
-实际上,tanh函数只是规模变化的sigmoid函数,将sigmoid函数值放大2倍之后再向下平移1个单位:tanh(x) = 2sigmoid(2x) - 1 。
+ 实际上,tanh函数只是规模变化的sigmoid函数,将sigmoid函数值放大2倍之后再向下平移1个单位:tanh(x) = 2sigmoid(2x) - 1 。
-- ReLU激活函数: `$ f(x) = max(0, x) $`
+- ReLU激活函数: $ f(x) = max(0, x) $
更详细的介绍请参考[维基百科激活函数](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Activation_function)。
@@ -107,35 +119,13 @@ Softmax回归模型采用了最简单的两层神经网络,即只有输入层
PaddlePaddle在API中提供了自动加载[MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)数据的模块`paddle.dataset.mnist`。加载后的数据位于`/home/username/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist`下:
-
-
-
-
- | 文件名称 |
- 说明 |
-
-
-
-
-
- | train-images-idx3-ubyte |
- 训练数据图片,60,000条数据 |
-
-
- | train-labels-idx1-ubyte |
- 训练数据标签,60,000条数据 |
-
-
- | t10k-images-idx3-ubyte |
- 测试数据图片,10,000条数据 |
-
-
- | t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte |
- 测试数据标签,10,000条数据 |
-
-
-
-
+
+| 文件名称 | 说明 |
+|----------------------|-------------------------|
+|train-images-idx3-ubyte| 训练数据图片,60,000条数据 |
+|train-labels-idx1-ubyte| 训练数据标签,60,000条数据 |
+|t10k-images-idx3-ubyte | 测试数据图片,10,000条数据 |
+|t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte | 测试数据标签,10,000条数据 |
## Fluid API 概述
@@ -165,6 +155,7 @@ PaddlePaddle在API中提供了自动加载[MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mni
```python
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
+from __future__ import print_function
```
### Program Functions 配置
@@ -177,51 +168,51 @@ import paddle.fluid as fluid
```python
def softmax_regression():
-img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
-predict = fluid.layers.fc(
-input=img, size=10, act='softmax')
-return predict
+ img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
+ predict = fluid.layers.fc(
+ input=img, size=10, act='softmax')
+ return predict
```
- 多层感知器:下面代码实现了一个含有两个隐藏层(即全连接层)的多层感知器。其中两个隐藏层的激活函数均采用ReLU,输出层的激活函数用Softmax。
```python
def multilayer_perceptron():
-img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
-# 第一个全连接层,激活函数为ReLU
-hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=img, size=200, act='relu')
-# 第二个全连接层,激活函数为ReLU
-hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden, size=200, act='relu')
-# 以softmax为激活函数的全连接输出层,输出层的大小必须为数字的个数10
-prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden, size=10, act='softmax')
-return prediction
+ img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
+ # 第一个全连接层,激活函数为ReLU
+ hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=img, size=200, act='relu')
+ # 第二个全连接层,激活函数为ReLU
+ hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden, size=200, act='relu')
+ # 以softmax为激活函数的全连接输出层,输出层的大小必须为数字的个数10
+ prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden, size=10, act='softmax')
+ return prediction
```
- 卷积神经网络LeNet-5: 输入的二维图像,首先经过两次卷积层到池化层,再经过全连接层,最后使用以softmax为激活函数的全连接层作为输出层。
```python
def convolutional_neural_network():
-img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
-# 第一个卷积-池化层
-conv_pool_1 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
-input=img,
-filter_size=5,
-num_filters=20,
-pool_size=2,
-pool_stride=2,
-act="relu")
-conv_pool_1 = fluid.layers.batch_norm(conv_pool_1)
-# 第二个卷积-池化层
-conv_pool_2 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
-input=conv_pool_1,
-filter_size=5,
-num_filters=50,
-pool_size=2,
-pool_stride=2,
-act="relu")
-# 以softmax为激活函数的全连接输出层,输出层的大小必须为数字的个数10
-prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=conv_pool_2, size=10, act='softmax')
-return prediction
+ img = fluid.layers.data(name='img', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
+ # 第一个卷积-池化层
+ conv_pool_1 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
+ input=img,
+ filter_size=5,
+ num_filters=20,
+ pool_size=2,
+ pool_stride=2,
+ act="relu")
+ conv_pool_1 = fluid.layers.batch_norm(conv_pool_1)
+ # 第二个卷积-池化层
+ conv_pool_2 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
+ input=conv_pool_1,
+ filter_size=5,
+ num_filters=50,
+ pool_size=2,
+ pool_stride=2,
+ act="relu")
+ # 以softmax为激活函数的全连接输出层,输出层的大小必须为数字的个数10
+ prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=conv_pool_2, size=10, act='softmax')
+ return prediction
```
#### Train Program 配置
@@ -234,18 +225,17 @@ return prediction
```python
def train_program():
-label = fluid.layers.data(name='label', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
+ label = fluid.layers.data(name='label', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
-# predict = softmax_regression() # uncomment for Softmax回归
-# predict = multilayer_perceptron() # uncomment for 多层感知器
-predict = convolutional_neural_network() # uncomment for LeNet5卷积神经网络
-cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
-avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
-acc = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=predict, label=label)
-return [avg_cost, acc]
+ # predict = softmax_regression() # uncomment for Softmax回归
+ # predict = multilayer_perceptron() # uncomment for 多层感知器
+ predict = convolutional_neural_network() # uncomment for LeNet5卷积神经网络
+ cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
+ avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
+ acc = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=predict, label=label)
+ return [avg_cost, acc]
-# 该模型运行在单个CPU上
```
#### Optimizer Function 配置
@@ -254,25 +244,25 @@ return [avg_cost, acc]
```python
def optimizer_program():
-return fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001)
+ return fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001)
```
### 数据集 Feeders 配置
下一步,我们开始训练过程。`paddle.dataset.movielens.train()`和`paddle.dataset.movielens.test()`分别做训练和测试数据集。这两个函数各自返回一个reader——PaddlePaddle中的reader是一个Python函数,每次调用的时候返回一个Python yield generator。
-下面`shuffle`是一个reader decorator,它接受一个reader A,返回另一个reader B —— reader B 每次读入`buffer_size`条训练数据到一个buffer里,然后随机打乱其顺序,并且逐条输出。
+下面`shuffle`是一个reader decorator,它接受一个reader A,返回另一个reader B。reader B 每次读入`buffer_size`条训练数据到一个buffer里,然后随机打乱其顺序,并且逐条输出。
-`batch`是一个特殊的decorator,它的输入是一个reader,输出是一个batched reader —— 在PaddlePaddle里,一个reader每次yield一条训练数据,而一个batched reader每次yield一个minibatch。
+`batch`是一个特殊的decorator,它的输入是一个reader,输出是一个batched reader。在PaddlePaddle里,一个reader每次yield一条训练数据,而一个batched reader每次yield一个minibatch。
```python
train_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.reader.shuffle(
-paddle.dataset.mnist.train(), buf_size=500),
-batch_size=64)
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(
+ paddle.dataset.mnist.train(), buf_size=500),
+ batch_size=64)
test_reader = paddle.batch(
-paddle.dataset.mnist.test(), batch_size=64)
+ paddle.dataset.mnist.test(), batch_size=64)
```
### Trainer 配置
@@ -285,7 +275,7 @@ use_cuda = False # set to True if training with GPU
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
trainer = fluid.Trainer(
-train_func=train_program, place=place, optimizer_func=optimizer_program)
+ train_func=train_program, place=place, optimizer_func=optimizer_program)
```
#### Event Handler 配置
@@ -300,27 +290,31 @@ Fluid API 在训练期间为回调函数提供了一个钩子。用户能够通
params_dirname = "recognize_digits_network.inference.model"
lists = []
def event_handler(event):
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
-if event.step % 100 == 0:
-# event.metrics maps with train program return arguments.
-# event.metrics[0] will yeild avg_cost and event.metrics[1] will yeild acc in this example.
-print "Pass %d, Batch %d, Cost %f" % (
-event.step, event.epoch, event.metrics[0])
-
-if isinstance(event, fluid.EndEpochEvent):
-avg_cost, acc = trainer.test(
-reader=test_reader, feed_order=['img', 'label'])
-
-print("Test with Epoch %d, avg_cost: %s, acc: %s" % (event.epoch, avg_cost, acc))
-
-# save parameters
-trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
-lists.append((event.epoch, avg_cost, acc))
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndStepEvent):
+ if event.step % 100 == 0:
+ # event.metrics maps with train program return arguments.
+ # event.metrics[0] will yeild avg_cost and event.metrics[1] will yeild acc in this example.
+ print("Pass %d, Batch %d, Cost %f" % (
+ event.step, event.epoch, event.metrics[0]))
+
+ if isinstance(event, fluid.EndEpochEvent):
+ avg_cost, acc = trainer.test(
+ reader=test_reader, feed_order=['img', 'label'])
+
+ print("Test with Epoch %d, avg_cost: %s, acc: %s" % (event.epoch, avg_cost, acc))
+
+ # save parameters
+ trainer.save_params(params_dirname)
+ lists.append((event.epoch, avg_cost, acc))
```
`event_handler_plot` 可以用来在训练过程中画图如下:
-
+
+

+图7 训练结果
+