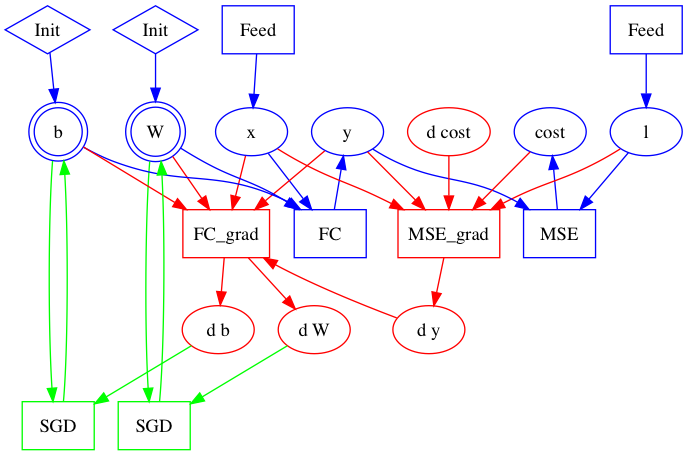
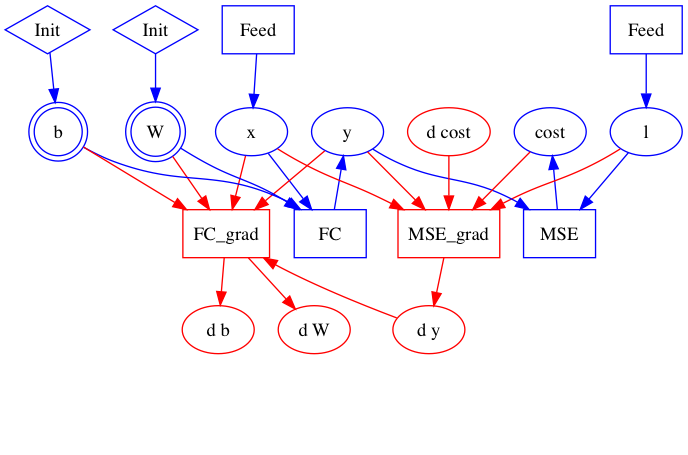
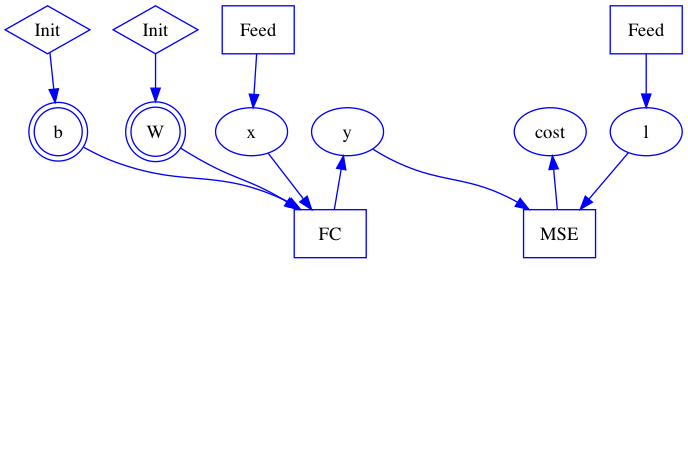
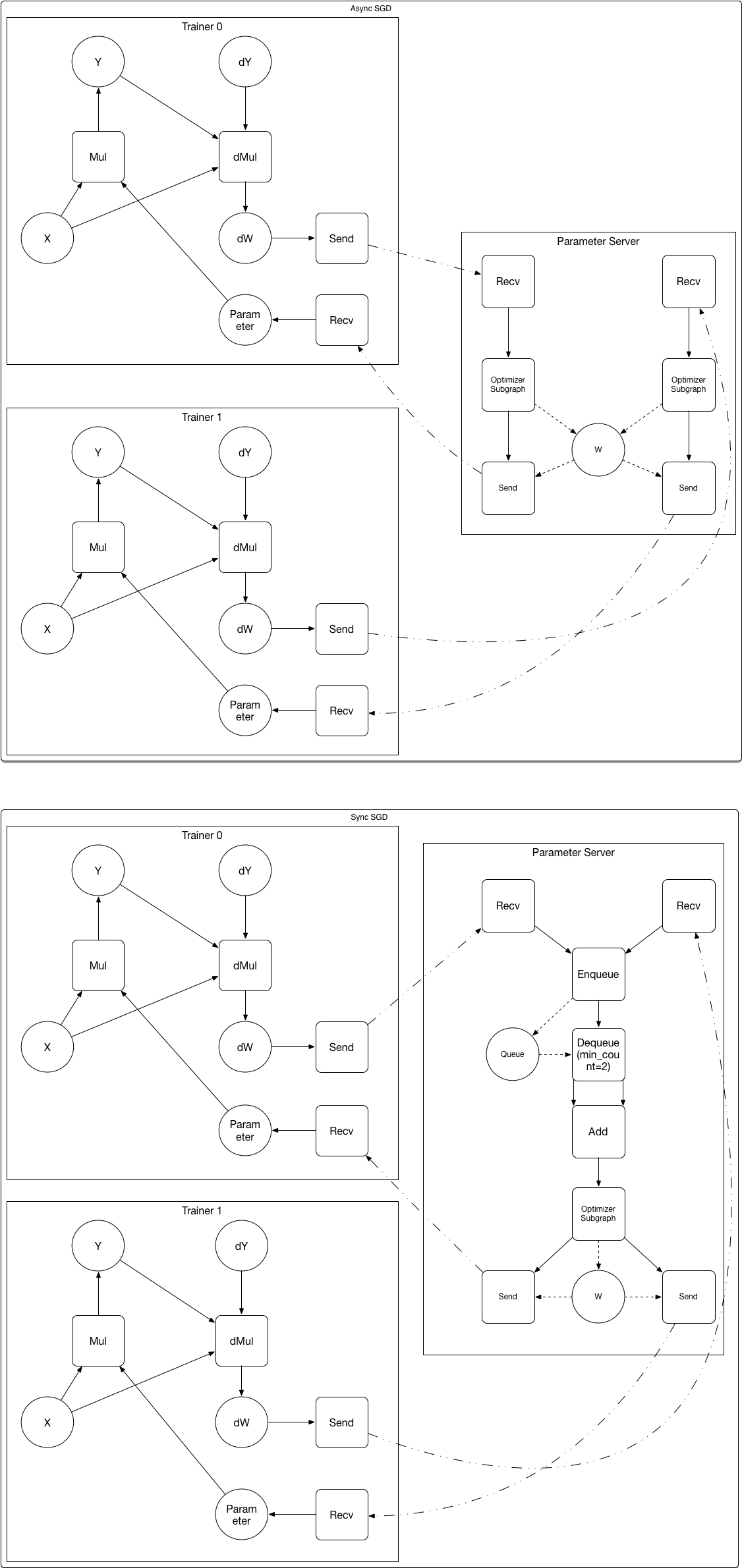
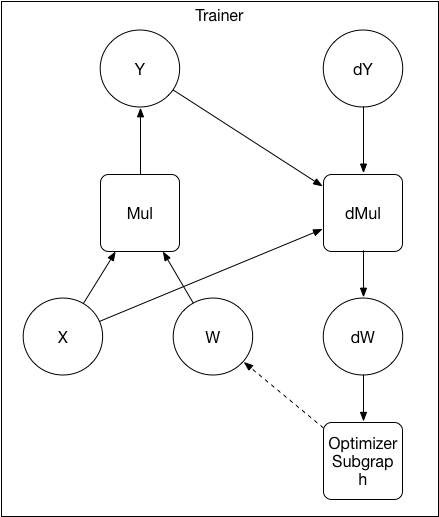
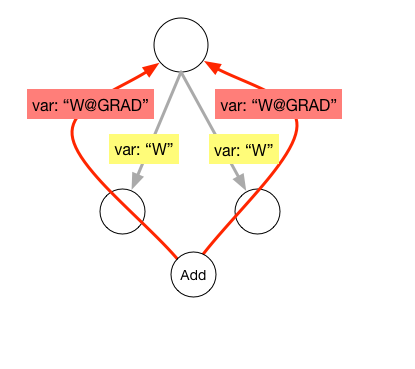
Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into crop_op
Conflicts: paddle/pybind/pybind.cc
Showing
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


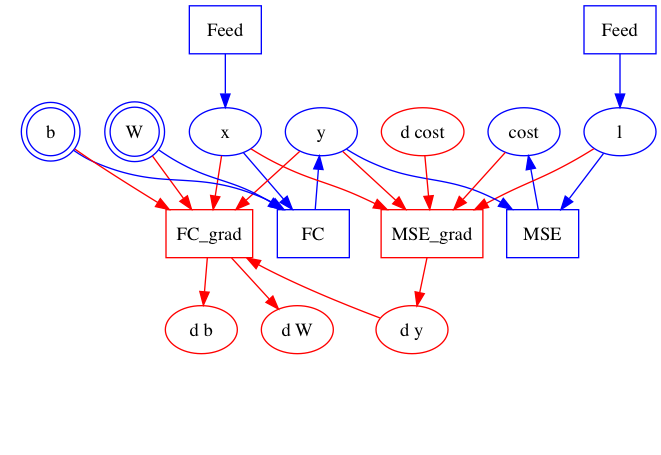
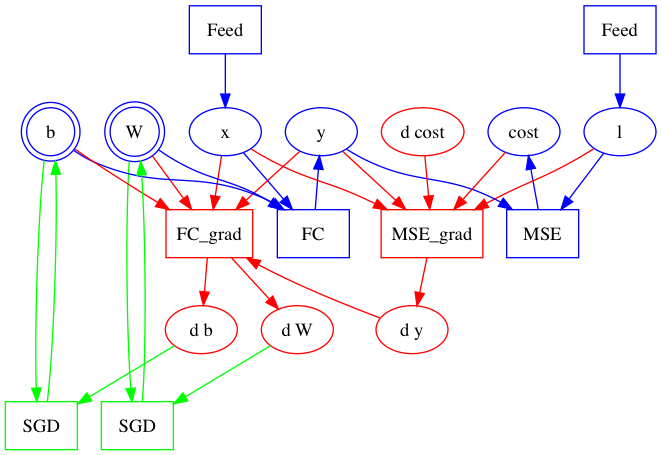
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


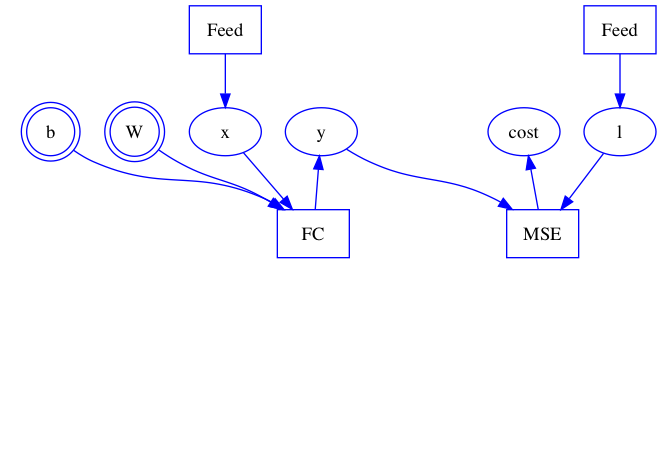
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


doc/design/ops/dist_train.md
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/design/ops/src/dist-graph.png
0 → 100644
222.2 KB
文件已添加
27.9 KB
doc/design/var_desc.md
0 → 100644
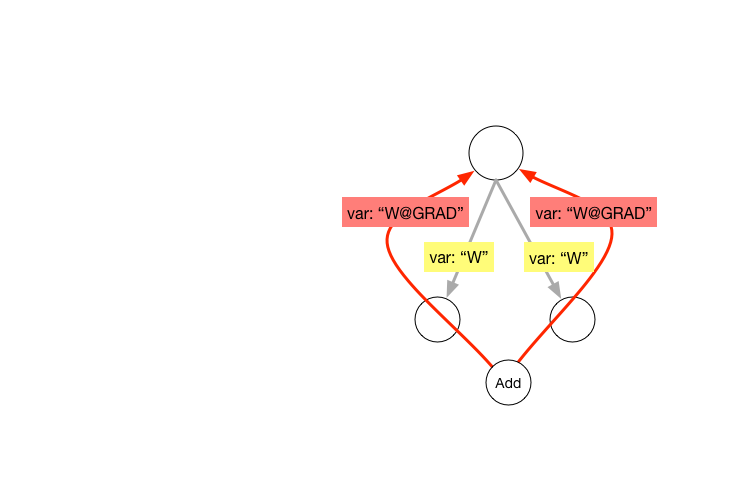
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


paddle/function/GruFunctor.h
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOp.cpp
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOp.h
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOpGpu.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/function/SwitchOpTest.cpp
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/identity_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/im2col.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/math/im2col.cu
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/math/im2col.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/sum_op.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/sum_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/top_k_op.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/top_k_op.cu
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/top_k_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。