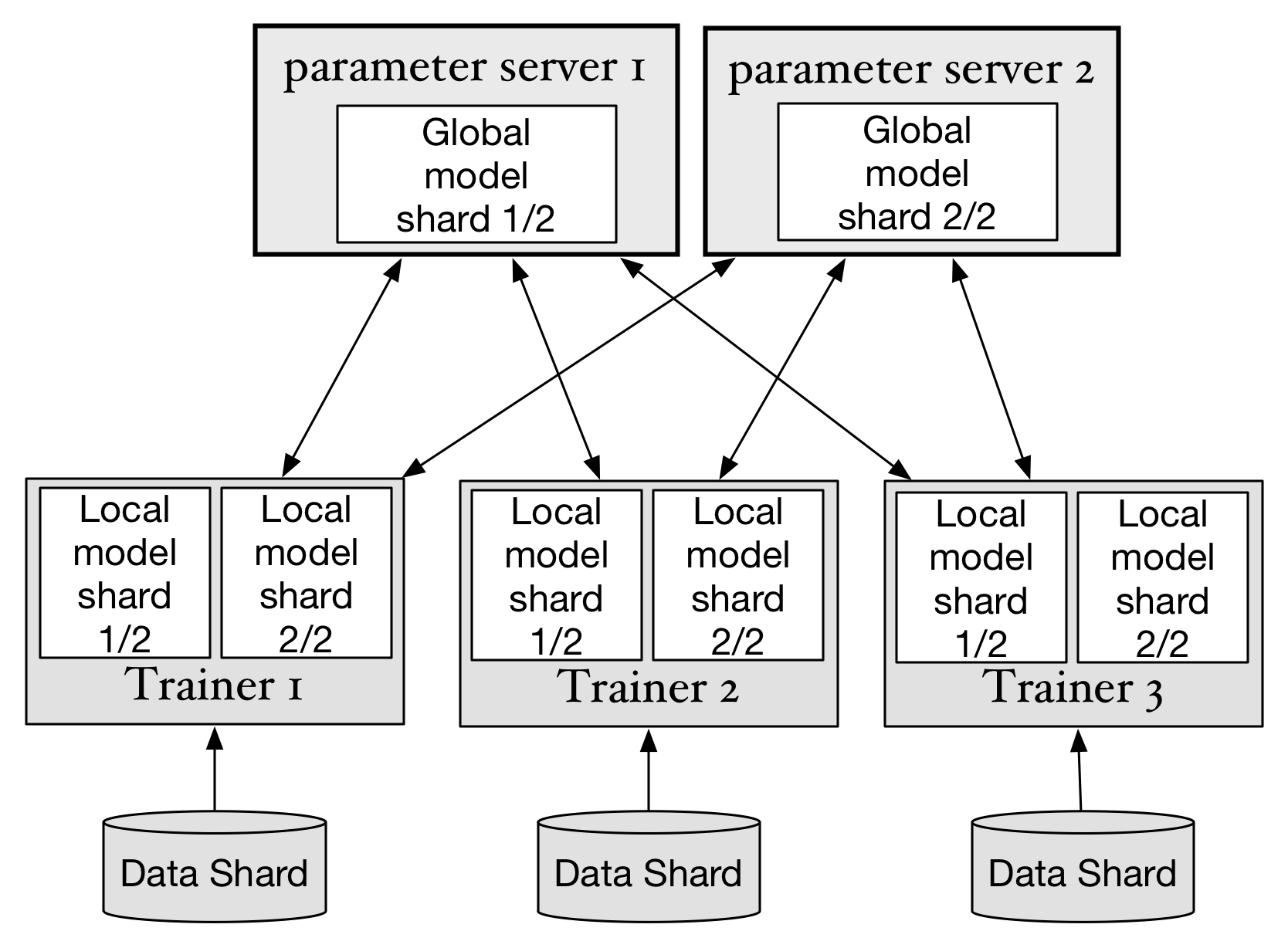
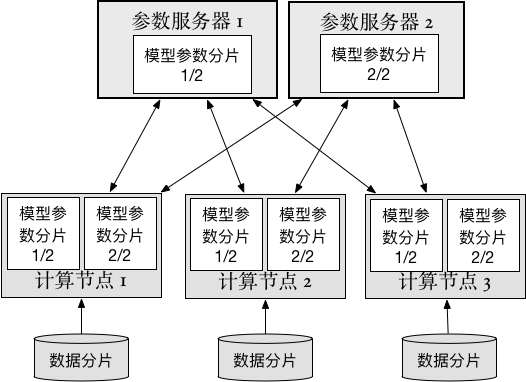
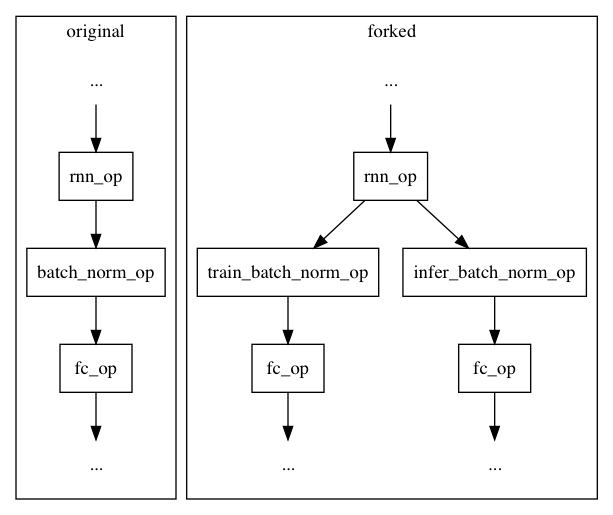
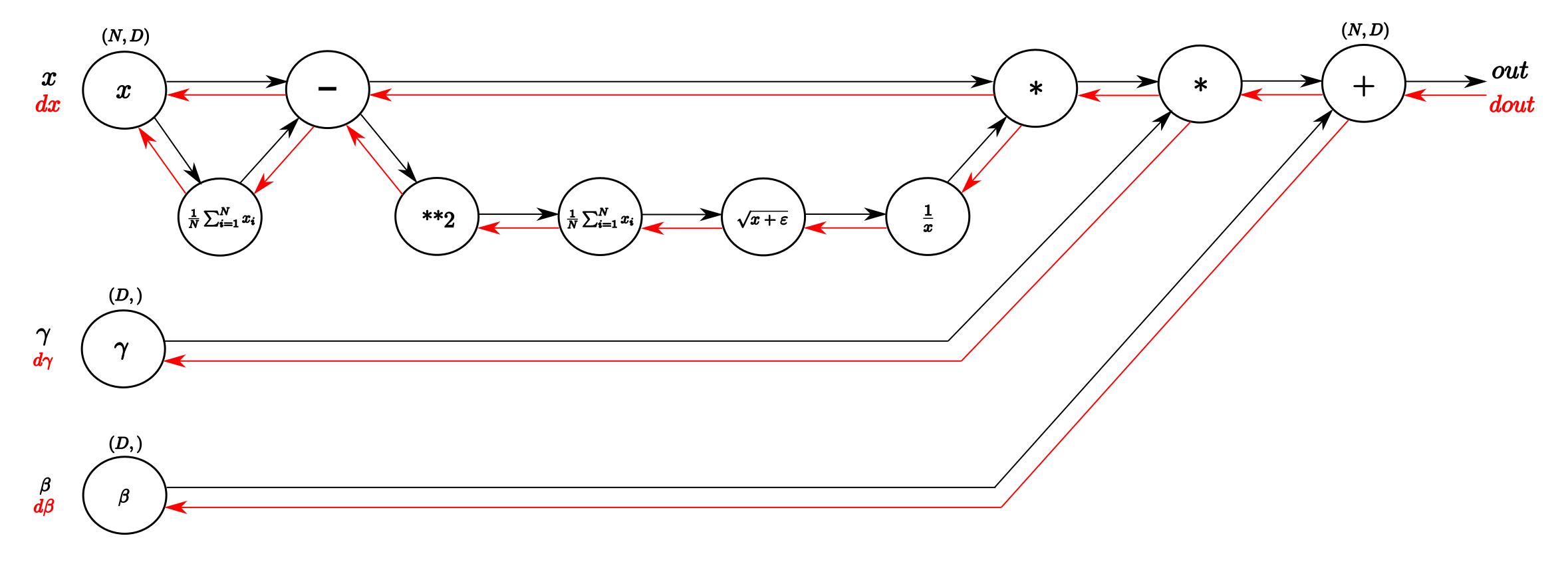
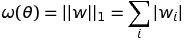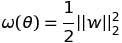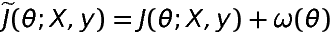Merge remote-tracking branch 'upstream/develop' into merge_grad_gtest
Showing
31.5 KB
45.0 KB
1.1 KB
989 字节
1.6 KB
doc/design/prune.md
0 → 100644
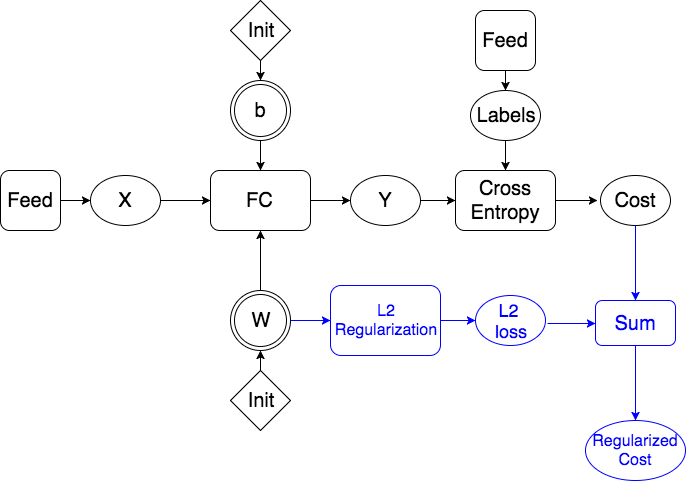
doc/design/regularization.md
0 → 100644
141.7 KB
33.1 KB
paddle/framework/prune.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/prune.h
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/prune_test.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/batch_norm_op.md
0 → 100644
23.3 KB
161.3 KB
paddle/operators/math/matmul.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/matmul_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/matmul_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/matmul_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/momentum_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/momentum_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/momentum_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/proximal_gd_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。