Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into gen_nccl_id_op
Showing
contrib/inference/README.md
0 → 100644
doc/fluid/images/op.dot
0 → 100644
doc/v2/images/FullyConnected.jpg
0 → 100644
49.7 KB
116.2 KB
doc/v2/images/bi_lstm.jpg
0 → 100644
34.8 KB
doc/v2/images/checkpointing.png
0 → 100644
179.1 KB
doc/v2/images/create_efs.png
0 → 100644
236.1 KB
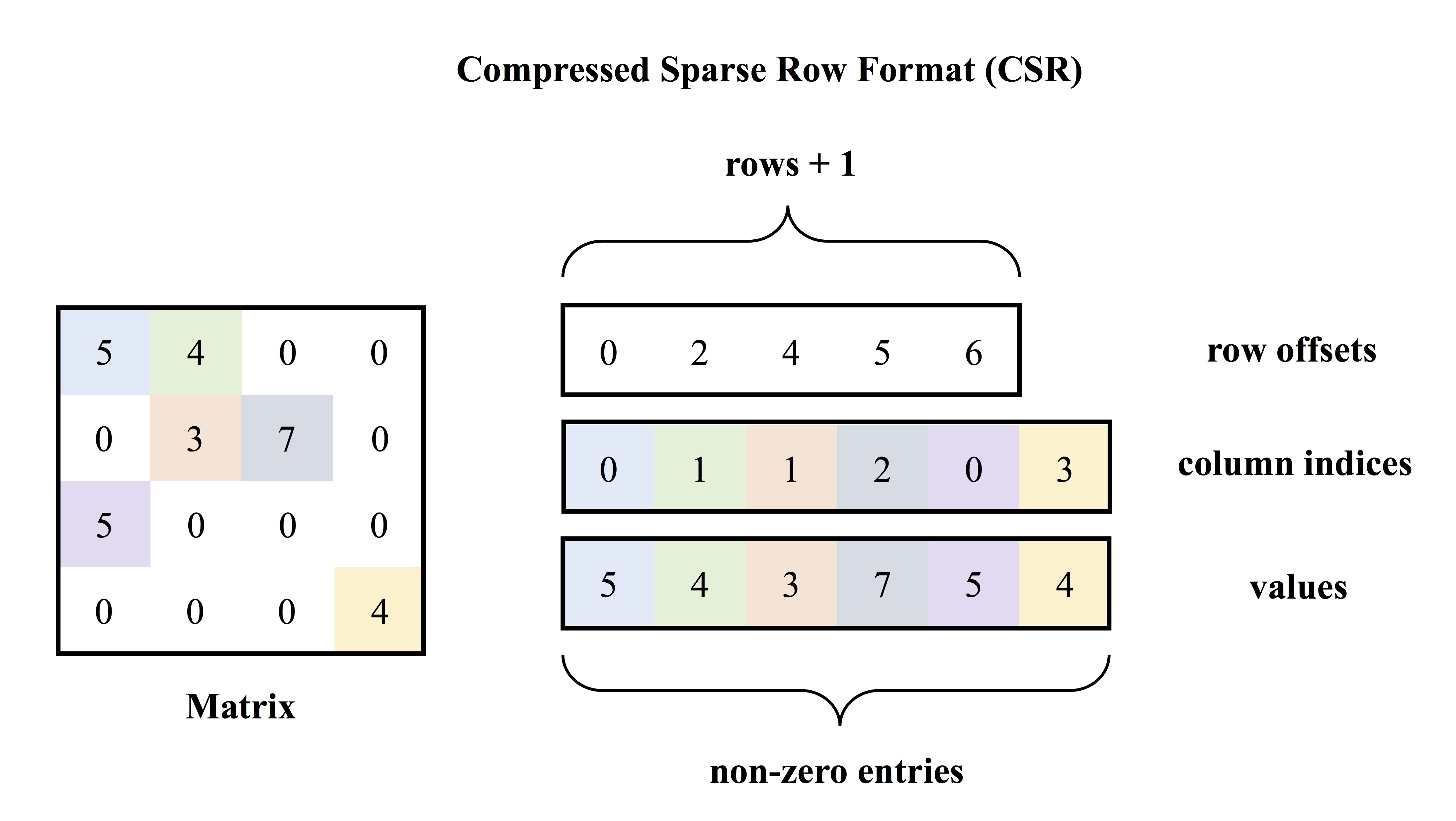
doc/v2/images/csr.png
0 → 100644
361.4 KB
doc/v2/images/data_dispatch.png
0 → 100644
33.1 KB
doc/v2/images/dataset.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/dataset.png
0 → 100644
10.6 KB
doc/v2/images/doc_en.png
0 → 100644
159.0 KB
doc/v2/images/efs_mount.png
0 → 100644
225.2 KB
66.5 KB
doc/v2/images/engine.png
0 → 100644
13.3 KB
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/file_storage.png
0 → 100644
42.4 KB
doc/v2/images/glossary_rnn.dot
0 → 100644
doc/v2/images/gradients.png
0 → 100644
22.4 KB
doc/v2/images/init_lock.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
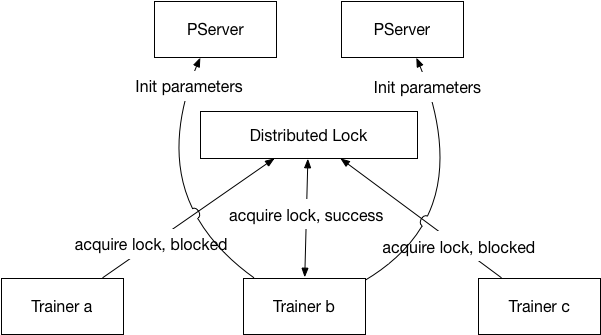
doc/v2/images/init_lock.png
0 → 100644
26.1 KB
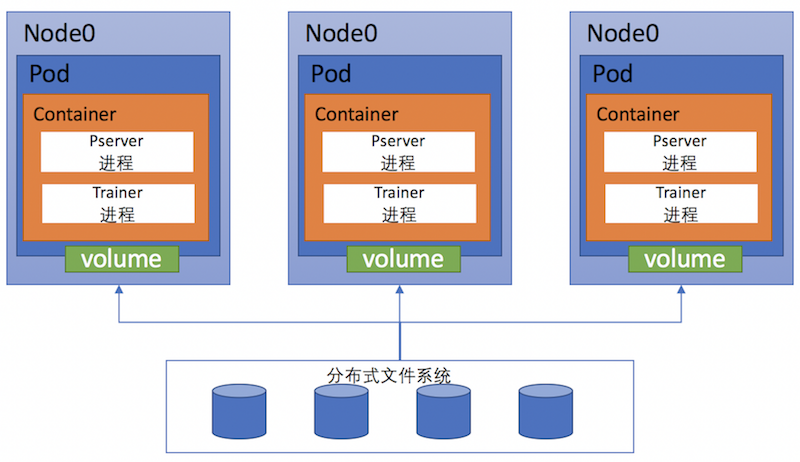
doc/v2/images/k8s-paddle-arch.png
0 → 100644
420.9 KB
doc/v2/images/layers.png
0 → 100644
11.4 KB
doc/v2/images/managed_policy.png
0 → 100644
241.5 KB
doc/v2/images/matrix.png
0 → 100644
18.0 KB
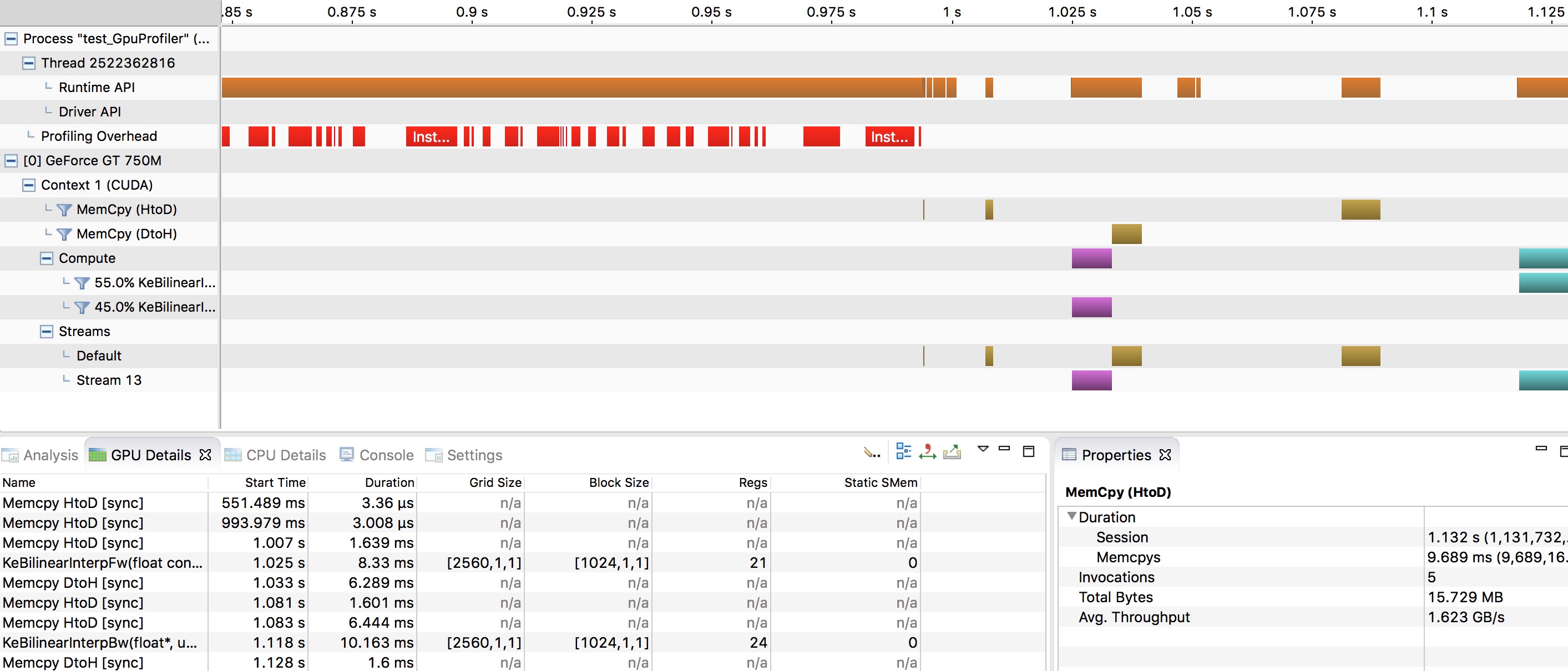
doc/v2/images/nvvp1.png
0 → 100644
416.1 KB
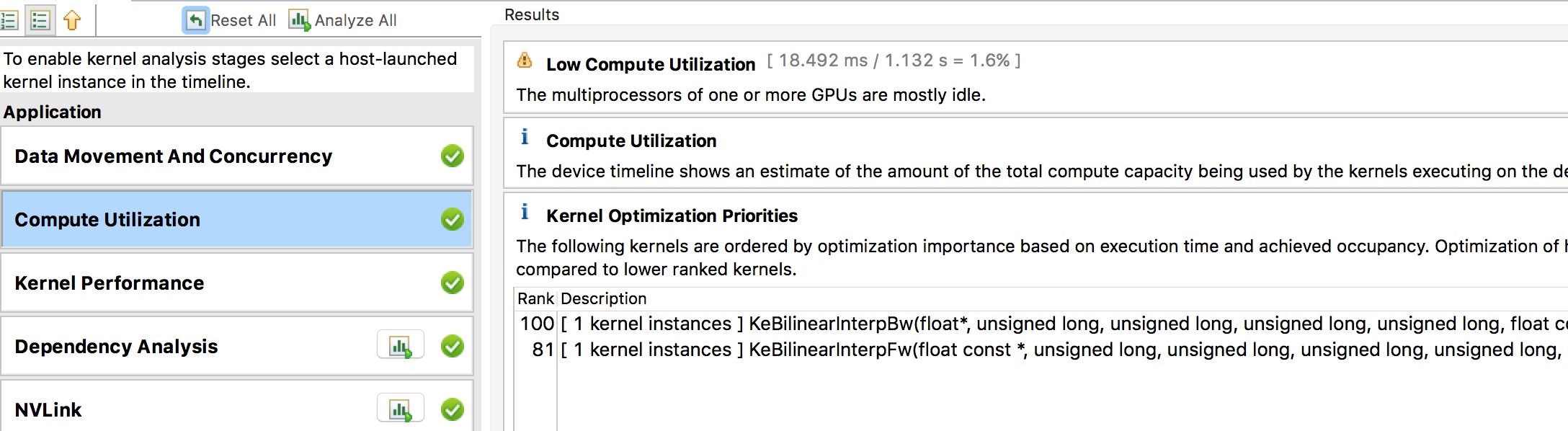
doc/v2/images/nvvp2.png
0 → 100644
483.5 KB
doc/v2/images/nvvp3.png
0 → 100644
247.8 KB
doc/v2/images/nvvp4.png
0 → 100644
276.6 KB
doc/v2/images/overview.png
0 → 100644
10.5 KB
76.7 KB
doc/v2/images/paddle-etcd.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/paddle-etcd.png
0 → 100644
49.2 KB
文件已添加
37.5 KB
doc/v2/images/paddle-ps-0.png
0 → 100644
20.9 KB
doc/v2/images/paddle-ps-1.png
0 → 100644
27.7 KB
doc/v2/images/paddle-ps.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
文件已添加
33.9 KB
文件已添加
17.8 KB
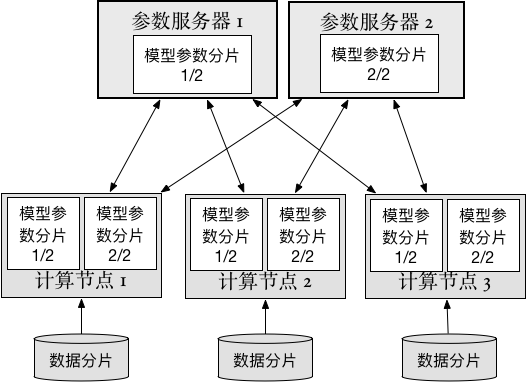
doc/v2/images/ps_cn.png
0 → 100644
33.1 KB
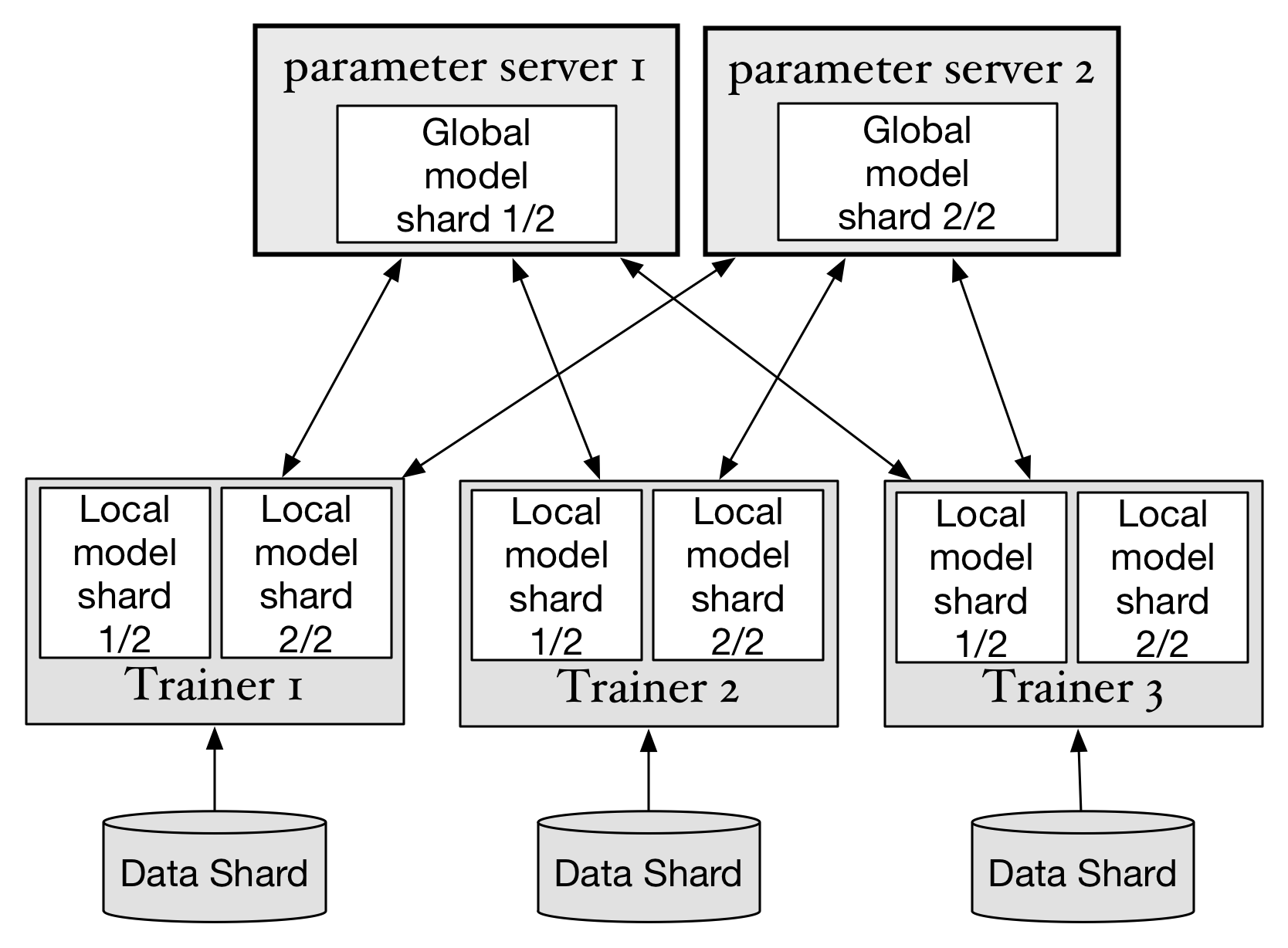
doc/v2/images/ps_en.png
0 → 100644
141.7 KB
70.0 KB
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/pserver_init.png
0 → 100644
27.9 KB
34.9 KB
50.8 KB
doc/v2/images/sequence_data.png
0 → 100644
470.2 KB
doc/v2/images/submit-job.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/submit-job.png
0 → 100644
51.5 KB
doc/v2/images/trainer.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/v2/images/trainer.png
0 → 100644
141.7 KB
doc/v2/images/trainer_cn.png
0 → 100644
33.1 KB
87.1 KB
447.8 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动