/api' |
+| open_browser | boolean | 是否打开浏览器,设置为True则在启动后自动打开浏览器并访问VisualDL面板,若设置api_only,则忽略此参数 |
针对上一步生成的日志,我们的启动脚本为:
@@ -155,7 +186,7 @@ app.run(logdir="./log")
在使用任意一种方式启动VisualDL面板后,打开浏览器访问VisualDL面板,即可查看日志的可视化结果,如图:
-
@@ -163,27 +194,31 @@ app.run(logdir="./log")
## 可视化功能概览
### Scalar
+
以图表形式实时展示训练过程参数,如loss、accuracy。让用户通过观察单组或多组训练参数变化,了解训练过程,加速模型调优。具有两大特点:
#### 动态展示
-在启动VisualDL Board后,LogReader将不断增量的读取日志中数据并供前端调用展示,因此能够在训练中同步观测指标变化,如下图:
+在启动VisualDL后,LogReader将不断增量的读取日志中数据并供前端调用展示,因此能够在训练中同步观测指标变化,如下图:
+
#### 多实验对比
-只需在启动VisualDL Board的时将每个实验日志所在路径同时传入即可,每个实验中相同tag的指标将绘制在一张图中同步呈现,如下图:
+只需在启动VisualDL时将每个实验日志所在路径同时传入即可,每个实验中相同tag的指标将绘制在一张图中同步呈现,如下图:
+
### Image
+
实时展示训练过程中的图像数据,用于观察不同训练阶段的图像变化,进而深入了解训练过程及效果。
@@ -191,6 +226,56 @@ app.run(logdir="./log")
+
+### Audio
+
+实时查看训练过程中的音频数据,监控语音识别与合成等任务的训练过程。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Graph
+
+一键可视化模型的网络结构。可查看模型属性、节点信息、节点输入输出等,并支持节点搜索,辅助用户快速分析模型结构与了解数据流向。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Histogram
+
+以直方图形式展示Tensor(weight、bias、gradient等)数据在训练过程中的变化趋势。深入了解模型各层效果,帮助开发者精准调整模型结构。
+
+- Offset模式
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- Overlay模式
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### PR Curve
+
+精度-召回率曲线,帮助开发者权衡模型精度和召回率之间的平衡,设定最佳阈值。
+
+
+
+
+
### High Dimensional
将高维数据进行降维展示,目前支持T-SNE、PCA两种降维方式,用于深入分析高维数据间的关系,方便用户根据数据特征进行算法优化。
@@ -201,9 +286,15 @@ app.run(logdir="./log")
## 开源贡献
-VisualDL 是由 [PaddlePaddle](http://www.paddlepaddle.org/) 和 [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) 合作推出的开源项目。欢迎所有人使用,提意见以及贡献代码。
+VisualDL 是由 [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org/) 和 [ECharts](https://echarts.apache.org/) 合作推出的开源项目。
+Graph 相关功能由 [Netron](https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron) 提供技术支持。
+欢迎所有人使用,提意见以及贡献代码。
## 更多细节
-想了解更多关于VisualDL可视化功能的使用详情介绍,请查看**Visual DL 使用指南**。
+想了解更多关于VisualDL可视化功能的使用详情介绍,请查看**VisualDL使用指南**。
+
+## 技术交流
+
+欢迎您加入VisualDL官方QQ群:1045783368 与飞桨团队以及其他用户共同针对VisualDL进行讨论与交流。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/evaluation_debugging/debug/visualdl_usage.md b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/evaluation_debugging/debug/visualdl_usage.md
index f191aa8cef12caf67d2e42666683fb2155aae437..e6a6445e3d4a89501f236bba6cf5623304ab3024 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/evaluation_debugging/debug/visualdl_usage.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/evaluation_debugging/debug/visualdl_usage.md
@@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
-
-
# VisualDL 使用指南
### 概述
VisualDL 是一个面向深度学习任务设计的可视化工具。VisualDL 利用了丰富的图表来展示数据,用户可以更直观、清晰地查看数据的特征与变化趋势,有助于分析数据、及时发现错误,进而改进神经网络模型的设计。
-目前,VisualDL 支持 scalar, image, high dimensional 三个组件,项目正处于高速迭代中,敬请期待新组件的加入。
-
-| 组件名称 | 展示图表 | 作用 |
-| :----------------------------------------------------------: | :--------: | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
-| [ Scalar](#Scalar -- 折线图组件) | 折线图 | 动态展示损失函数值、准确率等标量数据 |
-| [Image](#Image -- 图片可视化组件) | 图片可视化 | 显示图片,可显示输入图片和处理后的结果,便于查看中间过程的变化 |
-| [High Dimensional](#High Dimensional -- 数据降维组件) | 数据降维 | 将高维数据映射到 2D/3D 空间来可视化嵌入,便于观察不同数据的相关性 |
-
+目前,VisualDL 支持 scalar, image, audio, graph, histogram, pr curve, high dimensional 七个组件,项目正处于高速迭代中,敬请期待新组件的加入。
+| 组件名称 | 展示图表 | 作用 |
+| :-------------------------------------------------: | :--------: | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [ Scalar](#Scalar--标量组件) | 折线图 | 动态展示损失函数值、准确率等标量数据 |
+| [Image](#Image--图片可视化组件) | 图片可视化 | 显示图片,可显示输入图片和处理后的结果,便于查看中间过程的变化 |
+| [Audio](#Audio--音频播放组件) | 音频播放 | 播放训练过程中的音频数据,监控语音识别与合成等任务的训练过程 |
+| [Graph](#Graph--网络结构组件) | 网络结构 | 展示网络结构、节点属性及数据流向,辅助学习、优化网络结构 |
+| [Histogram](#Histogram--直方图组件) | 直方图 | 展示训练过程中权重、梯度等张量的分布 |
+| [PR Curve](#PR-Curve--PR曲线组件) | 折线图 | 权衡精度与召回率之间的平衡关系,便于选择最佳阈值 |
+| [High Dimensional](#High-Dimensional--数据降维组件) | 数据降维 | 将高维数据映射到 2D/3D 空间来可视化嵌入,便于观察不同数据的相关性 |
## Scalar -- 折线图组件
@@ -29,16 +29,22 @@ Scalar 组件的记录接口如下:
```python
add_scalar(tag, value, step, walltime=None)
```
+
接口参数说明如下:
-|参数|格式|含义|
-|-|-|-|
-|tag|string|记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%`|
-|value|float|要记录的数据值|
-|step|int|记录的步数|
-|walltime|int|记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳|
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| -------- | ------ | ------------------------------------------- |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%` |
+| value | float | 要记录的数据值 |
+| step | int | 记录的步数 |
+| walltime | int | 记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳 |
### Demo
-下面展示了使用 Scalar 组件记录数据的示例,代码见[Scalar组件](../../demo/components/scalar_test.py)
+
+- 基础使用
+
+下面展示了使用 Scalar 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[Scalar组件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/scalar_test.py)
+
```python
from visualdl import LogWriter
@@ -52,7 +58,9 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
# 向记录器添加一个tag为`loss`的数据
writer.add_scalar(tag="loss", step=step, value=1/(value[step] + 1))
```
+
运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
```shell
visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
```
@@ -60,11 +68,58 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
接着在浏览器打开`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看以下折线图。
-
+- 多组实验对比
+
+下面展示了使用Scalar组件实现多组实验对比
+
+多组实验对比的实现分为两步:
+
+1. 创建子日志文件储存每组实验的参数数据
+2. 将数据写入scalar组件时,**使用相同的tag**,即可实现对比**不同实验**的**同一类型参数**
+
+```python
+from visualdl import LogWriter
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ value = [i/1000.0 for i in range(1000)]
+ # 步骤一:创建父文件夹:log与子文件夹:scalar_test
+ with LogWriter(logdir="./log/scalar_test") as writer:
+ for step in range(1000):
+ # 步骤二:向记录器添加一个tag为`train/acc`的数据
+ writer.add_scalar(tag="train/acc", step=step, value=value[step])
+ # 步骤二:向记录器添加一个tag为`train/loss`的数据
+ writer.add_scalar(tag="train/loss", step=step, value=1/(value[step] + 1))
+ # 步骤一:创建第二个子文件夹scalar_test2
+ value = [i/500.0 for i in range(1000)]
+ with LogWriter(logdir="./log/scalar_test2") as writer:
+ for step in range(1000):
+ # 步骤二:在同样名为`train/acc`下添加scalar_test2的accuracy的数据
+ writer.add_scalar(tag="train/acc", step=step, value=value[step])
+ # 步骤二:在同样名为`train/loss`下添加scalar_test2的loss的数据
+ writer.add_scalar(tag="train/loss", step=step, value=1/(value[step] + 1))
+```
+
+运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
+```shell
+visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+```
+
+接着在浏览器打开`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看以下折线图,对比「scalar_test」和「scalar_test2」的Accuracy和Loss。
+
+
+
+
+
+*多组实验对比的应用案例可参考AI Studio项目:[VisualDL 2.0--眼疾识别训练可视化](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/502834)
+
+
### 功能操作说明
* 支持数据卡片「最大化」、「还原」、「坐标系转化」(y轴对数坐标)、「下载」折线图
@@ -75,6 +130,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
* 数据点Hover展示详细信息
@@ -83,6 +140,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
* 可搜索卡片标签,展示目标图像
@@ -91,6 +150,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
* 可搜索打点数据标签,展示特定数据
@@ -98,6 +159,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
* X轴有三种衡量尺度
1. Step:迭代次数
@@ -107,6 +170,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
* 可调整曲线平滑度,以便更好的展现参数整体的变化趋势
@@ -114,6 +179,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
## Image -- 图片可视化组件
### 介绍
@@ -127,16 +194,20 @@ Image 组件的记录接口如下:
```python
add_image(tag, img, step, walltime=None)
```
+
接口参数说明如下:
-|参数|格式|含义|
-|-|-|-|
-|tag|string|记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%`|
-|img|numpy.ndarray|以ndarray格式表示的图片|
-|step|int|记录的步数|
-|walltime|int|记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳|
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| -------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%` |
+| img | numpy.ndarray | 以ndarray格式表示的图片 |
+| step | int | 记录的步数 |
+| walltime | int | 记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳 |
### Demo
-下面展示了使用 Image 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[Image组件](../../demo/components/image_test.py)
+
+下面展示了使用 Image 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[Image组件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/image_test.py)
+
```python
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
@@ -159,11 +230,13 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
with LogWriter(logdir="./log/image_test/train") as writer:
for step in range(6):
# 添加一个图片数据
- writer.add_image(tag="doge",
+ writer.add_image(tag="eye",
img=random_crop("../../docs/images/eye.jpg"),
step=step)
```
+
运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
```shell
visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
```
@@ -171,10 +244,12 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
在浏览器输入`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看图片数据。
-
+
+
### 功能操作说明
可搜索图片标签显示对应图片数据
@@ -184,6 +259,8 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
支持滑动Step/迭代次数查看不同迭代次数下的图片数据
@@ -191,6 +268,442 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+
+
+## Audio--音频播放组件
+
+### 介绍
+
+Audio组件实时查看训练过程中的音频数据,监控语音识别与合成等任务的训练过程。
+
+### 记录接口
+
+Audio 组件的记录接口如下:
+
+```python
+add_audio(tag, audio_array, step, sample_rate)
+```
+
+接口参数说明如下:
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| ----------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`audio_tag`,不能含有`%` |
+| audio_arry | numpy.ndarray | 以ndarray格式表示的音频 |
+| step | int | 记录的步数 |
+| sample_rate | int | 采样率,**注意正确填写对应音频的原采样率** |
+
+### Demo
+
+下面展示了使用 Audio 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[Audio组件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/audio_test.py)
+
+```python
+from visualdl import LogWriter
+import numpy as np
+import wave
+
+
+def read_audio_data(audio_path):
+ """
+ Get audio data.
+ """
+ CHUNK = 4096
+ f = wave.open(audio_path, "rb")
+ wavdata = []
+ chunk = f.readframes(CHUNK)
+ while chunk:
+ data = np.frombuffer(chunk, dtype='uint8')
+ wavdata.extend(data)
+ chunk = f.readframes(CHUNK)
+ # 8k sample rate, 16bit frame, 1 channel
+ shape = [8000, 2, 1]
+ return shape, wavdata
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ with LogWriter(logdir="./log") as writer:
+ audio_shape, audio_data = read_audio_data("./testing.wav")
+ audio_data = np.array(audio_data)
+ writer.add_audio(tag="audio_tag",
+ audio_array=audio_data,
+ step=0,
+ sample_rate=8000)
+```
+
+运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
+```shell
+visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+```
+
+在浏览器输入`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看音频数据。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 功能操作说明
+
+- 可搜索音频标签显示对应音频数据
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持滑动Step/迭代次数试听不同迭代次数下的音频数据
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持播放/暂停音频数据
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持音量调节
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持音频下载
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Graph--网络结构组件
+
+### 介绍
+
+Graph组件一键可视化模型的网络结构。用于查看模型属性、节点信息、节点输入输出等,并进行节点搜索,协助开发者们快速分析模型结构与了解数据流向。
+
+### Demo
+
+共有两种启动方式:
+
+- 前端模型文件拖拽上传:
+
+ - 如只需使用Graph组件,则无需添加任何参数,在命令行执行`visualdl`后即可启动面板进行上传。
+ - 如果同时需使用其他功能,在命令行指定日志文件路径(以`./log`为例)即可启动面板进行上传:
+
+ ```shell
+ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 后端启动Graph:
+
+ - 在命令行加入参数`--model`并指定**模型文件**路径(非文件夹路径),即可启动并查看网络结构可视化:
+
+ ```shell
+ visualdl --model ./log/model --port 8080
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 功能操作说明
+
+- 一键上传模型
+ - 支持模型格式:PaddlePaddle、ONNX、Keras、Core ML、Caffe、Caffe2、Darknet、MXNet、ncnn、TensorFlow Lite
+ - 实验性支持模型格式:TorchScript、PyTorch、Torch、 ArmNN、BigDL、Chainer、CNTK、Deeplearning4j、MediaPipe、ML.NET、MNN、OpenVINO、Scikit-learn、Tengine、TensorFlow.js、TensorFlow
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持上下左右任意拖拽模型、放大和缩小模型
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 搜索定位到对应节点
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 点击查看模型属性
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持选择模型展示的信息
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持以PNG、SVG格式导出模型结构图
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 点击节点即可展示对应属性信息
+
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持一键更换模型
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Histogram--直方图组件
+
+### 介绍
+
+Histogram组件以直方图形式展示Tensor(weight、bias、gradient等)数据在训练过程中的变化趋势。深入了解模型各层效果,帮助开发者精准调整模型结构。
+
+### 记录接口
+
+Histogram 组件的记录接口如下:
+
+```python
+add_histogram(tag, values, step, walltime=None, buckets=10)
+```
+
+接口参数说明如下:
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| -------- | --------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%` |
+| values | numpy.ndarray or list | 以ndarray或list格式表示的数据 |
+| step | int | 记录的步数 |
+| walltime | int | 记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳 |
+| buckets | int | 生成直方图的分段数,默认为10 |
+
+### Demo
+
+下面展示了使用 Histogram组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[Histogram组件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/histogram_test.py)
+
+```python
+from visualdl import LogWriter
+import numpy as np
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ values = np.arange(0, 1000)
+ with LogWriter(logdir="./log/histogram_test/train") as writer:
+ for index in range(1, 101):
+ interval_start = 1 + 2 * index / 100.0
+ interval_end = 6 - 2 * index / 100.0
+ data = np.random.uniform(interval_start, interval_end, size=(10000))
+ writer.add_histogram(tag='default tag',
+ values=data,
+ step=index,
+ buckets=10)
+```
+
+运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
+```shell
+visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+```
+
+在浏览器输入`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看训练参数直方图。
+
+### 功能操作说明
+
+- 支持数据卡片「最大化」、直方图「下载」
+
+
+
+
+- 可选择Offset或Overlay模式
+
+
+
+
+
+ - Offset模式
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ - Overlay模式
+
+
+
+
+
+- 数据点Hover展示参数值、训练步数、频次
+
+ - 在第240次训练步数时,权重为-0.0031,且出现的频次是2734次
+
+
+
+
+- 可搜索卡片标签,展示目标直方图
+
+
+
+
+- 可搜索打点数据标签,展示特定数据流
+
+
+
+
+## PR Curve--PR曲线组件
+
+### 介绍
+
+PR Curve以折线图形式呈现精度与召回率的权衡分析,清晰直观了解模型训练效果,便于分析模型是否达到理想标准。
+
+### 记录接口
+
+PR Curve组件的记录接口如下:
+
+```python
+add_pr_curve(tag, labels, predictions, step=None, num_thresholds=10)
+```
+
+接口参数说明如下:
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| -------------- | --------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`train/loss`,不能含有`%` |
+| labels | numpy.ndarray or list | 以ndarray或list格式表示的实际类别 |
+| predictions | numpy.ndarray or list | 以ndarray或list格式表示的预测类别 |
+| step | int | 记录的步数 |
+| num_thresholds | int | 阈值设置的个数,默认为10,最大值为127 |
+
+### Demo
+
+下面展示了使用 PR Curve 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[PR Curve组件](#https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/pr_curve_test.py)
+
+```python
+from visualdl import LogWriter
+import numpy as np
+
+with LogWriter("./log/pr_curve_test/train") as writer:
+ for step in range(3):
+ labels = np.random.randint(2, size=100)
+ predictions = np.random.rand(100)
+ writer.add_pr_curve(tag='pr_curve',
+ labels=labels,
+ predictions=predictions,
+ step=step,
+ num_thresholds=5)
+```
+
+运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
+```shell
+visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
+```
+
+接着在浏览器打开`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看PR Curve
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 功能操作说明
+
+- 支持数据卡片「最大化」,「还原」、「下载」PR曲线
+
+
+
+
+- 数据点Hover展示详细信息:阈值对应的TP、TN、FP、FN
+
+
+
+
+- 可搜索卡片标签,展示目标图表
+
+
+
+
+- 可搜索打点数据标签,展示特定数据
+
+
+
+
+
+- 支持查看不同训练步数下的PR曲线
+
+
+
+
+- X轴-时间显示类型有三种衡量尺度
+
+ - Step:迭代次数
+ - Walltime:训练绝对时间
+ - Relative:训练时长
+
+
+
+
## High Dimensional -- 数据降维组件
### 介绍
@@ -207,16 +720,20 @@ High Dimensional 组件的记录接口如下:
```python
add_embeddings(tag, labels, hot_vectors, walltime=None)
```
+
接口参数说明如下:
-|参数|格式|含义|
-|-|-|-|
-|tag|string|记录指标的标志,如`default`,不能含有`%`|
-|labels|numpy.array 或 list|一维数组表示的标签,每个元素是一个string类型的字符串|
-|hot_vectors|numpy.array or list|与labels一一对应,每个元素可以看作是某个标签的特征|
-|walltime|int|记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳|
+
+| 参数 | 格式 | 含义 |
+| ----------- | ------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
+| tag | string | 记录指标的标志,如`default`,不能含有`%` |
+| labels | numpy.array 或 list | 一维数组表示的标签,每个元素是一个string类型的字符串 |
+| hot_vectors | numpy.array or list | 与labels一一对应,每个元素可以看作是某个标签的特征 |
+| walltime | int | 记录数据的时间戳,默认为当前时间戳 |
### Demo
-下面展示了使用 High Dimensional 组件记录数据的示例,代码见[High Dimensional组件](../../demo/components/high_dimensional_test.py)
+
+下面展示了使用 High Dimensional 组件记录数据的示例,代码文件请见[High Dimensional组件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL/blob/develop/demo/components/high_dimensional_test.py)
+
```python
from visualdl import LogWriter
@@ -237,7 +754,9 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
labels=labels,
hot_vectors=hot_vectors)
```
+
运行上述程序后,在命令行执行
+
```shell
visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
```
@@ -245,5 +764,11 @@ visualdl --logdir ./log --port 8080
接着在浏览器打开`http://127.0.0.1:8080`,即可查看降维后的可视化数据。
-
+
+
+
+
+
+#
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_cn.rst
index 6968eaddcdd44f689f108deb3f932a90471974bf..5d0d414725666c1d90f5d58c26dc4536f08f439f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_cn.rst
@@ -2,11 +2,22 @@
环境变量FLAGS
==================
+调用说明
+----------
+
+PaddlePaddle中的环境变量FLAGS支持两种设置方式。
+
+- 通过export来设置环境变量,如 :code:`export FLAGS_eager_delete_tensor_gb = 1.0` 。
+
+- 通过API::code:`get_flag` 和 :code:`set_flags` 来打印和设置环境变量FLAGS。API使用详情请参考 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_get_flags` 与 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_set_flags` 。
+
+
+环境变量FLAGS功能分类
+----------------------
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
-
cudnn_cn.rst
data_cn.rst
debug_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_en.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_en.rst
index 247c38f16d3cd73b498f0cfa32c8cc05767160dd..b24c551c78d7bc74a76901c717b792f78b4237e3 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_en.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/flags_en.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,17 @@
FLAGS
==================
+Usage
+------
+These FLAGS in PaddlePaddle can be set in two ways.
+
+- Set the FLAGS through export. For example: :code:`export FLAGS_eager_delete_tensor_gb = 1.0` .
+
+- Through :code:`get_flags` and :code:`set_flags` to print and set the environment variables. For more information of using these API, please refer to :ref:`api_fluid_get_flags` and :ref:`api_fluid_get_flags` .
+
+
+FLAGS Quick Search
+------------------
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_cn.rst
index cbafa94a0e5b28570cbb16a92f17a947bd3458fd..94676721c2d0baca9a2d744e7dbc7064c7eed279 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_cn.rst
@@ -11,13 +11,14 @@ FLAGS_allocator_strategy
取值范围
---------------
-String型,['naive_best_fit', 'auto_growth']中的一个。缺省值为'naive_best_fit'。
+String型,['naive_best_fit', 'auto_growth']中的一个。缺省值如果编译Paddle CMake时使用-DON_INFER=ON为'naive_best_fit'。
+其他默认情况为'auto_growth'。PaddlePaddle pip安装包的默认策略也是'auto_growth'
示例
--------
-FLAGS_allocator_strategy=naive_best_fit - 使用预分配best fit分配器。
+FLAGS_allocator_strategy=naive_best_fit - 使用预分配best fit分配器,PaddlePaddle会先占用大多比例的可用内存/显存,在Paddle具体数据使用时分配,这种方式预占空间较大,但内存/显存碎片较少(比如能够支持模型的最大batch size会变大)。
-FLAGS_allocator_strategy=auto_growth - 使用auto growth分配器。
+FLAGS_allocator_strategy=auto_growth - 使用auto growth分配器。PaddlePaddle会随着真实数据需要再占用内存/显存,但内存/显存可能会产生碎片(比如能够支持模型的最大batch size会变小)。
FLAGS_eager_delete_scope
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_en.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_en.rst
index 8702a4082006ab05b0a983f3b117fba7617b558f..0e630e7d93d51e668397b9c88fbfd75ad45f9395 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_en.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/flags/memory_en.rst
@@ -11,13 +11,13 @@ Use to choose allocator strategy of PaddlePaddle.
Values accepted
---------------
-String, enum in ['naive_best_fit', 'auto_growth']. The default value is 'naive_best_fit'.
+String, enum in ['naive_best_fit', 'auto_growth']. The default value will be 'naive_best_fit' if users compile PaddlePaddle with -DON_INFER=ON CMake flag, otherwise is 'auto_growth'. The default PaddlePaddle pip package uses 'auto_growth'.
Example
--------
-FLAGS_allocator_strategy=naive_best_fit would use the pre-allocated best fit allocator.
+FLAGS_allocator_strategy=naive_best_fit would use the pre-allocated best fit allocator. 'naive_best_fit' strategy would occupy almost all GPU memory by default but leads to less memory fragmentation (i.e., maximum batch size of models may be larger).
-FLAGS_allocator_strategy=auto_growth would use the auto growth allocator.
+FLAGS_allocator_strategy=auto_growth would use the auto growth allocator. 'auto_growth' strategy would allocate GPU memory on demand but may lead to more memory fragmentation (i.e., maximum batch size of models may be smaller).
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_cn.rst
index 74bdd3d0da0669a9350bf22a24682111f766c559..d866963d281d2c6faba85ee053dce238c9c42355 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_cn.rst
@@ -11,4 +11,4 @@
:hidden:
inference_deployment/index_cn.rst
-
+ flags/flags_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_en.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_en.rst
index 0e926da511f6f79ae2eb2348a9a8f211e1136851..d6401bceb56b9c185ee0559aeb9aa3234436d9c8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_en.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/index_en.rst
@@ -16,5 +16,5 @@ So far you have already been familiar with PaddlePaddle. And the next expectatio
:hidden:
inference_deployment/index_en.rst
-
+ flags/flags_en.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_cn.rst
index a0fe4b9fa4d9bf571f061c77f39e2aa14447d651..c1bfba460db6c12651ac6a04f823812642490c9f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_cn.rst
@@ -7,15 +7,15 @@
-------------
.. csv-table::
- :header: "版本说明", "预测库(1.8.1版本)", "预测库(develop版本)"
+ :header: "版本说明", "预测库(1.8.3版本)", "预测库(develop版本)"
:widths: 3, 2, 2
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_noavx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.1_cudnn7.6_avx_mkl_trt6", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_",
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_noavx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.1_cudnn7.6_avx_mkl_trt6", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_",
"nv-jetson-cuda10-cudnn7.5-trt5", "`fluid_inference.tar.gz `_",
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_en.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_en.rst
index 96205dc72b2657377ae728065e13cdcb15aa262d..545aba61360b0018e3d3a1c28f4e56f4f6005925 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_en.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/build_and_install_lib_en.rst
@@ -7,15 +7,15 @@ Direct Download and Installation
---------------------------------
.. csv-table:: c++ inference library list
- :header: "version description", "inference library(1.8.1 version)", "inference library(develop version)"
+ :header: "version description", "inference library(1.8.3 version)", "inference library(develop version)"
:widths: 3, 2, 2
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cpu_noavx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
- "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.1_cudnn7.6_avx_mkl_trt6", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_",
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_avx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cpu_noavx_openblas", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_"
+ "ubuntu14.04_cuda10.1_cudnn7.6_avx_mkl_trt6", "`fluid_inference.tgz `_",
"nv-jetson-cuda10-cudnn7.5-trt5", "`fluid_inference.tar.gz `_",
Build from Source Code
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference.md b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference.md
index 71dc617d96e8f1b4076c90d6d570a6a864bab21e..417eaf1e182535b69596876be2ca8cfb3304f6bd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference.md
@@ -5,13 +5,13 @@
下载安装包与对应的测试环境
-------------
-| 版本说明 | 预测库(1.8.1版本) | 编译器 | 构建工具 | cuDNN | CUDA |
+| 版本说明 | 预测库(1.8.3版本) | 编译器 | 构建工具 | cuDNN | CUDA |
|:---------|:-------------------|:-------------------|:----------------|:--------|:-------|
-| cpu_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
-| cpu_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/open/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
-| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
-| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/open/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
-| cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/post107/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 10.0 |
+| cpu_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
+| cpu_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/open/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
+| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
+| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/open/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
+| cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/post107/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.4.1 | 10.0 |
### 硬件环境
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference_en.md b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference_en.md
index 0f0e16fd3dc28e50419c83f276c12f49ee366f51..e25ae184810153421013c60c96c9533b00261ae0 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference_en.md
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/inference_deployment/inference/windows_cpp_inference_en.md
@@ -5,13 +5,13 @@ Install and Compile C++ Inference Library on Windows
Direct Download and Install
-------------
-| Version | Inference Libraries(v1.8.1) | Compiler | Build tools | cuDNN | CUDA |
+| Version | Inference Libraries(v1.8.3) | Compiler | Build tools | cuDNN | CUDA |
|:---------|:-------------------|:-------------------|:----------------|:--------|:-------|
-| cpu_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
-| cpu_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/open/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
-| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
-| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/open/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
-| cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.1/win-infer/mkl/post107/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 10.0 |
+| cpu_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
+| cpu_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/open/cpu/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3| CMake v3.16.0 |
+| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
+| cuda9.0_cudnn7_avx_openblas | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/open/post97/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.3.1 | 9.0 |
+| cuda10.0_cudnn7_avx_mkl | [fluid_inference.zip](https://paddle-wheel.bj.bcebos.com/1.8.3/win-infer/mkl/post107/fluid_inference_install_dir.zip) | MSVC 2015 update 3 | CMake v3.16.0 | 7.4.1 | 10.0 |
### Hardware Environment
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/amp/amp.md b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/amp/amp.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3a41a447f78cf3bc119abb7754292edbbc23050a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/amp/amp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
+# 混合精度训练最佳实践
+
+Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) 是一种自动混合使用半精度(FP16)和单精度(FP32)来加速模型训练的技术。AMP技术可方便用户快速将使用 FP32 训练的模型修改为使用混合精度训练,并通过黑白名单和动态`loss scaling`来保证训练时的数值稳定性进而避免梯度Infinite或者NaN(Not a Number)。借力于新一代NVIDIA GPU中Tensor Cores的计算性能,PaddlePaddle AMP技术在ResNet50、Transformer等模型上训练速度相对于FP32训练加速比可达1.5~2.9。
+
+### 半精度浮点类型FP16
+
+如图 1 所示,半精度(Float Precision16,FP16)是一种相对较新的浮点类型,在计算机中使用2字节(16位)存储。在IEEE 754-2008标准中,它亦被称作binary16。与计算中常用的单精度(FP32)和双精度(FP64)类型相比,FP16更适于在精度要求不高的场景中使用。
+
+
+ 图 1. 半精度和单精度数据示意图
+
+### 英伟达GPU的FP16算力
+
+在使用相同的超参数下,混合精度训练使用半精度浮点(FP16)和单精度(FP32)浮点即可达到与使用纯单精度训练相同的准确率,并可加速模型的训练速度。这主要得益于英伟达推出的Volta及Turing架构GPU在使用FP16计算时具有如下特点:
+
+* FP16可降低一半的内存带宽和存储需求,这使得在相同的硬件条件下研究人员可使用更大更复杂的模型以及更大的batch size大小。
+* FP16可以充分利用英伟达Volta及Turing架构GPU提供的Tensor Cores技术。在相同的GPU硬件上,Tensor Cores的FP16计算吞吐量是FP32的8倍。
+
+### PaddlePaddle AMP功能——牛刀小试
+
+如前文所述,使用FP16数据类型可能会造成计算精度上的损失,但对深度学习领域而言,并不是所有计算都要求很高的精度,一些局部的精度损失对最终训练效果影响很微弱,却能使吞吐和训练速度带来大幅提升。因此,混合精度计算的需求应运而生。具体而言,训练过程中将一些对精度损失不敏感且能利用Tensor Cores进行加速的运算使用半精度处理,而对精度损失敏感部分依然保持FP32计算精度,用以最大限度提升访存和计算效率。
+
+为了避免对每个具体模型人工地去设计和尝试精度混合的方法,PaddlePaadle框架提供自动混合精度训练(AMP)功能,解放"炼丹师"的双手。在PaddlePaddle中使用AMP训练是一件十分容易的事情,用户只需要增加一行代码即可将原有的FP32训练转变为AMP训练。下面以`MNIST`为例介绍PaddlePaddle AMP功能的使用示例。
+
+**MNIST网络定义**
+
+```python
+import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+def MNIST(data, class_dim):
+ conv1 = fluid.layers.conv2d(data, 16, 5, 1, act=None, data_format='NHWC')
+ bn1 = fluid.layers.batch_norm(conv1, act='relu', data_layout='NHWC')
+ pool1 = fluid.layers.pool2d(bn1, 2, 'max', 2, data_format='NHWC')
+ conv2 = fluid.layers.conv2d(pool1, 64, 5, 1, act=None, data_format='NHWC')
+ bn2 = fluid.layers.batch_norm(conv2, act='relu', data_layout='NHWC')
+ pool2 = fluid.layers.pool2d(bn2, 2, 'max', 2, data_format='NHWC')
+ fc1 = fluid.layers.fc(pool2, size=64, act='relu')
+ fc2 = fluid.layers.fc(fc1, size=class_dim, act='softmax')
+ return fc2
+```
+
+针对CV(Computer Vision)类模型组网,为获得更高的训练性能需要注意如下三点:
+
+* `conv2d`、`batch_norm`以及`pool2d`等需要将数据布局设置为`NHWC`,这样有助于使用TensorCore技术加速计算过程1 2 3
+ 图 2. 不同GPU卡之间传输梯度使用FP32数据类型(优化前)
+
+为了降低GPU多卡之间的梯度传输带宽,我们将梯度传输提前至`Cast`操作之前,而每个GPU卡在得到对应的FP16梯度后再执行`Cast`操作将其转变为FP32类型,具体操作详见图2。这一优化在训练大模型时对减少带宽占用尤其有效,如多卡训练BERT-Large模型。
+
+
+ 图 3. 不同GPU卡之间传输梯度使用FP16数据类型(优化后)
+
+### 训练性能对比(AMP VS FP32)
+
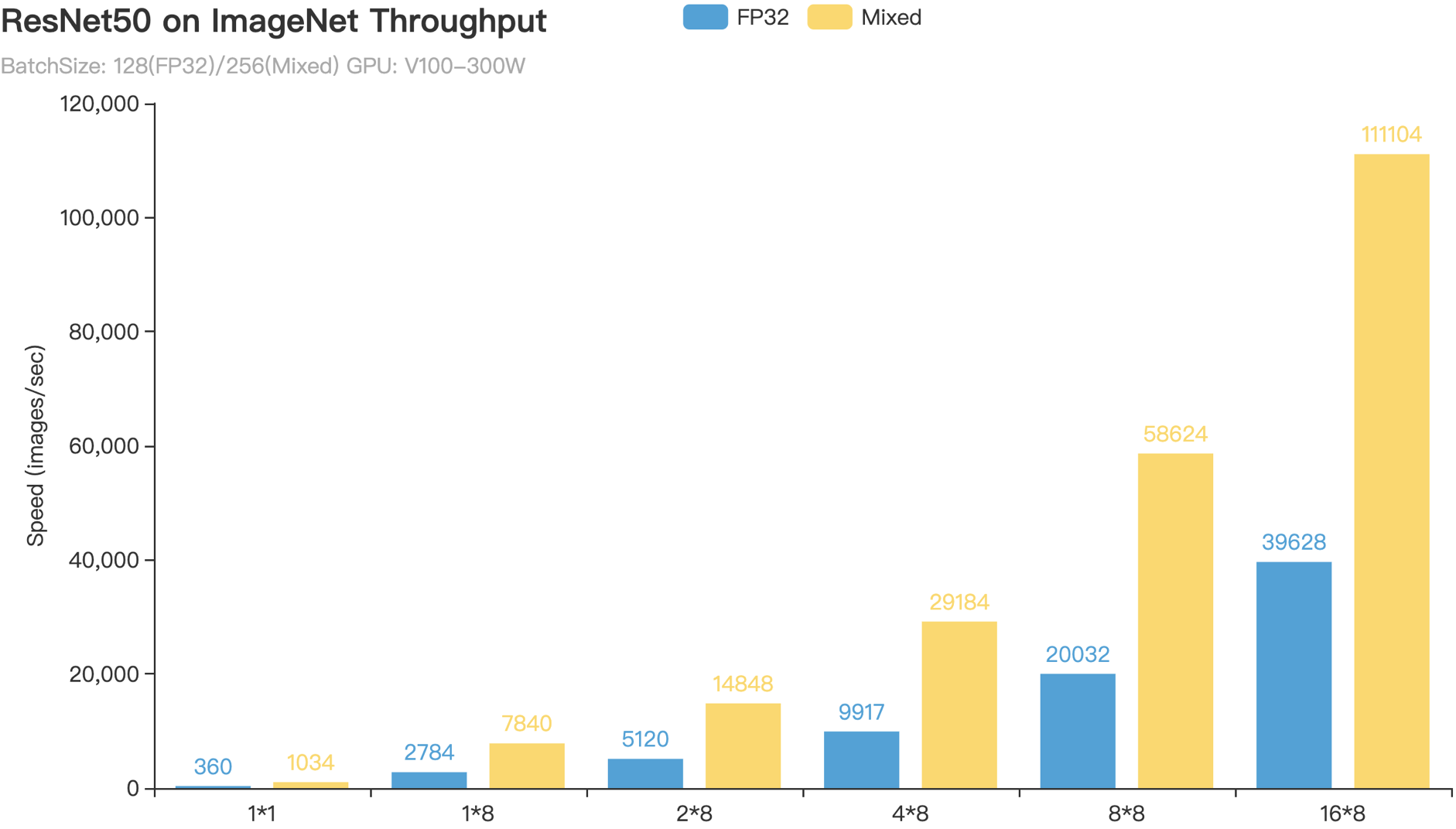
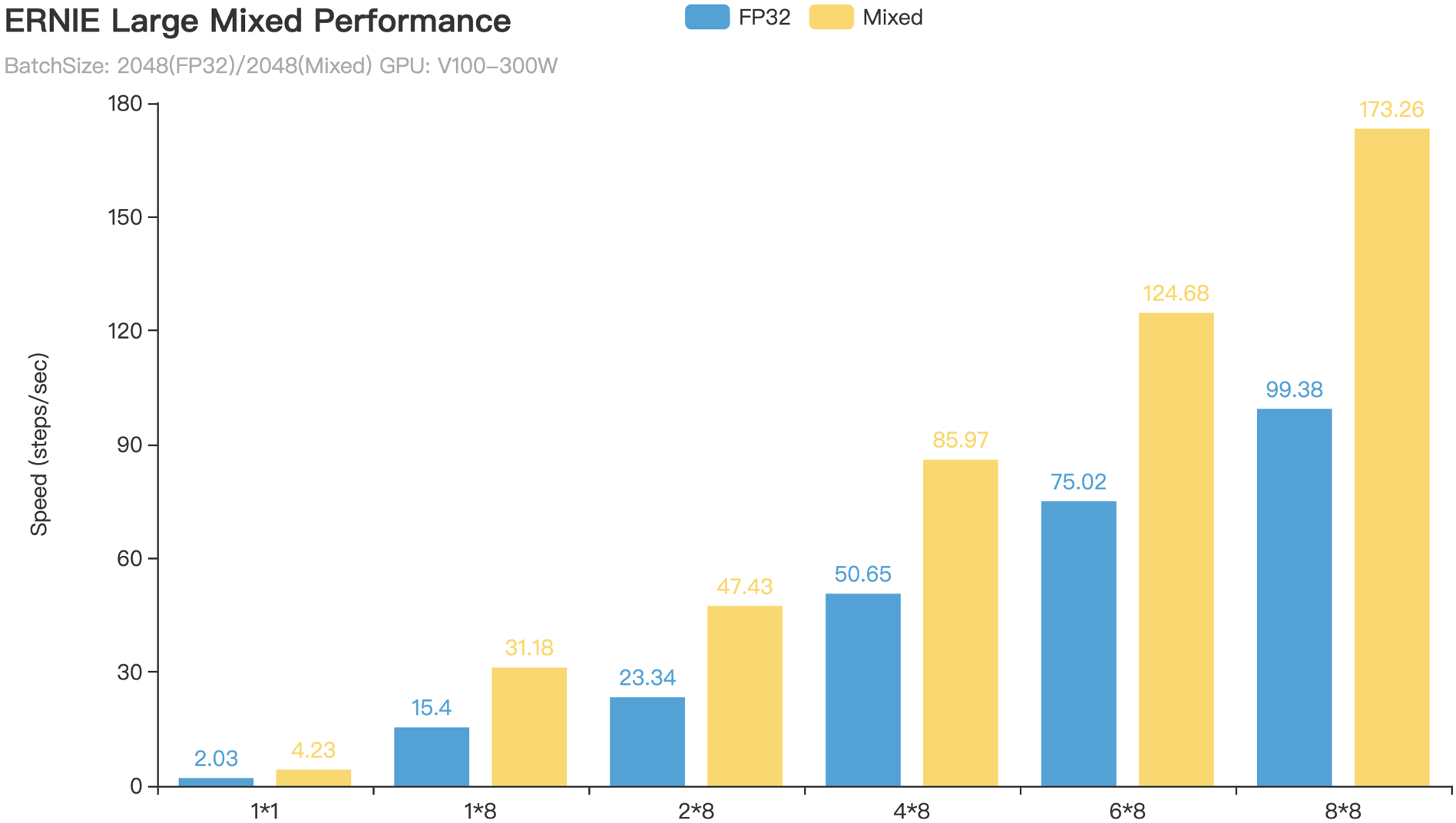
+PaddlePaddle AMP技术在ResNet50、Transformer等模型上训练速度相对于FP32训练上均有可观的加速比,下面是ResNet50和ERNIE Large模型的AMP训练相对于FP32训练的加速效果。
+
+
+图 4. Paddle AMP训练加速效果(横坐标为卡数,如8*8代表8机8卡)
+
+
+
+
+
+从图4所示的图表可以看出,ResNet50的AMP训练相对与FP32训练加速比可达$2.8 \times$以上,而ERNIE Large的AMP训练相对与FP32训练加速比亦可达 $1.7 \times -- 2.1 \times$ 。
+
+### 参考文献
+
+* Mixed Precision Training
+* 使用自动混合精度加速 PaddlePaddle 训练
+* Tensor Layouts In Memory: NCHW vs NHWC ↩
+* Channels In And Out Requirements ↩
+* Matrix-Matrix Multiplication Requirements ↩
diff --git a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/index_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/index_cn.rst
index a40594d13bf74398518f23ad923900ad1bed81d8..b50f091f8c70328d37c7cf3dc92a5b0f14a08f33 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/index_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/advanced_guide/performance_improving/index_cn.rst
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@
singlenode_training_improving/training_best_practice.rst
singlenode_training_improving/memory_optimize.rst
device_switching/device_switching.md
+ amp/amp.md
multinode_training_improving/cpu_train_best_practice.rst
multinode_training_improving/dist_training_gpu.rst
multinode_training_improving/gpu_training_with_recompute.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph.rst
index ac8ca052197935c9d23f2bab10ed5ceb26fa7f4b..397419a8bee35b419f7d23b7a7ce47eb764c56fd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph.rst
@@ -31,6 +31,7 @@ fluid.dygraph
dygraph/guard.rst
dygraph/InstanceNorm.rst
dygraph/InverseTimeDecay.rst
+ dygraph/jit.rst
dygraph/Layer.rst
dygraph/LayerList.rst
dygraph/LayerNorm.rst
@@ -48,10 +49,12 @@ fluid.dygraph
dygraph/PRelu.rst
dygraph/prepare_context.rst
dygraph/ProgramTranslator.rst
+ dygraph/ReduceLROnPlateau.rst
dygraph/save_dygraph.rst
dygraph/Sequential.rst
dygraph/SpectralNorm.rst
dygraph/to_variable.rst
dygraph/TracedLayer.rst
dygraph/Tracer.rst
+ dygraph/TranslatedLayer.rst
dygraph/TreeConv.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/ReduceLROnPlateau.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/ReduceLROnPlateau.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d03ce41e1d45d51c2fe611c3f5607a399ca6cf3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/ReduceLROnPlateau.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_fluid_dygraph_ReduceLROnPlateau:
+
+ReduceLROnPlateau
+-----------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.ReduceLROnPlateau
+ :members:
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/TranslatedLayer.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/TranslatedLayer.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a6f7fd9411e5179999a8bda3f1ae197092343a7a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/TranslatedLayer.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+.. _api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer:
+
+TranslatedLayer
+-----------------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.TranslatedLayer
+ :members:
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7853a048535c045bae18f71c8b4d7f1e44cc65eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+===
+jit
+===
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ jit/save.rst
+ jit/load.rst
+ jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8d1d3bfbc35eca0c05594b540a0cd15c19cebe1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+.. _api_fluid_dygraph_jit_SaveLoadConfig:
+
+SaveLoadConfig
+-------------------------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig
+ :members:
+ :noindex:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/load.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/load.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..51f59909873dd46bb43e42bdc2258a990580c24c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/load.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load:
+
+load
+------------
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.load
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/save.rst b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/save.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fb55029c2870b8c56edd93c4907ae0894036eabe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/dygraph/jit/save.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_fluid_dygraph_jit_save:
+
+save
+------------
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.save
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.sh b/doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.sh
index fe9612775fd31bfda1fe409de47527fe3f7fee57..b2ea86c2a0a99290935d6d9c112edfe3d86da869 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.sh
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.sh
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ python gen_doc.py --module_name "" --module_prefix "" --output fluid --output_na
python gen_module_index.py fluid fluid
# tensor
-for module in math random stat
+for module in math random stat linalg search
do
python gen_doc.py --module_name ${module} --module_prefix ${module} --output ${module} --output_name tensor --to_multiple_files True --output_dir tensor
python gen_module_index.py tensor.${module} ${module}
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/gen_index.py b/doc/fluid/api/gen_index.py
index 16bea3fd471e4d08ceb71d8a1150589f041292c9..4cc7272b03aa0fec3eefe543d7ff7ad791d6e1fd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/gen_index.py
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/gen_index.py
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ import glob
import os
if __name__ == '__main__':
- with open('index_en.rst', 'w') as file_object:
+ with open('index_en.rst', 'w') as file_object:
file_object = open('index_en.rst', 'w')
file_object.write('''=============
API Reference
@@ -25,16 +25,16 @@ API Reference
else:
pattern = target_dir + '/*.rst'
file_names.extend(glob.glob(pattern))
-
+
for file_name in sorted(file_names):
- with open(file_name, 'r')as f:
+ with open(file_name, 'r') as f:
for i in range(2):
line = f.readline().strip()
if line.find('paddle.') != -1:
- file_object.write(' '+file_name + "\n")
+ file_object.write(' ' + file_name + "\n")
file_names.remove(file_name)
- file_object.write(' '+'fluid.rst' + "\n")
+ file_object.write(' ' + 'fluid.rst' + "\n")
for file_name in sorted(file_names):
- if file_name not in ['index_en.rst', 'fluid.rst']:
- file_object.write(' '+file_name + "\n")
+ if file_name not in ['index_en.rst']:
+ file_object.write(' ' + file_name + "\n")
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative.rst
index 48aebcbfddf188d74dfa182559cffa25997bead4..f138e06701b138dc109dab2e3b1c17832658d390 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/imperative.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative.rst
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ paddle.imperative
imperative/grad.rst
imperative/guard.rst
imperative/InverseTimeDecay.rst
+ imperative/jit.rst
imperative/load.rst
imperative/NaturalExpDecay.rst
imperative/no_grad.rst
@@ -25,3 +26,4 @@ paddle.imperative
imperative/save.rst
imperative/to_variable.rst
imperative/TracedLayer.rst
+ imperative/TranslatedLayer.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative/TranslatedLayer.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/TranslatedLayer.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0299a9f57392e267ae015947345249784fd929f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/TranslatedLayer.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _api_imperative_TranslatedLayer:
+
+TranslatedLayer
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.io.TranslatedLayer
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7853a048535c045bae18f71c8b4d7f1e44cc65eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+===
+jit
+===
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ jit/save.rst
+ jit/load.rst
+ jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cab85776ec33f9cab2dc788ebbb3081fca1d4035
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/SaveLoadConfig.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _api_imperative_jit_SaveLoadConfig:
+
+SaveLoadConfig
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/load.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/load.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..723a87936a8f26653eb2b34f361aa35a4b3fd74f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/load.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _api_imperative_jit_load:
+
+load
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.load
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/save.rst b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/save.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b809a99166e35edd65af253dffe40053776a68dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/imperative/jit/save.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _api_imperative_jit_save:
+
+save
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.save
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/index_en.rst b/doc/fluid/api/index_en.rst
index efbe319fb04e9ad1cce54a760e955b51c311943f..f360715383903c2f6efae7a01e662a710fafc340 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/index_en.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/index_en.rst
@@ -6,15 +6,30 @@ API Reference
:maxdepth: 1
../api_guides/index_en.rst
- paddle.rst
dataset.rst
- tensor.rst
- nn.rst
- imperative.rst
declarative.rst
- optimizer.rst
- metric.rst
framework.rst
+ imperative.rst
io.rst
- utils.rst
- incubate.rst
+ metric.rst
+ nn.rst
+ optimizer.rst
+ tensor.rst
+ fluid.rst
+ backward.rst
+ clip.rst
+ data/data_reader.rst
+ data/dataset.rst
+ dygraph.rst
+ executor.rst
+ fluid.rst
+ initializer.rst
+ layers.rst
+ metrics.rst
+ nets.rst
+ paddle.rst
+ profiler.rst
+ regularizer.rst
+ transpiler.rst
+ unique_name.rst
+ review_tmp.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/layers.rst b/doc/fluid/api/layers.rst
index 3ad2eeaa2941b7a0b6df18eb51aaf7b3691504b5..0f1fe3c222c5266deacca8603ff10ce9fed33429 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/layers.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/layers.rst
@@ -182,6 +182,7 @@ fluid.layers
layers/mul.rst
layers/multi_box_head.rst
layers/multiclass_nms.rst
+ layers/matrix_nms.rst
layers/multiplex.rst
layers/MultivariateNormalDiag.rst
layers/natural_exp_decay.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/layers/matrix_nms.rst b/doc/fluid/api/layers/matrix_nms.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..60bbbeb151bdd87861c37b625139988ce7db9467
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/layers/matrix_nms.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_fluid_layers_matrix_nms:
+
+matrix_nms
+--------------
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.fluid.layers.matrix_nms
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn.rst
index b64a884221bdf398f2351ea26ae6d46eceb59c51..3d8ad814db7dfe9da66f6324117ad7c6c83c18fb 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/nn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn.rst
@@ -49,6 +49,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn/exponential_decay.rst
nn/filter_by_instag.rst
nn/fsp_matrix.rst
+ nn/functional.rst
nn/gather_tree.rst
nn/gelu.rst
nn/generate_mask_labels.rst
@@ -67,6 +68,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn/huber_loss.rst
nn/image_resize.rst
nn/image_resize_short.rst
+ nn/initializer.rst
nn/inverse_time_decay.rst
nn/iou_similarity.rst
nn/kldiv_loss.rst
@@ -82,7 +84,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn/logsigmoid.rst
nn/loss.rst
nn/lrn.rst
- nn/margin_rank_loss.rst
+ nn/matrix_nms.rst
nn/maxout.rst
nn/mse_loss.rst
nn/multiclass_nms.rst
@@ -91,14 +93,13 @@ paddle.nn
nn/npair_loss.rst
nn/one_hot.rst
nn/pad.rst
- nn/pad_constant_like.rst
nn/pad2d.rst
+ nn/pad_constant_like.rst
nn/ParameterList.rst
nn/piecewise_decay.rst
nn/pixel_shuffle.rst
nn/polygon_box_transform.rst
nn/polynomial_decay.rst
- nn/pool2d.rst
nn/Pool2D.rst
nn/pool3d.rst
nn/prior_box.rst
@@ -148,3 +149,5 @@ paddle.nn
nn/while_loop.rst
nn/yolo_box.rst
nn/yolov3_loss.rst
+ nn/functional/loss/margin_ranking_loss.rst
+ nn/layer/loss/MarginRankingLoss.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..551924348e956066edf7affedb78a60e7adf2df4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+==========
+functional
+==========
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ functional/l1_loss.rst
+ functional/nll_loss.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/l1_loss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/l1_loss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..01a3ea06e7d034eb70744146816e6d0a166b749d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/l1_loss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+.. _api_nn_functional_l1_loss:
+
+l1_loss
+------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.nn.functional.l1_loss
+ :members:
+ :inherited-members:
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/loss/margin_ranking_loss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/loss/margin_ranking_loss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e92eadc126a49d8a46bcfc06960eb39dcdc35fec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/loss/margin_ranking_loss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_nn_functional_loss_margin_ranking_loss:
+
+margin_ranking_loss
+-------------------
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.nn.functional.loss.margin_ranking_loss
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/nll_loss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/nll_loss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6f0ce4093ac8a9cefc202e4346457edd4b2c6ae1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/functional/nll_loss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+.. _api_nn_functional_nll_loss:
+
+nll_loss
+-------------------------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.nn.functional.nll_loss
+ :members:
+ :inherited-members:
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/layer/loss/MarginRankingLoss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/layer/loss/MarginRankingLoss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d69d1deff5defab24b2f12ea877c3a208a801478
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/layer/loss/MarginRankingLoss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_nn_layer_loss_MarginRankingLoss:
+
+MarginRankingLoss
+-----------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.nn.layer.loss.MarginRankingLoss
+ :members:
+ :inherited-members:
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/transpiler/RoundRobin.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/loss/NLLLoss.rst
similarity index 56%
rename from doc/fluid/api/transpiler/RoundRobin.rst
rename to doc/fluid/api/nn/loss/NLLLoss.rst
index 547757d20e8388b3ea51b52a0b4c9e23116f0645..c1a0c26de51b8869a8eccb2150c8e5635159f1de 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/transpiler/RoundRobin.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/loss/NLLLoss.rst
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
!DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
-.. _api_fluid_transpiler_RoundRobin:
+.. _api_nn_loss_NLLLoss:
-RoundRobin
-----------
+NLLLoss
+-------------------------------
-.. autoclass:: paddle.fluid.transpiler.RoundRobin
+.. autoclass:: paddle.nn.loss.NLLLoss
:members:
:inherited-members:
:noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/margin_rank_loss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/margin_rank_loss.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 1ef924d8728dce215f20372bd4f6ea4a87a27874..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/nn/margin_rank_loss.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_nn_margin_rank_loss:
-
-margin_rank_loss
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.margin_rank_loss
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/matrix_nms.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/matrix_nms.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..49529d0faf1118dc3c61018d1be232b5d7ff5b63
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/matrix_nms.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _api_nn_matrix_nms:
+
+matrix_nms
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.matrix_nms
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/nn/softmax.rst b/doc/fluid/api/nn/softmax.rst
index 5eba38ad90a2d587f09a01a653dc01c7f3f877bb..bb18407af36005b23ab911390b8be880c9695101 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/nn/softmax.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/nn/softmax.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
.. _api_nn_softmax:
softmax
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.softmax
+-------
+.. autofunction:: paddle.nn.functional.softmax
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/optimizer.rst b/doc/fluid/api/optimizer.rst
index a3a1736f15d8b0da8823d8b9dad8992c3b8581b6..06ccc695574c9d060dfe4c853c7d6c2c4ed8eb4f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/optimizer.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/optimizer.rst
@@ -28,7 +28,6 @@ paddle.optimizer
optimizer/ModelAverage.rst
optimizer/Momentum.rst
optimizer/MomentumOptimizer.rst
- optimizer/PipelineOptimizer.rst
optimizer/RecomputeOptimizer.rst
optimizer/RMSPropOptimizer.rst
optimizer/SGD.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/optimizer/PipelineOptimizer.rst b/doc/fluid/api/optimizer/PipelineOptimizer.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 87e6f4026d49f4db11dec390faf325082bb1fdbe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/optimizer/PipelineOptimizer.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
- !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
-
-.. _api_fluid_optimizer_PipelineOptimizer:
-
-PipelineOptimizer
------------------
-
-.. autoclass:: paddle.fluid.optimizer.PipelineOptimizer
- :members:
- :inherited-members:
- :exclude-members: apply_gradients, apply_optimize, backward, load
- :noindex:
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle.rst
index c4af7870125e5c794621f8d828bc29db91e29efe..1d69e4df54808d97d7876289469b0b5e6cf7fa91 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle.rst
@@ -45,10 +45,7 @@ paddle
paddle/dot.rst
paddle/elementwise_add.rst
paddle/elementwise_div.rst
- paddle/elementwise_equal.rst
paddle/elementwise_floordiv.rst
- paddle/elementwise_max.rst
- paddle/elementwise_min.rst
paddle/elementwise_mod.rst
paddle/elementwise_mul.rst
paddle/elementwise_pow.rst
@@ -56,6 +53,7 @@ paddle
paddle/elementwise_sum.rst
paddle/enable_imperative.rst
paddle/equal.rst
+ paddle/equal_all.rst
paddle/erf.rst
paddle/ExecutionStrategy.rst
paddle/Executor.rst
@@ -99,9 +97,11 @@ paddle
paddle/manual_seed.rst
paddle/matmul.rst
paddle/max.rst
+ paddle/maximum.rst
paddle/mean.rst
paddle/meshgrid.rst
paddle/min.rst
+ paddle/minimum.rst
paddle/mm.rst
paddle/mul.rst
paddle/multiplex.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/ExecutionStrategy.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/ExecutionStrategy.rst
index fd36fd620edda583bbd6570b6a1da78951a567be..6df5ca375f2e26b5bd9d4fe999461c41be9ad315 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/ExecutionStrategy.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/ExecutionStrategy.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
ExecutionStrategy
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.framework.ExecutionStrategy
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.ExecutionStrategy
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/argsort.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/argsort.rst
index 43be9de959815defb112d674db64f06410ffd4b7..716f7e79312bcc0f83abff33bf3684b6a6b68500 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/argsort.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/argsort.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
argsort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.argsort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/cumsum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/cumsum.rst
index 26211d9321da87942f4469ef47bfd78fa7173d64..673296e8836d1116f16d65b73a4f781241538dd4 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/cumsum.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/cumsum.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
cumsum
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.cumsum
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_equal.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 485738ee2b32b6735e3209638b2fa162546a41fc..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_equal.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_paddle_elementwise_equal:
-
-elementwise_equal
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.equal
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_max.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_max.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 76f9148ef2f600ada77f099fdd69a781aa72ab40..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_max.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_paddle_elementwise_max:
-
-elementwise_max
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_max
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_min.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_min.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index f2258a309201d5ea23a518a70d79dd8ca9d06929..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/elementwise_min.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_paddle_elementwise_min:
-
-elementwise_min
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_min
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/equal_all.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/equal_all.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..58fc331acc2b3f564dc73bb8c039c17b9b4720f2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/equal_all.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_paddle_equal_all
+
+equal_all
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.equal_all
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_equal.rst
index 8739113f3208d15efdd9c00a2619ae612a6e1873..54afe57ffab5185fc2c3fb92a671e0b726108ab3 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_than.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_than.rst
index f54f0e026f520176bc60b00a59e28adc69358915..04a874dd929d7dae274898c87029059b1b1d6261 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_than.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/greater_than.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_equal.rst
index 16cc1a647457e370ed105172936b61afad04f00c..3fc5e2ce2b819dfed7ca8b64841836229c86d3e4 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_than.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_than.rst
index 2c13074ad988e5a5138a76cff50619963964d55d..7df6eb441d37a2fe8bf95e43a48df8471115ad2c 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_than.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/less_than.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/max.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/max.rst
index 695f4d5b6bd97f460624650a206affe6b2140c41..0d28148a8dcc0ac31744450c954e9a125e475add 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/max.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/max.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
max
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_max
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.max
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/maximum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/maximum.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c85f8a97710efb559e5f73c586eb45798224e8db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/maximum.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_paddle_maximum:
+
+maximum
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.maximum
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/min.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/min.rst
index a05dd553f4827dd8feeb4ddc56ccfa3ce7d11eb9..bb99109471c0ab684fdd7646fc446abe8aafe6cb 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/min.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/min.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
min
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_min
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.min
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/minimum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/minimum.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..41391741da78620231f5fe1a9c5ee3ea73ce70be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/minimum.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_paddle_minimum:
+
+minimum
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.minimum
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/not_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/not_equal.rst
index fb5de71d0a79ec9be46c43c02414492acd087f89..4fd1cbe809d9dded938f2014124ee9b738b1d9cd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/not_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/not_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
not_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.not_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/sort.rst b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/sort.rst
index e22a93a5d3e1f657060756e6a49153423a344ef3..5f87357ccb39b52e975ef73c33b557f220c292a2 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/paddle/sort.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/paddle/sort.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
sort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.sort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp.rst b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e39366bcef08a15baa15c3cfbb318022a2dc47b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+=================
+paddle.review_tmp
+=================
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ review_tmp/MarginRankingLoss.rst
+ review_tmp/margin_ranking_loss.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/MarginRankingLoss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/MarginRankingLoss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..edc5d1cc57c85be5eb37312c6dc9b8b204b4d9b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/MarginRankingLoss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+.. _api_nn_loss_MarginRankingLoss_tmp:
+
+MarginRankingLoss
+-----------------
+
+.. autoclass:: paddle.nn.loss.MarginRankingLoss
+ :members:
+ :inherited-members:
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/margin_ranking_loss.rst b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/margin_ranking_loss.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..289d1928bf05925dc81238c7ff0dad2623a4d3fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/review_tmp/margin_ranking_loss.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_nn_functional_margin_ranking_loss_tmp:
+
+margin_ranking_loss
+-------------------
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.nn.functional.margin_ranking_loss
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor.rst
index 84b1501a1ed928960447bee4886d4c32be80b45d..a8eb2516782826e475c067311c765b50fddf4aaa 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor.rst
@@ -20,19 +20,18 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor/cos.rst
tensor/create_tensor.rst
tensor/crop_tensor.rst
+ tensor/cross.rst
tensor/cumsum.rst
tensor/diag.rst
tensor/div.rst
tensor/elementwise_add.rst
tensor/elementwise_div.rst
- tensor/elementwise_equal.rst
tensor/elementwise_floordiv.rst
- tensor/elementwise_max.rst
- tensor/elementwise_min.rst
tensor/elementwise_mod.rst
tensor/elementwise_mul.rst
tensor/elementwise_pow.rst
tensor/elementwise_sub.rst
+ tensor/equal_all.rst
tensor/erf.rst
tensor/exp.rst
tensor/expand.rst
@@ -63,8 +62,10 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor/logical_xor.rst
tensor/math.rst
tensor/max.rst
+ tensor/maximum.rst
tensor/mean.rst
tensor/min.rst
+ tensor/minimum.rst
tensor/mm.rst
tensor/mul.rst
tensor/multiplex.rst
@@ -92,6 +93,7 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor/scatter.rst
tensor/scatter_nd.rst
tensor/scatter_nd_add.rst
+ tensor/search.rst
tensor/shape.rst
tensor/shard_index.rst
tensor/shuffle.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/argsort.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/argsort.rst
index 927d474d151f63a9bb204f3adc54085574b0f1a6..2168777783e8ff4a2ba5e217ce3f9982f4f97d8f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/argsort.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/argsort.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
argsort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.argsort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cross.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cross.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3bb049f74d7232bd42020fee1b702c313395ba85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cross.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_tensor_cn_cos:
+
+cross
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.cross
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cumsum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cumsum.rst
index 835c7231150c7cf6d9de61f4907aca2cd558a192..96c1bf0abf8c06621b93624941025e4929652add 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cumsum.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/cumsum.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
cumsum
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.cumsum
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_equal.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index ae7944446507328d83969df26d22427aabee1777..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_equal.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_tensor_cn_elementwise_equal:
-
-elementwise_equal
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.equal
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_max.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_max.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f96581bba4dba88df4bfd4676e0e81050004844..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_max.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_tensor_cn_elementwise_max:
-
-elementwise_max
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_max
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_min.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_min.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 9b5641099c4afc4738bd6b495d61a323387a74d9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/elementwise_min.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _api_tensor_cn_elementwise_min:
-
-elementwise_min
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_min
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/equal_all.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/equal_all.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5149e6101d64b1e2c8626a1d35693fd503b2d230
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/equal_all.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_tensor_cn_equal_all:
+
+equal_all
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.equal_all
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_equal.rst
index ab967838e629e67052ae574e93098ebcae00c0bf..1a1394de05e7b4bf7b4cbfb463e3c9e79206d9cc 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_than.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_than.rst
index 789f212a75130d76546833207afd5761fea499ee..b0ff74910eb094120568dc4f3c7f792e221c91b7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_than.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/greater_than.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_equal.rst
index 5e7c7180a4899d380c6c1f2d49aba9597e8b456b..4adbeb1ccf2972ccb30cb1fb762dbea7a74114a4 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_than.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_than.rst
index c4614acf5f666af3242b01027aa379a1b4ad0cfc..592dc48d66bbdd4c6506e118c98b654bd55e93fe 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_than.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/less_than.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/max.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/max.rst
index cdd8e4239bf6e73b64775a9858ec0b9661e4d73c..61a8667f8cab06a8433d9ab9e143390d3c1ccbc8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/max.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/max.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
max
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_max
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.max
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/maximum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/maximum.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7c91c5f2bd465a17ceae3a2f602addbd115ed273
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/maximum.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_tensor_cn_maximum:
+
+maximum
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.maximum
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/mean.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/mean.rst
index dce657a2e57aa3b8d78136c9b9c311f8d23c76aa..d226a37107af8e67ef4d8ea0bf9a17e536fede36 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/mean.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/mean.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
-.. _api_tensor_cn_mean:
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_tensor_mean:
mean
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.mean
+---------
+.. autofunction:: paddle.tensor.mean
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/min.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/min.rst
index ea16448a6752464a582e3a2ea63960dcdcee6e40..cdb8df5c370ce66a5e8e39555699e09730bdcf23 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/min.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/min.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
min
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_min
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.min
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/minimum.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/minimum.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..725aaeb8a7f2fa0cf7b1a7fa1d8611a4c4967ac7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/minimum.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _api_tensor_cn_minimum:
+
+minimum
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.minimum
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/not_equal.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/not_equal.rst
index d4f506f99e814b0a578d474a2bcb78cc6dd7c582..8aeac42d73c7683ba037bef31a6b68c2acf01064 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/not_equal.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/not_equal.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
not_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.not_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/ones_like.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/ones_like.rst
index 4e1ae1407c2717619bb211a3e642e1d0e197db26..47ecd764f36b11d425863b0a09a111040aed31d2 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/ones_like.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/ones_like.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
-.. _api_tensor_cn_ones_like:
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_tensor_ones_like:
ones_like
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.ones_like
+---------
+.. autofunction:: paddle.tensor.ones_like
+ :noindex:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random.rst
index 687c6d5af6475436efc4c12c5ff93023cb32d526..fdc985d3de06f89ecc75c5f52dfe59d8f3747987 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random.rst
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ random
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
+ random/rand.rst
random/randint.rst
random/randn.rst
random/randperm.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random/randn.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random/randn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d332aaa1441ff4634a5674bd4765ac0534ab39b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/random/randn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+.. THIS FILE IS GENERATED BY `gen_doc.{py|sh}`
+ !DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY!
+
+.. _api_tensor_random_randn:
+
+randn
+-----
+
+.. autofunction:: paddle.tensor.random.randn
+ :noindex:
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/sort.rst b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/sort.rst
index 14cc6f45b41d5e7a832efdf2244bae362033ff83..21da4ab432d026f281b69183d95134f1fbadd553 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/tensor/sort.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/tensor/sort.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
sort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.sort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api/transpiler.rst b/doc/fluid/api/transpiler.rst
index 2492b98136f85ccb49922c08b096be4f7eb96d7d..28905bd06b502b30df36f03d6aea8c1295eef02f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api/transpiler.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api/transpiler.rst
@@ -10,4 +10,3 @@ fluid.transpiler
transpiler/HashName.rst
transpiler/memory_optimize.rst
transpiler/release_memory.rst
- transpiler/RoundRobin.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/clip_cn/GradientClipByGlobalNorm_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/clip_cn/GradientClipByGlobalNorm_cn.rst
index 58558411f3cd13208aebb6c5bf6050fe16c29854..4b714c9c42f52a525902c836f166d54b78e3f318 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/clip_cn/GradientClipByGlobalNorm_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/clip_cn/GradientClipByGlobalNorm_cn.rst
@@ -64,8 +64,8 @@ GradientClipByGlobalNorm
# return Parameter.name=="fc_0.w_0"
# clip = fluid.clip.GradientClipByGlobalNorm(clip_norm=1.0, need_clip=fileter_func)
- sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGDOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
- sgd_optimizer.minimize(loss, grad_clip=clip)
+ sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGDOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, grad_clip=clip)
+ sgd_optimizer.minimize(loss)
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
@@ -101,5 +101,7 @@ GradientClipByGlobalNorm
# clip = fluid.clip.GradientClipByGlobalNorm(clip_norm=1.0, need_clip=fileter_func)
sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(
- learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
- sgd_optimizer.minimize(loss, grad_clip=clip)
\ No newline at end of file
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ parameter_list=linear.parameters(),
+ grad_clip=clip)
+ sgd_optimizer.minimize(loss)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn.rst
index 2e3db69845edf063e67d863eab0982f26e7d50a9..7cf2de04add71995bdb359d5427f2e65f5190946 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn.rst
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@ fluid.dygraph
dygraph_cn/Conv2DTranspose_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Conv3D_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Conv3DTranspose_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/CosineAnnealingDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/CosineDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/declarative_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Dropout_cn.rst
@@ -27,11 +28,14 @@ fluid.dygraph
dygraph_cn/guard_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/InstanceNorm_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/InverseTimeDecay_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/jit_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/LambdaDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Layer_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/LayerList_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/LayerNorm_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Linear_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/load_dygraph_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/MultiStepDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/NCE_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/NoamDecay_cn.rst
@@ -44,10 +48,13 @@ fluid.dygraph
dygraph_cn/PRelu_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/prepare_context_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/ProgramTranslator_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/ReduceLROnPlateau_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/save_dygraph_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Sequential_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/SpectralNorm_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/StepDecay_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/to_variable_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/TracedLayer_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/Tracer_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
dygraph_cn/TreeConv_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Conv2D_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Conv2D_cn.rst
index c09cb6548135d5b713d3c63f01ca321311e09187..3e81c4a31738d78234527178a1408c7cc03519ef 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Conv2D_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Conv2D_cn.rst
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ Conv2D
参数:
- **num_channels** (int) - 输入图像的通道数。
- - **num_fliters** (int) - 滤波器的个数,和输出特征图个数相同。
+ - **num_filters** (int) - 滤波器的个数,和输出特征图个数相同。
- **filter_size** (int|tuple) - 滤波器大小。如果 ``filter_size`` 是一个元组,则必须包含两个整型数,分别表示滤波器高度和宽度。否则,表示滤波器高度和宽度均为 ``filter_size`` 。
- **stride** (int|tuple, 可选) - 步长大小。如果 ``stride`` 为元组,则必须包含两个整型数,分别表示垂直和水平滑动步长。否则,表示垂直和水平滑动步长均为 ``stride`` 。默认值:1。
- **padding** (int|tuple, 可选) - 填充大小。如果 ``padding`` 为元组,则必须包含两个整型数,分别表示竖直和水平边界填充大小。否则,表示竖直和水平边界填充大小均为 ``padding`` 。默认值:0。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/LambdaDecay_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/LambdaDecay_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1b59cfbaf888fe971e6d39a72579848108d57094
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/LambdaDecay_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_LambdaDecay:
+
+LambdaDecay
+-------------------------------
+
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.LambdaDecay(learning_rate, lr_lambda)
+
+:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
+
+
+该API提供 lambda函数 设置学习率的功能。 ``lr_lambda`` 为一个lambda函数,其通过 ``epoch`` 计算出一个因子,该因子会乘以初始学习率。
+
+算法可以描述为:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ learning_rate = 0.5 # init learning_rate
+ lr_lambda = lambda epoch: 0.95 ** epoch
+
+ learning_rate = 0.5 # epoch 0
+ learning_rate = 0.475 # epoch 1
+ learning_rate = 0.45125 # epoch 2
+
+参数:
+ - **learning_rate** (float|int) - 初始化的学习率。可以是Python的float或int。
+ - **lr_lambda** (function) - ``lr_lambda`` 为一个lambda函数,其通过 ``epoch`` 计算出一个因子,该因子会乘以初始学习率。
+
+返回: 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import numpy as np
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ x = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, [10, 10]).astype("float32")
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.Linear(10, 10)
+ input = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x)
+ scheduler = fluid.dygraph.LambdaDecay(0.5, lr_lambda=lambda x: 0.95**x)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate = scheduler, parameter_list = linear.parameters())
+ for epoch in range(6):
+ for batch_id in range(5):
+ out = linear(input)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(out)
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ scheduler.epoch()
+ print("epoch:%d, current lr is %f" .format(epoch, adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # epoch:0, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:1, current lr is 0.475
+ # epoch:2, current lr is 0.45125
+
+.. py:method:: epoch(epoch=None)
+通过当前的 epoch 调整学习率,调整后的学习率将会在下一次调用 ``optimizer.minimize`` 时生效。
+
+参数:
+ - **epoch** (int|float,可选) - 类型:int或float。指定当前的epoch数。默认:无,此时将会自动累计epoch数。
+
+返回:
+ 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ 参照上述示例代码。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Layer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Layer_cn.rst
index 914e07cbf3a6bf38f641d713427cfc67161ef9bc..ffce7959f30a98d46783db09b3c4f8b0a657777b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Layer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Layer_cn.rst
@@ -256,6 +256,87 @@ hook(Layer, input, output) -> None or modified output
for prefix, layer in model.named_sublayers():
print(prefix, layer)
+.. py:method:: register_buffer(name, variable, persistable=True)
+
+将一个Variable注册为buffer。
+
+buffer是一个非参数类型的变量,不会被优化器更新,但在评估或预测阶段可能是必要的状态变量。比如 ``BatchNorm`` 中的均值和方差。
+
+注册的buffer默认是可持久性的,会被保存到 ``state_dict`` 中。如果指定 ``persistable`` 参数为False,则会注册一个非持久性的buffer,即不会同步和保存到 ``state_dict`` 中。
+
+参数:
+ - **name** (str) - 注册buffer的名字。可以通过此名字来访问已注册的buffer。
+ - **variable** (Variable) - 将被注册为buffer的变量。
+ - **persistable** (bool, 可选) - 注册的buffer是否需要可持久性地保存到 ``state_dict`` 中。
+
+返回:None
+
+返回类型:None
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.Linear(10, 3)
+ value = np.array([0]).astype("float32")
+ buffer = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(value)
+ linear.register_buffer("buf_name", buffer, persistable=True)
+
+ # get the buffer by attribute.
+ print(linear.buf_name)
+
+.. py:method:: buffers(include_sublayers=True)
+
+返回一个由当前层及其子层的所有buffers组成的列表。
+
+参数:
+ - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 是否返回子层的buffers。如果为True,返回的列表中包含子层的buffers。默认值:True。
+
+返回:一个由当前层及其子层的所有buffers组成的列表,列表中的元素类型为Variable。
+
+返回类型:list
+
+.. py:method:: named_buffers(prefix='', include_sublayers=True)
+
+返回层中所有buffers的迭代器,生成名称和buffer的元组。
+
+参数:
+ - **prefix** (str, 可选) - 在所有buffer名称前加的前缀。默认值:''。
+ - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 是否返回子层的buffers。如果为True,返回的列表中包含子层的buffers。默认值:True。
+
+返回:产出名称和buffer的元组的迭代器。
+
+返回类型:iterator
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ fc1 = fluid.Linear(10, 3)
+ buffer1 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.array([0]).astype("float32"))
+ # register a variable as buffer by specific `persistable`
+ fc1.register_buffer("buf_name_1", buffer1, persistable=True)
+
+ fc2 = fluid.Linear(3, 10)
+ buffer2 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.array([1]).astype("float32"))
+ # register a buffer by assigning an attribute with Variable.
+ # The `persistable` can only be False by this way.
+ fc2.buf_name_2 = buffer2
+
+ model = fluid.dygraph.Sequential(fc1, fc2)
+
+ # get all named buffers
+ for name, buffer in model.named_buffers():
+ print(name, buffer)
+
.. py:method:: forward(*inputs, **kwargs)
定义每次调用时执行的计算。应该被所有子类覆盖。
@@ -290,13 +371,13 @@ hook(Layer, input, output) -> None or modified output
.. py:method:: state_dict(destination=None, include_sublayers=True)
-获取当前层及其子层的所有参数。并将所有参数存放在dict结构中。
+获取当前层及其子层的所有参数和可持久性buffers。并将所有参数和buffers存放在dict结构中。
参数:
- - **destination** (dict, 可选) - 如果提供 ``destination`` ,则所有参数都将存放在 ``destination`` 中。 默认值:None。
- - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则包括子层的参数。默认值:True。
+ - **destination** (dict, 可选) - 如果提供 ``destination`` ,则所有参数和可持久性buffers都将存放在 ``destination`` 中。 默认值:None。
+ - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则包括子层的参数和buffers。默认值:True。
-返回:包含所有参数的dict
+返回:包含所有参数和可持久行buffers的dict
返回类型:dict
@@ -312,11 +393,11 @@ hook(Layer, input, output) -> None or modified output
.. py:method:: set_dict(stat_dict, include_sublayers=True)
-根据传入的 ``stat_dict`` 设置参数。 所有参数将由 ``stat_dict`` 中的 ``Tensor`` 设置。
+根据传入的 ``stat_dict`` 设置参数和可持久性buffers。 所有参数和buffers将由 ``stat_dict`` 中的 ``Tensor`` 设置。
参数:
- - **state_dict** (dict) - 包含所有参数的dict。
- - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则还包括子层的参数。 默认值:True。
+ - **state_dict** (dict) - 包含所有参数和可持久性buffers的dict。
+ - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则还包括子层的参数和buffers。 默认值:True。
返回:None
@@ -337,11 +418,11 @@ hook(Layer, input, output) -> None or modified output
.. warning::
该函数将被弃用。请使用set_dict函数。
-根据传入的 ``stat_dict`` 设置参数。 所有参数将由 ``stat_dict`` 中的 ``Tensor`` 设置。
+根据传入的 ``stat_dict`` 设置参数和可持久性buffers。 所有参数和buffers将由 ``stat_dict`` 中的 ``Tensor`` 设置。
参数:
- - **state_dict** (dict) - 包含所有参数的dict。
- - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则还包括子层的参数。 默认值:True。
+ - **state_dict** (dict) - 包含所有参数和可持久性buffers的dict。
+ - **include_sublayers** (bool, 可选) - 如果设置为True,则还包括子层的参数和buffers。 默认值:True。
返回:None
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/MultiStepDecay_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/MultiStepDecay_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..896f90066ca8463f34bee8005b0f46bd4fd68a25
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/MultiStepDecay_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_MultiStepDecay:
+
+MultiStepDecay
+-------------------------------
+
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.MultiStepDecay(learning_rate, milestones, decay_rate=0.1)
+
+:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
+
+
+该接口提供 ``MultiStep`` 衰减学习率的功能。
+
+算法可以描述为:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ learning_rate = 0.5
+ milestones = [30, 50]
+ decay_rate = 0.1
+ if epoch < 30:
+ learning_rate = 0.5
+ elif epoch < 50:
+ learning_rate = 0.05
+ else:
+ learning_rate = 0.005
+
+参数:
+ - **learning_rate** (float|int) - 初始化的学习率。可以是Python的float或int。
+ - **milestones** (tuple|list) - 列表或元组。必须是递增的。
+ - **decay_rate** (float, optional) - 学习率的衰减率。 ``new_lr = origin_lr * decay_rate`` 。其值应该小于1.0。默认:0.1。
+
+返回: 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import numpy as np
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ x = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, [10, 10]).astype("float32")
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.Linear(10, 10)
+ input = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x)
+ scheduler = fluid.dygraph.MultiStepDecay(0.5, milestones=[3, 5])
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate = scheduler, parameter_list = linear.parameters())
+ for epoch in range(6):
+ for batch_id in range(5):
+ out = linear(input)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(out)
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ scheduler.epoch()
+ print("epoch:{}, current lr is {}" .format(epoch, adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # epoch:0, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:1, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:2, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:3, current lr is 0.05
+ # epoch:4, current lr is 0.05
+ # epoch:5, current lr is 0.005
+
+.. py:method:: epoch(epoch=None)
+通过当前的 epoch 调整学习率,调整后的学习率将会在下一次调用 ``optimizer.minimize`` 时生效。
+
+参数:
+ - **epoch** (int|float,可选) - 类型:int或float。指定当前的epoch数。默认:无,此时将会自动累计epoch数。
+
+返回:
+ 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ 参照上述示例代码。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NCE_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NCE_cn.rst
index 03a0a5fcbbbdb18736f3109d850d85c547970756..45302572ed5bfb377763073775d19cbed4310079 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NCE_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NCE_cn.rst
@@ -45,7 +45,6 @@ NCE
words.append(fluid.dygraph.base.to_variable(inp_word[i]))
emb = fluid.Embedding(
- 'embedding',
size=[dict_size, 32],
param_attr='emb.w',
is_sparse=False)
@@ -60,17 +59,17 @@ NCE
embs3 = fluid.layers.concat(input=embs3, axis=1)
nce = fluid.NCE(
- num_total_classes=dict_size,
- dim=embs3.shape[1],
- num_neg_samples=2,
- sampler="custom_dist",
- custom_dist=nid_freq_arr.tolist(),
- seed=1,
- param_attr='nce.w',
- bias_attr='nce.b')
+ num_total_classes=dict_size,
+ dim=embs3.shape[1],
+ num_neg_samples=2,
+ sampler="custom_dist",
+ custom_dist=nid_freq_arr.tolist(),
+ seed=1,
+ param_attr='nce.w',
+ bias_attr='nce.b')
wl = fluid.layers.unsqueeze(words[label_word], axes=[0])
- nce_loss3 = nce(embs3, words[label_word])
+ nce_loss3 = nce(embs3, wl)
属性
::::::::::::
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst
index 110fd198ff2a50412c6ad25b38431e6e2114ce03..03a7e10a1cc4b66180ff118d8408ce21d9f5a30a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ NaturalExpDecay
- **staircase** (bool,可选) - 若为True, 学习率变化曲线呈阶梯状,若为False,学习率变化值曲线为平滑的曲线。默认值为False。
- **begin** (int,可选) – 起始步,即以上运算式子中global_step的初始化值。默认值为0。
- **step** (int,可选) – 步大小,即以上运算式子中global_step的每次的增量值。默认值为1。
- - **dtype** – (str,可选) 初始化学习率变量的数据类型,可以为"float32", "float64"。默认值为"float32"。
+ - **dtype** (str,可选) – 学习率值的数据类型,可以为"float32", "float64"。默认值为"float32"。
返回: 无
@@ -53,12 +53,14 @@ NaturalExpDecay
import paddle.fluid as fluid
base_lr = 0.1
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ emb = fluid.dygraph.Embedding([10, 10])
sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(
learning_rate=fluid.dygraph.NaturalExpDecay(
- learning_rate=base_lr,
- decay_steps=10000,
- decay_rate=0.5,
- staircase=True))
+ learning_rate=base_lr,
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.5,
+ staircase=True),
+ parameter_list=emb.parameters())
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/PolynomialDecay_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/PolynomialDecay_cn.rst
index ca3c050406d442d3d9b1dad49f3f42ccab5ea87c..df03f3f10ef90733cf7fc2027efc2028018da1b0 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/PolynomialDecay_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/PolynomialDecay_cn.rst
@@ -55,10 +55,8 @@ PolynomialDecay
total_step = 5000
end_lr = 0
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ emb = fluid.dygraph.Embedding( [10, 10])
optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(
learning_rate = fluid.dygraph.PolynomialDecay(
- start_lr, total_step, end_lr, power=1.0) )
-
-
-
-
+ start_lr, total_step, end_lr, power=1.0),
+ parameter_list = emb.parameters())
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Pool2D_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Pool2D_cn.rst
index fb47ba8ab256f2895f2d85b803e76d833b70159e..e66ec6b3237edbe73446be147aef39efe3cb66a8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Pool2D_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/Pool2D_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
Pool2D
-------------------------------
-.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.Pool2D(pool_size=-1, pool_type='max', pool_stride=1, pool_padding=0, global_pooling=False, use_cudnn=True, ceil_mode=False, exclusive=True)
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.Pool2D(pool_size=-1, pool_type='max', pool_stride=1, pool_padding=0, global_pooling=False, use_cudnn=True, ceil_mode=False, exclusive=True, data_format="NCHW")
:alias_main: paddle.nn.Pool2D
:alias: paddle.nn.Pool2D,paddle.nn.layer.Pool2D,paddle.nn.layer.common.Pool2D
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Pool2D
该接口用于构建 ``Pool2D`` 类的一个可调用对象,具体用法参照 ``代码示例`` 。其将在神经网络中构建一个二维池化层,并使用上述输入参数的池化配置,为二维空间池化操作,根据 ``input`` , 池化类型 ``pool_type`` , 池化核大小 ``pool_size`` , 步长 ``pool_stride`` ,填充 ``pool_padding`` 这些参数得到输出。
-输入X和输出Out是NCHW格式,N为批大小,C是通道数,H是特征高度,W是特征宽度。参数( ``ksize``, ``strides``, ``paddings`` )含有两个整型元素。分别表示高度和宽度上的参数。输入X的大小和输出Out的大小可能不一致。
+输入X和输出Out默认是NCHW格式,N为批大小,C是通道数,H是特征高度,W是特征宽度。参数( ``ksize``, ``strides``, ``paddings`` )含有两个整型元素。分别表示高度和宽度上的参数。输入X的大小和输出Out的大小可能不一致。
例如:
@@ -66,13 +66,15 @@ Pool2D
- **use_cudnn** (bool, 可选)- 是否用cudnn核,只有已安装cudnn库时才有效。默认True。
- **ceil_mode** (bool, 可选)- 是否用ceil函数计算输出高度和宽度。如果设为False,则使用floor函数。默认为False。
- **exclusive** (bool, 可选) - 是否在平均池化模式忽略填充值。默认为True。
+ - **data_format** (str,可选) - 指定输入的数据格式,输出的数据格式将与输入保持一致,可以是"NCHW"和"NHWC"。N是批尺寸,C是通道数,H是特征高度,W是特征宽度。默认值:"NCHW"。
返回:无
抛出异常:
- - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``pool_type`` 既不是“max”也不是“avg”
- - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``global_pooling`` 为False并且‘pool_size’为-1
- - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``use_cudnn`` 不是bool值
+ - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``pool_type`` 既不是“max”也不是“avg”。
+ - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``global_pooling`` 为False并且 ``pool_size`` 为-1。
+ - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``use_cudnn`` 不是bool值。
+ - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``data_format`` 既不是"NCHW"也不是"NHWC"。
**代码示例**
@@ -80,9 +82,10 @@ Pool2D
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from paddle.fluid.dygraph.base import to_variable
+ import numpy as np
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- data = numpy.random.random((3, 32, 32, 5)).astype('float32')
+ data = np.random.random((3, 32, 32, 5)).astype('float32')
pool2d = fluid.dygraph.Pool2D(pool_size=2,
pool_type='max',
pool_stride=1,
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/ReduceLROnPlateau_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/ReduceLROnPlateau_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b0a0b75f7b31244421f02cab719a342461a9f7c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/ReduceLROnPlateau_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_ReduceLROnPlateau:
+
+ReduceLROnPlateau
+-------------------------------
+
+**注意:该API仅支持【动态图】模式**
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.ReduceLROnPlateau(learning_rate, mode='min', decay_rate=0.1, patience=10, verbose=False, threshold=1e-4, threshold_mode='rel', cooldown=0, min_lr=0, eps=1e-8, dtype='float32')
+
+该API为 ``loss`` 自适应的学习率衰减策略。默认情况下,当 ``loss`` 停止下降时,降低学习率(如果将 ``mode`` 设置为 `'max'` ,此时判断逻辑相反, ``loss`` 停止上升时降低学习率)。其思想是:一旦模型表现不再提升,将学习率降低2-10倍对模型的训练往往有益。
+
+``loss`` 是传入到该类方法 ``step`` 中的参数,其必须是shape为[1]的1-D Tensor。 如果 ``loss`` 停止下降(``mode`` 为 `min` 时)超过 ``patience`` 个epoch,学习率将会减小为
+`learning_rate * decay_rate` 。
+
+此外,每降低一次学习率后,将会进入一个时长为 ``cooldown`` 个epoch的冷静期,在冷静期内,将不会监控 ``loss`` 的变化情况,也不会衰减。
+在冷静期之后,会继续监控 ``loss`` 的上升或下降。
+
+参数:
+ - **learning_rate** (Variable|float|int) - 初始学习率。其类型可以是Python的float类型,如果输入int类型则会被转为float类型。其也可以是shape为[1]的
+ 1-D Tensor,且相应数据类型必须为 "float32" 或 "float64" 。
+ - **mode** (str,可选) - `'min'` 和 `'max'` 之一。通常情况下,为 `'min'` ,此时当 ``loss`` 停止下降时学习率将减小。默认:`'min'` 。
+ (注意:仅在特殊用法时,可以将其设置为 `'max'` ,此时判断逻辑相反, ``loss`` 停止上升学习率才减小)
+ - **decay_rate** (float,可选) - 学习率衰减的比例。`new_lr = origin_lr * decay_rate` ,它是值小于1.0的float型数字,默认: 0.1。
+ - **patience** (int,可选) - 当 ``loss`` 连续 ``patience`` 个epoch没有下降(mode: 'min')或上升(mode: 'max')时,学习率才会减小。默认:10。
+ - **verbose** (bool,可选) - 如果为 ``True`` , 会在每次更新optimizer中的learning_rate时,打印信息。默认:``False`` 。
+ - **threshold** (float,可选) - ``threshold`` 和 ``threshold_mode`` 两个参数将会决定 ``loss`` 最小变化的阈值。小于该阈值的变化
+ 将会被忽视。默认:1e-4。
+ - **threshold_mode** (str,可选) - `'rel'` 和 `'abs'` 之一。在 `'rel'` 模式下, ``loss`` 最小变化的阈值是 `last_loss * threshold` ,
+ 其中 ``last_loss`` 是 ``loss`` 在上个epoch的值。在 `'abs'` 模式下,``loss`` 最小变化的阈值是 `threshold` 。 默认:`'rel'`。
+ - **cooldown** (int,可选) - 在学习速率每次减小之后,会进入时长为 ``cooldown`` 个epoch的冷静期。默认:0。
+ - **min_lr** (float,可选) - 最小的学习率。减小后的学习率最低下界限。默认:0。
+ - **eps** (float,可选) - 如果新旧学习率间的差异小于 ``eps`` ,则不会更新。默认值:1e-8。
+ - **dtype** (str,可选) – 学习率值的数据类型,可以为"float32", "float64"。默认:"float32"。
+
+返回: ``loss`` 自适应的学习率
+
+返回类型:Variable
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import numpy as np
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ x = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, [10, 10]).astype("float32")
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.Linear(10, 10)
+ input = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x)
+
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(
+ learning_rate = fluid.dygraph.ReduceLROnPlateau(
+ learning_rate = 1.0,
+ decay_rate = 0.5,
+ patience = 5,
+ verbose = True,
+ cooldown = 3),
+ parameter_list = linear.parameters())
+
+ for epoch in range(10):
+ total_loss = 0
+ for bath_id in range(5):
+ out = linear(input)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(out)
+ total_loss += loss
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+
+ avg_loss = total_loss/5
+
+ # 根据传入total_loss,调整学习率
+ reduce_lr.step(avg_loss)
+ lr = adam.current_step_lr()
+ print("current avg_loss is %s, current lr is %s" % (avg_loss.numpy()[0], lr))
+
+
+
+.. py:method:: step(loss)
+需要在每个epoch调用该方法,其根据传入的 ``loss`` 调整optimizer中的学习率,调整后的学习率将会在下一次调用 ``optimizer.minimize`` 时生效。
+
+参数:
+ - **loss** (Variable) - 类型:Variable,shape为[1]的1-D Tensor。将被用来判断是否需要降低学习率。如果 ``loss`` 连续 ``patience`` 个epochs没有下降,
+ 将会降低学习率。
+
+返回:
+ 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ 参照其类中的说明。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/StepDecay_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/StepDecay_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0016cf85752bff268a481a389f37f69e964414b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/StepDecay_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_StepDecay:
+
+StepDecay
+-------------------------------
+
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.StepDecay(learning_rate, step_size, decay_rate=0.1)
+
+:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
+
+
+该接口提供 ``step_size`` 衰减学习率的功能,每经过 ``step_size`` 个 ``epoch`` 时会通过 ``decay_rate`` 衰减一次学习率。
+
+算法可以描述为:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ learning_rate = 0.5
+ step_size = 30
+ decay_rate = 0.1
+ learning_rate = 0.5 if epoch < 30
+ learning_rate = 0.05 if 30 <= epoch < 60
+ learning_rate = 0.005 if 60 <= epoch < 90
+ ...
+
+参数:
+ - **learning_rate** (float|int) - 初始化的学习率。可以是Python的float或int。
+ - **step_size** (int) - 学习率每衰减一次的间隔。
+ - **decay_rate** (float, optional) - 学习率的衰减率。 ``new_lr = origin_lr * decay_rate`` 。其值应该小于1.0。默认:0.1。
+
+返回: 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import numpy as np
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ x = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, [10, 10]).astype("float32")
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.Linear(10, 10)
+ input = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x)
+ scheduler = fluid.dygraph.StepDecay(0.5, step_size=3)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate = scheduler, parameter_list = linear.parameters())
+ for epoch in range(9):
+ for batch_id in range(5):
+ out = linear(input)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(out)
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ scheduler.epoch()
+ print("epoch:{}, current lr is {}" .format(epoch, adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # epoch:0, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:1, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:2, current lr is 0.5
+ # epoch:3, current lr is 0.05
+ # epoch:4, current lr is 0.05
+ # epoch:5, current lr is 0.05
+ # epoch:6, current lr is 0.005
+ # epoch:7, current lr is 0.005
+ # epoch:8, current lr is 0.005
+
+.. py:method:: epoch(epoch=None)
+通过当前的 epoch 调整学习率,调整后的学习率将会在下一次调用 ``optimizer.minimize`` 时生效。
+
+参数:
+ - **epoch** (int|float,可选) - 类型:int或float。指定当前的epoch数。默认:无,此时将会自动累计epoch数。
+
+返回:
+ 无
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+ 参照上述示例代码。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0924a155a0ffb8861dd0f233cf0b0eff3dd8b169
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer:
+
+TranslatedLayer
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.TranslatedLayer(programs, persistable_vars)
+
+``TranslatedLayer`` 是一个命令式编程模式 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 的继承类,
+通过 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load` 载入构建。能够像一般 ``Layer`` 一样在train或者eval模式下使用。
+
+.. note::
+ ``TranslatedLayer`` 对象不能够通过构造函数创建,仅能够通过 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load` 接口载入构建。
+
+**示例代码:**
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ BATCH_SIZE = 32
+ BATCH_NUM = 20
+ def random_batch_reader():
+ def _get_random_images_and_labels(image_shape, label_shape):
+ image = np.random.random(size=image_shape).astype('float32')
+ label = np.random.random(size=label_shape).astype('int64')
+ return image, label
+ def __reader__():
+ for _ in range(BATCH_NUM):
+ batch_image, batch_label = _get_random_images_and_labels(
+ [BATCH_SIZE, 784], [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
+ yield batch_image, batch_label
+ return __reader__
+ class LinearNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(LinearNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ return self._linear(x)
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 1. 训练存储模型.
+ # 创建网络
+ net = LinearNet(784, 1)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ # 创建DataLoader
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader())
+ # 训练
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = net(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(avg_loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ model_path = "linear.example.model"
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[img])
+ # 2. 载入模型构建TranslatedLayer
+ translated_layer = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path)
+ # 预测
+ translated_layer.eval()
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((1, 784)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = translated_layer(x)
+ # fine-tune训练
+ translated_layer.train()
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=translated_layer.parameters())
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader())
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = translated_layer(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(avg_loss)
+ translated_layer.clear_gradients()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4a9b90d5cab6ce86a1bd7689676e3ad844eae8ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+===
+jit
+===
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ jit_cn/save_cn.rst
+ jit_cn/load_cn.rst
+ jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cbee1bab234be6f53f83061c52139093513d321b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,273 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_SaveLoadConfig:
+
+SaveLoadConfig
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+
+用于配置接口 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_save` 和 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load` 存储载入 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer` 时的附加选项。
+
+**示例代码:**
+
+ 1. 在存储模型时使用 ``SaveLoadConfig``
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ class SimpleNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ y = self._linear(x)
+ z = self._linear(y)
+ return z
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 训练模型
+ net = SimpleNet(8, 8)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ for i in range(10):
+ out = net(x)
+ loss = fluid.layers.mean(out)
+ loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ # 在存储模型时使用SaveLoadConfig
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ configs.model_filename = "__simplenet__"
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[x],
+ configs=configs)
+
+ 2. 在载入模型时使用 ``SaveLoadConfig``
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 在载入模型时使用SaveLoadconfig
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ configs.model_filename = "__simplenet__"
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=configs)
+ # 预测
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = infer_net(x)
+
+属性
+::::::::::::
+
+.. py:attribute:: output_spec
+
+选择保存模型( :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer` )的输出变量,通过指定的这些变量能够使模型仅计算特定的结果。
+默认情况下,原始 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 的forward方法的所有返回变量都将配置为存储后模型 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer` 的输出变量。
+
+``output_spec`` 属性类型需要是 ``list[Variable]``。如果输入的 ``output_spec`` 列表不是原始 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 的forward方法的所有返回变量,
+将会依据输入的 ``output_spec`` 列表对存储的模型进行裁剪。
+
+.. note::
+ ``output_spec`` 属性仅在存储模型时使用。
+
+**示例代码:**
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ class SimpleNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ y = self._linear(x)
+ z = self._linear(y)
+ loss = fluid.layers.mean(z)
+ return z, loss
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 训练模型
+ net = SimpleNet(8, 8)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ for i in range(10):
+ out, loss = net(x)
+ loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ # 使用SaveLoadconfig.output_spec
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model.output_spec"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ # 仅在存储模型中保留预测结果,丢弃loss
+ configs.output_spec = [out]
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[x],
+ configs=configs)
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=configs)
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ # 仅有预测结果输出
+ pred = infer_net(x)
+
+
+.. py:attribute:: model_filename
+
+存储转写 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 模型结构 ``Program`` 的文件名称。默认文件名为 ``__model__``。
+
+**示例代码**
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ class SimpleNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ y = self._linear(x)
+ z = self._linear(y)
+ return z
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 训练模型
+ net = SimpleNet(8, 8)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ for i in range(10):
+ out = net(x)
+ loss = fluid.layers.mean(out)
+ loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model.model_filename"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ configs.model_filename = "__simplenet__"
+ # 配置configs.model_filename存储模型
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[x],
+ configs=configs)
+ # [结果] 存储模型目录文件包括:
+ # __simplenet__ __variables__ __variables.info__
+ # 配置configs.model_filename载入模型
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=configs)
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = infer_net(x)
+
+
+.. py:attribute:: params_filename
+
+存储转写 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 所有持久参数(包括 ``Parameters`` 和持久的 ``Buffers``)的文件名称。默认文件名称为 ``__variable__``。
+
+**示例代码**
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ class SimpleNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ y = self._linear(x)
+ z = self._linear(y)
+ return z
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 训练模型
+ net = SimpleNet(8, 8)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ for i in range(10):
+ out = net(x)
+ loss = fluid.layers.mean(out)
+ loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model.params_filename"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ configs.params_filename = "__params__"
+ # 配置configs.params_filename存储模型
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[x],
+ configs=configs)
+ # [结果] 存储模型目录文件包括:
+ # __model__ __params__ __variables.info__
+ # 配置configs.params_filename载入模型
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=configs)
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = infer_net(x)
+
+
+.. py:attribute:: separate_params
+
+配置是否将 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 的参数存储为分散的文件。
+(这是为了兼容接口 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_io_save_inference_model` 的行为)
+
+如果设置为 ``True`` ,每个参数将会被存储为一个文件,文件名为参数名,同时``SaveLoadConfig.params_filename`` 指定的文件名将不会生效。默认为 ``False``。
+
+**示例代码**
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ class SimpleNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ y = self._linear(x)
+ z = self._linear(y)
+ return z
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 训练模型
+ net = SimpleNet(8, 8)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ for i in range(10):
+ out = net(x)
+ loss = fluid.layers.mean(out)
+ loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ model_path = "simplenet.example.model.separate_params"
+ configs = fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig()
+ configs.separate_params = True
+ # 配置configs.separate_params存储模型
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[x],
+ configs=configs)
+ # [结果] 存储模型目录文件包括:
+ # linear_0.b_0 linear_0.w_0 __model__ __variables.info__
+ # 配置configs.params_filename载入模型
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=configs)
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((4, 8)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = infer_net(x)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f001976971c5e84eb93c62fa5a5d77c8f2a9a335
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load:
+
+load
+-----------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path, configs=None)
+
+:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
+
+将接口 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_save` 或者 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_io_save_inference_model` 存储的模型载入为 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer` ,用于预测推理或者fine-tune训练。
+
+.. note::
+ 由于一些历史原因,如果载入的模型是通过 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_io_save_inference_model` 存储的,
+ 在使用它进行fine-tune训练时会存在一些局限:
+ 1. 命令式编程模式不支持 ``LoDTensor`` ,所有原先输入变量或者参数依赖于LoD信息的模型暂时无法使用;
+ 2. 所有存储模型的feed变量都需要被传入 ``Translatedlayer`` 的forward方法;
+ 3. 原模型变量的 ``stop_gradient`` 信息已丢失且无法准确恢复;
+ 4. 原模型参数的 ``trainable`` 信息已丢失且无法准确恢复。
+
+参数:
+ - **model_path** (str) - 存储模型的目录。
+ - **configs** (SaveLoadConfig, 可选) - 用于指定额外配置选项的 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_SaveLoadConfig` 对象。默认为 ``None``。
+
+返回:TranslatedLayer - 一个能够执行存储模型的 ``Layer`` 对象。
+
+**示例代码**
+
+1. 载入由接口 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_save` 存储的模型进行预测推理及fine-tune训练。
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ BATCH_SIZE = 32
+ BATCH_NUM = 20
+ def random_batch_reader():
+ def _get_random_images_and_labels(image_shape, label_shape):
+ image = np.random.random(size=image_shape).astype('float32')
+ label = np.random.random(size=label_shape).astype('int64')
+ return image, label
+ def __reader__():
+ for _ in range(BATCH_NUM):
+ batch_image, batch_label = _get_random_images_and_labels(
+ [BATCH_SIZE, 784], [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
+ yield batch_image, batch_label
+ return __reader__
+ class LinearNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(LinearNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ return self._linear(x)
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 1. 训练存储模型.
+ # 创建网络
+ net = LinearNet(784, 1)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ # 创建DataLoader
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader())
+ # 训练
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = net(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(avg_loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ model_path = "linear.example.model"
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[img])
+ # 2. 载入模型 & 预测
+ # 载入模型
+ infer_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path)
+ # 预测
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((1, 784)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = infer_net(x)
+ # 3. 载入模型 & fine-tune训练
+ # 载入模型
+ train_net = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path)
+ train_net.train()
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=train_net.parameters())
+ # 创建DataLoader
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader())
+ # fine-tune训练
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = train_net(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(avg_loss)
+ train_net.clear_gradients()
+
+
+2. 载入由接口 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_io_save_inference_model` 存储的模型进行预测推理及fine-tune训练。
+
+ .. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ BATCH_SIZE = 32
+ BATCH_NUM = 20
+ def random_batch_reader():
+ def _get_random_images_and_labels(image_shape, label_shape):
+ image = np.random.random(size=image_shape).astype('float32')
+ label = np.random.random(size=label_shape).astype('int64')
+ return image, label
+ def __reader__():
+ for _ in range(BATCH_NUM):
+ batch_image, batch_label = _get_random_images_and_labels(
+ [BATCH_SIZE, 784], [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
+ yield batch_image, batch_label
+ return __reader__
+ img = fluid.data(name='img', shape=[None, 784], dtype='float32')
+ label = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[None, 1], dtype='int64')
+ pred = fluid.layers.fc(input=img, size=10, act='softmax')
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=pred, label=label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001)
+ optimizer.minimize(avg_loss)
+ place = fluid.CPUPlace()
+ exe = fluid.Executor(place)
+ exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+ loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(
+ feed_list=[img, label], capacity=5, iterable=True)
+ loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader(), places=place)
+ # 1. 训练 & 存储预测模型
+ for data in loader():
+ exe.run(
+ fluid.default_main_program(),
+ feed=data,
+ fetch_list=[avg_loss])
+ model_path = "fc.example.model"
+ fluid.io.save_inference_model(
+ model_path, ["img"], [pred], exe)
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 2. 载入模型 & 预测
+ fc = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path)
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.random((1, 784)).astype('float32'))
+ pred = fc(x)
+ # 3. 载入模型 & fine-tune训练
+ fc = fluid.dygraph.jit.load(model_path)
+ fc.train()
+ sgd = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001,
+ parameter_list=fc.parameters())
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(
+ random_batch_reader(), places=place)
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = fc(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ sgd.minimize(avg_loss)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f0276316bacd0d7b7cb7ef6df12b1f9ac08b759f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_save:
+
+save
+-----------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.save(layer, model_path, input_spec=None, configs=None)
+
+将输入的经过 ``@declarative`` 装饰的 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 存储为 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_TranslatedLayer` 格式的模型,
+载入后可用于预测推理或者fine-tune训练。
+
+该接口将会将输入 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 转写后的模型结构 ``Program`` 和所有必要的持久参数变量存储至输入路径 ``model_path`` 中。
+
+默认存储的 ``Program`` 文件名为 ``__model__``, 默认存储持久参数变量的文件名为 ``__variables__``,
+同时会将变量的一些描述信息存储至文件 ``__variables.info__``,这些额外的信息将在fine-tune训练中使用。
+
+存储的模型能够被以下API载入使用:
+ - :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_load`
+ - :ref:`cn_api_fluid_io_load_inference_model` (需要配置参数 ``params_filename='__variables__'`` )
+ - 其他预测库API
+
+参数:
+ - **layer** (Layer) - 需要存储的 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_Layer` 对象。输入的 ``Layer`` 需要经过 ``@declarative`` 装饰。
+ - **model_path** (str) - 存储模型的目录。
+ - **input_spec** (list[Variable], 可选) - 描述存储模型的输入。此参数是传入当前存储的 ``TranslatedLayer`` forward方法的一个示例输入。如果为 ``None`` ,所有原 ``Layer`` forward方法的输入变量将都会被配置为存储模型的输入变量。默认为 ``None``。
+ - **configs** (SaveLoadConfig, 可选) - 用于指定额外配置选项的 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_dygraph_jit_SaveLoadConfig` 对象。默认为 ``None``。
+
+返回:无
+
+**示例代码**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import Linear
+ from paddle.fluid.dygraph import declarative
+ BATCH_SIZE = 32
+ BATCH_NUM = 20
+ def random_batch_reader():
+ def _get_random_images_and_labels(image_shape, label_shape):
+ image = np.random.random(size=image_shape).astype('float32')
+ label = np.random.random(size=label_shape).astype('int64')
+ return image, label
+ def __reader__():
+ for _ in range(BATCH_NUM):
+ batch_image, batch_label = _get_random_images_and_labels(
+ [BATCH_SIZE, 784], [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
+ yield batch_image, batch_label
+ return __reader__
+ class LinearNet(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, in_size, out_size):
+ super(LinearNet, self).__init__()
+ self._linear = Linear(in_size, out_size)
+ @declarative
+ def forward(self, x):
+ return self._linear(x)
+ # 开启命令式编程模式
+ fluid.enable_dygraph()
+ # 创建网络
+ net = LinearNet(784, 1)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1, parameter_list=net.parameters())
+ # 创建DataLoader
+ train_loader = fluid.io.DataLoader.from_generator(capacity=5)
+ train_loader.set_batch_generator(random_batch_reader())
+ # 训练
+ for data in train_loader():
+ img, label = data
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ cost = net(img)
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(cost, label)
+ avg_loss = fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+ avg_loss.backward()
+ adam.minimize(avg_loss)
+ net.clear_gradients()
+ # 存储模型
+ model_path = "linear.example.model"
+ fluid.dygraph.jit.save(
+ layer=net,
+ model_path=model_path,
+ input_spec=[img])
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/no_grad_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
index e93287287b29e61256e51249792d57390033d040..b58357ae1c122d72f2a1b94ee0ee0a9bfbd02135 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
@@ -4,48 +4,51 @@ no_grad
-------------------------------
-.. py:method:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.no_grad(func=None)
+.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.no_grad
:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
-
+:alias_main: paddle.no_grad
+:alias: paddle.no_grad
+:old_api: paddle.fluid.dygraph.no_grad
创建一个上下文来禁用动态图梯度计算。在此模式下,每次计算的结果都将具有stop_gradient=True。
-也可以用作一个装饰器(确保不要用括号来初始化)。
+也可以用作一个装饰器(需要创建实例对象作为装饰器)。
**代码示例**
.. code-block:: python
-
import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
# 用作生成器
+
data = np.array([[2, 3], [4, 5]]).astype('float32')
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- l0 = fluid.Linear(2, 2) # l0.weight.gradient() is None
- l1 = fluid.Linear(2, 2)
- with fluid.dygraph.no_grad():
- # l1.weight.stop_gradient is False
- tmp = l1.weight * 2 # tmp.stop_gradient is True
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data)
- y = l0(x) + tmp
- o = l1(y)
- o.backward()
- print(tmp.gradient() is None) # True
- print(l0.weight.gradient() is None) # False
-
+ l0 = fluid.Linear(2, 2) # l0.weight.gradient() is None
+ l1 = fluid.Linear(2, 2)
+ with fluid.no_grad():
+ # l1.weight.stop_gradient is False
+ tmp = l1.weight * 2 # tmp.stop_gradient is True
+ x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data)
+ y = l0(x) + tmp
+ o = l1(y)
+ o.backward()
+ print(tmp.gradient() is None) # True
+ print(l0.weight.gradient() is None) # False
+
# 用作装饰器
- @fluid.dygraph.no_grad
+
+ @fluid.no_grad()
def test_layer():
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- inp = np.ones([3, 1024], dtype='float32')
- t = fluid.dygraph.base.to_variable(inp)
- linear1 = fluid.Linear(1024, 4, bias_attr=False)
- linear2 = fluid.Linear(4, 4)
- ret = linear1(t)
- dy_ret = linear2(ret)
+ inp = np.ones([3, 1024], dtype='float32')
+ t = fluid.dygraph.base.to_variable(inp)
+ linear1 = fluid.Linear(1024, 4, bias_attr=False)
+ linear2 = fluid.Linear(4, 4)
+ ret = linear1(t)
+ dy_ret = linear2(ret)
test_layer()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/to_variable_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/to_variable_cn.rst
index 76b8c01d928d7cad6855a3e11420567236742809..b562d2cafb0b5f90458ed194677ddee783118e1b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/to_variable_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/dygraph_cn/to_variable_cn.rst
@@ -6,19 +6,23 @@ to_variable
.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.dygraph.to_variable(value, name=None, zero_copy=None)
+
:api_attr: 命令式编程模式(动态图)
-该函数实现从numpy\.ndarray对象或者Variable对象创建一个 ``Variable`` 类型的对象。
+该函数实现从tuple、list、numpy\.ndarray、Variable、ComplexVariable 对象创建一个 ``Variable`` 类型的对象。
+
参数:
- - **value** (ndarray|Variable) – 需要转换的numpy\.ndarray或Variable对象,维度可以为多维,数据类型为numpy\.{float16, float32, float64, int16, int32, int64, uint8, uint16}中的一种。
+ - **value** (tuple|list|ndarray|Variable|Tensor|ComplexVariable) – 初始化的数据。可以是tuple、list、numpy\.ndarray、Variable、ComplexVariable。
+ 维度可以为多维,数据类型为numpy\.{float16, float32, float64, int16, int32, int64, uint8, uint16}中的一种。
- **name** (str, 可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
- **zero_copy** (bool, 可选) – 是否与输入的numpy数组共享内存。此参数仅适用于CPUPlace,当它为None时将设置为True。默认值为None。
+ - **dtype** (str, 可选) - 返回的 ``Variable`` 所需的数据类型。可以是 'bool','float16','float32','float64','int8','int16','int32','int64','uint8'。默认值: None。
-返回:如果 ``value`` 是numpy\.ndarray对象,返回由numpy\.ndarray对象创建的 ``Tensor`` ,其数据类型和维度与 ``value`` 一致;如果 ``value`` 是Variable对象,返回 ``value`` 。
+返回:如果 ``value`` 是tuple/list/numpy\.ndarray对象,返回对应numpy\.ndarray对象创建的 ``Tensor`` ;如果 ``value`` 是Variable对象,直接返回 ``value`` 。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -28,13 +32,25 @@ to_variable
import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
-
with fluid.dygraph.guard(fluid.CPUPlace()):
+
x = np.ones([2, 2], np.float32)
y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x, zero_copy=False)
x[0][0] = -1
y[0][0].numpy() # array([1.], dtype=float32)
+
y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(x)
x[0][0] = 0
y[0][0].numpy() # array([0.], dtype=float32)
+ c = np.array([2+1j, 2])
+ z = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(c)
+ z.numpy() # array([2.+1.j, 2.+0.j])
+ z.dtype # 'complex128'
+
+ y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable([[0.1, 1.2], [2.2, 3.1], [4.9, 5.2]])
+ y.shape # [3L, 2L]
+ y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(((0.1, 1.2), (2.2, 3.1), (4.9, 5.2)), dtype='int32')
+ y.shape # [3L, 2L]
+ y.dtype # core.VarDesc.VarType.INT32
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/executor_cn/Executor_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/executor_cn/Executor_cn.rst
index 09c3872c56ad2fb9b71e6ac3f082197ff65f6b13..273b6bc79031e78ee56f65b4f7dbf575748d6f6b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/executor_cn/Executor_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/executor_cn/Executor_cn.rst
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Executor支持单GPU、多GPU以及CPU运行。
train_program = fluid.Program()
startup_program = fluid.Program()
with fluid.program_guard(train_program, startup_program):
- data = fluid.layers.data(name='X', shape=[1], dtype='float32')
+ data = fluid.data(name='X', shape=[None, 1], dtype='float32')
hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=data, size=10)
loss = fluid.layers.mean(hidden)
fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(loss)
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ Executor支持单GPU、多GPU以及CPU运行。
exe.close()
-.. py:method:: run(program=None, feed=None, fetch_list=None, feed_var_name='feed', fetch_var_name='fetch', scope=None, return_numpy=True,use_program_cache=False)
+.. py:method:: run(program=None, feed=None, fetch_list=None, feed_var_name='feed', fetch_var_name='fetch', scope=None, return_numpy=True, use_program_cache=False, use_prune=False)
执行指定的Program或者CompiledProgram。需要注意的是,执行器会执行Program或CompiledProgram中的所有算子,而不会根据fetch_list对Program或CompiledProgram中的算子进行裁剪。同时,需要传入运行该模型用到的scope,如果没有指定scope,执行器将使用全局scope,即fluid.global_scope()。
@@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ Executor支持单GPU、多GPU以及CPU运行。
place = fluid.CPUPlace() # fluid.CUDAPlace(0)
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- data = fluid.layers.data(name='X', shape=[1], dtype='float32')
+ data = fluid.data(name='X', shape=[None, 1], dtype='float32')
hidden = fluid.layers.fc(input=data, size=10)
loss = fluid.layers.mean(hidden)
adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam()
@@ -175,8 +175,8 @@ train_from_dataset可以非常容易扩展到大规模分布式在线和离线
place = fluid.CPUPlace() # 通过设置place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0)使用GPU
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[10, 10], dtype="int64")
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[None, 10, 10], dtype="int64")
+ y = fluid.data(name="y", shape=[None, 1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
dataset = fluid.DatasetFactory().create_dataset()
dataset.set_use_var([x, y])
dataset.set_thread(1)
@@ -210,12 +210,13 @@ train_from_dataset可以非常容易扩展到大规模分布式在线和离线
import paddle.fluid as fluid
place = fluid.CPUPlace() # 使用GPU时可设置place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0)
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[10, 10], dtype="int64")
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[None, 10, 10], dtype="int64")
+ y = fluid.data(name="y", shape=[None, 1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
dataset = fluid.DatasetFactory().create_dataset()
dataset.set_use_var([x, y])
dataset.set_thread(1)
filelist = [] # 您可以设置您自己的filelist,如filelist = ["dataA.txt"]
dataset.set_filelist(filelist)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
- exe.infer_from_dataset(program=fluid.default_main_program(),dataset=dataset)
+ exe.infer_from_dataset(program=fluid.default_main_program(),
+ dataset=dataset)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn.rst
index 351d173a4e259df1ac64d78992dd2f2a3c5390c3..ae356abbb90744b68bbd3661c13bcc8a606351c6 100755
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn.rst
@@ -52,6 +52,7 @@ fluid
fluid_cn/save_cn.rst
fluid_cn/scope_guard_cn.rst
fluid_cn/set_flags_cn.rst
+ fluid_cn/set_global_initializer_cn.rst
fluid_cn/Tensor_cn.rst
fluid_cn/Variable_cn.rst
fluid_cn/WeightNormParamAttr_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn/set_global_initializer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn/set_global_initializer_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..023629cf753daf5ecfb29a1b1984fbd184604bc4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/fluid_cn/set_global_initializer_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_set_global_initializer:
+
+set_global_initializer
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.set_global_initializer(weight_init, bias_init=None)
+
+该API用于设置Paddle框架中全局的参数初始化方法。该API只对位于其后的代码生效。
+
+模型参数为模型中的weight和bias统称,在fluid中对应fluid.Parameter类,继承自fluid.Variable,是一种可持久化的variable。
+该API的设置仅对模型参数生效,对通过 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_create_global_var` 、 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_create_tensor` 等API创建的变量不会生效。
+
+如果创建网络层时还通过 ``param_attr`` 、 ``bias_attr`` 设置了初始化方式,这里的全局设置将不会生效,因为其优先级更低。
+
+参数:
+ - **weight_init** (Initializer) - 设置框架的全局的weight参数初始化方法。
+ - **bias_init** (Initializer,可选) - 设置框架的全局的bias参数初始化方法。默认:None。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ fluid.set_global_initializer(fluid.initializer.Uniform(), fluid.initializer.Constant())
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[1, 3, 32, 32])
+
+ # conv1的weight参数是通过Uniform来初始化
+ # conv1的bias参数是通过Constant来初始化
+ conv1 = fluid.layers.conv2d(x, 5, 3)
+
+ # 如果同时设置了param_attr/bias_attr, 全局初始化将不会生效
+ # conv2的weight参数是通过Xavier来初始化
+ # conv2的bias参数是通过Normal来初始化
+ conv2 = fluid.layers.conv2d(conv1, 5, 3,
+ param_attr=fluid.initializer.Xavier(),
+ bias_attr=fluid.initializer.Normal())
+
+ # 取消全局参数初始化的设置
+ fluid.set_global_initializer(None)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn.rst
index a47fbd2dab5417415877130db00f4e0e897289e0..0f99f1c8f7decf504eb675c70b8a81c2715cf6db 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn.rst
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ paddle.imperative
imperative_cn/grad_cn.rst
imperative_cn/guard_cn.rst
imperative_cn/InverseTimeDecay_cn.rst
+ imperative_cn/jit_cn.rst
imperative_cn/load_cn.rst
imperative_cn/load_dygraph_cn.rst
imperative_cn/NaturalExpDecay_cn.rst
@@ -27,3 +28,4 @@ paddle.imperative
imperative_cn/save_dygraph_cn.rst
imperative_cn/to_variable_cn.rst
imperative_cn/TracedLayer_cn.rst
+ imperative_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..546094acf65c4fb30341d60ea157576601ae8766
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/TranslatedLayer_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _cn_api_imperative_TranslatedLayer:
+
+TranslatedLayer
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.io.TranslatedLayer
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..491ead2e2f4d51993ca9579301d0e3fbfaba1253
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+===
+jit
+===
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ jit_cn/save_cn.rst
+ jit_cn/load_cn.rst
+ jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..154e987bdb3ed8d3d86858b13b797b897b8eed62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/SaveLoadConfig_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _cn_api_imperative_jit_SaveLoadConfig:
+
+SaveLoadConfig
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.SaveLoadConfig
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a326fa58f1bf3634a498113bccac46627df0d8e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/load_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _cn_api_imperative_jit_load:
+
+load
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.load
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0c36588fa37794a81db4c534e2f54ad8aaddd66f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/imperative_cn/jit_cn/save_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _cn_api_imperative_jit_save:
+
+save
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.jit.save
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/index_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/index_cn.rst
index c45a09e4de6b9568dad91b5e3e10f5f0dbf87558..94e629783cd3595519c7c42188c97b81ac55c29d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/index_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/index_cn.rst
@@ -107,3 +107,21 @@ Note。
io_cn.rst
utils_cn.rst
incubate_cn.rst
+ fluid_cn.rst
+ backward_cn.rst
+ clip_cn.rst
+ data_cn/data_reader_cn.rst
+ data_cn/dataset_cn.rst
+ dataset_cn.rst
+ dygraph_cn.rst
+ executor_cn.rst
+ initializer_cn.rst
+ io_cn.rst
+ layers_cn.rst
+ metrics_cn.rst
+ nets_cn.rst
+ optimizer_cn.rst
+ profiler_cn.rst
+ regularizer_cn.rst
+ transpiler_cn.rst
+ unique_name_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/MSRAInitializer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/MSRAInitializer_cn.rst
index b002b655a7ff6df93e50ad48963eac6fe7de1dfe..ac42f93ff6bf15bb95d7a1d6db68ba96705d8eca 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/MSRAInitializer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/MSRAInitializer_cn.rst
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ MSRAInitializer
该接口实现MSRA方式的权重初始化(a.k.a. Kaiming初始化)
该接口为权重初始化函数,方法来自Kaiming He,Xiangyu Zhang,Shaoqing Ren 和 Jian Sun所写的论文: `Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification `_ 。这是一个鲁棒性特别强的初始化方法,并且适应了非线性激活函数(rectifier nonlinearities)。
-可以选择使用均匀分布或者正太分布初始化权重;
+可以选择使用均匀分布或者正态分布初始化权重;
在均匀分布中,范围为[-x,x],其中:
.. math::
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/NumpyArrayInitializer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/NumpyArrayInitializer_cn.rst
index 03733bde7521eb32b3ec4797ba11f700ac2a6e92..7c0365ccba17c21f28907047bb902e25fb0df43b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/NumpyArrayInitializer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/initializer_cn/NumpyArrayInitializer_cn.rst
@@ -22,8 +22,9 @@ NumpyArrayInitializer
.. code-block:: python
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[5], dtype='float32')
- fc = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=10,
+ import numpy
+ x1 = fluid.data(name="x1", shape=[2, 1], dtype='float32')
+ fc = fluid.layers.fc(input=x1, size=10,
param_attr=fluid.initializer.NumpyArrayInitializer(numpy.array([1,2])))
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/Normal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/Normal_cn.rst
index 933e18aa464cd194557cfd93ad5c38335fb22e93..ce50e67bd12563ee7c24b6ab4141acf0ccf0c303 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/Normal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/Normal_cn.rst
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Normal
import numpy as np
from paddle.fluid import layers
- from paddle.fluid.layers import Normal
+ from paddle.fluid.layers import Normal
# 定义参数为float的正态分布。
dist = Normal(loc=0., scale=3.)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/abs_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/abs_cn.rst
index cf726de9f97c0bc5c621654cf07ff5787f8c9260..3c0cdf4f06dd720c7c1281ede892b01e2089521c 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/abs_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/abs_cn.rst
@@ -11,23 +11,29 @@ abs
-绝对值激活函数。
+绝对值函数。
.. math::
out = |x|
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 多维Tensor,数据类型为float32或float64。
- - **name** (str) – 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回:表示绝对值结果的Tensor,数据类型与x相同。
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
-返回类型:Variable
+返回类型:Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = fluid.layers.data(name="input", shape=[32, 784])
- result = fluid.layers.abs(data)
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([-1, -2, -3, -4]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.abs(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [1, 2, 3, 4]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/acos_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/acos_cn.rst
index 9185569aa0e9f5329c63bc734e3a96996042584e..dad19ff258cbf0b89b6d45fd86eb7cc69c730636 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/acos_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/acos_cn.rst
@@ -11,29 +11,30 @@ acos
-arccosine激活函数。
+arccosine函数。
.. math::
out = cos^{-1}(x)
参数:
- - **x(Variable)** - acos的输入Tensor,数据类型为 float32 或 float64
- - **name** (str|None) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`cn_api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回: `acos` 的输出Tensor,数据类型与 `x` 相同。
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回类型: Variable
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
+返回类型: Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = fluid.layers.data(name="input", shape=[4])
- # if data is [-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]
- result = fluid.layers.acos(data)
- # result is [2.5293, 1.0573, 2.2711, 1.5336]
-
-
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.acos(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [2.5293, 1.0573, 2.2711, 1.5336]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/asin_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/asin_cn.rst
index 03109d28ec3125c9f1cc5a3e8bd97e63484bde07..3635c8a3f1212b1cc83c4728eef7cca6188d3ab9 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/asin_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/asin_cn.rst
@@ -11,29 +11,29 @@ asin
-arcsine激活函数。
+arcsine函数。
.. math::
out = sin^{-1}(x)
-
参数:
- - **x(Variable)** - asin的输入Tensor,数据类型为 float32 或 float64
- - **name** (str|None) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`cn_api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回: `asin` 的输出Tensor,数据类型与 `x` 相同。
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
-返回类型: Variable
+返回类型: Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = fluid.layers.data(name="input", shape=[4])
- # if data is [-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]
- result = fluid.layers.asin(data)
- # result is [-0.9585, 0.5135, -0.7003, 0.0372]
-
-
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.asin(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [-0.9585, 0.5135, -0.7003, 0.0372]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/atan_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/atan_cn.rst
index 1c36f104731560ef4918730b21682497cbd415e2..5cd60cd447b2f1322d29842b2a1c3743126849f5 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/atan_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/atan_cn.rst
@@ -11,30 +11,29 @@ atan
-arctanh激活函数。
+arctangent函数。
.. math::
- out = tanh^{-1}(x)
+ out = tan^{-1}(x)
参数:
- - **x(Variable)** - atan的输入Tensor,数据类型为 float32 或 float64
- - **name** (str|None) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`cn_api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回: `atan` 的输出Tensor,数据类型与 `x` 相同。
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
-返回类型: Variable
+返回类型: Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = fluid.layers.data(name="input", shape=[4])
- # if data is [-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]
- result = fluid.layers.atan(data)
- # result is [-0.6858, 0.4566, -0.5724, 0.0371]
-
-
-
-
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([-0.8183, 0.4912, -0.6444, 0.0371]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.atan(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [-0.6858, 0.4566, -0.5724, 0.0371]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ceil_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ceil_cn.rst
index 27ca3dd547fb43ecf26ce0d499ce39049e2ef1bb..81a8265afe10cfcfa529ee65eb30f15d195cc28d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ceil_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ceil_cn.rst
@@ -19,24 +19,24 @@ ceil
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 该OP的输入为多维Tensor。数据类型为float32或float64。
- - **name** (str, 可选) - 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回: 输出为Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
-返回类型: Variable
+返回类型: Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
- input_ceil = np.array([[-1.5,6],[1,15.6]])
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(input_ceil)
- y = fluid.layers.ceil(x)
- print(y.numpy())
- # [[-1. 6.]
- # [ 1. 16.]]
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([[-1.5,6],[1,15.6]]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.ceil(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [[-1. 6.]
+ # [ 1. 16.]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/concat_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/concat_cn.rst
index 31f6d2cb67cdc9c718102e31ba5154a66d61e7fb..46b1b3c3d6b17cdd9eebd5959372756499ede8ff 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/concat_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/concat_cn.rst
@@ -3,24 +3,24 @@
concat
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.concat(input,axis=0,name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.concat(input, axis=0, name=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.concat
-:alias: paddle.concat,paddle.tensor.concat,paddle.tensor.manipulation.concat
-:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.concat
-
-
-该OP对输入沿 ``axis`` 轴进行联结。
+该OP对输入沿 ``axis`` 轴进行联结,返回一个新的Tensor。
参数:
- - **input** (list) - 输入是待联结的多维 ``Tensor`` 组成的 ``list`` ,支持的数据类型为:float32、float64、int32、int64。
- - **axis** (int|Variable,可选) - 整数或者形状为[1]的 ``Tensor``,数据类型为 ``int32``。指定对输入Tensor进行运算的轴, ``axis`` 的有效范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``input`` 中 ``Tensor`` 的维度, ``axis`` 为负值时与 :math:`axis + R` 等价。默认值为0。
+ - **input** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 待联结的Tensor list,Tensor tuple或者Tensor,支持的数据类型为:bool、float16、 float32、float64、int32、int64。 ``input`` 中所有Tensor的数据类型必须一致。
+ - **axis** (int|Tensor,可选) - 指定对输入Tensor进行运算的轴,可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或者int64。 ``axis`` 的有效范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``input`` 中Tensor 的维度, ``axis`` 为负值时与 :math:`axis + R` 等价。默认值为0。
- **name** (str,可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:联结后的 ``Tensor`` ,数据类型和 ``input`` 相同。
+返回:联结后的 ``Tensor`` ,数据类型和 ``input`` 中的Tensor相同。
+
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``input`` 的类型不是list、tuple或者Tensor的时候。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``input`` 的数据类型不是 bool,float16, float32, float64, int32, int64时。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当 ``axis`` 的类型不是int或者Tensor时。当 ``axis`` 是Tensor的时候其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``input`` 中的Tensor存在数据类型不一致时。
**代码示例**:
@@ -29,18 +29,18 @@ concat
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- in1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
- [4,5,6]])
- in2 = np.array([[11,12,13],
- [14,15,16]])
- in3 = np.array([[21,22],
- [23,24]])
+ in1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
+ [4, 5, 6]])
+ in2 = np.array([[11, 12, 13],
+ [14, 15, 16]])
+ in3 = np.array([[21, 22],
+ [23, 24]])
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
x1 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(in1)
x2 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(in2)
x3 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(in3)
- out1 = fluid.layers.concat(input=[x1,x2,x3], axis=-1)
- out2 = fluid.layers.concat(input=[x1,x2], axis=0)
+ out1 = fluid.layers.concat(input=[x1, x2, x3], axis=-1)
+ out2 = fluid.layers.concat(input=[x1, x2], axis=0)
print(out1.numpy())
# [[ 1 2 3 11 12 13 21 22]
# [ 4 5 6 14 15 16 23 24]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cos_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cos_cn.rst
index 4f31c473c95be1f3b4a46915c505fe29250d11e8..99e6b061f23e642e3ceb8227e77b2f25eeb57d71 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cos_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cos_cn.rst
@@ -13,32 +13,31 @@ cos
余弦函数。
+输入范围是 `(-inf, inf)` , 输出范围是 `[-1,1]`。若输入超出边界则结果为`nan`。
+
.. math::
out = cos(x)
-
-
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 该OP的输入为多维Tensor,数据类型为float32,float64。
- - **name** (str, 可选) - 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - name (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回:输出为Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
+返回:输出Tensor,与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同。
-返回类型:Variable
+返回类型:Tensor
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
- input_cos = np.array([[-1,np.pi],[1,15.6]])
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(input_cos)
- y = fluid.layers.cos(x)
- print(y.numpy())
- # [[ 0.54030231 -1. ]
- # [ 0.54030231 -0.99417763]]
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([[-1,np.pi],[1,15.6]]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.cos(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ # [[ 0.54030231 -1. ]
+ # [ 0.54030231 -0.99417763]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/crop_tensor_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/crop_tensor_cn.rst
index 5930ad3a8344fba96632ef2579a50e9afca010a6..79b2de8fcc0259615cb1f5eadc6ee2da4b71359d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/crop_tensor_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/crop_tensor_cn.rst
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ crop_tensor
# crop3.shape = [-1, 2, 3]
# offsets is a list in which each element is a constant or Tensor
- offsets_var = fluid.data(name="dim1", shape=[1], dtype="int32")
+ offsets_var = fluid.data(name="offset", shape=[1], dtype="int32")
crop4 = fluid.layers.crop_tensor(x, shape=[-1, 2, 3], offsets=[0, 1, offsets_var])
# crop4.shape = [-1, 2, 3]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cumsum_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
index fd9238e64bd85b90f4a54ced20b6dda1266b4e60..8e6f238b87381651e08b0a0dac4fa441b7605683 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
@@ -5,11 +5,6 @@ cumsum
.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum(x,axis=None,exclusive=None,reverse=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.cumsum
-:alias: paddle.cumsum,paddle.tensor.cumsum,paddle.tensor.math.cumsum
-:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum
-
-
沿给定轴(axis)的元素的累加和。默认结果的第一个元素和输入的第一个元素一致。如果exlusive为True,�结果的第一个元素则为0。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/deformable_roi_pooling_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/deformable_roi_pooling_cn.rst
index e1b19b7ac12a275fabafbef26b8a51dc68553617..bcccb58ca3fd10fd79903184f59362b936e63804 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/deformable_roi_pooling_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/deformable_roi_pooling_cn.rst
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ deformable_roi_pooling
.. code-block:: python
- #position_sensitive为False
+ #position_sensitive=False
import paddle.fluid as fluid
input = fluid.data(name="input",
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ deformable_roi_pooling
trans_std=0.1,
position_sensitive=False)
- #position_sensitive为True
+ #position_sensitive=True
import paddle.fluid as fluid
input = fluid.data(name="input",
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/double_buffer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/double_buffer_cn.rst
index 02597acc36776b4f7915a5285790fe98016ef4fb..f9fe3b110ab2db024599bf4be1687a15f4c1006c 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/double_buffer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/double_buffer_cn.rst
@@ -27,13 +27,13 @@ double_buffer
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- reader = fluid.layers.open_files(filenames=['mnist.recordio'],
- shapes=[[-1, 784], [-1, 1]],
- lod_levels=[0, 0],
- dtypes=['float32', 'int64'])
- reader = fluid.layers.double_buffer(reader)
- img, label = fluid.layers.read_file(reader)
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ reader = fluid.layers.py_reader(capacity=64,
+ shapes=[(-1, 1, 28, 28), (-1, 1)],
+ dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
+ use_double_buffer=False)
+ reader = fluid.layers.double_buffer(reader)
+ image, label = fluid.layers.read_file(reader)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst
index 91b9cece85ab1490bc0ff45cb22ba26e6871f060..7414eae16ca524e5388de7a09c2e104aa0174570 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst
@@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ elementwise_add
"y": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[5]).astype('float32')
}
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
+ y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[5], dtype='float32')
# z = x + y
z = fluid.layers.elementwise_add(x, y, axis=3)
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst
index a5b7544d305db7bd611baee677d223fc9335006e..d4d12f36b20d39247345933090f2c8b2215b14df 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst
@@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ elementwise_div
"y": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[5]).astype('float32')
}
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
+ y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[5], dtype='float32')
z = fluid.layers.elementwise_div(x, y, axis=3)
# z = x / y
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_mul_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_mul_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 1ba52febf6c11fc514315ef64caf0acad1550700..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_mul_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_mul:
-
-elementwise_mul
--------------------------------
-
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(x, y, axis=-1, act=None, name=None)
-
-:alias_main: paddle.elementwise_mul
-:alias: paddle.elementwise_mul,paddle.tensor.elementwise_mul,paddle.tensor.math.elementwise_mul
-:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_mul
-
-
-
-该OP是逐元素相乘算子,输入 ``x`` 与输入 ``y`` 逐元素相乘,并将各个位置的输出元素保存到返回结果中。
-
-等式是:
-
-.. math::
- Out = X \odot Y
-
-- :math:`X` :多维Tensor。
-- :math:`Y` :维度必须小于等于X维度的Tensor。
-
-对于这个运算算子有2种情况:
- 1. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 与 :math:`X` 相同。
- 2. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 是 :math:`X` 的连续子序列。
-
-对于情况2:
- 1. 用 :math:`Y` 匹配 :math:`X` 的形状(shape),其中 ``axis`` 是 :math:`Y` 在 :math:`X` 上的起始维度的位置。
- 2. 如果 ``axis`` 为-1(默认值),则 :math:`axis= rank(X)-rank(Y)` 。
- 3. 考虑到子序列, :math:`Y` 的大小为1的尾部维度将被忽略,例如shape(Y)=(2,1)=>(2)。
-
-例如:
-
-.. code-block:: text
-
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (,)
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (5,)
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (4, 5), with axis=-1(default) or axis=2
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (3, 4), with axis=1
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2), with axis=0
- shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2, 1), with axis=0
-
-参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 多维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
- - **y** (Variable)- 多维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
- - **axis** (int32,可选)- ``y`` 的维度对应到 ``x`` 维度上时的索引。默认值为 -1。
- - **act** (str,可选)- 激活函数名称,作用于输出上。默认值为None。详细请参考 :ref:`api_guide_activations` , 常见的激活函数有: ``relu`` ``tanh`` ``sigmoid`` 等。
- - **name** (str,可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-
-
-返回: 维度与 ``x`` 相同的 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` ,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
-
-返回类型: Variable。
-
-**代码示例 1**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- def gen_data():
- return {
- "x": np.array([2, 3, 4]),
- "y": np.array([1, 5, 2])
- }
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[3], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3], dtype='float32')
- z = fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(x, y)
- # z = x * y
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- z_value = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
- fetch_list=[z.name])
- print(z_value) # [2., 15., 8.]
-
-**代码示例 2**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- def gen_data():
- return {
- "x": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[2, 3, 4, 5]).astype('float32'),
- "y": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[3, 4]).astype('float32')
- }
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
- z = fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(x, y, axis=1)
- # z = x * y
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- z_value = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
- fetch_list=[z.name])
- print(z_value) # z.shape=[2,3,4,5]
-
-**代码示例 3**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- def gen_data():
- return {
- "x": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[2, 3, 4, 5]).astype('float32'),
- "y": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[5]).astype('float32')
- }
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
- z = fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(x, y, axis=3)
- # z = x * y
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- z_value = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
- fetch_list=[z.name])
- print(z_value) # z.shape=[2,3,4,5]
-
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_sub_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_sub_cn.rst
index 7bd8ac5e0549d6357c834a60d5a8d5a4fff2ef34..c5886ad2e0fa696aad8ae192ec8a0925aa6f1e6b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_sub_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/elementwise_sub_cn.rst
@@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ elementwise_sub
"y": np.random.randint(1, 5, size=[5]).astype('float32')
}
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
+ y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[5], dtype='float32')
z = fluid.layers.elementwise_sub(x, y, axis=3)
# z = x - y
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/equal_cn.rst
index 14b36d0947ecf2ffb7d858db93175a80e93db7d8..9a66e76cedc7d3997fe8e6cbfefca91232f5734b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/equal_cn.rst
@@ -3,9 +3,7 @@
equal
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.equal(x,y,cond=None)
-
-
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.equal(x, y, cond=None, name=None)
该OP返回 :math:`x==y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等,x和y的维度应该相同。
@@ -13,7 +11,8 @@ equal
参数:
- **x** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
- **y** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
- - **cond** (Variable,可选) - 逐元素比较的结果Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **cond** (Variable,可选) – 如果为None,则创建一个Tensor来作为进行比较的输出结果,该Tensor的shape和数据类型和输入x一致;如果不为None,则将Tensor作为该OP的输出,数据类型和数据shape需要和输入x一致。默认值为None。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/eye_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/eye_cn.rst
index 6fa81619f40dffe5c7a02571d6eb570f4cf32ebe..b0fb8b5ecb68711e3d196c92beaa87f9bb6e10fc 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/eye_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/eye_cn.rst
@@ -3,25 +3,24 @@
eye
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, batch_shape=None, dtype='float32')
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, batch_shape=None, dtype='float32', name=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.eye
-:alias: paddle.eye,paddle.tensor.eye,paddle.tensor.creation.eye
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.eye
-
-
-该OP用来构建单位矩阵,或一个批次的单位矩阵。
+该OP用来构建二维Tensor,或一个批次的二维Tensor。
参数:
- - **num_rows** (int) - 每一个批矩阵的行数,数据类型为非负int32。
- - **num_columns** (int) - 每一个批矩阵的列数,数据类型为非负int32。若为None,则默认等于num_rows。
- - **batch_shape** (list(int)) - 如若提供,则返回向量的主批次维度将为batch_shape。
- - **dtype** (string) - 返回张量的数据类型,可为int32,int64,float16,float32,float64。
+ - **num_rows** (int) - 该批次二维Tensor的行数,数据类型为非负int32。
+ - **num_columns** (int, 可选) - 该批次二维Tensor的列数,数据类型为非负int32。若为None,则默认等于num_rows。
+ - **batch_shape** (list(int), 可选) - 如若提供,则返回Tensor的主批次维度将为batch_shape。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str,可选) - 返回Tensor的数据类型,可为int32,int64,float16,float32,float64,默认数据类型为float32。
+ - **name** (str) – 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-返回:shape为batch_shape + [num_rows, num_columns]的张量。
+返回: ``shape`` 为batch_shape + [num_rows, num_columns]的Tensor。
+
-返回类型:Variable(Tensor|LoDTensor)数据类型为int32,int64,float16,float32,float64的Tensor或者LoDTensor。
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``dtype`` 的类型不是float16, float32, float64, int32, int64其中之一。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``num_columns`` 不是非负整数或者 ``num_rows`` 不是非负整数。
**代码示例**:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/fill_constant_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/fill_constant_cn.rst
index 1750069f8568850dea0f0028b9398c0809d208fb..f7af206495c0640ef87b2806666fdf919015463e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/fill_constant_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/fill_constant_cn.rst
@@ -28,7 +28,8 @@ fill_constant
返回类型:变量(Variable)
抛出异常:
- - :code:`TypeError`: dtype必须是bool,float16,float32,float64,int32和int64之一,并且输出Tensor的数据类型必须与dtype相同。
+ - :code:`TypeError`: dtype必须是bool,float16,float32,float64,int32和int64之一,输出Tensor的数据类型必须与dtype相同。
+ - :code:`TypeError`: 当 `shape` 的数据类型不是list、tuple、Variable。
**代码示例**:
@@ -43,6 +44,6 @@ fill_constant
positive_2 = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1], "int32", 2)
data3 = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[1, positive_2], dtype='float32', value=1.5) # data3=[1.5, 1.5]
- # attr shape is an Variable Tensor.
+ # attr shape is a Variable Tensor.
shape = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1,2], "int32", 2) # shape=[2,2]
data4 = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=shape, dtype='bool', value=True) # data4=[[True,True],[True,True]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/gaussian_random_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/gaussian_random_cn.rst
index 11cd3ccc706c31b3a8f775b1122d0ad2fccc0181..059f19be02e3982a43bcec9a3ccbcd25e9bda5fd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/gaussian_random_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/gaussian_random_cn.rst
@@ -3,30 +3,29 @@
gaussian_random
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.gaussian_random(shape, mean=0.0, std=1.0, seed=0, dtype='float32')
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.gaussian_random(shape, mean=0.0, std=1.0, seed=0, dtype='float32', name=None)
-生成数据符合高斯随机分布的 Tensor。
+该OP返回数值符合高斯随机分布的Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
参数:
- - **shape** (Tuple[int] | List[int])- 生成 Tensor 的形状。
- - **mean** (float)- 随机 Tensor 的均值,默认值为 0.0。
- - **std** (float)- 随机 Tensor 的标准差,默认值为 1.0。
- - **seed** (int)- 随机数种子,默认值为 0。注:seed 设置为 0 表示使用系统的随机数种子。注意如果 seed 不为 0,则此算子每次将始终生成相同的随机数。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype | core.VarDesc.VarType | str)- 输出 Tensor 的数据类型,可选值为 float32,float64。
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 生成的随机Tensor的形状。如果 ``shape`` 是list、tuple,则其中的元素可以是int,或者是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64的Tensor。如果 ``shape`` 是Tensor,则是数据类型为int32、int64的1-D Tensor。
+ - **mean** (float|int, 可选) - 输出Tensor的均值,支持的数据类型:float、int。默认值为0.0。
+ - **std** (float|int, 可选) - 输出Tensor的标准差,支持的数据类型:float、int。默认值为1.0。
+ - **seed** (int, 可选) - 随机数种子,默认值为 0。注:seed 设置为 0 表示使用系统的随机数种子。注意如果 seed 不为 0,则此算子每次将始终生成相同的随机数。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持float32、float64。默认值为float32。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:
+返回:
+ Tensor:符合高斯随机分布的Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
- - 符合高斯分布的随机 Tensor。形状为 shape,数据类型为 dtype。
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list、tuple、Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是float32、float64。
-返回类型:
-
- - Variable
-
-
-**代码示例:**
+**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
index 607e3ab0b02b3b2bfbdb8e28744c3187f5fd3f00..7141718419cc55b0fdb4546dcd16bc89c92a2e35 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
greater_equal
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal(x, y, cond=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal(x, y, cond=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.greater_equal
:alias: paddle.greater_equal,paddle.tensor.greater_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.greater_equal
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ greater_equal
- **x** (Variable) – 进行比较的第一个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **y** (Variable) – 进行比较的第二个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **cond** (Variable,可选) – 如果为None,则创建一个Tensor来作为进行比较的输出结果,该Tensor的shape,数据类型和输入x一致;如果不为None,则将Tensor作为该OP的输出,数据shape和数据类型需要和输入x一致。默认值为None。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的Tensor,数据的shape和输入x一致。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
index 29bb93d9284cf69796c51a9ac05b05ba440a1592..3f208e21ad5433125b3c22fa76ee06968a7c8153 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
greater_than
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than(x, y, cond=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than(x, y, cond=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.greater_than
:alias: paddle.greater_than,paddle.tensor.greater_than,paddle.tensor.logic.greater_than
@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ greater_than
- **x** (Variable) – 进行比较的第一个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **y** (Variable) – 进行比较的第二个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **cond** (Variable,可选) – 如果为None,则创建一个Tensor来作为进行比较的输出结果,该Tensor的shape和数据类型和输入x一致;如果不为None,则将Tensor作为该OP的输出,数据类型和数据shape需要和输入x一致。默认值为None。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的Tensor,数据的shape和输入x一致。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/hash_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/hash_cn.rst
index 8905028db60e93ccbb00184629eafa5ddb8e8caa..a25828a10dc67b9697541d6e83234272ffbbb81a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/hash_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/hash_cn.rst
@@ -36,8 +36,8 @@ hash
place = fluid.core.CPUPlace()
# 构建网络
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[1], dtype="int32", lod_level=1)
- res = fluid.layers.hash(name="res",input=x, hash_size=1000, num_hash=4)
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[2, 2], dtype="int32", lod_level=1)
+ res = fluid.layers.hash(name="res", input=x, hash_size=1000, num_hash=4)
# 创建CPU执行器
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
@@ -45,9 +45,7 @@ hash
in1 = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]).astype("int32")
print(in1)
- x_i = fluid.core.LoDTensor()
- x_i.set(in1,place)
- x_i.set_recursive_sequence_lengths([[0,2]])
+ x_i = fluid.create_lod_tensor(in1, [[0, 2]], place)
res = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i}, fetch_list=[res], return_numpy=False)
print(np.array(res[0]))
# [[[722]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
index 88add2c7fb86d395727ffbe16a97fd01dd31d33a..da8b1b83343ec06b21738177555c79855efbdb2f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
less_equal
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal(x, y, cond=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal(x, y, cond=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.less_equal
:alias: paddle.less_equal,paddle.tensor.less_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.less_equal
@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ less_equal
- **x** (Variable) – 进行比较的第一个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **y** (Variable) – 进行比较的第二个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **cond** (Variable,可选) – 如果为None,则创建一个Tensor来作为进行比较的输出结果,该Tensor的shape和数据类型和输入x一致;如果不为None,则将Tensor作为该OP的输出,数据类型和数据shape需要和输入x一致。默认值为None。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的Tensor,数据的shape和输入x一致。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_than_cn.rst
index be39cae55422cb9beb27c040c41704696b01ccdd..6ad37577315a293779e5b1da1a9e449179c9b52f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/less_than_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
less_than
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than(x, y, force_cpu=None, cond=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than(x, y, force_cpu=None, cond=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.less_than
:alias: paddle.less_than,paddle.tensor.less_than,paddle.tensor.logic.less_than
@@ -20,6 +20,7 @@ less_than
- **y** (Variable) - 进行比较的第二个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **force_cpu** (bool) – 如果为True则强制将输出变量写入CPU内存中,否则将其写入目前所在的运算设备上。默认值为False。注意:该属性已弃用,其值始终是False。
- **cond** (Variable,可选) – 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据的shape和输入x一致。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/linspace_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/linspace_cn.rst
index 9105b2ae95c5f0df7184edc377ceee6087ed576a..ca9775016b06c55b7504d31d913aeaad1df76466 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/linspace_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/linspace_cn.rst
@@ -3,22 +3,27 @@
linspace
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.linspace(start, stop, num, dtype)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.linspace(start, stop, num, dtype=None, name=None)
-该OP在给定区间内返回固定数目的均匀间隔的值。
+该OP返回一个Tensor,Tensor的值为在区间start和stop上均匀间隔的num个值,输出Tensor的长度为num。
+**注意:该OP不进行梯度计算**
参数:
- - **start** (float|Variable) – start是区间开始的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
- - **stop** (float|Variable) – end是区间结束的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
- - **num** (int|Variable) – num是给定区间内需要划分的区间数,可以是一个整型标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型需为int32。
- - **dtype** (string) – 输出Tensor的数据类型,可以是‘float32’或者是‘float64’。
+ - **start** (float|Tensor) – ``start`` 是区间开始的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
+ - **stop** (float|Tensor) – ``end`` 是区间结束的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
+ - **num** (int|Tensor) – ``num`` 是给定区间内需要划分的区间数,可以是一个整型标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型需为int32。
+ - **dtype** (string, 可选) – 输出Tensor的数据类型,可以是float32或者是float64,如果dtype的数据类型为None,输出Tensor数据类型为float32。
+ - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:表示等间隔划分结果的1-D Tensor,该Tensor的shape大小为 :math:`[num]` ,在mum为1的情况下,仅返回包含start元素值的Tensor。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当start或者stop的数据类型不是float32或者float64。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当num的数据类型不是float32或者float64。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当dtype的类型不是float32或者float64。
**代码示例**:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_and_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_and_cn.rst
index ea44c92c01b258c4135eada7cf0a71eb0fc6f96f..a5b0feeee80da6107ff8a0d2846a2008a74755e6 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_and_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_and_cn.rst
@@ -3,26 +3,26 @@
logical_and
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_and(x, y, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.logical_and(x, y, out=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.logical_and
-:alias: paddle.logical_and,paddle.tensor.logical_and,paddle.tensor.logic.logical_and
+:alias: paddle.logical_and, paddle.tensor.logical_and, paddle.tensor.logic.logical_and
:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_and
-该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` 和 ``Y`` 两LoDTensor/Tensor进行逻辑与运算。
+该OP逐元素的对 ``x`` 和 ``y`` 进行逻辑与运算。
.. math::
Out = X \&\& Y
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑与运算的第一个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑与运算的第二个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑与运算的第一个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑与运算的第二个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的 Variable,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- **name** (str,可选)- 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的LoDTensor/Tensor。
+返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的 Variable。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -31,24 +31,13 @@ logical_and
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle
import numpy as np
- # Graph organizing
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- res = fluid.layers.logical_and(x=x, y=y)
- # The comment lists another available method.
- # res = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='bool', value=0)
- # fluid.layers.logical_and(x=x, y=y, out=res)
-
- # Create an executor using CPU as an example
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-
- # Execute
- x_i = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]]).astype(np.bool)
- y_i = np.array([[1, 1], [0, 0]]).astype(np.bool)
- res_val, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i, 'y':y_i}, fetch_list=[res])
- print(res_val) # [[True, False], [False, False]]
-
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([True, True, False, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ y_data = np.array([True, False, True, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.logical_and(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [True False False False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_not_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_not_cn.rst
index a0a3a2dc5a6b84f3134950273dfb86732fd9d921..3eaf0f1719abac0ce3e63ed2867026f349e76fba 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_not_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_not_cn.rst
@@ -3,25 +3,25 @@
logical_not
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_not(x, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.logical_not(x, out=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.logical_not
-:alias: paddle.logical_not,paddle.tensor.logical_not,paddle.tensor.logic.logical_not
+:alias: paddle.logical_not, paddle.tensor.logical_not, paddle.tensor.logic.logical_not
:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_not
-该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` LoDTensor/Tensor进行逻辑非运算
+该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` Variable进行逻辑非运算
.. math::
Out = !X
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑非运算的输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑非运算的输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的 Variable,可以是程序中已经创建的任何 Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- **name** (str,可选)- 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的LoDTensor/Tensor。
+返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的 Variable。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -29,22 +29,11 @@ logical_not
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle
import numpy as np
- # Graph organizing
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- res = fluid.layers.logical_not(x)
- # The comment lists another availble method.
- # res = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='bool', value=0)
- # fluid.layers.logical_not(x, out=res)
-
- # Create an executor using CPU as an example
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-
- # Execute
- x_i = np.array([[1, 0]]).astype(np.bool)
- res_val, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i}, fetch_list=[res])
- print(res_val) # [[False, True]]
-
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([True, False, True, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.logical_not(x)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [False True False True]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_or_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_or_cn.rst
index b012c7ff4384c2e4193d6a91cdf4d82025103633..b95924ba3104aa1308483ee2f87c6bf43d711c25 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_or_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_or_cn.rst
@@ -3,26 +3,26 @@
logical_or
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_or(x, y, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.logical_or(x, y, out=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.logical_or
-:alias: paddle.logical_or,paddle.tensor.logical_or,paddle.tensor.logic.logical_or
+:alias: paddle.logical_or, paddle.tensor.logical_or, paddle.tensor.logic.logical_or
:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_or
-该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` 和 ``Y`` 两LoDTensor/Tensor进行逻辑或运算。
+该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` 和 ``Y`` 进行逻辑或运算。
.. math::
Out = X || Y
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑或运算的第一个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑或运算的第二个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑或运算的第一个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑或运算的第二个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的 Variable,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- **name** (str,可选)- 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的LoDTensor/Tensor。
+返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的 Variable。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -31,24 +31,13 @@ logical_or
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle
import numpy as np
- # Graph organizing
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- res = fluid.layers.logical_or(x=x, y=y)
- # The comment lists another available method.
- # res = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='bool', value=0)
- # fluid.layers.logical_or(x=x, y=y, out=res)
-
- # Create an executor using CPU as an example
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-
- # Execute
- x_i = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]]).astype(np.bool)
- y_i = np.array([[1, 1], [0, 0]]).astype(np.bool)
- res_val, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i, 'y':y_i}, fetch_list=[res])
- print(res_val) # [[True, True], [False, True]]
-
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([True, True, False, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ y_data = np.array([True, False, True, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.logical_or(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [True True True False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_xor_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_xor_cn.rst
index 12a8facec23f92d40b353d0942b2ab6f664d0c49..aefb5230c575fb9679d42b7fdafedaaef99c5dd9 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_xor_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/logical_xor_cn.rst
@@ -3,27 +3,27 @@
logical_xor
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_xor(x, y, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.logical_xor(x, y, out=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.logical_xor
-:alias: paddle.logical_xor,paddle.tensor.logical_xor,paddle.tensor.logic.logical_xor
+:alias: paddle.logical_xor, paddle.tensor.logical_xor, paddle.tensor.logic.logical_xor
:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.logical_xor
-该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` 和 ``Y`` 两LoDTensor/Tensor进行逻辑异或运算。
+该OP逐元素的对 ``X`` 和 ``Y`` 进行逻辑异或运算。
.. math::
Out = (X || Y) \&\& !(X \&\& Y)
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑异或运算的第一个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑异或运算的第二个输入,是一个多维的LoDTensor/Tensor,数据类型只能是bool。
- - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 逻辑异或运算的第一个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **y** (Variable)- 逻辑异或运算的第二个输入,是一个 Variable,数据类型只能是bool。
+ - **out** (Variable,可选)- 指定算子输出结果的 Variable,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- **name** (str,可选)- 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的LoDTensor/Tensor。
+返回:与 ``x`` 维度相同,数据类型相同的 Variable。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -32,24 +32,13 @@ logical_xor
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle
import numpy as np
- # Graph organizing
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[2], dtype='bool')
- res = fluid.layers.logical_xor(x=x, y=y)
- # The comment lists another available method.
- # res = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='bool', value=0)
- # fluid.layers.logical_xor(x=x, y=y, out=res)
-
- # Create an executor using CPU as an example
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-
- # Execute
- x_i = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]]).astype(np.bool)
- y_i = np.array([[1, 1], [0, 0]]).astype(np.bool)
- res_val, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i, 'y':y_i}, fetch_list=[res])
- print(res_val) # [[False, True], [False, True]]
-
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([True, True, False, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ y_data = np.array([True, False, True, False], dtype=np.bool)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.logical_xor(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [False True True False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f0c8af1e6cb09f7137d40bd4899395a3cb6e4e41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_layers_matrix_nms:
+
+matrix_nms
+-------------------------------
+
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.matrix_nms(bboxes, scores, score_threshold, post_threshold, nms_top_k, keep_top_k, use_gaussian=False, gaussian_sigma=2., background_label=0, normalized=True, return_index=False, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.nn.functional.matrix_nms
+:alias: paddle.nn.functional.matrix_nms,paddle.nn.functional.extension.matrix_nms
+:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.matrix_nms
+
+
+
+**Matrix NMS**
+
+该OP使用Matrix NMS算法对边界框(bounding box)和评分(scores)执行多类非极大值抑制(NMS)。
+
+如果提供 ``score_threshold`` 阈值且 ``nms_top_k`` 大于-1,则选择置信度分数最大的k个框。 然后按照Matrix NMS算法对分数进行衰减。经过抑制后,如果 ``keep_top_k`` 大于-1, 则每张图片最终保留 ``keep_top_k`` 个检测框。
+
+在NMS步骤后,如果keep_top_k大于-1,则每个图像最多保留keep_top_k个框(bounding box)。
+
+
+参数:
+ - **bboxes** (Variable) - 形为[N,M,4]的3-D张量,表示将预测M个边界框的预测位置, N是批大小(batch size)。当边界框(bounding box)大小等于4时,每个边界框有四个坐标值,布局为[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **scores** (Variable) – 形为[N,C,M]的3-D张量,表示预测的置信度。 N是批大小(batch size),C是种类数目,M是边界框bounding box的数量。对于每个类别,存在对应于M个边界框的总M个分数。请注意,M等于bboxes的第二维。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **score_threshold** (float) – 过滤掉低置信度分数的边界框的阈值。
+ - **post_threshold** (float) – 经过NMS衰减后,过滤掉低置信度分数的边界框的阈值。
+ - **nms_top_k** (int) – 基于 score_threshold 的过滤检测后,根据置信度保留的最大检测次数。
+ - **keep_top_k** (int) – 经过NMS抑制后, 最终保留的最大检测次数。如果设置为 -1 ,则则保留全部。
+ - **use_gaussian** (bool) – 是否使用高斯函数衰减。默认值:False 。
+ - **gaussian_sigma** (float) – 高斯函数的Sigma值,默认值:2.0 。
+ - **background_label** (int) – 背景标签(类别)的索引,如果设置为 0 ,则忽略背景标签(类别)。如果设置为 -1 ,则考虑所有类别。默认值:0
+ - **normalized** (bool) – 检测是否已经经过正则化。默认值:True 。
+ - **return_index** (bool) – 是否同时返回保留检测框的序号。默认值:False 。
+ - **name** (str|None) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`cn_api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+返回:
+ - **Out** (Variable) - 形为[No,6]的2-D LoDTensor,表示检测结果。每行有6个值:[标签label,置信度confidence,xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax]。或形为[No,10]的2-D LoDTensor,用来表示检测结果。 每行有10个值:[标签label,置信度confidence,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4]。 No是检测的总数。 如果对所有图像都没有检测到的box,则lod将设置为{1},而Out仅包含一个值-1。 (1.3版本之后,当未检测到box时,lod从{0}更改为{1})
+ - **Index** (Variable) - 形为[No,1]的2-D LoDTensor,表示检测结果在整个批次中的序号。
+
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ boxes = fluid.data(name='bboxes', shape=[None,81, 4],
+ dtype='float32', lod_level=1)
+ scores = fluid.data(name='scores', shape=[None,81],
+ dtype='float32', lod_level=1)
+ out = fluid.layers.matrix_nms(bboxes=boxes,
+ scores=scores,
+ background_label=0,
+ score_threshold=0.5,
+ post_threshold=0.1,
+ nms_top_k=400,
+ keep_top_k=200,
+ normalized=False)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/multiply_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/multiply_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4bb5ee012326ad9ae7ded391a124312f5654b769
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/multiply_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+.. _cn_api_fluid_layers_multiply:
+
+multiply
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.multiply(x, y, axis=-1, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.multiply
+:alias: paddle.multiply, paddle.tensor.multiply, paddle.tensor.math.multiply
+
+
+
+该OP是逐元素相乘算子,输入 ``x`` 与输入 ``y`` 逐元素相乘,并将各个位置的输出元素保存到返回结果中。
+
+等式是:
+
+.. math::
+ Out = X \odot Y
+
+- :math:`X` :多维Tensor。
+- :math:`Y` :维度必须小于等于X维度的Tensor。
+
+对于这个运算算子有2种情况:
+ 1. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 与 :math:`X` 相同。
+ 2. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 是 :math:`X` 的连续子序列。
+
+对于情况2:
+ 1. 用 :math:`Y` 匹配 :math:`X` 的形状(shape),其中 ``axis`` 是 :math:`Y` 在 :math:`X` 上的起始维度的位置。
+ 2. 如果 ``axis`` 为-1(默认值),则 :math:`axis= rank(X)-rank(Y)` 。
+ 3. 考虑到子序列, :math:`Y` 的大小为1的尾部维度将被忽略,例如shape(Y)=(2,1)=>(2)。
+
+例如:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (5,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (4, 5), with axis=-1(default) or axis=2
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (3, 4), with axis=1
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2), with axis=0
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2, 1), with axis=0
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Variable)- 多维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
+ - **y** (Variable)- 多维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
+ - **axis** (int32,可选)- ``y`` 的维度对应到 ``x`` 维度上时的索引。默认值为 -1。
+ - **name** (string,可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+
+返回: 维度与 ``x`` 相同的 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` ,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
+
+返回类型: Variable。
+
+**代码示例 1**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.multiply(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [[5, 12], [21, 32]]
+ x_data = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 2], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.multiply(x, y, axis=1)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [[[1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6]]]
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/nce_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/nce_cn.rst
index aea9b3598281d70b63d20789ec036a9425a35243..ef4532b84619f8444cd7a01c6821f7eb26c2739b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/nce_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/nce_cn.rst
@@ -43,35 +43,35 @@ nce
window_size = 5
words = []
- for i in xrange(window_size):
- words.append(fluid.layers.data(
- name='word_{0}'.format(i), shape=[1], dtype='int64'))
+ for i in range(window_size):
+ words.append(fluid.data(
+ name='word_{0}'.format(i), shape=[-1, 1], dtype='int64'))
dict_size = 10000
label_word = int(window_size / 2) + 1
embs = []
- for i in xrange(window_size):
+ for i in range(window_size):
if i == label_word:
continue
emb = fluid.layers.embedding(input=words[i], size=[dict_size, 32],
- param_attr='embed', is_sparse=True)
+ param_attr='embed', is_sparse=True)
embs.append(emb)
embs = fluid.layers.concat(input=embs, axis=1)
loss = fluid.layers.nce(input=embs, label=words[label_word],
- num_total_classes=dict_size, param_attr='nce.w_0',
- bias_attr='nce.b_0')
+ num_total_classes=dict_size, param_attr='nce.w_0',
+ bias_attr='nce.b_0')
- # 或使用自定义分布
+ #or use custom distribution
dist = np.array([0.05,0.5,0.1,0.3,0.05])
loss = fluid.layers.nce(input=embs, label=words[label_word],
- num_total_classes=5, param_attr='nce.w_1',
- bias_attr='nce.b_1',
- num_neg_samples=3,
- sampler="custom_dist",
- custom_dist=dist)
+ num_total_classes=5, param_attr='nce.w_1',
+ bias_attr='nce.b_1',
+ num_neg_samples=3,
+ sampler="custom_dist",
+ custom_dist=dist)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/not_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
index 9ec0336e9eb3ad320bfb7c842fa96bb7e651e47f..5a9cedf60cc03d67d8571424cffc2af62a583184 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
not_equal
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal(x, y, cond=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal(x, y, cond=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.not_equal
:alias: paddle.not_equal,paddle.tensor.not_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.not_equal
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ not_equal
- **x** (Variable) – 进行比较的第一个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **y** (Variable) – 进行比较的第二个输入,是一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **cond** (Variable,可选) – 如果为None,则创建一个Tensor来作为进行比较的输出结果,该Tensor的shape和数据类型和输入x一致;如果不为None,则将Tensor作为该OP的输出,数据类型和数据shape需要和输入x一致。默认值为None。
-
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的Tensor,数据的shape和输入x一致。
返回类型:变量(Variable),数据类型为bool类型。
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ones_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ones_cn.rst
index bc4b9fcc32637eba0d1e842f1f7fa593c3d23620..647b8d8c7caa1896a4a958712af7df325b986718 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ones_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/ones_cn.rst
@@ -5,21 +5,18 @@ ones
.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.ones(shape,dtype,force_cpu=False)
-
-
-
-**ones**
-
-该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为1的Tensor,该OP会将stop_gradient设置为True,即停止梯度更新。
+该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为1的Tensor。
参数:
- - **shape** (tuple|list) - 输出Tensor的形状。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
- - **force_cpu** (bool) – 是否强制将输出Tensor写入CPU内存。如果 ``force_cpu`` 为False,则将输出Tensor写入当前所在运算设备的内存,默认为False。
+ - **shape** (tuple|list|Tensor) - 输出Tensor的形状, ``shape`` 的数据类型为int32或者int64。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
+ - **force_cpu** (bool, 可选) – 是否强制将输出Tensor写入CPU内存。如果 ``force_cpu`` 为False,则将输出Tensor写入当前所在运算设备的内存,默认为False。
返回:值全为1的Tensor,数据类型和 ``dtype`` 定义的类型一致。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``dtype`` 不是bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32、int64和None时。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``shape`` 不是tuple、list、或者Tensor时, 当 ``shape`` 为Tensor,其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
**代码示例**:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/pow_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/pow_cn.rst
index f93dc252abae5678ac6149a2100862a3d48c1971..40eaf542138527856d25a002f16a4cf29c891f47 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/pow_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/pow_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
pow
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.pow(x, factor=1.0, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.pow(x, exponent, name=None)
@@ -12,16 +12,16 @@ pow
.. math::
- out = x^{factor}
+ out = x^{exponent}
**注意:如果需要对输入进行 elementwise_pow 操作,请查使用** :ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_pow` 。
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 多维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` ,数据类型为 ``float32`` 或 ``float64`` 。
- - **factor** (float32|Variable,可选)- ``float32`` 或形状为[1]的 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor``,数据类型为 ``float32``。Pow OP的指数因子。默认值:1.0。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 多维 ``Variable``,数据类型为 ``float32`` 或 ``float64`` 。
+ - **exponent** (float32|Variable)- ``float32`` 或形状为[1]的 ``Variable``,数据类型为 ``float32``。
- **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置。默认值: ``None``。
-返回:维度与输入 `x` 相同的 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor``,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
+返回:维度与输入 `x` 相同的 ``Variable``,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
返回类型:Variable。
@@ -30,18 +30,23 @@ pow
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[32,32], dtype="float32")
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ # example 1: exponent is a float
+ x_data = np.array([1, 2, 3])
+ exponent = 2
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.pow(x, exponent)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [1 4 9]
+
+ # example 2: exponent is a Variable
+ exponent = paddle.fill_constant(shape=[1], value=2, dtype='float32')
+ res = paddle.pow(x, exponent)
+ print(res.numpy()) # [1 4 9]
- x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[3,10,32,32], dtype="float32")
-
- # example 1: argument factor is float
- y_1 = fluid.layers.pow(x, factor=2.0)
- # y_1 is x^{2.0}
-
- # example 2: argument factor is Variable
- factor_tensor = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1], "float32", 3.0)
- y_2 = fluid.layers.pow(x, factor=factor_tensor)
- # y_2 is x^{3.0}
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/prroi_pool_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/prroi_pool_cn.rst
index 321c390d57ef836e0ab2a8a6f6b073df198bdb86..43221ea069434bd83fd066e6f1091ca9332f2e7f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/prroi_pool_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/prroi_pool_cn.rst
@@ -34,10 +34,18 @@ PRROIPool运算
.. code-block:: python
+ ## prroi_pool without batch_roi_num
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[490, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
- rois = fluid.layers.data(name='rois', shape=[4], lod_level=1, dtype='float32')
- pool_out = fluid.layers.prroi_pool(x, rois, 10, 1.0, 7, 7)
+ x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[None, 490, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
+ rois = fluid.data(name='rois', shape=[None, 4], lod_level=1, dtype='float32')
+ pool_out = fluid.layers.prroi_pool(x, rois, 1.0, 7, 7)
+
+ ## prroi_pool with batch_roi_num
+ batchsize=4
+ x2 = fluid.data(name='x2', shape=[batchsize, 490, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
+ rois2 = fluid.data(name='rois2', shape=[batchsize, 4], dtype='float32')
+ batch_rois_num = fluid.data(name='rois_nums', shape=[batchsize], dtype='int64')
+ pool_out2 = fluid.layers.prroi_pool(x2, rois2, 1.0, 7, 7, batch_roi_nums=batch_rois_num)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/py_reader_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/py_reader_cn.rst
index f302c7891f7debe6f37dac2bc8fa982c6cffccab..2f8f6f631479e9220221535b4ead4d0e753ead35 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/py_reader_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/py_reader_cn.rst
@@ -76,70 +76,69 @@ py_reader
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import paddle.dataset.mnist as mnist
-
- def network(reader):
- img, label = fluid.layers.read_file(reader)
- # 用户自定义网络,此处以softmax回归为例
- predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=img, size=10, act='softmax')
- loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
- return fluid.layers.mean(loss)
-
- # 新建 train_main_prog 和 train_startup_prog
- train_main_prog = fluid.Program()
- train_startup_prog = fluid.Program()
- with fluid.program_guard(train_main_prog, train_startup_prog):
- # 使用 fluid.unique_name.guard() 实现与test program的参数共享
- with fluid.unique_name.guard():
- train_reader = fluid.layers.py_reader(capacity=64,
- shapes=[(-1, 1, 28, 28), (-1, 1)],
- dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import paddle.dataset.mnist as mnist
+
+ def network(reader):
+ img, label = fluid.layers.read_file(reader)
+ # 用户自定义网络,此处以softmax回归为例
+ predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=img, size=10, act='softmax')
+ loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
+ return fluid.layers.mean(loss)
+
+ # 新建 train_main_prog 和 train_startup_prog
+ train_main_prog = fluid.Program()
+ train_startup_prog = fluid.Program()
+ with fluid.program_guard(train_main_prog, train_startup_prog):
+ # 使用 fluid.unique_name.guard() 实现与test program的参数共享
+ with fluid.unique_name.guard():
+ train_reader = fluid.layers.py_reader(capacity=64,
+ shapes=[(-1, 1, 28, 28), (-1, 1)],
+ dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
name='train_reader')
- train_reader.decorate_paddle_reader(
- paddle.reader.shuffle(paddle.batch(mnist.train(),
- batch_size=5),
+ train_reader.decorate_paddle_reader(
+ paddle.reader.shuffle(paddle.batch(mnist.train(),
+ batch_size=5),
buf_size=500))
- train_loss = network(train_reader) # 一些网络定义
- adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.01)
- adam.minimize(train_loss)
-
- # Create test_main_prog and test_startup_prog
- test_main_prog = fluid.Program()
- test_startup_prog = fluid.Program()
- with fluid.program_guard(test_main_prog, test_startup_prog):
- # 使用 fluid.unique_name.guard() 实现与train program的参数共享
- with fluid.unique_name.guard():
- test_reader = fluid.layers.py_reader(capacity=32,
- shapes=[(-1, 1, 28, 28), (-1, 1)],
- dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
- name='test_reader')
- test_reader.decorate_paddle_reader(paddle.batch(mnist.test(), 512))
-
- test_loss = network(test_reader)
-
- fluid.Executor(fluid.CUDAPlace(0)).run(train_startup_prog)
- fluid.Executor(fluid.CUDAPlace(0)).run(test_startup_prog)
-
- train_exe = fluid.ParallelExecutor(use_cuda=True,
- loss_name=train_loss.name, main_program=train_main_prog)
- test_exe = fluid.ParallelExecutor(use_cuda=True,
- loss_name=test_loss.name, main_program=test_main_prog)
- for epoch_id in range(10):
- train_reader.start()
- try:
- while True:
- train_exe.run(fetch_list=[train_loss.name])
- except fluid.core.EOFException:
- train_reader.reset()
-
- test_reader.start()
- try:
- while True:
- test_exe.run(fetch_list=[test_loss.name])
- except fluid.core.EOFException:
- test_reader.reset()
+ train_loss = network(train_reader) # 一些网络定义
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.01)
+ adam.minimize(train_loss)
+
+ # Create test_main_prog and test_startup_prog
+ test_main_prog = fluid.Program()
+ test_startup_prog = fluid.Program()
+ with fluid.program_guard(test_main_prog, test_startup_prog):
+ # 使用 fluid.unique_name.guard() 实现与train program的参数共享
+ with fluid.unique_name.guard():
+ test_reader = fluid.layers.py_reader(capacity=32,
+ shapes=[(-1, 1, 28, 28), (-1, 1)],
+ dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
+ name='test_reader')
+ test_reader.decorate_paddle_reader(paddle.batch(mnist.test(), 512))
+ test_loss = network(test_reader)
+
+ fluid.Executor(fluid.CUDAPlace(0)).run(train_startup_prog)
+ fluid.Executor(fluid.CUDAPlace(0)).run(test_startup_prog)
+
+ train_exe = fluid.ParallelExecutor(use_cuda=True,
+ loss_name=train_loss.name, main_program=train_main_prog)
+ test_exe = fluid.ParallelExecutor(use_cuda=True,
+ loss_name=test_loss.name, main_program=test_main_prog)
+ for epoch_id in range(10):
+ train_reader.start()
+ try:
+ while True:
+ train_exe.run(fetch_list=[train_loss.name])
+ except fluid.core.EOFException:
+ train_reader.reset()
+
+ test_reader.start()
+ try:
+ while True:
+ test_exe.run(fetch_list=[test_loss.name])
+ except fluid.core.EOFException:
+ test_reader.reset()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/range_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/range_cn.rst
index 292621d5f43bc66d6c81e23766128e2a6c169f5a..519f5e76f72b649cb924adc6c00342b7b5c54929 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/range_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/range_cn.rst
@@ -3,33 +3,32 @@
range
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.range(start, end, step, dtype)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.range(start, end, step, dtype, name=None)
+注意:推荐使用 paddle.arange
+该OP返回以步长 ``step`` 均匀分隔给定数值区间[``start``, ``end``)的1-D Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
-该API根据step均匀分隔给定数值区间[start, end),并返回该分隔结果。
-
+当 ``dtype`` 表示浮点类型时,为了避免浮点计算误差,建议给 ``end`` 加上一个极小值epsilon,使边界可以更加明确。
参数:
- - **start** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 区间起点,且区间包括此值, 当类型是Variable时,是shape为 `[1]` 的1-D Tensor。
- - **end** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 区间终点,通常区间不包括此值。但当step不是整数,且浮点数取整会影响输出的长度时例外。
- - **step** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 均匀分割的步长。
- - **dtype** (str | core.VarDesc.VarType) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,可为 `'float32'`, `'float64'`, `'int32'`, `'int64'` 。
-
-返回:均匀分割给定数值区间后得到的1-D Tensor, 数据类型为输入 `dtype` 。
+ - **start** (float|int|Tensor) - 区间起点(且区间包括此值)。当 ``start`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。
+ - **end** (float|int|Tensor) - 区间终点(且通常区间不包括此值)。当 ``end`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。
+ - **step** (float|int|Tensor) - 均匀分割的步长。当 ``step`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持int32、int64、float32、float64。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回类型:Variable
+返回:
+ Tensor: 以步长 ``step`` 均匀分割给定数值区间[``start``, ``end``)后得到的1-D Tensor, 数据类型为 ``dtype`` 。
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是int32、int64、float32、float64。
-**代码示例**:
+代码示例:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle.fluid as fluid
data = fluid.layers.range(0, 10, 2, 'int32')
-
-
-
-
-
+ # [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reciprocal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reciprocal_cn.rst
index 966c82cf90ee0423f37eeb6adbe0871c91caa652..a76a495a5112dc3404510b76bc310ad0b0f78e37 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reciprocal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reciprocal_cn.rst
@@ -29,17 +29,14 @@ reciprocal 对输入Tensor取倒数
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[2], value=4, dtype='float32') #data=[4.0, 4.0]
- result = fluid.layers.reciprocal(data) # result=[0.25, 0.25]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ res = paddle.%s(x)
+ print(res.numpy())
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank_cn.rst
index 5d5eb0d3e0d0ecf142b66e4891c1319b7d36eafb..7e67ee31003a74f34f64e9403336732388ca0ed2 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank_cn.rst
@@ -23,13 +23,8 @@ reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank
注意:该OP对 ``X`` 进行的排序所依据的 ``LoDRankTable`` 不一定是在 ``X`` 的基础上得出来的。它可以由其他不同的序列得出,并由该OP依据这个 ``LoDRankTable`` 来对 ``X`` 排序。
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 待根据提供的 ``rank_table`` 进行排序的LoDTensor
- - **rank_table** (Variable) - 提供对 ``x`` 重新排列的 ``LoDRankTable`` 类型的顺序信息,构造方法举例如下:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- rank_data = fluid.layers.data(name=data_desc[1][0], shape=data_desc[1][1])
- rank_table = fluid.layers.control_flow.lod_rank_table(rank_data)
+ - **x** (Variable) - 待根据提供的 ``rank_table`` 进行排序的LoDTensor.
+ - **rank_table** (Variable) - 提供对 ``x`` 重新排列的 ``LoDRankTable`` 类型的顺序信息.
返回: 重新排列后的LoDTensor
@@ -40,15 +35,33 @@ reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank
.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data_desc = (['input', [9], 0], ['ref', [5], 1])
- data = fluid.layers.data(name=data_desc[0][0], shape=data_desc[0][1])
- rank_data = fluid.layers.data(name=data_desc[1][0], shape=data_desc[1][1])
- table = fluid.layers.control_flow.lod_rank_table(rank_data)
+
+ rank_data = fluid.layers.data(name='rank_data', shape=[5], dtype='float32', lod_level=2)
+ table = fluid.layers.control_flow.lod_rank_table(rank_data, level=1)
+
+ data = fluid.layers.data(name='data', shape=[9], lod_level=2)
new_data = fluid.layers.reorder_lod_tensor_by_rank(
x=data, rank_table=table)
+ place=fluid.CPUPlace()
+ exe = fluid.Executor(place)
+ exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+
+ rank_tensor = fluid.create_lod_tensor(np.random.random([14,5]).astype("float32"), [[4,1], [3, 2, 2, 3, 4]], place)
+
+ data_ndarray = np.random.random([27, 9]).astype("float32")
+ data_lod = [[1, 2, 2, 4, 4], [2, 2, 4, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 2, 1]]
+ data_tensor = fluid.create_lod_tensor(data_ndarray, data_lod, place)
+
+ out = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(),feed={'data':data_tensor, 'rank_data':rank_tensor}, fetch_list=[new_data], return_numpy=False)
+ print(out[0])
+ # lod: {{0, 4, 5, 9, 11, 13}{0, 2, 6, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 23, 25, 27}}
+ #shape: [27, 9]
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/retinanet_target_assign_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/retinanet_target_assign_cn.rst
index 895433d93fe0a6d4e10ac85aedb464ab78fe074b..cd37a297b2b303429ee17ad9f2f2881245041ebe 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/retinanet_target_assign_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/retinanet_target_assign_cn.rst
@@ -68,9 +68,9 @@ retinanet_target_assign
gt_boxes = fluid.data(name='gt_boxes', shape=[10, 4],
dtype='float32')
gt_labels = fluid.data(name='gt_labels', shape=[10, 1],
- dtype='float32')
+ dtype='int32')
is_crowd = fluid.data(name='is_crowd', shape=[1],
- dtype='float32')
+ dtype='int32')
im_info = fluid.data(name='im_info', shape=[1, 3],
dtype='float32')
score_pred, loc_pred, score_target, loc_target, bbox_inside_weight, fg_num = \
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reverse_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reverse_cn.rst
index d0b724e6c8dbf0c487489741b92b51f21cb6a5c5..a4a552705b1dfc6bb389434a3f0cc771232f91c3 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reverse_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/reverse_cn.rst
@@ -15,10 +15,31 @@ reverse
该OP对输入Tensor ``x`` 在指定轴 ``axis`` 上进行数据的逆序操作。
-参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 多维Tensor,类型必须为int32,int64,float32,float64。
- - **axis** (int|tuple|list) - 指定逆序运算的轴,取值范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``x`` 的Rank, ``axis`` 为负时与 ``axis`` +R 等价。如果 ``axis`` 是一个元组或列表,则在``axis`` 每个元素值所指定的轴上进行逆序运算。
+::
+
+ 示例1:
+ 输入是 LoDTensor 类型:
+ x = [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]
+ axis = [0, 1]
+
+ 输出:
+ output = [[8, 7, 6], [5, 4, 3], [2, 1, 0]]
+
+ 示例2:
+ 输入是 LoDTensorArray 类型:
+ x = {[[0, 1], [2, 3]],
+ [[4, 5, 6]],
+ [[7], [8], [9]]}
+ axis = 0
+ 输出:
+ output = {[[7], [8], [9]],
+ [[4, 5, 6]],
+ [[0, 1], [2, 3]]}
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Variable) - 输入为Tensor或LoDTensorArray,数据类型支持bool,int8,int32,int64,float32和float64。若输入是LoDTensorArray类型,则返回一个逆序的LoDTensorArray,其内部Tensor元素的次序保持不变。
+ - **axis** (int|tuple|list) - 指定逆序运算的轴,取值范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``x`` 的Rank, ``axis`` 为负时与 ``axis`` +R 等价。如果 ``axis`` 是一个元组或列表,则在 ``axis`` 每个元素值所指定的轴上进行逆序运算。如果输入是LoDTensorArray类型,axis须是值为0的int,或shape为[1]的list ``[0]`` 、元组 ``(0,)`` 。
返回:逆序后的Tensor,形状、数据类型和 ``x`` 一致。
返回类型:Variable
@@ -32,3 +53,13 @@ reverse
data = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]], dtype='float32')) # [[0., 1., 2.], [3., 4., 5.], [6., 7., 8.]]
result1 = fluid.layers.reverse(data, 0) # [[6., 7., 8.], [3., 4., 5.], [0., 1., 2.]]
result2 = fluid.layers.reverse(data, [0, 1]) # [[8., 7., 6.], [5., 4., 3.], [2., 1., 0.]]
+
+ # 输入为LoDTensorArray时
+ data1 = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([[0, 1, 2]], dtype='float32'))
+ data2 = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([[3, 4, 5]], dtype='float32'))
+ tensor_array = fluid.layers.create_array(dtype='float32')
+ i = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[1], dtype='int64', value=0)
+ fluid.layers.array_write(data1, i, tensor_array)
+ fluid.layers.array_write(data2, i+1, tensor_array)
+
+ reversed_tensor_array = fluid.layers.reverse(tensor_array, 0) # {[[3, 4, 5]], [[0, 1, 2]]}
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/scale_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/scale_cn.rst
index f9ddd81f88ab446c144559cfc6f92538f7d44d3c..6623f9e451b594e71b28235a54dbe858d98ff9c9 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/scale_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/scale_cn.rst
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ scale
import numpy as np
inputs = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[2, 3], dtype='float32')
- scale = fluid.layers.data(name="scale", shape=[1], dtype='float32'
+ scale = fluid.layers.data(name="scale", shape=[1], dtype='float32',
append_batch_size=False)
output = fluid.layers.scale(inputs, scale = scale, bias = 1.0)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shape_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shape_cn.rst
index 5f5c2e67002fb0fe9091c92c77775deea6a8afb6..0672af0a3a203fd1d2e866705c2b52ee21421fe9 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shape_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shape_cn.rst
@@ -13,12 +13,30 @@ shape
shape层。
-获得输入Tensor的shape。
+获得输入Tensor或SelectedRows的shape。
+
+::
+
+ 示例1:
+ 输入是 N-D Tensor类型:
+ input = [ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8] ]
+
+ 输出shape:
+ input.shape = [2, 4]
+
+ 示例2:
+ 输入是 SelectedRows类型:
+ input.rows = [0, 4, 19]
+ input.height = 20
+ input.value = [ [1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6] ] # inner tensor
+ 输出shape:
+ input.shape = [3, 2]
参数:
- - **input** (Variable)- 输入的多维Tensor,数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **input** (Variable)- 输入的多维Tensor或SelectedRows,数据类型为float16,float32,float64,int32,int64。如果输入是SelectedRows类型,则返回其内部持有Tensor的shape。
+
-返回: 一个Tensor,表示输入Tensor的shape。
+返回: 一个Tensor,表示输入Tensor或SelectedRows的shape。
返回类型: Variable(Tensor)。
@@ -29,7 +47,7 @@ shape层。
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- inputs = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[3, 100, 100], dtype="float32")
+ inputs = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[3, 100, 100], dtype="float32")
output = fluid.layers.shape(inputs)
exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shuffle_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shuffle_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 3be4313d48586820adba07b298dabdac23fc86be..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/shuffle_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_fluid_layers_shuffle:
-
-shuffle
--------------------------------
-
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.shuffle(reader, buffer_size)
-
-创建一个特殊的数据读取器,它的输出数据会被重洗(shuffle)。由原始读取器创建的迭代器得到的输出将会被暂存到shuffle缓存区,其后
-会对其进行重洗运算。shuffle缓存区的大小由参数 ``buffer_size`` 决定。
-
-参数:
- - **reader** (callable) – 输出会被shuffle的原始reader
- - **buffer_size** (int) – 进行shuffle的buffer的大小
-
-返回:其输出会被shuffle的一个reader(读取器)
-
-返回类型:callable
-
-**代码示例**:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- raw_reader = fluid.layers.io.open_files(filenames=['./data1.recordio',
- './data2.recordio'],
- shapes=[(3,224,224), (1,)],
- lod_levels=[0, 0],
- dtypes=['float32', 'int64'],
- thread_num=2,
- buffer_size=2)
- batch_reader = fluid.layers.batch(reader=raw_reader, batch_size=5)
- shuffle_reader = fluid.layers.shuffle(reader=batch_reader, buffer_size=5000)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/sigmoid_focal_loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/sigmoid_focal_loss_cn.rst
index 27820b77e54dadc0da6230294736fee8c7ba307e..2f47561a89a4560e0c39553205b4d7fa68c7a841 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/sigmoid_focal_loss_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/sigmoid_focal_loss_cn.rst
@@ -47,13 +47,70 @@ Focal Loss的计算过程如下:
.. code-block:: python
+ import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
-
- input = fluid.data(name='data', shape=[10,80], dtype='float32')
- label = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[10,1], dtype='int32')
- fg_num = fluid.data(name='fg_num', shape=[1], dtype='int32')
- loss = fluid.layers.sigmoid_focal_loss(x=input,
- label=label,
- fg_num=fg_num,
- gamma=2.0,
- alpha=0.25)
+
+ num_classes = 10 # exclude background
+ image_width = 16
+ image_height = 16
+ batch_size = 32
+ max_iter = 20
+
+
+ def gen_train_data():
+ x_data = np.random.uniform(0, 255, (batch_size, 3, image_height,
+ image_width)).astype('float64')
+ label_data = np.random.randint(0, num_classes,
+ (batch_size, 1)).astype('int32')
+ return {"x": x_data, "label": label_data}
+
+
+ def get_focal_loss(pred, label, fg_num, num_classes):
+ pred = fluid.layers.reshape(pred, [-1, num_classes])
+ label = fluid.layers.reshape(label, [-1, 1])
+ label.stop_gradient = True
+ loss = fluid.layers.sigmoid_focal_loss(
+ pred, label, fg_num, gamma=2.0, alpha=0.25)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(loss)
+ return loss
+
+
+ def build_model(mode='train'):
+ x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[-1, 3, -1, -1], dtype='float64')
+ output = fluid.layers.pool2d(input=x, pool_type='avg', global_pooling=True)
+ output = fluid.layers.fc(
+ input=output,
+ size=num_classes,
+ # Notice: size is set to be the number of target classes (excluding backgorund)
+ # because sigmoid activation will be done in the sigmoid_focal_loss op.
+ act=None)
+ if mode == 'train':
+ label = fluid.data(name="label", shape=[-1, 1], dtype='int32')
+ # Obtain the fg_num needed by the sigmoid_focal_loss op:
+ # 0 in label represents background, >=1 in label represents foreground,
+ # find the elements in label which are greater or equal than 1, then
+ # computed the numbers of these elements.
+ data = fluid.layers.fill_constant(shape=[1], value=1, dtype='int32')
+ fg_label = fluid.layers.greater_equal(label, data)
+ fg_label = fluid.layers.cast(fg_label, dtype='int32')
+ fg_num = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(fg_label)
+ fg_num.stop_gradient = True
+ avg_loss = get_focal_loss(output, label, fg_num, num_classes)
+ return avg_loss
+ else:
+ # During evaluating or testing phase,
+ # output of the final fc layer should be connected to a sigmoid layer.
+ pred = fluid.layers.sigmoid(output)
+ return pred
+
+
+ loss = build_model('train')
+ moment_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.MomentumOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.001, momentum=0.9)
+ moment_optimizer.minimize(loss)
+ place = fluid.CPUPlace()
+ exe = fluid.Executor(place)
+ exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+ for i in range(max_iter):
+ outs = exe.run(feed=gen_train_data(), fetch_list=[loss.name])
+ print(outs)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/softmax_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/softmax_cn.rst
index a11f955072ab19183abde10ce55469e81bc1c696..21052f227cd42db24536fd67b97c77cb6bdc5057 100755
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/softmax_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/softmax_cn.rst
@@ -5,12 +5,6 @@ softmax
.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.softmax(input, use_cudnn=False, name=None, axis=-1)
-:alias_main: paddle.nn.functional.softmax
-:alias: paddle.nn.functional.softmax,paddle.nn.functional.activation.softmax
-:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.softmax
-
-
-
该OP实现了softmax层。OP的计算过程如下:
步骤1:输入 ``input`` 的 ``axis`` 维会被置换到最后一维;
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/split_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/split_cn.rst
index c05da2a5cae6586df69edcb14e49889299270400..ca1607ee55c07488cd3a343ec72bf5c216ae2614 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/split_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/split_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
split
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.split(input,num_or_sections,dim=-1,name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections, dim=-1, name=None)
@@ -11,18 +11,18 @@ split
该OP将输入Tensor分割成多个子Tensor。
参数:
- - **input** (Variable) - 输入变量,数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64的多维Tensor或者LoDTensor。
+ - **input** (Tensor) - 输入变量,数据类型为bool, float16,float32,float64,int32,int64的多维Tensor。
- **num_or_sections** (int|list|tuple) - 如果 ``num_or_sections`` 是一个整数,则表示Tensor平均划分为相同大小子Tensor的数量。如果 ``num_or_sections`` 是一个list或tuple,那么它的长度代表子Tensor的数量,它的元素可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,依次代表子Tensor需要分割成的维度的大小。list或tuple的长度不能超过输入Tensor待分割的维度的大小。至多有一个元素值为-1,-1表示该值是由 ``input`` 待分割的维度值和 ``num_or_sections`` 的剩余元素推断出来的。
- - **dim** (int|Variable,可选) - 整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或int64。表示需要分割的维度。如果dim < 0,则划分的维度为rank(input) + dim。默认值为-1。
+ - **dim** (int|Tenspr,可选) - 整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或int64。表示需要分割的维度。如果 ``dim < 0`` ,则划分的维度为 ``rank(input) + dim`` 。默认值为-1。
- **name** (str,可选) - 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:分割后的Tensor列表。
-返回类型:列表(Variable(Tensor|LoDTensor)),数据类型为int32,int64,float32,float64。
抛出异常:
- - :code:`TypeError`:``num_or_sections`` 不是int、list 或 tuple。
- - :code:`TypeError`:``dim`` 不是 int 或 Variable。
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``input`` 的数据类型不是bool、float16、float32、float64、int32或int64时 。
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``num_or_sections`` 不是int、list 或 tuple时。
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``dim`` 不是 int 或 Tensor时。当 ``dim`` 为Tensor,其数据类型不是int32或int64时。
**代码示例**:
@@ -30,27 +30,31 @@ split
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- # 输入是维度为[3, 9, 5]的Tensor:
+ # input is a Tensor which shape is [3, 9, 5]
input = fluid.data(
name="input", shape=[3, 9, 5], dtype="float32")
- # 传入num_or_sections为一个整数
- x0, x1, x2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=3, dim=1)
- x0.shape # [3, 3, 5]
- x1.shape # [3, 3, 5]
- x2.shape # [3, 3, 5]
-
- # 传入num_or_sections为一个整数列表
- x0, x1, x2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=[2, 3, 4], dim=1)
- x0.shape # [3, 2, 5]
- x1.shape # [3, 3, 5]
- x2.shape # [3, 4, 5]
-
- # 传入num_or_sections为一个整数列表,其中有一个元素为-1
- x0, x1, x2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=[2, 3, -1], dim=1)
- x0.shape # [3, 2, 5]
- x1.shape # [3, 3, 5]
- x2.shape # [3, 4, 5]
+ out0, out1, out2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=3, dim=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 3, 5]
+
+ out0, out1, out2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=[2, 3, 4], dim=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 2, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 4, 5]
+
+ out0, out1, out2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=[2, 3, -1], dim=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 2, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 4, 5]
+
+ # dim is negative, the real dim is (rank(input) + axis) which real
+ # value is 1.
+ out0, out1, out2 = fluid.layers.split(input, num_or_sections=3, dim=-2)
+ # out0.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 3, 5]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/uniform_random_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/uniform_random_cn.rst
index 51bfc1c0015e90e068d735ccedf581687fc6a583..14e921926463fb4f02aa1b1bf133e2bc2f8c9bd7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/uniform_random_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/uniform_random_cn.rst
@@ -3,12 +3,12 @@
uniform_random
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.uniform_random(shape, dtype='float32', min=-1.0, max=1.0, seed=0)
+.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.uniform_random(shape, dtype='float32', min=-1.0, max=1.0, seed=0, name=None)
-该OP使用从范围[min,max)内均匀分布采样的随机值初始化一个Tensor。
+该OP返回数值服从范围[``min``, ``max``)内均匀分布的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
::
@@ -19,18 +19,19 @@ uniform_random
result=[[0.8505902, 0.8397286]]
参数:
- - **shape** (list|tuple|Variable)-输出Tensor的维度,shape类型支持list,tuple,Variable。如果shape类型是list或者tuple,它的元素可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,其中整数的数据类型为int,Tensor的数据类型为int32或int64。如果shape的类型是Variable,则是1D的Tensor,Tensor的数据类型为int32或int64。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str,可选) – 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持float32(默认), float64。
- - **min** (float,可选)-要生成的随机值范围的下限,min包含在范围中。支持的数据类型:float。默认值为-1.0。
- - **max** (float,可选)-要生成的随机值范围的上限,max不包含在范围中。支持的数据类型:float。默认值为1.0。
- - **seed** (int,可选)-随机种子,用于生成样本。0表示使用系统生成的种子。注意如果种子不为0,该操作符每次都生成同样的随机数。支持的数据类型:int。默认为 0。
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 生成的随机Tensor的形状。如果 ``shape`` 是list、tuple,则其中的元素可以是int,或者是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64的Tensor。如果 ``shape`` 是Tensor,则是数据类型为int32、int64的1-D Tensor。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持float32、float64。默认值为float32。
+ - **min** (float|int,可选) - 要生成的随机值范围的下限,min包含在范围中。支持的数据类型:float、int。默认值为-1.0。
+ - **max** (float|int,可选) - 要生成的随机值范围的上限,max不包含在范围中。支持的数据类型:float、int。默认值为1.0。
+ - **seed** (int,可选) - 随机种子,用于生成样本。0表示使用系统生成的种子。注意如果种子不为0,该操作符每次都生成同样的随机数。支持的数据类型:int。默认为 0。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:表示一个随机初始化结果的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型由dtype参数决定,该Tensor的维度由shape参数决定。
-
-返回类型:Variable
+返回:
+ Tensor:数值服从范围[``min``, ``max``)内均匀分布的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
抛出异常:
- - :code:`TypeError`: shape的类型应该是list、tuple 或 Variable。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list、tuple、Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是float32、float64。
**代码示例**:
@@ -43,17 +44,17 @@ uniform_random
train_program = fluid.Program()
with fluid.program_guard(train_program, startup_program):
# example 1:
- # attr shape is a list which doesn't contain tensor Variable.
+ # attr shape is a list which doesn't contain Tensor.
result_1 = fluid.layers.uniform_random(shape=[3, 4])
# example 2:
- # attr shape is a list which contains tensor Variable.
+ # attr shape is a list which contains Tensor.
dim_1 = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1],"int64",3)
dim_2 = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1],"int32",5)
result_2 = fluid.layers.uniform_random(shape=[dim_1, dim_2])
# example 3:
- # attr shape is a Variable, the data type must be int32 or int64
+ # attr shape is a Tensor, the data type must be int32 or int64
var_shape = fluid.data(name='var_shape', shape=[2], dtype="int64")
result_3 = fluid.layers.uniform_random(var_shape)
var_shape_int32 = fluid.data(name='var_shape_int32', shape=[2], dtype="int32")
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unique_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unique_cn.rst
index 6dcf44005f5a55eda5f2f2b8f5377321a7a1807c..0877f8686aa1101fff05377404492f8d45aa493f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unique_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unique_cn.rst
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ unique为 ``x`` 返回一个unique张量和一个指向该unique张量的索引
import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.assign(np.array([2, 3, 3, 1, 5, 3], dtype='int32'))
+ x = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([2, 3, 3, 1, 5, 3], dtype='int32'))
out, index = fluid.layers.unique(x) # out is [2, 3, 1, 5]; index is [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 1]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unstack_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unstack_cn.rst
index cc4324c6b5764b7a03cfe509345e14aa43e505ee..00b8cfe97a1409bc9b845690ba7ec3dd29a77c86 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unstack_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/unstack_cn.rst
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ unstack
该OP将单个dim为 ``D`` 的Tensor沿 ``axis`` 轴unpack为 ``num`` 个dim为 ``(D-1)`` 的Tensor
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) – 输入x为 ``dim > 0`` 的Tensor,
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 输入x为 ``dim > 0`` 的Tensor,
支持的数据类型: float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **axis** (int | 可选) – 输入Tensor进行unpack运算所在的轴,axis的范围为:``[-D, D)`` ,
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ unstack
返回: 长度为num的Tensor列表, 数据类型与输入Tensor相同,dim为 ``(D-1)``。
-返回类型: list(Variable)
+返回类型: list(Tensor)
抛出异常:
- :code:`ValueError`:``x.shape[axis]`` <= 0 或 ``axis`` 不在[-D, D)范围内
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ unstack
.. code-block:: python
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2, 3, 5], dtype='float32') #创建一个shape=[2, 3, 5]的Tensor
+ x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[2, 3, 5], dtype='float32') #创建一个shape=[2, 3, 5]的Tensor
y = fluid.layers.unstack(x, axis=1) #沿着第1轴进行unpack, unpack后为3个shape=[2,5]的Tensor
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/zeros_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/zeros_cn.rst
index a3c7d2929b66ee6a9e83193c54dd2068595dcef2..7e9973e1080d68abd2d9d2a0ccbe1e8733b02a98 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/zeros_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/layers_cn/zeros_cn.rst
@@ -5,21 +5,18 @@ zeros
.. py:function:: paddle.fluid.layers.zeros(shape,dtype,force_cpu=False)
-
-
-
-**zeros**
-
-该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为0的Tensor,该OP会将stop_gradient设置为True,即停止梯度更新。
+该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为0的Tensor。
参数:
- - **shape** (tuple|list) - 输出Tensor的形状。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
- - **force_cpu** (bool) - 是否强制将输出Tensor写入CPU内存。如果 ``force_cpu`` 为False,则将输出Tensor写入当前所在运算设备的内存,默认为False。
+ - **shape** (tuple|list|Tensor) - 输出Tensor的形状, ``shape`` 的数据类型为int32或者int64。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
+ - **force_cpu** (bool, 可选) - 是否强制将输出Tensor写入CPU内存。如果 ``force_cpu`` 为False,则将输出Tensor写入当前所在运算设备的内存,默认为False。
返回:值全为0的Tensor,数据类型和 ``dtype`` 定义的类型一致。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``dtype`` 不是bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32、int64。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``shape`` 不是tuple、list、或者Tensor时。 当 ``shape`` 为Tensor,其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
**代码示例**:
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn.rst
index fd6aa4c90670eafa3a35c3a3705d9d5f59ae6507..b42ec565b8cdb613db774a5630cfa6e7575d850e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn.rst
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn_cn/Upsample_cn.rst
nn_cn/activation_cn.rst
nn_cn/loss_cn.rst
+ nn_cn/functional_cn.rst
nn_cn/adaptive_pool2d_cn.rst
nn_cn/adaptive_pool3d_cn.rst
nn_cn/add_position_encoding_cn.rst
@@ -94,7 +95,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn_cn/logsigmoid_cn.rst
nn_cn/log_loss_cn.rst
nn_cn/lrn_cn.rst
- nn_cn/margin_rank_loss_cn.rst
+ nn_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst
nn_cn/maxout_cn.rst
nn_cn/mse_loss_cn.rst
nn_cn/multiclass_nms_cn.rst
@@ -105,6 +106,7 @@ paddle.nn
nn_cn/pad2d_cn.rst
nn_cn/pad_cn.rst
nn_cn/pad_constant_like_cn.rst
+ nn_cn/PairwiseDistance_cn.rst
nn_cn/ParameterList_cn.rst
nn_cn/piecewise_decay_cn.rst
nn_cn/pixel_shuffle_cn.rst
@@ -160,3 +162,6 @@ paddle.nn
nn_cn/while_loop_cn.rst
nn_cn/yolov3_loss_cn.rst
nn_cn/yolo_box_cn.rst
+ nn_cn/loss_cn/MarginRankingLoss_cn.rst
+ nn_cn/functional_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/PairwiseDistance_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/PairwiseDistance_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..94e1d04bbe23d9c5e49277902c9fd206a6e02c12
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/PairwiseDistance_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_PairwiseDistance:
+
+PairwiseDistance
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.PairwiseDistance(p=2., epsilon=1e-6, keepdim=False, name=None)
+
+该OP计算两个向量(输入 ``x``、``y`` )之间pairwise的距离。该距离通过p范数计算:
+
+ .. math::
+
+ \Vert x \Vert _p = \left( \sum_{i=1}^n \vert x_i \vert ^ p \right ) ^ {1/p}.
+
+参数
+::::::::
+ - **p** (float,可选)- 指定p阶的范数。默认值为2。
+ - **epsilon** (float,可选)- 添加到分母的一个很小值,避免发生除零错误。默认值为1e-6。
+ - **keepdim** (bool,可选)- 是否保留输出张量减少的维度。输出结果相对于 ``|x-y|`` 的结果减少一维,除非 :attr:`keepdim` 为True,默认值为False。
+ - **name** (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+形状
+::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor) - :math:`(N, D)` ,其中D是向量的维度,数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - :math:`(N, D)` ,与 ``x`` 的形状、数据类型相同。
+ - **output** (Tensor) - :math:`(N)` ,如果 :attr:`keepdim` 为True,则形状为 :math:`(N, 1)` 。数据类型与 ``x``、 ``y`` 相同。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_np = np.array([[1., 3.], [3., 5.]]).astype(np.float64)
+ y_np = np.array([[5., 6.], [7., 8.]]).astype(np.float64)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_np)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_np)
+ dist = paddle.nn.PairwiseDistance()
+ distance = dist(x, y)
+ print(distance.numpy()) # [5. 5.]
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn.rst
index 9bd3fa86689a40936ccccd5acae95a6ab433c2cd..79d1258944cf3cc467ec059b87a5ffeaea6ba678 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn.rst
@@ -8,4 +8,5 @@ activation
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
+ activation_cn/LeakyReLU_cn.rst
activation_cn/Sigmoid_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn/LeakyReLU_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn/LeakyReLU_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9b9c61818c72a4a8aefcaa356ffd0b0fbf4d81df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/activation_cn/LeakyReLU_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_LeakyReLU:
+
+LeakyReLU
+-------------------------------
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01, name=None)
+
+ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)激活层
+
+.. math::
+
+ \\Out = max(x, alpha*x)\\
+
+其中,:math:`x` 为输入的 Tensor
+
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - alpha (float,可选) - :math:`x < 0` 时的斜率。默认值为0.01。
+ - name (str, 可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+形状:
+ - input: 任意形状的Tensor。
+ - output: 和input具有相同形状的Tensor。
+
+代码示例
+:::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ lrelu = paddle.nn.LeakyReLU()
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([-2, 0, 1], 'float32'))
+ out = lrelu(x) # [-0.02, 0, 1]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b314bbe0ef25f09151745db0d91bdc8404eb540f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+=======================
+functional
+=======================
+
+
+
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 1
+
+ functional_cn/l1_loss_cn.rst
+ functional_cn/nll_loss_cn.rst
+ functional_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/l1_loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/l1_loss_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d7bf747f4d1720f65bfbab23738cc0ddc2389b3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/l1_loss_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+l1_loss
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.nn.functional.l1_loss(x, label, reduction='mean', name=None)
+
+该接口计算输入 ``x`` 和标签 ``label`` 间的 `L1 loss` 损失。
+
+该损失函数的数学计算公式如下:
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'none'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = \lvert x - label\rvert
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'mean'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = MEAN(\lvert x - label\rvert)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = SUM(\lvert x - label\rvert)
+
+
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor): - 输入的Tensor,维度是[N, *], 其中N是batch size, `*` 是任意数量的额外维度。数据类型为:float32、float64、int32、int64。
+ - **label** (Tensor): - 标签,维度是[N, *], 与 ``x`` 相同。数据类型为:float32、float64、int32、int64。
+ - **reduction** (str, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: ``'none'``, ``'mean'``, ``'sum'`` 。默认为 ``'mean'``,计算 `L1Loss` 的均值;设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,计算 `L1Loss` 的总和;设置为 ``'none'`` 时,则返回 `L1Loss`。
+ - **name** (str,可选): - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+返回
+:::::::::
+``Tensor``, 输入 ``x`` 和标签 ``label`` 间的 `L1 loss` 损失。如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'none'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [N, *], 与输入 ``x`` 相同。如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'mean'`` 或 ``'sum'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [1]。
+
+
+代码示例
+:::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([[1.5, 0.8], [0.2, 1.3]]).astype("float32")
+ label_data = np.array([[1.7, 1], [0.4, 0.5]]).astype("float32")
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ label = paddle.to_variable(label_data)
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.functional.l1_loss(x, label)
+ print(l1_loss.numpy())
+ # [0.35]
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.functional.l1_loss(x, label, reduction='none')
+ print(l1_loss.numpy())
+ # [[0.20000005 0.19999999]
+ # [0.2 0.79999995]]
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.functional.l1_loss(x, label, reduction='sum')
+ print(l1_loss.numpy())
+ # [1.4]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..edc1d7c7d1ffe659255e1f92a6a43e0d78af1bcf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/margin_ranking_loss_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_cn_margin_ranking_loss:
+
+margin_ranking_loss
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.nn.functional.margin_ranking_loss(input, other, label, margin=0.0, reduction='mean', name=None)
+
+该算子计算输入input,other 和 标签label间的 `margin rank loss` 损失。该损失函数的数学计算公式如下:
+
+ .. math::
+ margin\_rank\_loss = max(0, -label * (input - other) + margin)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'mean'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = MEAN(margin\_rank\_loss)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = SUM(margin\_rank\_loss)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'none'`` 时,直接返回最原始的 `margin_rank_loss` 。
+
+参数
+::::::::
+ - **input** (Tensor):第一个输入的 `Tensor` ,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - **other** (Tensor):第二个输入的 `Tensor` ,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - **label** (Tensor):训练数据的标签,数据类型为:float32, float64。
+ - **margin** (float,可选): - 用于加和的margin值,默认值为0。
+ - **reduction** (string,可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: ``'none'`` 、 ``'mean'`` 、 ``'sum'`` 。如果设置为 ``'none'`` ,则直接返回 最原始的 ``margin_rank_loss`` 。如果设置为 ``'sum'`` ,则返回 ``margin_rank_loss`` 的总和。如果设置为 ``'mean'`` ,则返回 ``margin_rank_loss`` 的平均值。默认值为 ``'none'`` 。
+ - **name** (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+返回
+::::::::
+Tensor, 如果 :attr:`reduction` 为 ``'sum'`` 或者是 ``'mean'`` ,则形状为 :math:`[1]` ,否则shape和输入 `input` 保持一致 。数据类型与 ``input``、 ``other`` 相同。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ input = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).astype('float32'))
+ other = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[2, 1], [2, 4]]).astype('float32'))
+ label = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[1, -1], [-1, -1]]).astype('float32'))
+ loss = paddle.nn.functional.margin_ranking_loss(input, other, label)
+ print(loss.numpy()) # [0.75]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/nll_loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/nll_loss_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..59a1c6355e304b7ac6d9dca44031408bda008f78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/functional_cn/nll_loss_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_functional_nll_loss:
+
+nll_loss
+-------------------------------
+.. py:function:: paddle.nn.functional.nll_loss(input, label, weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean', name=None)
+
+该接口返回 `negative log likelihood` 。可在 :ref:`cn_api_nn_loss_NLLLoss` 查看详情。
+
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **input** (Tensor): - 输入 `Tensor`, 其形状为 :math:`[N, C]` , 其中 `C` 为类别数。但是对于多维度的情形下,它的形状为 :math:`[N, C, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **label** (Tensor): - 输入x对应的标签值。其形状为 :math:`[N,]` 或者 :math:`[N, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]`, 数据类型为int64。
+ - **weight** (Tensor, 可选): - 手动指定每个类别的权重。其默认为 `None` 。如果提供该参数的话,长度必须为 `num_classes` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **ignore_index** (int64, 可选): - 指定一个忽略的标签值,此标签值不参与计算。默认值为-100。数据类型为int64。
+ - **reduction** (str, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: `none`, `mean`, `sum` 。默认为 `mean` ,计算 `mini-batch` loss均值。设置为 `sum` 时,计算 `mini-batch` loss的总和。设置为 `none` 时,则返回loss Tensor。数据类型为string。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+返回
+:::::::::
+`Tensor` ,返回存储表示 `negative log likelihood loss` 的损失值。
+
+代码示例
+:::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ from paddle.nn.functional import nll_loss
+ log_softmax = paddle.nn.LogSoftmax(axis=1)
+
+ input_np = np.array([[0.88103855, 0.9908683 , 0.6226845 ],
+ [0.53331435, 0.07999352, 0.8549948 ],
+ [0.25879037, 0.39530203, 0.698465 ],
+ [0.73427284, 0.63575995, 0.18827209],
+ [0.05689114, 0.0862954 , 0.6325046 ]]).astype(np.float32)
+ label_np = np.array([0, 2, 1, 1, 0]).astype(np.int64)
+
+ place = paddle.CPUPlace()
+ paddle.disable_static(place)
+ input = paddle.to_variable(input_np)
+ log_out = log_softmax(input)
+ label = paddle.to_variable(label_np)
+ result = nll_loss(log_out, label)
+ print(result.numpy()) # [1.0720209]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn.rst
index 3c4c2c33fbb37343f91713b25bba8af86f8943a5..c463d12c463c9a0b686687a3cf09f4b66b44759a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn.rst
@@ -11,5 +11,6 @@ loss
loss_cn/BCELoss_cn.rst
loss_cn/CrossEntropyLoss_cn.rst
loss_cn/L1Loss_cn.rst
+ loss_cn/MarginRankingLoss_cn.rst
loss_cn/MSELoss_cn.rst
loss_cn/NLLLoss_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/L1Loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/L1Loss_cn.rst
index c2cc4e38e6ffbb6322dce8ca29656b49cd12705a..71f366e326e910ee35528ee4c299cc2175a8e329 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/L1Loss_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/L1Loss_cn.rst
@@ -1,67 +1,66 @@
L1Loss
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='mean', name=None)
-该接口用于创建一个L1Loss的可调用类,L1Loss计算输入input和标签label间的 `L1 loss` 损失。
+该接口用于创建一个L1Loss的可调用类,L1Loss计算输入x和标签label间的 `L1 loss` 损失。
该损失函数的数学计算公式如下:
当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'none'`` 时,
.. math::
- Out = |input - label|
+ Out = \lvert x - label\rvert
当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'mean'`` 时,
.. math::
- Out = MEAN(|input - label|)
+ Out = MEAN(\lvert x - label\rvert)
当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,
.. math::
- Out = SUM(|input - label|)
+ Out = SUM(\lvert x - label\rvert)
-输入input和标签label的维度是[N, *], 其中N是batch_size, `*` 是任意其他维度。
-如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'none'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [N, *], 与输入input相同。
-如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'mean'`` 或 ``'sum'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [1]。
-参数:
- - **reduction** (string, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: ``'none'``, ``'mean'``, ``'sum'`` 。默认为 ``'mean'``,计算 `L1Loss` 的均值;设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,计算 `L1Loss` 的总和;设置为 ``'none'`` 时,则返回L1Loss。数据类型为string。
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **reduction** (str, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: ``'none'``, ``'mean'``, ``'sum'`` 。默认为 ``'mean'``,计算 `L1Loss` 的均值;设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,计算 `L1Loss` 的总和;设置为 ``'none'`` 时,则返回 `L1Loss`。
+ - **name** (str,可选): - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
-返回:返回计算L1Loss的可调用对象。
+形状
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor): - 输入的Tensor,维度是[N, *], 其中N是batch size, `*` 是任意数量的额外维度。数据类型为:float32、float64、int32、int64。
+ - **label** (Tensor): - 标签,维度是[N, *], 与 ``x`` 相同。数据类型为:float32、float64、int32、int64。
+ - **output** (Tensor): - 输入 ``x`` 和标签 ``label`` 间的 `L1 loss` 损失。如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'none'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [N, *], 与输入 ``x`` 相同。如果 :attr:`reduction` 是 ``'mean'`` 或 ``'sum'``, 则输出Loss的维度为 [1]。
-**代码示例**
+代码示例
+:::::::::
.. code-block:: python
- # declarative mode
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
import paddle
- input = fluid.data(name="input", shape=[1])
- label = fluid.data(name="label", shape=[1])
- l1_loss = paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
- output = l1_loss(input,label)
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
-
- input_data = np.array([1.5]).astype("float32")
- label_data = np.array([1.7]).astype("float32")
- output_data = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(),
- feed={"input":input_data, "label":label_data},
- fetch_list=[output],
- return_numpy=True)
-
- print(output_data) # [array([0.2], dtype=float32)]
-
- # imperative mode
- import paddle.fluid.dygraph as dg
- with dg.guard(place) as g:
- input = dg.to_variable(input_data)
- label = dg.to_variable(label_data)
- l1_loss = paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
- output = l1_loss(input,label)
- print(output.numpy()) # [0.2]
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ x_data = np.array([[1.5, 0.8], [0.2, 1.3]]).astype("float32")
+ label_data = np.array([[1.7, 1], [0.4, 0.5]]).astype("float32")
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ label = paddle.to_variable(label_data)
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss()
+ output = l1_loss(x, label)
+ print(output.numpy())
+ # [0.35]
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='sum')
+ output = l1_loss(x, label)
+ print(output.numpy())
+ # [1.4]
+
+ l1_loss = paddle.nn.loss.L1Loss(reduction='none')
+ output = l1_loss(x, label)
+ print(output.numpy())
+ # [[0.20000005 0.19999999]
+ # [0.2 0.79999995]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MSELoss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MSELoss_cn.rst
index 4dfa7bfba423c2a12005da89c07fe562442b6a5a..3ddeca33f5034d569fdf9362ceb83e05f1b35943 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MSELoss_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MSELoss_cn.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
MSELoss
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.nn.loss.MSELoss(input,label)
+.. py:function:: paddle.nn.loss.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
该OP用于计算预测值和目标值的均方差误差。
@@ -23,13 +23,15 @@ MSELoss
Out = \operatorname{sum}((input - label)^2)
参数:
- - **input** (Variable) - 预测值,维度为 :math:`[N_1, N_2, ..., N_k, D]` 的多维Tensor,其中最后一维D是类别数目。数据类型为float32或float64。
- - **label** (Variable) - 目标值,维度为 :math:`[N_1, N_2, ..., N_k, D]` 的多维Tensor,其中最后一维D是类别数目。数据类型为float32或float64。
- **reduction** (str, 可选) - 约简方式,可以是 'none' | 'mean' | 'sum'。设为'none'时不使用约简,设为'mean'时返回loss的均值,设为'sum'时返回loss的和。
-返回:预测值和目标值的均方差
+形状:
+ - **input** (Tensor) - 预测值,维度为 :math:`[N_1, N_2, ..., N_k]` 的多维Tensor。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **label** (Tensor) - 目标值,维度为 :math:`[N_1, N_2, ..., N_k]` 的多维Tensor。数据类型为float32或float64。
+
+
+返回:变量(Tensor), 预测值和目标值的均方差, 数值类型与输入相同
-返回类型:变量(Variable)
**代码示例**:
@@ -37,32 +39,32 @@ MSELoss
import numpy as np
import paddle
- from paddle import fluid
- import paddle.fluid.dygraph as dg
+
+ # static graph mode
+ paddle.enable_static()
mse_loss = paddle.nn.loss.MSELoss()
- input = fluid.data(name="input", shape=[1])
- label = fluid.data(name="label", shape=[1])
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
+ input = paddle.data(name="input", shape=[1])
+ label = paddle.data(name="label", shape=[1])
+ place = paddle.CPUPlace()
input_data = np.array([1.5]).astype("float32")
label_data = np.array([1.7]).astype("float32")
- # declarative mode
output = mse_loss(input,label)
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+ exe = paddle.static.Executor(place)
+ exe.run(paddle.static.default_startup_program())
output_data = exe.run(
- fluid.default_main_program(),
+ paddle.static.default_main_program(),
feed={"input":input_data, "label":label_data},
fetch_list=[output],
return_numpy=True)
print(output_data)
# [array([0.04000002], dtype=float32)]
- # imperative mode
- with dg.guard(place) as g:
- input = dg.to_variable(input_data)
- label = dg.to_variable(label_data)
- output = mse_loss(input, label)
- print(output.numpy())
- # [0.04000002]
+ # dynamic graph mode
+ paddle.disable_static()
+ input = paddle.to_variable(input_data)
+ label = paddle.to_variable(label_data)
+ output = mse_loss(input, label)
+ print(output.numpy())
+ # [0.04000002]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MarginRankingLoss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MarginRankingLoss_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ab7cd2175d25e3f3e724c3417e1b02db2158a895
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/MarginRankingLoss_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_loss_MarginRankingLoss:
+
+MarginRankingLoss
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.loss.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean', name=None)
+
+该接口用于创建一个 ``MarginRankingLoss`` 的可调用类,计算输入input,other 和 标签label间的 `margin rank loss` 损失。
+
+该损失函数的数学计算公式如下:
+
+ .. math::
+ margin\_rank\_loss = max(0, -label * (input - other) + margin)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'mean'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = MEAN(margin\_rank\_loss)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'sum'`` 时,
+
+ .. math::
+ Out = SUM(margin\_rank\_loss)
+
+当 `reduction` 设置为 ``'none'`` 时,直接返回最原始的 `margin_rank_loss` 。
+
+参数
+::::::::
+ - **margin** (float,可选): - 用于加和的margin值,默认值为0。
+ - **reduction** (string,可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: ``'none'`` 、 ``'mean'`` 、 ``'sum'`` 。如果设置为 ``'none'`` ,则直接返回 最原始的 ``margin_rank_loss`` 。如果设置为 ``'sum'`` ,则返回 ``margin_rank_loss`` 的总和。如果设置为 ``'mean'`` ,则返回 ``margin_rank_loss`` 的平均值。默认值为 ``'none'`` 。
+ - **name** (str,可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+形状
+::::::::
+ - **input** - N-D Tensor, 维度是[N,*] 其中N 是batch size,`*` 是任意数量的额外维度,数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **other** - 与 ``input`` 的形状、数据类型相同。
+ - **label** - 与 ``input`` 的形状、数据类型相同。
+ - **output** - 如果 :attr:`reduction` 为 ``'sum'`` 或者是 ``'mean'`` ,则形状为 :math:`[1]` ,否则shape和输入 `input` 保持一致 。数据类型与 ``input``、 ``other`` 相同。
+
+返回
+::::::::
+返回计算MarginRankingLoss的可调用对象。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ input = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).astype("float32"))
+ other = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[2, 1], [2, 4]]).astype("float32"))
+ label = paddle.to_variable(np.array([[1, -1], [-1, -1]]).astype("float32"))
+ margin_rank_loss = paddle.nn.MarginRankingLoss()
+ loss = margin_rank_loss(input, other, label)
+ print(loss.numpy()) # [0.75]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/NLLLoss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/NLLLoss_cn.rst
index 7d3e46dc66a0a6587f786de999cae3ddbcc9c5fc..f2b1559091cc5c6f211a4fa64f2eaa77e869fc3a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/NLLLoss_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/loss_cn/NLLLoss_cn.rst
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_loss_NLLLoss:
+
NLLLoss
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.nn.loss.NLLLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean', ignore_index=-100)
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.loss.NLLLoss(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean', name=None)
-该OP计算输入input和标签label间的 `negative log likelihood loss` 损失 ,可用于训练一个 `n` 类分类器。
+该接口可创建一个NLLLoss可调用类,计算输入x和标签label间的 `negative log likelihood loss` 损失 ,可用于训练一个 `n` 类分类器。
如果提供 `weight` 参数的话,它是一个 `1-D` 的tensor, 里面的值对应类别的权重。当你的训练集样本
不均衡的话,使用这个参数是非常有用的。
@@ -28,48 +30,41 @@ NLLLoss
\text{if reduction} = \text{'sum'.}
\end{cases}
-参数:
- - **input** (Variable): - 输入 `Tensor`, 其形状为 :math:`[N, C]` , 其中 `C` 为类别数。但是对于多维度的情形下,它的形状为 :math:`[N, C, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
- - **label** (Variable): - 输入input对应的标签值。其形状为 :math:`[N,]` 或者 :math:`[N, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]`, 数据类型为int64。
- - **weight** (Variable, 可选): - 手动指定每个类别的权重。其默认为 `None` 。如果提供该参数的话,长度必须为 `num_classes` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
- - **reduction** (string, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: `none`, `mean`, `sum` 。默认为 `mean` ,计算 `mini-batch` loss均值。设置为 `sum` 时,计算 `mini-batch` loss的总和。设置为 `none` 时,则返回loss Tensor。数据类型为string。
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **weight** (Tensor, 可选): - 手动指定每个类别的权重。其默认为 `None` 。如果提供该参数的话,长度必须为 `num_classes` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
- **ignore_index** (int64, 可选): - 指定一个忽略的标签值,此标签值不参与计算。默认值为-100。数据类型为int64。
+ - **reduction** (str, 可选): - 指定应用于输出结果的计算方式,可选值有: `none`, `mean`, `sum` 。默认为 `mean` ,计算 `mini-batch` loss均值。设置为 `sum` 时,计算 `mini-batch` loss的总和。设置为 `none` 时,则返回loss Tensor。数据类型为string。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+形状
+:::::::::
+ - **input** (Tensor): - 输入 `Tensor`, 其形状为 :math:`[N, C]` , 其中 `C` 为类别数。但是对于多维度的情形下,它的形状为 :math:`[N, C, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]` 。数据类型为float32或float64。
+ - **label** (Tensor): - 输入 `input` 对应的标签值。其形状为 :math:`[N,]` 或者 :math:`[N, d_1, d_2, ..., d_K]`, 数据类型为int64。
+ - **output** (Tensor): - 输入 `input` 和 `label` 间的 `negative log likelihood loss` 损失。如果 `reduction` 为 `'none'` ,则输出Loss形状为 `[N, *]` 。 如果 `reduction` 为 `'sum'` 或者 `'mean'` ,则输出Loss形状为 `'[1]'` 。
+
+代码示例
+:::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ nll_loss = paddle.nn.layer.NLLLoss()
+ log_softmax = paddle.nn.LogSoftmax(axis=1)
-返回:返回存储表示 `negative log likihood loss` 的损失值。
-
-返回类型:Variable
-
-**代码示例**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- # declarative mode
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- import paddle
- input_np = np.random.random(size=(10, 10)).astype(np.float32)
- label_np = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(10,)).astype(np.int64)
- prog = fluid.Program()
- startup_prog = fluid.Program()
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- with fluid.program_guard(prog, startup_prog):
- input = fluid.data(name='input', shape=[10, 10], dtype='float32')
- label = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[10], dtype='int64')
- nll_loss = paddle.nn.loss.NLLLoss()
- res = nll_loss(input, label)
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- static_result = exe.run(
- prog,
- feed={"input": input_np,
- "label": label_np},
- fetch_list=[res])
- print(static_result)
-
- # imperative mode
- import paddle.fluid.dygraph as dg
- with dg.guard(place) as g:
- input = dg.to_variable(input_np)
- label = dg.to_variable(label_np)
- output = nll_loss(input, label)
- print(output.numpy())
+ input_np = np.array([[0.88103855, 0.9908683 , 0.6226845 ],
+ [0.53331435, 0.07999352, 0.8549948 ],
+ [0.25879037, 0.39530203, 0.698465 ],
+ [0.73427284, 0.63575995, 0.18827209],
+ [0.05689114, 0.0862954 , 0.6325046 ]]).astype(np.float32)
+ label_np = np.array([0, 2, 1, 1, 0]).astype(np.int64)
+ place = paddle.CPUPlace()
+ paddle.disable_static(place)
+ input = paddle.to_variable(input_np)
+ log_out = log_softmax(input)
+ label = paddle.to_variable(label_np)
+ result = nll_loss(log_out, label)
+ print(result.numpy()) # [1.0720209]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/margin_rank_loss_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/margin_rank_loss_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 9669e8b1431eee9df9fcfe8850ed67894390f053..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/margin_rank_loss_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_nn_cn_margin_rank_loss:
-
-margin_rank_loss
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.margin_rank_loss
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..44eb539c03b92839d202f3fed0ac8b37879dbb7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/matrix_nms_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _cn_api_nn_cn_matrix_nms:
+
+matrix_nms
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.matrix_nms
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/softmax_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/softmax_cn.rst
index 0b0139b0f5b54489c91bcbe1db01d64f71273cfe..5879cfa4368af1de5b006a02e533a6b46627eb7f 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/softmax_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/nn_cn/softmax_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,118 @@
softmax
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.softmax
+.. py:class:: paddle.nn.functional.softmax(x, axis=-1, name=None)
+该OP实现了softmax层。OP的计算过程如下:
+步骤1:输入 ``x`` 的 ``axis`` 维会被置换到最后一维;
+
+步骤2:将输入 ``x`` 在逻辑上变换为二维矩阵。二维矩阵第一维(列长度)是输入除最后一维之外的其他维度值的乘积,第二维(行长度)和输入 ``axis`` 维的长度相同;对于矩阵的每一行,softmax操作对其进行重新缩放,使得该行的每个元素在 \[0,1\] 范围内,并且总和为1;
+
+步骤3:softmax操作执行完成后,执行步骤1和步骤2的逆运算,将二维矩阵恢复至和输入 ``x`` 相同的维度。
+
+上述步骤2中softmax操作计算过程如下:
+
+ - 对于二维矩阵的每一行,计算K维向量(K是输入第 ``axis`` 维的长度)中指定位置的指数值和全部位置指数值的和。
+
+ - 指定位置指数值与全部位置指数值之和的比值就是softmax操作的输出。
+
+对于二维矩阵中的第i行和第j列有:
+
+.. math::
+
+
+ Out[i,j] = \frac{exp(X[i,j])}{\sum_j exp(X[i,j])}
+
+- 示例1(矩阵一共有三维。axis = -1,表示沿着最后一维(即第三维)做softmax操作)
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ 输入
+
+ x.shape = [2, 3, 4]
+
+ x.data = [[[2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0],
+ [3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0],
+ [7.0, 8.0, 8.0, 9.0]],
+ [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
+ [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0],
+ [6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0]]]
+
+ axis = -1
+
+ 输出
+
+ out.shape = [2, 3, 4]
+
+ out.data = [[[0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ [0.07232949, 0.19661193, 0.19661193, 0.53444665]],
+ [[0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426]]]
+
+- 示例2(矩阵一共有三维。axis = 1,表示沿着第二维做softmax操作)
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ 输入
+
+ x.shape = [2, 3, 4]
+
+ x.data = [[[2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0],
+ [3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0],
+ [7.0, 8.0, 8.0, 9.0]],
+ [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
+ [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0],
+ [6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0]]]
+
+ axis = 1
+
+ 输出
+
+ out.shape = [2, 3, 4]
+
+ out.data = [[[0.00657326, 0.00657326, 0.01714783, 0.01714783],
+ [0.01786798, 0.01786798, 0.04661262, 0.04661262],
+ [0.97555875, 0.97555875, 0.93623955, 0.93623955]],
+ [[0.00490169, 0.00490169, 0.00490169, 0.00490169],
+ [0.26762315, 0.26762315, 0.26762315, 0.26762315],
+ [0.72747516, 0.72747516, 0.72747516, 0.72747516]]]
+
+
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的多维 ``Tensor`` ,数据类型为:float32、float64。
+ - axis (int, 可选) - 指定对输入 ``x`` 进行运算的轴。``axis`` 的有效范围是[-D, D),D是输入 ``x`` 的维度, ``axis`` 为负值时与 :math:`axis + D` 等价。默认值为-1。
+ - name (str, 可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+返回
+::::::::::
+ ``Tensor`` ,数据类型和形状同 ``x`` 一致。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.nn.functional as F
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ x = np.array([[[2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0],
+ [3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0],
+ [7.0, 8.0, 8.0, 9.0]],
+ [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
+ [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0],
+ [6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0]]], 'float32')
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x)
+ out = F.softmax(x)
+ # [[[0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ # [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ # [0.07232949, 0.19661193, 0.19661193, 0.53444665]],
+ # [[0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ # [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426],
+ # [0.0320586 , 0.08714432, 0.23688282, 0.64391426]]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn.rst
index 53f740cc450e9ba500cf7df825a03d61bc180f78..766c9d885ef84841eb9ceb1dc17cb90870ee9b35 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn.rst
@@ -31,7 +31,6 @@ paddle.optimizer
optimizer_cn/ModelAverage_cn.rst
optimizer_cn/Momentum_cn.rst
optimizer_cn/MomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
- optimizer_cn/PipelineOptimizer_cn.rst
optimizer_cn/RecomputeOptimizer_cn.rst
optimizer_cn/RMSPropOptimizer_cn.rst
optimizer_cn/SGD_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdadeltaOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdadeltaOptimizer_cn.rst
index 2f05a9e4b119006348f75796b70c1d947895e897..e1d5168744d910a7b930eb1f2ff1dc532707dd49 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdadeltaOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdadeltaOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -101,6 +101,49 @@ Adadelta优化器,具体细节可参考论文 `ADADELTA: AN ADAPTIVE LEARNING
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdagradOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
index 8c3179c447340e0dfb6be1bb20bdb1dc17470ed4..0837c86c5a6298dde6b75e9c937699fa7e2c91c8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -120,6 +120,49 @@ Adaptive Gradient 优化器(自适应梯度优化器,简称Adagrad)可以针
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamOptimizer_cn.rst
index 208209f0267b6eec070491bb3e76550c0bac7b54..8e07f80b205f836e3d08f5af4989d6246e988769 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Adam优化器出自 `Adam论文 `_ 的第二节
.. math::
moment\_2\_out=\beta_2∗moment\_2+(1−\beta_2)∗grad*grad
.. math::
- learning\_rate=\frac{learning\_rate}{1-\beta_1^t}
+ learning\_rate=learning\_rate*\frac{\sqrt{1-\beta_2^t}}{1-\beta_1^t}
.. math::
param\_out=param-learning\_rate*\frac{moment\_1}{\sqrt{moment\_2}+\epsilon}\\
@@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Adam优化器出自 `Adam论文 `_ 的第二节
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
# define beta decay variable
- def get_decayed_betas(beta1_init, beta2_init, decay_steps, decay_rate)
+ def get_decayed_betas(beta1_init, beta2_init, decay_steps, decay_rate):
global_step = lr_scheduler._decay_step_counter()
beta1 = fluid.layers.create_global_var(
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Adam优化器出自 `Adam论文 `_ 的第二节
beta1, beta2 = get_decayed_betas(0.9, 0.99, 1e5, 0.9)
adam_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(
learning_rate=0.01,
- beta1=beta1
+ beta1=beta1,
beta2=beta2)
adam_optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
@@ -194,6 +194,49 @@ Adam优化器出自 `Adam论文 `_ 的第二节
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamaxOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamaxOptimizer_cn.rst
index e1cef76dd4470357ea8ffd6aac7161cbb6c441e0..1260ec166e3ac646520e7e20da85ff1712d96448 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamaxOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/AdamaxOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -134,6 +134,49 @@ Adamax优化器是参考 `Adam论文 `_ 第7节
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DGCMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DGCMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
index be5b5640c37c0e59658ec09600d62cb3fb61d4f4..f3b97033584826804284250a97d134650b813b17 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DGCMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DGCMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -73,6 +73,29 @@ DGC还使用动量因子掩藏(momentum factor masking)和预训练(warm-u
.. code-block:: python
import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ def network():
+ x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=0)
+ y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=0)
+ emb_x = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=x,
+ size=[10, 2],
+ is_sparse=False)
+ emb_y = fluid.layers.embedding(
+ input=y,
+ size=[10, 2],
+ is_sparse=False)
+
+ concat = fluid.layers.concat([emb_x, emb_y], axis=1)
+
+ fc = fluid.layers.fc(input=concat,
+ name="fc",
+ size=1,
+ num_flatten_dims=1,
+ bias_attr=False)
+ loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(fc)
+ return loss
+
loss = network()
optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.1)
params_grads = optimizer.backward(loss)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DecayedAdagradOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DecayedAdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
index 62d2d1cb79d18d96e123f2e8dbe6286e79d305a3..7777b674d3aa0c0cebd4f3a39c3a53f00634e239 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DecayedAdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/DecayedAdagradOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -114,6 +114,49 @@ Decayed Adagrad优化器,可以看做是引入了衰减率的 `Adagrad `_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/FtrlOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/FtrlOptimizer_cn.rst
index 494937baf094f1578321b2c43e3b7ce9f7a800c3..149c890ea37a12d5983a34d3a6ee0a677d7ad65a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/FtrlOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/FtrlOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -125,6 +125,48 @@ FTRL 原始论文: ( `https://www.eecs.tufts.edu/~dsculley/papers/ad-click-predi
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LambOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LambOptimizer_cn.rst
index 13eebf27ef0d48be970d296a1a2dda28ca78221c..0be07027ecd6260fc691b11ee1cb38fbf72ba143 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LambOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LambOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -131,6 +131,49 @@ Deep Learning: Training BERT in 76 minutes `_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LarsMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LarsMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
index dee1f6fda7c8e053e992c581ac08976de6b3390c..63f22d05a09267924e4e5081fec6d2e4b757910d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LarsMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LarsMomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ LarsMomentumOptimizer
.. code-block:: python
import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ import numpy as np
np_inp = np.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]], dtype=np.float32)
inp = fluid.layers.data(
@@ -100,6 +101,49 @@ LarsMomentumOptimizer
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LookaheadOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LookaheadOptimizer_cn.rst
index d4bd795a5ccbc5aa0ddb1eb6da6ca07a2e4516ef..2ea449f453bdeecc0e2d9e9e473218b04cfb767e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LookaheadOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/LookaheadOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ LookaheadOptimizer
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
+ import numpy.random as random
x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='float32')
label = fluid.layers.data(name="label", shape=[1], dtype="int64")
@@ -46,11 +46,14 @@ LookaheadOptimizer
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
+ def train_reader(limit=5):
+ for i in range(limit):
+ yield random.random([2]).astype('float32'), random.random([1]).astype('int64')
+
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list=[x, label], place=place)
-
- step = 0
- while(step < 10):
- step += 1
+ reader = paddle.batch(paddle.reader.shuffle(train_reader, buf_size=50000),batch_size=1)
+
+ for batch_data in reader():
exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(),
feed=feeder.feed(batch_data))
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/MomentumOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/MomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
index baf3df7ac0378a6939b8d8d3204cce0234def083..c2c39c5a8fad49c25a80ba2668eb0a332698dda7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/MomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/MomentumOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -134,6 +134,50 @@ MomentumOptimizer
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
+
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
**注意:**
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/PipelineOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/PipelineOptimizer_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 5da5dc780d2c94e960961a62816686b93f91b3d7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/PipelineOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_fluid_optimizer_PipelineOptimizer:
-
-PipelineOptimizer
--------------------------------
-
-
-.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.optimizer.PipelineOptimizer(optimizer, cut_list=None, place_list=None, concurrency_list=None, queue_size=30, sync_steps=1, start_cpu_core_id=0)
-
-:api_attr: 声明式编程模式(静态图)
-
-
-
-使用流水线模式进行训练。
-Program会根据切分列表cut_list进行分割。如果cut_list的长度是k,则整个program(包括反向部分)将被分割为2*k-1个section。 所以place_list和concurrency_list的长度也必须是2*k-1。
-
-.. note::
-
- 虽然我们在流水线训练模式中采用异步更新的方式来加速,但最终的效果会依赖于每条流水线的训练进程。我们将在未来尝试同步模式。
-
-参数:
- - **optimizer** (Optimizer) - 基础优化器,如SGD
- - **cut_list** (list of Variable list) - main_program的cut变量列表
- - **place_list** (list of Place) - 对应section运行所在的place
- - **concurrency_list** (list of int) - 指定每个section的并发度列表
- - **queue_size** (int) - 每个section都会消费其输入队列(in-scope queue)中的scope,并向输出队列(out-scope queue)产出scope。 此参数的作用就是指定队列的大小。 可选,默认值:30
- - **sync_steps** (int) - 不同显卡之间的同步周期数。可选,默认值:1
- - **start_cpu_core_id** (int) - 指定所使用的第一个CPU核的id。可选,默认值:0
-
-**代码示例**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import paddle.fluid.layers as layers
- x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=0)
- y = fluid.layers.data(name='y', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=0)
- emb_x = layers.embedding(input=x, param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name="embx"), size=[10,2], is_sparse=False)
- emb_y = layers.embedding(input=y, param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name="emby",learning_rate=0.9), size=[10,2], is_sparse=False)
- concat = layers.concat([emb_x, emb_y], axis=1)
- fc = layers.fc(input=concat, name="fc", size=1, num_flatten_dims=1, bias_attr=False)
- loss = layers.reduce_mean(fc)
- optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.5)
- optimizer = fluid.optimizer.PipelineOptimizer(optimizer,
- cut_list=[[emb_x, emb_y], [loss]],
- place_list=[fluid.CPUPlace(), fluid.CUDAPlace(0), fluid.CPUPlace()],
- concurrency_list=[1, 1, 4],
- queue_size=2,
- sync_steps=1,
- )
- optimizer.minimize(loss)
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
- filelist = [] # you should set your own filelist, e.g. filelist = ["dataA.txt"]
- dataset = fluid.DatasetFactory().create_dataset("FileInstantDataset")
- dataset.set_use_var([x,y])
- dataset.set_batch_size(batch_size)
- dataset.set_filelist(filelist)
- exe.train_from_dataset(
- fluid.default_main_program(),
- dataset,
- thread=2,
- debug=False,
- fetch_list=[],
- fetch_info=[],
- print_period=1)
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/RMSPropOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/RMSPropOptimizer_cn.rst
index 5017529d71b9c1c58d150b1c93efa3c787ca61a1..ac30efa78236c14772c6e5df08cec327e2abede1 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/RMSPropOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/RMSPropOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -151,6 +151,48 @@ RMSPropOptimizer
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/SGDOptimizer_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/SGDOptimizer_cn.rst
index 0691a8c9e0f2f676e87d2a9b0bd72a6ae0b97fda..582c590bb04393acd13add208c5b75b2032d0167 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/SGDOptimizer_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/optimizer_cn/SGDOptimizer_cn.rst
@@ -127,6 +127,48 @@ SGDOptimizer
optimizer.minimize(out)
optimizer.clear_gradients()
+.. py:method:: set_lr()
+
+**注意:**
+
+ **1. 该API只在** `Dygraph <../../user_guides/howto/dygraph/DyGraph.html>`_ **模式下生效**
+
+手动设置当前 ``optimizer`` 的学习率。当使用LearningRateDecay时,无法使用该API手动设置学习率,因为这将导致冲突。
+
+参数:
+ value (float|Variable) - 需要设置的学习率的值。
+
+返回:无
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle.fluid as fluid
+
+ with fluid.dygraph.guard():
+ linear = fluid.dygraph.nn.Linear(10, 10)
+ adam = fluid.optimizer.Adam(0.1, parameter_list=linear.parameters())
+ # 通过Python float数值手动设置学习率
+ lr_list = [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
+ for i in range(5):
+ adam.set_lr(lr_list[i])
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.2
+ # current lr is 0.3
+ # current lr is 0.4
+ # current lr is 0.5
+ # current lr is 0.6
+
+
+ # 通过 框架的Variable 设置学习率
+ lr_var = fluid.layers.create_global_var(shape=[1], value=0.7, dtype='float32')
+ adam.set_lr(lr_var)
+ print("current lr is {}".format(adam.current_step_lr()))
+ # 打印结果:
+ # current lr is 0.7
+
.. py:method:: current_step_lr()
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn.rst
index de355d4708ead0cddf1f940fbea59ffba8c898c6..7497eb21ac79150aa3284c151896158813524989 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn.rst
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ paddle
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
- paddle_cn/abs_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/abs_cn.rst
paddle_cn/acos_cn.rst
paddle_cn/addcmul_cn.rst
paddle_cn/addmm_cn.rst
@@ -44,8 +44,6 @@ paddle
paddle_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst
paddle_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst
paddle_cn/elementwise_floordiv_cn.rst
- paddle_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
- paddle_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
paddle_cn/elementwise_mod_cn.rst
paddle_cn/elementwise_mul_cn.rst
paddle_cn/elementwise_pow_cn.rst
@@ -95,11 +93,16 @@ paddle
paddle_cn/log_cn.rst
paddle_cn/manual_seed_cn.rst
paddle_cn/matmul_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/max_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/maximum_cn.rst
paddle_cn/mean_cn.rst
paddle_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/min_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/minimum_cn.rst
paddle_cn/multiplex_cn.rst
paddle_cn/mul_cn.rst
- paddle_cn/name_scope_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/name_scope_cn.rst
+ paddle_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
paddle_cn/nonzero_cn.rst
paddle_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
paddle_cn/ones_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/ExecutionStrategy_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/ExecutionStrategy_cn.rst
index b2bc7ca0b65fdbb3680db7dc7b19435ca18e26fa..1e929c0114cfaf4324bf3d43f9473fd0895ad7e7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/ExecutionStrategy_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/ExecutionStrategy_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
ExecutionStrategy
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.framework.ExecutionStrategy
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.ExecutionStrategy
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/argsort_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/argsort_cn.rst
index 26f231fcca6407cab2e849de6efa95e3ceda4d5e..e9f128a9ae18a775306eb869b4e3e769270ed1e3 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/argsort_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/argsort_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
argsort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.argsort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/cumsum_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
index 4422de0e441e93db84d2990c4936b46c9757ab68..89fbc20a319e12b7ffff36e2b241d316f9616dbe 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
cumsum
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.cumsum
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 4c0f65404fed01682b9c9e1fff82c48c775e0539..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_paddle_cn_elementwise_equal:
-
-elementwise_equal
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.equal
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 7c4af7dd578acbab01be37dc8da25dc793bf9be6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_paddle_cn_elementwise_max:
-
-elementwise_max
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_max
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 0b4a2d8ec667e04b4b4d644438764589c8fb4cdc..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_paddle_cn_elementwise_min:
-
-elementwise_min
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_min
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/equal_all_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/equal_all_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..72c333de05f5fc7ea25242077485211fe07c8e8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/equal_all_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+.. _cn_api_paddle_cn_equal_all:
+
+equal_all
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.equal_all
+
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
index 8fb516705e2749abcfb9ef216456f45a213ea2fb..1f4367acce3364471e5c5ab8cb5a91ede96de6a2 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
index f228df1de80ff5ae2113bbc0ead958f50e84d06b..f15865d063c8f972e040d24c3d508a6dd11d2264 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
greater_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.greater_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
index ca9bb26b766bbada944852be00bd3bd37b6f597d..481e3f2863f10cee11765e97eb46ae5f252a3357 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_than_cn.rst
index 0085d27a7d1016d6e36dd1feed4f56477d420ac2..3f0802843bed23a6547b36efb3abe1d51a8e1519 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/less_than_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
less_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.less_than
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/no_grad_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..afd06deffa35a3d71c4a23593d1caedcdea21b67
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/no_grad_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+.. _cn_api_paddle_cn_name_scope:
+
+name_scope
+-------------------------------
+:doc_source: paddle.fluid.dygraph.no_grad
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/not_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
index 987d966970a6c2b05effc4b5c156580ec0745216..872637f9e816a7fd1fa910d91441994b58c884f8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
not_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.not_equal
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/sort_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/sort_cn.rst
index 69444809a61f1ae58fea852f6265b22bbd2ddc45..d4ee20b7e89a316cb2d7e72f54c2d58ec6191fc5 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/sort_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/paddle_cn/sort_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,6 @@
sort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+:doc_source: paddle.tensor.sort
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn.rst
index eadd071532aa1f8bcc47449c4c0b46c54c0031ca..259cf4ab97da44815ff7a40a24ff959eae8bf8c8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn.rst
@@ -38,16 +38,14 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor_cn/einsum_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_add_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_div_cn.rst
- tensor_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_floordiv_cn.rst
- tensor_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
- tensor_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_mod_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_mul_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_pow_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_sub_cn.rst
tensor_cn/elementwise_sum_cn.rst
tensor_cn/equal_cn.rst
+ tensor_cn/equal_all_cn.rst
tensor_cn/erf_cn.rst
tensor_cn/exp_cn.rst
tensor_cn/expand_as_cn.rst
@@ -65,6 +63,7 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
tensor_cn/has_inf_cn.rst
tensor_cn/has_nan_cn.rst
+ tensor_cn/histogram_cn.rst
tensor_cn/increment_cn.rst
tensor_cn/index_sample_cn.rst
tensor_cn/index_select_cn.rst
@@ -88,9 +87,11 @@ paddle.tensor
tensor_cn/math_cn.rst
tensor_cn/matmul_cn.rst
tensor_cn/max_cn.rst
+ tensor_cn/maximum_cn.rst
tensor_cn/mean_cn.rst
tensor_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst
tensor_cn/min_cn.rst
+ tensor_cn/minimum_cn.rst
tensor_cn/mm_cn.rst
tensor_cn/mul_cn.rst
tensor_cn/multiplex_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/arange_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/arange_cn.rst
index 727d071a75b11de3ea274cdb601088ef022ca80c..10f343f3399364e490f0ec6c2ebd87a2dca62c59 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/arange_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/arange_cn.rst
@@ -3,33 +3,53 @@
arange
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.arange(start, end, step=1, dtype=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.arange(start=0, end=None, step=1, dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.arange
-:alias: paddle.arange,paddle.tensor.arange,paddle.tensor.creation.arange
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.range
+:alias: paddle.tensor.arange, paddle.tensor.creation.arange
-该API根据step均匀分隔给定数值区间[start, end),并返回该分隔结果。
+该OP返回以步长 ``step`` 均匀分隔给定数值区间[``start``, ``end``)的1-D Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
-**参数**:
- - **start** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 区间起点,且区间包括此值, 当类型是Variable时,是shape为 [1] 的1-D Tensor。
- - **end** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 区间终点,通常区间不包括此值。但当step不是整数,且浮点数取整会影响输出的长度时例外。
- - **step** (float32 | float64 | int32 | int64 | Variable) - 均匀分割的步长。
- - **dtype** (str | core.VarDesc.VarType) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,可为 'float32', 'float64', 'int32', 'int64' 。
+当 ``dtype`` 表示浮点类型时,为了避免浮点计算误差,建议给 ``end`` 加上一个极小值epsilon,使边界可以更加明确。
-**返回**:均匀分割给定数值区间后得到的1-D Tensor, 数据类型为输入 dtype 。
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **start** (float|int|Tensor) - 区间起点(且区间包括此值)。当 ``start`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。如果仅指定 ``start`` ,而 ``end`` 为None,则区间为[0, ``start``)。默认值为0。
+ - **end** (float|int|Tensor, 可选) - 区间终点(且通常区间不包括此值)。当 ``end`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。默认值为None。
+ - **step** (float|int|Tensor, 可选) - 均匀分割的步长。当 ``step`` 类型是Tensor时,是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64、float32、float64的Tensor。默认值为1。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持int32、int64、float32、float64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型为int64。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-**返回类型**:Variable
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor: 以步长 ``step`` 均匀分割给定数值区间[``start``, ``end``)后得到的1-D Tensor, 数据类型为 ``dtype`` 。
-**代码示例**
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是int32、int64、float32、float64。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = paddle.arange(0, 6, 2)
- # x: [0, 2, 4]
- # x dtype: float32
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ out1 = paddle.arange(5)
+ # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
+
+ out2 = paddle.arange(3, 9, 2.0)
+ # [3, 5, 7]
+
+ # use 4.999 instead of 5.0 to avoid floating point rounding errors
+ out3 = paddle.arange(4.999, dtype='float32')
+ # [0., 1., 2., 3., 4.]
+
+ start_var = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([3]))
+ out4 = paddle.arange(start_var, 7)
+ # [3, 4, 5, 6]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/argsort_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/argsort_cn.rst
index ecf72edcbdaf9720429fcdfad918ca5bd9155e6d..43d2dd420eb8fa255e35ff229272f7b3aeb50df0 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/argsort_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/argsort_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,61 @@
argsort
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
+.. py:function:: paddle.argsort(x, axis=-1, descending=False, name=None)
+:alias_main: paddle.argsort
+:alias: paddle.argsort,paddle.tensor.argsort,paddle.tensor.search.argsort
+
+对输入变量沿给定轴进行排序,输出排序好的数据的相应索引,其维度和输入相同。默认升序排列,如果需要降序排列设置 ``descending=True`` 。
+
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入的多维 ``Tensor`` ,支持的数据类型:float32、float64、int16、int32、int64、uint8。
+ - **axis** (int,可选) - 指定对输入Tensor进行运算的轴, ``axis`` 的有效范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``x`` 的Rank, ``axis`` 为负时与 ``axis`` +R 等价。默认值为0。
+ - **descending** (bool,可选) - 指定算法排序的方向。如果设置为True,算法按照降序排序。如果设置为False或者不设置,按照升序排序。默认值为False。
+ - **name** (str,可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+返回:Tensor, 排序后索引信息(与 ``x`` 维度信息一致),数据类型为int64。
+
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ input_array = np.array([[[5,8,9,5],
+ [0,0,1,7],
+ [6,9,2,4]],
+ [[5,2,4,2],
+ [4,7,7,9],
+ [1,7,0,6]]]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = imperative.to_variable(input_array)
+ out1 = paddle.argsort(x=x, axis=-1)
+ out2 = paddle.argsort(x=x, axis=0)
+ out3 = paddle.argsort(x=x, axis=1)
+ print(out1.numpy())
+ #[[[0 3 1 2]
+ # [0 1 2 3]
+ # [2 3 0 1]]
+ # [[1 3 2 0]
+ # [0 1 2 3]
+ # [2 0 3 1]]]
+ print(out2.numpy())
+ #[[[0 1 1 1]
+ # [0 0 0 0]
+ # [1 1 1 0]]
+ # [[1 0 0 0]
+ # [1 1 1 1]
+ # [0 0 0 1]]]
+ print(out3.numpy())
+ #[[[1 1 1 2]
+ # [0 0 2 0]
+ # [2 2 0 1]]
+ # [[2 0 2 0]
+ # [1 1 0 2]
+ # [0 2 1 1]]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cholesky_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cholesky_cn.rst
index c318bf86b40804b91304deea716292d4b34dad03..5c2b0b8e07a99d837333e389ef9d61eef338689a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cholesky_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cholesky_cn.rst
@@ -1,3 +1,42 @@
+.. _cn_api_tensor_cholesky:
+
cholesky
-------------------------------
-**版本升级,文档正在开发中**
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.cholesky(x, upper=False, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.cholesky
+:alias: paddle.cholesky, paddle.tensor.cholesky, paddle.tensor.linalg.cholesky
+
+
+
+计算一个对称正定矩阵或一批对称正定矩阵的Cholesky分解。如果 `upper` 是 `True` ,
+则分解形式为 :math:`A = U ^ {T} U` , 返回的矩阵U是上三角矩阵。
+否则,分解形式为 :math:`A = LL ^ {T}` ,并返回矩阵 :math:`L` 是下三角矩阵。
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Variable)- 输入变量为多维Tensor,它的维度应该为 `[*, M, N]` ,其中*为零或更大的批次尺寸,并且最里面的两个维度上的矩阵都应为对称的正定矩阵,支持数据类型为float32,float64。
+ - **upper** (bool)- 指示是否返回上三角矩阵或下三角矩阵。默认值:False。
+ - **name** (str , 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+返回: 与 `x` 具有相同形状和数据类型的Tensor。它代表了Cholesky分解生成的三角矩阵。
+
+返回类型: 变量(Variable)
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ a = np.random.rand(3, 3)
+ a_t = np.transpose(a, [1, 0])
+ x_data = np.matmul(a, a_t) + 1e-03
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ out = paddle.cholesky(x, upper=False)
+ print(out.numpy())
+ # [[1.190523 0. 0. ]
+ # [0.9906703 0.27676893 0. ]
+ # [1.25450498 0.05600871 0.06400121]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/concat_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/concat_cn.rst
index e439959e9f07df7ad3bcafc6269692485b9d9958..aa36dd238d01ef6804bb8e4175650ab3b0244429 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/concat_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/concat_cn.rst
@@ -1,3 +1,54 @@
+.. _cn_api_tensor_concat:
+
concat
-------------------------------
-**版本升级,文档正在开发中**
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.concat(x, axis=0, name=None)
+
+
+该OP对输入沿 ``axis`` 轴进行联结,返回一个新的Tensor。
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (list|tuple) - 待联结的Tensor list或者Tensor tuple ,支持的数据类型为:bool, float16, float32、float64、int32、int64, ``x`` 中所有Tensor的数据类型应该一致。
+ - **axis** (int|Tensor,可选) - 指定对输入 ``x`` 进行运算的轴,可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或者int64。 ``axis`` 的有效范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``x`` 中Tensor的维度, ``axis`` 为负值时与 :math:`axis + R` 等价。默认值为0。
+ - **name** (str,可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+返回:联结后的Tensor ,数据类型和 ``x`` 中的Tensor相同。
+
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``x`` 的类型不是list或者tuple时。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``x`` 的数据类型不是 bool,float16, float32, float64, int32, int64时。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当 ``axis`` 的类型不是int或者Tensor时。 当 ``axis`` 是Tensor的时候其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当输入 ``x`` 中的Tensor存在数据类型不一致时。
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative() # Now we are in imperative mode
+ in1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
+ [4, 5, 6]])
+ in2 = np.array([[11, 12, 13],
+ [14, 15, 16]])
+ in3 = np.array([[21, 22],
+ [23, 24]])
+ x1 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(in1)
+ x2 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(in2)
+ x3 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(in3)
+ zero = paddle.full(shape=[1], dtype='int32', fill_value=0)
+ # When the axis is negative, the real axis is (axis + Rank(x))
+ # As follow, axis is -1, Rank(x) is 2, the real axis is 1
+ out1 = paddle.concat(x=[x1, x2, x3], axis=-1)
+ out2 = paddle.concat(x=[x1, x2], axis=0)
+ out3 = paddle.concat(x=[x1, x2], axis=zero)
+ # out1
+ # [[ 1 2 3 11 12 13 21 22]
+ # [ 4 5 6 14 15 16 23 24]]
+ # out2 out3
+ # [[ 1 2 3]
+ # [ 4 5 6]
+ # [11 12 13]
+ # [14 15 16]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cross_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cross_cn.rst
index 9541c6ef690a97e2f637a5cfc5d09be4990859ff..4bfb4ed980490ece02796281afd9a7b527367ac7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cross_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cross_cn.rst
@@ -3,51 +3,55 @@
cross
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.cross(input, other, dim=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.cross(x, y, axis=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.cross
:alias: paddle.cross,paddle.tensor.cross,paddle.tensor.linalg.cross
-该OP返回在 ``dim`` 维度上,两个张量 ``input`` 和 ``other`` 的向量积(叉积)。 ``input`` 和 ``other`` 必须有相同的形状,
-且指定的 ``dim`` 维上 ``size`` 必须为3,如果 ``dim`` 未指定,默认选取第一个 ``size`` 等于3的维度。
+计算张量 ``x`` 和 ``y`` 在 ``axis`` 维度上的向量积(叉积)。 ``x`` 和 ``y`` 必须有相同的形状,
+且指定的 ``axis`` 的长度必须为3. 如果未指定 ``axis`` ,默认选取第一个长度为3的 ``axis`` .
**参数**:
- - **input** (Variable)– 第一个输入张量。
- - **other** (Variable)– 第二个输入张量。
- - **dim** (int, optional) – 沿着此维进行叉积操作,若未指定,则默认选取第一个 ``size`` 等于3的维度
+ - **x** (Variable)– 第一个输入张量。
+ - **y** (Variable)– 第二个输入张量。
+ - **axis** (int, optional) – 沿着此维进行向量积操作。默认选取第一个长度为3的 ``axis`` .
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+**返回**:向量积的结果。
+
+**返回类型**:Variable
-**返回**:
- - **Variable** ,数据类型同输入。
-
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
+ from paddle.imperative import to_variable
import numpy as np
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
data_x = np.array([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[2.0, 2.0, 2.0],
[3.0, 3.0, 3.0]])
data_y = np.array([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0]])
-
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data_x)
- y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data_y)
- out_z1 = paddle.cross(x, y)
- print(out_z1.numpy())
- #[[-1. -1. -1.]
- # [ 2. 2. 2.]
- # [-1. -1. -1.]]
- out_z2 = paddle.cross(x, y, dim=1)
- print(out_z2.numpy())
- #[[0. 0. 0.]
- # [0. 0. 0.]
- # [0. 0. 0.]]
+ x = to_variable(data_x)
+ y = to_variable(data_y)
+
+ z1 = paddle.cross(x, y)
+ print(z1.numpy())
+ # [[-1. -1. -1.]
+ # [ 2. 2. 2.]
+ # [-1. -1. -1.]]
+
+ z2 = paddle.cross(x, y, axis=1)
+ print(z2.numpy())
+ # [[0. 0. 0.]
+ # [0. 0. 0.]
+ # [0. 0. 0.]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cumsum_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
index 5aadad95718195f4ae391051bb7f2e04a92d0ec1..71896b1bc17808d6b70873ef45a5587d1ad6cce1 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/cumsum_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,53 @@
cumsum
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.cumsum
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.cumsum(x, axis=None, dtype=None, name=None)
+
+
+
+沿给定 ``axis`` 计算张量 ``x`` 的累加和。结果的第一个元素和输入的第一个元素相同。
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 累加的输入,需要进行累加操作的Tensor.
+ - **axis** (int,可选) - 指明需要累加的维度。-1代表最后一维。默认:None,将输入展开为一维变量再进行累加计算。
+ - **dtype** (str,可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持int32、int64、float32、float64. 如果指定了,那么在执行操作之前,输入张量将被转换为dtype. 这对于防止数据类型溢出非常有用。默认为:None.
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+返回:累加的结果,即累加器的输出。
+
+返回类型:Tensor
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ from paddle.imperative import to_variable
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ data_np = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
+ data = to_variable(data_np)
+
+ y = paddle.cumsum(data)
+ print(y.numpy())
+ # [ 0 1 3 6 10 15 21 28 36 45 55 66]
+
+ y = paddle.cumsum(data, axis=0)
+ print(y.numpy())
+ # [[ 0 1 2 3]
+ # [ 4 6 8 10]
+ # [12 15 18 21]]
+
+ y = paddle.cumsum(data, axis=-1)
+ print(y.numpy())
+ # [[ 0 1 3 6]
+ # [ 4 9 15 22]
+ # [ 8 17 27 38]]
+
+ y = paddle.cumsum(data, dtype='float64')
+ print(y.dtype)
+ # VarType.FP64
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/dot_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/dot_cn.rst
index 6d6d56c88aff94097cc6acfc79508cc500ce34c9..70cadfbe67736bcbe560de0556d1f1d11425d9fa 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/dot_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/dot_cn.rst
@@ -6,22 +6,23 @@ dot
.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.linalg.dot(x, y, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.dot
-:alias: paddle.dot,paddle.tensor.dot,paddle.tensor.linalg.dot
+:alias: paddle.dot, paddle.tensor.dot, paddle.tensor.linalg.dot
该OP计算向量的内积
.. note::
+
仅支持1维Tensor(向量).
参数:
- - **x** (Variable)- 1维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
- - **y** (Variable)- 1维 ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64``。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 1维 ``Tensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
+ - **y** (Variable)- 1维 ``Tensor`` 。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
- **name** (str,可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回: ``Tensor`` 或 ``LoDTensor`` ,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
+返回: ``Tensor`` ,数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
返回类型: Variable。
@@ -30,13 +31,12 @@ dot
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.uniform(0.1, 1, [10]).astype(np.float32))
- y = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(np.random.uniform(1, 3, [10]).astype(np.float32))
- z = paddle.dot(x, y)
- print(z.numpy())
-
-
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x_data = np.random.uniform(0.1, 1, [10]).astype(np.float32)
+ y_data = np.random.uniform(1, 3, [10]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.imperative.to_variable(y_data)
+ z = paddle.dot(x, y)
+ print(z.numpy())
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index c7006ffda4aefe7bc10a8ece96d2b3ed2f30f883..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_equal_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_tensor_elementwise_equal:
-
-elementwise_equal
--------------------------------
-
-.. py:function:: paddle.elementwise_equal(x, y, name=None)
-
-:alias_main: paddle.elementwise_equal
-:alias: paddle.elementwise_equal,paddle.tensor.elementwise_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.elementwise_equal
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.equal
-
-
-
-该OP返回 :math:`x==y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等。
-
-参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
- - **y** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
- - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-
-返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
-
-返回类型:变量(Variable)
-
-**代码示例**:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
-
- label = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([3, 3], dtype="int32"))
- limit = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([3, 2], dtype="int32"))
- out1 = paddle.elementwise_equal(x=label, y=limit) #out1=[True, False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 12c2246e6d9c9dc0ca3e33b0f77c1bdb3511ac76..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_max_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_tensor_cn_elementwise_max:
-
-elementwise_max
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_max
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index b7b81110936a3226ff9b978e018c42ae8b90ec6b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/elementwise_min_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_tensor_cn_elementwise_min:
-
-elementwise_min
--------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.elementwise_min
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_all_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_all_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b1269776011012b2c33df1101ad6c97948728a3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_all_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+.. _cn_api_tensor_equal_all:
+
+equal_all
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.equal_all(x, y, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.equal_all
+:alias: paddle.equal_all,paddle.tensor.equal_all,paddle.tensor.logic.equal_all
+
+该OP返回:返回的结果只有一个元素值,如果所有相同位置的元素相同返回True,否则返回False。
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+返回:输出结果为Tensor,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ z = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 4, 3]))
+ result1 = paddle.equal_all(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [True ]
+ result2 = paddle.equal_all(x, z)
+ print(result2.numpy()) # result2 = [False ]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_cn.rst
index d25ec01088b79dea39cb3f9af2930f650660feb7..e8b1dff6087609b56b406dc5680e176a48faca22 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,54 +2,35 @@
equal
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.equal(x, y, axis=-1, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.equal(x, y, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.equal
:alias: paddle.equal,paddle.tensor.equal,paddle.tensor.logic.equal
+该OP返回 :math:`x==y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等,相同位置的元素相同则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `==` 可以有相同的计算函数效果
-
-该OP返回 :math:`x==y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等,所有的元素都相同则返回True,否则返回False。
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
- - **y** (Variable) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
- - **axis** (int, 可选) - 如果输入的两个Tensor的维度不相同,并且如果y的维度是x的一部分, 那就可以通过broadcast的方式来进行op计算。axis是进行broadcast的开始的维度,具体broadcast的方式可以参考elementwise_add。
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
- **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor只有一个元素值,元素值是True或者False,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
-返回类型:变量(Variable)
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import paddle
- import numpy as np
- label = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([3, 4], dtype="int32"))
- label_1 = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([1, 2], dtype="int32"))
- limit = fluid.layers.assign(np.array([3, 4], dtype="int32"))
- out1 = paddle.equal(x=label, y=limit) #out1=[True]
- out2 = paddle.equal(x=label_1, y=limit) #out2=[False]
-
-.. code-block:: python
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.equal(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [True False False]
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import paddle
- import numpy as np
- def gen_data():
- return {
- "x": np.ones((2, 3, 4, 5)).astype('float32'),
- "y": np.zeros((3, 4)).astype('float32')
- }
- x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[2,3,4,5], dtype='float32')
- y = fluid.data(name="y", shape=[3,4], dtype='float32')
- out = paddle.equal(x, y, axis=1)
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- res = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
- fetch_list=[out])
- print(res[0]) #[False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/eye_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/eye_cn.rst
index 7eca6037cb766dcacade10ce79427edb20949569..87e746f90024e97ad56e1bc05dc89ca683e10018 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/eye_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/eye_cn.rst
@@ -3,35 +3,36 @@
eye
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, out=None, dtype='float32', stop_gradient=True, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, dtype=None, name=None)
-该OP用来构建单位矩阵。
+该OP用来构建二维Tensor(主对角线元素为1,其他元素为0)。
参数:
- - **num_rows** (int) - 生成单位矩阵的行数,数据类型为非负int32。
- - **num_columns** (int) - 生成单位矩阵的列数,数据类型为非负int32。若为None,则默认等于num_rows。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) - 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- - **dtype** (string, 可选) - 返回张量的数据类型,可为int32,int64,float16,float32,float64。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool, 可选) - 是否对此OP停止计算梯度,默认值为False。
+ - **num_rows** (int) - 生成二维Tensor的行数,数据类型为非负int32。
+ - **num_columns** (int,可选) - 生成二维Tensor的列数,数据类型为非负int32。若为None,则默认等于num_rows。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选) - 返回Tensor的数据类型,可为float16,float32,float64, int32, int64。若为None, 则默认等于float32。
- **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:shape为 [num_rows, num_columns]的张量。
+返回: ``shape`` 为 [num_rows, num_columns]的Tensor。
-返回类型:Variable(Tensor|LoDTensor)数据类型为int32,int64,float16,float32,float64的Tensor或者LoDTensor。
+
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``dtype`` 的类型不是float16, float32, float64, int32, int64其中之一。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``num_columns`` 不是非负整数或者 ``num_rows`` 不是非负整数。
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- data = paddle.eye(3, dtype='int32') # paddle.eye 等价于 paddle.tensor.eye
- # [[1, 0, 0]
- # [0, 1, 0]
- # [0, 0, 1]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative() # Now we are in imperative mode
+ data = paddle.eye(3, dtype='int32')
+ # [[1 0 0]
+ # [0 1 0]
+ # [0 0 1]]
data = paddle.eye(2, 3, dtype='int32')
- # [[1, 0, 0]
- # [0, 1, 0]]
-
+ # [[1 0 0]
+ # [0 1 0]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/flip_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/flip_cn.rst
index b70ecf28bbffb083a276d777f2923983a0af6ce4..d8f1f7efd1b9a2c74d9902ae4c0c58d6dafa6f22 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/flip_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/flip_cn.rst
@@ -3,53 +3,41 @@
flip
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.flip(input, dims, name=None):
+.. py:function:: paddle.flip(x, axis, name=None):
:alias_main: paddle.flip
-:alias: paddle.flip,paddle.tensor.flip,paddle.tensor.manipulation.flip
+:alias: paddle.flip, paddle.tensor.flip, paddle.tensor.manipulation.flip
该OP沿指定轴反转n维tensor.
参数:
- - **input** (Variable) - 输入Tensor。维度为多维,数据类型为bool, int32, int64, float32或float64。
- - **dims** (list) - 需要翻转的轴。当 ``dims[i] < 0`` 时,实际的计算维度为 rank(input) + dims[i],其中i为dims的索引。
+ - **x** (Variable) - 输入张量。维度为多维,数据类型为bool, int32, int64, float32或float64。
+ - **axis** (list) - 需要翻转的轴。当 ``axis[i] < 0`` 时,实际的计算维度为 ndim(x) + axis[i],其中i为axis的索引。
- **name** (str|None) - 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。默认值为None。
-返回:在指定dims上翻转后的Tensor,与输入input数据类型相同。
+返回:在指定axis上翻转后的张量,与输入x数据类型相同。
-返回类型:Variable,与输入input数据类型相同。
+返回类型:Variable,与输入x数据类型相同。
抛出异常:
- - ``TypeError`` - 当输出 ``out`` 和输入 ``input`` 数据类型不一致时候。
- - ``ValueError`` - 当参数 ``dims`` 不合法时。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当输出 ``out`` 和输入 ``x`` 数据类型不一致时候。
+ - ``ValueError`` - 当参数 ``axis`` 不合法时。
**代码示例1**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- input = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[-1, 2, 2], dtype='float32')
- output = paddle.flip(input, dims=[0, 1])
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
- img = np.arange(12).reshape((3,2,2)).astype(np.float32)
- res = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':img}, fetch_list=[output])
- print(res) # [[[10,11][8, 9]],[[6, 7],[4, 5]] [[2, 3],[0, 1]]]
-**代码示例2**:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- img = np.arange(12).reshape((3,2,2)).astype(np.float32)
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- inputs = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(img)
- ret = paddle.flip(inputs, [0, 1])
- print(ret.numpy()) # [[[10,11][8, 9]],[[6, 7],[4, 5]] [[2, 3],[0, 1]]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ image_shape=(3, 2, 2)
+ x = np.arange(image_shape[0] * image_shape[1] * image_shape[2]).reshape(image_shape)
+ x = x.astype('float32')
+ img = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x)
+ out = paddle.flip(img, [0,1])
+ print(out) # [[[10,11][8, 9]],[[6, 7],[4, 5]] [[2, 3],[0, 1]]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_cn.rst
index 529c7403646dd7c675381d1de132871d31724cc7..68dc4d658d9fe4b33ac852f1a8c91191a56363bf 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_cn.rst
@@ -3,33 +3,24 @@
full
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.full(shape, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, device=None, stop_gradient=True, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.full(shape, fill_value, dtype=None, name=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.full
-:alias: paddle.full,paddle.tensor.full,paddle.tensor.creation.full
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.fill_constant
-
-该OP创建一个和具有相同的形状和数据类型的Tensor,其中元素值均为fill_value。
+该OP创建形状大小为shape并且数据类型为dtype的Tensor,其中元素值均为 ``fill_value``。
参数:
- - **shape** (list|tuple|Variable) – 指定创建Tensor的形状(shape)。
- - **fill_value** (bool|float16|float32|int32|int64|Variable) - 用于初始化输出Tensor的常量数据的值。默认为0。注意:该参数不可超过输出变量数据类型的表示范围。
- - **out** (Variable,可选) - 输出Tensor。如果为None,则创建一个新的Tensor作为输出Tensor,默认值为None。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若参数为空,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool,可选) – 是否从此 Variable 开始,之前的相关部分都停止梯度计算,默认为True。
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) – 指定创建Tensor的形状(shape), 数据类型为int32 或者int64。
+ - **fill_value** (bool|float|int|Tensor) - 用于初始化输出Tensor的常量数据的值。注意:该参数不可超过输出变量数据类型的表示范围。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若为None,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor。
+返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor,数据类型和dtype相同。
-返回类型:Variable
抛出异常:
- - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 的类型不是bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64其中之一。
- - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``out`` 的元素的类型不是Variable。
- - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list或tuple或Varibable。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``dtype`` 的类型不是bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64其中之一。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list或tuple或Tensor。当 ``shape`` 是Tensor的时候,其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
**代码示例**:
@@ -37,17 +28,24 @@ full
import paddle
- data1 = paddle.full(shape=[2,1], fill_value=0, dtype='int64') # data1=[[0],[0]]
- data2 = paddle.full(shape=[2,1], fill_value=5, dtype='int64', device='gpu') # data2=[[5],[5]]
-
- # attr shape is a list which contains Variable Tensor.
- positive_2 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int32", 2)
- data3 = paddle.full(shape=[1, positive_2], dtype='float32', fill_value=1.5) # data3=[1.5, 1.5]
-
- # attr shape is an Variable Tensor.
- shape = paddle.fill_constant([1,2], "int32", 2) # shape=[2,2]
- data4 = paddle.full(shape=shape, dtype='bool', fill_value=True) # data4=[[True,True],[True,True]]
-
- # attr value is an Variable Tensor.
- val = paddle.fill_constant([1], "float32", 2.0) # val=[2.0]
- data5 = paddle.full(shape=[2,1], fill_value=val, dtype='float32') #data5=[[2.0],[2.0]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative() # Now we are in imperative mode
+ data1 = paddle.full(shape=[2,1], fill_value=0, dtype='int64')
+ #[[0]
+ # [0]]
+
+ # attr shape is a list which contains Tensor.
+ positive_3 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int32", 2)
+ data3 = paddle.full(shape=[1, positive_2], dtype='float32', fill_value=1.5)
+ # [[1.5 1.5]]
+
+ # attr shape is a Tensor.
+ shape = paddle.fill_constant([2], "int32", 2)
+ data4 = paddle.full(shape=shape, dtype='bool', fill_value=True)
+ # [[True True]
+ # [True True]]
+
+ # attr fill_value is a Tensor.
+ val = paddle.fill_constant([1], "float32", 2.0)
+ data5 = paddle.full(shape=[2,1], fill_value=val, dtype='float32') i
+ # [[2.0]
+ # [2.0]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_like_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_like_cn.rst
index bba7b101ed9ede3d881ec2be12121b7f6a8edafa..f0f26348adf85937abf5ad43d992918a557b2826 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_like_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/full_like_cn.rst
@@ -3,40 +3,33 @@
full_like
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.full_like(input, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, device=None, stop_gradient=True, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.full_like(x, fill_value, dtype=None, name=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.full_like
-:alias: paddle.full_like,paddle.tensor.full_like,paddle.tensor.creation.full_like
-
-
-该OP创建一个和input具有相同的形状和数据类型的Tensor,其中元素值均为fill_value。
+该OP创建一个和 ``x`` 具有相同的形状并且数据类型为 ``dtype`` 的Tensor,其中元素值均为 ``fill_value`` , 当 ``dtype`` 为None的时候,Tensor数据类型和输入 ``x`` 相同。
参数:
- - **input** (Variable) – 指定输入为一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是bool,float16,float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **fill_value** (bool|float|int) - 用于初始化输出Tensor的常量数据的值。默认为0。注意:该参数不可超过输出变量数据类型的表示范围。
- - **out** (Variable,可选) - 输出Tensor。如果为None,则创建一个新的Tensor作为输出Tensor,默认值为None。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若参数为空,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool,可选) – 是否从此 Variable 开始,之前的相关部分都停止梯度计算,默认为True。
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 输入Tensor, 输出Tensor和x具有相同的形状,x的数据类型可以是bool,float16,float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **fill_value** (bool|float|int) - 用于初始化输出张量的常量数据的值。注意:该参数不可超过输出变量数据类型的表示范围。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若参数为None,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor。
+返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor,数据类型和dtype相同。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当 ``x`` 的数据类型不是bool、float16、float32、float64、int32、int64其中之一。
+ - ``TypeError``: - 当 ``dtype`` 不是bool、float16、float32、float64、int32、int64或者None其中之一。
-**代码示例**:
+ **代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- input = fluid.data(name='input', dtype='float32', shape=[2, 3])
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative() # Now we are in imperative mode
+ input = paddle.full(shape=[2, 3], fill_value=0.0, dtype='float32', name='input')
output = paddle.full_like(input, 2.0)
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
- exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
- img=np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]).astype(np.float32)
- res = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'input':img}, fetch_list=[output])
- print(res) # [array([[2., 2., 2.], [2., 2., 2.]], dtype=float32)]
+ # [[2. 2. 2.]
+ # [2. 2. 2.]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
index 21d26726177ae2d0321d0350b65e5ab9b36eb5c0..6eedd6c3bdcfd5fe971dad36fea0452eea45b10b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,36 @@
greater_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_equal
+.. py:function:: paddle.greater_equal(x, y, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.greater_equal
+:alias: paddle.greater_equal,paddle.tensor.greater_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.greater_equal
+
+该OP逐元素地返回 :math:`x >= y` 的逻辑值,相同位置前者输入大于等于后者输入则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `>=` 可以有相同的计算函数效果。
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.greater_equal(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [True False True]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
index 40ad68f703d1784dc4361c09c3f7e25def154d6d..33df3e31c019f4b0ce943f40d5f838cd3d22b19a 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/greater_than_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,34 @@
greater_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.greater_than
+.. py:function:: paddle.greater_than(x, y, name=None)
+:alias_main: paddle.greater_than
+:alias: paddle.greater_than,paddle.tensor.greater_than,paddle.tensor.logic.greater_than
+该OP返回 :math:`x>y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等,相同位置前者输入大于等于后者输入则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `>` 可以有相同的计算函数效果
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.greater_than(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [False False True]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/histogram_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/histogram_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d57084fa6f76f8640688f8d2fb0b2a84d81a8994
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/histogram_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+.. _cn_api_tensor_histogram:
+
+histogram
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.histogram(input, bins=100, min=0, max=0):
+
+计算输入张量的直方图。以min和max为range边界,将其均分成bins个直条,然后将排序好的数据划分到各个直条(bins)中。如果min和max都为0, 则利用数据中的最大最小值作为边界。
+
+参数:
+ - **input** (Variable) - 输入Tensor。维度为多维,数据类型为int32, int64, float32或float64。
+ - **bins** (int) - 直方图 bins(直条)的个数,默认为100。
+ - **min** (int) - range的下边界(包含),默认为0。
+ - **max** (int) - range的上边界(包含),默认为0。
+
+返回:直方图。
+
+返回类型:Variable,数据为int64类型,维度为(nbins,)。
+
+抛出异常:
+ - ``ValueError`` - 当输入 ``bin``, ``min``, ``max``不合法时。
+
+**代码示例1**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ startup_program = paddle.Program()
+ train_program = paddle.Program()
+ with paddle.program_guard(train_program, startup_program):
+ inputs = paddle.data(name='input', dtype='int32', shape=[2,3])
+ output = paddle.histogram(inputs, bins=5, min=1, max=5)
+ place = paddle.CPUPlace()
+ exe = paddle.Executor(place)
+ exe.run(startup_program)
+ img = np.array([[2, 4, 2], [2, 5, 4]]).astype(np.int32)
+ res = exe.run(train_program,
+ feed={'input': img},
+ fetch_list=[output])
+ print(np.array(res[0])) # [0, 3, 0, 2, 1]
+
+**代码示例2**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ with paddle.imperative.guard(paddle.CPUPlace()):
+ inputs_np = np.array([0.5, 1.5, 2.5]).astype(np.float)
+ inputs = paddle.imperative.to_variable(inputs_np)
+ result = paddle.histogram(inputs, bins=5, min=1, max=5)
+ print(result) # [1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/index_select_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/index_select_cn.rst
index 5177558d16883287430f4ebeb2404d3e52f0cc0c..dfb235db5b4f72f04c85dd6b878b7b5568f4344e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/index_select_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/index_select_cn.rst
@@ -3,48 +3,47 @@
index_select
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.index_select(input, index, dim=0)
+.. py:function:: paddle.index_select(x, index, axis=0, name=None)
-:alias_main: paddle.index_select
-:alias: paddle.index_select,paddle.tensor.index_select,paddle.tensor.search.index_select
-
-该OP沿着指定维度 ``dim`` 对输入 ``input`` 进行索引,取 ``index`` 中指定的相应项,然后返回到一个新的张量。这里 ``index`` 是一个 ``1-D`` 张量。除 ``dim`` 维外,返回的张量其余维度大小同输入 ``input`` , ``dim`` 维大小等于 ``index`` 的大小。
+该OP沿着指定轴 ``axis`` 对输入 ``x`` 进行索引,取 ``index`` 中指定的相应项,创建并返回到一个新的Tensor。这里 ``index`` 是一个 ``1-D`` Tensor。除 ``axis`` 轴外,返回的Tensor其余维度大小和输入 ``x`` 相等 , ``axis`` 维度的大小等于 ``index`` 的大小。
**参数**:
- - **input** (Variable)– 输入张量。
- - **index** (Variable)– 包含索引下标的一维张量。
- - **dim** (int, optional) – 索引轴,若未指定,则默认选取第一维。
+ - **x** (Tensor)– 输入Tensor。 ``x`` 的数据类型可以是float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **index** (Tensor)– 包含索引下标的一维Tensor。
+ - **axis** (int, 可选) – 索引轴,若未指定,则默认选取第0维。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
**返回**:
- -**Variable** ,数据类型同输入。
+ -**Tensor**: 返回一个数据类型同输入的Tensor。
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``x`` 或者 ``index`` 的类型不是Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``x`` 的数据类型不是float32、float64、int32、int64其中之一或者 ``index`` 的数据类型不是int32、int64其中之一。
+
+
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static() # Now we are in imperative mode
data = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
- [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0],
- [9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0]])
+ [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0],
+ [9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0]])
data_index = np.array([0, 1, 1]).astype('int32')
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data)
- index = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data_index)
- out_z1 = paddle.index_select(x, index)
- print(out_z1.numpy())
- #[[1. 2. 3. 4.]
- # [5. 6. 7. 8.]
- # [5. 6. 7. 8.]]
- out_z2 = paddle.index_select(x, index, dim=1)
- print(out_z2.numpy())
- #[[ 1. 2. 2.]
- # [ 5. 6. 6.]
- # [ 9. 10. 10.]]
-
+ x = paddle.to_variable(data)
+ index = paddle.to_variable(data_index)
+ out_z1 = paddle.index_select(x=x, index=index)
+ #[[1. 2. 3. 4.]
+ # [5. 6. 7. 8.]
+ # [5. 6. 7. 8.]]
+ out_z2 = paddle.index_select(x=x, index=index, axis=1)
+ #[[ 1. 2. 2.]
+ # [ 5. 6. 6.]
+ # [ 9. 10. 10.]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/inverse_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/inverse_cn.rst
index 131b041378dfc91da94486491c99d7225d8a6116..a8f79737f9f3e71afbd4f1e4896ed6c3b0e6e5da 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/inverse_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/inverse_cn.rst
@@ -3,30 +3,28 @@
inverse
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.inverse(input, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.inverse(x, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.inverse
-:alias: paddle.inverse,paddle.tensor.inverse,paddle.tensor.math.inverse
+:alias: paddle.inverse, paddle.tensor.inverse, paddle.tensor.math.inverse
计算方阵的逆。方阵是行数和列数相等的矩阵。输入可以是一个方阵(2-D张量),或者是批次方阵(维数大于2时)。
-**参数**:
- - **input** (Variable) – 输入张量,最后两维的大小必须相等。如果输入张量的维数大于2,则高维部分代表2-D矩阵的批次(batch)。支持的数据类型:float32,float64。
- - **out** (Variable,可选) – 指定求和的结果Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+**参数**:
+ - **x** (Variable) – 输入张量,最后两维的大小必须相等。如果输入张量的维数大于2,则被视为2-D矩阵的批次(batch)。支持的数据类型:float32,float64。
- **name** (str,可选) – 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
-**返回**:数据类型同输入。
+**返回**: 数据类型同输入。
-返回类型:Variable
+返回类型: Variable
抛出异常:
- - :code:`TypeError` ,input不是Variable类型,或者数据类型不是float32、float64时
- - :code:`ValueError` ,input的维数小于2时
- - :code:`TypeError` ,out不是Variable类型,或者数据类型和input不相同时
+ - :code:`TypeError` ,x不是Variable类型,或者数据类型不是float32、float64时
+ - :code:`ValueError` ,x的维数小于2时
-**代码示例**:
+**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
@@ -34,7 +32,7 @@ inverse
import paddle
mat_np = np.array([[2, 0], [0, 2]]).astype("float32")
- with paddle.imperative.guard():
- mat = paddle.imperative.to_variable(mat_np)
- inv = paddle.inverse(mat)
- print(inv.numpy()) # [[0.5, 0], [0, 0.5]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ mat = paddle.imperative.to_variable(mat_np)
+ inv = paddle.inverse(mat)
+ print(inv) # [[0.5, 0], [0, 0.5]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
index f2b9381cad039bc6b4200d73c5fa604b9ff7f03e..63427b1442ca0cab965045eff3b7bde02fee137e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_equal_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,36 @@
less_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_equal
+.. py:function:: paddle.less_equal(x, y, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.less_equal
+:alias: paddle.less_equal,paddle.tensor.less_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.less_equal
+
+该OP逐元素地返回 :math:`x <= y` 的逻辑值,相同位置前者输入小于等于后者输入则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `<=` 可以有相同的计算函数效果。
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.less_equal(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [True True False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_than_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_than_cn.rst
index 8a89d50b15b135173842875a969a3ee14e73a33a..e49b092cc2d5ce062cfac8551026c616d7befca2 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_than_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/less_than_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,36 @@
less_than
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.less_than
+.. py:function:: paddle.less_than(x, y, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.less_than
+:alias: paddle.less_than,paddle.tensor.less_than,paddle.tensor.logic.less_than
+
+该OP逐元素地返回 :math:`x < y` 的逻辑值,相同位置前者输入小于后者输入则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `<` 可以有相同的计算函数效果。
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.less_than(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [False True False]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/linspace_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/linspace_cn.rst
index c38617e3a3beb81d2b68ec526fefe7d1575babe2..7c228c413e9f167ca92fd547a25c8aa3ad233aeb 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/linspace_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/linspace_cn.rst
@@ -3,31 +3,33 @@
linspace
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.linspace(start, stop, num, dtype, out=None, device=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.linspace(start, stop, num, dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.linspace
-:alias: paddle.linspace,paddle.tensor.linspace,paddle.tensor.creation.linspace
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.linspace
+:alias: paddle.tensor.linspace, paddle.tensor.creation.linspace
-该OP在给定区间内返回固定数目的均匀间隔的值。
+该OP返回一个Tensor,Tensor的值为在区间start和stop上均匀间隔的num个值,输出Tensor的长度为num。
**注意:该OP不进行梯度计算**
参数:
- - **start** (float|Variable) – start是区间开始的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
- - **stop** (float|Variable) – end是区间结束的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
- - **num** (int|Variable) – num是给定区间内需要划分的区间数,可以是一个整型标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型需为int32。
- - **dtype** (string) – 输出Tensor的数据类型,可以是‘float32’或者是‘float64’。
- - **out** (Variable,可选) – 指定存储运算结果的Tensor。如果设置为None或者不设置,将创建新的Tensor存储运算结果,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
+ - **start** (float|Tensor) – ``start`` 是区间开始的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
+ - **stop** (float|Tensor) – ``end`` 是区间结束的变量,可以是一个浮点标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型可以是float32或者是float64。
+ - **num** (int|Tensor) – ``num`` 是给定区间内需要划分的区间数,可以是一个整型标量,或是一个shape为[1]的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型需为int32。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str,可选) – 输出Tensor的数据类型,可以是float32或者是float64。如果dtype为None,默认类型为float32。
- **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:输出结果的数据类型是float32或float64,表示等间隔划分结果的1-D Tensor,该Tensor的shape大小为 :math:`[num]` ,在mum为1的情况下,仅返回包含start元素值的Tensor。
返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当start或者stop的数据类型不是float32或者float64。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当num的数据类型不是float32或者float64。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当dtype的类型不是float32或者float64。
+
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log1p_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log1p_cn.rst
index dab3f158a2d20ee31db2d492f647140ec80eea6f..ff96c608014e706910dbfc30fd11df02995717a8 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log1p_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log1p_cn.rst
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
log1p
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.log1p(x, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.log1p(x, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.log1p
:alias: paddle.log1p,paddle.tensor.log1p,paddle.tensor.math.log1p
@@ -18,32 +18,27 @@ log1p
参数:
- - **x** (Variable) – 该OP的输入为LodTensor/Tensor。数据类型为float32,float64。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) - 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 指定输入为一个多维的Tensor。数据类型为float32,float64。
- **name** (str,可选) – 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
返回:Log1p算子自然对数输出
-返回类型: Variable - 该OP的输出为LodTensor/Tensor,数据类型为输入一致。
+返回类型: Tensor - 该OP的输出为一个多维的Tensor,数据类型为输入一致。
**代码示例**
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
-
- x = fluid.data(name="x", shape=[2,1], dtype="float32")
- res = paddle.log1p(x) # paddle.log1p等价于 paddle.tensor.log1p
-
- # 举例选择CPU计算环境
- exe = fluid.Executor(fluid.CPUPlace())
-
- # 执行静态图,输出结果
- x_i = np.array([[0], [1]]).astype(np.float32)
- res_val, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={'x':x_i}, fetch_list=[res])
- print(res_val) # [[0.], [0.6931472]]
-
-
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).astype('float32')
+ x1 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x)
+
+ out1 = paddle.log1p(x1)
+ print(out1.numpy())
+ # [[0.6931472 1.0986123]
+ # [1.3862944 1.609438 ]]
+
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log_cn.rst
index 960019d43a20943654c6e3481eca1f29346feee9..5cfc4f49472eda096bafea023bc329d6a8934943 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/log_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,43 @@
log
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.log
+.. py:function:: paddle.log(x, name=None)
+:alias_main: paddle.log
+:alias: paddle.log,paddle.tensor.log,paddle.tensor.math.log
+:old_api: paddle.fluid.layers.log
+
+
+
+
+Log激活函数(计算自然对数)
+
+.. math::
+ \\Out=ln(x)\\
+
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 指定输入为一个多维的Tensor。数据类型为float32,float64。
+ - **name** (str,可选) – 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
+
+返回:Log算子自然对数输出
+
+返回类型: Tensor - 该OP的输出为一个多维的Tensor,数据类型为输入一致。
+
+
+**代码示例**
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).astype('float32')
+ x1 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x)
+
+ out1 = paddle.log(x1)
+ print(out1.numpy())
+ # [[0. 0.6931472]
+ # [1.0986123 1.3862944]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/max_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/max_cn.rst
index 24eb34761ef45323fa211f954bdf77b4d8c9d020..e3f1620fa1064f0db21f5fc308cd31521da95354 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/max_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/max_cn.rst
@@ -1,60 +1,64 @@
-
.. _cn_api_paddle_tensor_max:
max
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.max(input, dim=None, keep_dim=False, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.max(x, axis=None, keepdim=False, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.max
:alias: paddle.max,paddle.tensor.max,paddle.tensor.math.max
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_max
-
-
-该OP是对指定维度上的Tensor元素求最大值运算,并输出相应的计算结果。等价于 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_max`
+该OP是对指定维度上的Tensor元素求最大值运算,并输出相应的计算结果。
-参数:
- - **input** (Variable)- 输入变量为多维Tensor或LoDTensor,支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **dim** (list | int ,可选)- 求最大值运算的维度。如果为None,则计算所有元素的最大值并返回包含单个元素的Tensor变量,否则必须在 :math:`[−rank(input),rank(input)]` 范围内。如果 :math:`dim [i] <0` ,则维度将变为 :math:`rank+dim[i]` ,默认值为None。
- - **keep_dim** (bool)- 是否在输出Tensor中保留减小的维度。如 keep_dim 为true,否则结果张量的维度将比输入张量小,默认值为False。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) - 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor)- Tensor,支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **axis** (list | int ,可选)- 求最大值运算的维度。如果为None,则计算所有元素的最大值并返回包含单个元素的Tensor变量,否则必须在 :math:`[-x.ndim, x.ndim]` 范围内。如果 :math:`axis[i] <0` ,则维度将变为 :math:`x.ndim+axis[i]` ,默认值为None。
+ - **keepdim** (bool)- 是否在输出Tensor中保留减小的维度。如果keepdim 为 False,结果张量的维度将比输入张量的小,默认值为False。
+ - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回: 在指定dim上进行求最大值运算的Tensor,数据类型和输入数据类型一致。
+返回
+:::::::::
+ Tensor, 在指定axis上进行求最大值运算的Tensor,数据类型和输入数据类型一致。
-返回类型: 变量(Variable)
-**代码示例**
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
+ import numpy as np
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- # x是一个Tensor,元素如下:
- # [[0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9]
- # [0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 0.7]]
- # 接下来的示例中,我们在每处函数调用后面都标注出了它的结果张量。
- x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[2, 4], dtype='float32')
- # paddle.max 等价于 paddle.tensor.max
- paddle.max(x) # [0.9]
- paddle.max(x, dim=0) # [0.2, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9]
- paddle.max(x, dim=-1) # [0.9, 0.7]
- paddle.max(x, dim=1, keep_dim=True) # [[0.9], [0.7]]
-
- # y是一个shape为[2, 2, 2]的Tensor,元素如下:
- # [[[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]],
- # [[5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0]]]
- # 接下来的示例中,我们在每处函数调用后面都标注出了它的结果张量。
- y = fluid.data(name='y', shape=[2, 2, 2], dtype='float32')
- paddle.max(y, dim=[1, 2]) # [4.0, 8.0]
- paddle.max(y, dim=[0, 1]) # [7.0, 8.0]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ # data_x is a variable with shape [2, 4]
+ # the axis is a int element
+ data_x = np.array([[0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9],
+ [0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 0.7]])
+ x = paddle.to_variable(data_x)
+ result1 = paddle.max(x)
+ print(result1.numpy())
+ #[0.9]
+ result2 = paddle.max(x, axis=0)
+ print(result2.numpy())
+ #[0.2 0.3 0.6 0.9]
+ result3 = paddle.max(x, axis=-1)
+ print(result3.numpy())
+ #[0.9 0.7]
+ result4 = paddle.max(x, axis=1, keepdim=True)
+ print(result4.numpy())
+ #[[0.9]
+ # [0.7]]
+
+ # data_y is a variable with shape [2, 2, 2]
+ # the axis is list
+ data_y = np.array([[[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]],
+ [[5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0]]])
+ y = paddle.to_variable(data_y)
+ result5 = paddle.max(y, axis=[1, 2])
+ print(result5.numpy())
+ #[4. 8.]
+ result6 = paddle.max(y, axis=[0, 1])
+ print(result6.numpy())
+ #[7. 8.]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/maximum_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/maximum_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3db694f291098d8ed4c8d2bd08bd4a56adb49f81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/maximum_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+.. _cn_api_paddle_tensor_maximum:
+
+maximum
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.maximum(x, y, axis=-1, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.maximum
+:alias: paddle.maximum,paddle.tensor.maximum,paddle.tensor.math.maximum
+
+该OP逐元素对比输入的两个多维Tensor,并且把各个位置更大的元素保存到返回结果中。
+
+等式是:
+
+.. math::
+ Out = max(X, Y)
+
+- :math:`X` :多维Tensor。
+- :math:`Y` :多维Tensor。
+
+此运算算子有两种情况:
+ 1. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 与 :math:`X` 相同。
+ 2. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 是 :math:`X` 的连续子序列。
+
+对于情况2:
+ 1. 用 :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 匹配 :math:`X` 的 ``shape``,其中 ``axis`` 是 :math:`Y` 在 :math:`X` 上的起始维度的位置。
+ 2. 如果 ``axis`` < 0(默认值为-1),则 :math:`axis = abs(X.ndim - Y.ndim) - axis - 1` 。
+ 3. 考虑到子序列, :math:`Y` 的大小为1的尾部维度将被忽略,例如shape(Y)=(2,1)=>(2)。
+
+例如:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (5,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (4, 5), with axis=-1(default) or axis=2
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (3, 4), with axis=1
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2), with axis=0
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2, 1), with axis=0
+
+具体的飞桨的广播(broadcasting)机制可以参考 `<> `_ 。
+
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor)- 多维Tensor。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
+ - **y** (Tensor)- 多维Tensor。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
+ - **axis** (int32, 可选)- Y的维度对应到X维度上时的索引。默认值为 -1。
+ - **name** (string, 可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+返回
+:::::::::
+ Tensor,维度和数据类型与 ``x`` 相同的多维Tensor。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ x_data = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.maximum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[[5. 6.]
+ # [7. 8.]]
+
+ x_data = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 2], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.maximum(x, y, axis=1)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[[[1. 2. 3.]
+ # [2. 2. 3.]]]
+
+ x_data = np.array([2, 3, 5], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 4, np.nan], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.maximum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[ 2. 4. nan]
+
+ x_data = np.array([5, 3, np.inf], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 4, 5], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.maximum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[ 5. 4. inf]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/mean_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/mean_cn.rst
index fe7f53d6f6cd5218b7f6d884bafeb7c7e12000cc..bc838016e17b8d4992aee8802128eb69c983cb71 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/mean_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/mean_cn.rst
@@ -2,6 +2,52 @@
mean
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.mean
+.. py:function:: paddle.mean(x, axis=None, keepdim=False, name=None)
+
+
+该OP沿 ``axis`` 计算 ``x`` 的平均值。
+
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - x (Tensor) - 输入的Tensor,数据类型为:float32、float64、int32.int64 。
+ - axis (int|list|tuple, 可选) - 指定对 ``x`` 进行计算的轴。``axis`` 可以是int、list(int)、tuple(int)。如果 ``axis`` 包含多个维度,则沿着 ``axis`` 中的所有轴进行计算。``axis`` 或者其中的元素值应该在范围[-D, D)内,D是 ``x`` 的维度。如果 ``axis`` 或者其中的元素值小于0,则等价于 :math:`axis + D` 。如果 ``axis`` 是None,则对 ``x`` 的全部元素计算平均值。默认值为None。
+ - keepdim (bool, 可选) - 是否在输出Tensor中保留减小的维度。如果 ``keep_dim`` 为True,则输出Tensor和 ``x`` 具有相同的维度(减少的维度除外,减少的维度的大小为1)。否则,输出Tensor的形状会在 ``axsi`` 上进行squeeze操作。默认值为False。
+ - name (str, 可选) - 操作的名称(可选,默认值为None)。更多信息请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name`。
+
+返回
+::::::::::
+ ``Tensor`` ,沿着 ``axis`` 进行平均值计算的结果,数据类型和 ``x`` 相同。
+
+代码示例
+::::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ x = np.array([[[1, 2, 3, 4],
+ [5, 6, 7, 8],
+ [9, 10, 11, 12]],
+ [[13, 14, 15, 16],
+ [17, 18, 19, 20],
+ [21, 22, 23, 24]]], 'float32')
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x)
+ out1 = paddle.mean(x)
+ # [12.5]
+ out2 = paddle.mean(x, axis=-1)
+ # [[ 2.5 6.5 10.5]
+ # [14.5 18.5 22.5]]
+ out3 = paddle.mean(x, axis=-1, keepdim=True)
+ # [[[ 2.5]
+ # [ 6.5]
+ # [10.5]]
+ # [[14.5]
+ # [18.5]
+ # [22.5]]]
+ out4 = paddle.mean(x, axis=[0, 2])
+ # [ 8.5 12.5 16.5]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst
index fc65f330c1b29cc400605390d113ad15ca4d6600..6c8aedc1a1aa24a952e668c1f5c0ce53756f8d9e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/meshgrid_cn.rst
@@ -4,58 +4,40 @@
meshgrid
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.meshgrid(input, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.meshgrid(*args, **kargs)
:alias_main: paddle.meshgrid
-:alias: paddle.meshgrid,paddle.tensor.meshgrid,paddle.tensor.creation.meshgrid
+:alias: paddle.meshgrid, paddle.tensor.meshgrid, paddle.tensor.creation.meshgrid
-该OP的输入是tensor list, 包含 k 个一维Tensor,对每个Tensor做扩充操作,输出 k 个 k 维tensor。
+该OP的输入是张量或者包含张量的列表, 包含 k 个一维张量,对每个张量做扩充操作,输出 k 个 k 维张量。
参数:
- - **input** (Variable)- 输入变量为 k 个一维Tensor,形状分别为(N1,), (N2,), ..., (Nk, )。支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+ - \* **args** (Variable|Variable数组)- 输入变量为 k 个一维张量,形状分别为(N1,), (N2,), ..., (Nk, )。支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - ** **kargs** (可选)- 目前只接受name参数(str),具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:
-k 个 k 维Tensor,每个Tensor的形状均为(N1, N2, ..., Nk)。
+k 个 k 维张量,每个张量的形状均为(N1, N2, ..., Nk)。
返回类型: 变量(Variable)
**代码示例**
-.. code-block:: python
-
- #静态图示例
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
- x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[100], dtype='int32')
- y = fluid.data(name='y', shape=[200], dtype='int32')
- input_1 = np.random.randint(0, 100, [100, ]).astype('int32')
- input_2 = np.random.randint(0, 100, [200, ]).astype('int32')
- exe = fluid.Executor(place=fluid.CPUPlace())
- grid_x, grid_y = paddle.tensor.meshgrid([x, y])
- res_1, res_2 = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(),
- feed={'x': input_1,
- 'y': input_2},
- fetch_list=[grid_x, grid_y])
-
- #the shape of res_1 is (100, 200)
- #the shape of res_2 is (100, 200)
.. code-block:: python
#动态图示例
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
input_3 = np.random.randint(0, 100, [100, ]).astype('int32')
input_4 = np.random.randint(0, 100, [200, ]).astype('int32')
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- tensor_3 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(input_3)
- tensor_4 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(input_4)
- grid_x, grid_y = paddle.tensor.meshgrid([tensor_3, tensor_4])
+ tensor_3 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(input_3)
+ tensor_4 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(input_4)
+ grid_x, grid_y = paddle.tensor.meshgrid(tensor_3, tensor_4)
#the shape of grid_x is (100, 200)
#the shape of grid_y is (100, 200)
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/min_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/min_cn.rst
index d3417080c79bcc5df682feff99fd29c8d4a1057f..7231c1b20519c2fb807a05d6d35354177763830e 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/min_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/min_cn.rst
@@ -3,57 +3,61 @@
min
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.min(input, dim=None, keep_dim=False, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.min(x, axis=None, keepdim=False, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.min
:alias: paddle.min,paddle.tensor.min,paddle.tensor.math.min
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_min
+该OP是对指定维度上的Tensor元素求最小值运算,并输出相应的计算结果。
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor)- Tensor,支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **axis** (list | int ,可选)- 求最小值运算的维度。如果为None,则计算所有元素的最小值并返回包含单个元素的Tensor变量,否则必须在 :math:`[−x.ndim, x.ndim]` 范围内。如果 :math:`axis[i] < 0` ,则维度将变为 :math:`x.ndim+axis[i]` ,默认值为None。
+ - **keepdim** (bool)- 是否在输出Tensor中保留减小的维度。如果keepdim 为False,结果张量的维度将比输入张量的小,默认值为False。
+ - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-该OP是对指定维度上的Tensor元素求最小值运算,并输出相应的计算结果。等价于 :ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_min`
+返回
+:::::::::
+ Tensor,在指定axis上进行求最小值运算的Tensor,数据类型和输入数据类型一致。
-参数:
- - **input** (Variable)- 输入变量为多维Tensor或LoDTensor,支持数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **dim** (list | int ,可选)- 求最小值运算的维度。如果为None,则计算所有元素的最小值并返回包含单个元素的Tensor变量,否则必须在 :math:`[−rank(input),rank(input)]` 范围内。如果 :math:`dim [i] <0` ,则维度将变为 :math:`rank+dim[i]` ,默认值为None。
- - **keep_dim** (bool)- 是否在输出Tensor中保留减小的维度。如 keep_dim 为true,否则结果张量的维度将比输入张量小,默认值为False。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) - 指定算子输出结果的LoDTensor/Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- - **name** (str, 可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-
-返回: 在指定dim上进行求最小值运算的Tensor,数据类型和输入数据类型一致。
-
-返回类型: 变量(Variable)
-
-**代码示例**
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
+ import numpy as np
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- # x是一个Tensor,元素如下:
- # [[0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9]
- # [0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 0.7]]
- # 接下来的示例中,我们在每处函数调用后面都标注出了它的结果张量。
- x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[2, 4], dtype='float32')
- # paddle.min 等价于 paddle.tensor.min
- paddle.min(x) # [0.1]
- paddle.min(x, dim=0) # [0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.7]
- paddle.min(x, dim=-1) # [0.2, 0.1]
- paddle.min(x, dim=1, keep_dim=True) # [[0.2], [0.1]]
-
- # y是一个shape为[2, 2, 2]的Tensor,元素如下:
- # [[[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]],
- # [[5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0]]]
- # 接下来的示例中,我们在每处函数调用后面都标注出了它的结果张量。
- y = fluid.data(name='y', shape=[2, 2, 2], dtype='float32')
- paddle.min(y, dim=[1, 2]) # [1.0, 5.0]
- paddle.min(y, dim=[0, 1]) # [1.0, 2.0]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ # data_x is a variable with shape [2, 4]
+ # the axis is a int element
+ data_x = np.array([[0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9],
+ [0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 0.7]])
+ x = paddle.to_variable(data_x)
+ result1 = paddle.min(x)
+ print(result1.numpy())
+ #[0.1]
+ result2 = paddle.min(x, axis=0)
+ print(result2.numpy())
+ #[0.1 0.2 0.5 0.7]
+ result3 = paddle.min(x, axis=-1)
+ print(result3.numpy())
+ #[0.2 0.1]
+ result4 = paddle.min(x, axis=1, keepdim=True)
+ print(result4.numpy())
+ #[[0.2]
+ # [0.1]]
+
+ # data_y is a variable with shape [2, 2, 2]
+ # the axis is list
+ data_y = np.array([[[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]],
+ [[5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0]]])
+ y = paddle.to_variable(data_y)
+ result5 = paddle.min(y, axis=[1, 2])
+ print(result5.numpy())
+ #[1. 5.]
+ result6 = paddle.min(y, axis=[0, 1])
+ print(result6.numpy())
+ #[1. 2.]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/minimum_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/minimum_cn.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1d04313385ff36c3104ec9fd173939bcae8e5c6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/minimum_cn.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+.. _cn_api_paddle_tensor_minimum:
+
+minimum
+-------------------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.minimum(x, y, axis=-1, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.minimum
+:alias: paddle.minimum,paddle.tensor.minimum,paddle.tensor.math.minimum
+
+该OP逐元素对比输入的两个多维Tensor,并且把各个位置更小的元素保存到返回结果中。
+
+等式是:
+
+.. math::
+ Out = min(X, Y)
+
+- :math:`X` :多维Tensor。
+- :math:`Y` :多维Tensor。
+
+此运算算子有两种情况:
+ 1. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 与 :math:`X` 相同。
+ 2. :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 是 :math:`X` 的连续子序列。
+
+对于情况2:
+ 1. 用 :math:`Y` 的 ``shape`` 匹配 :math:`X` 的 ``shape``,其中 ``axis`` 是 :math:`Y` 在 :math:`X` 上的起始维度的位置。
+ 2. 如果 ``axis`` < 0(默认值为-1),则 :math:`axis = abs(X.ndim - Y.ndim) - axis - 1` 。
+ 3. 考虑到子序列, :math:`Y` 的大小为1的尾部维度将被忽略,例如shape(Y)=(2,1)=>(2)。
+
+例如:
+
+.. code-block:: text
+
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (5,)
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (4, 5), with axis=-1(default) or axis=2
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (3, 4), with axis=1
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2), with axis=0
+ shape(X) = (2, 3, 4, 5), shape(Y) = (2, 1), with axis=0
+
+具体的飞桨的广播(broadcasting)机制可以参考 `<> `_ 。
+
+参数
+:::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor)- 多维Tensor。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
+ - **y** (Tensor)- 多维Tensor。数据类型为 ``float32`` 、 ``float64`` 、 ``int32`` 或 ``int64`` 。
+ - **axis** (int32, 可选)- Y的维度对应到X维度上时的索引。默认值为 -1。
+ - **name** (string, 可选)- 输出的名字。默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+返回
+:::::::::
+ Tensor,维度和数据类型与 ``x`` 相同的多维Tensor。
+
+
+代码示例
+::::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+ paddle.disable_static()
+
+ x_data = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.minimum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[[1. 2.]
+ # [3. 4.]]
+
+ x_data = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 2], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.minimum(x, y, axis=1)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[[[1. 1. 1.]
+ # [2. 2. 2.]]]
+
+ x_data = np.array([2, 3, 5], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 4, np.nan], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.minimum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[ 1. 3. nan]
+
+ x_data = np.array([5, 3, np.inf], dtype=np.float32)
+ y_data = np.array([1, 4, 5], dtype=np.float32)
+ x = paddle.to_variable(x_data)
+ y = paddle.to_variable(y_data)
+ res = paddle.minimum(x, y)
+ print(res.numpy())
+ #[1. 3. 5.]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/norm_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/norm_cn.rst
index 5fed454842b9292b2240cd8d3b575143064b0597..ea6ebd82d2aff71ea5164ce22063a5bf5723cdd7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/norm_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/norm_cn.rst
@@ -7,7 +7,6 @@ norm
:alias_main: paddle.norm
:alias: paddle.norm,paddle.tensor.norm,paddle.tensor.linalg.norm
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.l2_normalize
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/not_equal_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
index 5cd088f25e1e21587d24bfc6bf84a1139e181f63..8a81f4f08ff2b31d4f434c169be51d3ca3703103 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/not_equal_cn.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,37 @@
-.. _cn_api_tensor_cn_not_equal:
+.. _cn_api_tensor_not_equal:
not_equal
-------------------------------
-:doc_source: paddle.fluid.layers.not_equal
+.. py:function:: paddle.not_equal(x, y, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.not_equal
+:alias: paddle.not_equal,paddle.tensor.not_equal,paddle.tensor.logic.not_equal
+
+该OP返回 :math:`x!=y` 逐元素比较x和y是否相等,相同位置的元素不相同则返回True,否则返回False。使用重载算子 `!=` 可以有相同的计算函数效果
+
+**注:该OP输出的结果不返回梯度。**
+
+参数:
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64,int32, int64。
+ - **y** (Tensor) - 输入Tensor,支持的数据类型包括 float32, float64, int32, int64。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+
+
+返回:输出结果的Tensor,输出Tensor的shape和输入一致,Tensor数据类型为bool。
+
+返回类型:变量(Tensor)
+
+**代码示例**:
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import numpy as np
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ y = imperative.to_variable(np.array([1, 3, 2]))
+ result1 = paddle.not_equal(x, y)
+ print(result1.numpy()) # result1 = [False True True]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_cn.rst
index dc07e0970bd8bad63a51d4a2af94e20f7fd710f1..fa13c3412fd1d741d129987b415e4ac33a956557 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_cn.rst
@@ -3,32 +3,44 @@
ones
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.ones(shape, dtype, out=None, device=None)
-
-:alias_main: paddle.ones
-:alias: paddle.ones,paddle.tensor.ones,paddle.tensor.creation.ones
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.ones
-
+.. py:function:: paddle.ones(shape, dtype=None)
该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为1的Tensor。
参数:
- - **shape** (tuple|list) - 输出Tensor的形状。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) – 指定存储运算结果的Tensor。如果设置为None或者不设置,将创建新的Tensor存储运算结果,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
+ - **shape** (tuple|list|Tensor) - 输出Tensor的形状, ``shape`` 的数据类型为int32或者int64。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。如果 ``dtype`` 为None,默认数据类型为float32。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回:值全为1的Tensor,数据类型和 ``dtype`` 定义的类型一致。
-返回类型:Variable
+
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``dtype`` 不是bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32、int64和None时。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``shape`` 不是tuple、list、或者Tensor的时, 当 ``shape`` 为Tensor时,其数据类型不是int32或者int64。
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- data = paddle.ones(shape=[3, 2], dtype='float32') # [[1., 1.], [1., 1.], [1., 1.]]
- data = paddle.ones(shape=[2, 2], dtype='float32', device='cpu') # [[1., 1.], [1., 0.]]
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ #default dtype for ones OP
+ data1 = paddle.ones(shape=[3, 2])
+ # [[1. 1.]
+ # [1. 1.]
+ # [1. 1.]]
+ data2 = paddle.ones(shape=[2, 2], dtype='int32')
+ # [[1 1]
+ # [1 1]]
+
+ #attr shape is a Variable Tensor
+ shape = paddle.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='int32', value=2)
+ data3 = paddle.ones(shape=shape, dtype='int32')
+ # [[1 1]
+ # [1 1]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_like_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_like_cn.rst
index 6eebf69ebdf2fbb8c6b59c1d17355fa9aa64321c..33b189c7aaeebf5cc9f54f9f3d4fca38cb5de752 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_like_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/ones_like_cn.rst
@@ -3,33 +3,37 @@
ones_like
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.ones_like(input, dtype=None, device=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.ones_like(x, dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.ones_like
-:alias: paddle.ones_like,paddle.tensor.ones_like,paddle.tensor.creation.ones_like
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.ones_like
+:alias: paddle.tensor.ones_like, paddle.tensor.creation.ones_like
+该OP返回一个和 ``x`` 具有相同形状的数值都为1的Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype`` 或者和 ``x`` 相同。
-
-
-该OP创建一个和input具有相同的形状和数据类型的全1Tensor。
-
-参数:
- - **input** (Variable) – 指定输入为一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是bool,float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若参数为空,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
- - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 输入的Tensor,数据类型可以是bool,float16, float32,float64,int32,int64。输出Tensor的形状和 ``x`` 相同。如果 ``dtype`` 为None,则输出Tensor的数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持bool,float16, float32,float64,int32,int64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor。
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor:和 ``x`` 具有相同形状的数值都为1的Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype`` 或者和 ``x`` 相同。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是bool、float16、float32、float64、int32、int64。
-**代码示例**:
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.data(name='x', dtype='float32', shape=[3])
- data = paddle.ones_like(x) # data=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
- data1 = paddle.ones_like(input=x, device="gpu") # data1=[1.0, 1.0. 1.0]
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([1,2,3], dtype='float32'))
+ out1 = paddle.ones_like(x) # [1., 1., 1.]
+ out2 = paddle.ones_like(x, dtype='int32') # [1, 1, 1]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/rand_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/rand_cn.rst
index b1c5e32b1a5779506d4f962463f561e890b15211..36fc3f1a6fdecf051a212e7099382e75c859702d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/rand_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/rand_cn.rst
@@ -1,3 +1,59 @@
+.. _cn_api_tensor_random_rand:
+
rand
--------------------------------
-**版本升级,文档正在开发中**
+----------------------
+
+.. py:function:: paddle.rand(shape, dtype=None, name=None)
+
+:alias_main: paddle.rand
+:alias: paddle.tensor.rand, paddle.tensor.random.rand
+
+
+
+该OP返回符合均匀分布的,范围在[0, 1)的Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
+
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 生成的随机Tensor的形状。如果 ``shape`` 是list、tuple,则其中的元素可以是int,或者是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64的Tensor。如果 ``shape`` 是Tensor,则是数据类型为int32、int64的1-D Tensor。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持float32、float64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型为float32。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
+
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor: 符合均匀分布的范围为[0, 1)的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
+
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list、tuple、Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是float32、float64。
+
+示例代码
+::::::::::
+
+.. code-block:: python
+
+ import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ # example 1: attr shape is a list which doesn't contain Tensor.
+ result_1 = paddle.rand(shape=[2, 3])
+ # [[0.451152 , 0.55825245, 0.403311 ],
+ # [0.22550228, 0.22106001, 0.7877319 ]]
+
+ # example 2: attr shape is a list which contains Tensor.
+ dim_1 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int64", 2)
+ dim_2 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int32", 3)
+ result_2 = paddle.rand(shape=[dim_1, dim_2, 2])
+ # [[[0.8879919 0.25788337]
+ # [0.28826773 0.9712097 ]
+ # [0.26438272 0.01796806]]
+ # [[0.33633623 0.28654453]
+ # [0.79109055 0.7305809 ]
+ # [0.870881 0.2984597 ]]]
+
+ # example 3: attr shape is a Tensor, the data type must be int64 or int32.
+ var_shape = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([2, 3]))
+ result_3 = paddle.rand(var_shape)
+ # [[0.22920267 0.841956 0.05981819]
+ # [0.4836288 0.24573246 0.7516129 ]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randint_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randint_cn.rst
index 083fff351fd0d64fb44c8f5ad85a487a779feb9f..e2ef78ff5d2294b795bce9e136f039a5270a15dd 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randint_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randint_cn.rst
@@ -3,60 +3,70 @@
randint
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.randint(low, high=None, shape=None, out=None, dtype=None, device=None, stop_gradient=False, seed=0, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.randint(low=0, high=None, shape=[1], dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.randint
-:alias: paddle.randint,paddle.tensor.randint,paddle.tensor.random.randint
+:alias: paddle.tensor.randint, paddle.tensor.random.randint
-该OP使用从区间[low,high)内均匀分布采样的随机整数初始化一个Tensor。当high为None时(默认),均匀采样的区间为[0,low)。
+该OP返回服从均匀分布的、范围在[``low``, ``high``)的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。当 ``high`` 为None时(默认),均匀采样的区间为[0, ``low``)。
-参数:
- - **low** (int)-要生成的随机值范围的下限,low包含在范围中。当high为None时,均匀采样的区间为[0,low)。
- - **high** (int,可选)-要生成的随机值范围的上限,high不包含在范围中。默认值为None。
- - **shape** (list|tuple|Variable,可选)-输出Tensor的维度,shape类型支持list,tuple,Variable。如果shape类型是list或者tuple,它的元素可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,其中整数的数据类型为int,Tensor的数据类型为int32或int64。如果shape的类型是Variable,则是1D的Tensor,Tensor的数据类型为int32或int64。如果shape为None,则会将shape设置为[1]。默认值为None。
- - **out** (Variable,可选)-用于存储创建的Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。默认值为None,此时将创建新的Variable来保存输出结果。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str,可选)- 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持数据类型为int32,int64。如果dtype为None,则会将dtype设置为int64。默认值为None。
- - **device** (str, 可选)-指定在GPU或CPU上创建Tensor。如果device为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool,可选)-指定是否停止梯度计算,默认值为False。
- - **seed** (int,可选)-随机种子,用于生成样本。0表示使用系统生成的种子。注意如果种子不为0,该操作符每次都生成同样的随机数。默认为 0。
- - **name** (str,可选)-具体用法请参见:ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **low** (int) - 要生成的随机值范围的下限,``low`` 包含在范围中。当 ``high`` 为None时,均匀采样的区间为[0, ``low``)。默认值为0。
+ - **high** (int, 可选) - 要生成的随机值范围的上限,``high`` 不包含在范围中。默认值为None,此时范围是[0, ``low``)。
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 生成的随机Tensor的形状。如果 ``shape`` 是list、tuple,则其中的元素可以是int,或者是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64的Tensor。如果 ``shape`` 是Tensor,则是数据类型为int32、int64的1-D Tensor。。默认值为[1]。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持int32、int64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型为int64。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:表示一个随机初始化结果的Tensor,该Tensor的数据类型由dtype参数决定,该Tensor的维度由shape参数决定。
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor:从区间[``low``,``high``)内均匀分布采样的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list、tuple、Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是int32、int64。
+ - ``ValueError`` - 如果 ``high`` 不大于 ``low``;或者 ``high`` 为None,且 ``low`` 不大于0。
-抛出异常:
- - :code:`TypeError`: shape的类型应该是list、tuple 或 Variable。
- - :code:`TypeError`: dtype的类型应该是int32或int64。
- - :code:`ValueError`: 该OP的high必须大于low(high为None时,则会先将high设置为low,将low设置为0,再判断low和high的大小关系)。
-
-**代码示例**:
+代码示例
+:::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import paddle
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
# example 1:
- # attr shape is a list which doesn't contain tensor Variable.
- result_1 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=[3, 4], dtype="int64")
+ # attr shape is a list which doesn't contain Tensor.
+ result_1 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=[3])
+ # [0, -3, 2]
# example 2:
- # attr shape is a list which contains tensor Variable.
- dim_1 = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1],"int64",3)
- dim_2 = fluid.layers.fill_constant([1],"int32",5)
+ # attr shape is a list which contains Tensor.
+ dim_1 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int64", 2)
+ dim_2 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int32", 3)
result_2 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=[dim_1, dim_2], dtype="int32")
+ print(result_2.numpy())
+ # [[ 0, -1, -3],
+ # [ 4, -2, 0]]
# example 3:
- # attr shape is a Variable, the data type must be int64 or int32.
- var_shape = fluid.data(name='var_shape', shape=[2], dtype="int64")
- result_3 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=var_shape, dtype="int32")
- var_shape_int32 = fluid.data(name='var_shape_int32', shape=[2], dtype="int32")
- result_4 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=var_shape_int32, dtype="int64")
+ # attr shape is a Tensor
+ var_shape = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([3]))
+ result_3 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=var_shape)
+ # [-2, 2, 3]
# example 4:
+ # date type is int32
+ result_4 = paddle.randint(low=-5, high=5, shape=[3], dtype='int32')
+ # [-5, 4, -4]
+
+ # example 5:
# Input only one parameter
# low=0, high=10, shape=[1], dtype='int64'
- result_4 = paddle.randint(10)
+ result_5 = paddle.randint(10)
+ # [7]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randn_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randn_cn.rst
index 5acbf1d611e8b5ca12dba6ab4de2e5262d79d772..e465b0c75eb5dbb06386abfc5d6f41746b6e967b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randn_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randn_cn.rst
@@ -3,52 +3,58 @@
randn
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.random.randn(shape, out=None, dtype=None, device=None, stop_gradient=True, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.randn(shape, dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.randn
-:alias: paddle.randn,paddle.tensor.randn,paddle.tensor.random.randn
+:alias: paddle.tensor.randn, paddle.tensor.random.randn
-该 API 用于生成数据符合标准正态随机分布(均值为 0,方差为 1 的正态随机分布)的 Tensor。
+该OP返回符合标准正态分布(均值为0,标准差为1的正态随机分布)的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
-参数:
- - **shape** (list|tuple): 生成的随机 Tensor 的形状。
- - **out** (Variable, optional): 用于存储创建的 Tensor,可以是程序中已经创建的任何Variable。当该参数值为 `None` 时,将创建新的 Variable 来保存输出结果。默认值为 None。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, optional): 输出 Tensor 的数据类型,可选值为 float32,float64。当该参数值为 `None` 时, 输出当 Tensor 的数据类型为 `float32` 。默认值为 None.
- - **device** (str, optional): 用于指定输出变量是保存在 CPU 还是 GPU 内存中。可选值为 None,'cpu','gpu'。当该参数为 None 时, 输出变量将会自动的分配到相对应内存中。默认值为 None。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool, optional): 是否停止输出当前变量(输出变量)的梯度值。默认值为 True。
- - **name** (str, optional): 该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,默认值为None。
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **shape** (list|tuple|Tensor) - 生成的随机Tensor的形状。如果 ``shape`` 是list、tuple,则其中的元素可以是int,或者是形状为[1]且数据类型为int32、int64的Tensor。如果 ``shape`` 是Tensor,则是数据类型为int32、int64的1-D Tensor。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持float32、float64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型为float32。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:符合标准正态分布的随机 Tensor。形状为 shape,数据类型为 dtype。
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor:符合标准正态分布的随机Tensor,形状为 ``shape``,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``shape`` 的类型不是list、tuple、Tensor。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是float32、float64。
-**示例代码**
+示例代码
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
- # declarative mode
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- data = paddle.randn([2, 4])
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- exe = fluid.Executor(place)
- res, = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(), feed={}, fetch_list=[data])
- print(res)
- # [[-1.4187592 0.7368311 -0.53748125 -0.0146909 ]
- # [-0.66294265 -1.3090698 0.1898754 -0.14065823]]
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- # imperative mode
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import paddle.fluid.dygraph as dg
- place = fluid.CPUPlace()
- with dg.guard(place) as g:
- x = paddle.randn([2, 4])
- x_np = x.numpy()
- print(x_np)
- # [[ 1.5149173 -0.26234224 -0.592486 1.4523455 ]
- # [ 0.04581212 -0.85345626 1.1687907 -0.02512913]]
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ # example 1: attr shape is a list which doesn't contain Tensor.
+ result_1 = paddle.randn(shape=[2, 3])
+ # [[-2.923464 0.11934398 -0.51249987]
+ # [ 0.39632758 0.08177969 0.2692008 ]]
+
+ # example 2: attr shape is a list which contains Tensor.
+ dim_1 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int64", 2)
+ dim_2 = paddle.fill_constant([1], "int32", 3)
+ result_2 = paddle.randn(shape=[dim_1, dim_2, 2])
+ # [[[-2.8852394 -0.25898588]
+ # [-0.47420555 0.17683524]
+ # [-0.7989969 0.00754541]]
+ # [[ 0.85201347 0.32320443]
+ # [ 1.1399018 0.48336947]
+ # [ 0.8086993 0.6868893 ]]]
+
+ # example 3: attr shape is a Tensor, the data type must be int64 or int32.
+ var_shape = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([2, 3]))
+ result_3 = paddle.randn(var_shape)
+ # [[-2.878077 0.17099959 0.05111201]
+ # [-0.3761474 -1.044801 1.1870178 ]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randperm_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randperm_cn.rst
index efba9587f320f63ae111471bed4819ba17d15ead..d3c756a0fc9ded21c9b78d95dd532b9ba4aa26e9 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randperm_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/randperm_cn.rst
@@ -3,49 +3,39 @@
randperm
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.random.randperm(n, out=None, dtype="int64", device=None, stop_gradient=True, seed=0)
+.. py:function:: paddle.randperm(n, dtype="int64", name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.randperm
-:alias: paddle.randperm,paddle.tensor.randperm,paddle.tensor.random.randperm
+:alias: paddle.tensor.randperm, paddle.tensor.random.randperm
+该OP返回一个数值在0到n-1、随机排列的1-D Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype``。
+参数:
+::::::::::
+ - **n** (int) - 随机序列的上限(不包括在序列中),应该大于0。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持int32、int64、float32、float64。默认值为"int64".
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-该OP返回一个数值在0到n-1、顺序随机的整数排列。
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor:一个数值在0到n-1、随机排列的1-D Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype`` 。
-参数:
- - **n** (int): 整数排列的上限,应该大于0。
- - **out** (Variable, optional): 可选的输出变量,如果不为 `None` ,返回的整数排列保存在该变量中,默认是 `None` 。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, optional): 整数排列的数据类型,支持 `int64` 和 `int32` ,默认是 `int64` 。
- - **device** (str, optional): 指定整数排列所在的设备内存。设置为 `cpu` 则保存在 `cpu` 内存中,设置为 `gpu` ,则保存在 `gpu` 内存中,设置为 `None` 则保存在运行的设备内存中。默认是 `None` 。
- - **stop_gradient** (bool, optional): 返回的整数排列是否记录并更新梯度,默认是 `True` 。
- - **seed** (int, optional): 设置随机种子。`seed` 等于0时,每次返回不同的整数排列;`seed` 不等于0时,相同的 `seed` 返回相同的整数排列。
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ValueError - 如果 ``n`` 不大于0.
+ - TypeError - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是int32、int64、float32、float64.
-返回: 一个数值在0到n-1、顺序随机的整数排列。
-
-返回类型: Variable
-
-**代码示例**:
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
-
- # Note that, the random permutation returned by randperm depends
- # the random seed in computer, so the output in the next example
- # will be change.
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- out_1 = paddle.randperm(6)
- print(out_1.numpy()) # Random permutation, for example [2 4 5 0 3 1]
-
- out_2 = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(
- np.array([0, 1, 2, 3])).astype(np.int64)
- paddle.randperm(6, out_2)
- print(out_2.numpy()) # Random permutation, for example [5 0 2 4 1 3]
-
- out_3 = paddle.randperm(6, dtype="int32", device="cpu")
- print(out_3.numpy()) # Random permutation, for example [3 1 4 2 5 0]
-
- out_4 = paddle.randperm(6, device="cpu", stop_gradient=True)
- print(out_4.numpy()) # Random permutation, for example [3 1 5 2 0 4]
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+
+ result_1 = paddle.randperm(5)
+ # [4 1 2 3 0]
+
+ result_2 = paddle.randperm(7, 'int32')
+ # [1 6 2 0 4 3 5]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/roll_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/roll_cn.rst
index 0c4a1a3edc1a35d31e12a0da092232937033782b..2b5f2685ef1fbeeeda52030f99065e83c76723c5 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/roll_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/roll_cn.rst
@@ -3,19 +3,20 @@
roll
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.roll(input, shifts, dims=None):
+.. py:function:: paddle.roll(x, shifts, axis=None, name=None):
:alias_main: paddle.roll
-:alias: paddle.roll,paddle.tensor.roll,paddle.tensor.manipulation.roll
+:alias: paddle.roll, paddle.tensor.roll, paddle.tensor.manipulation.roll
-该OP沿着指定维度对输入 ``input`` 进行循环滚动,当元素移动到最后位置时,会从第一个位置重新插入。如果 ``dims`` 为 ``None`` ,则输入在被循环滚动之前,会先展平成 ``1-D Tensor`` ,滚动操作完成后恢复成原来的形状。
+该OP沿着指定维度 ``axis`` 对输入 ``x`` 进行循环滚动,当元素移动到最后位置时,会从第一个位置重新插入。如果 ``axis`` 为 ``None`` ,则输入在被循环滚动之前,会先展平成 ``1-D Tensor`` ,滚动操作完成后恢复成原来的形状。
**参数**:
- - **input** (Variable)– 输入张量。
- - **shifts** (int|list|tuple) - 滚动位移。如果 ``shifts`` 是一个元组或者列表,则 ``dims`` 必须是相同大小的元组或者列表,输入张量将依次沿着每个维度滚动相应的数值。
- - **dim** (int|list|tuple, optinal) – 滚动轴。
+ - **x** (Variable)– 输入张量。
+ - **shifts** (int|list|tuple) - 滚动位移。如果 ``shifts`` 是一个元组或者列表,则 ``axis`` 必须是相同大小的元组或者列表,输入张量将依次沿着每个维度滚动相应的数值。
+ - **axis** (int|list|tuple, optinal) – 滚动轴。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
**返回**:
- **Variable**,数据类型同输入。
@@ -26,22 +27,21 @@ roll
import numpy as np
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
data = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0],
[4.0, 5.0, 6.0],
[7.0, 8.0, 9.0]])
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(data)
- out_z1 = paddle.roll(x, shifts=1)
- print(out_z1.numpy())
- #[[9. 1. 2.]
- # [3. 4. 5.]
- # [6. 7. 8.]]
- out_z2 = paddle.roll(x, shifts=1, dims=0)
- print(out_z2.numpy())
- #[[7. 8. 9.]
- # [1. 2. 3.]
- # [4. 5. 6.]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(data)
+ out_z1 = paddle.roll(x, shifts=1)
+ print(out_z1.numpy())
+ #[[9. 1. 2.]
+ # [3. 4. 5.]
+ # [6. 7. 8.]]
+ out_z2 = paddle.roll(x, shifts=1, axis=0)
+ print(out_z2.numpy())
+ #[[7. 8. 9.]
+ # [1. 2. 3.]
+ # [4. 5. 6.]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/sort_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/sort_cn.rst
index 9f627143f3ce7834c17c065280e53129c827c475..dc791485e0327e588091e628b3efdb8e3b04fe00 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/sort_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/sort_cn.rst
@@ -3,73 +3,61 @@
sort
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.sort(input, axis=-1, descending=False, out=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.sort(x, axis=-1, descending=False, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.sort
:alias: paddle.sort,paddle.tensor.sort,paddle.tensor.search.sort
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.argsort
-
-对输入变量沿给定轴进行排序,输出排序好的数据和相应的索引,其维度和输入相同。**默认升序排列,如果需要降序排列设置** ``descending=True`` 。
+对输入变量沿给定轴进行排序,输出排序好的数据,其维度和输入相同。默认升序排列,如果需要降序排列设置 ``descending=True`` 。
参数:
- - **input** (Variable) - 输入的多维 ``Tensor`` ,支持的数据类型:float32、float64、int16、int32、int64、uint8。
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入的多维 ``Tensor`` ,支持的数据类型:float32、float64、int16、int32、int64、uint8。
- **axis** (int,可选) - 指定对输入Tensor进行运算的轴, ``axis`` 的有效范围是[-R, R),R是输入 ``x`` 的Rank, ``axis`` 为负时与 ``axis`` +R 等价。默认值为0。
- **descending** (bool,可选) - 指定算法排序的方向。如果设置为True,算法按照降序排序。如果设置为False或者不设置,按照升序排序。默认值为False。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) – 指定存储运算结果的Tensor(与 ``input`` 维度相同、数据类型相同)。如果设置为None或者不设置,将创建新的Tensor存储运算结果,默认值为None。
- **name** (str,可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-返回:一组已排序的输出(与 ``input`` 维度相同、数据类型相同)和索引(数据类型为int64)。
+返回:Tensor, 排序后的输出(与 ``x`` 维度相同、数据类型相同)。
-返回类型:tuple[Variable]
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- import numpy as np
-
- in1 = np.array([[[5,8,9,5],
- [0,0,1,7],
- [6,9,2,4]],
- [[5,2,4,2],
- [4,7,7,9],
- [1,7,0,6]]]).astype(np.float32)
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- x = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(in1)
- out1 = paddle.sort(input=x, axis=-1) # same as axis==2
- out2 = paddle.sort(input=x, axis=0)
- out3 = paddle.sort(input=x, axis=1)
- print(out1[0].numpy())
- # [[[5. 5. 8. 9.]
- # [0. 0. 1. 7.]
- # [2. 4. 6. 9.]]
- # [[2. 2. 4. 5.]
- # [4. 7. 7. 9.]
- # [0. 1. 6. 7.]]]
- print(out1[1].numpy())
- # [[[0 3 1 2]
- # [0 1 2 3]
- # [2 3 0 1]]
- # [[1 3 2 0]
- # [0 1 2 3]
- # [2 0 3 1]]]
- print(out2[0].numpy())
- # [[[5. 2. 4. 2.]
- # [0. 0. 1. 7.]
- # [1. 7. 0. 4.]]
- # [[5. 8. 9. 5.]
- # [4. 7. 7. 9.]
- # [6. 9. 2. 6.]]]
- print(out3[0].numpy())
- # [[[0. 0. 1. 4.]
- # [5. 8. 2. 5.]
- # [6. 9. 9. 7.]]
- # [[1. 2. 0. 2.]
- # [4. 7. 4. 6.]
- # [5. 7. 7. 9.]]]
-
+ import paddle
+ import paddle.imperative as imperative
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ input_array = np.array([[[5,8,9,5],
+ [0,0,1,7],
+ [6,9,2,4]],
+ [[5,2,4,2],
+ [4,7,7,9],
+ [1,7,0,6]]]).astype(np.float32)
+ x = imperative.to_variable(input_array)
+ out1 = paddle.sort(x=x, axis=-1)
+ out2 = paddle.sort(x=x, axis=0)
+ out3 = paddle.sort(x=x, axis=1)
+ print(out1.numpy())
+ #[[[5. 5. 8. 9.]
+ # [0. 0. 1. 7.]
+ # [2. 4. 6. 9.]]
+ # [[2. 2. 4. 5.]
+ # [4. 7. 7. 9.]
+ # [0. 1. 6. 7.]]]
+ print(out2.numpy())
+ #[[[5. 2. 4. 2.]
+ # [0. 0. 1. 7.]
+ # [1. 7. 0. 4.]]
+ # [[5. 8. 9. 5.]
+ # [4. 7. 7. 9.]
+ # [6. 9. 2. 6.]]]
+ print(out3.numpy())
+ #[[[0. 0. 1. 4.]
+ # [5. 8. 2. 5.]
+ # [6. 9. 9. 7.]]
+ # [[1. 2. 0. 2.]
+ # [4. 7. 4. 6.]
+ # [5. 7. 7. 9.]]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/split_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/split_cn.rst
index 4f3aca783c3bd2ca5cf105dce727c3475fc7a06b..52f85fcccef62b2dc97d34bb4626b8fbefa1435b 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/split_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/split_cn.rst
@@ -2,39 +2,55 @@
split
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.split(input, num_or_sections, dim=-1, name=None)
-
-:alias_main: paddle.split
-:alias: paddle.split,paddle.tensor.split,paddle.tensor.manipulation.split
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.split
+.. py:function:: paddle.tensor.split(x, num_or_sections, axis=0, name=None)
该OP将输入Tensor分割成多个子Tensor。
**参数**:
- - **input** (Variable) - 输入变量,数据类型为float32,float64,int32,int64的多维Tensor或者LoDTensor。
- - **num_or_sections** (int|list|tuple) - 如果 num_or_sections 是一个整数,则表示Tensor平均划分为相同大小子Tensor的数量。如果 num_or_sections 是一个list或tuple,那么它的长度代表子Tensor的数量,它的元素可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,依次代表子Tensor需要分割成的维度的大小。list或tuple的长度不能超过输入Tensor待分割的维度的大小。在list或tuple中,至多有一个元素值为-1,表示该值是由input的维度和其他num_or_sections中元素推断出来的。例如对一个维度为[4,6,6]Tensor的第三维进行分割时,指定num_or_sections=[2,-1,1],输出的三个Tensor维度分别为:[4,6,2],[4,6,3],[4,6,1]。
- - **dim** (int|Variable,可选) - 整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或int64。表示需要分割的维度。如果dim < 0,则划分的维度为rank(input) + dim。默认值为-1。
- - **name** (str,可选) - 一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+ - **x** (Tensor) - 输入变量,数据类型为bool, float16, float32,float64,int32,int64的多维Tensor。
+ - **num_or_sections** (int|list|tuple) - 如果 ``num_or_sections`` 是一个整数,则表示Tensor平均划分为相同大小子Tensor的数量。如果 ``num_or_sections`` 是一个list或tuple,那么它的长度代表子Tensor的数量,它的元素可以是整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,依次代表子Tensor需要分割成的维度的大小。list或tuple的长度不能超过输入Tensor待分割的维度的大小。在list或tuple中,至多有一个元素值为-1,表示该值是由 ``x`` 的维度和其他 ``num_or_sections`` 中元素推断出来的。例如对一个维度为[4,6,6]Tensor的第三维进行分割时,指定 ``num_or_sections=[2,-1,1]`` ,输出的三个Tensor维度分别为:[4,6,2],[4,6,3],[4,6,1]。
+ - **axis** (int|Tensor,可选) - 整数或者形状为[1]的Tensor,数据类型为int32或int64。表示需要分割的维度。如果 ``axis < 0`` ,则划分的维度为 ``rank(x) + axis`` 。默认值为0。
+ - **name** (str,可选) – 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
-**返回**:分割后的Tensor列表。
+返回:分割后的Tensor列表。
-**返回类型**:列表(Variable(Tensor|LoDTensor)),数据类型为int32,int64,float32,float64。
+抛出异常:
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``x`` 的数据类型不是float16、float32、float64、int32或int64时 。
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``num_or_sections`` 不是int、list 或 tuple时。
+ - :code:`TypeError`:``axis`` 不是 int 或 Tensor时。当 ``axis`` 为Tensor,其数据类型不是int32或int64时。
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
- with fluid.dygraph.guard():
- input_1 = np.random.random([4, 6, 6]).astype("int32")
- # input is a variable which shape is [4, 6, 6]
- input = fluid.dygraph.to_variable(input_1)
-
- x0, x1, x2 = paddle.split(input, num_or_sections= 3, dim=1)
- # x0.shape [4, 2, 6]
- # x1.shape [4, 2, 6]
- # x2.shape [4, 2, 6]
+ import paddle
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ # x is a Tensor which shape is [3, 9, 5]
+ x_np = np.random.random([3, 9, 5]).astype("int32")
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(x_np)
+
+ out0, out1, out22 = paddle.split(x, num_or_sections=3, axis=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 3, 5]
+
+ out0, out1, out2 = paddle.split(x, num_or_sections=[2, 3, 4], axis=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 2, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 4, 5]
+
+ out0, out1, out2 = paddle.split(x, num_or_sections=[2, 3, -1], axis=1)
+ # out0.shape [3, 2, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 4, 5]
+
+ # axis is negative, the real axis is (rank(x) + axis) which real
+ # value is 1.
+ out0, out1, out2 = paddle.split(x, num_or_sections=3, axis=-2)
+ # out0.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out1.shape [3, 3, 5]
+ # out2.shape [3, 3, 5]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/trace_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/trace_cn.rst
index e2f0e3b9456672c2b848f6eac3915045aa976606..53fb3edc54ffac22508d792ea34971c85d50b471 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/trace_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/trace_cn.rst
@@ -3,10 +3,10 @@
trace
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.trace(input, offset=0, dim1=0, dim2=1)
+.. py:function:: paddle.trace(x, offset=0, axis1=0, axis2=1, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.trace
-:alias: paddle.trace,paddle.tensor.trace,paddle.tensor.math.trace
+:alias: paddle.trace, paddle.tensor.trace, paddle.tensor.math.trace
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ trace
如果输入是 2D Tensor,则返回对角线元素之和。
-如果输入的维度大于 2D,则返回一个由对角线元素之和组成的数组,其中对角线从由 dim1 和 dim2 指定的二维平面中获得。默认由输入的前两维组成获得对角线的 2D 平面。
+如果输入的维度大于 2D,则返回一个由对角线元素之和组成的数组,其中对角线从由 axis1 和 axis2 指定的二维平面中获得。默认由输入的前两维组成获得对角线的 2D 平面。
参数 ``offset`` 确定从指定的二维平面中获取对角线的位置:
@@ -23,10 +23,11 @@ trace
- 如果 offset < 0,则取主对角线左下的对角线。
参数:
- - **input** (Variable)- 输入变量,至少为 2D 数组,支持数据类型为 float32,float64,int32,int64。
+ - **x** (Variable)- 输入张量,至少为 2D 数组,支持数据类型为 float32,float64,int32,int64。
- **offset** (int ,可选)- 从指定的二维平面中获取对角线的位置,默认值为 0,既主对角线。
- - **dim1** (int , 可选)- 获取对角线的二维平面的第一维,默认值为 0。
- - **dim2** (int , 可选)- 获取对角线的二维平面的第二维,默认值为 1。
+ - **axis1** (int , 可选)- 获取对角线的二维平面的第一维,默认值为 0。
+ - **axis2** (int , 可选)- 获取对角线的二维平面的第二维,默认值为 1。
+ - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回: 指定二维平面的对角线元素之和。数据类型和输入数据类型一致。
@@ -36,18 +37,17 @@ trace
.. code-block:: python
- import paddle.tensor as tensor
- import paddle.fluid.dygraph as dg
+ import paddle
import numpy as np
-
+
case1 = np.random.randn(2, 3).astype('float32')
case2 = np.random.randn(3, 10, 10).astype('float32')
case3 = np.random.randn(3, 10, 5, 10).astype('float32')
-
- with dg.guard():
- case1 = dg.to_variable(case1)
- case2 = dg.to_variable(case2)
- case3 = dg.to_variable(case3)
- data1 = tensor.trace(case1) # data1.shape = [1]
- data2 = tensor.trace(case2, offset=1, dim1=1, dim2=2) # data2.shape = [3]
- data3 = tensor.trace(case3, offset=-3, dim1=1, dim2=-1) # data2.shape = [3, 5]
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ case1 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(case1)
+ case2 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(case2)
+ case3 = paddle.imperative.to_variable(case3)
+ data1 = paddle.trace(case1) # data1.shape = [1]
+ data2 = paddle.trace(case2, offset=1, axis1=1, axis2=2) # data2.shape = [3]
+ data3 = paddle.trace(case3, offset=-3, axis1=1, axis2=-1) # data2.shape = [3, 5]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_cn.rst
index 0734e744979b08b8bed3dd8724242fbb325d9eb3..e84538f784551d1d0becbf6933bfcadcaaa26413 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_cn.rst
@@ -3,31 +3,41 @@
zeros
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.zeros(shape, dtype, out=None, device=None)
-
-:alias_main: paddle.zeros
-:alias: paddle.zeros,paddle.tensor.zeros,paddle.tensor.creation.zeros
-:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.zeros
+.. py:function:: paddle.zeros(shape, dtype=None, name=None)
该OP创建形状为 ``shape`` 、数据类型为 ``dtype`` 且值全为0的Tensor。
参数:
- - **shape** (tuple|list) - 输出Tensor的形状。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。
- - **out** (Variable, 可选) – 指定存储运算结果的Tensor。如果设置为None或者不设置,将创建新的Tensor存储运算结果,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
+ - **shape** (tuple|list|Tensor) - 输出Tensor的形状, ``shape`` 的数据类型为int32或者int64。
+ - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str,可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,数据类型必须为bool、float16、float32、float64、int32或int64。若为None,数据类型为float32, 默认为None。
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
返回:值全为0的Tensor,数据类型和 ``dtype`` 定义的类型一致。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常:
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``dtype`` 不是bool、 float16、float32、float64、int32、int64和None时。
+ - ``TypeError`` - 当 ``shape`` 不是tuple、list、或者Tensor时, 当 ``shape`` 为Tensor,其数据类型不是int32或者int64时。
**代码示例**:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- data = paddle.zeros(shape=[3, 2], dtype='float32') # [[0., 0.], [0., 0.], [0., 0.]]
- data = paddle.zeros(shape=[2, 2], dtype='float32', device='cpu') # [[0., 0.], [0., 0.]]
+ paddle.enable_imperative() # Now we are in imperative mode
+ data = paddle.zeros(shape=[3, 2], dtype='float32')
+ # [[0. 0.]
+ # [0. 0.]
+ # [0. 0.]]
+
+ data = paddle.zeros(shape=[2, 2])
+ # [[0. 0.]
+ # [0. 0.]]
+
+ # shape is a Tensor
+ shape = paddle.fill_constant(shape=[2], dtype='int32', value=2)
+ data3 = paddle.zeros(shape=shape, dtype='int32')
+ # [[0 0]
+ # [0 0]]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_like_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_like_cn.rst
index bf1c923573df4a0eab94c291a267d5324edd3013..7cdacfeb44ff8553cc98230f10e309340dab5cd7 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_like_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/tensor_cn/zeros_like_cn.rst
@@ -3,33 +3,38 @@
zeros_like
-------------------------------
-.. py:function:: paddle.zeros_like(input, dtype=None, device=None, name=None)
+.. py:function:: paddle.zeros_like(x, dtype=None, name=None)
:alias_main: paddle.zeros_like
-:alias: paddle.zeros_like,paddle.tensor.zeros_like,paddle.tensor.creation.zeros_like
+:alias: paddle.tensor.zeros_like, paddle.tensor.creation.zeros_like
:update_api: paddle.fluid.layers.zeros_like
+该OP返回一个和 ``x`` 具有相同的形状的全零Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype`` 或者和 ``x`` 相同。
-
-
-该OP创建一个和input具有相同的形状和数据类型的全零Tensor。
-
-参数:
- - **input** (Variable) – 指定输入为一个多维的Tensor,数据类型可以是bool,float32,float64,int32,int64。
- - **dtype** (np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType|str, 可选)- 输出变量的数据类型。若参数为空,则输出变量的数据类型和输入变量相同,默认值为None。
- - **device** (str,可选) – 选择在哪个设备运行该操作,可选值包括None,'cpu'和'gpu'。如果 ``device`` 为None,则将选择运行Paddle程序的设备,默认为None。
- - **name** (str,可选)- 具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` ,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
+参数
+::::::::::
+ - **x** (Tensor) – 输入的多维Tensor,数据类型可以是bool,float16, float32,float64,int32,int64。输出Tensor的形状和 ``x`` 相同。如果 ``dtype`` 为None,则输出Tensor的数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。
+ - **dtype** (str|np.dtype|core.VarDesc.VarType, 可选) - 输出Tensor的数据类型,支持bool,float16, float32,float64,int32,int64。当该参数值为None时, 输出Tensor的数据类型与 ``x`` 相同。默认值为None.
+ - **name** (str, 可选) - 输出的名字。一般无需设置,默认值为None。该参数供开发人员打印调试信息时使用,具体用法请参见 :ref:`api_guide_Name` 。
-返回:返回一个存储结果的Tensor。
+返回
+::::::::::
+ Tensor:和 ``x`` 具有相同的形状全零Tensor,数据类型为 ``dtype`` 或者和 ``x`` 相同。
-返回类型:Variable
+抛出异常
+::::::::::
+ - ``TypeError`` - 如果 ``dtype`` 不是bool、float16、float32、float64、int32、int64。
-**代码示例**:
+代码示例
+::::::::::
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
- import paddle.fluid as fluid
- x = fluid.data(name='x', dtype='float32', shape=[3])
- data1 = paddle.ones_like(input=x, device="gpu") # data1=[1.0, 1.0. 1.0]
+ import numpy as np
+
+ paddle.enable_imperative()
+ x = paddle.imperative.to_variable(np.array([1,2,3], dtype='float32'))
+ out1 = paddle.zeros_like(x) # [0., 0., 0.]
+ out2 = paddle.zeros_like(x, dtype='int32') # [0, 0, 0]
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn.rst
index 4a84c5fbc465f0f8be342a0abcf07dc886b1eea5..ebf4661d09d8b21dba989e162e13fed5a9bda454 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn.rst
@@ -13,4 +13,3 @@ fluid.transpiler
transpiler_cn/HashName_cn.rst
transpiler_cn/memory_optimize_cn.rst
transpiler_cn/release_memory_cn.rst
- transpiler_cn/RoundRobin_cn.rst
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn/RoundRobin_cn.rst b/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn/RoundRobin_cn.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index aa4b7d3890d40c58ca568ece75d9e5d26a311559..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/doc/fluid/api_cn/transpiler_cn/RoundRobin_cn.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-.. _cn_api_fluid_transpiler_RoundRobin:
-
-RoundRobin
--------------------------------
-
-
-.. py:class:: paddle.fluid.transpiler.RoundRobin(pserver_endpoints)
-
-:api_attr: 声明式编程模式(静态图)
-
-
-
-该方法使用 ``RoundRobin`` 的方式将变量散列到多个parameter server终端。
-
-`RondRobin `_
-
-参数:
- - **pserver_endpoints** (list) - endpoint (ip:port)的 list
-
-返回:实例化后的RoundRobin的对象
-
-返回类型:RoundRobin
-
-**代码示例**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import paddle.fluid.transpiler.RoundRobin as RoundRobin
-
- pserver_endpoints = [“127.0.0.1:6007”, “127.0.0.1:6008”]
- vars = [“var1”,”var2”,”var3”,”var4”,”var5”]
- rr = RoundRobin(pserver_endpoints)
- rr.dispatch(vars)
-
-
-.. py:method:: dispatch(varlist)
-
-该方法使用RoundRobin的方式将多个参数散列到多个parameter Server终端。
-
-参数:
- - **varlist** (list) - 参数 (var1, var2, var3) 的 list
-
-返回:基于varlist中var的顺序,返回参数服务器(ip:port)的列表, 列表中的数据量和varlist的数据量一致。
-
-返回类型:list
-
-**代码示例**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- pserver_endpoints = [“127.0.0.1:6007”, “127.0.0.1:6008”]
- vars = [“var1”,”var2”,”var3”,”var4”,”var5”]
- rr = RoundRobin(pserver_endpoints)
- rr.dispatch(vars)
-
-
-.. py:method:: reset()
-
-该方法将重置RoundRobin内置的计数, 计数将重置为0。
-
-返回:无。
-
-**代码示例**
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- pserver_endpoints = [“127.0.0.1:6007”, “127.0.0.1:6008”]
- vars = [“var1”,”var2”,”var3”,”var4”,”var5”]
- rr = RoundRobin(pserver_endpoints)
- rr.reset()
-
-
diff --git a/doc/fluid/api_guides/X2Paddle/TensorFlow-Fluid.rst b/doc/fluid/api_guides/X2Paddle/TensorFlow-Fluid.rst
index 20ee91c8cd7c19c6521b68962647f46620b436aa..e219eb272ed508e70350ed3a0dfa69f416337a1d 100644
--- a/doc/fluid/api_guides/X2Paddle/TensorFlow-Fluid.rst
+++ b/doc/fluid/api_guides/X2Paddle/TensorFlow-Fluid.rst
@@ -4,151 +4,152 @@
TensorFlow-Fluid常用接口对应表
###############################
-本文档基于TensorFlow v1.13梳理了常用API与PaddlePaddle API对应关系和差异分析。根据文档对应关系,有TensorFlow使用经验的用户,可根据对应关系,快速熟悉PaddlePaddle的接口使用。
+本文档基于TensorFlow v1.15梳理了常用API与PaddlePaddle API对应关系和差异分析。根据文档对应关系,有TensorFlow使用经验的用户,可根据对应关系,快速熟悉PaddlePaddle的接口使用。
.. csv-table::
:header: "序号", "TensorFlow接口", "Fluid接口", "备注"
:widths: 1, 8, 8, 3
- "1", "`tf.abs `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_abs`", "功能一致"
- "2", "`tf.add `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_add`", "功能一致"
- "3", "`tf.argmax `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_argmax`", "功能一致"
- "4", "`tf.argmin `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_argmin`", "功能一致"
- "5", "`tf.assign `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_assign`", "功能一致"
- "6", "`tf.assign_add `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_increment`", "功能一致"
- "7", "`tf.case `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_Switch`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "8", "`tf.cast `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_cast`", "功能一致"
- "9", "`tf.clip_by_global_norm `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_clip_GradientClipByGlobalNorm`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "10", "`tf.clip_by_norm `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_clip_by_norm`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "11", "`tf.clip_by_value `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_clip`", "功能一致"
- "12", "`tf.concat `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_concat`", "功能一致"
- "13", "`tf.cond `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_ifElse`", "功能一致"
- "14", "`tf.constant `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_fill_constant`", "功能一致"
- "15", "`tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_batch_norm`", "功能一致"
- "16", "`tf.contrib.layers.flatten `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_flatten`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "17", "`tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_fc`", "功能一致"
- "18", "`tf.contrib.layers.one_hot_encoding `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_one_hot`", "功能一致"
- "19", "`tf.contrib.layers.softmax `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softmax`", "功能一致"
- "20", "`tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_initializer_Xavier`", "功能一致"
- "21", "`tf.nn.rnn.GRUCell `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_gru_unit`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "22", "`tf.nn.rnn.MultiRNNCell `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "23", "`tf.nn.rnn.static_rnn `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_DynamicRNN`", "功能一致"
- "24", "`tf.convert_to_tensor `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_assign`", "功能一致"
- "25", "`tf.cos `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_cos`", "功能一致"
- "26", "`tf.div `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_div`", "功能一致"
- "27", "`tf.divide `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_div`", "功能一致"
- "28", "`tf.dropout `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_dropout`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "29", "`tf.equal `_", "`运算符== `_", "功能一致"
- "30", "`tf.exp `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_exp`", "功能一致"
- "31", "`tf.expand_dims `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_unsqueeze`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "32", "`tf.fill `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_fill_constant`", "功能一致"
- "33", "`tf.floor `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_floor`", "功能一致"
- "34", "`tf.gather `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_gather`", "功能一致"
- "35", "`tf.greater `_", "`运算符> `_", "功能一致"
- "36", "`tf.greater_equal `_", "`运算符>= `_", "功能一致"
- "37", "`tf.image.non_max_suppression `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_multiclass_nms`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "38", "`tf.image.resize_bilinear `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_resize_bilinear`", "功能一致"
- "39", "`tf.image.resize_images `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_image_resize`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "40", "`tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_resize_nearest`", "功能一致"
- "41", "`tf.is_finite `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_isfinite`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "42", "`tf.layers.batch_normalization `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_batch_norm`", "功能一致"
- "43", "`tf.layers.conv2d `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_conv2d`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "44", "`tf.layers.dense `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_fc`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "45", "`tf.layers.dropout `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_dropout`", "功能一致"
- "46", "`tf.layers.Dropout `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_dropout`", "功能一致"
- "47", "`tf.layers.flatten `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_flatten`", "功能一致"
- "48", "`tf.less `_", "`运算符< `_", "功能一致"
- "49", "`tf.less_equal `_", "`运算符<= `_", "功能一致"
- "50", "`tf.log `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_log`", "功能一致"
- "51", "`tf.logical_and `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_logical_and`", "功能一致"
- "52", "`tf.logical_not `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_logical_not`", "功能一致"
- "53", "`tf.logical_or `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_logical_or`", "功能一致"
- "54", "`tf.losses.mean_squared_error `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_square_error_cost`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "55", "`tf.losses.sigmoid_cross_entropy `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "56", "`tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softmax_with_cross_entropy`", "功能一致"
- "57", "`tf.matmul `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_matmul`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "58", "`tf.maximum `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_max`", "功能一致"
- "59", "`tf.metrics.accuracy `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_accuracy`", "功能一致"
- "60", "`tf.metrics.mean `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_mean`", "功能一致"
- "61", "`tf.minimum `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_min`", "功能一致"
- "62", "`tf.multiply `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_mul`", "功能一致"
- "63", "`tf.nn.avg_pool `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_pool2d`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "64", "`tf.nn.batch_normalization `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_batch_norm`", "功能一致"
- "65", "`tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "66", "`tf.nn.conv2d `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_conv2d`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "67", "`tf.nn.conv2d_transpose `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_conv2d_transpose`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "68", "`tf.nn.conv3d_transpose `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_conv3d_transpose`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "69", "`tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_conv2d`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "70", "`tf.nn.dynamic_rnn `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_DynamicRNN`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "71", "`tf.nn.l2_normalize `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_l2_normalize`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "72", "`tf.nn.leaky_relu `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_leaky_relu`", "功能一致"
- "73", "`tf.nn.lrn `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_lrn`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "74", "`tf.nn.max_pool `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_pool2d`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "75", "`tf.nn.relu `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_relu`", "功能一致"
- "76", "`tf.nn.relu6 `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_relu6`", "功能一致"
- "77", "`tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_lstm_unit`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "78", "`tf.nn.separable_conv2d `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "79", "`tf.nn.sigmoid `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sigmoid`", "功能一致"
- "80", "`tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits`", "功能一致"
- "81", "`tf.nn.softmax `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softmax`", "功能一致"
- "82", "`tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softmax_with_cross_entropy`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "83", "`tf.nn.softplus `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softplus`", "功能一致"
- "84", "`tf.nn.softsign `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_softsign`", "功能一致"
- "85", "`tf.nn.tanh `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_tanh`", "功能一致"
- "86", "`tf.one_hot `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_one_hot`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "87", "`tf.ones `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_ones`", "功能一致"
- "88", "`tf.intializers.ones `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_initializer_Constant`", "功能一致"
- "89", "`tf.pad `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_pad`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "90", "`tf.placeholder `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_data`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "91", "`tf.pow `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_pow`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "92", "`tf.print `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_print`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "93", "`tf.py_func `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_py_func`", "功能一致"
- "94", "`tf.random_normal `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_gaussian_random`", "功能一致"
- "95", "`tf.random_normal_initializer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_initializer_Normal`", "功能一致"
- "96", "`tf.random_uniform `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_uniform_random`", "功能一致"
- "97", "`tf.random_uniform_initializer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_initializer_UniformInitializer`", "功能一致"
- "98", "`tf.reduce_logsumexp `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "99", "`tf.reduce_max `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_max`", "功能一致"
- "100", "`tf.reduce_mean `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_mean`", "功能一致"
- "101", "`tf.reduce_min `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_min`", "功能一致"
- "102", "`tf.reduce_sum `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reduce_sum`", "功能一致"
- "103", "`tf.reshape `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reshape`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "104", "`tf.reverse `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reverse`", "功能一致"
- "105", "`tf.reverse_sequence `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sequence_reverse`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "106", "`tf.reverse_v2 `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_reverse`", "功能一致"
- "107", "`tf.round `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_round`", "功能一致"
- "108", "`tf.rsqrt `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_rsqrt`", "功能一致"
- "109", "`tf.scalar_mul `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_scale`", "功能一致"
- "110", "`tf.scatter_update `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_scatter`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "111", "`tf.sequence_mask `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sequence_mask`", "功能一致"
- "112", "`tf.shape `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_shape`", "功能一致"
- "113", "`tf.sigmoid `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sigmoid`", "功能一致"
- "114", "`tf.sin `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sin`", "功能一致"
- "115", "`tf.slice `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_slice`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "116", "`tf.split `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_split`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "117", "`tf.sqrt `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_sqrt`", "功能一致"
- "118", "`tf.square `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_square`", "功能一致"
- "119", "`tf.squared_difference `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "120", "`tf.squeeze `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_squeeze`", "功能一致"
- "121", "`tf.stack `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_stack`", "功能一致"
- "122", "`tf.stop_gradient `_", "无相应接口", "`Fluid实现 `_"
- "123", "`tf.subtract `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_elementwise_sub`", "功能一致"
- "124", "`tf.tanh `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_tanh`", "功能一致"
- "125", "`tf.tile `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_expand`", "功能一致"
- "126", "`tf.top_k `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_topk`", "`差异对比 `_"
- "127", "`tf.train.AdagradOptimizer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_optimizer_AdagradOptimizer`", "功能一致"
- "128", "`tf.train.AdamOptimizer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_optimizer_Adam`", "功能一致"
- "129", "`tf.train.exponential_decay `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_layers_exponential_decay`", "功能一致"
- "130", "`tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_optimizer_SGDOptimizer`", "功能一致"
- "131", "`tf.train.MomentumOptimizer `_", ":ref:`cn_api_fluid_optimizer_MomentumOptimizer`", "功能一致"
- "132", "`tf.train.polynomial_decay  +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ 


 +
+ +
+ +
+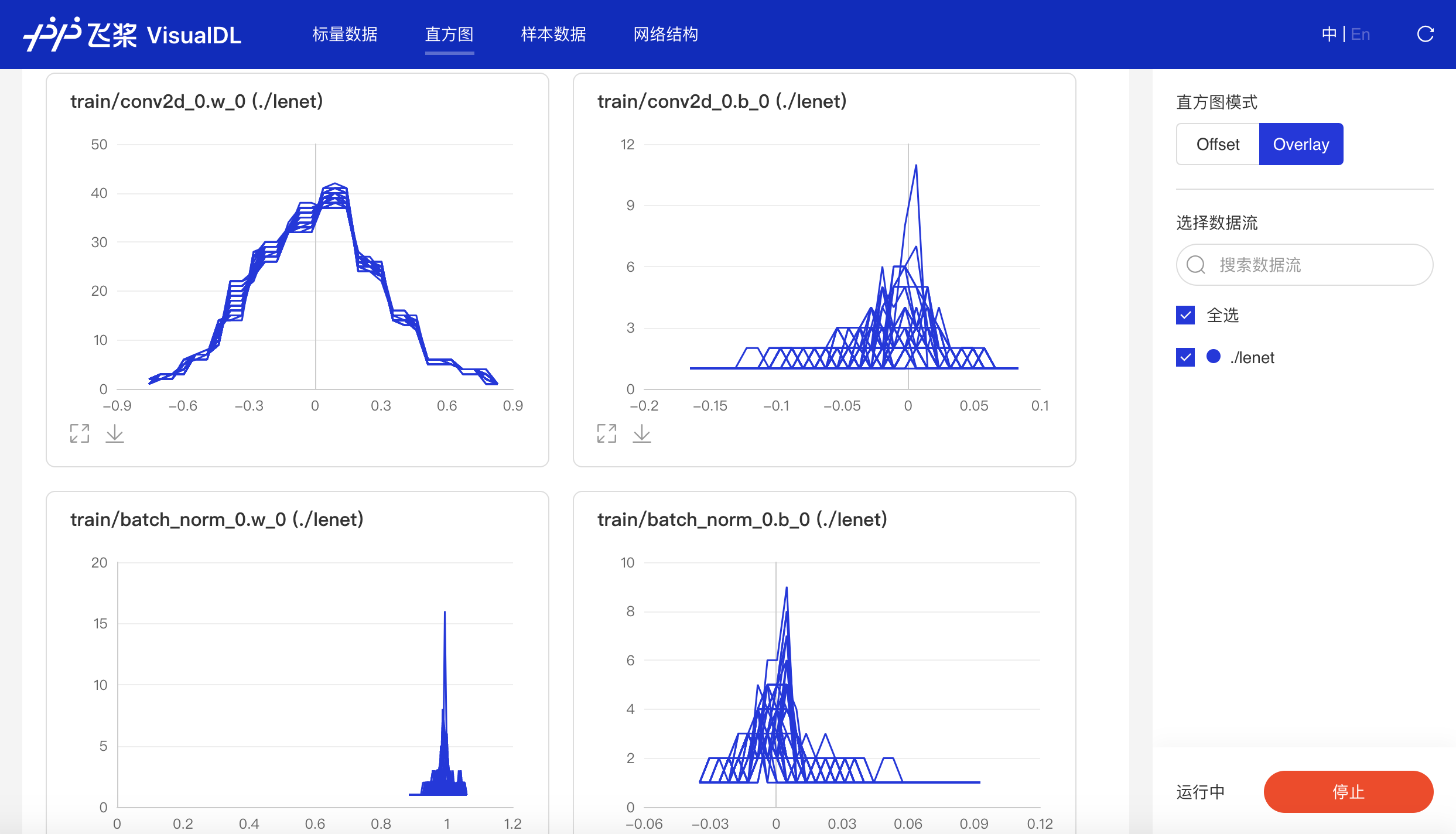 +
+ +
+ +
+ 
 +
+
 +
+ 
 +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+ +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+ 
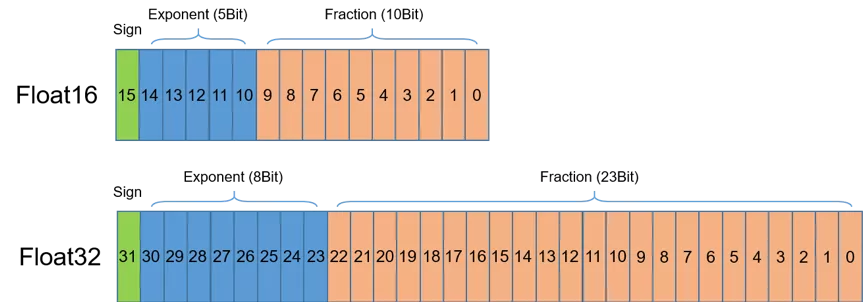 +
+ 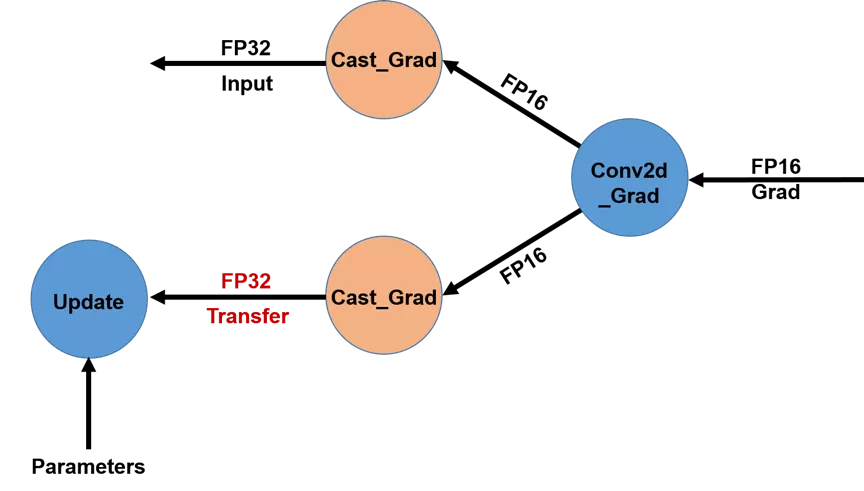 +
+ 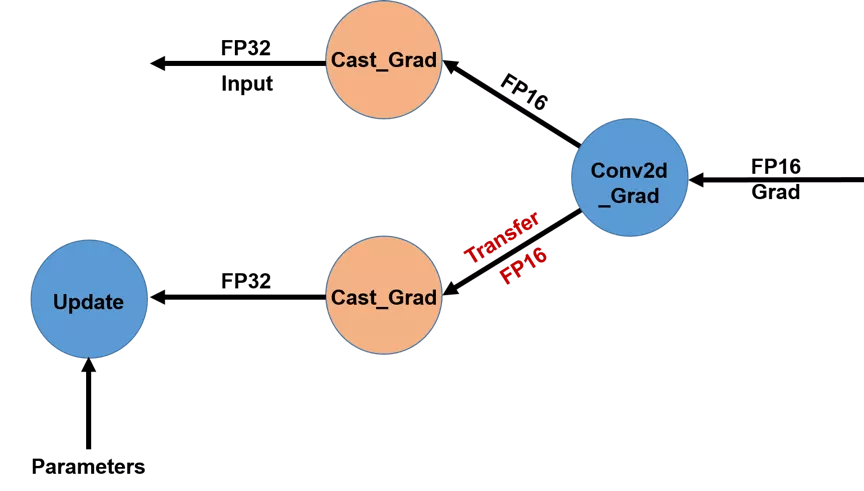 +
+