# Models introduction
## Streaming DeepSpeech2
The implemented arcitecure of Deepspeech2 online model is based on [Deepspeech2 model](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.02595.pdf) with some changes.
The model is mainly composed of 2D convolution subsampling layer and stacked single direction rnn layers.
To illustrate the model implementation clearly, 3 parts are described in detail.
- Data Preparation
- Encoder
- Decoder
In addition, the training process and the testing process are also introduced.
The arcitecture of the model is shown in Fig.1.
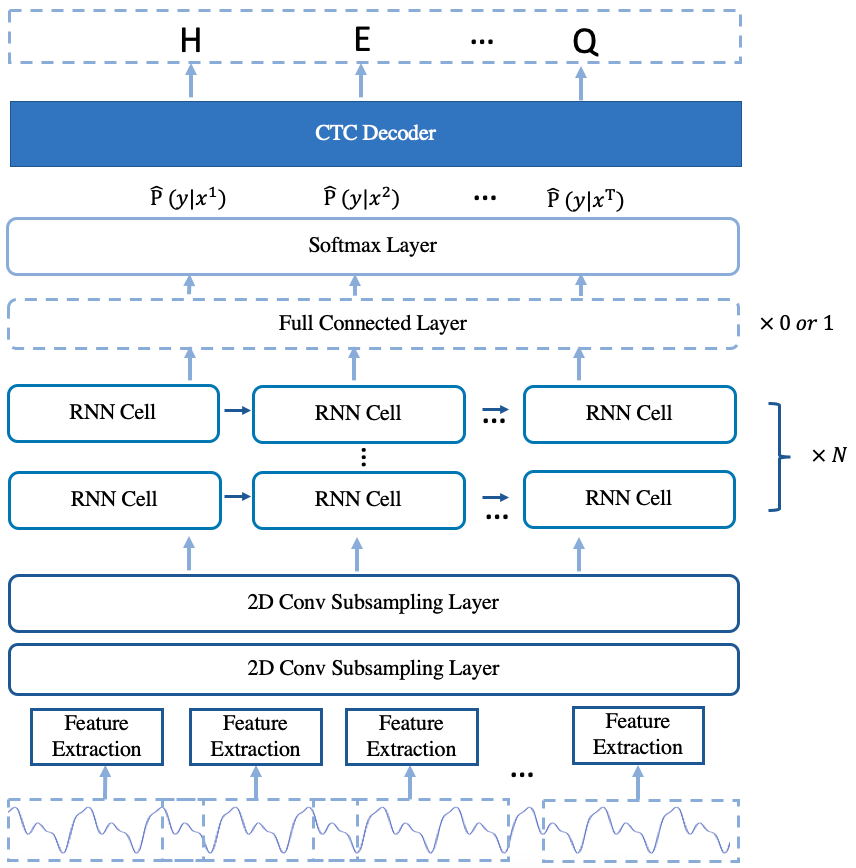
Fig.1 The Arcitecture of deepspeech2 online model
### Data Preparation
#### Vocabulary
For English data, the vocabulary dictionary is composed of 26 English characters with " ' ", space, \ and \. The \ represents the blank label in CTC, the \ represents the unknown character and the \ represents the start and the end characters. For mandarin, the vocabulary dictionary is composed of chinese characters statisticed from the training set and three additional characters are added. The added characters are \, \ and \. For both English and mandarin data, we set the default indexs that \=0, \=1 and \= last index.
```
# The code to build vocabulary
cd examples/aishell/s0
python3 ../../../utils/build_vocab.py \
--unit_type="char" \
--count_threshold=0 \
--vocab_path="data/vocab.txt" \
--manifest_paths "data/manifest.train.raw" "data/manifest.dev.raw"
# vocabulary for aishell dataset (Mandarin)
vi examples/aishell/s0/data/vocab.txt
# vocabulary for librispeech dataset (English)
vi examples/librispeech/s0/data/vocab.txt
```
#### CMVN
For CMVN, a subset or the full of traininig set is chosed and be used to compute the feature mean and std.
```
# The code to compute the feature mean and std
cd examples/aishell/s0
python3 ../../../utils/compute_mean_std.py \
--manifest_path="data/manifest.train.raw" \
--spectrum_type="linear" \
--delta_delta=false \
--stride_ms=10.0 \
--window_ms=20.0 \
--sample_rate=16000 \
--use_dB_normalization=True \
--num_samples=2000 \
--num_workers=10 \
--output_path="data/mean_std.json"
```
#### Feature Extraction
For feature extraction, three methods are implemented, which are linear (FFT without using filter bank), fbank and mfcc.
Currently, the released deepspeech2 online model use the linear feature extraction method.
```
The code for feature extraction
vi deepspeech/frontend/featurizer/audio_featurizer.py
```
### Encoder
The encoder is composed of two 2D convolution subsampling layers and a number of stacked single direction rnn layers. The 2D convolution subsampling layers extract feature representation from the raw audio feature and reduce the length of audio feature at the same time. After passing through the convolution subsampling layers, then the feature representation are input into the stacked rnn layers. For the stacked rnn layers, LSTM cell and GRU cell are provided to use. Adding one fully connected (fc) layer after the stacked rnn layers is optional. If the number of stacked rnn layers is less than 5, adding one fc layer after stacked rnn layers is recommand.
The code of Encoder is in:
```
vi deepspeech/models/ds2_online/deepspeech2.py
```
### Decoder
To got the character possibilities of each frame, the feature representation of each frame output from the encoder are input into a projection layer which is implemented as a dense layer to do feature projection. The output dim of the projection layer is same with the vocabulary size. After projection layer, the softmax function is used to transform the frame-level feature representation be the possibilities of characters. While making model inference, the character possibilities of each frame are input into the CTC decoder to get the final speech recognition results.
The code of the decoder is in:
```
# The code of constructing the decoder in model
vi deepspeech/models/ds2_online/deepspeech2.py
# The code of CTC Decoder
vi deepspeech/modules/ctc.py
```
### Training Process
Using the command below, you can train the deepspeech2 online model.
```
cd examples/aishell/s0
bash run.sh --stage 0 --stop_stage 2 --model_type online --conf_path conf/deepspeech2_online.yaml
```
The detail commands are:
```
# The code for training in run.sh
set -e
source path.sh
gpus=2,3,5,7
stage=0
stop_stage=5
conf_path=conf/deepspeech2_online.yaml # conf/deepspeech2.yaml | conf/deepspeech2_online.yaml
avg_num=1
model_type=online # online | offline
source ${MAIN_ROOT}/utils/parse_options.sh || exit 1;
avg_ckpt=avg_${avg_num}
ckpt=$(basename ${conf_path} | awk -F'.' '{print $1}')
echo "checkpoint name ${ckpt}"
if [ ${stage} -le 0 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 0 ]; then
# prepare data
bash ./local/data.sh || exit -1
fi
if [ ${stage} -le 1 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 1 ]; then
# train model, all `ckpt` under `exp` dir
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${gpus} ./local/train.sh ${conf_path} ${ckpt} ${model_type}
fi
if [ ${stage} -le 2 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 2 ]; then
# avg n best model
avg.sh exp/${ckpt}/checkpoints ${avg_num}
fi
```
By using the command above, the training process can be started. There are 5 stages in "run.sh", and the first 3 stages are used for training process. The stage 0 is used for data preparation, in which the dataset will be downloaded, and the manifest files of the datasets, vocabulary dictionary and CMVN file will be generated in "./data/". The stage 1 is used for training the model, the log files and model checkpoint is saved in "exp/deepspeech2_online/". The stage 2 is used to generated final model for predicting by averaging the top-k model parameters based on validation loss.
### Testing Process
Using the command below, you can test the deepspeech2 online model.
```
bash run.sh --stage 3 --stop_stage 5 --model_type online --conf_path conf/deepspeech2_online.yaml
```
The detail commands are:
```
conf_path=conf/deepspeech2_online.yaml
avg_num=1
model_type=online
avg_ckpt=avg_${avg_num}
if [ ${stage} -le 3 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 3 ]; then
# test ckpt avg_n
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 ./local/test.sh ${conf_path} exp/${ckpt}/checkpoints/${avg_ckpt} ${model_type}|| exit -1
fi
if [ ${stage} -le 4 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 4 ]; then
# export ckpt avg_n
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=5 ./local/export.sh ${conf_path} exp/${ckpt}/checkpoints/${avg_ckpt} exp/${ckpt}/checkpoints/${avg_ckpt}.jit ${model_type}
fi
if [ ${stage} -le 5 ] && [ ${stop_stage} -ge 5 ]; then
# test export ckpt avg_n
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 ./local/test_export.sh ${conf_path} exp/${ckpt}/checkpoints/${avg_ckpt}.jit ${model_type}|| exit -1
fi
```
After the training process, we use stage 3,4,5 for testing process. The stage 3 is for testing the model generated in the stage 2 and provided the CER index of the test set. The stage 4 is for transforming the model from dynamic graph to static graph by using "paddle.jit" library. The stage 5 is for testing the model in static graph.
## Non-Streaming DeepSpeech2
The deepspeech2 offline model is similarity to the deepspeech2 online model. The main difference between them is the offline model use the stacked bi-directional rnn layers while the online model use the single direction rnn layers and the fc layer is not used. For the stacked bi-directional rnn layers in the offline model, the rnn cell and gru cell are provided to use.
The arcitecture of the model is shown in Fig.2.
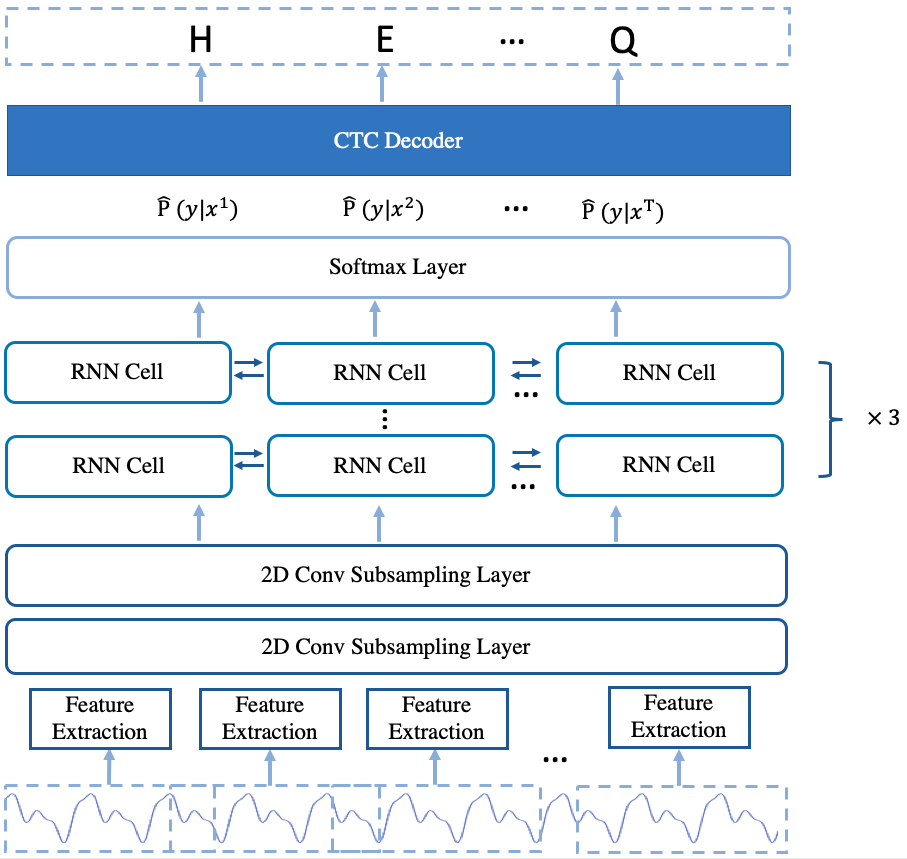
Fig.2 The Arcitecture of deepspeech2 offline model
For data preparation and decoder, the deepspeech2 offline model is same with the deepspeech2 online model.
The code of encoder and decoder for deepspeech2 offline model is in:
```
vi deepspeech/models/ds2/deepspeech2.py
```
The training process and testing process of deepspeech2 offline model is very similary to deepspeech2 online model.
Only some changes should be noticed.
For training and testing, the "model_type" and the "conf_path" must be set.
```
# Training offline
cd examples/aishell/s0
bash run.sh --stage 0 --stop_stage 2 --model_type offline --conf_path conf/deepspeech2.yaml
```
```
# Testing offline
cd examples/aishell/s0
bash run.sh --stage 3 --stop_stage 5 --model_type offline --conf_path conf/deepspeech2.yaml
```


