!14322 翻译完成:13297 新增avplayer avrecorder接口
Merge pull request !14322 from wusongqing/TR13297
Showing
25.6 KB
37.5 KB
34.4 KB
81.9 KB
55.2 KB
因为 它太大了无法显示 source diff 。你可以改为 查看blob。
Merge pull request !14322 from wusongqing/TR13297
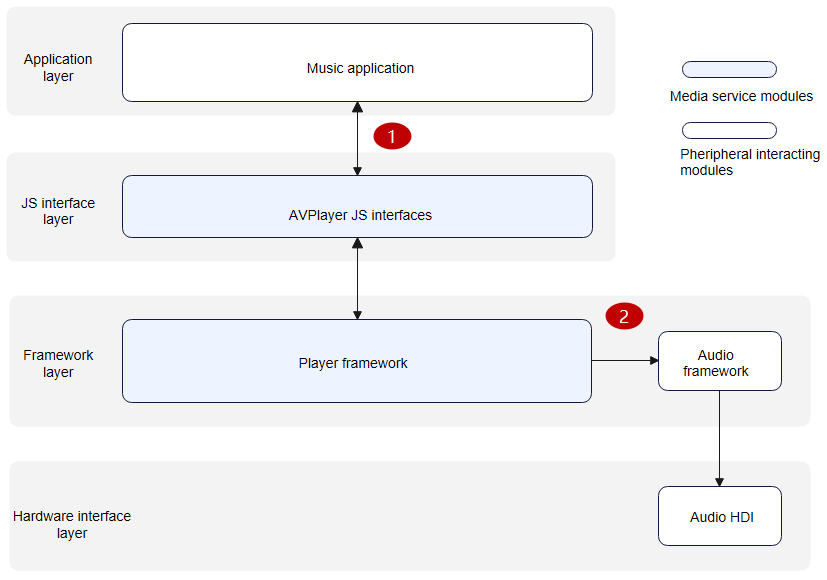
25.6 KB
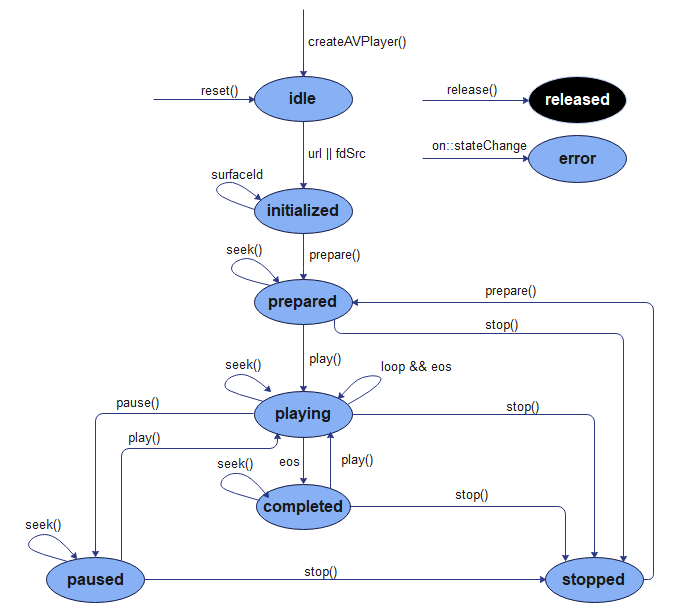
37.5 KB
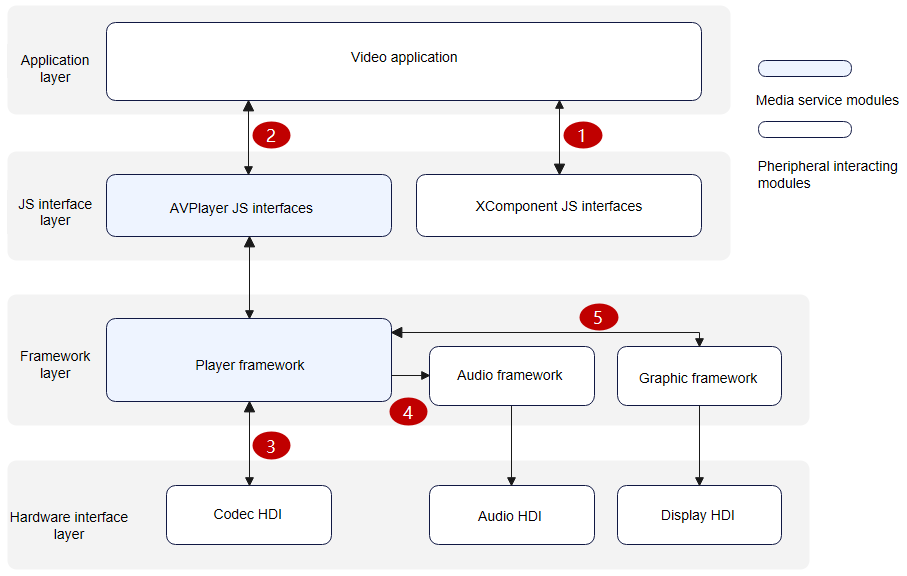
34.4 KB

81.9 KB

55.2 KB
