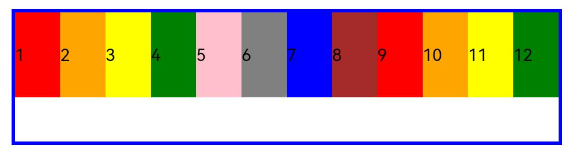
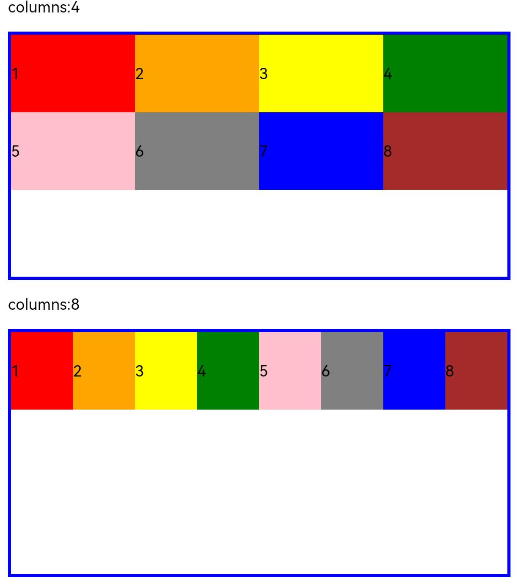
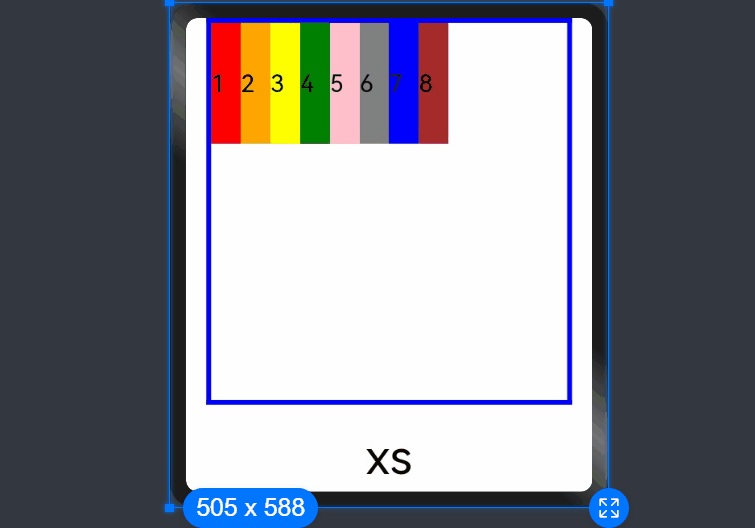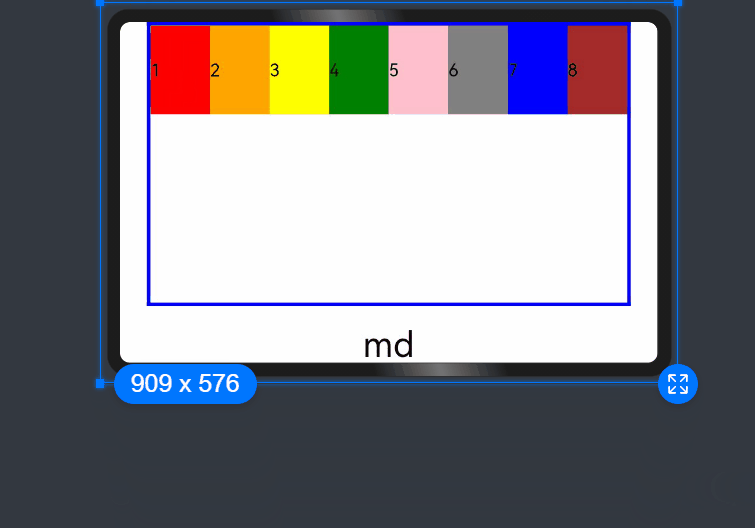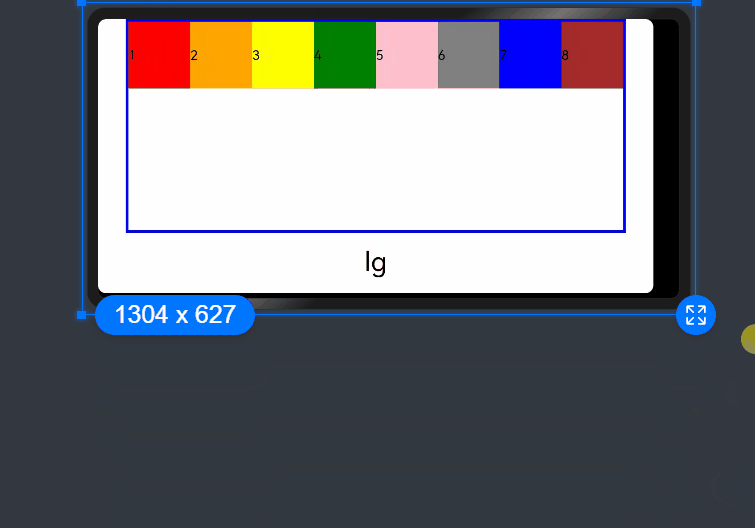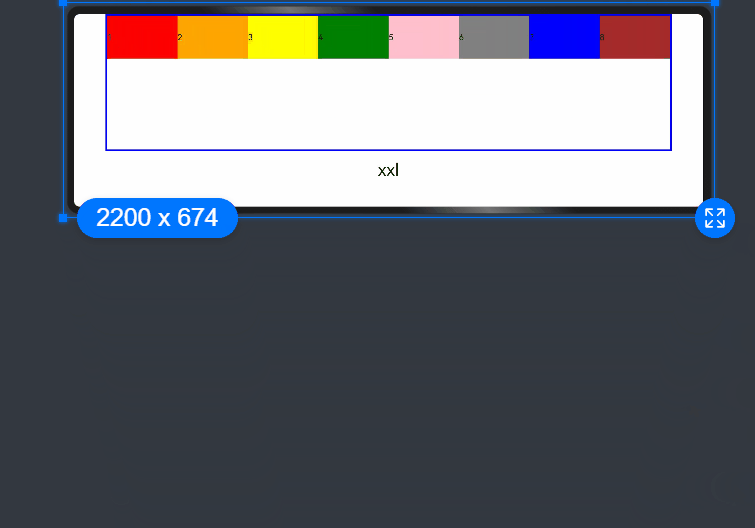
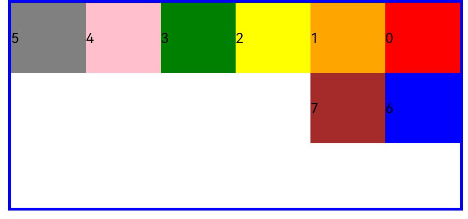
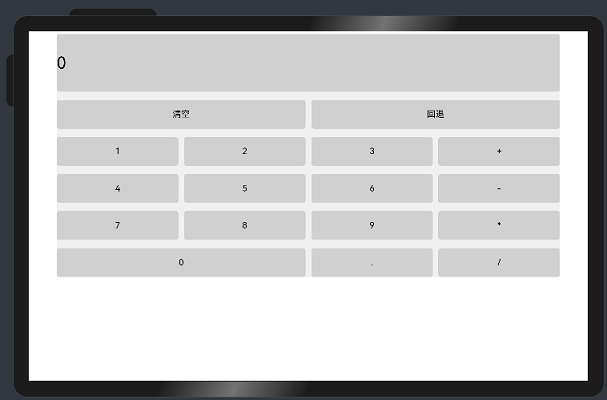
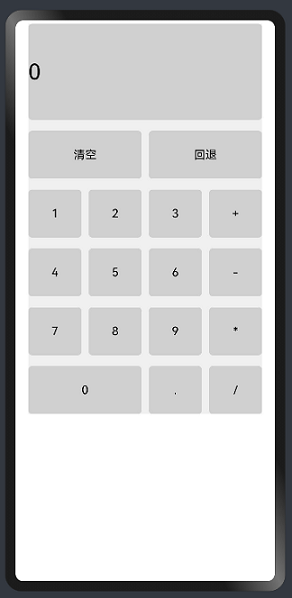
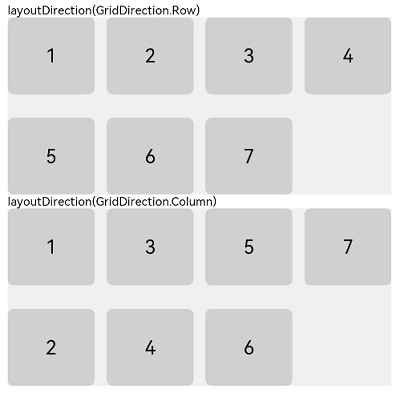
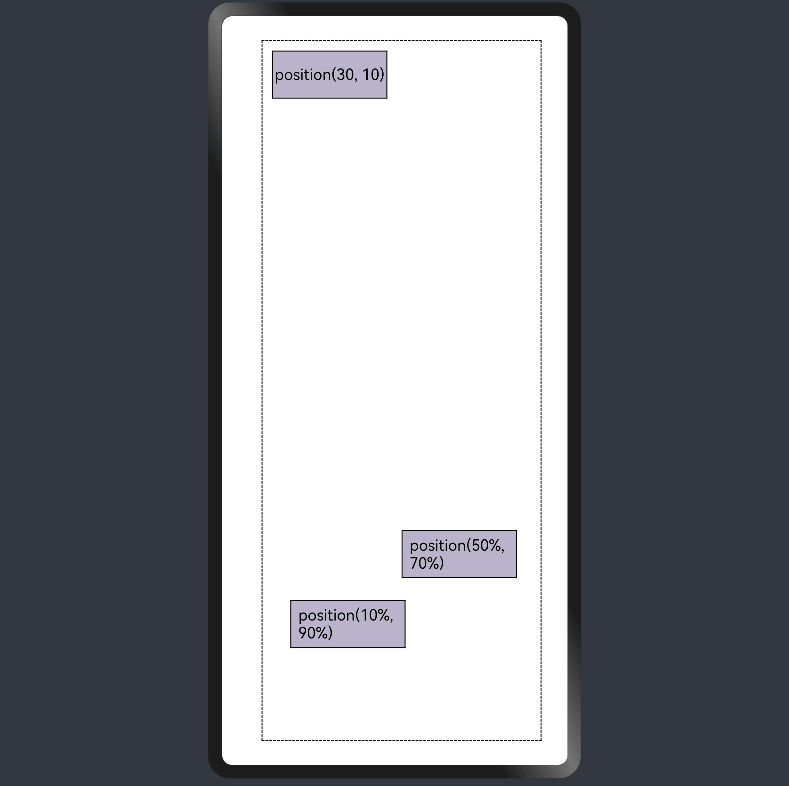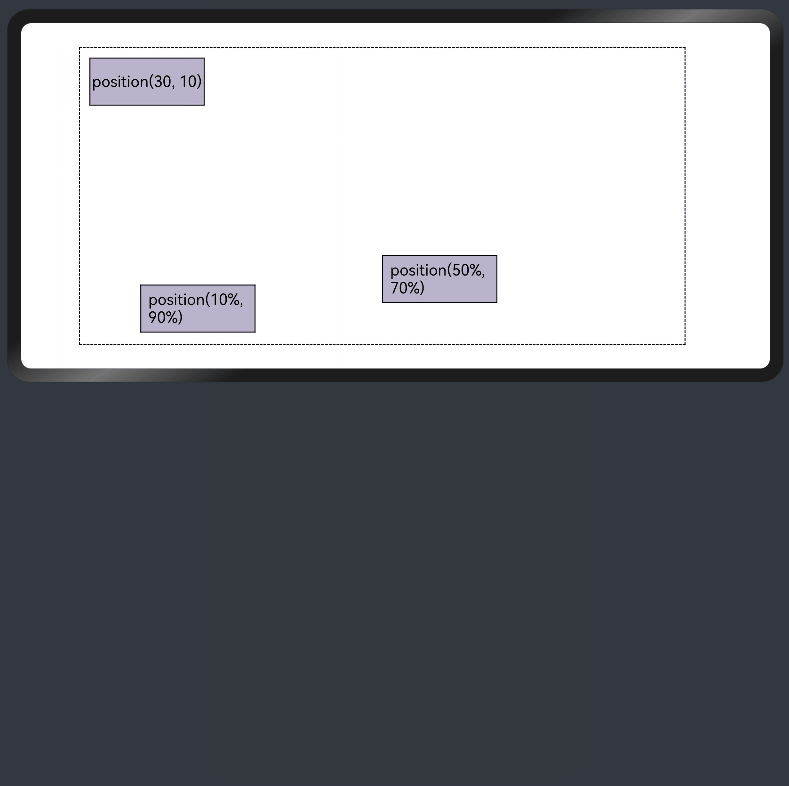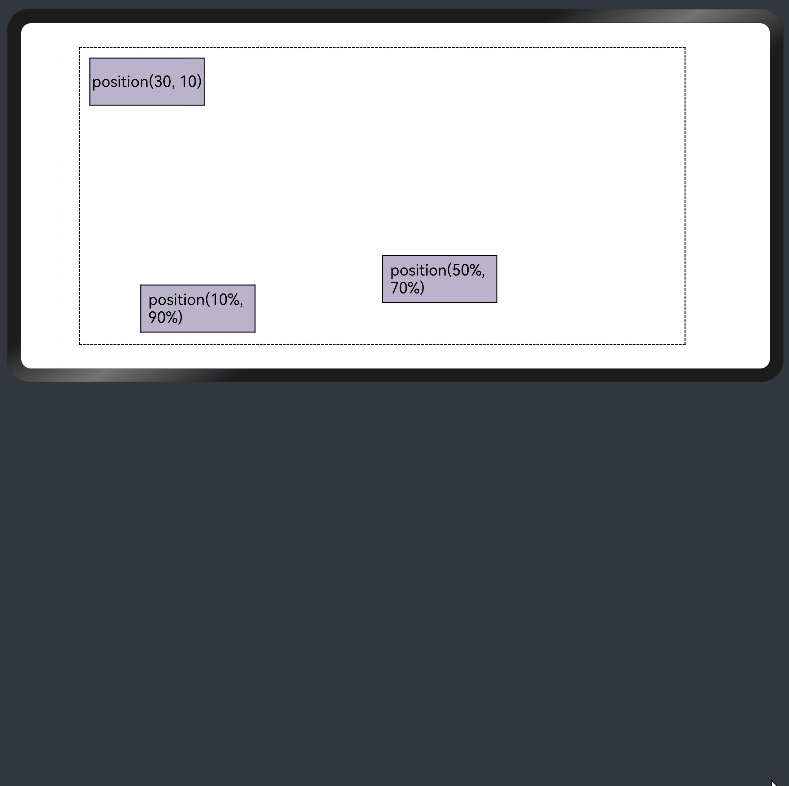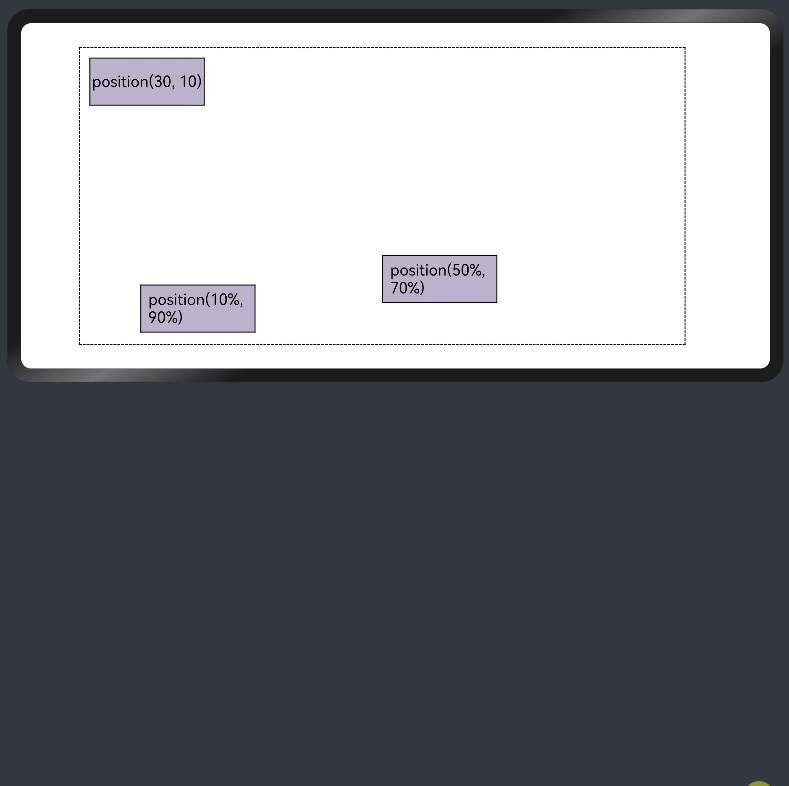
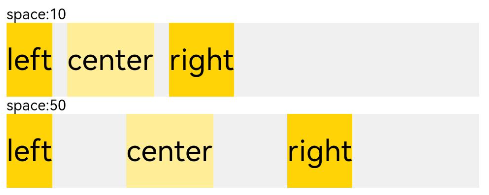
ui cherryPick 3.2beta
Signed-off-by: Nyamila <tianyu55@huawei.com>
5.3 KB
5.1 KB
16.3 KB
144.9 KB
1.5 MB
12.4 KB
3.1 MB
9.9 KB
9.6 KB
24.7 KB
79.6 KB
162.3 KB
20.8 KB
34.6 KB
2.2 MB
45.6 KB
10.3 KB
28.6 KB
8.7 KB
8.6 KB
8.8 KB
8.7 KB
9.4 KB
7.9 KB
15.0 KB
12.4 KB
12.3 KB
96.4 KB
2.8 KB
16.2 KB
2.8 KB
5.2 KB
4.9 KB
9.7 KB
10.3 KB
21.3 KB
17.8 KB
3.1 KB
6.9 KB
18.0 KB
11.4 KB
14.1 KB
23.7 KB
30.4 KB
13.7 KB
22.7 KB
13.9 KB
12.6 KB
28.2 KB
16.8 KB
44.9 KB
3.7 KB
1.2 MB
736.1 KB
2.0 MB
1.7 MB
6.7 KB
5.7 KB
7.8 KB
6.9 KB
6.0 KB
5.6 KB
30.5 KB
23.2 KB
1.8 MB
9.8 KB
1.6 MB
65.0 KB
16.1 KB
72.3 KB
151.1 KB
38.5 KB
382.5 KB
321.5 KB
15.9 KB
2.4 MB
26.1 KB
6.3 KB
6.6 KB
6.3 KB
6.4 KB
6.4 KB
6.2 KB
6.3 KB
6.7 KB
6.5 KB
6.3 KB
20.7 KB
369.9 KB
20.3 KB
13.9 KB
| W: | H:
| W: | H:

| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:


135.6 KB

| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:


20.8 KB