!23880 翻译完成:22255+22190 onCreate()与onNewWant()接口中参数名修改
Merge pull request !23880 from wusongqing/TR22255
Showing
77.6 KB
76.0 KB
22.5 KB
53.0 KB
62.3 KB
64.4 KB
60.4 KB
Merge pull request !23880 from wusongqing/TR22255
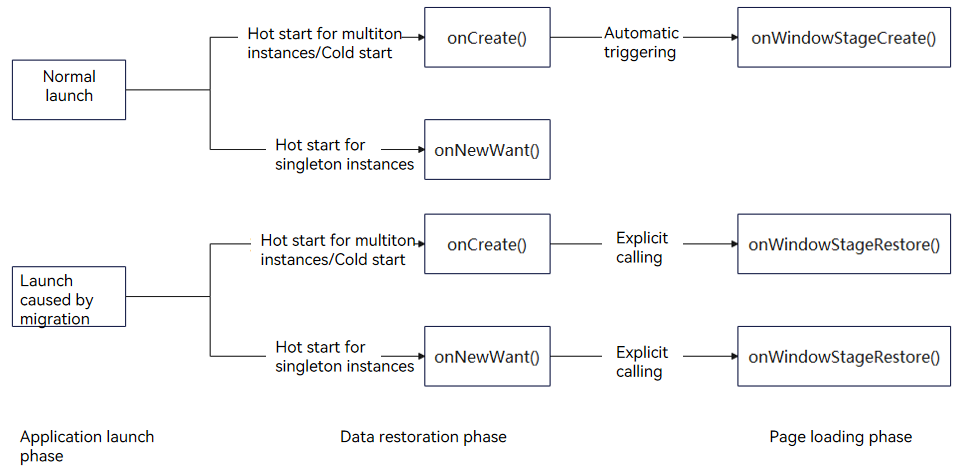
77.6 KB
76.0 KB
22.5 KB
53.0 KB
62.3 KB

64.4 KB
60.4 KB
