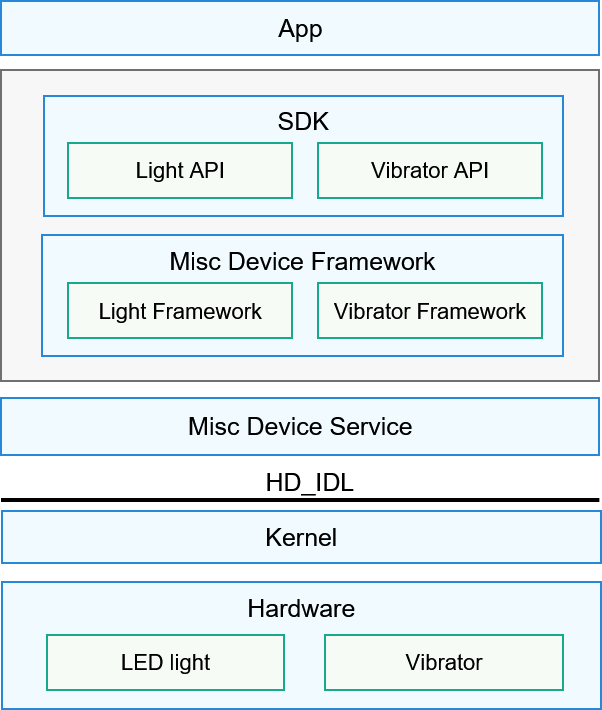
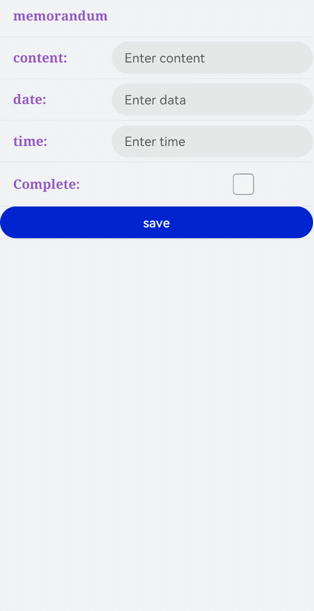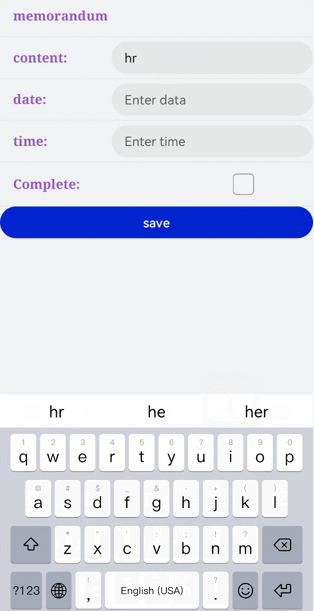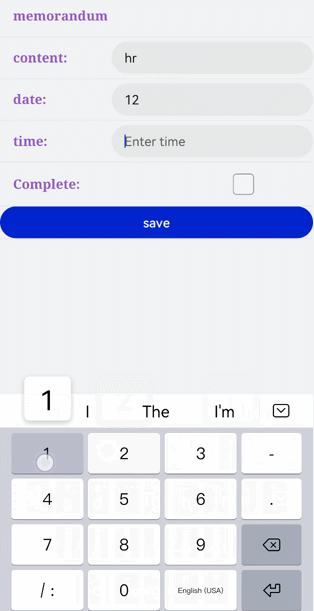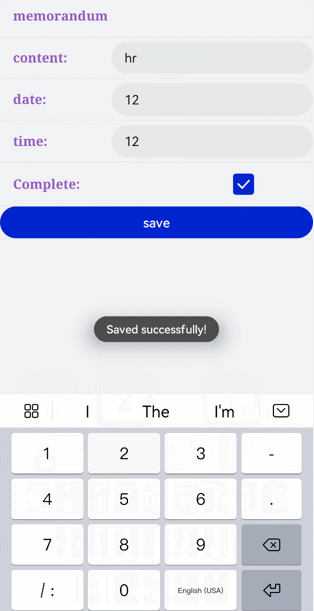
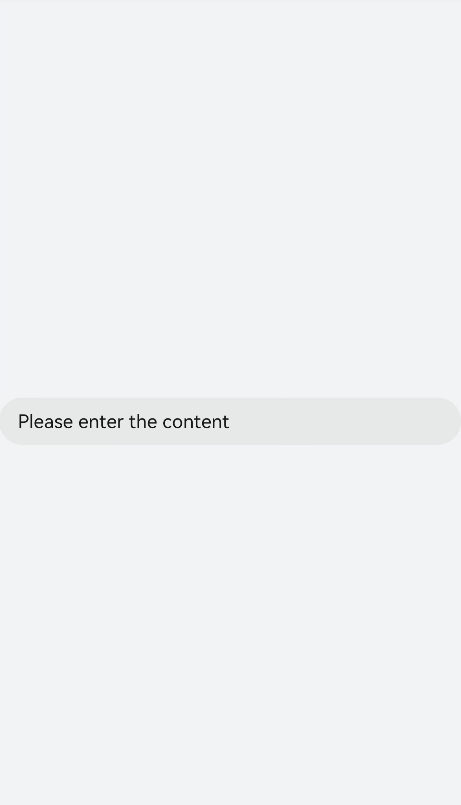
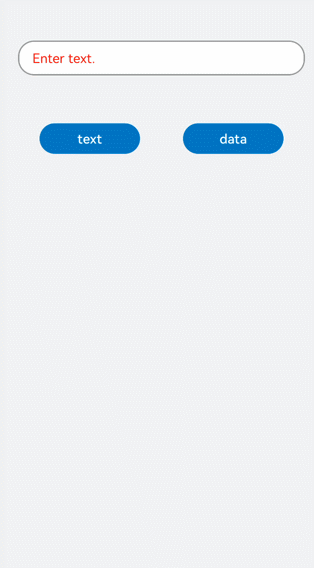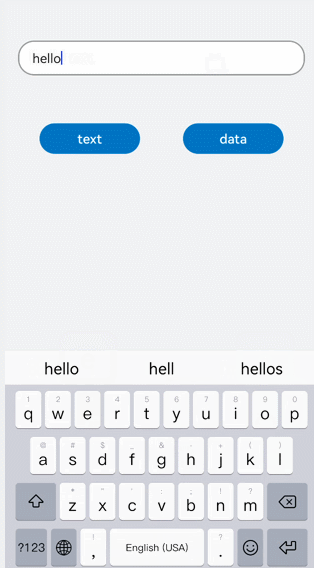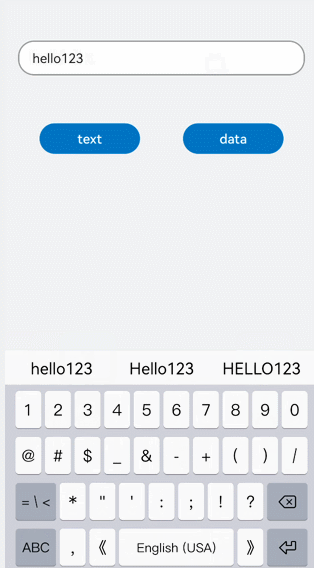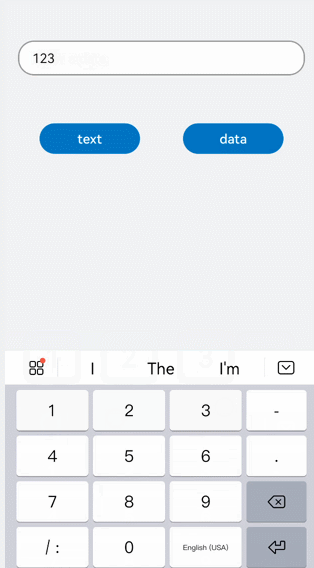
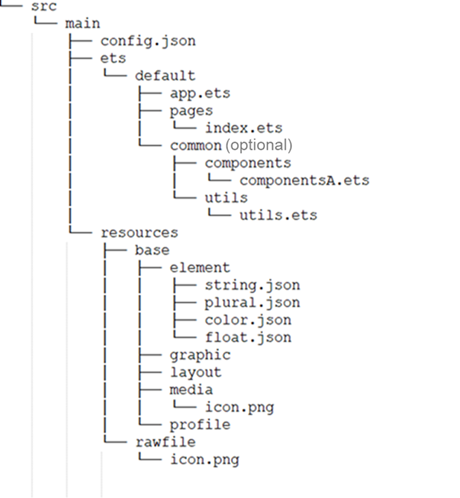
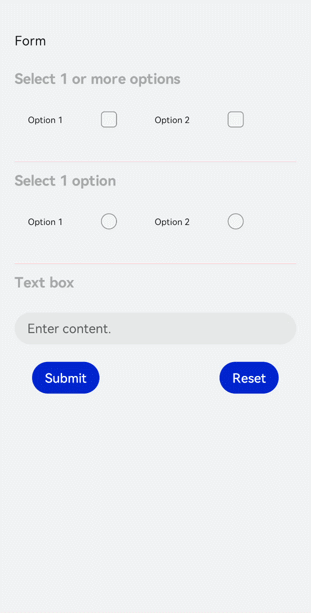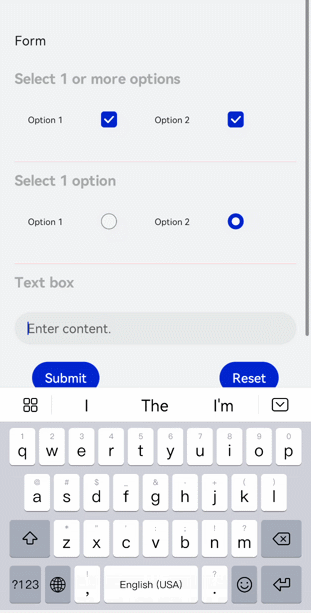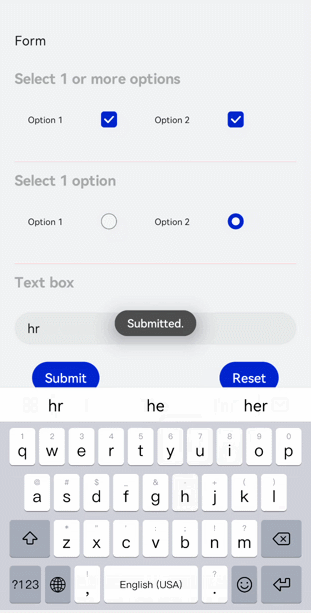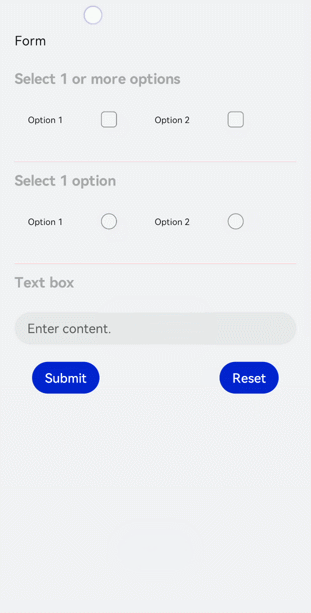
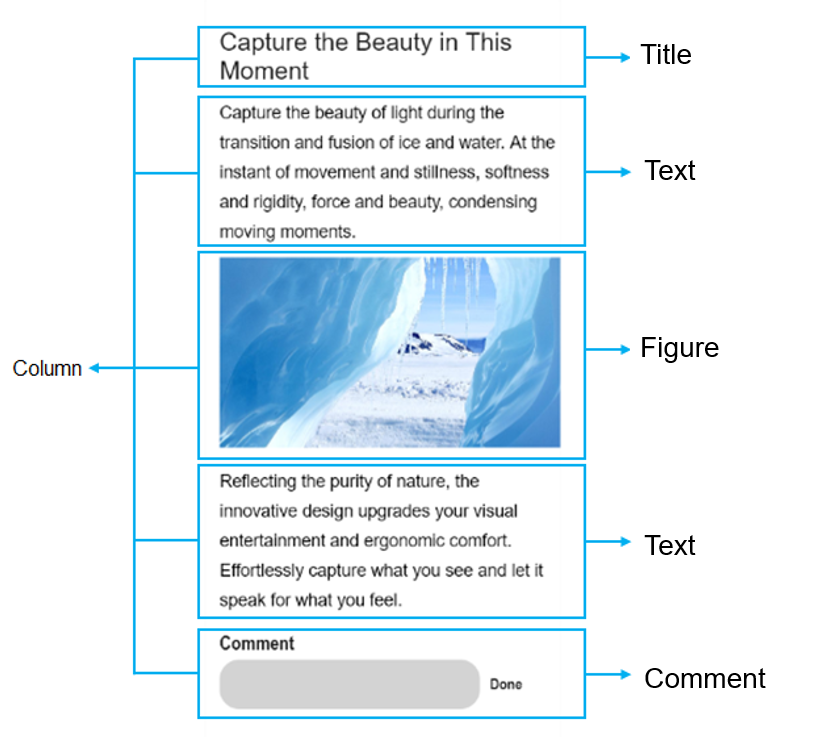
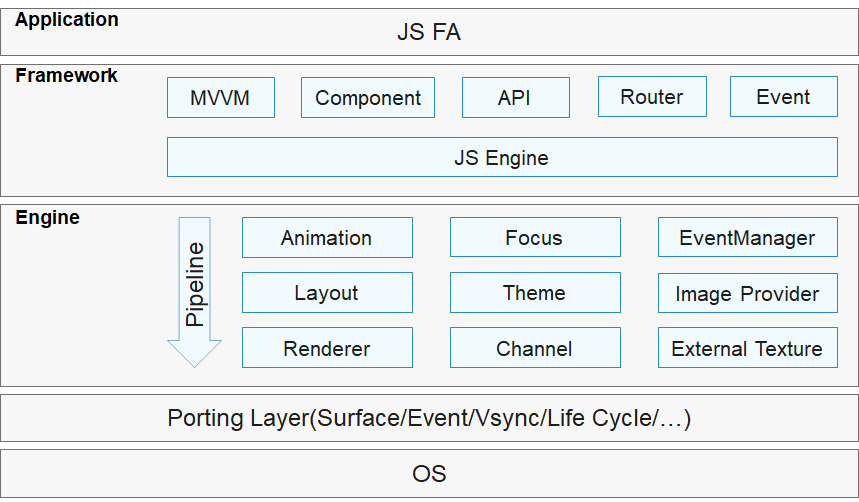
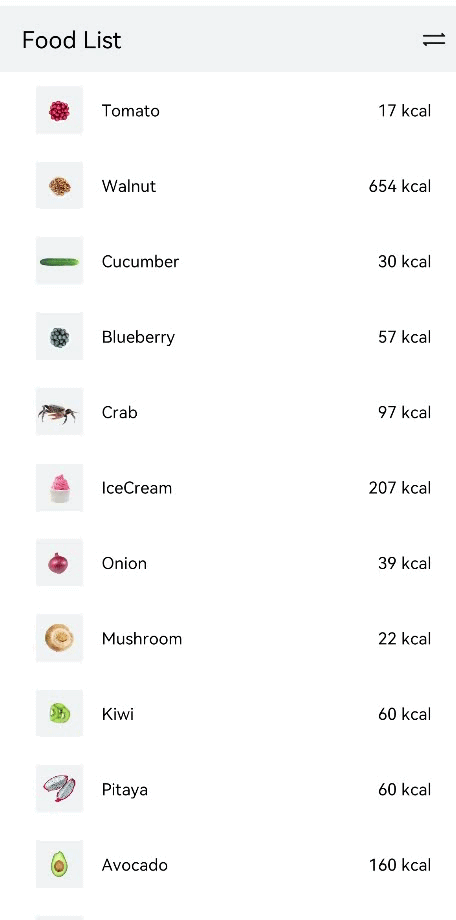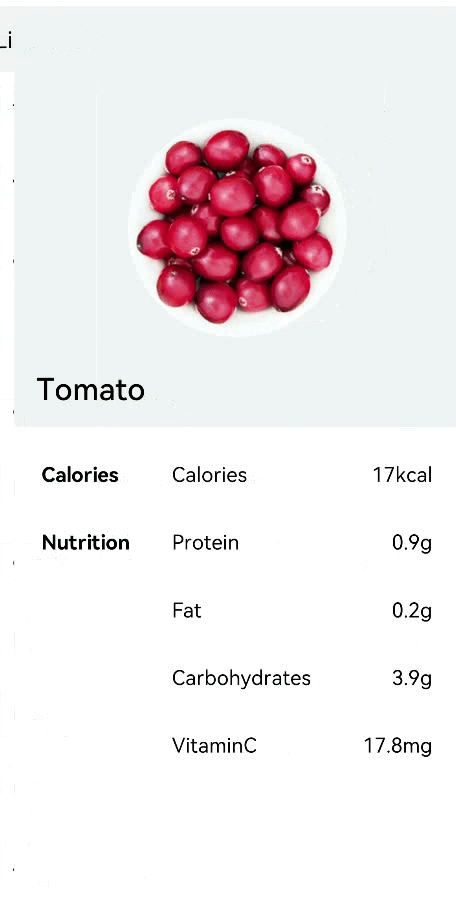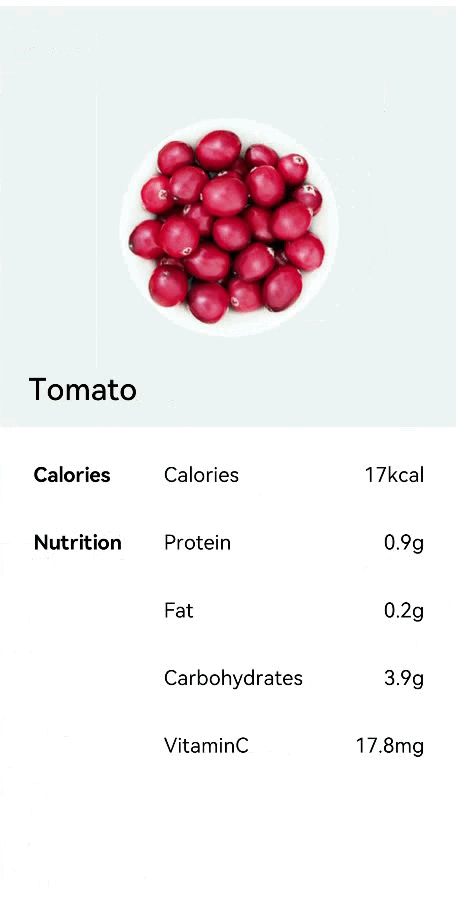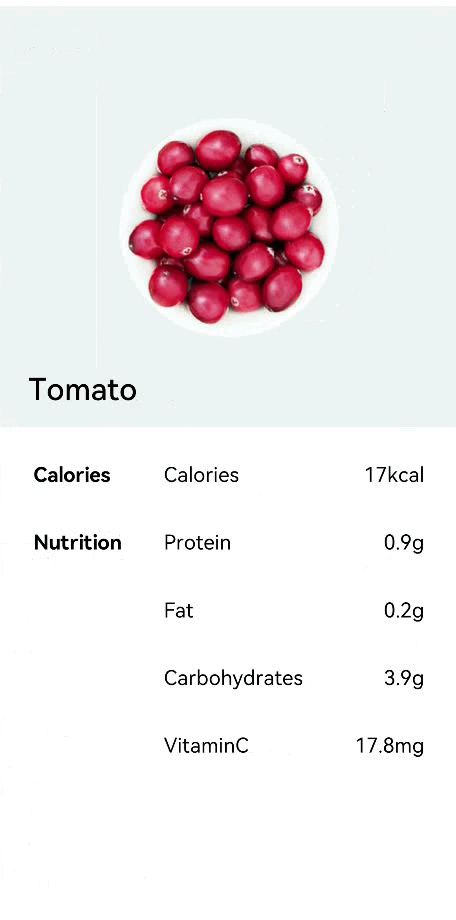
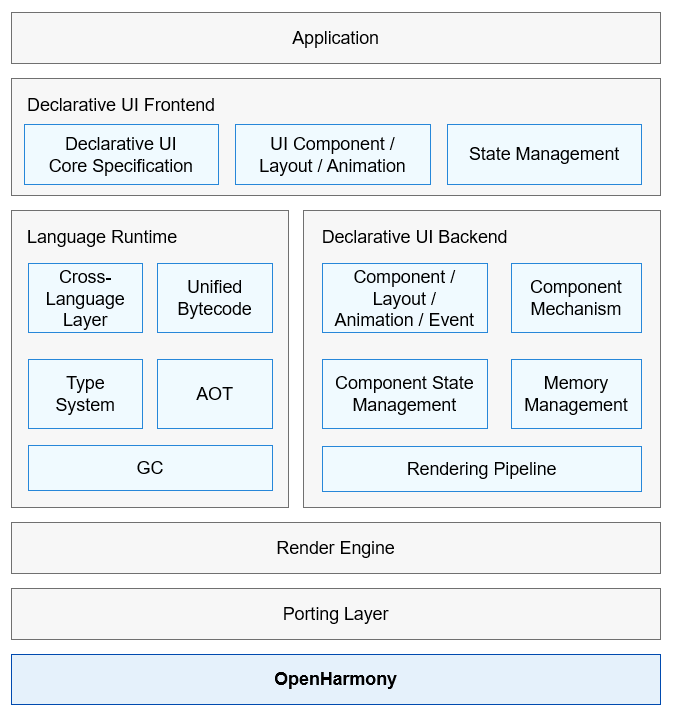
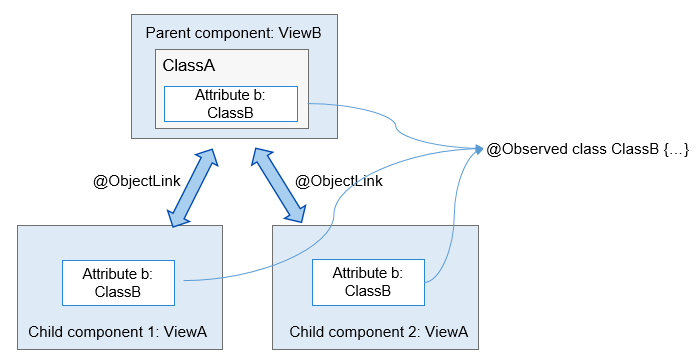
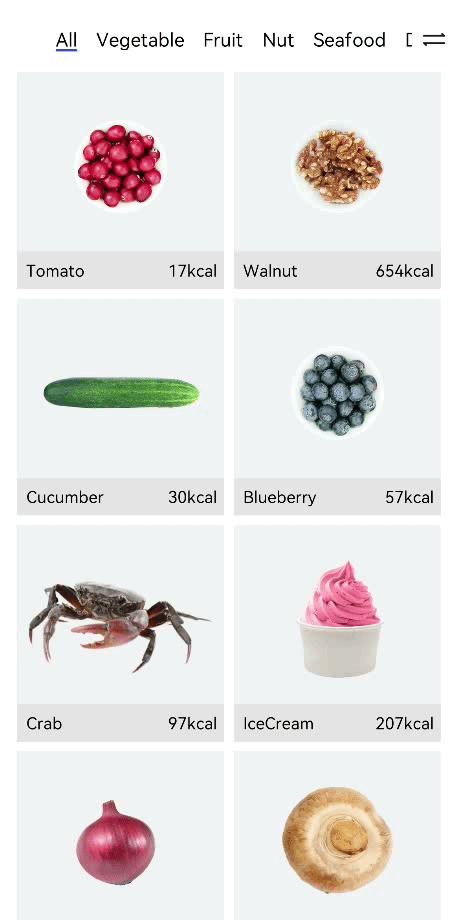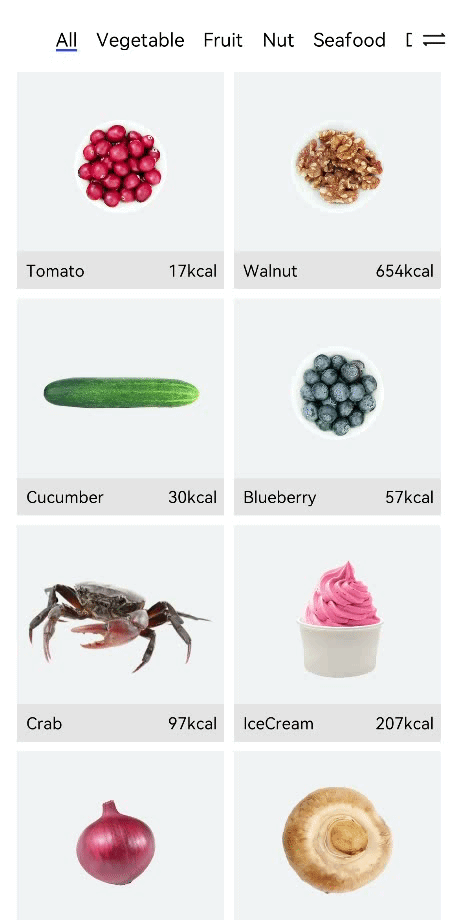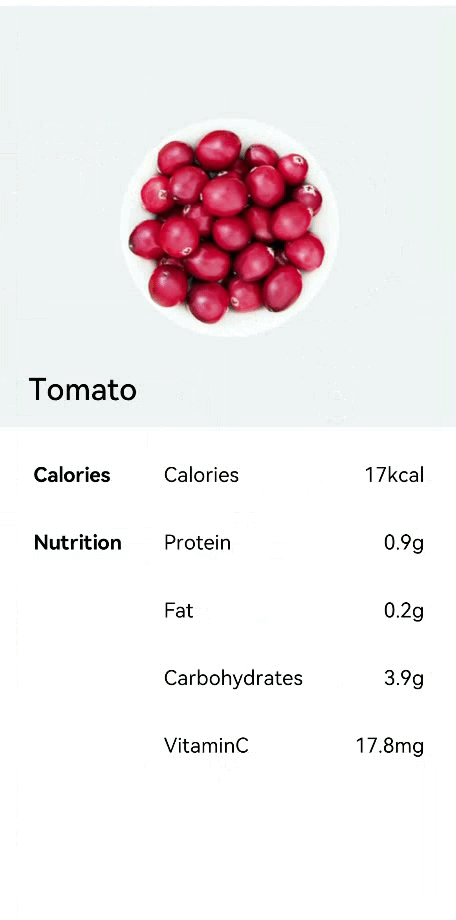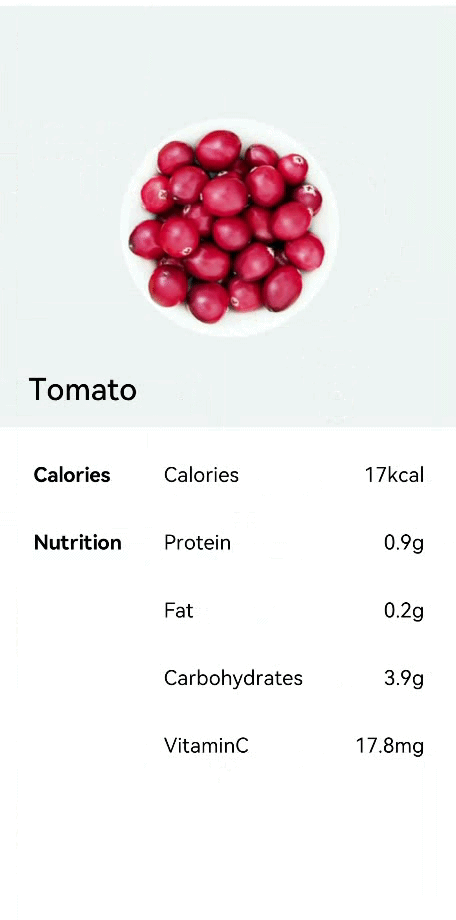
!2747 device下ui文件夹删除,无需翻译
Merge pull request !2747 from 葛亚芳/master
Showing
14.5 KB
11.8 KB
117 字节
117 字节
117 字节
117 字节
117 字节
323.5 KB
93.5 KB
118 字节
120 字节
117 字节
119 字节
117 字节
51.0 KB
33.8 KB
242.9 KB
11.0 KB
242.5 KB
393.0 KB
6.2 KB
3.9 KB
144.9 KB
189.8 KB
906.3 KB
355.5 KB
18.3 KB
55.9 KB
280.2 KB
16.2 KB
68.2 KB
214.9 KB
158.7 KB
20.1 KB
29.7 KB
117.9 KB
115.0 KB
33.9 KB
13.8 KB
259.2 KB
223.4 KB
36.4 KB
12.8 KB
34.7 KB
42.4 KB
68.2 KB
502.8 KB
233.9 KB
7.6 KB
21.0 KB
2.2 KB
106.9 KB
258.8 KB
51.6 KB
1.8 MB
184.1 KB
550.0 KB
840.9 KB
2.8 KB
124.7 KB
71.0 KB
8.2 KB
233.6 KB
50.7 KB
4.5 KB
94.4 KB
20.3 KB
555.5 KB
30.4 KB
3.3 MB
36.9 KB
141.8 KB
342.7 KB
842.8 KB
41.7 KB
60.2 KB
4.9 KB
270.0 KB
1.0 MB
62.7 KB
24.8 KB
535.3 KB
2.2 KB
14.9 KB
133.2 KB
752.2 KB
2.9 MB
160.1 KB
279.8 KB
18.1 KB
39.5 KB
428.0 KB
245.9 KB
15.1 KB
5.9 KB
21.3 KB
110.6 KB
11.3 KB
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。