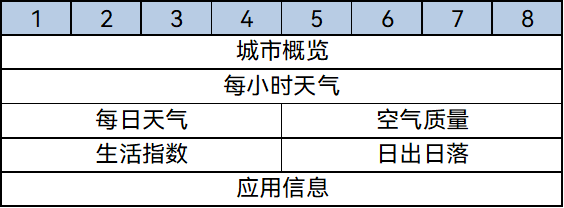
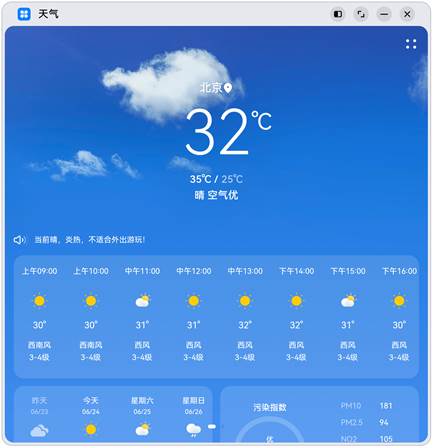
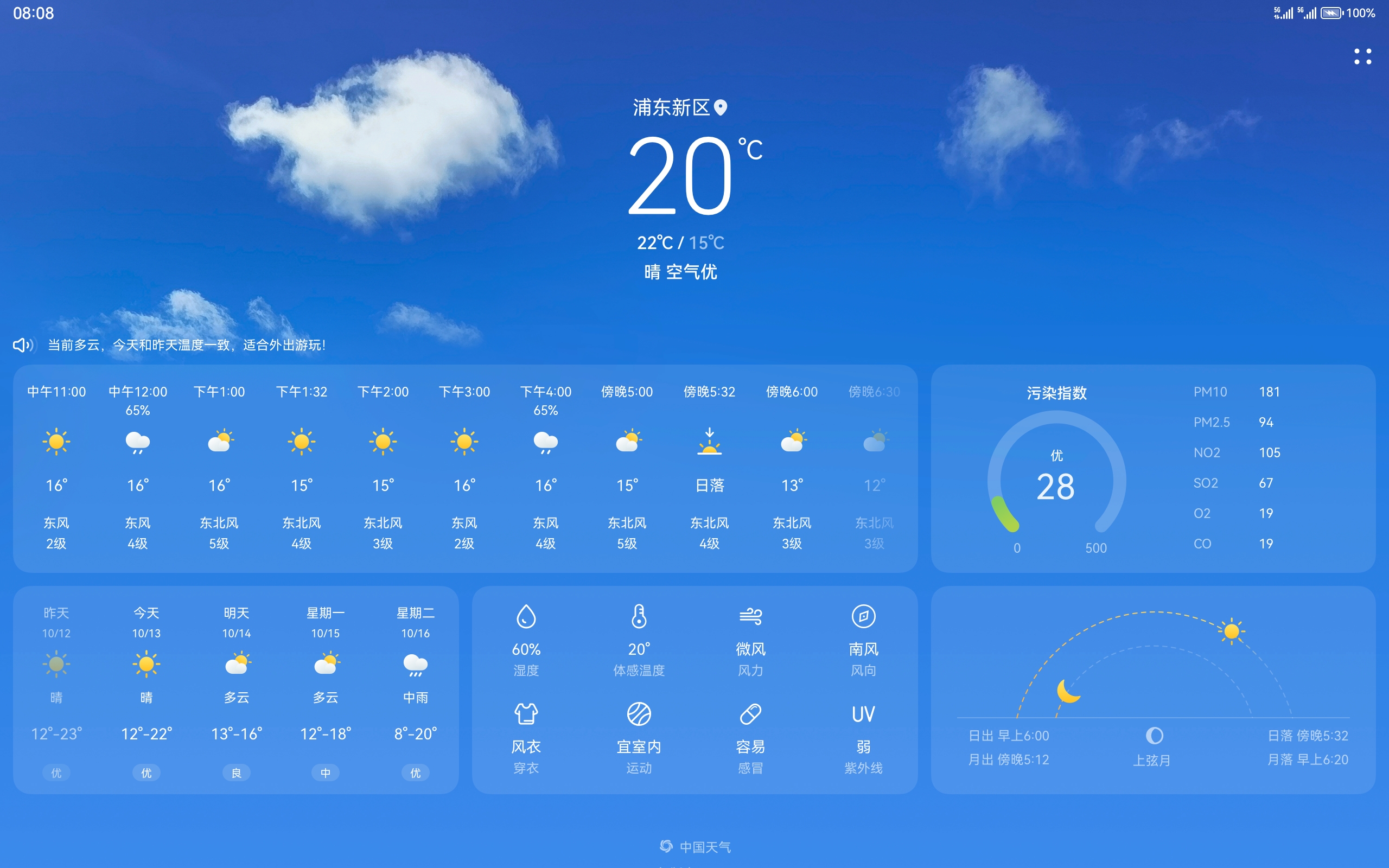
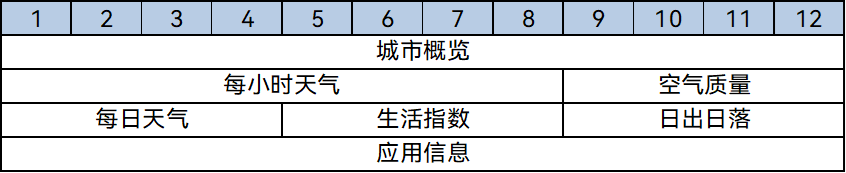
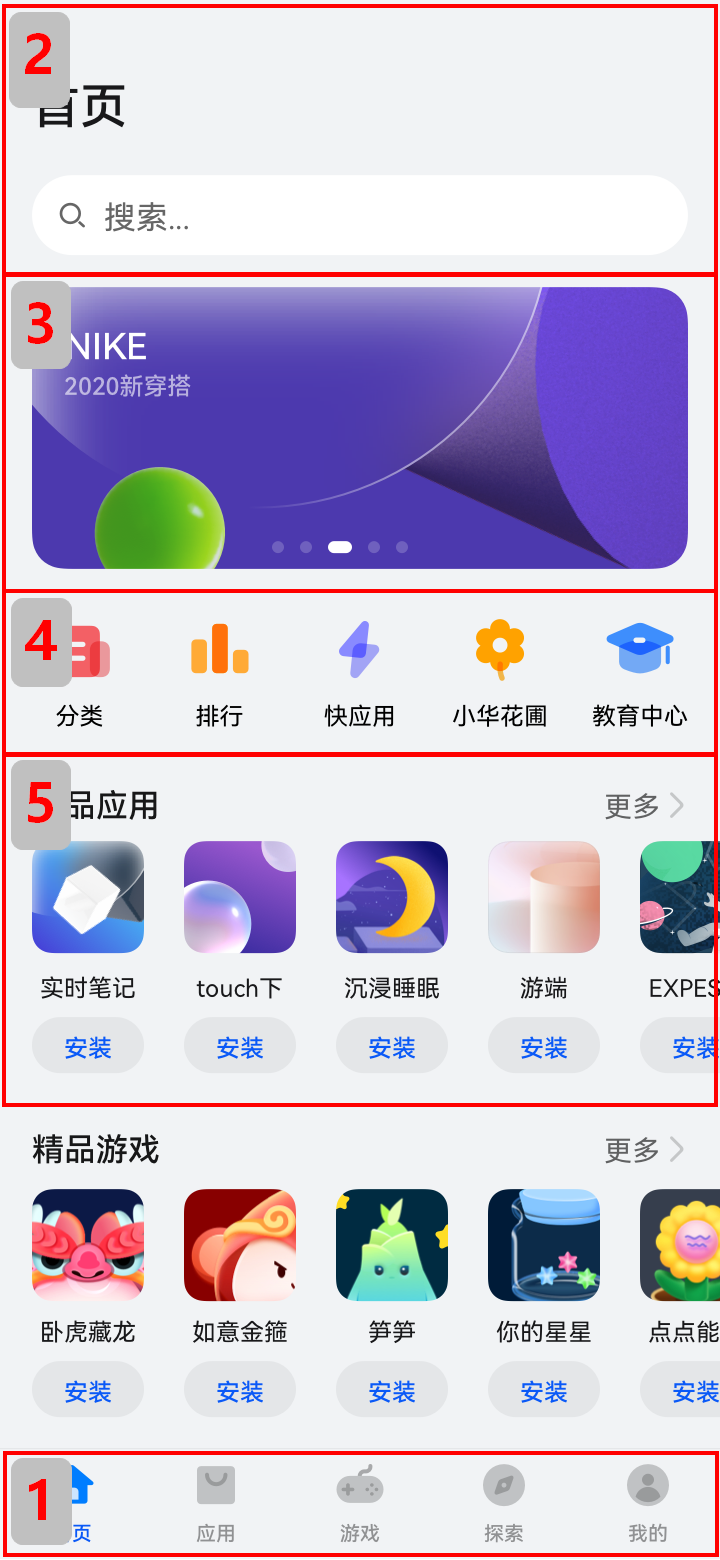
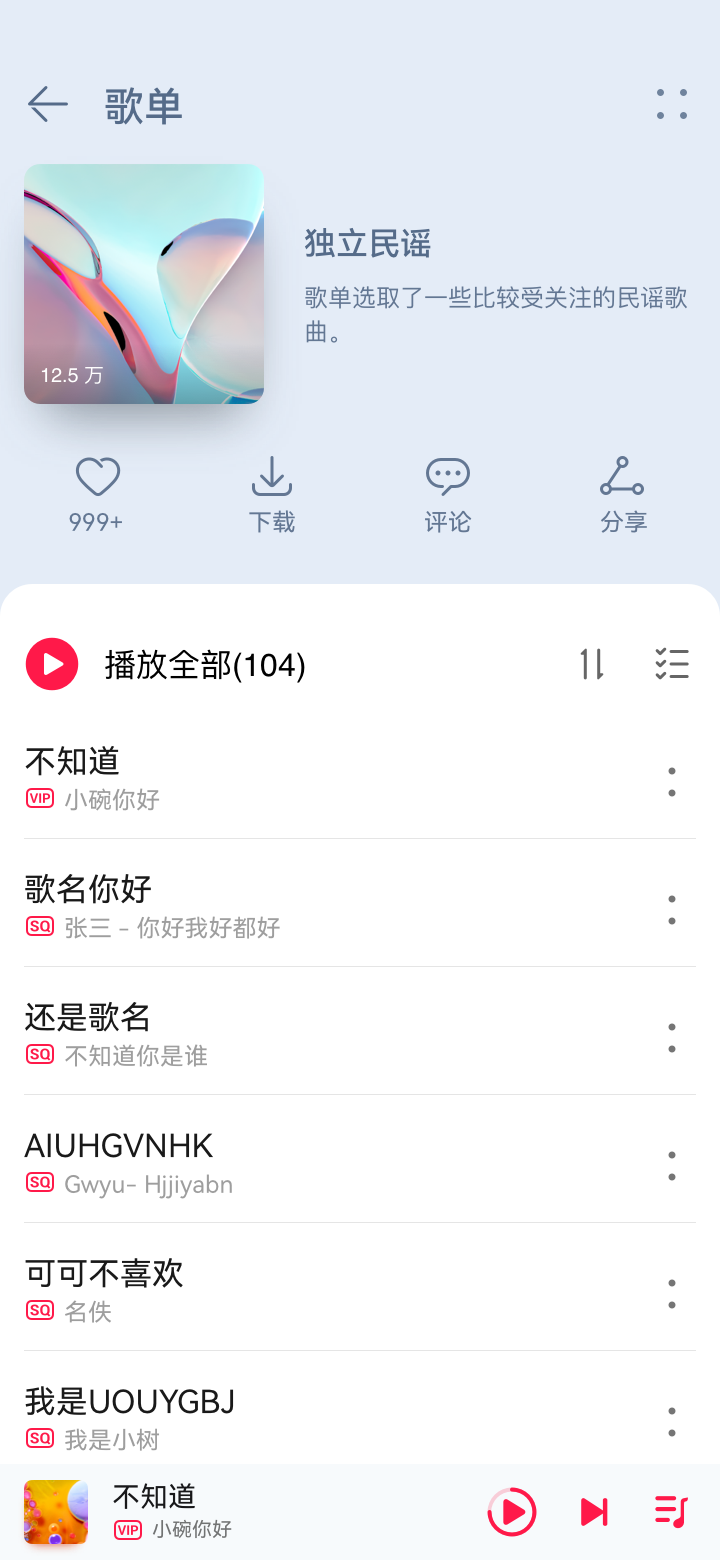
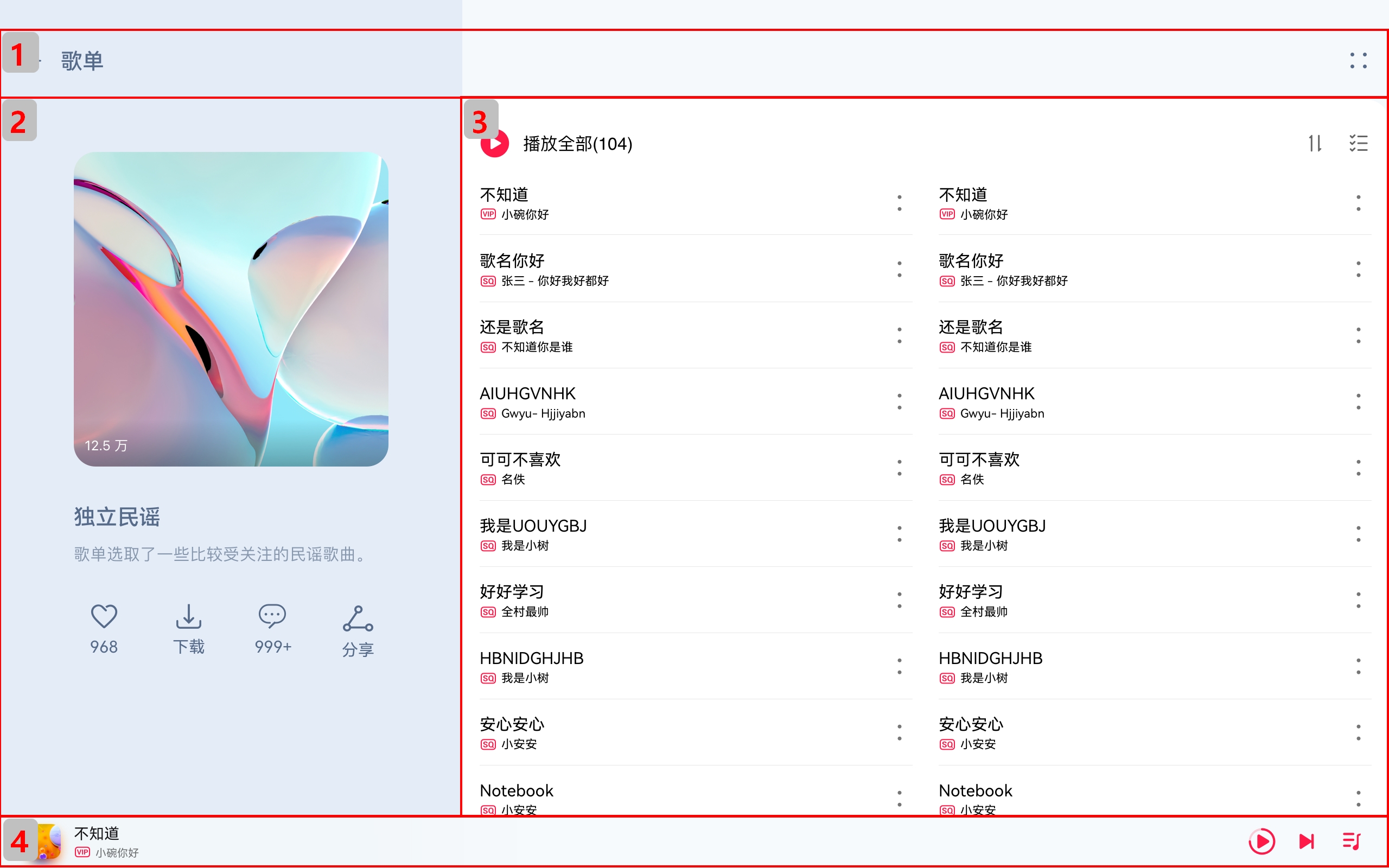
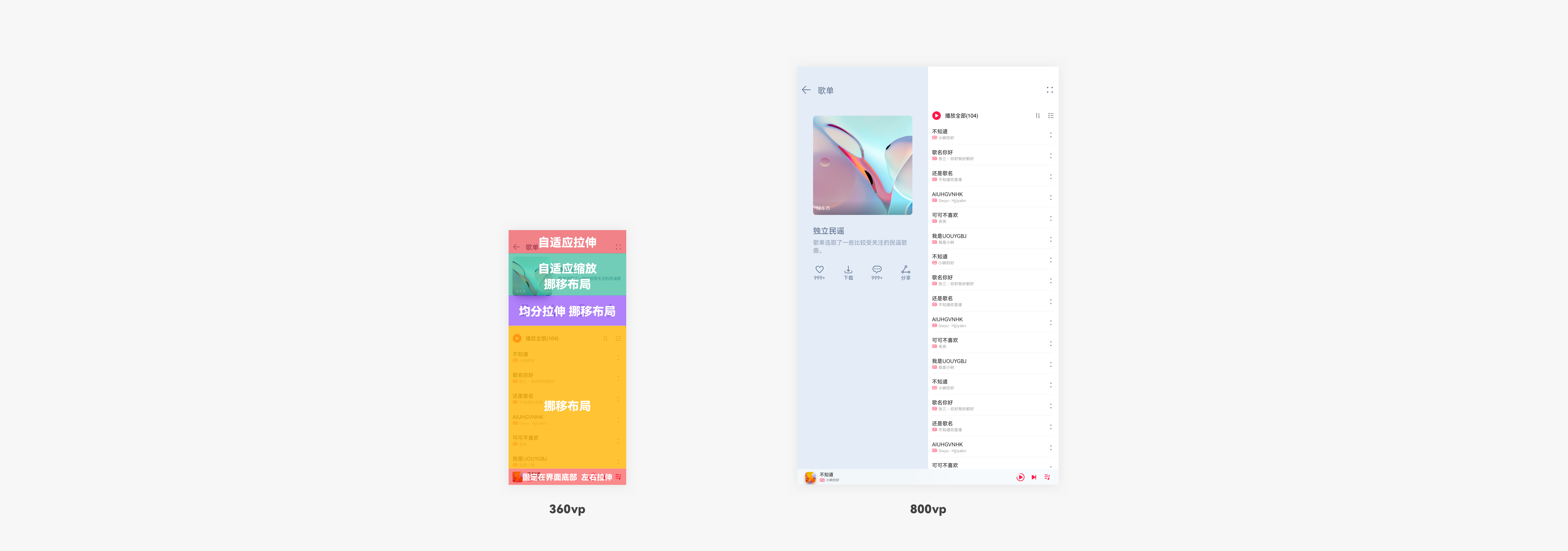
Merge branch 'master' of gitee.com:openharmony/docs into gesture
Signed-off-by: Nsienna1128 <lixiaoyan45@huawei.com>
213.8 KB
150.1 KB
130.6 KB
2.2 MB
3.8 MB
1.1 MB
5.0 MB
1.9 MB
2.8 MB
2.0 MB
721.7 KB
485.8 KB
438.3 KB
139.9 KB
53.8 KB
119.0 KB
103.8 KB
647.7 KB
29.5 KB
19.8 KB
16.7 KB
3.0 MB
347.7 KB
62.0 KB
186.1 KB
353.4 KB
643.9 KB
467.5 KB
22.3 KB
15.7 KB
10.8 KB
14.2 KB
22.1 KB
136.9 KB
20.1 KB
25.4 KB
17.2 KB
10.0 KB
24.6 KB
8.0 MB
113.9 KB
40.6 KB
3.3 KB
10.9 KB
13.6 KB
227.5 KB
15.6 KB
235.7 KB
19.0 KB
16.5 KB
106.4 KB
127.5 KB
55.5 KB
122.3 KB
111.9 KB
96.4 KB
21.8 KB
3.2 KB
367.9 KB
16.8 KB
242.8 KB
22.0 KB
22.8 KB
5.6 KB
70.2 KB
54.6 KB
200.5 KB
102.3 KB
30.4 KB
683.0 KB
644.3 KB
422.6 KB
12.9 KB
9.5 KB
12.4 KB
9.6 KB
691.0 KB
4.8 KB
15.0 KB
376.0 KB
9.0 KB
8.0 KB
1.0 MB
21.5 KB
15.0 KB
6.2 KB
5.8 KB
3.8 KB
5.9 KB
5.7 KB
20.0 KB
5.0 KB
5.0 KB
3.4 KB
10.6 KB
5.0 KB
7.0 KB
6.4 KB
14.1 KB
16.1 KB
21.0 KB
1.4 MB
19.9 KB
1.3 MB
1.3 MB
384.1 KB
4.5 KB
1.4 KB
8.3 KB
208.6 KB
232.9 KB
538.2 KB
3.2 KB
6.9 KB
574.1 KB
1.1 KB
8.0 KB
9.6 KB
10.2 KB
8.5 KB
292.5 KB
12.9 KB
26.6 KB
26.7 KB
16.7 KB
21.3 KB
936.4 KB
4.9 KB
7.0 KB
6.0 KB
5.2 KB
6.1 KB
6.9 KB
4.3 KB
19.3 KB
5.5 KB
4.8 KB
5.5 KB
5.5 KB
5.0 KB
7.0 KB
58.3 KB
21.7 KB
31.0 KB
224.0 KB
515.5 KB
415.4 KB
548.2 KB
854.9 KB
170.8 KB
801.3 KB
126.6 KB
92.6 KB
154.3 KB
102.1 KB
31.5 KB
17.7 KB
22.6 KB
1007.7 KB
512.8 KB
586.6 KB
35.1 KB
112.1 KB
36.9 KB
1.0 MB
9.5 KB