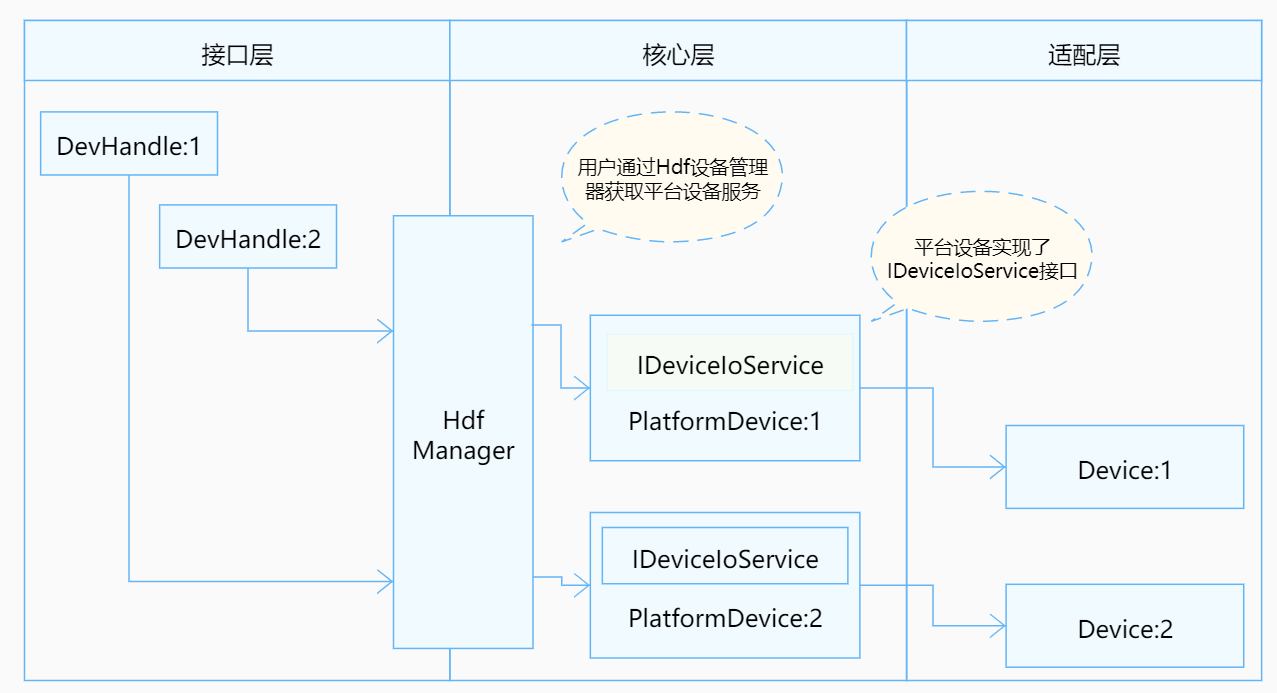
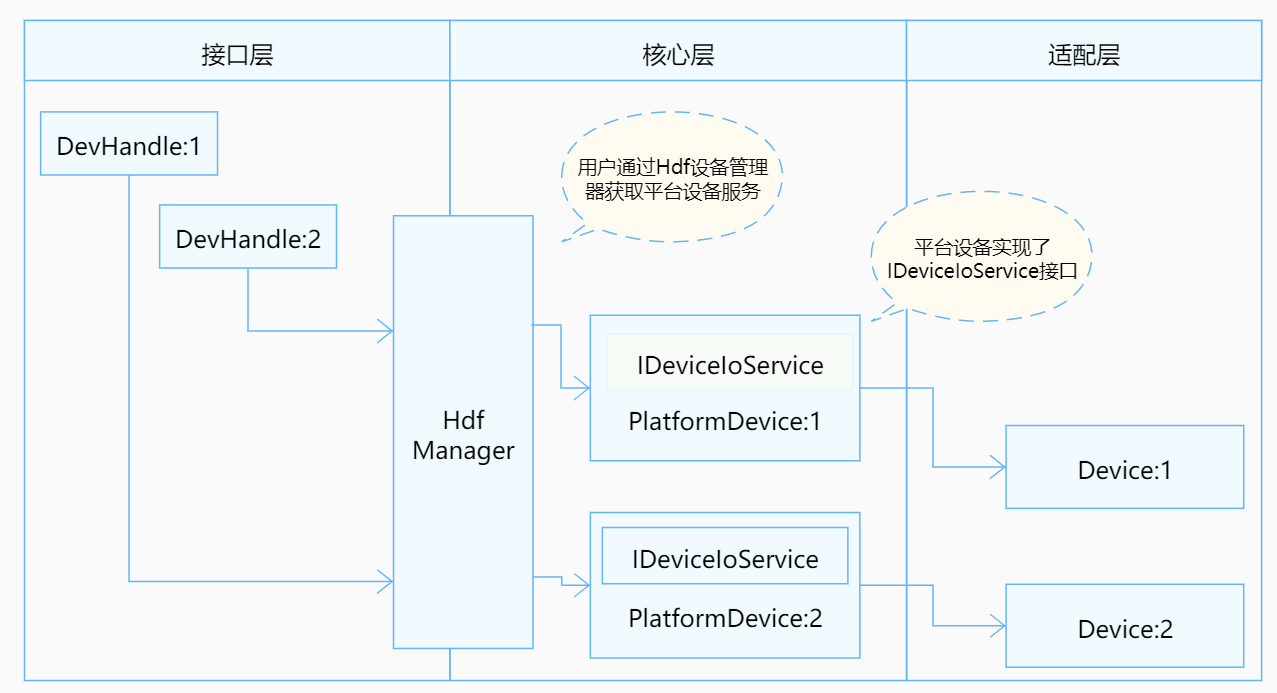
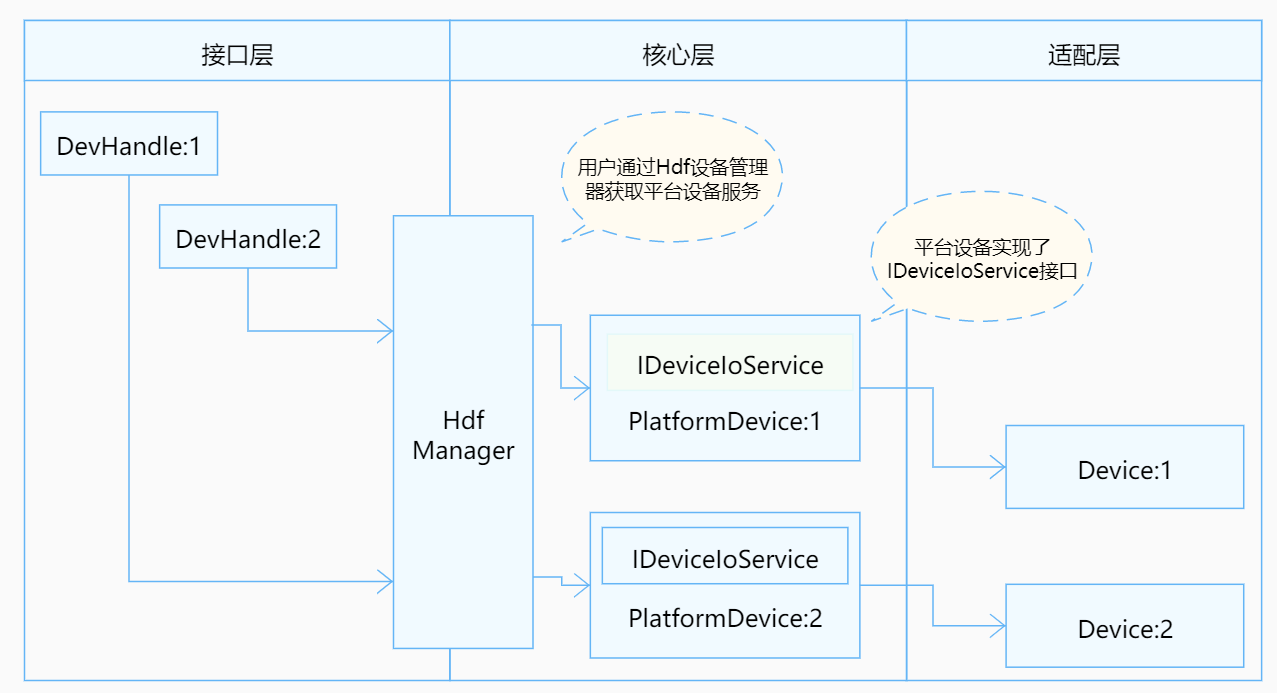
docs: add some guidance documents for platform drivers.
Signed-off-by: Nyafeng_wang <wangyafeng15@huawei.com>
Showing
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
3.4 KB
4.3 KB
39.3 KB
39.3 KB
7.3 KB
14.8 KB
57.2 KB
8.0 KB
25.9 KB
51.0 KB
51.0 KB
51.0 KB
51.0 KB
51.0 KB
51.0 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动