 *
* Window object is a top-level window with no borders and no
* menubar.
* The default layout for a window is BorderLayout.
* * A window must have either a frame, dialog, or another window defined as its * owner when it's constructed. *
* In a multi-screen environment, you can create a Window
* on a different screen device by constructing the Window
* with {@link #Window(Window, GraphicsConfiguration)}. The
* GraphicsConfiguration object is one of the
* GraphicsConfiguration objects of the target screen device.
*
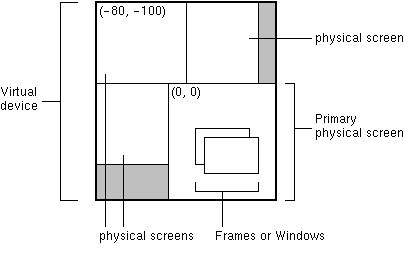
* In a virtual device multi-screen environment in which the desktop * area could span multiple physical screen devices, the bounds of all * configurations are relative to the virtual device coordinate system. * The origin of the virtual-coordinate system is at the upper left-hand * corner of the primary physical screen. Depending on the location of * the primary screen in the virtual device, negative coordinates are * possible, as shown in the following figure. *
*  *
*
* In such an environment, when calling setLocation,
* you must pass a virtual coordinate to this method. Similarly,
* calling getLocationOnScreen on a Window returns
* virtual device coordinates. Call the getBounds method
* of a GraphicsConfiguration to find its origin in the virtual
* coordinate system.
*
* The following code sets the location of a Window
* at (10, 10) relative to the origin of the physical screen
* of the corresponding GraphicsConfiguration. If the
* bounds of the GraphicsConfiguration is not taken
* into account, the Window location would be set
* at (10, 10) relative to the virtual-coordinate system and would appear
* on the primary physical screen, which might be different from the
* physical screen of the specified GraphicsConfiguration.
*
*
* Window w = new Window(Window owner, GraphicsConfiguration gc); * Rectangle bounds = gc.getBounds(); * w.setLocation(10 + bounds.x, 10 + bounds.y); ** *
* Note: the location and size of top-level windows (including
* Windows, Frames, and Dialogs)
* are under the control of the desktop's window management system.
* Calls to setLocation, setSize, and
* setBounds are requests (not directives) which are
* forwarded to the window management system. Every effort will be
* made to honor such requests. However, in some cases the window
* management system may ignore such requests, or modify the requested
* geometry in order to place and size the Window in a way
* that more closely matches the desktop settings.
*
* Due to the asynchronous nature of native event handling, the results
* returned by getBounds, getLocation,
* getLocationOnScreen, and getSize might not
* reflect the actual geometry of the Window on screen until the last
* request has been processed. During the processing of subsequent
* requests these values might change accordingly while the window
* management system fulfills the requests.
*
* An application may set the size and location of an invisible * {@code Window} arbitrarily, but the window management system may * subsequently change its size and/or location when the * {@code Window} is made visible. One or more {@code ComponentEvent}s * will be generated to indicate the new geometry. *
* Windows are capable of generating the following WindowEvents: * WindowOpened, WindowClosed, WindowGainedFocus, WindowLostFocus. * * @author Sami Shaio * @author Arthur van Hoff * @see WindowEvent * @see #addWindowListener * @see java.awt.BorderLayout * @since JDK1.0 */ public class Window extends Container implements Accessible { /** * Enumeration of available window types. * * A window type defines the generic visual appearance and behavior of a * top-level window. For example, the type may affect the kind of * decorations of a decorated {@code Frame} or {@code Dialog} instance. *
* Some platforms may not fully support a certain window type. Depending on
* the level of support, some properties of the window type may be
* disobeyed.
*
* @see #getType
* @see #setType
* @since 1.7
*/
public static enum Type {
/**
* Represents a normal window.
*
* This is the default type for objects of the {@code Window} class or
* its descendants. Use this type for regular top-level windows.
*/
NORMAL,
/**
* Represents a utility window.
*
* A utility window is usually a small window such as a toolbar or a
* palette. The native system may render the window with smaller
* title-bar if the window is either a {@code Frame} or a {@code
* Dialog} object, and if it has its decorations enabled.
*/
UTILITY,
/**
* Represents a popup window.
*
* A popup window is a temporary window such as a drop-down menu or a
* tooltip. On some platforms, windows of that type may be forcibly
* made undecorated even if they are instances of the {@code Frame} or
* {@code Dialog} class, and have decorations enabled.
*/
POPUP
}
/**
* This represents the warning message that is
* to be displayed in a non secure window. ie :
* a window that has a security manager installed for
* which calling SecurityManager.checkTopLevelWindow()
* is false. This message can be displayed anywhere in
* the window.
*
* @serial
* @see #getWarningString
*/
String warningString;
/**
* {@code icons} is the graphical way we can
* represent the frames and dialogs.
* {@code Window} can't display icon but it's
* being inherited by owned {@code Dialog}s.
*
* @serial
* @see #getIconImages
* @see #setIconImages(List)
*/
transient java.util.List
* If there is a security manager, this method first calls
* the security manager's First, if there is a security manager, its
*
* If there is a security manager, this method first calls
* the security manager's
* If there is a security manager, this method first calls
* the security manager's
* If there is a security manager, this method first calls
* the security manager's
* This method returns a copy of the internally stored list, so all operations
* on the returned object will not affect the window's behavior.
*
* @return the copy of icon images' list for this window, or
* empty list if this window doesn't have icon images.
* @see #setIconImages
* @see #setIconImage(Image)
* @since 1.6
*/
public java.util.List
* Depending on the platform capabilities one or several images
* of different dimensions will be used as the window's icon.
*
* The {@code icons} list is scanned for the images of most
* appropriate dimensions from the beginning. If the list contains
* several images of the same size, the first will be used.
*
* Ownerless windows with no icon specified use platfrom-default icon.
* The icon of an owned window may be inherited from the owner
* unless explicitly overridden.
* Setting the icon to {@code null} or empty list restores
* the default behavior.
*
* Note : Native windowing systems may use different images of differing
* dimensions to represent a window, depending on the context (e.g.
* window decoration, window list, taskbar, etc.). They could also use
* just a single image for all contexts or no image at all.
*
* @param icons the list of icon images to be displayed.
* @see #getIconImages()
* @see #setIconImage(Image)
* @since 1.6
*/
public synchronized void setIconImages(java.util.List icons) {
this.icons = (icons == null) ? new ArrayList
* This method can be used instead of {@link #setIconImages setIconImages()}
* to specify a single image as a window's icon.
*
* The following statement:
*
* Note : Native windowing systems may use different images of differing
* dimensions to represent a window, depending on the context (e.g.
* window decoration, window list, taskbar, etc.). They could also use
* just a single image for all contexts or no image at all.
*
* @param image the icon image to be displayed.
* @see #setIconImages
* @see #getIconImages()
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setIconImage(Image image) {
ArrayList
* If the window and/or its owner are not displayable yet,
* both of them are made displayable before calculating
* the preferred size. The Window is validated after its
* size is being calculated.
*
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #setMinimumSize
*/
public void pack() {
Container parent = this.parent;
if (parent != null && parent.getPeer() == null) {
parent.addNotify();
}
if (peer == null) {
addNotify();
}
Dimension newSize = getPreferredSize();
if (peer != null) {
setClientSize(newSize.width, newSize.height);
}
if(beforeFirstShow) {
isPacked = true;
}
validateUnconditionally();
}
/**
* Sets the minimum size of this window to a constant
* value. Subsequent calls to {@code getMinimumSize}
* will always return this value. If current window's
* size is less than {@code minimumSize} the size of the
* window is automatically enlarged to honor the minimum size.
*
* If the {@code setSize} or {@code setBounds} methods
* are called afterwards with a width or height less than
* that was specified by the {@code setMinimumSize} method
* the window is automatically enlarged to meet
* the {@code minimumSize} value. The {@code minimumSize}
* value also affects the behaviour of the {@code pack} method.
*
* The default behavior is restored by setting the minimum size
* parameter to the {@code null} value.
*
* Resizing operation may be restricted if the user tries
* to resize window below the {@code minimumSize} value.
* This behaviour is platform-dependent.
*
* @param minimumSize the new minimum size of this window
* @see Component#setMinimumSize
* @see #getMinimumSize
* @see #isMinimumSizeSet
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #pack
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setMinimumSize(Dimension minimumSize) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
super.setMinimumSize(minimumSize);
Dimension size = getSize();
if (isMinimumSizeSet()) {
if (size.width < minimumSize.width || size.height < minimumSize.height) {
int nw = Math.max(width, minimumSize.width);
int nh = Math.max(height, minimumSize.height);
setSize(nw, nh);
}
}
if (peer != null) {
((WindowPeer)peer).updateMinimumSize();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code d.width} and {@code d.height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getSize
* @see #setBounds
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setSize(Dimension d) {
super.setSize(d);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code width} and {@code height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getSize
* @see #setBounds
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setSize(int width, int height) {
super.setSize(width, height);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*/
@Override
public void setLocation(int x, int y) {
super.setLocation(x, y);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*/
@Override
public void setLocation(Point p) {
super.setLocation(p);
}
/**
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.1,
* replaced by
* If the method shows the window then the window is also made
* focused under the following conditions:
*
* Developers must never assume that the window is the focused or active window
* until it receives a WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS or WINDOW_ACTIVATED event.
* @param b if {@code true}, makes the {@code Window} visible,
* otherwise hides the {@code Window}.
* If the {@code Window} and/or its owner
* are not yet displayable, both are made displayable. The
* {@code Window} will be validated prior to being made visible.
* If the {@code Window} is already visible, this will bring the
* {@code Window} to the front.
* If {@code false}, hides this {@code Window}, its subcomponents, and all
* of its owned children.
* The {@code Window} and its subcomponents can be made visible again
* with a call to {@code #setVisible(true)}.
* @see java.awt.Component#isDisplayable
* @see java.awt.Component#setVisible
* @see java.awt.Window#toFront
* @see java.awt.Window#dispose
* @see java.awt.Window#setAutoRequestFocus
* @see java.awt.Window#isFocusableWindow
*/
public void setVisible(boolean b) {
super.setVisible(b);
}
/**
* Makes the Window visible. If the Window and/or its owner
* are not yet displayable, both are made displayable. The
* Window will be validated prior to being made visible.
* If the Window is already visible, this will bring the Window
* to the front.
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #toFront
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.5, replaced by
* {@link #setVisible(boolean)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void show() {
if (peer == null) {
addNotify();
}
validateUnconditionally();
isInShow = true;
if (visible) {
toFront();
} else {
beforeFirstShow = false;
closeSplashScreen();
Dialog.checkShouldBeBlocked(this);
super.show();
locationByPlatform = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if ((child != null) && child.showWithParent) {
child.show();
child.showWithParent = false;
} // endif
} // endfor
if (!isModalBlocked()) {
updateChildrenBlocking();
} else {
// fix for 6532736: after this window is shown, its blocker
// should be raised to front
modalBlocker.toFront_NoClientCode();
}
if (this instanceof Frame || this instanceof Dialog) {
updateChildFocusableWindowState(this);
}
}
isInShow = false;
// If first time shown, generate WindowOpened event
if ((state & OPENED) == 0) {
postWindowEvent(WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED);
state |= OPENED;
}
}
static void updateChildFocusableWindowState(Window w) {
if (w.getPeer() != null && w.isShowing()) {
((WindowPeer)w.getPeer()).updateFocusableWindowState();
}
for (int i = 0; i < w.ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = w.ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if (child != null) {
updateChildFocusableWindowState(child);
}
}
}
synchronized void postWindowEvent(int id) {
if (windowListener != null
|| (eventMask & AWTEvent.WINDOW_EVENT_MASK) != 0
|| Toolkit.enabledOnToolkit(AWTEvent.WINDOW_EVENT_MASK)) {
WindowEvent e = new WindowEvent(this, id);
Toolkit.getEventQueue().postEvent(e);
}
}
/**
* Hide this Window, its subcomponents, and all of its owned children.
* The Window and its subcomponents can be made visible again
* with a call to {@code show}.
*
* The
* Note: When the last displayable window
* within the Java virtual machine (VM) is disposed of, the VM may
* terminate. See
* AWT Threading Issues for more information.
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #pack
* @see #show
*/
public void dispose() {
doDispose();
}
/*
* Fix for 4872170.
* If dispose() is called on parent then its children have to be disposed as well
* as reported in javadoc. So we need to implement this functionality even if a
* child overrides dispose() in a wrong way without calling super.dispose().
*/
void disposeImpl() {
dispose();
if (getPeer() != null) {
doDispose();
}
}
void doDispose() {
class DisposeAction implements Runnable {
public void run() {
disposing = true;
try {
// Check if this window is the fullscreen window for the
// device. Exit the fullscreen mode prior to disposing
// of the window if that's the case.
GraphicsDevice gd = getGraphicsConfiguration().getDevice();
if (gd.getFullScreenWindow() == Window.this) {
gd.setFullScreenWindow(null);
}
Object[] ownedWindowArray;
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
ownedWindowArray = new Object[ownedWindowList.size()];
ownedWindowList.copyInto(ownedWindowArray);
}
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowArray.length; i++) {
Window child = (Window) (((WeakReference)
(ownedWindowArray[i])).get());
if (child != null) {
child.disposeImpl();
}
}
hide();
beforeFirstShow = true;
removeNotify();
synchronized (inputContextLock) {
if (inputContext != null) {
inputContext.dispose();
inputContext = null;
}
}
clearCurrentFocusCycleRootOnHide();
} finally {
disposing = false;
}
}
}
DisposeAction action = new DisposeAction();
if (EventQueue.isDispatchThread()) {
action.run();
}
else {
try {
EventQueue.invokeAndWait(action);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("Disposal was interrupted:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
System.err.println("Exception during disposal:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Execute outside the Runnable because postWindowEvent is
// synchronized on (this). We don't need to synchronize the call
// on the EventQueue anyways.
postWindowEvent(WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED);
}
/*
* Should only be called while holding the tree lock.
* It's overridden here because parent == owner in Window,
* and we shouldn't adjust counter on owner
*/
void adjustListeningChildrenOnParent(long mask, int num) {
}
// Should only be called while holding tree lock
void adjustDecendantsOnParent(int num) {
// do nothing since parent == owner and we shouldn't
// ajust counter on owner
}
/**
* If this Window is visible, brings this Window to the front and may make
* it the focused Window.
*
* Places this Window at the top of the stacking order and shows it in
* front of any other Windows in this VM. No action will take place if this
* Window is not visible. Some platforms do not allow Windows which own
* other Windows to appear on top of those owned Windows. Some platforms
* may not permit this VM to place its Windows above windows of native
* applications, or Windows of other VMs. This permission may depend on
* whether a Window in this VM is already focused. Every attempt will be
* made to move this Window as high as possible in the stacking order;
* however, developers should not assume that this method will move this
* Window above all other windows in every situation.
*
* Developers must never assume that this Window is the focused or active
* Window until this Window receives a WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS or WINDOW_ACTIVATED
* event. On platforms where the top-most window is the focused window, this
* method will probably focus this Window (if it is not already focused)
* under the following conditions:
*
* If this method causes this Window to be focused, and this Window is a
* Frame or a Dialog, it will also become activated. If this Window is
* focused, but it is not a Frame or a Dialog, then the first Frame or
* Dialog that is an owner of this Window will be activated.
*
* If this window is blocked by modal dialog, then the blocking dialog
* is brought to the front and remains above the blocked window.
*
* @see #toBack
* @see #setAutoRequestFocus
* @see #isFocusableWindow
*/
public void toFront() {
toFront_NoClientCode();
}
// This functionality is implemented in a final package-private method
// to insure that it cannot be overridden by client subclasses.
final void toFront_NoClientCode() {
if (visible) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.toFront();
}
if (isModalBlocked()) {
modalBlocker.toFront_NoClientCode();
}
}
}
/**
* If this Window is visible, sends this Window to the back and may cause
* it to lose focus or activation if it is the focused or active Window.
*
* Places this Window at the bottom of the stacking order and shows it
* behind any other Windows in this VM. No action will take place is this
* Window is not visible. Some platforms do not allow Windows which are
* owned by other Windows to appear below their owners. Every attempt will
* be made to move this Window as low as possible in the stacking order;
* however, developers should not assume that this method will move this
* Window below all other windows in every situation.
*
* Because of variations in native windowing systems, no guarantees about
* changes to the focused and active Windows can be made. Developers must
* never assume that this Window is no longer the focused or active Window
* until this Window receives a WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS or WINDOW_DEACTIVATED
* event. On platforms where the top-most window is the focused window,
* this method will probably cause this Window to lose focus. In
* that case, the next highest, focusable Window in this VM will receive
* focus. On platforms where the stacking order does not typically affect
* the focused window, this method will probably leave the focused
* and active Windows unchanged.
*
* @see #toFront
*/
public void toBack() {
toBack_NoClientCode();
}
// This functionality is implemented in a final package-private method
// to insure that it cannot be overridden by client subclasses.
final void toBack_NoClientCode() {
if(isAlwaysOnTop()) {
try {
setAlwaysOnTop(false);
}catch(SecurityException e) {
}
}
if (visible) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.toBack();
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the toolkit of this frame.
* @return the toolkit of this window.
* @see Toolkit
* @see Toolkit#getDefaultToolkit
* @see Component#getToolkit
*/
public Toolkit getToolkit() {
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
}
/**
* Gets the warning string that is displayed with this window.
* If this window is insecure, the warning string is displayed
* somewhere in the visible area of the window. A window is
* insecure if there is a security manager, and the security
* manager's
* If the window is secure, then
* The method may have no visual effect if the Java platform
* implementation and/or the native system do not support
* changing the mouse cursor shape.
* @param cursor One of the constants defined
* by the
* Warning: this method may return system created windows, such
* as a print dialog. Applications should not assume the existence of
* these dialogs, nor should an application assume anything about these
* dialogs such as component positions,
* Warning: this method may return system created windows, such
* as a print dialog. Applications should not assume the existence of
* these dialogs, nor should an application assume anything about these
* dialogs such as component positions,
* If the given type is not supported,
* Note: changing the modal exclusion type for a visible window may have no
* effect until it is hidden and then shown again.
*
* @param exclusionType the modal exclusion type for this window; a Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window listener
* @see #removeWindowListener
* @see #getWindowListeners
*/
public synchronized void addWindowListener(WindowListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
newEventsOnly = true;
windowListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowListener, l);
}
/**
* Adds the specified window state listener to receive window
* events from this window. If Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window state listener
* @see #removeWindowStateListener
* @see #getWindowStateListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void addWindowStateListener(WindowStateListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowStateListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowStateListener, l);
newEventsOnly = true;
}
/**
* Adds the specified window focus listener to receive window events
* from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window focus listener
* @see #removeWindowFocusListener
* @see #getWindowFocusListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void addWindowFocusListener(WindowFocusListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowFocusListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowFocusListener, l);
newEventsOnly = true;
}
/**
* Removes the specified window listener so that it no longer
* receives window events from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window listener
* @see #addWindowListener
* @see #getWindowListeners
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowListener(WindowListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowListener, l);
}
/**
* Removes the specified window state listener so that it no
* longer receives window events from this window. If
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window state listener
* @see #addWindowStateListener
* @see #getWindowStateListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowStateListener(WindowStateListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowStateListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowStateListener, l);
}
/**
* Removes the specified window focus listener so that it no longer
* receives window events from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window focus listener
* @see #addWindowFocusListener
* @see #getWindowFocusListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowFocusListener(WindowFocusListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowFocusListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowFocusListener, l);
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's
*
* You can specify the Note that if the event parameter is Note that if the event parameter is Note that if the event parameter is Note that if the event parameter is
* If some other window is already always-on-top then the
* relative order between these windows is unspecified (depends on
* platform). No window can be brought to be over the always-on-top
* window except maybe another always-on-top window.
*
* All windows owned by an always-on-top window inherit this state and
* automatically become always-on-top. If a window ceases to be
* always-on-top, the windows that it owns will no longer be
* always-on-top. When an always-on-top window is sent {@link #toBack
* toBack}, its always-on-top state is set to When this method is called on a window with a value of
* When this method is called on a window with a value of
* Note: some platforms might not support always-on-top
* windows. To detect if always-on-top windows are supported by the
* current platform, use {@link Toolkit#isAlwaysOnTopSupported()} and
* {@link Window#isAlwaysOnTopSupported()}. If always-on-top mode
* isn't supported by the toolkit or for this window, calling this
* method has no effect.
*
* If a SecurityManager is installed, the calling thread must be
* granted the AWTPermission "setWindowAlwaysOnTop" in
* order to set the value of this property. If this
* permission is not granted, this method will throw a
* SecurityException, and the current value of the property will
* be left unchanged.
*
* @param alwaysOnTop true if the window should always be above other
* windows
* @throws SecurityException if the calling thread does not have
* permission to set the value of always-on-top property
* @see #isAlwaysOnTop
* @see #toFront
* @see #toBack
* @see AWTPermission
* @see #isAlwaysOnTopSupported
* @see Toolkit#isAlwaysOnTopSupported
* @since 1.5
*/
public final void setAlwaysOnTop(boolean alwaysOnTop) throws SecurityException {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.AWT.SET_WINDOW_ALWAYS_ON_TOP_PERMISSION);
}
boolean oldAlwaysOnTop;
synchronized(this) {
oldAlwaysOnTop = this.alwaysOnTop;
this.alwaysOnTop = alwaysOnTop;
}
if (oldAlwaysOnTop != alwaysOnTop ) {
if (isAlwaysOnTopSupported()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
synchronized(getTreeLock()) {
if (peer != null) {
peer.setAlwaysOnTop(alwaysOnTop);
}
}
}
firePropertyChange("alwaysOnTop", oldAlwaysOnTop, alwaysOnTop);
}
}
/**
* Returns whether the always-on-top mode is supported for this
* window. Some platforms may not support always-on-top windows, some
* may support only some kinds of top-level windows; for example,
* a platform may not support always-on-top modal dialogs.
* @return
* If the focused Window is a Frame or a Dialog it is also the active
* Window. Otherwise, the active Window is the first Frame or Dialog that
* is an owner of the focused Window.
*
* @return whether this is the focused Window.
* @see #isActive
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean isFocused() {
return (KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
getGlobalFocusedWindow() == this);
}
/**
* Gets a focus traversal key for this Window. (See
* If the traversal key has not been explicitly set for this Window,
* then this Window's parent's traversal key is returned. If the
* traversal key has not been explicitly set for any of this Window's
* ancestors, then the current KeyboardFocusManager's default traversal key
* is returned.
*
* @param id one of KeyboardFocusManager.FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS, or
* KeyboardFocusManager.DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @return the AWTKeyStroke for the specified key
* @see Container#setFocusTraversalKeys
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if id is not one of
* KeyboardFocusManager.FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS, or
* KeyboardFocusManager.DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @since 1.4
*/
public Set
* By default, all Windows have a focusable Window state of
*
* Setting a Window's focusability state to
* Note that {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)} may be called indirectly
* (e.g. when showing an owner of the window makes the window to be shown).
* {@link #toFront} may also be called indirectly (e.g. when
* {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)} is called on already visible window).
* In all such cases this property takes effect as well.
*
* The value of the property is not inherited by owned windows.
*
* @param autoRequestFocus whether this window should be focused on
* subsequently being shown or being moved to the front
* @see #isAutoRequestFocus
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #setVisible
* @see #toFront
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setAutoRequestFocus(boolean autoRequestFocus) {
this.autoRequestFocus = autoRequestFocus;
}
/**
* Returns whether this window should receive focus on subsequently being shown
* (with a call to {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)}), or being moved to the front
* (with a call to {@link #toFront}).
*
* By default, the window has {@code autoRequestFocus} value of {@code true}.
*
* @return {@code autoRequestFocus} value
* @see #setAutoRequestFocus
* @since 1.7
*/
public boolean isAutoRequestFocus() {
return autoRequestFocus;
}
/**
* Adds a PropertyChangeListener to the listener list. The listener is
* registered for all bound properties of this class, including the
* following:
*
* If listener is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
*
* @param listener the PropertyChangeListener to be added
*
* @see Component#removePropertyChangeListener
* @see #addPropertyChangeListener(java.lang.String,java.beans.PropertyChangeListener)
*/
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
super.addPropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
/**
* Adds a PropertyChangeListener to the listener list for a specific
* property. The specified property may be user-defined, or one of the
* following:
*
* If listener is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
*
* @param propertyName one of the property names listed above
* @param listener the PropertyChangeListener to be added
*
* @see #addPropertyChangeListener(java.beans.PropertyChangeListener)
* @see Component#removePropertyChangeListener
*/
public void addPropertyChangeListener(String propertyName,
PropertyChangeListener listener) {
super.addPropertyChangeListener(propertyName, listener);
}
/**
* Indicates if this container is a validate root.
*
* {@code Window} objects are the validate roots, and, therefore, they
* override this method to return {@code true}.
*
* @return {@code true}
* @since 1.7
* @see java.awt.Container#isValidateRoot
*/
@Override
public boolean isValidateRoot() {
return true;
}
/**
* Dispatches an event to this window or one of its sub components.
* @param e the event
*/
void dispatchEventImpl(AWTEvent e) {
if (e.getID() == ComponentEvent.COMPONENT_RESIZED) {
invalidate();
validate();
}
super.dispatchEventImpl(e);
}
/**
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.1
* replaced by
* The target screen mentioned below is a screen to which
* the window should be placed after the setLocationRelativeTo
* method is called.
*
* If the screens configuration does not allow the window to
* be moved from one screen to another, then the window is
* only placed at the location determined according to the
* above conditions and its {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is
* not changed.
*
* Note: If the lower edge of the window is out of the screen,
* then the window is placed to the side of the
* If after the window location has been calculated, the upper,
* left, or right edge of the window is out of the screen,
* then the window is located in such a way that the upper,
* left, or right edge of the window coincides with the
* corresponding edge of the screen. If both left and right
* edges of the window are out of the screen, the window is
* placed at the left side of the screen. The similar placement
* will occur if both top and bottom edges are out of the screen.
* In that case, the window is placed at the top side of the screen.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @param c the component in relation to which the window's location
* is determined
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#getCenterPoint
* @since 1.4
*/
public void setLocationRelativeTo(Component c) {
// target location
int dx = 0, dy = 0;
// target GC
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration_NoClientCode();
Rectangle gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Dimension windowSize = getSize();
// search a top-level of c
Window componentWindow = SunToolkit.getContainingWindow(c);
if ((c == null) || (componentWindow == null)) {
GraphicsEnvironment ge = GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
gc = ge.getDefaultScreenDevice().getDefaultConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Point centerPoint = ge.getCenterPoint();
dx = centerPoint.x - windowSize.width / 2;
dy = centerPoint.y - windowSize.height / 2;
} else if (!c.isShowing()) {
gc = componentWindow.getGraphicsConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
dx = gcBounds.x + (gcBounds.width - windowSize.width) / 2;
dy = gcBounds.y + (gcBounds.height - windowSize.height) / 2;
} else {
gc = componentWindow.getGraphicsConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Dimension compSize = c.getSize();
Point compLocation = c.getLocationOnScreen();
dx = compLocation.x + ((compSize.width - windowSize.width) / 2);
dy = compLocation.y + ((compSize.height - windowSize.height) / 2);
// Adjust for bottom edge being offscreen
if (dy + windowSize.height > gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height) {
dy = gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height - windowSize.height;
if (compLocation.x - gcBounds.x + compSize.width / 2 < gcBounds.width / 2) {
dx = compLocation.x + compSize.width;
} else {
dx = compLocation.x - windowSize.width;
}
}
}
// Avoid being placed off the edge of the screen:
// bottom
if (dy + windowSize.height > gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height) {
dy = gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height - windowSize.height;
}
// top
if (dy < gcBounds.y) {
dy = gcBounds.y;
}
// right
if (dx + windowSize.width > gcBounds.x + gcBounds.width) {
dx = gcBounds.x + gcBounds.width - windowSize.width;
}
// left
if (dx < gcBounds.x) {
dx = gcBounds.x;
}
setLocation(dx, dy);
}
/**
* Overridden from Component. Top-level Windows should not propagate a
* MouseWheelEvent beyond themselves into their owning Windows.
*/
void deliverMouseWheelToAncestor(MouseWheelEvent e) {}
/**
* Overridden from Component. Top-level Windows don't dispatch to ancestors
*/
boolean dispatchMouseWheelToAncestor(MouseWheelEvent e) {return false;}
/**
* Creates a new strategy for multi-buffering on this component.
* Multi-buffering is useful for rendering performance. This method
* attempts to create the best strategy available with the number of
* buffers supplied. It will always create a
* Each time this method is called,
* the existing buffer strategy for this component is discarded.
* @param numBuffers number of buffers to create
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if numBuffers is less than 1.
* @exception IllegalStateException if the component is not displayable
* @see #isDisplayable
* @see #getBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public void createBufferStrategy(int numBuffers) {
super.createBufferStrategy(numBuffers);
}
/**
* Creates a new strategy for multi-buffering on this component with the
* required buffer capabilities. This is useful, for example, if only
* accelerated memory or page flipping is desired (as specified by the
* buffer capabilities).
*
* Each time this method
* is called, the existing buffer strategy for this component is discarded.
* @param numBuffers number of buffers to create, including the front buffer
* @param caps the required capabilities for creating the buffer strategy;
* cannot be
* This behavior can also be enabled by setting the System Property
* "java.awt.Window.locationByPlatform" to "true", though calls to this method
* take precedence.
*
* Calls to
* For example, after the following code is executed:
*
* In the following sample:
*
* The {@code width} or {@code height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getBounds
* @see #setLocation(int, int)
* @see #setLocation(Point)
* @see #setSize(int, int)
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (getBoundsOp() == ComponentPeer.SET_LOCATION ||
getBoundsOp() == ComponentPeer.SET_BOUNDS)
{
locationByPlatform = false;
}
super.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code r.width} or {@code r.height} values
* will be automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getBounds
* @see #setLocation(int, int)
* @see #setLocation(Point)
* @see #setSize(int, int)
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setBounds(Rectangle r) {
setBounds(r.x, r.y, r.width, r.height);
}
/**
* Determines whether this component will be displayed on the screen.
* @return
* The opacity value is in the range [0..1]. Note that setting the opacity
* level of 0 may or may not disable the mouse event handling on this
* window. This is a platform-dependent behavior.
*
* The following conditions must be met in order to set the opacity value
* less than {@code 1.0f}:
*
* If the requested opacity value is less than {@code 1.0f}, and any of the
* above conditions are not met, the window opacity will not change,
* and the {@code IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* The translucency levels of individual pixels may also be effected by the
* alpha component of their color (see {@link Window#setBackground(Color)}) and the
* current shape of this window (see {@link #setShape(Shape)}).
*
* @param opacity the opacity level to set to the window
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the opacity is out of the range
* [0..1]
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window is decorated and
* the opacity is less than {@code 1.0f}
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window is in full screen
* mode, and the opacity is less than {@code 1.0f}
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#TRANSLUCENT TRANSLUCENT}
* translucency is not supported and the opacity is less than
* {@code 1.0f}
*
* @see Window#getOpacity
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setOpacity(float opacity) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (opacity < 0.0f || opacity > 1.0f) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The value of opacity should be in the range [0.0f .. 1.0f].");
}
if (opacity < 1.0f) {
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Setting opacity for full-screen window is not supported.");
}
if (!gd.isWindowTranslucencySupported(
GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency.TRANSLUCENT))
{
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"TRANSLUCENT translucency is not supported.");
}
}
this.opacity = opacity;
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.setOpacity(opacity);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the shape of the window.
*
* The value returned by this method may not be the same as
* previously set with {@code setShape(shape)}, but it is guaranteed
* to represent the same shape.
*
* @return the shape of the window or {@code null} if no
* shape is specified for the window
*
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public Shape getShape() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
return shape == null ? null : new Path2D.Float(shape);
}
}
/**
* Sets the shape of the window.
*
* Setting a shape cuts off some parts of the window. Only the parts that
* belong to the given {@link Shape} remain visible and clickable. If
* the shape argument is {@code null}, this method restores the default
* shape, making the window rectangular on most platforms.
*
* The following conditions must be met to set a non-null shape:
*
* If the requested shape is not {@code null}, and any of the above
* conditions are not met, the shape of this window will not change,
* and either the {@code UnsupportedOperationException} or {@code
* IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* The tranlucency levels of individual pixels may also be effected by the
* alpha component of their color (see {@link Window#setBackground(Color)}) and the
* opacity value (see {@link #setOpacity(float)}). See {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency} for more details.
*
* @param shape the shape to set to the window
*
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and the window is decorated
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and the window is in full-screen mode
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and {@link GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT
* PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT} translucency is not supported
*
* @see Window#getShape()
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setShape(Shape shape) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (shape != null) {
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Setting shape for full-screen window is not supported.");
}
if (!gd.isWindowTranslucencySupported(
GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency.PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT))
{
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT translucency is not supported.");
}
}
this.shape = (shape == null) ? null : new Path2D.Float(shape);
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.applyShape(shape == null ? null : Region.getInstance(shape, null));
}
}
}
/**
* Gets the background color of this window.
*
* Note that the alpha component of the returned color indicates whether
* the window is in the non-opaque (per-pixel translucent) mode.
*
* @return this component's background color
*
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#isOpaque
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*/
@Override
public Color getBackground() {
return super.getBackground();
}
/**
* Sets the background color of this window.
*
* If the windowing system supports the {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT}
* tranclucency, the alpha component of the given background color
* may effect the mode of operation for this window: it indicates whether
* this window must be opaque (alpha equals {@code 1.0f}) or per-pixel translucent
* (alpha is less than {@code 1.0f}). If the given background color is
* {@code null}, the window is considered completely opaque.
*
* All the following conditions must be met to enable the per-pixel
* transparency mode for this window:
*
* If the alpha component of the requested background color is less than
* {@code 1.0f}, and any of the above conditions are not met, the background
* color of this window will not change, the alpha component of the given
* background color will not affect the mode of operation for this window,
* and either the {@code UnsupportedOperationException} or {@code
* IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* When the window is per-pixel translucent, the drawing sub-system
* respects the alpha value of each individual pixel. If a pixel gets
* painted with the alpha color component equal to zero, it becomes
* visually transparent. If the alpha of the pixel is equal to 1.0f, the
* pixel is fully opaque. Interim values of the alpha color component make
* the pixel semi-transparent. In this mode, the background of the window
* gets painted with the alpha value of the given background color. If the
* alpha value of the argument of this method is equal to {@code 0}, the
* background is not painted at all.
*
* The actual level of translucency of a given pixel also depends on window
* opacity (see {@link #setOpacity(float)}), as well as the current shape of
* this window (see {@link #setShape(Shape)}).
*
* Note that painting a pixel with the alpha value of {@code 0} may or may
* not disable the mouse event handling on this pixel. This is a
* platform-dependent behavior. To make sure the mouse events do not get
* dispatched to a particular pixel, the pixel must be excluded from the
* shape of the window.
*
* Enabling the per-pixel translucency mode may change the graphics
* configuration of this window due to the native platform requirements.
*
* @param bgColor the color to become this window's background color.
*
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and the window is decorated
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and the window is in
* full-screen mode
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT
* PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT} translucency is not supported
*
* @see Window#getBackground
* @see Window#isOpaque
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
* @see GraphicsConfiguration#isTranslucencyCapable()
*/
@Override
public void setBackground(Color bgColor) {
Color oldBg = getBackground();
super.setBackground(bgColor);
if (oldBg != null && oldBg.equals(bgColor)) {
return;
}
int oldAlpha = oldBg != null ? oldBg.getAlpha() : 255;
int alpha = bgColor != null ? bgColor.getAlpha() : 255;
if ((oldAlpha == 255) && (alpha < 255)) { // non-opaque window
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Making full-screen window non opaque is not supported.");
}
if (!gc.isTranslucencyCapable()) {
GraphicsConfiguration capableGC = gd.getTranslucencyCapableGC();
if (capableGC == null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT translucency is not supported");
}
setGraphicsConfiguration(capableGC);
}
setLayersOpaque(this, false);
} else if ((oldAlpha < 255) && (alpha == 255)) {
setLayersOpaque(this, true);
}
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.setOpaque(alpha == 255);
}
}
/**
* Indicates if the window is currently opaque.
*
* The method returns {@code false} if the background color of the window
* is not {@code null} and the alpha component of the color is less than
* {@code 1.0f}. The method returns {@code true} otherwise.
*
* @return {@code true} if the window is opaque, {@code false} otherwise
*
* @see Window#getBackground
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @since 1.7
*/
@Override
public boolean isOpaque() {
Color bg = getBackground();
return bg != null ? bg.getAlpha() == 255 : true;
}
private void updateWindow() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.updateWindow();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 1.7
*/
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
if (!isOpaque()) {
Graphics gg = g.create();
try {
if (gg instanceof Graphics2D) {
gg.setColor(getBackground());
((Graphics2D)gg).setComposite(AlphaComposite.getInstance(AlphaComposite.SRC));
gg.fillRect(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
} finally {
gg.dispose();
}
}
super.paint(g);
}
private static void setLayersOpaque(Component component, boolean isOpaque) {
// Shouldn't use instanceof to avoid loading Swing classes
// if it's a pure AWT application.
if (SunToolkit.isInstanceOf(component, "javax.swing.RootPaneContainer")) {
javax.swing.RootPaneContainer rpc = (javax.swing.RootPaneContainer)component;
javax.swing.JRootPane root = rpc.getRootPane();
javax.swing.JLayeredPane lp = root.getLayeredPane();
Container c = root.getContentPane();
javax.swing.JComponent content =
(c instanceof javax.swing.JComponent) ? (javax.swing.JComponent)c : null;
lp.setOpaque(isOpaque);
root.setOpaque(isOpaque);
if (content != null) {
content.setOpaque(isOpaque);
// Iterate down one level to see whether we have a JApplet
// (which is also a RootPaneContainer) which requires processing
int numChildren = content.getComponentCount();
if (numChildren > 0) {
Component child = content.getComponent(0);
// It's OK to use instanceof here because we've
// already loaded the RootPaneContainer class by now
if (child instanceof javax.swing.RootPaneContainer) {
setLayersOpaque(child, isOpaque);
}
}
}
}
}
// ************************** MIXING CODE *******************************
// A window has a parent, but it does NOT have a container
@Override
final Container getContainer() {
return null;
}
/**
* Applies the shape to the component
* @param shape Shape to be applied to the component
*/
@Override
final void applyCompoundShape(Region shape) {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final void applyCurrentShape() {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final void mixOnReshaping() {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final Point getLocationOnWindow() {
return new Point(0, 0);
}
// ****************** END OF MIXING CODE ********************************
/**
* Limit the given double value with the given range.
*/
private static double limit(double value, double min, double max) {
value = Math.max(value, min);
value = Math.min(value, max);
return value;
}
/**
* Calculate the position of the security warning.
*
* This method gets the window location/size as reported by the native
* system since the locally cached values may represent outdated data.
*
* The method is used from the native code, or via AWTAccessor.
*
* NOTE: this method is invoked on the toolkit thread, and therefore is not
* supposed to become public/user-overridable.
*/
private Point2D calculateSecurityWarningPosition(double x, double y,
double w, double h)
{
// The position according to the spec of SecurityWarning.setPosition()
double wx = x + w * securityWarningAlignmentX + securityWarningPointX;
double wy = y + h * securityWarningAlignmentY + securityWarningPointY;
// First, make sure the warning is not too far from the window bounds
wx = Window.limit(wx,
x - securityWarningWidth - 2,
x + w + 2);
wy = Window.limit(wy,
y - securityWarningHeight - 2,
y + h + 2);
// Now make sure the warning window is visible on the screen
GraphicsConfiguration graphicsConfig =
getGraphicsConfiguration_NoClientCode();
Rectangle screenBounds = graphicsConfig.getBounds();
Insets screenInsets =
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenInsets(graphicsConfig);
wx = Window.limit(wx,
screenBounds.x + screenInsets.left,
screenBounds.x + screenBounds.width - screenInsets.right
- securityWarningWidth);
wy = Window.limit(wy,
screenBounds.y + screenInsets.top,
screenBounds.y + screenBounds.height - screenInsets.bottom
- securityWarningHeight);
return new Point2D.Double(wx, wy);
}
static {
AWTAccessor.setWindowAccessor(new AWTAccessor.WindowAccessor() {
public float getOpacity(Window window) {
return window.opacity;
}
public void setOpacity(Window window, float opacity) {
window.setOpacity(opacity);
}
public Shape getShape(Window window) {
return window.getShape();
}
public void setShape(Window window, Shape shape) {
window.setShape(shape);
}
public void setOpaque(Window window, boolean opaque) {
Color bg = window.getBackground();
if (bg == null) {
bg = new Color(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
window.setBackground(new Color(bg.getRed(), bg.getGreen(), bg.getBlue(),
opaque ? 255 : 0));
}
public void updateWindow(Window window) {
window.updateWindow();
}
public Dimension getSecurityWarningSize(Window window) {
return new Dimension(window.securityWarningWidth,
window.securityWarningHeight);
}
public void setSecurityWarningSize(Window window, int width, int height)
{
window.securityWarningWidth = width;
window.securityWarningHeight = height;
}
public void setSecurityWarningPosition(Window window,
Point2D point, float alignmentX, float alignmentY)
{
window.securityWarningPointX = point.getX();
window.securityWarningPointY = point.getY();
window.securityWarningAlignmentX = alignmentX;
window.securityWarningAlignmentY = alignmentY;
synchronized (window.getTreeLock()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)window.getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.repositionSecurityWarning();
}
}
}
public Point2D calculateSecurityWarningPosition(Window window,
double x, double y, double w, double h)
{
return window.calculateSecurityWarningPosition(x, y, w, h);
}
public void setLWRequestStatus(Window changed, boolean status) {
changed.syncLWRequests = status;
}
public boolean isAutoRequestFocus(Window w) {
return w.autoRequestFocus;
}
public boolean isTrayIconWindow(Window w) {
return w.isTrayIconWindow;
}
public void setTrayIconWindow(Window w, boolean isTrayIconWindow) {
w.isTrayIconWindow = isTrayIconWindow;
}
}); // WindowAccessor
} // static
// a window doesn't need to be updated in the Z-order.
@Override
void updateZOrder() {}
} // class Window
/**
* This class is no longer used, but is maintained for Serialization
* backward-compatibility.
*/
class FocusManager implements java.io.Serializable {
Container focusRoot;
Component focusOwner;
/*
* JDK 1.1 serialVersionUID
*/
static final long serialVersionUID = 2491878825643557906L;
}
GraphicsConfiguration.
* checkTopLevelWindow
* method with this
* as its argument to determine whether or not the window
* must be displayed with a warning banner.
*
* @param gc the GraphicsConfiguration of the target screen
* device. If gc is null, the system default
* GraphicsConfiguration is assumed
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if gc
* is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless() returns true
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow
*/
Window(GraphicsConfiguration gc) {
init(gc);
}
transient Object anchor = new Object();
static class WindowDisposerRecord implements sun.java2d.DisposerRecord {
final WeakReferencecheckTopLevelWindow
* method is called with this
* as its argument
* to see if it's ok to display the window without a warning banner.
* If the default implementation of checkTopLevelWindow
* is used (that is, that method is not overriden), then this results in
* a call to the security manager's checkPermission method
* with an AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")
* permission. It that method raises a SecurityException,
* checkTopLevelWindow returns false, otherwise it
* returns true. If it returns false, a warning banner is created.
*
* @exception HeadlessException when
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless() returns true
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow
*/
Window() throws HeadlessException {
GraphicsEnvironment.checkHeadless();
init((GraphicsConfiguration)null);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified
* Frame as its owner. The window will not be focusable
* unless its owner is showing on the screen.
* checkTopLevelWindow
* method with this
* as its argument to determine whether or not the window
* must be displayed with a warning banner.
*
* @param owner the Frame to act as owner or null
* if this window has no owner
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the owner's
* GraphicsConfiguration is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless returns true
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow
* @see #isShowing
*/
public Window(Frame owner) {
this(owner == null ? (GraphicsConfiguration)null :
owner.getGraphicsConfiguration());
ownedInit(owner);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified
* Window as its owner. This window will not be focusable
* unless its nearest owning Frame or Dialog
* is showing on the screen.
* checkTopLevelWindow
* method with this
* as its argument to determine whether or not the window
* must be displayed with a warning banner.
*
* @param owner the Window to act as owner or
* null if this window has no owner
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the owner's
* GraphicsConfiguration is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless() returns
* true
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow
* @see #isShowing
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window(Window owner) {
this(owner == null ? (GraphicsConfiguration)null :
owner.getGraphicsConfiguration());
ownedInit(owner);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified owner
* Window and a GraphicsConfiguration
* of a screen device. The Window will not be focusable unless
* its nearest owning Frame or Dialog
* is showing on the screen.
* checkTopLevelWindow
* method with this
* as its argument to determine whether or not the window
* must be displayed with a warning banner.
*
* @param owner the window to act as owner or null
* if this window has no owner
* @param gc the GraphicsConfiguration of the target
* screen device; if gc is null,
* the system default GraphicsConfiguration is assumed
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if gc
* is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless() returns
* true
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow
* @see GraphicsConfiguration#getBounds
* @see #isShowing
* @since 1.3
*/
public Window(Window owner, GraphicsConfiguration gc) {
this(gc);
ownedInit(owner);
}
private void ownedInit(Window owner) {
this.parent = owner;
if (owner != null) {
owner.addOwnedWindow(weakThis);
}
// Fix for 6758673: this call is moved here from init(gc), because
// WindowDisposerRecord requires a proper value of parent field.
Disposer.addRecord(anchor, new WindowDisposerRecord(appContext, this));
}
/**
* Construct a name for this component. Called by getName() when the
* name is null.
*/
String constructComponentName() {
synchronized (Window.class) {
return base + nameCounter++;
}
}
/**
* Returns the sequence of images to be displayed as the icon for this window.
*
* setIconImage(image);
*
* is equivalent to:
*
* ArrayList<Image> imageList = new ArrayList<Image>();
* imageList.add(image);
* setIconImages(imageList);
*
* setBounds(int, int, int, int).
*/
@Deprecated
public void reshape(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
if (isMinimumSizeSet()) {
Dimension minSize = getMinimumSize();
if (width < minSize.width) {
width = minSize.width;
}
if (height < minSize.height) {
height = minSize.height;
}
}
super.reshape(x, y, width, height);
}
void setClientSize(int w, int h) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
setBoundsOp(ComponentPeer.SET_CLIENT_SIZE);
setBounds(x, y, w, h);
}
}
static private final AtomicBoolean
beforeFirstWindowShown = new AtomicBoolean(true);
final void closeSplashScreen() {
if (isTrayIconWindow) {
return;
}
if (beforeFirstWindowShown.getAndSet(false)) {
// We don't use SplashScreen.getSplashScreen() to avoid instantiating
// the object if it hasn't been requested by user code explicitly
SunToolkit.closeSplashScreen();
SplashScreen.markClosed();
}
}
/**
* Shows or hides this {@code Window} depending on the value of parameter
* {@code b}.
*
*
* There is an exception for the second condition (the value of the
* {@code autoRequestFocus} property). The property is not taken into account if the
* window is a modal dialog, which blocks the currently focused window.
* Window, its subcomponents, and all of its owned
* children. That is, the resources for these Components
* will be destroyed, any memory they consume will be returned to the
* OS, and they will be marked as undisplayable.
* Window and its subcomponents can be made displayable
* again by rebuilding the native resources with a subsequent call to
* pack or show. The states of the recreated
* Window and its subcomponents will be identical to the
* states of these objects at the point where the Window
* was disposed (not accounting for additional modifications between
* those actions).
*
*
* On platforms where the stacking order does not typically affect the focused
* window, this method will probably leave the focused and active
* Windows unchanged.
* checkTopLevelWindow method returns
* false when this window is passed to it as an
* argument.
* getWarningString
* returns null. If the window is insecure, this
* method checks for the system property
* awt.appletWarning
* and returns the string value of that property.
* @return the warning string for this window.
* @see java.lang.SecurityManager#checkTopLevelWindow(java.lang.Object)
*/
public final String getWarningString() {
return warningString;
}
private void setWarningString() {
warningString = null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
if (!sm.checkTopLevelWindow(this)) {
// make sure the privileged action is only
// for getting the property! We don't want the
// above checkTopLevelWindow call to always succeed!
warningString = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("awt.appletWarning",
"Java Applet Window"));
}
}
}
/**
* Gets the Locale object that is associated
* with this window, if the locale has been set.
* If no locale has been set, then the default locale
* is returned.
* @return the locale that is set for this window.
* @see java.util.Locale
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public Locale getLocale() {
if (this.locale == null) {
return Locale.getDefault();
}
return this.locale;
}
/**
* Gets the input context for this window. A window always has an input context,
* which is shared by subcomponents unless they create and set their own.
* @see Component#getInputContext
* @since 1.2
*/
public InputContext getInputContext() {
synchronized (inputContextLock) {
if (inputContext == null) {
inputContext = InputContext.getInstance();
}
}
return inputContext;
}
/**
* Set the cursor image to a specified cursor.
* Cursor class. If this parameter is null
* then the cursor for this window will be set to the type
* Cursor.DEFAULT_CURSOR.
* @see Component#getCursor
* @see Cursor
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public void setCursor(Cursor cursor) {
if (cursor == null) {
cursor = Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.DEFAULT_CURSOR);
}
super.setCursor(cursor);
}
/**
* Returns the owner of this window.
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window getOwner() {
return getOwner_NoClientCode();
}
final Window getOwner_NoClientCode() {
return (Window)parent;
}
/**
* Return an array containing all the windows this
* window currently owns.
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window[] getOwnedWindows() {
return getOwnedWindows_NoClientCode();
}
final Window[] getOwnedWindows_NoClientCode() {
Window realCopy[];
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
// Recall that ownedWindowList is actually a Vector of
// WeakReferences and calling get() on one of these references
// may return null. Make two arrays-- one the size of the
// Vector (fullCopy with size fullSize), and one the size of
// all non-null get()s (realCopy with size realSize).
int fullSize = ownedWindowList.size();
int realSize = 0;
Window fullCopy[] = new Window[fullSize];
for (int i = 0; i < fullSize; i++) {
fullCopy[realSize] = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if (fullCopy[realSize] != null) {
realSize++;
}
}
if (fullSize != realSize) {
realCopy = Arrays.copyOf(fullCopy, realSize);
} else {
realCopy = fullCopy;
}
}
return realCopy;
}
boolean isModalBlocked() {
return modalBlocker != null;
}
void setModalBlocked(Dialog blocker, boolean blocked, boolean peerCall) {
this.modalBlocker = blocked ? blocker : null;
if (peerCall) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.setModalBlocked(blocker, blocked);
}
}
}
Dialog getModalBlocker() {
return modalBlocker;
}
/*
* Returns a list of all displayable Windows, i. e. all the
* Windows which peer is not null.
*
* @see #addNotify
* @see #removeNotify
*/
static IdentityArrayListLayoutManagers
* or serialization.
*
* @see Frame#getFrames
* @see Window#getOwnerlessWindows
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static Window[] getWindows() {
return getWindows(AppContext.getAppContext());
}
/**
* Returns an array of all {@code Window}s created by this application
* that have no owner. They include {@code Frame}s and ownerless
* {@code Dialog}s and {@code Window}s.
* If called from an applet, the array includes only the {@code Window}s
* accessible by that applet.
* LayoutManagers
* or serialization.
*
* @see Frame#getFrames
* @see Window#getWindows()
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static Window[] getOwnerlessWindows() {
Window[] allWindows = Window.getWindows();
int ownerlessCount = 0;
for (Window w : allWindows) {
if (w.getOwner() == null) {
ownerlessCount++;
}
}
Window[] ownerless = new Window[ownerlessCount];
int c = 0;
for (Window w : allWindows) {
if (w.getOwner() == null) {
ownerless[c++] = w;
}
}
return ownerless;
}
Window getDocumentRoot() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
Window w = this;
while (w.getOwner() != null) {
w = w.getOwner();
}
return w;
}
}
/**
* Specifies the modal exclusion type for this window. If a window is modal
* excluded, it is not blocked by some modal dialogs. See {@link
* java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType Dialog.ModalExclusionType} for
* possible modal exclusion types.
* NO_EXCLUDE is used.
* null
* value is equivivalent to {@link Dialog.ModalExclusionType#NO_EXCLUDE
* NO_EXCLUDE}
* @throws SecurityException if the calling thread does not have permission
* to set the modal exclusion property to the window with the given
* exclusionType
* @see java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Window#getModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Toolkit#isModalExclusionTypeSupported
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setModalExclusionType(Dialog.ModalExclusionType exclusionType) {
if (exclusionType == null) {
exclusionType = Dialog.ModalExclusionType.NO_EXCLUDE;
}
if (!Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().isModalExclusionTypeSupported(exclusionType)) {
exclusionType = Dialog.ModalExclusionType.NO_EXCLUDE;
}
if (modalExclusionType == exclusionType) {
return;
}
if (exclusionType == Dialog.ModalExclusionType.TOOLKIT_EXCLUDE) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.AWT.TOOLKIT_MODALITY_PERMISSION);
}
}
modalExclusionType = exclusionType;
// if we want on-fly changes, we need to uncomment the lines below
// and override the method in Dialog to use modalShow() instead
// of updateChildrenBlocking()
/*
if (isModalBlocked()) {
modalBlocker.unblockWindow(this);
}
Dialog.checkShouldBeBlocked(this);
updateChildrenBlocking();
*/
}
/**
* Returns the modal exclusion type of this window.
*
* @return the modal exclusion type of this window
*
* @see java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Window#setModalExclusionType
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public Dialog.ModalExclusionType getModalExclusionType() {
return modalExclusionType;
}
boolean isModalExcluded(Dialog.ModalExclusionType exclusionType) {
if ((modalExclusionType != null) &&
modalExclusionType.compareTo(exclusionType) >= 0)
{
return true;
}
Window owner = getOwner_NoClientCode();
return (owner != null) && owner.isModalExcluded(exclusionType);
}
void updateChildrenBlocking() {
Vectorl is null,
* no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* l is null, no exception is thrown and
* no action is performed.
* WindowListeners
* or an empty array if no window
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowListener
* @see #removeWindowListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowListener[] getWindowListeners() {
return (WindowListener[])(getListeners(WindowListener.class));
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window focus listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's WindowFocusListeners
* or an empty array if no window focus
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowFocusListener
* @see #removeWindowFocusListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowFocusListener[] getWindowFocusListeners() {
return (WindowFocusListener[])(getListeners(WindowFocusListener.class));
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window state listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's WindowStateListeners
* or an empty array if no window state
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowStateListener
* @see #removeWindowStateListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowStateListener[] getWindowStateListeners() {
return (WindowStateListener[])(getListeners(WindowStateListener.class));
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the objects currently registered
* as FooListeners
* upon this Window.
* FooListeners are registered using the
* addFooListener method.
*
* listenerType argument
* with a class literal, such as
* FooListener.class.
* For example, you can query a
* Window w
* for its window listeners with the following code:
*
* WindowListener[] wls = (WindowListener[])(w.getListeners(WindowListener.class));
*
* If no such listeners exist, this method returns an empty array.
*
* @param listenerType the type of listeners requested; this parameter
* should specify an interface that descends from
* java.util.EventListener
* @return an array of all objects registered as
* FooListeners on this window,
* or an empty array if no such
* listeners have been added
* @exception ClassCastException if listenerType
* doesn't specify a class or interface that implements
* java.util.EventListener
* @exception NullPointerException if {@code listenerType} is {@code null}
*
* @see #getWindowListeners
* @since 1.3
*/
public WindowEvent, it invokes the
* processWindowEvent method, else it invokes its
* superclass's processEvent.
* null
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the event
*/
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e) {
if (e instanceof WindowEvent) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSING:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ICONIFIED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEICONIFIED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ACTIVATED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEACTIVATED:
processWindowEvent((WindowEvent)e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS:
processWindowFocusEvent((WindowEvent)e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED:
processWindowStateEvent((WindowEvent)e);
default:
break;
}
return;
}
super.processEvent(e);
}
/**
* Processes window events occurring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered WindowListener objects.
* NOTE: This method will not be called unless window events
* are enabled for this component; this happens when one of the
* following occurs:
*
*
* addWindowListener
* enableEvents
* null
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window event
* @see Component#enableEvents
*/
protected void processWindowEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowListener listener = windowListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch(e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED:
listener.windowOpened(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSING:
listener.windowClosing(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED:
listener.windowClosed(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ICONIFIED:
listener.windowIconified(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEICONIFIED:
listener.windowDeiconified(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ACTIVATED:
listener.windowActivated(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEACTIVATED:
listener.windowDeactivated(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Processes window focus event occuring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered WindowFocusListener objects.
* NOTE: this method will not be called unless window focus events
* are enabled for this window. This happens when one of the
* following occurs:
*
*
* addWindowFocusListener
* enableEvents
* null
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window focus event
* @see Component#enableEvents
* @since 1.4
*/
protected void processWindowFocusEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowFocusListener listener = windowFocusListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS:
listener.windowGainedFocus(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS:
listener.windowLostFocus(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Processes window state event occuring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered WindowStateListener
* objects.
* NOTE: this method will not be called unless window state events
* are enabled for this window. This happens when one of the
* following occurs:
*
*
* WindowStateListener is registered via
* addWindowStateListener
* enableEvents
* null
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window state event
* @see java.awt.Component#enableEvents
* @since 1.4
*/
protected void processWindowStateEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowStateListener listener = windowStateListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED:
listener.windowStateChanged(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Implements a debugging hook -- checks to see if
* the user has typed control-shift-F1. If so,
* the list of child windows is dumped to System.out.
* @param e the keyboard event
*/
void preProcessKeyEvent(KeyEvent e) {
// Dump the list of child windows to System.out.
if (e.isActionKey() && e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_F1 &&
e.isControlDown() && e.isShiftDown() &&
e.getID() == KeyEvent.KEY_PRESSED) {
list(System.out, 0);
}
}
void postProcessKeyEvent(KeyEvent e) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* Sets whether this window should always be above other windows. If
* there are multiple always-on-top windows, their relative order is
* unspecified and platform dependent.
* false.
*
* true, and the window is visible and the platform
* supports always-on-top for this window, the window is immediately
* brought forward, "sticking" it in the top-most position. If the
* window isn`t currently visible, this method sets the always-on-top
* state to true but does not bring the window forward.
* When the window is later shown, it will be always-on-top.
*
* false the always-on-top state is set to normal. The
* window remains in the top-most position but it`s z-order can be
* changed as for any other window. Calling this method with a value
* of false on a window that has a normal state has no
* effect. Setting the always-on-top state to false has no effect on
* the relative z-order of the windows if there are no other
* always-on-top windows.
*
* true, if the always-on-top mode is
* supported by the toolkit and for this window,
* false, if always-on-top mode is not supported
* for this window or toolkit doesn't support always-on-top windows.
* @see #setAlwaysOnTop(boolean)
* @see Toolkit#isAlwaysOnTopSupported
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean isAlwaysOnTopSupported() {
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().isAlwaysOnTopSupported();
}
/**
* Returns whether this window is an always-on-top window.
* @return true, if the window is in always-on-top state,
* false otherwise
* @see #setAlwaysOnTop
* @since 1.5
*/
public final boolean isAlwaysOnTop() {
return alwaysOnTop;
}
/**
* Returns the child Component of this Window that has focus if this Window
* is focused; returns null otherwise.
*
* @return the child Component with focus, or null if this Window is not
* focused
* @see #getMostRecentFocusOwner
* @see #isFocused
*/
public Component getFocusOwner() {
return (isFocused())
? KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
getFocusOwner()
: null;
}
/**
* Returns the child Component of this Window that will receive the focus
* when this Window is focused. If this Window is currently focused, this
* method returns the same Component as getFocusOwner(). If
* this Window is not focused, then the child Component that most recently
* requested focus will be returned. If no child Component has ever
* requested focus, and this is a focusable Window, then this Window's
* initial focusable Component is returned. If no child Component has ever
* requested focus, and this is a non-focusable Window, null is returned.
*
* @return the child Component that will receive focus when this Window is
* focused
* @see #getFocusOwner
* @see #isFocused
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @since 1.4
*/
public Component getMostRecentFocusOwner() {
if (isFocused()) {
return getFocusOwner();
} else {
Component mostRecent =
KeyboardFocusManager.getMostRecentFocusOwner(this);
if (mostRecent != null) {
return mostRecent;
} else {
return (isFocusableWindow())
? getFocusTraversalPolicy().getInitialComponent(this)
: null;
}
}
}
/**
* Returns whether this Window is active. Only a Frame or a Dialog may be
* active. The native windowing system may denote the active Window or its
* children with special decorations, such as a highlighted title bar. The
* active Window is always either the focused Window, or the first Frame or
* Dialog that is an owner of the focused Window.
*
* @return whether this is the active Window.
* @see #isFocused
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean isActive() {
return (KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
getActiveWindow() == this);
}
/**
* Returns whether this Window is focused. If there exists a focus owner,
* the focused Window is the Window that is, or contains, that focus owner.
* If there is no focus owner, then no Window is focused.
*
* setFocusTraversalKeys for a full description of each key.)
* true because all Windows must be roots of a
* focus traversal cycle.
*
* @return true
* @see #setFocusCycleRoot
* @see Container#setFocusTraversalPolicy
* @see Container#getFocusTraversalPolicy
* @since 1.4
*/
public final boolean isFocusCycleRoot() {
return true;
}
/**
* Always returns null because Windows have no ancestors; they
* represent the top of the Component hierarchy.
*
* @return null
* @see Container#isFocusCycleRoot()
* @since 1.4
*/
public final Container getFocusCycleRootAncestor() {
return null;
}
/**
* Returns whether this Window can become the focused Window, that is,
* whether this Window or any of its subcomponents can become the focus
* owner. For a Frame or Dialog to be focusable, its focusable Window state
* must be set to true. For a Window which is not a Frame or
* Dialog to be focusable, its focusable Window state must be set to
* true, its nearest owning Frame or Dialog must be
* showing on the screen, and it must contain at least one Component in
* its focus traversal cycle. If any of these conditions is not met, then
* neither this Window nor any of its subcomponents can become the focus
* owner.
*
* @return true if this Window can be the focused Window;
* false otherwise
* @see #getFocusableWindowState
* @see #setFocusableWindowState
* @see #isShowing
* @see Component#isFocusable
* @since 1.4
*/
public final boolean isFocusableWindow() {
// If a Window/Frame/Dialog was made non-focusable, then it is always
// non-focusable.
if (!getFocusableWindowState()) {
return false;
}
// All other tests apply only to Windows.
if (this instanceof Frame || this instanceof Dialog) {
return true;
}
// A Window must have at least one Component in its root focus
// traversal cycle to be focusable.
if (getFocusTraversalPolicy().getDefaultComponent(this) == null) {
return false;
}
// A Window's nearest owning Frame or Dialog must be showing on the
// screen.
for (Window owner = getOwner(); owner != null;
owner = owner.getOwner())
{
if (owner instanceof Frame || owner instanceof Dialog) {
return owner.isShowing();
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns whether this Window can become the focused Window if it meets
* the other requirements outlined in isFocusableWindow. If
* this method returns false, then
* isFocusableWindow will return false as well.
* If this method returns true, then
* isFocusableWindow may return true or
* false depending upon the other requirements which must be
* met in order for a Window to be focusable.
* true.
*
* @return whether this Window can be the focused Window
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #setFocusableWindowState
* @see #isShowing
* @see Component#setFocusable
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean getFocusableWindowState() {
return focusableWindowState;
}
/**
* Sets whether this Window can become the focused Window if it meets
* the other requirements outlined in isFocusableWindow. If
* this Window's focusable Window state is set to false, then
* isFocusableWindow will return false. If this
* Window's focusable Window state is set to true, then
* isFocusableWindow may return true or
* false depending upon the other requirements which must be
* met in order for a Window to be focusable.
* false is the
* standard mechanism for an application to identify to the AWT a Window
* which will be used as a floating palette or toolbar, and thus should be
* a non-focusable Window.
*
* Setting the focusability state on a visible Window
* can have a delayed effect on some platforms — the actual
* change may happen only when the Window becomes
* hidden and then visible again. To ensure consistent behavior
* across platforms, set the Window's focusable state
* when the Window is invisible and then show it.
*
* @param focusableWindowState whether this Window can be the focused
* Window
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #getFocusableWindowState
* @see #isShowing
* @see Component#setFocusable
* @since 1.4
*/
public void setFocusableWindowState(boolean focusableWindowState) {
boolean oldFocusableWindowState;
synchronized (this) {
oldFocusableWindowState = this.focusableWindowState;
this.focusableWindowState = focusableWindowState;
}
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.updateFocusableWindowState();
}
firePropertyChange("focusableWindowState", oldFocusableWindowState,
focusableWindowState);
if (oldFocusableWindowState && !focusableWindowState && isFocused()) {
for (Window owner = getOwner();
owner != null;
owner = owner.getOwner())
{
Component toFocus =
KeyboardFocusManager.getMostRecentFocusOwner(owner);
if (toFocus != null && toFocus.requestFocus(false, CausedFocusEvent.Cause.ACTIVATION)) {
return;
}
}
KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
clearGlobalFocusOwner();
}
}
/**
* Sets whether this window should receive focus on
* subsequently being shown (with a call to {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)}),
* or being moved to the front (with a call to {@link #toFront}).
*
*
* Note that if this Window is inheriting a bound property, then no
* event will be fired in response to a change in the inherited property.
*
*
* Note that if this Window is inheriting a bound property, then no
* event will be fired in response to a change in the inherited property.
* dispatchEvent(AWTEvent).
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean postEvent(Event e) {
if (handleEvent(e)) {
e.consume();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Checks if this Window is showing on screen.
* @see Component#setVisible
*/
public boolean isShowing() {
return visible;
}
boolean isDisposing() {
return disposing;
}
/**
* @deprecated As of J2SE 1.4, replaced by
* {@link Component#applyComponentOrientation Component.applyComponentOrientation}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void applyResourceBundle(ResourceBundle rb) {
applyComponentOrientation(ComponentOrientation.getOrientation(rb));
}
/**
* @deprecated As of J2SE 1.4, replaced by
* {@link Component#applyComponentOrientation Component.applyComponentOrientation}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void applyResourceBundle(String rbName) {
applyResourceBundle(ResourceBundle.getBundle(rbName));
}
/*
* Support for tracking all windows owned by this window
*/
void addOwnedWindow(WeakReference weakWindow) {
if (weakWindow != null) {
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
// this if statement should really be an assert, but we don't
// have asserts...
if (!ownedWindowList.contains(weakWindow)) {
ownedWindowList.addElement(weakWindow);
}
}
}
}
void removeOwnedWindow(WeakReference weakWindow) {
if (weakWindow != null) {
// synchronized block not required since removeElement is
// already synchronized
ownedWindowList.removeElement(weakWindow);
}
}
void connectOwnedWindow(Window child) {
child.parent = this;
addOwnedWindow(child.weakThis);
}
private void addToWindowList() {
synchronized (Window.class) {
VectorWindowListeners and
* WindowFocusListeners as optional data.
* Writes a list of child windows as optional data.
* Writes a list of icon images as optional data
*
* @param s the ObjectOutputStream to write
* @serialData null terminated sequence of
* 0 or more pairs; the pair consists of a String
* and and Object; the String
* indicates the type of object and is one of the following:
* windowListenerK indicating a
* WindowListener object;
* windowFocusWindowK indicating a
* WindowFocusListener object;
* ownedWindowK indicating a child
* Window object
*
* @see AWTEventMulticaster#save(java.io.ObjectOutputStream, java.lang.String, java.util.EventListener)
* @see Component#windowListenerK
* @see Component#windowFocusListenerK
* @see Component#ownedWindowK
* @see #readObject(ObjectInputStream)
*/
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
// Update old focusMgr fields so that our object stream can be read
// by previous releases
focusMgr = new FocusManager();
focusMgr.focusRoot = this;
focusMgr.focusOwner = getMostRecentFocusOwner();
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Clear fields so that we don't keep extra references around
focusMgr = null;
AWTEventMulticaster.save(s, windowListenerK, windowListener);
AWTEventMulticaster.save(s, windowFocusListenerK, windowFocusListener);
AWTEventMulticaster.save(s, windowStateListenerK, windowStateListener);
}
s.writeObject(null);
synchronized (ownedWindowList) {
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if (child != null) {
s.writeObject(ownedWindowK);
s.writeObject(child);
}
}
}
s.writeObject(null);
//write icon array
if (icons != null) {
for (Image i : icons) {
if (i instanceof Serializable) {
s.writeObject(i);
}
}
}
s.writeObject(null);
}
//
// Part of deserialization procedure to be called before
// user's code.
//
private void initDeserializedWindow() {
setWarningString();
inputContextLock = new Object();
// Deserialized Windows are not yet visible.
visible = false;
weakThis = new WeakReference(this);
anchor = new Object();
sun.java2d.Disposer.addRecord(anchor, new WindowDisposerRecord(appContext, this));
addToWindowList();
initGC(null);
}
private void deserializeResources(ObjectInputStream s)
throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException, HeadlessException {
ownedWindowList = new Vector();
if (windowSerializedDataVersion < 2) {
// Translate old-style focus tracking to new model. For 1.4 and
// later releases, we'll rely on the Window's initial focusable
// Component.
if (focusMgr != null) {
if (focusMgr.focusOwner != null) {
KeyboardFocusManager.
setMostRecentFocusOwner(this, focusMgr.focusOwner);
}
}
// This field is non-transient and relies on default serialization.
// However, the default value is insufficient, so we need to set
// it explicitly for object data streams prior to 1.4.
focusableWindowState = true;
}
Object keyOrNull;
while(null != (keyOrNull = s.readObject())) {
String key = ((String)keyOrNull).intern();
if (windowListenerK == key) {
addWindowListener((WindowListener)(s.readObject()));
} else if (windowFocusListenerK == key) {
addWindowFocusListener((WindowFocusListener)(s.readObject()));
} else if (windowStateListenerK == key) {
addWindowStateListener((WindowStateListener)(s.readObject()));
} else // skip value for unrecognized key
s.readObject();
}
try {
while (null != (keyOrNull = s.readObject())) {
String key = ((String)keyOrNull).intern();
if (ownedWindowK == key)
connectOwnedWindow((Window) s.readObject());
else // skip value for unrecognized key
s.readObject();
}
//read icons
Object obj = s.readObject(); //Throws OptionalDataException
//for pre1.6 objects.
icons = new ArrayListObjectInputStream and an optional
* list of listeners to receive various events fired by
* the component; also reads a list of
* (possibly null) child windows.
* Unrecognized keys or values will be ignored.
*
* @param s the ObjectInputStream to read
* @exception HeadlessException if
* GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless returns
* true
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see #writeObject
*/
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException, HeadlessException
{
GraphicsEnvironment.checkHeadless();
initDeserializedWindow();
ObjectInputStream.GetField f = s.readFields();
syncLWRequests = f.get("syncLWRequests", systemSyncLWRequests);
state = f.get("state", 0);
focusableWindowState = f.get("focusableWindowState", true);
windowSerializedDataVersion = f.get("windowSerializedDataVersion", 1);
locationByPlatform = f.get("locationByPlatform", locationByPlatformProp);
// Note: 1.4 (or later) doesn't use focusMgr
focusMgr = (FocusManager)f.get("focusMgr", null);
Dialog.ModalExclusionType et = (Dialog.ModalExclusionType)
f.get("modalExclusionType", Dialog.ModalExclusionType.NO_EXCLUDE);
setModalExclusionType(et); // since 6.0
boolean aot = f.get("alwaysOnTop", false);
if(aot) {
setAlwaysOnTop(aot); // since 1.5; subject to permission check
}
shape = (Shape)f.get("shape", null);
opacity = (Float)f.get("opacity", 1.0f);
this.securityWarningWidth = 0;
this.securityWarningHeight = 0;
this.securityWarningPointX = 2.0;
this.securityWarningPointY = 0.0;
this.securityWarningAlignmentX = RIGHT_ALIGNMENT;
this.securityWarningAlignmentY = TOP_ALIGNMENT;
deserializeResources(s);
}
/*
* --- Accessibility Support ---
*
*/
/**
* Gets the AccessibleContext associated with this Window.
* For windows, the AccessibleContext takes the form of an
* AccessibleAWTWindow.
* A new AccessibleAWTWindow instance is created if necessary.
*
* @return an AccessibleAWTWindow that serves as the
* AccessibleContext of this Window
* @since 1.3
*/
public AccessibleContext getAccessibleContext() {
if (accessibleContext == null) {
accessibleContext = new AccessibleAWTWindow();
}
return accessibleContext;
}
/**
* This class implements accessibility support for the
* Window class. It provides an implementation of the
* Java Accessibility API appropriate to window user-interface elements.
* @since 1.3
*/
protected class AccessibleAWTWindow extends AccessibleAWTContainer
{
/*
* JDK 1.3 serialVersionUID
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4215068635060671780L;
/**
* Get the role of this object.
*
* @return an instance of AccessibleRole describing the role of the
* object
* @see javax.accessibility.AccessibleRole
*/
public AccessibleRole getAccessibleRole() {
return AccessibleRole.WINDOW;
}
/**
* Get the state of this object.
*
* @return an instance of AccessibleStateSet containing the current
* state set of the object
* @see javax.accessibility.AccessibleState
*/
public AccessibleStateSet getAccessibleStateSet() {
AccessibleStateSet states = super.getAccessibleStateSet();
if (getFocusOwner() != null) {
states.add(AccessibleState.ACTIVE);
}
return states;
}
} // inner class AccessibleAWTWindow
@Override
void setGraphicsConfiguration(GraphicsConfiguration gc) {
if (gc == null) {
gc = GraphicsEnvironment.
getLocalGraphicsEnvironment().
getDefaultScreenDevice().
getDefaultConfiguration();
}
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
super.setGraphicsConfiguration(gc);
if (log.isLoggable(PlatformLogger.FINER)) {
log.finer("+ Window.setGraphicsConfiguration(): new GC is \n+ " + getGraphicsConfiguration_NoClientCode() + "\n+ this is " + this);
}
}
}
/**
* Sets the location of the window relative to the specified
* component according to the following scenarios.
*
*
* Component
* that is closest to the center of the screen. So if the
* component is on the right part of the screen, the window
* is placed to its left, and vice versa.
* BufferStrategy
* with that number of buffers.
* A page-flipping strategy is attempted first, then a blitting strategy
* using accelerated buffers. Finally, an unaccelerated blitting
* strategy is used.
* null
* @exception AWTException if the capabilities supplied could not be
* supported or met; this may happen, for example, if there is not enough
* accelerated memory currently available, or if page flipping is specified
* but not possible.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if numBuffers is less than 1, or if
* caps is null
* @see #getBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public void createBufferStrategy(int numBuffers,
BufferCapabilities caps) throws AWTException {
super.createBufferStrategy(numBuffers, caps);
}
/**
* Returns the BufferStrategy used by this component. This
* method will return null if a BufferStrategy has not yet
* been created or has been disposed.
*
* @return the buffer strategy used by this component
* @see #createBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public BufferStrategy getBufferStrategy() {
return super.getBufferStrategy();
}
Component getTemporaryLostComponent() {
return temporaryLostComponent;
}
Component setTemporaryLostComponent(Component component) {
Component previousComp = temporaryLostComponent;
// Check that "component" is an acceptable focus owner and don't store it otherwise
// - or later we will have problems with opposite while handling WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS
if (component == null || component.canBeFocusOwner()) {
temporaryLostComponent = component;
} else {
temporaryLostComponent = null;
}
return previousComp;
}
/**
* Checks whether this window can contain focus owner.
* Verifies that it is focusable and as container it can container focus owner.
* @since 1.5
*/
boolean canContainFocusOwner(Component focusOwnerCandidate) {
return super.canContainFocusOwner(focusOwnerCandidate) && isFocusableWindow();
}
private boolean locationByPlatform = locationByPlatformProp;
/**
* Sets whether this Window should appear at the default location for the
* native windowing system or at the current location (returned by
* getLocation) the next time the Window is made visible.
* This behavior resembles a native window shown without programmatically
* setting its location. Most windowing systems cascade windows if their
* locations are not explicitly set. The actual location is determined once the
* window is shown on the screen.
* setVisible, setLocation and
* setBounds after calling setLocationByPlatform clear
* this property of the Window.
*
* The window will be shown at platform's default location and
*
* setLocationByPlatform(true);
* setVisible(true);
* boolean flag = isLocationByPlatform();
*
flag will be false.
*
* The window will be shown at (10, 10) and
* setLocationByPlatform(true);
* setLocation(10, 10);
* boolean flag = isLocationByPlatform();
* setVisible(true);
*
flag will be
* false.
*
* @param locationByPlatform true if this Window should appear
* at the default location, false if at the current location
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window
* is showing on screen and locationByPlatform is true.
* @see #setLocation
* @see #isShowing
* @see #setVisible
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @see java.lang.System#getProperty(String)
* @since 1.5
*/
public void setLocationByPlatform(boolean locationByPlatform) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (locationByPlatform && isShowing()) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException("The window is showing on screen.");
}
this.locationByPlatform = locationByPlatform;
}
}
/**
* Returns true if this Window will appear at the default location
* for the native windowing system the next time this Window is made visible.
* This method always returns false if the Window is showing on the
* screen.
*
* @return whether this Window will appear at the default location
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isShowing
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean isLocationByPlatform() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
return locationByPlatform;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* true if the component and all of its ancestors
* until a toplevel window are visible, false otherwise
*/
boolean isRecursivelyVisible() {
// 5079694 fix: for a toplevel to be displayed, its parent doesn't have to be visible.
// We're overriding isRecursivelyVisible to implement this policy.
return visible;
}
// ******************** SHAPES & TRANSPARENCY CODE ********************
/**
* Returns the opacity of the window.
*
* @return the opacity of the window
*
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public float getOpacity() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
return opacity;
}
}
/**
* Sets the opacity of the window.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*