String class provides methods for dealing with
* Unicode code points (i.e., characters), in addition to those for
* dealing with Unicode code units (i.e., char values).
*
* @author Lee Boynton
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
* @see java.lang.StringBuffer
* @see java.lang.StringBuilder
* @see java.nio.charset.Charset
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable
* TC_STRING (utf String)
*
* The String is written by method DataOutput.writeUTF.
* A new handle is generated to refer to all future references to the
* string instance within the stream.
*/
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
new ObjectStreamField[0];
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* an empty character sequence. Note that use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*/
public String() {
this.offset = 0;
this.count = 0;
this.value = new char[0];
}
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the
* newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an
* explicit copy of {@code original} is needed, use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*
* @param original
* A {@code String}
*/
public String(String original) {
int size = original.count;
char[] originalValue = original.value;
char[] v;
if (originalValue.length > size) {
// The array representing the String is bigger than the new
// String itself. Perhaps this constructor is being called
// in order to trim the baggage, so make a copy of the array.
int off = original.offset;
v = Arrays.copyOfRange(originalValue, off, off+size);
} else {
// The array representing the String is the same
// size as the String, so no point in making a copy.
v = originalValue;
}
this.offset = 0;
this.count = size;
this.value = v;
}
/**
* Allocates a new {@code String} so that it represents the sequence of
* characters currently contained in the character array argument. The
* contents of the character array are copied; subsequent modification of
* the character array does not affect the newly created string.
*
* @param value
* The initial value of the string
*/
public String(char value[]) {
int size = value.length;
this.offset = 0;
this.count = size;
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, size);
}
/**
* Allocates a new {@code String} that contains characters from a subarray
* of the character array argument. The {@code offset} argument is the
* index of the first character of the subarray and the {@code count}
* argument specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the
* subarray are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does
* not affect the newly created string.
*
* @param value
* Array that is the source of characters
*
* @param offset
* The initial offset
*
* @param count
* The length
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* If the {@code offset} and {@code count} arguments index
* characters outside the bounds of the {@code value} array
*/
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.offset = 0;
this.count = count;
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
/**
* Allocates a new {@code String} that contains characters from a subarray
* of the Unicode code point array
* argument. The {@code offset} argument is the index of the first code
* point of the subarray and the {@code count} argument specifies the
* length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray are converted to
* {@code char}s; subsequent modification of the {@code int} array does not
* affect the newly created string.
*
* @param codePoints
* Array that is the source of Unicode code points
*
* @param offset
* The initial offset
*
* @param count
* The length
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If any invalid Unicode code point is found in {@code
* codePoints}
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* If the {@code offset} and {@code count} arguments index
* characters outside the bounds of the {@code codePoints} array
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
// Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[]
int n = 0;
for (int i = offset; i < offset + count; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (c >= Character.MIN_CODE_POINT &&
c < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)
n += 1;
else if (Character.isSupplementaryCodePoint(c))
n += 2;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
}
// Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[]
char[] v = new char[n];
for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < offset + count; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (c < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
v[j++] = (char) c;
} else {
Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j);
j += 2;
}
}
this.value = v;
this.count = v.length;
this.offset = 0;
}
/**
* Allocates a new {@code String} constructed from a subarray of an array
* of 8-bit integer values.
*
* The {@code offset} argument is the index of the first byte of the * subarray, and the {@code count} argument specifies the length of the * subarray. * *
Each {@code byte} in the subarray is converted to a {@code char} as * specified in the method above. * * @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. * As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the * {@code String} constructors that take a {@link * java.nio.charset.Charset}, charset name, or that use the platform's * default charset. * * @param ascii * The bytes to be converted to characters * * @param hibyte * The top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode code unit * * @param offset * The initial offset * @param count * The length * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * If the {@code offset} or {@code count} argument is invalid * * @see #String(byte[], int) * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String) * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset) * @see #String(byte[], int, int) * @see #String(byte[], java.lang.String) * @see #String(byte[], java.nio.charset.Charset) * @see #String(byte[]) */ @Deprecated public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte, int offset, int count) { checkBounds(ascii, offset, count); char value[] = new char[count]; if (hibyte == 0) { for (int i = count ; i-- > 0 ;) { value[i] = (char) (ascii[i + offset] & 0xff); } } else { hibyte <<= 8; for (int i = count ; i-- > 0 ;) { value[i] = (char) (hibyte | (ascii[i + offset] & 0xff)); } } this.offset = 0; this.count = count; this.value = value; } /** * Allocates a new {@code String} containing characters constructed from * an array of 8-bit integer values. Each character cin the * resulting string is constructed from the corresponding component * b in the byte array such that: * *
* c == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8)
* | (b & 0xff))
* The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid * in the given charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @param offset * The index of the first byte to decode * * @param length * The number of bytes to decode * @param charsetName * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset * charset} * * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException * If the named charset is not supported * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * If the {@code offset} and {@code length} arguments index * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array * * @since JDK1.1 */ public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { if (charsetName == null) throw new NullPointerException("charsetName"); checkBounds(bytes, offset, length); char[] v = StringCoding.decode(charsetName, bytes, offset, length); this.offset = 0; this.count = v.length; this.value = v; } /** * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified subarray of * bytes using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. * The length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and * hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray. * *
This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character * sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @param offset * The index of the first byte to decode * * @param length * The number of bytes to decode * * @param charset * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset} to be used to * decode the {@code bytes} * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * If the {@code offset} and {@code length} arguments index * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array * * @since 1.6 */ public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset) { if (charset == null) throw new NullPointerException("charset"); checkBounds(bytes, offset, length); char[] v = StringCoding.decode(charset, bytes, offset, length); this.offset = 0; this.count = v.length; this.value = v; } /** * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of bytes * using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. The * length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and hence * may not be equal to the length of the byte array. * *
The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid * in the given charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @param charsetName * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset * charset} * * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException * If the named charset is not supported * * @since JDK1.1 */ public String(byte bytes[], String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charsetName); } /** * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of * bytes using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. * The length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and * hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array. * *
This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character * sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @param charset * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset} to be used to * decode the {@code bytes} * * @since 1.6 */ public String(byte bytes[], Charset charset) { this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charset); } /** * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified subarray of * bytes using the platform's default charset. The length of the new * {@code String} is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal * to the length of the subarray. * *
The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid * in the default charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @param offset * The index of the first byte to decode * * @param length * The number of bytes to decode * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * If the {@code offset} and the {@code length} arguments index * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array * * @since JDK1.1 */ public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) { checkBounds(bytes, offset, length); char[] v = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length); this.offset = 0; this.count = v.length; this.value = v; } /** * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of bytes * using the platform's default charset. The length of the new {@code * String} is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the * length of the byte array. * *
The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid * in the default charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control * over the decoding process is required. * * @param bytes * The bytes to be decoded into characters * * @since JDK1.1 */ public String(byte bytes[]) { this(bytes, 0, bytes.length); } /** * Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters * currently contained in the string buffer argument. The contents of the * string buffer are copied; subsequent modification of the string buffer * does not affect the newly created string. * * @param buffer * A {@code StringBuffer} */ public String(StringBuffer buffer) { String result = buffer.toString(); this.value = result.value; this.count = result.count; this.offset = result.offset; } /** * Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters * currently contained in the string builder argument. The contents of the * string builder are copied; subsequent modification of the string builder * does not affect the newly created string. * *
This constructor is provided to ease migration to {@code
* StringBuilder}. Obtaining a string from a string builder via the {@code
* toString} method is likely to run faster and is generally preferred.
*
* @param builder
* A {@code StringBuilder}
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public String(StringBuilder builder) {
String result = builder.toString();
this.value = result.value;
this.count = result.count;
this.offset = result.offset;
}
// Package private constructor which shares value array for speed.
String(int offset, int count, char value[]) {
this.value = value;
this.offset = offset;
this.count = count;
}
/**
* Returns the length of this string.
* The length is equal to the number of Unicode
* code units in the string.
*
* @return the length of the sequence of characters represented by this
* object.
*/
public int length() {
return count;
}
/**
* Returns true if, and only if, {@link #length()} is 0.
*
* @return true if {@link #length()} is 0, otherwise
* false
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the char value at the
* specified index. An index ranges from 0 to
* length() - 1. The first char value of the sequence
* is at index 0, the next at index 1,
* and so on, as for array indexing.
*
*
If the char value specified by the index is a
* surrogate, the surrogate
* value is returned.
*
* @param index the index of the char value.
* @return the char value at the specified index of this string.
* The first char value is at index 0.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index
* argument is negative or not less than the length of this
* string.
*/
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index + offset];
}
/**
* Returns the character (Unicode code point) at the specified
* index. The index refers to char values
* (Unicode code units) and ranges from 0 to
* {@link #length()} - 1.
*
*
If the char value specified at the given index
* is in the high-surrogate range, the following index is less
* than the length of this String, and the
* char value at the following index is in the
* low-surrogate range, then the supplementary code point
* corresponding to this surrogate pair is returned. Otherwise,
* the char value at the given index is returned.
*
* @param index the index to the char values
* @return the code point value of the character at the
* index
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index
* argument is negative or not less than the length of this
* string.
* @since 1.5
*/
public int codePointAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return Character.codePointAtImpl(value, offset + index, offset + count);
}
/**
* Returns the character (Unicode code point) before the specified
* index. The index refers to char values
* (Unicode code units) and ranges from 1 to {@link
* CharSequence#length() length}.
*
*
If the char value at (index - 1)
* is in the low-surrogate range, (index - 2) is not
* negative, and the char value at (index -
* 2) is in the high-surrogate range, then the
* supplementary code point value of the surrogate pair is
* returned. If the char value at index -
* 1 is an unpaired low-surrogate or a high-surrogate, the
* surrogate value is returned.
*
* @param index the index following the code point that should be returned
* @return the Unicode code point value before the given index.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index
* argument is less than 1 or greater than the length
* of this string.
* @since 1.5
*/
public int codePointBefore(int index) {
int i = index - 1;
if ((i < 0) || (i >= count)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return Character.codePointBeforeImpl(value, offset + index, offset);
}
/**
* Returns the number of Unicode code points in the specified text
* range of this String. The text range begins at the
* specified beginIndex and extends to the
* char at index endIndex - 1. Thus the
* length (in chars) of the text range is
* endIndex-beginIndex. Unpaired surrogates within
* the text range count as one code point each.
*
* @param beginIndex the index to the first char of
* the text range.
* @param endIndex the index after the last char of
* the text range.
* @return the number of Unicode code points in the specified text
* range
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the
* beginIndex is negative, or endIndex
* is larger than the length of this String, or
* beginIndex is larger than endIndex.
* @since 1.5
*/
public int codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0 || endIndex > count || beginIndex > endIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return Character.codePointCountImpl(value, offset+beginIndex, endIndex-beginIndex);
}
/**
* Returns the index within this String that is
* offset from the given index by
* codePointOffset code points. Unpaired surrogates
* within the text range given by index and
* codePointOffset count as one code point each.
*
* @param index the index to be offset
* @param codePointOffset the offset in code points
* @return the index within this String
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if index
* is negative or larger then the length of this
* String, or if codePointOffset is positive
* and the substring starting with index has fewer
* than codePointOffset code points,
* or if codePointOffset is negative and the substring
* before index has fewer than the absolute value
* of codePointOffset code points.
* @since 1.5
*/
public int offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) {
if (index < 0 || index > count) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return Character.offsetByCodePointsImpl(value, offset, count,
offset+index, codePointOffset) - offset;
}
/**
* Copy characters from this string into dst starting at dstBegin.
* This method doesn't perform any range checking.
*/
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) {
System.arraycopy(value, offset, dst, dstBegin, count);
}
/**
* Copies characters from this string into the destination character
* array.
*
* The first character to be copied is at index srcBegin;
* the last character to be copied is at index srcEnd-1
* (thus the total number of characters to be copied is
* srcEnd-srcBegin). The characters are copied into the
* subarray of dst starting at index dstBegin
* and ending at index:
*
* dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
* srcBeginis negative. *srcBeginis greater thansrcEnd*srcEndis greater than the length of this * string *dstBeginis negative *dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)is larger than *dst.length
The first character to be copied is at index {@code srcBegin}; the * last character to be copied is at index {@code srcEnd-1}. The total * number of characters to be copied is {@code srcEnd-srcBegin}. The * characters, converted to bytes, are copied into the subarray of {@code * dst} starting at index {@code dstBegin} and ending at index: * *
* dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
* -
*
- {@code srcBegin} is negative *
- {@code srcBegin} is greater than {@code srcEnd} *
- {@code srcEnd} is greater than the length of this String *
- {@code dstBegin} is negative *
- {@code dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)} is larger than {@code * dst.length} *
The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in * the given charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more control * over the encoding process is required. * * @param charsetName * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset * charset} * * @return The resultant byte array * * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException * If the named charset is not supported * * @since JDK1.1 */ public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { if (charsetName == null) throw new NullPointerException(); return StringCoding.encode(charsetName, value, offset, count); } /** * Encodes this {@code String} into a sequence of bytes using the given * {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}, storing the result into a * new byte array. * *
This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character * sequences with this charset's default replacement byte array. The * {@link java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more * control over the encoding process is required. * * @param charset * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset} to be used to encode * the {@code String} * * @return The resultant byte array * * @since 1.6 */ public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset) { if (charset == null) throw new NullPointerException(); return StringCoding.encode(charset, value, offset, count); } /** * Encodes this {@code String} into a sequence of bytes using the * platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array. * *
The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in * the default charset is unspecified. The {@link * java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more control * over the encoding process is required. * * @return The resultant byte array * * @since JDK1.1 */ public byte[] getBytes() { return StringCoding.encode(value, offset, count); } /** * Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code * true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code * String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this * object. * * @param anObject * The object to compare this {@code String} against * * @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String} * equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise * * @see #compareTo(String) * @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String) */ public boolean equals(Object anObject) { if (this == anObject) { return true; } if (anObject instanceof String) { String anotherString = (String)anObject; int n = count; if (n == anotherString.count) { char v1[] = value; char v2[] = anotherString.value; int i = offset; int j = anotherString.offset; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) return false; } return true; } } return false; } /** * Compares this string to the specified {@code StringBuffer}. The result * is {@code true} if and only if this {@code String} represents the same * sequence of characters as the specified {@code StringBuffer}. * * @param sb * The {@code StringBuffer} to compare this {@code String} against * * @return {@code true} if this {@code String} represents the same * sequence of characters as the specified {@code StringBuffer}, * {@code false} otherwise * * @since 1.4 */ public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) { synchronized(sb) { return contentEquals((CharSequence)sb); } } /** * Compares this string to the specified {@code CharSequence}. The result * is {@code true} if and only if this {@code String} represents the same * sequence of char values as the specified sequence. * * @param cs * The sequence to compare this {@code String} against * * @return {@code true} if this {@code String} represents the same * sequence of char values as the specified sequence, {@code * false} otherwise * * @since 1.5 */ public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs) { if (count != cs.length()) return false; // Argument is a StringBuffer, StringBuilder if (cs instanceof AbstractStringBuilder) { char v1[] = value; char v2[] = ((AbstractStringBuilder)cs).getValue(); int i = offset; int j = 0; int n = count; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) return false; } return true; } // Argument is a String if (cs.equals(this)) return true; // Argument is a generic CharSequence char v1[] = value; int i = offset; int j = 0; int n = count; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i++] != cs.charAt(j++)) return false; } return true; } /** * Compares this {@code String} to another {@code String}, ignoring case * considerations. Two strings are considered equal ignoring case if they * are of the same length and corresponding characters in the two strings * are equal ignoring case. * *
Two characters {@code c1} and {@code c2} are considered the same * ignoring case if at least one of the following is true: *
-
*
- The two characters are the same (as compared by the * {@code ==} operator) *
- Applying the method {@link * java.lang.Character#toUpperCase(char)} to each character * produces the same result *
- Applying the method {@link * java.lang.Character#toLowerCase(char)} to each character * produces the same result *
String object is compared lexicographically to the
* character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is
* a negative integer if this String object
* lexicographically precedes the argument string. The result is a
* positive integer if this String object lexicographically
* follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings
* are equal; compareTo returns 0 exactly when
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method would return true.
*
* This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are
* different, then either they have different characters at some index
* that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different,
* or both. If they have different characters at one or more index
* positions, let k be the smallest such index; then the string
* whose character at position k has the smaller value, as
* determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the
* other string. In this case, compareTo returns the
* difference of the two character values at position k in
* the two string -- that is, the value:
*
* this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
* compareTo returns the difference of the lengths of the
* strings -- that is, the value:
*
* this.length()-anotherString.length()
* String to be compared.
* @return the value 0 if the argument string is equal to
* this string; a value less than 0 if this string
* is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a
* value greater than 0 if this string is
* lexicographically greater than the string argument.
*/
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = count;
int len2 = anotherString.count;
int n = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = offset;
int j = anotherString.offset;
if (i == j) {
int k = i;
int lim = n + i;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
} else {
while (n-- != 0) {
char c1 = v1[i++];
char c2 = v2[j++];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
return len1 - len2;
}
/**
* A Comparator that orders String objects as by
* compareToIgnoreCase. This comparator is serializable.
*
* Note that this Comparator does not take locale into account,
* and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
* The java.text package provides Collators to allow
* locale-sensitive ordering.
*
* @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
* @since 1.2
*/
public static final Comparator
* Note that this method does not take locale into account,
* and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
* The java.text package provides collators to allow
* locale-sensitive ordering.
*
* @param str the
* A substring of this String object is compared to a substring
* of the argument other. The result is true if these substrings
* represent identical character sequences. The substring of this
* String object to be compared begins at index toffset
* and has length len. The substring of other to be compared
* begins at index ooffset and has length len. The
* result is false if and only if at least one of the following
* is true:
*
* A substring of this String object is compared to a substring
* of the argument other. The result is true if these
* substrings represent character sequences that are the same, ignoring
* case if and only if ignoreCase is true. The substring of
* this String object to be compared begins at index
* toffset and has length len. The substring of
* other to be compared begins at index ooffset and
* has length len. The result is false if and only if
* at least one of the following is true:
*
* If a character with value
* There is no restriction on the value of All indices are specified in All indices are specified in
* Examples:
*
* Examples:
* An invocation of this method of the form
*
* compareTo with normalized versions of the strings
* where case differences have been eliminated by calling
* Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(character)) on
* each character.
* String to be compared.
* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
* specified String is greater than, equal to, or less
* than this String, ignoring case considerations.
* @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
* @since 1.2
*/
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
/**
* Tests if two string regions are equal.
*
*
* @param toffset the starting offset of the subregion in this string.
* @param other the string argument.
* @param ooffset the starting offset of the subregion in the string
* argument.
* @param len the number of characters to compare.
* @return true if the specified subregion of this string
* exactly matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset,
int len) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = offset + toffset;
char pa[] = other.value;
int po = other.offset + ooffset;
// Note: toffset, ooffset, or len might be near -1>>>1.
if ((ooffset < 0) || (toffset < 0) || (toffset > (long)count - len)
|| (ooffset > (long)other.count - len)) {
return false;
}
while (len-- > 0) {
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Tests if two string regions are equal.
*
*
* @param ignoreCase if
*
* this.charAt(toffset+k) != other.charAt(ooffset+k)
*
* and:
*
* Character.toLowerCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
Character.toLowerCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
*
*
* Character.toUpperCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
* Character.toUpperCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
* true, ignore case when comparing
* characters.
* @param toffset the starting offset of the subregion in this
* string.
* @param other the string argument.
* @param ooffset the starting offset of the subregion in the string
* argument.
* @param len the number of characters to compare.
* @return true if the specified subregion of this string
* matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
* false otherwise. Whether the matching is exact
* or case insensitive depends on the ignoreCase
* argument.
*/
public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset,
String other, int ooffset, int len) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = offset + toffset;
char pa[] = other.value;
int po = other.offset + ooffset;
// Note: toffset, ooffset, or len might be near -1>>>1.
if ((ooffset < 0) || (toffset < 0) || (toffset > (long)count - len) ||
(ooffset > (long)other.count - len)) {
return false;
}
while (len-- > 0) {
char c1 = ta[to++];
char c2 = pa[po++];
if (c1 == c2) {
continue;
}
if (ignoreCase) {
// If characters don't match but case may be ignored,
// try converting both characters to uppercase.
// If the results match, then the comparison scan should
// continue.
char u1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
char u2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (u1 == u2) {
continue;
}
// Unfortunately, conversion to uppercase does not work properly
// for the Georgian alphabet, which has strange rules about case
// conversion. So we need to make one last check before
// exiting.
if (Character.toLowerCase(u1) == Character.toLowerCase(u2)) {
continue;
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Tests if the substring of this string beginning at the
* specified index starts with the specified prefix.
*
* @param prefix the prefix.
* @param toffset where to begin looking in this string.
* @return true if the character sequence represented by the
* argument is a prefix of the substring of this object starting
* at index toffset; false otherwise.
* The result is false if toffset is
* negative or greater than the length of this
* String object; otherwise the result is the same
* as the result of the expression
*
* this.substring(toffset).startsWith(prefix)
*
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = offset + toffset;
char pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = prefix.offset;
int pc = prefix.count;
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > count - pc)) {
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.
*
* @param prefix the prefix.
* @return true if the character sequence represented by the
* argument is a prefix of the character sequence represented by
* this string; false otherwise.
* Note also that true will be returned if the
* argument is an empty string or is equal to this
* String object as determined by the
* {@link #equals(Object)} method.
* @since 1. 0
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, 0);
}
/**
* Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.
*
* @param suffix the suffix.
* @return true if the character sequence represented by the
* argument is a suffix of the character sequence represented by
* this object; false otherwise. Note that the
* result will be true if the argument is the
* empty string or is equal to this String object
* as determined by the {@link #equals(Object)} method.
*/
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, count - suffix.count);
}
/**
* Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for a
* String object is computed as
*
* using
* s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
* int arithmetic, where s[i] is the
* ith character of the string, n is the length of
* the string, and ^ indicates exponentiation.
* (The hash value of the empty string is zero.)
*
* @return a hash code value for this object.
*/
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0) {
int off = offset;
char val[] = value;
int len = count;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
h = 31*h + val[off++];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of
* the specified character. If a character with value
* ch occurs in the character sequence represented by
* this String object, then the index (in Unicode
* code units) of the first such occurrence is returned. For
* values of ch in the range from 0 to 0xFFFF
* (inclusive), this is the smallest value k such that:
*
* is true. For other values of
* this.charAt(k) == ch
* ch, it is the
* smallest value k such that:
*
* is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
* string, then
* this.codePointAt(k) == ch
* -1 is returned.
*
* @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
* character sequence represented by this object, or
* -1 if the character does not occur.
*/
public int indexOf(int ch) {
return indexOf(ch, 0);
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
* specified character, starting the search at the specified index.
* ch occurs in the
* character sequence represented by this String
* object at an index no smaller than fromIndex, then
* the index of the first such occurrence is returned. For values
* of ch in the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive),
* this is the smallest value k such that:
*
* is true. For other values of
* (this.charAt(k) == ch) && (k >= fromIndex)
* ch, it is the
* smallest value k such that:
*
* is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
* string at or after position
* (this.codePointAt(k) == ch) && (k >= fromIndex)
* fromIndex, then
* -1 is returned.
*
* fromIndex. If it
* is negative, it has the same effect as if it were zero: this entire
* string may be searched. If it is greater than the length of this
* string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to the length of
* this string: -1 is returned.
*
* char values
* (Unicode code units).
*
* @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
* @param fromIndex the index to start the search from.
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
* character sequence represented by this object that is greater
* than or equal to fromIndex, or -1
* if the character does not occur.
*/
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
int max = offset + count;
char v[] = value;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
} else if (fromIndex >= count) {
// Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
return -1;
}
int i = offset + fromIndex;
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
for (; i < max ; i++) {
if (v[i] == ch) {
return i - offset;
}
}
return -1;
}
if (ch <= Character.MAX_CODE_POINT) {
// handle supplementary characters here
char[] surrogates = Character.toChars(ch);
for (; i < max; i++) {
if (v[i] == surrogates[0]) {
if (i + 1 == max) {
break;
}
if (v[i+1] == surrogates[1]) {
return i - offset;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
* the specified character. For values of ch in the
* range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index (in Unicode code
* units) returned is the largest value k such that:
*
* is true. For other values of
* this.charAt(k) == ch
* ch, it is the
* largest value k such that:
*
* is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
* string, then
* this.codePointAt(k) == ch
* -1 is returned. The
* String is searched backwards starting at the last
* character.
*
* @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
* character sequence represented by this object, or
* -1 if the character does not occur.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(int ch) {
return lastIndexOf(ch, count - 1);
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
* the specified character, searching backward starting at the
* specified index. For values of ch in the range
* from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index returned is the largest
* value k such that:
*
* is true. For other values of
* (this.charAt(k) == ch) && (k <= fromIndex)
* ch, it is the
* largest value k such that:
*
* is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
* string at or before position
* (this.codePointAt(k) == ch) && (k <= fromIndex)
* fromIndex, then
* -1 is returned.
*
* char values
* (Unicode code units).
*
* @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
* @param fromIndex the index to start the search from. There is no
* restriction on the value of fromIndex. If it is
* greater than or equal to the length of this string, it has
* the same effect as if it were equal to one less than the
* length of this string: this entire string may be searched.
* If it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were -1:
* -1 is returned.
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
* character sequence represented by this object that is less
* than or equal to fromIndex, or -1
* if the character does not occur before that point.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
int min = offset;
char v[] = value;
int i = offset + ((fromIndex >= count) ? count - 1 : fromIndex);
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
for (; i >= min ; i--) {
if (v[i] == ch) {
return i - offset;
}
}
return -1;
}
int max = offset + count;
if (ch <= Character.MAX_CODE_POINT) {
// handle supplementary characters here
char[] surrogates = Character.toChars(ch);
for (; i >= min; i--) {
if (v[i] == surrogates[0]) {
if (i + 1 == max) {
break;
}
if (v[i+1] == surrogates[1]) {
return i - offset;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
* specified substring. The integer returned is the smallest value
* k such that:
*
* is
* this.startsWith(str, k)
* true.
*
* @param str any string.
* @return if the string argument occurs as a substring within this
* object, then the index of the first character of the first
* such substring is returned; if it does not occur as a
* substring, -1 is returned.
*/
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
* specified substring, starting at the specified index. The integer
* returned is the smallest value k for which:
*
* If no such value of k exists, then -1 is returned.
*
* @param str the substring for which to search.
* @param fromIndex the index from which to start the search.
* @return the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
* specified substring, starting at the specified index.
*/
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return indexOf(value, offset, count,
str.value, str.offset, str.count, fromIndex);
}
/**
* Code shared by String and StringBuffer to do searches. The
* source is the character array being searched, and the target
* is the string being searched for.
*
* @param source the characters being searched.
* @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
* @param sourceCount count of the source string.
* @param target the characters being searched for.
* @param targetOffset offset of the target string.
* @param targetCount count of the target string.
* @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
*/
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
}
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
char first = target[targetOffset];
int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
/* Look for first character. */
if (source[i] != first) {
while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
}
/* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */
if (i <= max) {
int j = i + 1;
int end = j + targetCount - 1;
for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j] ==
target[k]; j++, k++);
if (j == end) {
/* Found whole string. */
return i - sourceOffset;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the rightmost occurrence
* of the specified substring. The rightmost empty string "" is
* considered to occur at the index value
* k >= Math.min(fromIndex, this.length()) && this.startsWith(str, k)
* this.length().
* The returned index is the largest value k such that
*
* is true.
*
* @param str the substring to search for.
* @return if the string argument occurs one or more times as a substring
* within this object, then the index of the first character of
* the last such substring is returned. If it does not occur as
* a substring,
* this.startsWith(str, k)
* -1 is returned.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(String str) {
return lastIndexOf(str, count);
}
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
* specified substring, searching backward starting at the specified index.
* The integer returned is the largest value k such that:
*
* If no such value of k exists, then -1 is returned.
*
* @param str the substring to search for.
* @param fromIndex the index to start the search from.
* @return the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
* specified substring.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return lastIndexOf(value, offset, count,
str.value, str.offset, str.count, fromIndex);
}
/**
* Code shared by String and StringBuffer to do searches. The
* source is the character array being searched, and the target
* is the string being searched for.
*
* @param source the characters being searched.
* @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
* @param sourceCount count of the source string.
* @param target the characters being searched for.
* @param targetOffset offset of the target string.
* @param targetCount count of the target string.
* @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
*/
static int lastIndexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
/*
* Check arguments; return immediately where possible. For
* consistency, don't check for null str.
*/
int rightIndex = sourceCount - targetCount;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (fromIndex > rightIndex) {
fromIndex = rightIndex;
}
/* Empty string always matches. */
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
int strLastIndex = targetOffset + targetCount - 1;
char strLastChar = target[strLastIndex];
int min = sourceOffset + targetCount - 1;
int i = min + fromIndex;
startSearchForLastChar:
while (true) {
while (i >= min && source[i] != strLastChar) {
i--;
}
if (i < min) {
return -1;
}
int j = i - 1;
int start = j - (targetCount - 1);
int k = strLastIndex - 1;
while (j > start) {
if (source[j--] != target[k--]) {
i--;
continue startSearchForLastChar;
}
}
return start - sourceOffset + 1;
}
}
/**
* Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The
* substring begins with the character at the specified index and
* extends to the end of this string.
* k <= Math.min(fromIndex, this.length()) && this.startsWith(str, k)
*
*
* @param beginIndex the beginning index, inclusive.
* @return the specified substring.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if
*
* "unhappy".substring(2) returns "happy"
* "Harbison".substring(3) returns "bison"
* "emptiness".substring(9) returns "" (an empty string)
* beginIndex is negative or larger than the
* length of this String object.
*/
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
return substring(beginIndex, count);
}
/**
* Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The
* substring begins at the specified beginIndex and
* extends to the character at index endIndex - 1.
* Thus the length of the substring is endIndex-beginIndex.
*
*
* @param beginIndex the beginning index, inclusive.
* @param endIndex the ending index, exclusive.
* @return the specified substring.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the
*
* "hamburger".substring(4, 8) returns "urge"
* "smiles".substring(1, 5) returns "mile"
* beginIndex is negative, or
* endIndex is larger than the length of
* this String object, or
* beginIndex is larger than
* endIndex.
*/
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
if (beginIndex > endIndex) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex - beginIndex);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == count)) ? this :
new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex, value);
}
/**
* Returns a new character sequence that is a subsequence of this sequence.
*
*
*
* behaves in exactly the same way as the invocation
*
*
* str.subSequence(begin, end)
*
* This method is defined so that the String class can implement
* the {@link CharSequence} interface.
* str.substring(begin, end)
* If the length of the argument string is 0, then this
* String object is returned. Otherwise, a new
* String object is created, representing a character
* sequence that is the concatenation of the character sequence
* represented by this String object and the character
* sequence represented by the argument string.
* Examples: *
* "cares".concat("s") returns "caress"
* "to".concat("get").concat("her") returns "together"
* String that is concatenated to the end
* of this String.
* @return a string that represents the concatenation of this object's
* characters followed by the string argument's characters.
*/
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
char buf[] = new char[count + otherLen];
getChars(0, count, buf, 0);
str.getChars(0, otherLen, buf, count);
return new String(0, count + otherLen, buf);
}
/**
* Returns a new string resulting from replacing all occurrences of
* oldChar in this string with newChar.
*
* If the character oldChar does not occur in the
* character sequence represented by this String object,
* then a reference to this String object is returned.
* Otherwise, a new String object is created that
* represents a character sequence identical to the character sequence
* represented by this String object, except that every
* occurrence of oldChar is replaced by an occurrence
* of newChar.
*
* Examples: *
* "mesquite in your cellar".replace('e', 'o')
* returns "mosquito in your collar"
* "the war of baronets".replace('r', 'y')
* returns "the way of bayonets"
* "sparring with a purple porpoise".replace('p', 't')
* returns "starring with a turtle tortoise"
* "JonL".replace('q', 'x') returns "JonL" (no change)
* oldChar with newChar.
*/
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = count;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
int off = offset; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[off + i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0 ; j < i ; j++) {
buf[j] = val[off+j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[off + i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(0, len, buf);
}
}
return this;
}
/**
* Tells whether or not this string matches the given regular expression.
*
* An invocation of this method of the form * str.matches(regex) yields exactly the * same result as the expression * *
{@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link * java.util.regex.Pattern#matches(String,CharSequence) * matches}(regex, str)* * @param regex * the regular expression to which this string is to be matched * * @return true if, and only if, this string matches the * given regular expression * * @throws PatternSyntaxException * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid * * @see java.util.regex.Pattern * * @since 1.4 * @spec JSR-51 */ public boolean matches(String regex) { return Pattern.matches(regex, this); } /** * Returns true if and only if this string contains the specified * sequence of char values. * * @param s the sequence to search for * @return true if this string contains
s, false otherwise
* @throws NullPointerException if s is null
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
}
/**
* Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the
* given replacement.
*
* An invocation of this method of the form * str.replaceFirst(regex, repl) * yields exactly the same result as the expression * *
* {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link java.util.regex.Pattern#compile * compile}(regex).{@link * java.util.regex.Pattern#matcher(java.lang.CharSequence) * matcher}(str).{@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceFirst * replaceFirst}(repl)* *
* Note that backslashes (\) and dollar signs ($) in the * replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were * being treated as a literal replacement string; see * {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceFirst}. * Use {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#quoteReplacement} to suppress the special * meaning of these characters, if desired. * * @param regex * the regular expression to which this string is to be matched * @param replacement * the string to be substituted for the first match * * @return The resulting String * * @throws PatternSyntaxException * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid * * @see java.util.regex.Pattern * * @since 1.4 * @spec JSR-51 */ public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) { return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceFirst(replacement); } /** * Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the * given replacement. * *
An invocation of this method of the form * str.replaceAll(regex, repl) * yields exactly the same result as the expression * *
* {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link java.util.regex.Pattern#compile * compile}(regex).{@link * java.util.regex.Pattern#matcher(java.lang.CharSequence) * matcher}(str).{@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceAll * replaceAll}(repl)* *
* Note that backslashes (\) and dollar signs ($) in the
* replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were
* being treated as a literal replacement string; see
* {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceAll Matcher.replaceAll}.
* Use {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#quoteReplacement} to suppress the special
* meaning of these characters, if desired.
*
* @param regex
* the regular expression to which this string is to be matched
* @param replacement
* the string to be substituted for each match
*
* @return The resulting String
*
* @throws PatternSyntaxException
* if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
*
* @see java.util.regex.Pattern
*
* @since 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
}
/**
* Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target
* sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence. The
* replacement proceeds from the beginning of the string to the end, for
* example, replacing "aa" with "b" in the string "aaa" will result in
* "ba" rather than "ab".
*
* @param target The sequence of char values to be replaced
* @param replacement The replacement sequence of char values
* @return The resulting string
* @throws NullPointerException if target or
* replacement is null.
* @since 1.5
*/
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(target.toString(), Pattern.LITERAL).matcher(
this).replaceAll(Matcher.quoteReplacement(replacement.toString()));
}
/**
* Splits this string around matches of the given
* regular expression.
*
*
The array returned by this method contains each substring of this * string that is terminated by another substring that matches the given * expression or is terminated by the end of the string. The substrings in * the array are in the order in which they occur in this string. If the * expression does not match any part of the input then the resulting array * has just one element, namely this string. * *
The limit parameter controls the number of times the * pattern is applied and therefore affects the length of the resulting * array. If the limit n is greater than zero then the pattern * will be applied at most n - 1 times, the array's * length will be no greater than n, and the array's last entry * will contain all input beyond the last matched delimiter. If n * is non-positive then the pattern will be applied as many times as * possible and the array can have any length. If n is zero then * the pattern will be applied as many times as possible, the array can * have any length, and trailing empty strings will be discarded. * *
The string "boo:and:foo", for example, yields the * following results with these parameters: * *
* **
* *Regex *Limit *Result ** : *2 *{ "boo", "and:foo" } * : *5 *{ "boo", "and", "foo" } * : *-2 *{ "boo", "and", "foo" } * o *5 *{ "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" } * o *-2 *{ "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" } * o *0 *{ "b", "", ":and:f" }
An invocation of this method of the form * str.split(regex, n) * yields the same result as the expression * *
* {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link java.util.regex.Pattern#compile * compile}(regex).{@link * java.util.regex.Pattern#split(java.lang.CharSequence,int) * split}(str, n) ** * * @param regex * the delimiting regular expression * * @param limit * the result threshold, as described above * * @return the array of strings computed by splitting this string * around matches of the given regular expression * * @throws PatternSyntaxException * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid * * @see java.util.regex.Pattern * * @since 1.4 * @spec JSR-51 */ public String[] split(String regex, int limit) { /* fastpath if the regex is a (1)one-char String and this character is not one of the RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or (2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter. */ char ch = 0; if (((regex.count == 1 && ".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) || (regex.length() == 2 && regex.charAt(0) == '\\' && (((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 && ((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 && ((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) && (ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE || ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE)) { int off = 0; int next = 0; boolean limited = limit > 0; ArrayList
This method works as if by invoking the two-argument {@link * #split(String, int) split} method with the given expression and a limit * argument of zero. Trailing empty strings are therefore not included in * the resulting array. * *
The string "boo:and:foo", for example, yields the following * results with these expressions: * *
* * * @param regex * the delimiting regular expression * * @return the array of strings computed by splitting this string * around matches of the given regular expression * * @throws PatternSyntaxException * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid * * @see java.util.regex.Pattern * * @since 1.4 * @spec JSR-51 */ public String[] split(String regex) { return split(regex, 0); } /** * Converts all of the characters in this*
* *Regex *Result ** : *{ "boo", "and", "foo" } * o *{ "b", "", ":and:f" }
String to lower
* case using the rules of the given Locale. Case mapping is based
* on the Unicode Standard version specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character}
* class. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resulting
* String may be a different length than the original String.
* * Examples of lowercase mappings are in the following table: *
| Language Code of Locale | *Upper Case | *Lower Case | *Description | *
|---|---|---|---|
| tr (Turkish) | *\u0130 | *\u0069 | *capital letter I with dot above -> small letter i | *
| tr (Turkish) | *\u0049 | *\u0131 | *capital letter I -> small letter dotless i | *
| (all) | *French Fries | *french fries | *lowercased all chars in String | *
| (all) | *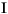 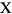 *
* 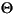 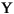 *
* 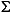 |
* 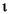 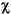 *
* 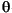 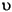 *
* 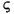 |
* lowercased all chars in String | *
String, converted to lowercase.
* @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase()
* @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase()
* @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase(Locale)
* @since 1.1
*/
public String toLowerCase(Locale locale) {
if (locale == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
int firstUpper;
/* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */
scan: {
for (firstUpper = 0 ; firstUpper < count; ) {
char c = value[offset+firstUpper];
if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE) &&
(c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) {
int supplChar = codePointAt(firstUpper);
if (supplChar != Character.toLowerCase(supplChar)) {
break scan;
}
firstUpper += Character.charCount(supplChar);
} else {
if (c != Character.toLowerCase(c)) {
break scan;
}
firstUpper++;
}
}
return this;
}
char[] result = new char[count];
int resultOffset = 0; /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset
* is the write location in result */
/* Just copy the first few lowerCase characters. */
System.arraycopy(value, offset, result, 0, firstUpper);
String lang = locale.getLanguage();
boolean localeDependent =
(lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt");
char[] lowerCharArray;
int lowerChar;
int srcChar;
int srcCount;
for (int i = firstUpper; i < count; i += srcCount) {
srcChar = (int)value[offset+i];
if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE &&
(char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) {
srcChar = codePointAt(i);
srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar);
} else {
srcCount = 1;
}
if (localeDependent || srcChar == '\u03A3') { // GREEK CAPITAL LETTER SIGMA
lowerChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseEx(this, i, locale);
} else if (srcChar == '\u0130') { // LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I DOT
lowerChar = Character.ERROR;
} else {
lowerChar = Character.toLowerCase(srcChar);
}
if ((lowerChar == Character.ERROR) ||
(lowerChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) {
if (lowerChar == Character.ERROR) {
if (!localeDependent && srcChar == '\u0130') {
lowerCharArray =
ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseCharArray(this, i, Locale.ENGLISH);
} else {
lowerCharArray =
ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseCharArray(this, i, locale);
}
} else if (srcCount == 2) {
resultOffset += Character.toChars(lowerChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount;
continue;
} else {
lowerCharArray = Character.toChars(lowerChar);
}
/* Grow result if needed */
int mapLen = lowerCharArray.length;
if (mapLen > srcCount) {
char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount];
System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0,
i + resultOffset);
result = result2;
}
for (int x=0; xtoLowerCase(Locale.getDefault()).
*
* Note: This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected
* results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale
* independently.
* Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML
* tags.
* For instance, "TITLE".toLowerCase() in a Turkish locale
* returns "t\u0131tle", where '\u0131' is the LATIN SMALL
* LETTER DOTLESS I character.
* To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, use
* toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).
*
* @return the String, converted to lowercase.
* @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase(Locale)
*/
public String toLowerCase() {
return toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
/**
* Converts all of the characters in this String to upper
* case using the rules of the given Locale. Case mapping is based
* on the Unicode Standard version specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character}
* class. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resulting
* String may be a different length than the original String.
*
* Examples of locale-sensitive and 1:M case mappings are in the following table. *
*
| Language Code of Locale | *Lower Case | *Upper Case | *Description | *
|---|---|---|---|
| tr (Turkish) | *\u0069 | *\u0130 | *small letter i -> capital letter I with dot above | *
| tr (Turkish) | *\u0131 | *\u0049 | *small letter dotless i -> capital letter I | *
| (all) | *\u00df | *\u0053 \u0053 | *small letter sharp s -> two letters: SS | *
| (all) | *Fahrvergnügen | *FAHRVERGNÜGEN | ** |
String, converted to uppercase.
* @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase()
* @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase()
* @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase(Locale)
* @since 1.1
*/
public String toUpperCase(Locale locale) {
if (locale == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
int firstLower;
/* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */
scan: {
for (firstLower = 0 ; firstLower < count; ) {
int c = (int)value[offset+firstLower];
int srcCount;
if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE) &&
(c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) {
c = codePointAt(firstLower);
srcCount = Character.charCount(c);
} else {
srcCount = 1;
}
int upperCaseChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(c);
if ((upperCaseChar == Character.ERROR) ||
(c != upperCaseChar)) {
break scan;
}
firstLower += srcCount;
}
return this;
}
char[] result = new char[count]; /* may grow */
int resultOffset = 0; /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset
* is the write location in result */
/* Just copy the first few upperCase characters. */
System.arraycopy(value, offset, result, 0, firstLower);
String lang = locale.getLanguage();
boolean localeDependent =
(lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt");
char[] upperCharArray;
int upperChar;
int srcChar;
int srcCount;
for (int i = firstLower; i < count; i += srcCount) {
srcChar = (int)value[offset+i];
if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE &&
(char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) {
srcChar = codePointAt(i);
srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar);
} else {
srcCount = 1;
}
if (localeDependent) {
upperChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseEx(this, i, locale);
} else {
upperChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(srcChar);
}
if ((upperChar == Character.ERROR) ||
(upperChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) {
if (upperChar == Character.ERROR) {
if (localeDependent) {
upperCharArray =
ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseCharArray(this, i, locale);
} else {
upperCharArray = Character.toUpperCaseCharArray(srcChar);
}
} else if (srcCount == 2) {
resultOffset += Character.toChars(upperChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount;
continue;
} else {
upperCharArray = Character.toChars(upperChar);
}
/* Grow result if needed */
int mapLen = upperCharArray.length;
if (mapLen > srcCount) {
char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount];
System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0,
i + resultOffset);
result = result2;
}
for (int x=0; xtoUpperCase(Locale.getDefault()).
*
* Note: This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected
* results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale
* independently.
* Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML
* tags.
* For instance, "title".toUpperCase() in a Turkish locale
* returns "T\u0130TLE", where '\u0130' is the LATIN CAPITAL
* LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE character.
* To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, use
* toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH).
*
* @return the String, converted to uppercase.
* @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase(Locale)
*/
public String toUpperCase() {
return toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
/**
* Returns a copy of the string, with leading and trailing whitespace
* omitted.
*
* If this String object represents an empty character
* sequence, or the first and last characters of character sequence
* represented by this String object both have codes
* greater than '\u0020' (the space character), then a
* reference to this String object is returned.
*
* Otherwise, if there is no character with a code greater than
* '\u0020' in the string, then a new
* String object representing an empty string is created
* and returned.
*
* Otherwise, let k be the index of the first character in the
* string whose code is greater than '\u0020', and let
* m be the index of the last character in the string whose code
* is greater than '\u0020'. A new String
* object is created, representing the substring of this string that
* begins with the character at index k and ends with the
* character at index m-that is, the result of
* this.substring(k, m+1).
*
* This method may be used to trim whitespace (as defined above) from * the beginning and end of a string. * * @return A copy of this string with leading and trailing white * space removed, or this string if it has no leading or * trailing white space. */ public String trim() { int len = count; int st = 0; int off = offset; /* avoid getfield opcode */ char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */ while ((st < len) && (val[off + st] <= ' ')) { st++; } while ((st < len) && (val[off + len - 1] <= ' ')) { len--; } return ((st > 0) || (len < count)) ? substring(st, len) : this; } /** * This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned. * * @return the string itself. */ public String toString() { return this; } /** * Converts this string to a new character array. * * @return a newly allocated character array whose length is the length * of this string and whose contents are initialized to contain * the character sequence represented by this string. */ public char[] toCharArray() { char result[] = new char[count]; getChars(0, count, result, 0); return result; } /** * Returns a formatted string using the specified format string and * arguments. * *
The locale always used is the one returned by {@link
* java.util.Locale#getDefault() Locale.getDefault()}.
*
* @param format
* A format string
*
* @param args
* Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format
* string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the
* extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is
* variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is
* limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by
* the Java
* Virtual Machine Specification. The behaviour on a
* null argument depends on the conversion.
*
* @throws IllegalFormatException
* If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format
* specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments,
* insufficient arguments given the format string, or other
* illegal conditions. For specification of all possible
* formatting errors, see the Details section of the
* formatter class specification.
*
* @throws NullPointerException
* If the format is null
*
* @return A formatted string
*
* @see java.util.Formatter
* @since 1.5
*/
public static String format(String format, Object ... args) {
return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
}
/**
* Returns a formatted string using the specified locale, format string,
* and arguments.
*
* @param l
* The {@linkplain java.util.Locale locale} to apply during
* formatting. If l is null then no localization
* is applied.
*
* @param format
* A format string
*
* @param args
* Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format
* string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the
* extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is
* variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is
* limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by
* the Java
* Virtual Machine Specification. The behaviour on a
* null argument depends on the conversion.
*
* @throws IllegalFormatException
* If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format
* specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments,
* insufficient arguments given the format string, or other
* illegal conditions. For specification of all possible
* formatting errors, see the Details section of the
* formatter class specification
*
* @throws NullPointerException
* If the format is null
*
* @return A formatted string
*
* @see java.util.Formatter
* @since 1.5
*/
public static String format(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) {
return new Formatter(l).format(format, args).toString();
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the Object argument.
*
* @param obj an Object.
* @return if the argument is null, then a string equal to
* "null"; otherwise, the value of
* obj.toString() is returned.
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the char array
* argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent
* modification of the character array does not affect the newly
* created string.
*
* @param data a char array.
* @return a newly allocated string representing the same sequence of
* characters contained in the character array argument.
*/
public static String valueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of the
* char array argument.
*
* The offset argument is the index of the first
* character of the subarray. The count argument
* specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray
* are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not
* affect the newly created string.
*
* @param data the character array.
* @param offset the initial offset into the value of the
* String.
* @param count the length of the value of the String.
* @return a string representing the sequence of characters contained
* in the subarray of the character array argument.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if offset is
* negative, or count is negative, or
* offset+count is larger than
* data.length.
*/
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
/**
* Returns a String that represents the character sequence in the
* array specified.
*
* @param data the character array.
* @param offset initial offset of the subarray.
* @param count length of the subarray.
* @return a String that contains the characters of the
* specified subarray of the character array.
*/
public static String copyValueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
// All public String constructors now copy the data.
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
/**
* Returns a String that represents the character sequence in the
* array specified.
*
* @param data the character array.
* @return a String that contains the characters of the
* character array.
*/
public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) {
return copyValueOf(data, 0, data.length);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the boolean argument.
*
* @param b a boolean.
* @return if the argument is true, a string equal to
* "true" is returned; otherwise, a string equal to
* "false" is returned.
*/
public static String valueOf(boolean b) {
return b ? "true" : "false";
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the char
* argument.
*
* @param c a char.
* @return a string of length 1 containing
* as its single character the argument c.
*/
public static String valueOf(char c) {
char data[] = {c};
return new String(0, 1, data);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the int argument.
*
* The representation is exactly the one returned by the
* Integer.toString method of one argument.
*
* @param i an int.
* @return a string representation of the int argument.
* @see java.lang.Integer#toString(int, int)
*/
public static String valueOf(int i) {
return Integer.toString(i, 10);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the long argument.
*
* The representation is exactly the one returned by the
* Long.toString method of one argument.
*
* @param l a long.
* @return a string representation of the long argument.
* @see java.lang.Long#toString(long)
*/
public static String valueOf(long l) {
return Long.toString(l, 10);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the float argument.
*
* The representation is exactly the one returned by the
* Float.toString method of one argument.
*
* @param f a float.
* @return a string representation of the float argument.
* @see java.lang.Float#toString(float)
*/
public static String valueOf(float f) {
return Float.toString(f);
}
/**
* Returns the string representation of the double argument.
*
* The representation is exactly the one returned by the
* Double.toString method of one argument.
*
* @param d a double.
* @return a string representation of the double argument.
* @see java.lang.Double#toString(double)
*/
public static String valueOf(double d) {
return Double.toString(d);
}
/**
* Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
*
* A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the
* class String.
*
* When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
* string equal to this String object as determined by
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method, then the string from the pool is
* returned. Otherwise, this String object is added to the
* pool and a reference to this String object is returned.
*
* It follows that for any two strings s and t,
* s.intern() == t.intern() is true
* if and only if s.equals(t) is true.
*
* All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are * interned. String literals are defined in §3.10.5 of the * Java Language * Specification * * @return a string that has the same contents as this string, but is * guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings. */ public native String intern(); }