 *
* * A window must have either a frame, dialog, or another window defined as its * owner when it's constructed. *
* In a multi-screen environment, you can create a {@code Window} * on a different screen device by constructing the {@code Window} * with {@link #Window(Window, GraphicsConfiguration)}. The * {@code GraphicsConfiguration} object is one of the * {@code GraphicsConfiguration} objects of the target screen device. *
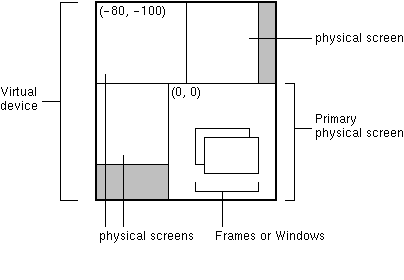
* In a virtual device multi-screen environment in which the desktop * area could span multiple physical screen devices, the bounds of all * configurations are relative to the virtual device coordinate system. * The origin of the virtual-coordinate system is at the upper left-hand * corner of the primary physical screen. Depending on the location of * the primary screen in the virtual device, negative coordinates are * possible, as shown in the following figure. *
*  *
*
* In such an environment, when calling {@code setLocation}, * you must pass a virtual coordinate to this method. Similarly, * calling {@code getLocationOnScreen} on a {@code Window} returns * virtual device coordinates. Call the {@code getBounds} method * of a {@code GraphicsConfiguration} to find its origin in the virtual * coordinate system. *
* The following code sets the location of a {@code Window} * at (10, 10) relative to the origin of the physical screen * of the corresponding {@code GraphicsConfiguration}. If the * bounds of the {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is not taken * into account, the {@code Window} location would be set * at (10, 10) relative to the virtual-coordinate system and would appear * on the primary physical screen, which might be different from the * physical screen of the specified {@code GraphicsConfiguration}. * *
* Window w = new Window(Window owner, GraphicsConfiguration gc); * Rectangle bounds = gc.getBounds(); * w.setLocation(10 + bounds.x, 10 + bounds.y); ** *
* Note: the location and size of top-level windows (including * {@code Window}s, {@code Frame}s, and {@code Dialog}s) * are under the control of the desktop's window management system. * Calls to {@code setLocation}, {@code setSize}, and * {@code setBounds} are requests (not directives) which are * forwarded to the window management system. Every effort will be * made to honor such requests. However, in some cases the window * management system may ignore such requests, or modify the requested * geometry in order to place and size the {@code Window} in a way * that more closely matches the desktop settings. *
* Due to the asynchronous nature of native event handling, the results * returned by {@code getBounds}, {@code getLocation}, * {@code getLocationOnScreen}, and {@code getSize} might not * reflect the actual geometry of the Window on screen until the last * request has been processed. During the processing of subsequent * requests these values might change accordingly while the window * management system fulfills the requests. *
* An application may set the size and location of an invisible * {@code Window} arbitrarily, but the window management system may * subsequently change its size and/or location when the * {@code Window} is made visible. One or more {@code ComponentEvent}s * will be generated to indicate the new geometry. *
* Windows are capable of generating the following WindowEvents: * WindowOpened, WindowClosed, WindowGainedFocus, WindowLostFocus. * * @author Sami Shaio * @author Arthur van Hoff * @see WindowEvent * @see #addWindowListener * @see java.awt.BorderLayout * @since JDK1.0 */ public class Window extends Container implements Accessible { /** * Enumeration of available window types. * * A window type defines the generic visual appearance and behavior of a * top-level window. For example, the type may affect the kind of * decorations of a decorated {@code Frame} or {@code Dialog} instance. *
* Some platforms may not fully support a certain window type. Depending on
* the level of support, some properties of the window type may be
* disobeyed.
*
* @see #getType
* @see #setType
* @since 1.7
*/
public static enum Type {
/**
* Represents a normal window.
*
* This is the default type for objects of the {@code Window} class or
* its descendants. Use this type for regular top-level windows.
*/
NORMAL,
/**
* Represents a utility window.
*
* A utility window is usually a small window such as a toolbar or a
* palette. The native system may render the window with smaller
* title-bar if the window is either a {@code Frame} or a {@code
* Dialog} object, and if it has its decorations enabled.
*/
UTILITY,
/**
* Represents a popup window.
*
* A popup window is a temporary window such as a drop-down menu or a
* tooltip. On some platforms, windows of that type may be forcibly
* made undecorated even if they are instances of the {@code Frame} or
* {@code Dialog} class, and have decorations enabled.
*/
POPUP
}
/**
* This represents the warning message that is
* to be displayed in a non secure window. ie :
* a window that has a security manager installed that denies
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}.
* This message can be displayed anywhere in the window.
*
* @serial
* @see #getWarningString
*/
String warningString;
/**
* {@code icons} is the graphical way we can
* represent the frames and dialogs.
* {@code Window} can't display icon but it's
* being inherited by owned {@code Dialog}s.
*
* @serial
* @see #getIconImages
* @see #setIconImages
*/
transient java.util.List
* If there is a security manager, then it is invoked to check
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}
* to determine whether or not the window must be displayed with
* a warning banner.
*
* @param gc the {@code GraphicsConfiguration} of the target screen
* device. If {@code gc} is {@code null}, the system default
* {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is assumed
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if {@code gc}
* is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* {@code GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()} returns {@code true}
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
*/
Window(GraphicsConfiguration gc) {
init(gc);
}
transient Object anchor = new Object();
static class WindowDisposerRecord implements sun.java2d.DisposerRecord {
WeakReference
* If there is a security manager set, it is invoked to check
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}.
* If that check fails with a {@code SecurityException} then a warning
* banner is created.
*
* @exception HeadlessException when
* {@code GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()} returns {@code true}
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
*/
Window() throws HeadlessException {
GraphicsEnvironment.checkHeadless();
init((GraphicsConfiguration)null);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified
* {@code Frame} as its owner. The window will not be focusable
* unless its owner is showing on the screen.
*
* If there is a security manager set, it is invoked to check
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}.
* If that check fails with a {@code SecurityException} then a warning
* banner is created.
*
* @param owner the {@code Frame} to act as owner or {@code null}
* if this window has no owner
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the {@code owner}'s
* {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* {@code GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless} returns {@code true}
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see #isShowing
*/
public Window(Frame owner) {
this(owner == null ? (GraphicsConfiguration)null :
owner.getGraphicsConfiguration());
ownedInit(owner);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified
* {@code Window} as its owner. This window will not be focusable
* unless its nearest owning {@code Frame} or {@code Dialog}
* is showing on the screen.
*
* If there is a security manager set, it is invoked to check
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}.
* If that check fails with a {@code SecurityException} then a
* warning banner is created.
*
* @param owner the {@code Window} to act as owner or
* {@code null} if this window has no owner
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the {@code owner}'s
* {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* {@code GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()} returns
* {@code true}
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see #isShowing
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window(Window owner) {
this(owner == null ? (GraphicsConfiguration)null :
owner.getGraphicsConfiguration());
ownedInit(owner);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, initially invisible window with the specified owner
* {@code Window} and a {@code GraphicsConfiguration}
* of a screen device. The Window will not be focusable unless
* its nearest owning {@code Frame} or {@code Dialog}
* is showing on the screen.
*
* If there is a security manager set, it is invoked to check
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}. If that
* check fails with a {@code SecurityException} then a warning banner
* is created.
*
* @param owner the window to act as owner or {@code null}
* if this window has no owner
* @param gc the {@code GraphicsConfiguration} of the target
* screen device; if {@code gc} is {@code null},
* the system default {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is assumed
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if {@code gc}
* is not from a screen device
* @exception HeadlessException when
* {@code GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()} returns
* {@code true}
*
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#isHeadless
* @see GraphicsConfiguration#getBounds
* @see #isShowing
* @since 1.3
*/
public Window(Window owner, GraphicsConfiguration gc) {
this(gc);
ownedInit(owner);
}
private void ownedInit(Window owner) {
this.parent = owner;
if (owner != null) {
owner.addOwnedWindow(weakThis);
if (owner.isAlwaysOnTop()) {
try {
setAlwaysOnTop(true);
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
}
}
}
// WindowDisposerRecord requires a proper value of parent field.
disposerRecord.updateOwner();
}
/**
* Construct a name for this component. Called by getName() when the
* name is null.
*/
String constructComponentName() {
synchronized (Window.class) {
return base + nameCounter++;
}
}
/**
* Returns the sequence of images to be displayed as the icon for this window.
*
* This method returns a copy of the internally stored list, so all operations
* on the returned object will not affect the window's behavior.
*
* @return the copy of icon images' list for this window, or
* empty list if this window doesn't have icon images.
* @see #setIconImages
* @see #setIconImage(Image)
* @since 1.6
*/
public java.util.List
* Depending on the platform capabilities one or several images
* of different dimensions will be used as the window's icon.
*
* The {@code icons} list is scanned for the images of most
* appropriate dimensions from the beginning. If the list contains
* several images of the same size, the first will be used.
*
* Ownerless windows with no icon specified use platfrom-default icon.
* The icon of an owned window may be inherited from the owner
* unless explicitly overridden.
* Setting the icon to {@code null} or empty list restores
* the default behavior.
*
* Note : Native windowing systems may use different images of differing
* dimensions to represent a window, depending on the context (e.g.
* window decoration, window list, taskbar, etc.). They could also use
* just a single image for all contexts or no image at all.
*
* @param icons the list of icon images to be displayed.
* @see #getIconImages()
* @see #setIconImage(Image)
* @since 1.6
*/
public synchronized void setIconImages(java.util.List icons) {
this.icons = (icons == null) ? new ArrayList
* This method can be used instead of {@link #setIconImages setIconImages()}
* to specify a single image as a window's icon.
*
* The following statement:
*
* Note : Native windowing systems may use different images of differing
* dimensions to represent a window, depending on the context (e.g.
* window decoration, window list, taskbar, etc.). They could also use
* just a single image for all contexts or no image at all.
*
* @param image the icon image to be displayed.
* @see #setIconImages
* @see #getIconImages()
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setIconImage(Image image) {
ArrayList
* If the window and/or its owner are not displayable yet,
* both of them are made displayable before calculating
* the preferred size. The Window is validated after its
* size is being calculated.
*
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #setMinimumSize
*/
public void pack() {
Container parent = this.parent;
if (parent != null && parent.getPeer() == null) {
parent.addNotify();
}
if (peer == null) {
addNotify();
}
Dimension newSize = getPreferredSize();
if (peer != null) {
setClientSize(newSize.width, newSize.height);
}
if(beforeFirstShow) {
isPacked = true;
}
validateUnconditionally();
}
/**
* Sets the minimum size of this window to a constant
* value. Subsequent calls to {@code getMinimumSize}
* will always return this value. If current window's
* size is less than {@code minimumSize} the size of the
* window is automatically enlarged to honor the minimum size.
*
* If the {@code setSize} or {@code setBounds} methods
* are called afterwards with a width or height less than
* that was specified by the {@code setMinimumSize} method
* the window is automatically enlarged to meet
* the {@code minimumSize} value. The {@code minimumSize}
* value also affects the behaviour of the {@code pack} method.
*
* The default behavior is restored by setting the minimum size
* parameter to the {@code null} value.
*
* Resizing operation may be restricted if the user tries
* to resize window below the {@code minimumSize} value.
* This behaviour is platform-dependent.
*
* @param minimumSize the new minimum size of this window
* @see Component#setMinimumSize
* @see #getMinimumSize
* @see #isMinimumSizeSet
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #pack
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setMinimumSize(Dimension minimumSize) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
super.setMinimumSize(minimumSize);
Dimension size = getSize();
if (isMinimumSizeSet()) {
if (size.width < minimumSize.width || size.height < minimumSize.height) {
int nw = Math.max(width, minimumSize.width);
int nh = Math.max(height, minimumSize.height);
setSize(nw, nh);
}
}
if (peer != null) {
((WindowPeer)peer).updateMinimumSize();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code d.width} and {@code d.height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getSize
* @see #setBounds
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setSize(Dimension d) {
super.setSize(d);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code width} and {@code height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getSize
* @see #setBounds
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setSize(int width, int height) {
super.setSize(width, height);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*/
@Override
public void setLocation(int x, int y) {
super.setLocation(x, y);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*/
@Override
public void setLocation(Point p) {
super.setLocation(p);
}
/**
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.1,
* replaced by {@code setBounds(int, int, int, int)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void reshape(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
if (isMinimumSizeSet()) {
Dimension minSize = getMinimumSize();
if (width < minSize.width) {
width = minSize.width;
}
if (height < minSize.height) {
height = minSize.height;
}
}
super.reshape(x, y, width, height);
}
void setClientSize(int w, int h) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
setBoundsOp(ComponentPeer.SET_CLIENT_SIZE);
setBounds(x, y, w, h);
}
}
static private final AtomicBoolean
beforeFirstWindowShown = new AtomicBoolean(true);
final void closeSplashScreen() {
if (isTrayIconWindow) {
return;
}
if (beforeFirstWindowShown.getAndSet(false)) {
// We don't use SplashScreen.getSplashScreen() to avoid instantiating
// the object if it hasn't been requested by user code explicitly
SunToolkit.closeSplashScreen();
SplashScreen.markClosed();
}
}
/**
* Shows or hides this {@code Window} depending on the value of parameter
* {@code b}.
*
* If the method shows the window then the window is also made
* focused under the following conditions:
*
* Developers must never assume that the window is the focused or active window
* until it receives a WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS or WINDOW_ACTIVATED event.
* @param b if {@code true}, makes the {@code Window} visible,
* otherwise hides the {@code Window}.
* If the {@code Window} and/or its owner
* are not yet displayable, both are made displayable. The
* {@code Window} will be validated prior to being made visible.
* If the {@code Window} is already visible, this will bring the
* {@code Window} to the front.
* If {@code false}, hides this {@code Window}, its subcomponents, and all
* of its owned children.
* The {@code Window} and its subcomponents can be made visible again
* with a call to {@code #setVisible(true)}.
* @see java.awt.Component#isDisplayable
* @see java.awt.Component#setVisible
* @see java.awt.Window#toFront
* @see java.awt.Window#dispose
* @see java.awt.Window#setAutoRequestFocus
* @see java.awt.Window#isFocusableWindow
*/
public void setVisible(boolean b) {
super.setVisible(b);
}
/**
* Makes the Window visible. If the Window and/or its owner
* are not yet displayable, both are made displayable. The
* Window will be validated prior to being made visible.
* If the Window is already visible, this will bring the Window
* to the front.
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #toFront
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.5, replaced by
* {@link #setVisible(boolean)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void show() {
if (peer == null) {
addNotify();
}
validateUnconditionally();
isInShow = true;
if (visible) {
toFront();
} else {
beforeFirstShow = false;
closeSplashScreen();
Dialog.checkShouldBeBlocked(this);
super.show();
locationByPlatform = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if ((child != null) && child.showWithParent) {
child.show();
child.showWithParent = false;
} // endif
} // endfor
if (!isModalBlocked()) {
updateChildrenBlocking();
} else {
// fix for 6532736: after this window is shown, its blocker
// should be raised to front
modalBlocker.toFront_NoClientCode();
}
if (this instanceof Frame || this instanceof Dialog) {
updateChildFocusableWindowState(this);
}
}
isInShow = false;
// If first time shown, generate WindowOpened event
if ((state & OPENED) == 0) {
postWindowEvent(WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED);
state |= OPENED;
}
}
static void updateChildFocusableWindowState(Window w) {
if (w.getPeer() != null && w.isShowing()) {
((WindowPeer)w.getPeer()).updateFocusableWindowState();
}
for (int i = 0; i < w.ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = w.ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if (child != null) {
updateChildFocusableWindowState(child);
}
}
}
synchronized void postWindowEvent(int id) {
if (windowListener != null
|| (eventMask & AWTEvent.WINDOW_EVENT_MASK) != 0
|| Toolkit.enabledOnToolkit(AWTEvent.WINDOW_EVENT_MASK)) {
WindowEvent e = new WindowEvent(this, id);
Toolkit.getEventQueue().postEvent(e);
}
}
/**
* Hide this Window, its subcomponents, and all of its owned children.
* The Window and its subcomponents can be made visible again
* with a call to {@code show}.
* @see #show
* @see #dispose
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.5, replaced by
* {@link #setVisible(boolean)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void hide() {
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowList.size(); i++) {
Window child = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if ((child != null) && child.visible) {
child.hide();
child.showWithParent = true;
}
}
}
if (isModalBlocked()) {
modalBlocker.unblockWindow(this);
}
super.hide();
locationByPlatform = false;
}
final void clearMostRecentFocusOwnerOnHide() {
/* do nothing */
}
/**
* Releases all of the native screen resources used by this
* {@code Window}, its subcomponents, and all of its owned
* children. That is, the resources for these {@code Component}s
* will be destroyed, any memory they consume will be returned to the
* OS, and they will be marked as undisplayable.
*
* The {@code Window} and its subcomponents can be made displayable
* again by rebuilding the native resources with a subsequent call to
* {@code pack} or {@code show}. The states of the recreated
* {@code Window} and its subcomponents will be identical to the
* states of these objects at the point where the {@code Window}
* was disposed (not accounting for additional modifications between
* those actions).
*
* Note: When the last displayable window
* within the Java virtual machine (VM) is disposed of, the VM may
* terminate. See
* AWT Threading Issues for more information.
* @see Component#isDisplayable
* @see #pack
* @see #show
*/
public void dispose() {
doDispose();
}
/*
* Fix for 4872170.
* If dispose() is called on parent then its children have to be disposed as well
* as reported in javadoc. So we need to implement this functionality even if a
* child overrides dispose() in a wrong way without calling super.dispose().
*/
void disposeImpl() {
dispose();
if (getPeer() != null) {
doDispose();
}
}
void doDispose() {
class DisposeAction implements Runnable {
public void run() {
disposing = true;
try {
// Check if this window is the fullscreen window for the
// device. Exit the fullscreen mode prior to disposing
// of the window if that's the case.
GraphicsDevice gd = getGraphicsConfiguration().getDevice();
if (gd.getFullScreenWindow() == Window.this) {
gd.setFullScreenWindow(null);
}
Object[] ownedWindowArray;
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
ownedWindowArray = new Object[ownedWindowList.size()];
ownedWindowList.copyInto(ownedWindowArray);
}
for (int i = 0; i < ownedWindowArray.length; i++) {
Window child = (Window) (((WeakReference)
(ownedWindowArray[i])).get());
if (child != null) {
child.disposeImpl();
}
}
hide();
beforeFirstShow = true;
removeNotify();
synchronized (inputContextLock) {
if (inputContext != null) {
inputContext.dispose();
inputContext = null;
}
}
clearCurrentFocusCycleRootOnHide();
} finally {
disposing = false;
}
}
}
boolean fireWindowClosedEvent = isDisplayable();
DisposeAction action = new DisposeAction();
if (EventQueue.isDispatchThread()) {
action.run();
}
else {
try {
EventQueue.invokeAndWait(this, action);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("Disposal was interrupted:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
System.err.println("Exception during disposal:");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Execute outside the Runnable because postWindowEvent is
// synchronized on (this). We don't need to synchronize the call
// on the EventQueue anyways.
if (fireWindowClosedEvent) {
postWindowEvent(WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED);
}
}
/*
* Should only be called while holding the tree lock.
* It's overridden here because parent == owner in Window,
* and we shouldn't adjust counter on owner
*/
void adjustListeningChildrenOnParent(long mask, int num) {
}
// Should only be called while holding tree lock
void adjustDecendantsOnParent(int num) {
// do nothing since parent == owner and we shouldn't
// ajust counter on owner
}
/**
* If this Window is visible, brings this Window to the front and may make
* it the focused Window.
*
* Places this Window at the top of the stacking order and shows it in
* front of any other Windows in this VM. No action will take place if this
* Window is not visible. Some platforms do not allow Windows which own
* other Windows to appear on top of those owned Windows. Some platforms
* may not permit this VM to place its Windows above windows of native
* applications, or Windows of other VMs. This permission may depend on
* whether a Window in this VM is already focused. Every attempt will be
* made to move this Window as high as possible in the stacking order;
* however, developers should not assume that this method will move this
* Window above all other windows in every situation.
*
* Developers must never assume that this Window is the focused or active
* Window until this Window receives a WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS or WINDOW_ACTIVATED
* event. On platforms where the top-most window is the focused window, this
* method will probably focus this Window (if it is not already focused)
* under the following conditions:
*
* If this method causes this Window to be focused, and this Window is a
* Frame or a Dialog, it will also become activated. If this Window is
* focused, but it is not a Frame or a Dialog, then the first Frame or
* Dialog that is an owner of this Window will be activated.
*
* If this window is blocked by modal dialog, then the blocking dialog
* is brought to the front and remains above the blocked window.
*
* @see #toBack
* @see #setAutoRequestFocus
* @see #isFocusableWindow
*/
public void toFront() {
toFront_NoClientCode();
}
// This functionality is implemented in a final package-private method
// to insure that it cannot be overridden by client subclasses.
final void toFront_NoClientCode() {
if (visible) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.toFront();
}
if (isModalBlocked()) {
modalBlocker.toFront_NoClientCode();
}
}
}
/**
* If this Window is visible, sends this Window to the back and may cause
* it to lose focus or activation if it is the focused or active Window.
*
* Places this Window at the bottom of the stacking order and shows it
* behind any other Windows in this VM. No action will take place is this
* Window is not visible. Some platforms do not allow Windows which are
* owned by other Windows to appear below their owners. Every attempt will
* be made to move this Window as low as possible in the stacking order;
* however, developers should not assume that this method will move this
* Window below all other windows in every situation.
*
* Because of variations in native windowing systems, no guarantees about
* changes to the focused and active Windows can be made. Developers must
* never assume that this Window is no longer the focused or active Window
* until this Window receives a WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS or WINDOW_DEACTIVATED
* event. On platforms where the top-most window is the focused window,
* this method will probably cause this Window to lose focus. In
* that case, the next highest, focusable Window in this VM will receive
* focus. On platforms where the stacking order does not typically affect
* the focused window, this method will probably leave the focused
* and active Windows unchanged.
*
* @see #toFront
*/
public void toBack() {
toBack_NoClientCode();
}
// This functionality is implemented in a final package-private method
// to insure that it cannot be overridden by client subclasses.
final void toBack_NoClientCode() {
if(isAlwaysOnTop()) {
try {
setAlwaysOnTop(false);
}catch(SecurityException e) {
}
}
if (visible) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.toBack();
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the toolkit of this frame.
* @return the toolkit of this window.
* @see Toolkit
* @see Toolkit#getDefaultToolkit
* @see Component#getToolkit
*/
public Toolkit getToolkit() {
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
}
/**
* Gets the warning string that is displayed with this window.
* If this window is insecure, the warning string is displayed
* somewhere in the visible area of the window. A window is
* insecure if there is a security manager and the security
* manager denies
* {@code AWTPermission("showWindowWithoutWarningBanner")}.
*
* If the window is secure, then {@code getWarningString}
* returns {@code null}. If the window is insecure, this
* method checks for the system property
* {@code awt.appletWarning}
* and returns the string value of that property.
* @return the warning string for this window.
*/
public final String getWarningString() {
return warningString;
}
private void setWarningString() {
warningString = null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
try {
sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.AWT.TOPLEVEL_WINDOW_PERMISSION);
} catch (SecurityException se) {
// make sure the privileged action is only
// for getting the property! We don't want the
// above checkPermission call to always succeed!
warningString = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("awt.appletWarning",
"Java Applet Window"));
}
}
}
/**
* Gets the {@code Locale} object that is associated
* with this window, if the locale has been set.
* If no locale has been set, then the default locale
* is returned.
* @return the locale that is set for this window.
* @see java.util.Locale
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public Locale getLocale() {
if (this.locale == null) {
return Locale.getDefault();
}
return this.locale;
}
/**
* Gets the input context for this window. A window always has an input context,
* which is shared by subcomponents unless they create and set their own.
* @see Component#getInputContext
* @since 1.2
*/
public InputContext getInputContext() {
synchronized (inputContextLock) {
if (inputContext == null) {
inputContext = InputContext.getInstance();
}
}
return inputContext;
}
/**
* Set the cursor image to a specified cursor.
*
* The method may have no visual effect if the Java platform
* implementation and/or the native system do not support
* changing the mouse cursor shape.
* @param cursor One of the constants defined
* by the {@code Cursor} class. If this parameter is null
* then the cursor for this window will be set to the type
* Cursor.DEFAULT_CURSOR.
* @see Component#getCursor
* @see Cursor
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public void setCursor(Cursor cursor) {
if (cursor == null) {
cursor = Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.DEFAULT_CURSOR);
}
super.setCursor(cursor);
}
/**
* Returns the owner of this window.
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window getOwner() {
return getOwner_NoClientCode();
}
final Window getOwner_NoClientCode() {
return (Window)parent;
}
/**
* Return an array containing all the windows this
* window currently owns.
* @since 1.2
*/
public Window[] getOwnedWindows() {
return getOwnedWindows_NoClientCode();
}
final Window[] getOwnedWindows_NoClientCode() {
Window realCopy[];
synchronized(ownedWindowList) {
// Recall that ownedWindowList is actually a Vector of
// WeakReferences and calling get() on one of these references
// may return null. Make two arrays-- one the size of the
// Vector (fullCopy with size fullSize), and one the size of
// all non-null get()s (realCopy with size realSize).
int fullSize = ownedWindowList.size();
int realSize = 0;
Window fullCopy[] = new Window[fullSize];
for (int i = 0; i < fullSize; i++) {
fullCopy[realSize] = ownedWindowList.elementAt(i).get();
if (fullCopy[realSize] != null) {
realSize++;
}
}
if (fullSize != realSize) {
realCopy = Arrays.copyOf(fullCopy, realSize);
} else {
realCopy = fullCopy;
}
}
return realCopy;
}
boolean isModalBlocked() {
return modalBlocker != null;
}
void setModalBlocked(Dialog blocker, boolean blocked, boolean peerCall) {
this.modalBlocker = blocked ? blocker : null;
if (peerCall) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.setModalBlocked(blocker, blocked);
}
}
}
Dialog getModalBlocker() {
return modalBlocker;
}
/*
* Returns a list of all displayable Windows, i. e. all the
* Windows which peer is not null.
*
* @see #addNotify
* @see #removeNotify
*/
static IdentityArrayList
* Warning: this method may return system created windows, such
* as a print dialog. Applications should not assume the existence of
* these dialogs, nor should an application assume anything about these
* dialogs such as component positions, {@code LayoutManager}s
* or serialization.
*
* @see Frame#getFrames
* @see Window#getOwnerlessWindows
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static Window[] getWindows() {
return getWindows(AppContext.getAppContext());
}
/**
* Returns an array of all {@code Window}s created by this application
* that have no owner. They include {@code Frame}s and ownerless
* {@code Dialog}s and {@code Window}s.
* If called from an applet, the array includes only the {@code Window}s
* accessible by that applet.
*
* Warning: this method may return system created windows, such
* as a print dialog. Applications should not assume the existence of
* these dialogs, nor should an application assume anything about these
* dialogs such as component positions, {@code LayoutManager}s
* or serialization.
*
* @see Frame#getFrames
* @see Window#getWindows()
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static Window[] getOwnerlessWindows() {
Window[] allWindows = Window.getWindows();
int ownerlessCount = 0;
for (Window w : allWindows) {
if (w.getOwner() == null) {
ownerlessCount++;
}
}
Window[] ownerless = new Window[ownerlessCount];
int c = 0;
for (Window w : allWindows) {
if (w.getOwner() == null) {
ownerless[c++] = w;
}
}
return ownerless;
}
Window getDocumentRoot() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
Window w = this;
while (w.getOwner() != null) {
w = w.getOwner();
}
return w;
}
}
/**
* Specifies the modal exclusion type for this window. If a window is modal
* excluded, it is not blocked by some modal dialogs. See {@link
* java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType Dialog.ModalExclusionType} for
* possible modal exclusion types.
*
* If the given type is not supported, {@code NO_EXCLUDE} is used.
*
* Note: changing the modal exclusion type for a visible window may have no
* effect until it is hidden and then shown again.
*
* @param exclusionType the modal exclusion type for this window; a {@code null}
* value is equivalent to {@link Dialog.ModalExclusionType#NO_EXCLUDE
* NO_EXCLUDE}
* @throws SecurityException if the calling thread does not have permission
* to set the modal exclusion property to the window with the given
* {@code exclusionType}
* @see java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Window#getModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Toolkit#isModalExclusionTypeSupported
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setModalExclusionType(Dialog.ModalExclusionType exclusionType) {
if (exclusionType == null) {
exclusionType = Dialog.ModalExclusionType.NO_EXCLUDE;
}
if (!Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().isModalExclusionTypeSupported(exclusionType)) {
exclusionType = Dialog.ModalExclusionType.NO_EXCLUDE;
}
if (modalExclusionType == exclusionType) {
return;
}
if (exclusionType == Dialog.ModalExclusionType.TOOLKIT_EXCLUDE) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.AWT.TOOLKIT_MODALITY_PERMISSION);
}
}
modalExclusionType = exclusionType;
// if we want on-fly changes, we need to uncomment the lines below
// and override the method in Dialog to use modalShow() instead
// of updateChildrenBlocking()
/*
if (isModalBlocked()) {
modalBlocker.unblockWindow(this);
}
Dialog.checkShouldBeBlocked(this);
updateChildrenBlocking();
*/
}
/**
* Returns the modal exclusion type of this window.
*
* @return the modal exclusion type of this window
*
* @see java.awt.Dialog.ModalExclusionType
* @see java.awt.Window#setModalExclusionType
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public Dialog.ModalExclusionType getModalExclusionType() {
return modalExclusionType;
}
boolean isModalExcluded(Dialog.ModalExclusionType exclusionType) {
if ((modalExclusionType != null) &&
modalExclusionType.compareTo(exclusionType) >= 0)
{
return true;
}
Window owner = getOwner_NoClientCode();
return (owner != null) && owner.isModalExcluded(exclusionType);
}
void updateChildrenBlocking() {
Vector Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window listener
* @see #removeWindowListener
* @see #getWindowListeners
*/
public synchronized void addWindowListener(WindowListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
newEventsOnly = true;
windowListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowListener, l);
}
/**
* Adds the specified window state listener to receive window
* events from this window. If {@code l} is {@code null},
* no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window state listener
* @see #removeWindowStateListener
* @see #getWindowStateListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void addWindowStateListener(WindowStateListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowStateListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowStateListener, l);
newEventsOnly = true;
}
/**
* Adds the specified window focus listener to receive window events
* from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window focus listener
* @see #removeWindowFocusListener
* @see #getWindowFocusListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void addWindowFocusListener(WindowFocusListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowFocusListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(windowFocusListener, l);
newEventsOnly = true;
}
/**
* Removes the specified window listener so that it no longer
* receives window events from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window listener
* @see #addWindowListener
* @see #getWindowListeners
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowListener(WindowListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowListener, l);
}
/**
* Removes the specified window state listener so that it no
* longer receives window events from this window. If
* {@code l} is {@code null}, no exception is thrown and
* no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window state listener
* @see #addWindowStateListener
* @see #getWindowStateListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowStateListener(WindowStateListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowStateListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowStateListener, l);
}
/**
* Removes the specified window focus listener so that it no longer
* receives window events from this window.
* If l is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
* Refer to AWT Threading Issues for details on AWT's threading model.
*
* @param l the window focus listener
* @see #addWindowFocusListener
* @see #getWindowFocusListeners
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized void removeWindowFocusListener(WindowFocusListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
windowFocusListener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(windowFocusListener, l);
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's {@code WindowListener}s
* or an empty array if no window
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowListener
* @see #removeWindowListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowListener[] getWindowListeners() {
return getListeners(WindowListener.class);
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window focus listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's {@code WindowFocusListener}s
* or an empty array if no window focus
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowFocusListener
* @see #removeWindowFocusListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowFocusListener[] getWindowFocusListeners() {
return getListeners(WindowFocusListener.class);
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the window state listeners
* registered on this window.
*
* @return all of this window's {@code WindowStateListener}s
* or an empty array if no window state
* listeners are currently registered
*
* @see #addWindowStateListener
* @see #removeWindowStateListener
* @since 1.4
*/
public synchronized WindowStateListener[] getWindowStateListeners() {
return getListeners(WindowStateListener.class);
}
/**
* Returns an array of all the objects currently registered
* as
*
* You can specify the {@code listenerType} argument
* with a class literal, such as
* Note that if the event parameter is {@code null}
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the event
*/
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e) {
if (e instanceof WindowEvent) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSING:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ICONIFIED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEICONIFIED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ACTIVATED:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEACTIVATED:
processWindowEvent((WindowEvent)e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS:
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS:
processWindowFocusEvent((WindowEvent)e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED:
processWindowStateEvent((WindowEvent)e);
break;
}
return;
}
super.processEvent(e);
}
/**
* Processes window events occurring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered WindowListener objects.
* NOTE: This method will not be called unless window events
* are enabled for this component; this happens when one of the
* following occurs:
* Note that if the event parameter is {@code null}
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window event
* @see Component#enableEvents
*/
protected void processWindowEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowListener listener = windowListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch(e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_OPENED:
listener.windowOpened(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSING:
listener.windowClosing(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_CLOSED:
listener.windowClosed(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ICONIFIED:
listener.windowIconified(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEICONIFIED:
listener.windowDeiconified(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_ACTIVATED:
listener.windowActivated(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_DEACTIVATED:
listener.windowDeactivated(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Processes window focus event occurring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered WindowFocusListener objects.
* NOTE: this method will not be called unless window focus events
* are enabled for this window. This happens when one of the
* following occurs:
* Note that if the event parameter is {@code null}
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window focus event
* @see Component#enableEvents
* @since 1.4
*/
protected void processWindowFocusEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowFocusListener listener = windowFocusListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS:
listener.windowGainedFocus(e);
break;
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_LOST_FOCUS:
listener.windowLostFocus(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Processes window state event occurring on this window by
* dispatching them to any registered {@code WindowStateListener}
* objects.
* NOTE: this method will not be called unless window state events
* are enabled for this window. This happens when one of the
* following occurs:
* Note that if the event parameter is {@code null}
* the behavior is unspecified and may result in an
* exception.
*
* @param e the window state event
* @see java.awt.Component#enableEvents
* @since 1.4
*/
protected void processWindowStateEvent(WindowEvent e) {
WindowStateListener listener = windowStateListener;
if (listener != null) {
switch (e.getID()) {
case WindowEvent.WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED:
listener.windowStateChanged(e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Implements a debugging hook -- checks to see if
* the user has typed control-shift-F1. If so,
* the list of child windows is dumped to {@code System.out}.
* @param e the keyboard event
*/
void preProcessKeyEvent(KeyEvent e) {
// Dump the list of child windows to System.out.
if (e.isActionKey() && e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_F1 &&
e.isControlDown() && e.isShiftDown() &&
e.getID() == KeyEvent.KEY_PRESSED) {
list(System.out, 0);
}
}
void postProcessKeyEvent(KeyEvent e) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* Sets whether this window should always be above other windows. If
* there are multiple always-on-top windows, their relative order is
* unspecified and platform dependent.
*
* If some other window is already always-on-top then the
* relative order between these windows is unspecified (depends on
* platform). No window can be brought to be over the always-on-top
* window except maybe another always-on-top window.
*
* All windows owned by an always-on-top window inherit this state and
* automatically become always-on-top. If a window ceases to be
* always-on-top, the windows that it owns will no longer be
* always-on-top. When an always-on-top window is sent {@link #toBack
* toBack}, its always-on-top state is set to {@code false}.
*
* When this method is called on a window with a value of
* {@code true}, and the window is visible and the platform
* supports always-on-top for this window, the window is immediately
* brought forward, "sticking" it in the top-most position. If the
* window isn`t currently visible, this method sets the always-on-top
* state to {@code true} but does not bring the window forward.
* When the window is later shown, it will be always-on-top.
*
* When this method is called on a window with a value of
* {@code false} the always-on-top state is set to normal. It may also
* cause an unspecified, platform-dependent change in the z-order of
* top-level windows, but other always-on-top windows will remain in
* top-most position. Calling this method with a value of {@code false}
* on a window that has a normal state has no effect.
*
* Note: some platforms might not support always-on-top
* windows. To detect if always-on-top windows are supported by the
* current platform, use {@link Toolkit#isAlwaysOnTopSupported()} and
* {@link Window#isAlwaysOnTopSupported()}. If always-on-top mode
* isn't supported for this window or this window's toolkit does not
* support always-on-top windows, calling this method has no effect.
*
* If a SecurityManager is installed, the calling thread must be
* granted the AWTPermission "setWindowAlwaysOnTop" in
* order to set the value of this property. If this
* permission is not granted, this method will throw a
* SecurityException, and the current value of the property will
* be left unchanged.
*
* @param alwaysOnTop true if the window should always be above other
* windows
* @throws SecurityException if the calling thread does not have
* permission to set the value of always-on-top property
*
* @see #isAlwaysOnTop
* @see #toFront
* @see #toBack
* @see AWTPermission
* @see #isAlwaysOnTopSupported
* @see #getToolkit
* @see Toolkit#isAlwaysOnTopSupported
* @since 1.5
*/
public final void setAlwaysOnTop(boolean alwaysOnTop) throws SecurityException {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.AWT.SET_WINDOW_ALWAYS_ON_TOP_PERMISSION);
}
boolean oldAlwaysOnTop;
synchronized(this) {
oldAlwaysOnTop = this.alwaysOnTop;
this.alwaysOnTop = alwaysOnTop;
}
if (oldAlwaysOnTop != alwaysOnTop ) {
if (isAlwaysOnTopSupported()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
synchronized(getTreeLock()) {
if (peer != null) {
peer.updateAlwaysOnTopState();
}
}
}
firePropertyChange("alwaysOnTop", oldAlwaysOnTop, alwaysOnTop);
}
setOwnedWindowsAlwaysOnTop(alwaysOnTop);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void setOwnedWindowsAlwaysOnTop(boolean alwaysOnTop) {
WeakReference
* If the focused Window is a Frame or a Dialog it is also the active
* Window. Otherwise, the active Window is the first Frame or Dialog that
* is an owner of the focused Window.
*
* @return whether this is the focused Window.
* @see #isActive
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean isFocused() {
return (KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
getGlobalFocusedWindow() == this);
}
/**
* Gets a focus traversal key for this Window. (See {@code
* setFocusTraversalKeys} for a full description of each key.)
*
* If the traversal key has not been explicitly set for this Window,
* then this Window's parent's traversal key is returned. If the
* traversal key has not been explicitly set for any of this Window's
* ancestors, then the current KeyboardFocusManager's default traversal key
* is returned.
*
* @param id one of KeyboardFocusManager.FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS, or
* KeyboardFocusManager.DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @return the AWTKeyStroke for the specified key
* @see Container#setFocusTraversalKeys
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @see KeyboardFocusManager#DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if id is not one of
* KeyboardFocusManager.FORWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.BACKWARD_TRAVERSAL_KEYS,
* KeyboardFocusManager.UP_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS, or
* KeyboardFocusManager.DOWN_CYCLE_TRAVERSAL_KEYS
* @since 1.4
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Set
* By default, all Windows have a focusable Window state of
* {@code true}.
*
* @return whether this Window can be the focused Window
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #setFocusableWindowState
* @see #isShowing
* @see Component#setFocusable
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean getFocusableWindowState() {
return focusableWindowState;
}
/**
* Sets whether this Window can become the focused Window if it meets
* the other requirements outlined in {@code isFocusableWindow}. If
* this Window's focusable Window state is set to {@code false}, then
* {@code isFocusableWindow} will return {@code false}. If this
* Window's focusable Window state is set to {@code true}, then
* {@code isFocusableWindow} may return {@code true} or
* {@code false} depending upon the other requirements which must be
* met in order for a Window to be focusable.
*
* Setting a Window's focusability state to {@code false} is the
* standard mechanism for an application to identify to the AWT a Window
* which will be used as a floating palette or toolbar, and thus should be
* a non-focusable Window.
*
* Setting the focusability state on a visible {@code Window}
* can have a delayed effect on some platforms — the actual
* change may happen only when the {@code Window} becomes
* hidden and then visible again. To ensure consistent behavior
* across platforms, set the {@code Window}'s focusable state
* when the {@code Window} is invisible and then show it.
*
* @param focusableWindowState whether this Window can be the focused
* Window
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #getFocusableWindowState
* @see #isShowing
* @see Component#setFocusable
* @since 1.4
*/
public void setFocusableWindowState(boolean focusableWindowState) {
boolean oldFocusableWindowState;
synchronized (this) {
oldFocusableWindowState = this.focusableWindowState;
this.focusableWindowState = focusableWindowState;
}
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)this.peer;
if (peer != null) {
peer.updateFocusableWindowState();
}
firePropertyChange("focusableWindowState", oldFocusableWindowState,
focusableWindowState);
if (oldFocusableWindowState && !focusableWindowState && isFocused()) {
for (Window owner = getOwner();
owner != null;
owner = owner.getOwner())
{
Component toFocus =
KeyboardFocusManager.getMostRecentFocusOwner(owner);
if (toFocus != null && toFocus.requestFocus(false, CausedFocusEvent.Cause.ACTIVATION)) {
return;
}
}
KeyboardFocusManager.getCurrentKeyboardFocusManager().
clearGlobalFocusOwnerPriv();
}
}
/**
* Sets whether this window should receive focus on
* subsequently being shown (with a call to {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)}),
* or being moved to the front (with a call to {@link #toFront}).
*
* Note that {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)} may be called indirectly
* (e.g. when showing an owner of the window makes the window to be shown).
* {@link #toFront} may also be called indirectly (e.g. when
* {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)} is called on already visible window).
* In all such cases this property takes effect as well.
*
* The value of the property is not inherited by owned windows.
*
* @param autoRequestFocus whether this window should be focused on
* subsequently being shown or being moved to the front
* @see #isAutoRequestFocus
* @see #isFocusableWindow
* @see #setVisible
* @see #toFront
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setAutoRequestFocus(boolean autoRequestFocus) {
this.autoRequestFocus = autoRequestFocus;
}
/**
* Returns whether this window should receive focus on subsequently being shown
* (with a call to {@link #setVisible setVisible(true)}), or being moved to the front
* (with a call to {@link #toFront}).
*
* By default, the window has {@code autoRequestFocus} value of {@code true}.
*
* @return {@code autoRequestFocus} value
* @see #setAutoRequestFocus
* @since 1.7
*/
public boolean isAutoRequestFocus() {
return autoRequestFocus;
}
/**
* Adds a PropertyChangeListener to the listener list. The listener is
* registered for all bound properties of this class, including the
* following:
*
* If listener is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
*
* @param listener the PropertyChangeListener to be added
*
* @see Component#removePropertyChangeListener
* @see #addPropertyChangeListener(java.lang.String,java.beans.PropertyChangeListener)
*/
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
super.addPropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
/**
* Adds a PropertyChangeListener to the listener list for a specific
* property. The specified property may be user-defined, or one of the
* following:
*
* If listener is null, no exception is thrown and no action is performed.
*
* @param propertyName one of the property names listed above
* @param listener the PropertyChangeListener to be added
*
* @see #addPropertyChangeListener(java.beans.PropertyChangeListener)
* @see Component#removePropertyChangeListener
*/
public void addPropertyChangeListener(String propertyName,
PropertyChangeListener listener) {
super.addPropertyChangeListener(propertyName, listener);
}
/**
* Indicates if this container is a validate root.
*
* {@code Window} objects are the validate roots, and, therefore, they
* override this method to return {@code true}.
*
* @return {@code true}
* @since 1.7
* @see java.awt.Container#isValidateRoot
*/
@Override
public boolean isValidateRoot() {
return true;
}
/**
* Dispatches an event to this window or one of its sub components.
* @param e the event
*/
void dispatchEventImpl(AWTEvent e) {
if (e.getID() == ComponentEvent.COMPONENT_RESIZED) {
invalidate();
validate();
}
super.dispatchEventImpl(e);
}
/**
* @deprecated As of JDK version 1.1
* replaced by {@code dispatchEvent(AWTEvent)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean postEvent(Event e) {
if (handleEvent(e)) {
e.consume();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Checks if this Window is showing on screen.
* @see Component#setVisible
*/
public boolean isShowing() {
return visible;
}
boolean isDisposing() {
return disposing;
}
/**
* @deprecated As of J2SE 1.4, replaced by
* {@link Component#applyComponentOrientation Component.applyComponentOrientation}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void applyResourceBundle(ResourceBundle rb) {
applyComponentOrientation(ComponentOrientation.getOrientation(rb));
}
/**
* @deprecated As of J2SE 1.4, replaced by
* {@link Component#applyComponentOrientation Component.applyComponentOrientation}.
*/
@Deprecated
public void applyResourceBundle(String rbName) {
applyResourceBundle(ResourceBundle.getBundle(rbName));
}
/*
* Support for tracking all windows owned by this window
*/
void addOwnedWindow(WeakReference
* The target screen mentioned below is a screen to which
* the window should be placed after the setLocationRelativeTo
* method is called.
*
* If the screens configuration does not allow the window to
* be moved from one screen to another, then the window is
* only placed at the location determined according to the
* above conditions and its {@code GraphicsConfiguration} is
* not changed.
*
* Note: If the lower edge of the window is out of the screen,
* then the window is placed to the side of the {@code Component}
* that is closest to the center of the screen. So if the
* component is on the right part of the screen, the window
* is placed to its left, and vice versa.
*
* If after the window location has been calculated, the upper,
* left, or right edge of the window is out of the screen,
* then the window is located in such a way that the upper,
* left, or right edge of the window coincides with the
* corresponding edge of the screen. If both left and right
* edges of the window are out of the screen, the window is
* placed at the left side of the screen. The similar placement
* will occur if both top and bottom edges are out of the screen.
* In that case, the window is placed at the top side of the screen.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @param c the component in relation to which the window's location
* is determined
* @see java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment#getCenterPoint
* @since 1.4
*/
public void setLocationRelativeTo(Component c) {
// target location
int dx = 0, dy = 0;
// target GC
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration_NoClientCode();
Rectangle gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Dimension windowSize = getSize();
// search a top-level of c
Window componentWindow = SunToolkit.getContainingWindow(c);
if ((c == null) || (componentWindow == null)) {
GraphicsEnvironment ge = GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
gc = ge.getDefaultScreenDevice().getDefaultConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Point centerPoint = ge.getCenterPoint();
dx = centerPoint.x - windowSize.width / 2;
dy = centerPoint.y - windowSize.height / 2;
} else if (!c.isShowing()) {
gc = componentWindow.getGraphicsConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
dx = gcBounds.x + (gcBounds.width - windowSize.width) / 2;
dy = gcBounds.y + (gcBounds.height - windowSize.height) / 2;
} else {
gc = componentWindow.getGraphicsConfiguration();
gcBounds = gc.getBounds();
Dimension compSize = c.getSize();
Point compLocation = c.getLocationOnScreen();
dx = compLocation.x + ((compSize.width - windowSize.width) / 2);
dy = compLocation.y + ((compSize.height - windowSize.height) / 2);
// Adjust for bottom edge being offscreen
if (dy + windowSize.height > gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height) {
dy = gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height - windowSize.height;
if (compLocation.x - gcBounds.x + compSize.width / 2 < gcBounds.width / 2) {
dx = compLocation.x + compSize.width;
} else {
dx = compLocation.x - windowSize.width;
}
}
}
// Avoid being placed off the edge of the screen:
// bottom
if (dy + windowSize.height > gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height) {
dy = gcBounds.y + gcBounds.height - windowSize.height;
}
// top
if (dy < gcBounds.y) {
dy = gcBounds.y;
}
// right
if (dx + windowSize.width > gcBounds.x + gcBounds.width) {
dx = gcBounds.x + gcBounds.width - windowSize.width;
}
// left
if (dx < gcBounds.x) {
dx = gcBounds.x;
}
setLocation(dx, dy);
}
/**
* Overridden from Component. Top-level Windows should not propagate a
* MouseWheelEvent beyond themselves into their owning Windows.
*/
void deliverMouseWheelToAncestor(MouseWheelEvent e) {}
/**
* Overridden from Component. Top-level Windows don't dispatch to ancestors
*/
boolean dispatchMouseWheelToAncestor(MouseWheelEvent e) {return false;}
/**
* Creates a new strategy for multi-buffering on this component.
* Multi-buffering is useful for rendering performance. This method
* attempts to create the best strategy available with the number of
* buffers supplied. It will always create a {@code BufferStrategy}
* with that number of buffers.
* A page-flipping strategy is attempted first, then a blitting strategy
* using accelerated buffers. Finally, an unaccelerated blitting
* strategy is used.
*
* Each time this method is called,
* the existing buffer strategy for this component is discarded.
* @param numBuffers number of buffers to create
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if numBuffers is less than 1.
* @exception IllegalStateException if the component is not displayable
* @see #isDisplayable
* @see #getBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public void createBufferStrategy(int numBuffers) {
super.createBufferStrategy(numBuffers);
}
/**
* Creates a new strategy for multi-buffering on this component with the
* required buffer capabilities. This is useful, for example, if only
* accelerated memory or page flipping is desired (as specified by the
* buffer capabilities).
*
* Each time this method
* is called, the existing buffer strategy for this component is discarded.
* @param numBuffers number of buffers to create, including the front buffer
* @param caps the required capabilities for creating the buffer strategy;
* cannot be {@code null}
* @exception AWTException if the capabilities supplied could not be
* supported or met; this may happen, for example, if there is not enough
* accelerated memory currently available, or if page flipping is specified
* but not possible.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if numBuffers is less than 1, or if
* caps is {@code null}
* @see #getBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public void createBufferStrategy(int numBuffers,
BufferCapabilities caps) throws AWTException {
super.createBufferStrategy(numBuffers, caps);
}
/**
* Returns the {@code BufferStrategy} used by this component. This
* method will return null if a {@code BufferStrategy} has not yet
* been created or has been disposed.
*
* @return the buffer strategy used by this component
* @see #createBufferStrategy
* @since 1.4
*/
public BufferStrategy getBufferStrategy() {
return super.getBufferStrategy();
}
Component getTemporaryLostComponent() {
return temporaryLostComponent;
}
Component setTemporaryLostComponent(Component component) {
Component previousComp = temporaryLostComponent;
// Check that "component" is an acceptable focus owner and don't store it otherwise
// - or later we will have problems with opposite while handling WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS
if (component == null || component.canBeFocusOwner()) {
temporaryLostComponent = component;
} else {
temporaryLostComponent = null;
}
return previousComp;
}
/**
* Checks whether this window can contain focus owner.
* Verifies that it is focusable and as container it can container focus owner.
* @since 1.5
*/
boolean canContainFocusOwner(Component focusOwnerCandidate) {
return super.canContainFocusOwner(focusOwnerCandidate) && isFocusableWindow();
}
private volatile boolean locationByPlatform = locationByPlatformProp;
/**
* Sets whether this Window should appear at the default location for the
* native windowing system or at the current location (returned by
* {@code getLocation}) the next time the Window is made visible.
* This behavior resembles a native window shown without programmatically
* setting its location. Most windowing systems cascade windows if their
* locations are not explicitly set. The actual location is determined once the
* window is shown on the screen.
*
* This behavior can also be enabled by setting the System Property
* "java.awt.Window.locationByPlatform" to "true", though calls to this method
* take precedence.
*
* Calls to {@code setVisible}, {@code setLocation} and
* {@code setBounds} after calling {@code setLocationByPlatform} clear
* this property of the Window.
*
* For example, after the following code is executed:
*
* In the following sample:
*
* The {@code width} or {@code height} values
* are automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getBounds
* @see #setLocation(int, int)
* @see #setLocation(Point)
* @see #setSize(int, int)
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (getBoundsOp() == ComponentPeer.SET_LOCATION ||
getBoundsOp() == ComponentPeer.SET_BOUNDS)
{
locationByPlatform = false;
}
super.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* The {@code r.width} or {@code r.height} values
* will be automatically enlarged if either is less than
* the minimum size as specified by previous call to
* {@code setMinimumSize}.
*
* The method changes the geometry-related data. Therefore,
* the native windowing system may ignore such requests, or it may modify
* the requested data, so that the {@code Window} object is placed and sized
* in a way that corresponds closely to the desktop settings.
*
* @see #getBounds
* @see #setLocation(int, int)
* @see #setLocation(Point)
* @see #setSize(int, int)
* @see #setSize(Dimension)
* @see #setMinimumSize
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @since 1.6
*/
public void setBounds(Rectangle r) {
setBounds(r.x, r.y, r.width, r.height);
}
/**
* Determines whether this component will be displayed on the screen.
* @return {@code true} if the component and all of its ancestors
* until a toplevel window are visible, {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean isRecursivelyVisible() {
// 5079694 fix: for a toplevel to be displayed, its parent doesn't have to be visible.
// We're overriding isRecursivelyVisible to implement this policy.
return visible;
}
// ******************** SHAPES & TRANSPARENCY CODE ********************
/**
* Returns the opacity of the window.
*
* @return the opacity of the window
*
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public float getOpacity() {
return opacity;
}
/**
* Sets the opacity of the window.
*
* The opacity value is in the range [0..1]. Note that setting the opacity
* level of 0 may or may not disable the mouse event handling on this
* window. This is a platform-dependent behavior.
*
* The following conditions must be met in order to set the opacity value
* less than {@code 1.0f}:
*
* If the requested opacity value is less than {@code 1.0f}, and any of the
* above conditions are not met, the window opacity will not change,
* and the {@code IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* The translucency levels of individual pixels may also be effected by the
* alpha component of their color (see {@link Window#setBackground(Color)}) and the
* current shape of this window (see {@link #setShape(Shape)}).
*
* @param opacity the opacity level to set to the window
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the opacity is out of the range
* [0..1]
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window is decorated and
* the opacity is less than {@code 1.0f}
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window is in full screen
* mode, and the opacity is less than {@code 1.0f}
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#TRANSLUCENT TRANSLUCENT}
* translucency is not supported and the opacity is less than
* {@code 1.0f}
*
* @see Window#getOpacity
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setOpacity(float opacity) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (opacity < 0.0f || opacity > 1.0f) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The value of opacity should be in the range [0.0f .. 1.0f].");
}
if (opacity < 1.0f) {
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Setting opacity for full-screen window is not supported.");
}
if (!gd.isWindowTranslucencySupported(
GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency.TRANSLUCENT))
{
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"TRANSLUCENT translucency is not supported.");
}
}
this.opacity = opacity;
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.setOpacity(opacity);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the shape of the window.
*
* The value returned by this method may not be the same as
* previously set with {@code setShape(shape)}, but it is guaranteed
* to represent the same shape.
*
* @return the shape of the window or {@code null} if no
* shape is specified for the window
*
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public Shape getShape() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
return shape == null ? null : new Path2D.Float(shape);
}
}
/**
* Sets the shape of the window.
*
* Setting a shape cuts off some parts of the window. Only the parts that
* belong to the given {@link Shape} remain visible and clickable. If
* the shape argument is {@code null}, this method restores the default
* shape, making the window rectangular on most platforms.
*
* The following conditions must be met to set a non-null shape:
*
* If the requested shape is not {@code null}, and any of the above
* conditions are not met, the shape of this window will not change,
* and either the {@code UnsupportedOperationException} or {@code
* IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* The translucency levels of individual pixels may also be effected by the
* alpha component of their color (see {@link Window#setBackground(Color)}) and the
* opacity value (see {@link #setOpacity(float)}). See {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency} for more details.
*
* @param shape the shape to set to the window
*
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and the window is decorated
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and the window is in full-screen mode
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the shape is not {@code
* null} and {@link GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT
* PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT} translucency is not supported
*
* @see Window#getShape()
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
*
* @since 1.7
*/
public void setShape(Shape shape) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (shape != null) {
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Setting shape for full-screen window is not supported.");
}
if (!gd.isWindowTranslucencySupported(
GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency.PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT))
{
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"PERPIXEL_TRANSPARENT translucency is not supported.");
}
}
this.shape = (shape == null) ? null : new Path2D.Float(shape);
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.applyShape(shape == null ? null : Region.getInstance(shape, null));
}
}
}
/**
* Gets the background color of this window.
*
* Note that the alpha component of the returned color indicates whether
* the window is in the non-opaque (per-pixel translucent) mode.
*
* @return this component's background color
*
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @see Window#isOpaque
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
*/
@Override
public Color getBackground() {
return super.getBackground();
}
/**
* Sets the background color of this window.
*
* If the windowing system supports the {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT}
* translucency, the alpha component of the given background color
* may effect the mode of operation for this window: it indicates whether
* this window must be opaque (alpha equals {@code 1.0f}) or per-pixel translucent
* (alpha is less than {@code 1.0f}). If the given background color is
* {@code null}, the window is considered completely opaque.
*
* All the following conditions must be met to enable the per-pixel
* transparency mode for this window:
*
* If the alpha component of the requested background color is less than
* {@code 1.0f}, and any of the above conditions are not met, the background
* color of this window will not change, the alpha component of the given
* background color will not affect the mode of operation for this window,
* and either the {@code UnsupportedOperationException} or {@code
* IllegalComponentStateException} will be thrown.
*
* When the window is per-pixel translucent, the drawing sub-system
* respects the alpha value of each individual pixel. If a pixel gets
* painted with the alpha color component equal to zero, it becomes
* visually transparent. If the alpha of the pixel is equal to 1.0f, the
* pixel is fully opaque. Interim values of the alpha color component make
* the pixel semi-transparent. In this mode, the background of the window
* gets painted with the alpha value of the given background color. If the
* alpha value of the argument of this method is equal to {@code 0}, the
* background is not painted at all.
*
* The actual level of translucency of a given pixel also depends on window
* opacity (see {@link #setOpacity(float)}), as well as the current shape of
* this window (see {@link #setShape(Shape)}).
*
* Note that painting a pixel with the alpha value of {@code 0} may or may
* not disable the mouse event handling on this pixel. This is a
* platform-dependent behavior. To make sure the mouse events do not get
* dispatched to a particular pixel, the pixel must be excluded from the
* shape of the window.
*
* Enabling the per-pixel translucency mode may change the graphics
* configuration of this window due to the native platform requirements.
*
* @param bgColor the color to become this window's background color.
*
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and the window is decorated
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and the window is in
* full-screen mode
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the alpha value of the given
* background color is less than {@code 1.0f} and {@link
* GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency#PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT
* PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT} translucency is not supported
*
* @see Window#getBackground
* @see Window#isOpaque
* @see Window#setOpacity(float)
* @see Window#setShape(Shape)
* @see Frame#isUndecorated
* @see Dialog#isUndecorated
* @see GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency
* @see GraphicsDevice#isWindowTranslucencySupported(GraphicsDevice.WindowTranslucency)
* @see GraphicsConfiguration#isTranslucencyCapable()
*/
@Override
public void setBackground(Color bgColor) {
Color oldBg = getBackground();
super.setBackground(bgColor);
if (oldBg != null && oldBg.equals(bgColor)) {
return;
}
int oldAlpha = oldBg != null ? oldBg.getAlpha() : 255;
int alpha = bgColor != null ? bgColor.getAlpha() : 255;
if ((oldAlpha == 255) && (alpha < 255)) { // non-opaque window
GraphicsConfiguration gc = getGraphicsConfiguration();
GraphicsDevice gd = gc.getDevice();
if (gc.getDevice().getFullScreenWindow() == this) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException(
"Making full-screen window non opaque is not supported.");
}
if (!gc.isTranslucencyCapable()) {
GraphicsConfiguration capableGC = gd.getTranslucencyCapableGC();
if (capableGC == null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"PERPIXEL_TRANSLUCENT translucency is not supported");
}
setGraphicsConfiguration(capableGC);
}
setLayersOpaque(this, false);
} else if ((oldAlpha < 255) && (alpha == 255)) {
setLayersOpaque(this, true);
}
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.setOpaque(alpha == 255);
}
}
/**
* Indicates if the window is currently opaque.
*
* The method returns {@code false} if the background color of the window
* is not {@code null} and the alpha component of the color is less than
* {@code 1.0f}. The method returns {@code true} otherwise.
*
* @return {@code true} if the window is opaque, {@code false} otherwise
*
* @see Window#getBackground
* @see Window#setBackground(Color)
* @since 1.7
*/
@Override
public boolean isOpaque() {
Color bg = getBackground();
return bg != null ? bg.getAlpha() == 255 : true;
}
private void updateWindow() {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.updateWindow();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 1.7
*/
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
if (!isOpaque()) {
Graphics gg = g.create();
try {
if (gg instanceof Graphics2D) {
gg.setColor(getBackground());
((Graphics2D)gg).setComposite(AlphaComposite.getInstance(AlphaComposite.SRC));
gg.fillRect(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
} finally {
gg.dispose();
}
}
super.paint(g);
}
private static void setLayersOpaque(Component component, boolean isOpaque) {
// Shouldn't use instanceof to avoid loading Swing classes
// if it's a pure AWT application.
if (SunToolkit.isInstanceOf(component, "javax.swing.RootPaneContainer")) {
javax.swing.RootPaneContainer rpc = (javax.swing.RootPaneContainer)component;
javax.swing.JRootPane root = rpc.getRootPane();
javax.swing.JLayeredPane lp = root.getLayeredPane();
Container c = root.getContentPane();
javax.swing.JComponent content =
(c instanceof javax.swing.JComponent) ? (javax.swing.JComponent)c : null;
lp.setOpaque(isOpaque);
root.setOpaque(isOpaque);
if (content != null) {
content.setOpaque(isOpaque);
// Iterate down one level to see whether we have a JApplet
// (which is also a RootPaneContainer) which requires processing
int numChildren = content.getComponentCount();
if (numChildren > 0) {
Component child = content.getComponent(0);
// It's OK to use instanceof here because we've
// already loaded the RootPaneContainer class by now
if (child instanceof javax.swing.RootPaneContainer) {
setLayersOpaque(child, isOpaque);
}
}
}
}
}
// ************************** MIXING CODE *******************************
// A window has an owner, but it does NOT have a container
@Override
final Container getContainer() {
return null;
}
/**
* Applies the shape to the component
* @param shape Shape to be applied to the component
*/
@Override
final void applyCompoundShape(Region shape) {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final void applyCurrentShape() {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final void mixOnReshaping() {
// The shape calculated by mixing code is not intended to be applied
// to windows or frames
}
@Override
final Point getLocationOnWindow() {
return new Point(0, 0);
}
// ****************** END OF MIXING CODE ********************************
/**
* Limit the given double value with the given range.
*/
private static double limit(double value, double min, double max) {
value = Math.max(value, min);
value = Math.min(value, max);
return value;
}
/**
* Calculate the position of the security warning.
*
* This method gets the window location/size as reported by the native
* system since the locally cached values may represent outdated data.
*
* The method is used from the native code, or via AWTAccessor.
*
* NOTE: this method is invoked on the toolkit thread, and therefore is not
* supposed to become public/user-overridable.
*/
private Point2D calculateSecurityWarningPosition(double x, double y,
double w, double h)
{
// The position according to the spec of SecurityWarning.setPosition()
double wx = x + w * securityWarningAlignmentX + securityWarningPointX;
double wy = y + h * securityWarningAlignmentY + securityWarningPointY;
// First, make sure the warning is not too far from the window bounds
wx = Window.limit(wx,
x - securityWarningWidth - 2,
x + w + 2);
wy = Window.limit(wy,
y - securityWarningHeight - 2,
y + h + 2);
// Now make sure the warning window is visible on the screen
GraphicsConfiguration graphicsConfig =
getGraphicsConfiguration_NoClientCode();
Rectangle screenBounds = graphicsConfig.getBounds();
Insets screenInsets =
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenInsets(graphicsConfig);
wx = Window.limit(wx,
screenBounds.x + screenInsets.left,
screenBounds.x + screenBounds.width - screenInsets.right
- securityWarningWidth);
wy = Window.limit(wy,
screenBounds.y + screenInsets.top,
screenBounds.y + screenBounds.height - screenInsets.bottom
- securityWarningHeight);
return new Point2D.Double(wx, wy);
}
static {
AWTAccessor.setWindowAccessor(new AWTAccessor.WindowAccessor() {
public float getOpacity(Window window) {
return window.opacity;
}
public void setOpacity(Window window, float opacity) {
window.setOpacity(opacity);
}
public Shape getShape(Window window) {
return window.getShape();
}
public void setShape(Window window, Shape shape) {
window.setShape(shape);
}
public void setOpaque(Window window, boolean opaque) {
Color bg = window.getBackground();
if (bg == null) {
bg = new Color(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
window.setBackground(new Color(bg.getRed(), bg.getGreen(), bg.getBlue(),
opaque ? 255 : 0));
}
public void updateWindow(Window window) {
window.updateWindow();
}
public Dimension getSecurityWarningSize(Window window) {
return new Dimension(window.securityWarningWidth,
window.securityWarningHeight);
}
public void setSecurityWarningSize(Window window, int width, int height)
{
window.securityWarningWidth = width;
window.securityWarningHeight = height;
}
public void setSecurityWarningPosition(Window window,
Point2D point, float alignmentX, float alignmentY)
{
window.securityWarningPointX = point.getX();
window.securityWarningPointY = point.getY();
window.securityWarningAlignmentX = alignmentX;
window.securityWarningAlignmentY = alignmentY;
synchronized (window.getTreeLock()) {
WindowPeer peer = (WindowPeer)window.getPeer();
if (peer != null) {
peer.repositionSecurityWarning();
}
}
}
public Point2D calculateSecurityWarningPosition(Window window,
double x, double y, double w, double h)
{
return window.calculateSecurityWarningPosition(x, y, w, h);
}
public void setLWRequestStatus(Window changed, boolean status) {
changed.syncLWRequests = status;
}
public boolean isAutoRequestFocus(Window w) {
return w.autoRequestFocus;
}
public boolean isTrayIconWindow(Window w) {
return w.isTrayIconWindow;
}
public void setTrayIconWindow(Window w, boolean isTrayIconWindow) {
w.isTrayIconWindow = isTrayIconWindow;
}
public Window[] getOwnedWindows(Window w) {
return w.getOwnedWindows_NoClientCode();
}
}); // WindowAccessor
} // static
// a window doesn't need to be updated in the Z-order.
@Override
void updateZOrder() {}
} // class Window
/**
* This class is no longer used, but is maintained for Serialization
* backward-compatibility.
*/
class FocusManager implements java.io.Serializable {
Container focusRoot;
Component focusOwner;
/*
* JDK 1.1 serialVersionUID
*/
static final long serialVersionUID = 2491878825643557906L;
}
* setIconImage(image);
*
* is equivalent to:
*
* ArrayList<Image> imageList = new ArrayList<Image>();
* imageList.add(image);
* setIconImages(imageList);
*
*
*
* There is an exception for the second condition (the value of the
* {@code autoRequestFocus} property). The property is not taken into account if the
* window is a modal dialog, which blocks the currently focused window.
*
*
* On platforms where the stacking order does not typically affect the focused
* window, this method will probably leave the focused and active
* Windows unchanged.
* FooListeners
* upon this {@code Window}.
* FooListeners are registered using the
* addFooListener method.
*
* FooListener.class.
* For example, you can query a
* {@code Window} {@code w}
* for its window listeners with the following code:
*
* WindowListener[] wls = (WindowListener[])(w.getListeners(WindowListener.class));
*
* If no such listeners exist, this method returns an empty array.
*
* @param listenerType the type of listeners requested; this parameter
* should specify an interface that descends from
* {@code java.util.EventListener}
* @return an array of all objects registered as
* FooListeners on this window,
* or an empty array if no such
* listeners have been added
* @exception ClassCastException if {@code listenerType}
* doesn't specify a class or interface that implements
* {@code java.util.EventListener}
* @exception NullPointerException if {@code listenerType} is {@code null}
*
* @see #getWindowListeners
* @since 1.3
*/
public
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Note that if this Window is inheriting a bound property, then no
* event will be fired in response to a change in the inherited property.
*
*
* Note that if this Window is inheriting a bound property, then no
* event will be fired in response to a change in the inherited property.
*
*
*
* setLocationByPlatform(true);
* setVisible(true);
* boolean flag = isLocationByPlatform();
*
* The window will be shown at platform's default location and
* {@code flag} will be {@code false}.
*
* setLocationByPlatform(true);
* setLocation(10, 10);
* boolean flag = isLocationByPlatform();
* setVisible(true);
*
* The window will be shown at (10, 10) and {@code flag} will be
* {@code false}.
*
* @param locationByPlatform {@code true} if this Window should appear
* at the default location, {@code false} if at the current location
* @throws IllegalComponentStateException if the window
* is showing on screen and locationByPlatform is {@code true}.
* @see #setLocation
* @see #isShowing
* @see #setVisible
* @see #isLocationByPlatform
* @see java.lang.System#getProperty(String)
* @since 1.5
*/
public void setLocationByPlatform(boolean locationByPlatform) {
synchronized (getTreeLock()) {
if (locationByPlatform && isShowing()) {
throw new IllegalComponentStateException("The window is showing on screen.");
}
this.locationByPlatform = locationByPlatform;
}
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this Window will appear at the default location
* for the native windowing system the next time this Window is made visible.
* This method always returns {@code false} if the Window is showing on the
* screen.
*
* @return whether this Window will appear at the default location
* @see #setLocationByPlatform
* @see #isShowing
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean isLocationByPlatform() {
return locationByPlatform;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
*
*
*
*
*
*