BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 初始化 BSTIterator 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 root 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。boolean hasNext() 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
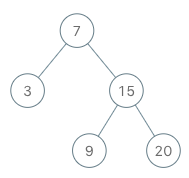
输入 ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] 输出 [null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false] 解释 BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]); bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3 bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
提示:
[1, 105] 内0 <= Node.val <= 106105 次 hasNext 和 next 操作
进阶:
next() 和 hasNext() 操作均摊时间复杂度为 O(1) ,并使用 O(h) 内存。其中 h 是树的高度。