# 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
给定一个二叉树
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
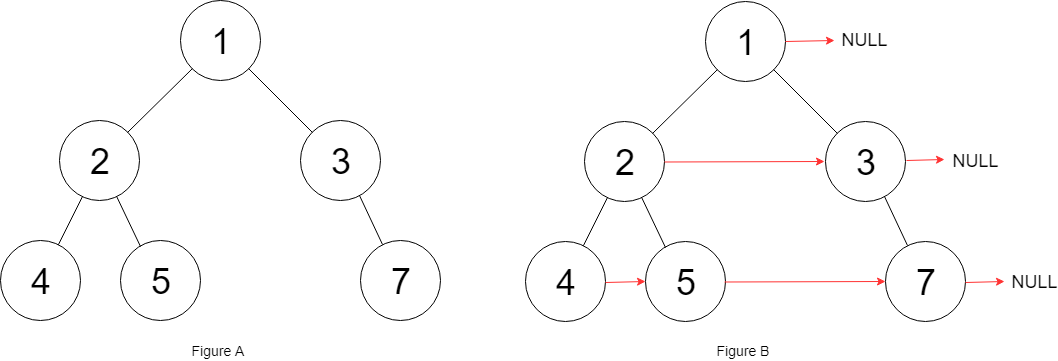
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化输出按层序遍历顺序(由 next 指针连接),'#' 表示每层的末尾。
提示:
- 树中的节点数小于
6000
-100 <= node.val <= 100
## template
```java
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) {
return root;
}
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
root.left.next = root.right;
root.next = getrightnext(root);
}
if (root.left != null) {
root.left.next = getrightnext(root);
}
if (root.right != null) {
root.right.next = getrightnext(root);
}
connect(root.right);
connect(root.left);
return root;
}
public static Node getrightnext(Node root) {
while (root.next != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
return root.left;
}
if (root.right != null) {
return root.right;
}
root = root.next;
}
return null;
}
}
```
## 答案
```java
```
## 选项
### A
```java
```
### B
```java
```
### C
```java
``` 
