# 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
示例 1:
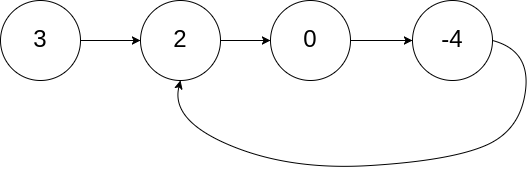
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
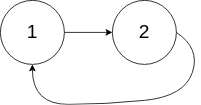
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105pos 的值为 -1 或者链表中的一个有效索引
以下错误的选项是?
## aop
### before
```c
#include
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
```
### after
```c
```
## 答案
```c
class Solution
{
public:
vector searchRange(vector &nums, int target)
{
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
vector res = {-1, -1};
bool find = false;
while (right >= left && find == false && nums[left] <= target)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else
{
find = true;
while (mid > 0 && nums[mid - 1] == target)
mid++;
res[0] = mid;
while (mid < nums.size() - 1 && nums[mid + 1] == target)
mid--;
res[1] = mid;
}
}
return res;
}
};
```
## 选项
### A
```c
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head)
{
set node_set;
while (head)
{
if (node_set.find(head) != node_set.end())
{
return head;
}
node_set.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
```
### B
```c
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *meet = NULL;
while (slow && fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
meet = slow;
break;
}
}
while (head && meet)
{
if (meet == head)
{
break;
}
head = head->next;
meet = meet->next;
}
return meet;
}
};
```
### C
```c
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head)
{
if (!head || !head->next)
return NULL;
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
break;
}
if (slow != fast)
return NULL;
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
```



