Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
CSDN 技术社区
skill_tree_algorithm
提交
987907e1
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
CSDN 技术社区
/
skill_tree_algorithm
通知
9
Star
8
Fork
1
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
1
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
合并请求
0
Pages
DevOps
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
流水线任务
提交
Issue看板
提交
987907e1
编写于
11月 17, 2021
作者:
每日一练社区
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
电子邮件补丁
差异文件
add 28 exercises
上级
da282d4a
变更
191
显示空白变更内容
内联
并排
Showing
191 changed file
with
10413 addition
and
117 deletion
+10413
-117
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/desc.md
+23
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.cpp
+23
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.md
+101
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/desc.md
+13
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.cpp
+20
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.md
+54
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/desc.md
+34
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.cpp
+27
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.md
+188
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/desc.md
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.cpp
+41
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.md
+50
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/desc.md
+1021
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.cpp
+56
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
+1062
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.cpp
+18
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.md
+49
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/desc.md
+4
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.cpp
+25
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.md
+47
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/desc.md
+25
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.cpp
+40
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.md
+121
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/desc.md
+19
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.cpp
+22
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.md
+93
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/desc.md
+46
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.cpp
+37
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.md
+141
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/desc.md
+4
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.cpp
+84
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.md
+47
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/desc.md
+27
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.cpp
+25
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.md
+70
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/desc.md
+123
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.cpp
+51
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.md
+164
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/desc.md
+33
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.cpp
+36
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.md
+122
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.cpp
+41
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.md
+92
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/desc.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.cpp
+33
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.md
+89
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/desc.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.cpp
+29
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.md
+76
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/desc.md
+36
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.cpp
+40
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.md
+275
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/desc.md
+40
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.cpp
+45
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.md
+362
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/desc.md
+54
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.cpp
+68
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.md
+412
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/desc.md
+40
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.cpp
+67
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.md
+167
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/desc.md
+33
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.cpp
+47
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.md
+74
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/desc.md
+42
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.cpp
+98
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.md
+198
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/desc.md
+46
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.cpp
+73
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
+215
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/desc.md
+36
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.cpp
+45
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.md
+198
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/6.糖果/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/6.糖果/solution.md
+1
-1
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/desc.md
+6
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.cpp
+21
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.md
+73
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/config.json
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/desc.md
+38
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.cpp
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.cpp
+79
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.java
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.java
+0
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.json
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.json
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.md
+408
-0
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/170.幸运数/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/170.幸运数/solution.md
+189
-5
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/38.小朋友排队/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/38.小朋友排队/solution.md
+272
-5
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/39.灵能传输/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/39.灵能传输/solution.md
+304
-5
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/42.振兴中华/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/42.振兴中华/solution.md
+23
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/43.格子中输出/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/43.格子中输出/solution.md
+50
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/44.最大公共子串/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/44.最大公共子串/solution.md
+41
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/46.黄金连分数/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/46.黄金连分数/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/47.k倍区间/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/47.k倍区间/solution.md
+31
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/48.压缩变换/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/48.压缩变换/solution.md
+76
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/49.纸牌三角形/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/49.纸牌三角形/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/50.字串排序/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/50.字串排序/solution.md
+109
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/52.矩阵/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/52.矩阵/solution.md
+30
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/55.交换瓶子/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/55.交换瓶子/solution.md
+116
-5
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/56.排它平方数/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/56.排它平方数/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/57.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/57.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/59.明码/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/59.明码/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/60.三体攻击/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/60.三体攻击/solution.md
+105
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/61.字母阵列/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/61.字母阵列/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/62.煤球数目/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/62.煤球数目/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/64.垒骰子/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/64.垒骰子/solution.md
+321
-6
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/66.门牌制作/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/66.门牌制作/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/68.平面切分/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/68.平面切分/solution.md
+49
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/70.消除尾一/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/70.消除尾一/solution.md
+29
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/71.四平方和/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/71.四平方和/solution.md
+58
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/72.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/72.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
+118
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/73.完美平方数/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/73.完美平方数/solution.md
+4
-4
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/74.字符串编码/solution.md
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/74.字符串编码/solution.md
+40
-4
leetcode_helper.py
leetcode_helper.py
+29
-2
未找到文件。
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-13d46f0dd9654171b165f27130012263"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"k倍区间"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
给定一个长度为N的数列,$A_1, A_2, … A_N,$如果其中一段连续的子序列$A_i, A_{i+1}, … A_j(i <= j)$之和是K的倍数,我们就称这个区间[i, j]是K倍区间。
你能求出数列中总共有多少个K倍区间吗?
#### 输入格式
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含一个整数$A_i$。(1 <= $A_i$ <= 100000)
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,代表K倍区间的数目。
#### 样例输入
```
5 2
1
2
3
4
5
```
#### 样例输出
```
6
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
long
long
n
,
k
,
ans
=
0
,
son
[
100000
],
sum
[
100000
],
b
[
100000
]
=
{
0
};
cin
>>
n
>>
k
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
son
[
i
];
if
(
i
!=
0
)
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
;
else
sum
[
i
]
=
son
[
i
]
%
k
;
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
++
;
ans
+=
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
-
1
;
if
(
sum
[
i
]
==
0
)
ans
++
;
}
cout
<<
ans
;
return
0
;
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"d5ad2458a40a46daaf75bbb9291e6d4b"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/30.k倍区间/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# k倍区间
**问题描述**
给定一个长度为N的数列,$A_1, A_2, … A_N,$如果其中一段连续的子序列$A_i, A_{i+1}, … A_j(i <= j)$之和是K的倍数,我们就称这个区间[i, j]是K倍区间。
你能求出数列中总共有多少个K倍区间吗?
**输入格式**
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含一个整数$A_i$。(1 <= $A_i$ <= 100000)
**输出格式**
输出一个整数,代表K倍区间的数目。
**样例输入**
```
5 2
1
2
3
4
5
```
**样例输出**
```
6
```
以下程序实现了该功能,请你补全空白处代码:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
long
long
n
,
k
,
ans
=
0
,
son
[
100000
],
sum
[
100000
],
b
[
100000
]
=
{
0
};
cin
>>
n
>>
k
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
son
[
i
];
if
(
i
!=
0
)
__________________
else
sum
[
i
]
=
son
[
i
]
%
k
;
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
++
;
ans
+=
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
-
1
;
if
(
sum
[
i
]
==
0
)
ans
++
;
}
cout
<<
ans
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
;
```
### B
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
-
1
;
```
### C
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
-
1
])
%
k
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-aa21244fb1374002acf29ed59bee7978"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"纸牌三角形"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要求每个边的和相等。
下面就是一种排法
```
A
9 6
4 8
3 7 5 2
```
这样的排法可能会有很多。
如果考虑旋转、镜像后相同的算同一种,一共有多少种不同的排法呢?
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
int
a
[
9
]
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
,
9
};
int
res
=
0
;
do
{
int
x1
=
a
[
0
]
+
a
[
1
]
+
a
[
2
]
+
a
[
3
];
int
x2
=
a
[
3
]
+
a
[
4
]
+
a
[
5
]
+
a
[
6
];
int
x3
=
a
[
6
]
+
a
[
7
]
+
a
[
8
]
+
a
[
0
];
if
(
x1
==
x2
&&
x2
==
x3
)
{
res
++
;
}
}
while
(
next_permutation
(
a
,
a
+
9
));
//全排列
cout
<<
res
/
3
/
2
<<
endl
;
//翻转除以3,镜像除以2
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"d0cf3c7a3d9d4f5183383e01522aaba3"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/31.纸牌三角形/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 纸牌三角形
A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要求每个边的和相等。
下面就是一种排法
```
A
9 6
4 8
3 7 5 2
```
这样的排法可能会有很多。
如果考虑旋转、镜像后相同的算同一种,一共有多少种不同的排法呢?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
144
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
124
```
### B
```
cpp
128
```
### C
```
cpp
132
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-6e714b19660c43b6a68d1b01070c3273"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"交换瓶子"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
有N个瓶子,编号 1 ~ N,放在架子上。
比如有5个瓶子:
2 1 3 5 4
要求每次拿起2个瓶子,交换它们的位置。
经过若干次后,使得瓶子的序号为:
1 2 3 4 5
对于这么简单的情况,显然,至少需要交换2次就可以复位。
如果瓶子更多呢?你可以通过编程来解决。
输入格式为两行:
第一行: 一个正整数N(N<10000), 表示瓶子的数目
第二行:N个正整数,用空格分开,表示瓶子目前的排列情况。
输出数据为一行一个正整数,表示至少交换多少次,才能完成排序。
例如,输入:
```
5
3 1 2 5 4
```
程序应该输出:
```
3
```
再例如,输入:
```
5
5 4 3 2 1
```
程序应该输出:
```
2
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
1e4
+
10
;
bool
st
[
N
];
int
a
[
N
],
n
,
k
;
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
cin
>>
a
[
i
];
//瓶子初始序号
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
//从每个正确序号出发
if
(
!
st
[
i
])
//如果没有走过
{
k
++
;
//环数量加一
for
(
int
j
=
i
;
!
st
[
j
];
j
=
a
[
j
])
//走完这个环 每次变更指向a[j] 即瓶子初始序号的第j个
st
[
j
]
=
true
;
}
cout
<<
n
-
k
;
//环最简情况为自指 则最多有n个环 当前有k个环 从K达到n则需要n-k次
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"eb1d232696874fe88ac354c1fd9af35f"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/32.交换瓶子/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 交换瓶子
有N个瓶子,编号 1 ~ N,放在架子上。
比如有5个瓶子:
2 1 3 5 4
要求每次拿起2个瓶子,交换它们的位置。
经过若干次后,使得瓶子的序号为:
1 2 3 4 5
对于这么简单的情况,显然,至少需要交换2次就可以复位。
如果瓶子更多呢?你可以通过编程来解决。
输入格式为两行:
第一行: 一个正整数N(N<10000), 表示瓶子的数目
第二行:N个正整数,用空格分开,表示瓶子目前的排列情况。
输出数据为一行一个正整数,表示至少交换多少次,才能完成排序。
例如,输入:
```
5
3 1 2 5 4
```
程序应该输出:
```
3
```
再例如,输入:
```
5
5 4 3 2 1
```
程序应该输出:
```
2
```
以下
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的一项是?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
int
search
(
int
i
);
int
n
;
int
a
[
10000
]
=
{
0
};
int
main
(
void
)
{
int
index
,
count
,
i
;
index
=
count
=
0
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
a
[
i
]);
}
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
int
j
=
search
(
i
);
if
(
a
[
index
]
!=
a
[
j
])
{
int
t
=
a
[
index
];
a
[
index
]
=
a
[
j
];
a
[
j
]
=
t
;
count
++
;
index
++
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
count
);
return
0
;
}
int
search
(
int
i
)
{
int
index
,
j
,
k
,
min
;
min
=
99999
;
for
(
j
=
i
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
min
>
a
[
j
])
{
min
=
a
[
j
];
index
=
j
;
}
}
return
index
;
}
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
,
a
[
10005
];
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
cin
>>
a
[
i
];
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
while
(
a
[
i
]
!=
i
)
{
swap
(
a
[
i
],
a
[
a
[
i
]]);
num
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
### B
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
int
a
[
n
+
5
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
cin
>>
a
[
i
];
int
min
;
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
min
=
i
;
for
(
int
j
=
i
+
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
min
]
>
a
[
j
])
min
=
j
;
}
if
(
min
!=
i
)
{
num
++
;
swap
(
a
[
i
],
a
[
min
]);
}
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
### C
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
int
num
=
0
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
int
a
[
n
+
5
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
a
[
i
]);
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
-
1
]
>
a
[
i
])
{
swap
(
a
[
i
-
1
],
a
[
i
]);
num
++
;
}
}
if
(
num
==
n
-
1
)
{
num
=
n
/
2
;
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-ef16a8876b2446c0981c5b9cf28f278d"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"排它平方数"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
203879
*
203879 = 41566646641
这有什么神奇呢?仔细观察,203879 是个6位数,并且它的每个数位上的数字都是不同的,并且它平方后的所有数位上都不出现组成它自身的数字。
具有这样特点的6位数还有一个,请你找出它!
再归纳一下筛选要求:
1.
6位正整数
2.
每个数位上的数字不同
3.
其平方数的每个数位不含原数字的任何组成数位
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
for
(
long
long
i
=
100000
;
i
<
1000000
;
i
++
)
{
//i要用longlong,不然相乘会溢出
set
<
int
>
s1
,
s2
;
int
t1
=
i
;
while
(
t1
)
{
s1
.
insert
(
t1
%
10
);
t1
/=
10
;
}
long
long
t2
=
i
*
i
;
if
(
s1
.
size
()
==
6
)
{
while
(
t2
)
{
s2
.
insert
(
t2
%
10
);
t2
/=
10
;
}
bool
flag
=
1
;
for
(
auto
it
:
s1
)
{
if
(
s2
.
find
(
it
)
!=
s2
.
end
())
{
flag
=
0
;
break
;
}
}
if
(
flag
==
1
)
cout
<<
i
<<
' '
<<
i
*
i
<<
endl
;
}
s1
.
clear
();
s2
.
clear
();
}
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"75807f45a1224b23adabd23547defe58"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/33.排它平方数/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 排它平方数
203879
*
203879 = 41566646641
这有什么神奇呢?仔细观察,203879 是个6位数,并且它的每个数位上的数字都是不同的,并且它平方后的所有数位上都不出现组成它自身的数字。
具有这样特点的6位数还有一个,请你找出它!
再归纳一下筛选要求:
1.
6位正整数
2.
每个数位上的数字不同
3.
其平方数的每个数位不含原数字的任何组成数位
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
639172
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
629173
```
### B
```
cpp
691372
```
### C
```
cpp
627193
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-31b85d9ebb8d4d249586825531c04643"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"REPEAT 程序"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
附件 prog.txt 中是一个用某种语言写的程序。附件在本文的末尾。
其中 REPEAT k 表示一个次数为 k 的循环。循环控制的范围由缩进表达,从次行开始连续的缩进比该行多的(前面的空白更长的)为循环包含的内容。

该片段中从 A = A + 4 所在的行到 A = A + 8 所在的行都在第一行的循环两次中。
REPEAT 6: 所在的行到 A = A + 7 所在的行都在 REPEAT 5: 循环中。
A = A + 5 实际总共的循环次数是 2 × 5 × 6 = 60 次。
请问该程序执行完毕之后,A 的值是多少?
题目给出的 prog.txt 文件:
```
A = 0
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 8
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 4
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 3
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
1e3
+
10
;
char
mp
[
N
][
N
];
int
s
[
N
],
t
[
N
],
top
;
int
main
()
{
FILE
*
fp
;
fp
=
fopen
(
"prog.txt"
,
"r"
);
///文件读操作
char
ch
;
int
tot
=
0
;
int
i
=
0
;
while
((
ch
=
fgetc
(
fp
))
!=
EOF
)
///一个字符一个字符的读入
{
if
(
ch
==
'\n'
)
{
mp
[
tot
][
i
]
=
'\0'
;
tot
++
;
i
=
0
;
continue
;
}
mp
[
tot
][
i
++
]
=
ch
;
}
/*
for(int i=0;i<tot;i++)
printf("%s\n",mp[i]);*/
///将txt中的数据已经全部保存在了mp数组中
top
=
0
;
int
p
,
w
=
1
,
sum
=
0
;
s
[
top
]
=
-
1
,
t
[
top
]
=
-
1
;
///防止栈空的时候进行出栈操作
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
tot
;
i
++
)
{
int
len
=
strlen
(
mp
[
i
]);
p
=
0
;
while
(
mp
[
i
][
p
]
==
' '
)
///统计缩进
p
++
;
while
(
s
[
top
]
>=
p
)
///开始新的循环,上一层的循环不包括
w
/=
t
[
top
--
];
if
(
mp
[
i
][
len
-
1
]
==
':'
)
///当前是循环语句
{
int
num
=
mp
[
i
][
len
-
2
]
-
'0'
;
top
++
;
w
*=
num
;
///累计循环了几次
s
[
top
]
=
p
,
t
[
top
]
=
num
;
///第top层循环语句的缩进量和循环次数
}
else
{
int
num
=
mp
[
i
][
len
-
1
]
-
'0'
;
sum
+=
w
*
num
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
sum
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"38a8afcec1fc4054b7f35f8577fb6724"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/34.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# REPEAT 程序
附件 prog.txt 中是一个用某种语言写的程序。附件在本文的末尾。
其中 REPEAT k 表示一个次数为 k 的循环。循环控制的范围由缩进表达,从次行开始连续的缩进比该行多的(前面的空白更长的)为循环包含的内容。

该片段中从 A = A + 4 所在的行到 A = A + 8 所在的行都在第一行的循环两次中。
REPEAT 6: 所在的行到 A = A + 7 所在的行都在 REPEAT 5: 循环中。
A = A + 5 实际总共的循环次数是 2 × 5 × 6 = 60 次。
请问该程序执行完毕之后,A 的值是多少?
题目给出的 prog.txt 文件:
```
A = 0
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 8
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 4
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 3
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 2:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 3
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 8
A = A + 6
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 2
A = A + 7
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 2
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
A = A + 9
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 3
A = A + 4
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 4:
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 1
A = A + 2
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
A = A + 3
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 5
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
A = A + 8
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 4
A = A + 6
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 9
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 4
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 4
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
A = A + 3
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
A = A + 8
A = A + 2
A = A + 5
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 6
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 2
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
A = A + 5
A = A + 2
A = A + 1
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 4
A = A + 3
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 6:
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 5
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
A = A + 8
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 3
REPEAT 5:
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 5
A = A + 5
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 5
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 9
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 8
A = A + 1
A = A + 4
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 3
A = A + 9
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
A = A + 4
A = A + 2
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 2
A = A + 9
A = A + 7
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 7:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
A = A + 1
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 4
A = A + 1
REPEAT 6:
A = A + 8
A = A + 5
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 4
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 8
A = A + 7
A = A + 2
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 3
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 1
REPEAT 8:
A = A + 7
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
A = A + 7
A = A + 6
A = A + 9
A = A + 5
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
REPEAT 9:
A = A + 1
A = A + 7
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 8
A = A + 4
REPEAT 8:
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 2
REPEAT 4:
A = A + 6
A = A + 6
REPEAT 1:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
REPEAT 9:
REPEAT 5:
A = A + 6
A = A + 5
REPEAT 7:
A = A + 3
A = A + 6
A = A + 8
REPEAT 2:
A = A + 7
A = A + 1
A = A + 9
REPEAT 3:
REPEAT 3:
A = A + 5
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
403
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
400
```
### B
```
cpp
401
```
### C
```
cpp
402
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-1a8f872bd3c841808a2bdd47008051f7"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"煤球数目"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
有一堆煤球,堆成三角棱锥形。具体:
第一层放1个,
第二层3个(排列成三角形),
第三层6个(排列成三角形),
第四层10个(排列成三角形),
....
如果一共有100层,共有多少个煤球?
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
j
;
long
long
int
sum
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
100
;
i
++
)
{
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
i
;
j
++
)
num
+=
j
;
sum
+=
num
;
}
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
sum
);
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"3fca71a7f8294b87bf1af7214c6fc064"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/35.煤球数目/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 煤球数目
有一堆煤球,堆成三角棱锥形。具体:
第一层放1个,
第二层3个(排列成三角形),
第三层6个(排列成三角形),
第四层10个(排列成三角形),
....
如果一共有100层,共有多少个煤球?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
171700
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
166650
```
### B
```
cpp
176851
```
### C
```
cpp
182104
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-b7a24f3dc0894922b58174677d4a1e4a"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"门牌制作"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
小蓝要为一条街的住户制作门牌号。
这条街一共有 2020 位住户,门牌号从 1 到 2020 编号。
小蓝制作门牌的方法是先制作 0 到 9 这几个数字字符,最后根据需要将字符粘贴到门牌上,例如门牌 1017 需要依次粘贴字符 1、0、1、7,即需要 1 个字符 0,2 个字符 1,1 个字符 7。
请问要制作所有的 1 到 2020 号门牌,总共需要多少个字符 2?
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
int
ans
;
int
cal
(
int
n
)
{
int
sum
=
0
;
while
(
n
)
{
if
(
n
%
10
==
2
)
sum
++
;
n
/=
10
;
}
return
sum
;
}
int
main
()
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
2020
;
i
++
)
{
ans
+=
cal
(
i
);
}
cout
<<
ans
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"94978df2ba4c4b21a6c8666be6e7c735"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/36.门牌制作/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 门牌制作
小蓝要为一条街的住户制作门牌号。
这条街一共有 2020 位住户,门牌号从 1 到 2020 编号。
小蓝制作门牌的方法是先制作 0 到 9 这几个数字字符,最后根据需要将字符粘贴到门牌上,例如门牌 1017 需要依次粘贴字符 1、0、1、7,即需要 1 个字符 0,2 个字符 1,1 个字符 7。
请问要制作所有的 1 到 2020 号门牌,总共需要多少个字符 2?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
624
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
626
```
### B
```
cpp
622
```
### C
```
cpp
628
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-03f5a1063e9948dab7d89631695b4323"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"平面切分"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
平面上有 N条直线,其中第 i条直线是$ y = A_i
*
x + B_i$。
请计算这些直线将平面分成了几个部分。
#### 输入格式
第一行包含一个整数N。
以下N行,每行包含两个整数 $A_i, B_i$。
#### 输出格式
一个整数代表答案。
#### 样例输入
```
3
1 1
2 2
3 3
```
#### 样例输出
```
6
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
long
double
s
[
1010
][
2
];
//存储直线的A,B
long
long
ans
;
bool
st
[
1010
];
//false表示不是重边
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>
p
;
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
s
[
i
][
0
]
>>
s
[
i
][
1
];
set
<
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>>
points
;
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
st
[
j
])
continue
;
//直线是重边,跳过
if
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
==
s
[
j
][
0
])
{
//两条直线斜率相等时,判断是平行还是重合
if
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
==
s
[
j
][
1
])
{
st
[
i
]
=
true
;
//待添加直线是重边,退出循环
break
;
}
else
continue
;
//直线平行,不需要计算交点
}
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
1
]
-
s
[
i
][
1
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
-
s
[
j
][
0
]);
//交点的x坐标
p
.
second
=
s
[
i
][
0
]
*
p
.
first
+
s
[
i
][
1
];
//交点的y坐标
points
.
insert
(
p
);
}
if
(
!
st
[
i
])
ans
+=
points
.
size
()
+
1
;
//若当前直线不是重边,更新答案
}
cout
<<
ans
+
1
;
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"e572003202d0462fa95f635381897624"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/37.平面切分/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 平面切分
**问题描述**
平面上有 N条直线,其中第 i条直线是$ y = A_i
*
x + B_i$。
请计算这些直线将平面分成了几个部分。
**输入格式**
第一行包含一个整数N。
以下N行,每行包含两个整数 $A_i, B_i$。
**输出格式**
一个整数代表答案。
**样例输入**
```
3
1 1
2 2
3 3
```
**样例输出**
```
6
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
long
double
s
[
1010
][
2
];
long
long
ans
;
bool
st
[
1010
];
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>
p
;
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
s
[
i
][
0
]
>>
s
[
i
][
1
];
set
<
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>>
points
;
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
st
[
j
])
continue
;
if
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
==
s
[
j
][
0
])
{
if
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
==
s
[
j
][
1
])
{
st
[
i
]
=
true
;
break
;
}
else
continue
;
}
__________________
p
.
second
=
s
[
i
][
0
]
*
p
.
first
+
s
[
i
][
1
];
points
.
insert
(
p
);
}
if
(
!
st
[
i
])
ans
+=
points
.
size
()
+
1
;
}
cout
<<
ans
+
1
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
1
]
-
s
[
i
][
1
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
-
s
[
j
][
0
]);
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
1
]
-
s
[
i
][
1
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
-
s
[
j
][
1
]);
```
### B
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
0
]
-
s
[
i
][
0
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
-
s
[
j
][
0
]);
```
### C
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
0
]
-
s
[
i
][
0
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
-
s
[
j
][
1
]);
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-a897b32f6a7244088c8d4a3383ef1902"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"消除尾一"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
下面的代码把一个整数的二进制表示的最右边的连续的1全部变成0
如果最后一位是0,则原数字保持不变。
#### 输入:
```
00000000000000000000000001100111
```
#### 输出:
```
00000000000000000000000001100000
```
#### 输入:
```
00000000000000000000000000001100
```
#### 输出:
```
00000000000000000000000000001100
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <stdio.h>
void
f
(
int
x
)
{
int
i
;
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
" "
);
x
=
x
&
(
x
+
1
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
"
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
f
(
103
);
f
(
12
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"c2a45eb8e39b4be681fc3d28c1f9bacd"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/38.消除尾一/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 消除尾一
下面的代码把一个整数的二进制表示的最右边的连续的1全部变成0
如果最后一位是0,则原数字保持不变。
**输入:**
```
00000000000000000000000001100111
```
**输出:**
```
00000000000000000000000001100000
```
**输入:**
```
00000000000000000000000000001100
```
**输出:**
```
00000000000000000000000000001100
```
请你填补空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
void
f
(
int
x
)
{
int
i
;
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
" "
);
__________________
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
"
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
f
(
103
);
f
(
12
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
x
=
x
&
(
x
+
1
);
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
x
=
x
&
(
x
-
1
);
```
### B
```
cpp
x
=
x
&&
(
x
-
1
);
```
### C
```
cpp
x
=
x
&&
(
x
+
1
);
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-8e17d142f5aa4b57a697571be7b2fd94"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"四平方和"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
四平方和定理,又称为拉格朗日定理:
每个正整数都可以表示为至多4个正整数的平方和。
如果把0包括进去,就正好可以表示为4个数的平方和。
比如:
```
5 = 0^ 2 + 0^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 2^2
7 = 1^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 2^2
(^符号表示乘方的意思)
```
对于一个给定的正整数,可能存在多种平方和的表示法。
要求你对4个数排序:
```
0 <= a <= b <= c <= d
```
并对所有的可能表示法按 a,b,c,d 为联合主键升序排列,最后输出第一个表示法
程序输入为一个正整数N (N<5000000)
要求输出4个非负整数,按从小到大排序,中间用空格分开
例如,输入:
```
5
```
则程序应该输出:
```
0 0 1 2
```
再例如,输入:
```
12
```
则程序应该输出:
```
0 2 2 2
```
再例如,输入:
```
773535
```
则程序应该输出:
```
1 1 267 838
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
using
namespace
std
;
int
N
;
map
<
int
,
int
>
cache
;
//int和int映射,哈希表用于缓存数值
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
N
);
for
(
int
c
=
0
;
c
*
c
<=
N
/
2
;
c
++
)
{
for
(
int
d
=
c
;
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
<=
N
;
d
++
)
{
if
(
cache
.
find
(
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
)
==
cache
.
end
())
//如果未找到,再去存,已经存在就不需要去存了
cache
[
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
]
=
c
;
//查平方数,先要看cache里面有没有,没有说明它不是一个平方数存起来
//有的话通过较小的数映射找到它
}
}
//c*c+d*d要比a*a+d*d要大(至少相同)
for
(
int
a
=
0
;
a
*
a
<=
N
/
4
;
a
++
)
{
//单独看a*a小于等于N/4
for
(
int
b
=
a
;
a
*
a
+
b
*
b
<=
N
/
2
;
b
++
)
{
//a*a+b*b小于等于N/2
if
(
cache
.
find
(
N
-
a
*
a
-
b
*
b
)
!=
cache
.
end
())
{
//查表,能找到
int
c
=
cache
[
N
-
a
*
a
-
b
*
b
];
//c就可以知道
int
d
=
int
(
sqrt
(
N
-
a
*
a
-
b
*
b
-
c
*
c
));
//d开方
printf
(
"%d %d %d %d
\n
"
,
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
);
return
0
;
//跳出整个主函数
}
}
}
return
0
;
}
//整个过程不需要再排序,因为一开始在写代码时,就已经限定了顺序大小,c*c+d*d要比a*a+d*d要大
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"d9e609310d30429bbd1aa87b4b9c6a75"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/39.四平方和/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 四平方和
四平方和定理,又称为拉格朗日定理:
每个正整数都可以表示为至多4个正整数的平方和。
如果把0包括进去,就正好可以表示为4个数的平方和。
比如:
```
5 = 0^ 2 + 0^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 2^2
7 = 1^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 1^ 2 + 2^2
(^符号表示乘方的意思)
```
对于一个给定的正整数,可能存在多种平方和的表示法。
要求你对4个数排序:
```
0 <= a <= b <= c <= d
```
并对所有的可能表示法按 a,b,c,d 为联合主键升序排列,最后输出第一个表示法
程序输入为一个正整数N (N<5000000)
要求输出4个非负整数,按从小到大排序,中间用空格分开
例如,输入:
```
5
```
则程序应该输出:
```
0 0 1 2
```
再例如,输入:
```
12
```
则程序应该输出:
```
0 2 2 2
```
再例如,输入:
```
773535
```
则程序应该输出:
```
1 1 267 838
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
MAXN
=
2500010
;
struct
Node
{
int
s
,
c
,
d
;
bool
operator
<
(
const
Node
&
t
)
const
{
if
(
s
!=
t
.
s
)
return
s
<
t
.
s
;
if
(
c
!=
t
.
c
)
return
c
<
t
.
c
;
return
d
<
t
.
d
;
}
}
sum
[
MAXN
];
int
n
,
m
;
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
c
=
0
;
c
*
c
<=
n
;
c
++
)
for
(
int
d
=
c
;
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
<=
n
;
d
++
)
sum
[
m
++
]
=
{
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
,
c
,
d
};
sort
(
sum
,
sum
+
m
);
for
(
int
a
=
0
;
a
*
a
<=
n
;
a
++
)
{
for
(
int
b
=
0
;
a
*
a
+
b
*
b
<=
n
;
b
++
)
{
int
t
=
n
-
a
*
a
-
b
*
b
;
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
m
-
1
;
while
(
l
<
r
)
{
__________________
if
(
sum
[
mid
].
s
>=
t
)
r
=
mid
;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
if
(
sum
[
l
].
s
==
t
)
{
printf
(
"%d %d %d %d"
,
a
,
b
,
sum
[
l
].
c
,
sum
[
l
].
d
);
return
0
;
}
}
}
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
>>
1
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
(
r
>>
1
);
```
### B
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
;
```
### C
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
+
1
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-92facd5e0f8d4b6d88589bcddba9f3d7"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"完美平方数"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
如果整个整数 X 本身是完全平方数,同时它的每一位数字也都是完全平方数,我们就称 X 是完美平方数。
前几个完美平方数是 0、1、4、9、49、100、144……
即第 1 个完美平方数是 0,第 2 个是 1,第 3 个是 4,……
请你计算第 2020 个完美平方数是多少?
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
struct
bign
{
int
d
[
1000
];
int
len
;
bign
()
{
memset
(
d
,
0
,
sizeof
(
d
));
len
=
0
;
}
}
a
,
b
;
bign
add
(
bign
&
a
,
bign
&
b
)
{
bign
c
;
int
carry
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
a
.
len
||
i
<
b
.
len
;
i
++
)
{
int
temp
=
a
.
d
[
i
]
+
b
.
d
[
i
]
+
carry
;
c
.
d
[
c
.
len
++
]
=
temp
%
10
;
carry
=
temp
/
10
;
}
if
(
carry
)
{
c
.
d
[
c
.
len
++
]
=
carry
;
}
return
c
;
}
bign
multi
(
bign
&
a
,
int
&
b
)
{
bign
c
;
int
carry
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
a
.
len
;
i
++
)
{
int
temp
=
a
.
d
[
i
]
*
b
+
carry
;
c
.
d
[
c
.
len
++
]
=
temp
%
10
;
carry
=
temp
/
10
;
}
while
(
carry
)
{
c
.
d
[
c
.
len
++
]
=
carry
%
10
;
carry
/=
10
;
}
return
c
;
}
void
print
(
bign
&
a
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
a
.
len
-
1
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
{
printf
(
"%d"
,
a
.
d
[
i
]);
}
printf
(
"
\n
"
);
}
bool
vis
[
10
]
=
{
false
};
bool
judge
(
bign
&
c
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<=
c
.
len
-
1
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
!
vis
[
c
.
d
[
i
]])
return
false
;
}
return
true
;
}
int
main
()
{
vis
[
0
]
=
vis
[
1
]
=
vis
[
4
]
=
vis
[
9
]
=
true
;
b
.
d
[
0
]
=
1
,
b
.
len
=
1
;
a
.
d
[
0
]
=
0
,
a
.
len
=
1
;
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
num
<
2020
;
i
++
)
{
bign
c
=
multi
(
a
,
i
);
if
(
judge
(
c
))
{
num
++
;
printf
(
"%d:"
,
num
);
print
(
c
);
}
a
=
add
(
a
,
b
);
}
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"6b9511a8ea9e47c4a4ba3e01fc8f461e"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.完美平方数/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 完美平方数
如果整个整数 X 本身是完全平方数,同时它的每一位数字也都是完全平方数,我们就称 X 是完美平方数。
前几个完美平方数是 0、1、4、9、49、100、144……
即第 1 个完美平方数是 0,第 2 个是 1,第 3 个是 4,……
请你计算第 2020 个完美平方数是多少?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
1499441040
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
1949990009
```
### B
```
cpp
914140441
```
### C
```
cpp
1101001
```
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-be788b02c56e4c8bbc442449c753daf0"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"黄金连分数"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
黄金分割数0.61803… 是个无理数,这个常数十分重要,在许多工程问题中会出现。有时需要把这个数字求得很精确。
对于某些精密工程,常数的精度很重要。也许你听说过哈勃太空望远镜,它首次升空后就发现了一处人工加工错误,对那样一个庞然大物,其实只是镜面加工时有比头发丝还细许多倍的一处错误而已,却使它成了“近视眼”!!
言归正传,我们如何求得黄金分割数的尽可能精确的值呢?有许多方法。
比较简单的一种是用连分数:
```
1
黄金数 = ---------------------
1
1 + -----------------
1
1 + -------------
1
1 + ---------
1 + ...
```
这个连分数计算的“层数”越多,它的值越接近黄金分割数。
请你利用这一特性,求出黄金分割数的足够精确值,要求四舍五入到小数点后100位。
小数点后3位的值为:0.618
小数点后4位的值为:0.6180
小数点后5位的值为:0.61803
小数点后7位的值为:0.6180340
(注意尾部的0,不能忽略)
你的任务是:写出精确到小数点后100位精度的黄金分割值。
注意:尾数的四舍五入! 尾数是0也要保留!
显然答案是一个小数,其小数点后有100位数字
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
void
div
(
LL
a
,
LL
b
,
int
end
,
int
begin
)
//模拟手工除法
{
if
(
begin
>
end
)
return
;
int
tmpans
=
a
/
b
;
cout
<<
tmpans
;
div
((
a
%
b
)
*
10
,
b
,
end
,
begin
+
1
);
}
int
main
()
{
unsigned
long
long
f
[
500
]
=
{
0
,
1
};
for
(
int
i
=
2
;
i
<
100
;
i
++
)
f
[
i
]
=
f
[
i
-
1
]
+
f
[
i
-
2
];
div
(
f
[
48
],
f
[
49
],
100
,
0
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"4c45c0253bca421fb0d1c8d7fb246832"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/10.黄金连分数/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 黄金连分数
黄金分割数0.61803… 是个无理数,这个常数十分重要,在许多工程问题中会出现。有时需要把这个数字求得很精确。
对于某些精密工程,常数的精度很重要。也许你听说过哈勃太空望远镜,它首次升空后就发现了一处人工加工
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
,对那样一个庞然大物,其实只是镜面加工时有比头发丝还细许多倍的一处
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
而已,却使它成了“近视眼”!!
言归正传,我们如何求得黄金分割数的尽可能精确的值呢?有许多方法。
比较简单的一种是用连分数:
```
1
黄金数 = ---------------------
1
1 + -----------------
1
1 + -------------
1
1 + ---------
1 + ...
```
这个连分数计算的“层数”越多,它的值越接近黄金分割数。
请你利用这一特性,求出黄金分割数的足够精确值,要求四舍五入到小数点后100位。
小数点后3位的值为:0.618
小数点后4位的值为:0.6180
小数点后5位的值为:0.61803
小数点后7位的值为:0.6180340
(注意尾部的0,不能忽略)
你的任务是:写出精确到小数点后100位精度的黄金分割值。
注意:尾数的四舍五入! 尾数是0也要保留!
显然答案是一个小数,其小数点后有100位数字
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656381177203091798057628621354486227052604628189024497072072041893911375
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656389332927878467731611281824609112882717278172075687340936512886003869
```
### B
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656381177203091798057628621354486227052604628189024496923340122463725713
```
### C
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656382367107301981874040757690591496236273680999331990382076023866480180
```
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-dc6f30bd00214f50b5ba70dcfcb8c35f"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"字母阵列"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
仔细寻找,会发现:在下面的8x8的方阵中,隐藏着字母序列:“LANQIAO”。
```
SLANQIAO
ZOEXCCGB
MOAYWKHI
BCCIPLJQ
SLANQIAO
RSFWFNYA
XIFZVWAL
COAIQNAL
```
我们约定: 序列可以水平,垂直,或者是斜向;并且走向不限(实际上就是有一共8种方向)。
上面一共有4个满足要求的串。
下面有一个更大的(100x100)的字母方阵。
你能算出其中隐藏了多少个“LANQIAO”吗?
我就把这些东西放在了txt文件里
```
FOAIQNALWIKEGNICJWAOSXDHTHZPOLGYELORAUHOHCZIERPTOOJUITQJCFNIYYQHSBEABBQZPNGYQTCLSKZFCYWDGOAIADKLSNGJ
GSOZTQKCCSDWGUWAUOZKNILGVNLMCLXQVBJENIHIVLRPVVXXFTHQUXUAVZZOFFJHYLMGTLANQIAOQQILCDCJERJASNCTLYGRMHGF
TSDFYTLVIBHKLJVVJUDMKGJZGNNSTPVLCKTOFMUEUFSVQIAUVHNVFTGBDDARPKYNNCUOYUAZXQJNOEEYKLFRMOEMHUKJTPETHLES
FKVINSLWEVGAGMKVFVIUBMYOIAFHLVNKNTYKTZWVXQWRWIGPENFXYDTKRVPKRTHMGHVYOCLDCKMEKRLGEKBYUCLOLYPAKPFSOREH
KWPUOLOVMOFBIXYACWRDYBINTMPASPCEOKHXQIGBQQMCEOIVULIEOPFSCSIHENAJCVDPJDOIWIIULFDNOZOFVAMCABVGKAKCOZMG
XWMYRTAFGFOCNHLBGNGOXPJSTWLZUNNAGIRETGXFWAQSSJPFTQAXMTQWMZWYVEPQERKSWTSCHSQOOBGXAQTBCHOEGBDVKGWJIFTG
ZWWJEIISPLMXIMGHOOGDRZFTGNDDWDWMNUFWJYJGULPHNUFSAQNNIUVAAFZIAZKFXXNWCEABGJAUMGYEIEFVQXVHHHEDYUITRCQB
XZHDPZQTOBECJVBZLACVXACZEDYOGVAVQRNWEOWGRAQYUEUESTEDQTYJUTEFOOITSHDDZHONJGBRCWNEQLZUTBNQIADKNFIOMWZR
EBFKCVNLURZSNPOLTISRPDTNUMCDGKTYRGIOVEPTUTSBAWQKWWEUWIWHAANUZUADGZEATZOQICWFUJTWNZDBKLQNELWVTBNDLNFH
PESISEATZNCDFRMXBQUKBFTIGYSFCWVHPMSUSDKPSCOMVLDOHYQVFHAJKRDTAVLIMNZBZSMLMRTLRPSLAHXDBASDMWAAYBPYVJZF
SCCWYHLQOUKBMCEYENQNJXFOMOOJMTKDSHJJOHDKEGATFZHGWJJAZJROWHAZUFGEQKPYXLCAAXHHQBDALPYUDWZQHBASBBCFGQCQ
ZKNXUBRYZVSPQHOVLAEUAUITMPWXNXJQVIBJVBCSVXKWFAFRPRWOLYVSDVTGGOFFMNQJZOBUDJLFHJTCYMPNOBHQJHGKLIKLZMLA
POCKVEQXUAVHERIAQLGJHYOOVOMTXQFRTBFSETOZICPCHZHFBWNESVJJLSVSVOOGYYABFESWNWDNYBGBNAKRCFQMTCUMIFTESVIN
JCAULIQRYUMAMAOVVWSEUTMECXSDTONRMMROQUISYEURSAYNZUVOPXLIFBDOHPXMABBLEQZGLJXQJOEYYRRRCFTEZQAOIWKRJQDL
ZNUUDWZXZZURPMHGXQGNQBIQWWNERZWULSAPIBODBFFQQIHEQKCKLJYQNXQUTAAYGRBXSLLQNOQPZJEWHETQHPXJANMJFOHINWOW
KJGAWWFSVIZHFNUWBLWYVPIWAEICCAHOEIWRADSLOZGPSVGPUBUUQAVYCHOIGINKYKJABWAQCZCXOBKTNJZQRHLUFKQLACAAOIWJ
SIKWLXQHKDFJVGBVXWDWJKUSFRQRTDJYQMNFOQQALHRLMHSDMCFLAOVKDMTKMTPVTLAZLYJNJXZCFRHHSDIXYUUSVIMIICLUJHFW
JHWUSMCFYHPIXHAPBBSHYDQCKVGQFTENLVERFVOVDCLSTQFUSEPUMTFODLZLYQXDOXAEPONIQWTDWSAWBNSZYACGSJQSHAUMIKXT
MVBNFXMFNPAYSODPXEAYNRKTEZJWMUACSIUYPIORUFPMXAOZZJPJXPFLNSKNIAMETMOVULZPQIJJIRCSYQXOEVRHCNACSBRHKYNW
KGKBTBHGWKVJYZCOVNSKUREKZEIWVLOHAMUAYKLUGHEUESICBZAHURNTJAECTHRNKSIJQFIPVZANSZYSPJWHPKHCAPEYWNXUYQSD
RRRFYQFIQSWYRQTSNGNUFOBMSLGAFWPJGYEHGASFKTJCCZPXFIQLSXNKNWCYVTETOAPCOZJNHEWOCCAWVDEZUQCLLAVUQJJTQCKJ
NMBKMUENVGXXVMQCLXPJDQIQCFWYADIFDSGINGZDJYHPUPXVRMWDIPJRWPNRYOFGYYPEAVKDEMLYRRRMNCRQXPTDSQIVKKGJWDEF
SBAEKIFZCKDOMIQKBDWVQGBYWPDIBOLQUGAQRXLJDAZMXVZXYSNWEWTNZKYREMBEUHOTFOCKEJSXCMUBCKXNGQXTQJRCRCLWJTOI
YXBFBIBRAAFNPKBLTSMCFERZURZNWHMOEHIHNQTBWXNPJGIDYDPRGEWACCBULJRACOFLANQIAOIHMYCNQHVKXSIGAMWAHUSNBBTD
QDGPTRONXHAZWOUPNBFJFEWAMFZUQZFDKAPNJUBQPWBPYGPZHKUDZZDLCCWHGAUKJCSLLFWGPYJKJQBNLCZESOGXXSQCVVKVRVAW
NXPGQOUEFLUZHHSAODIWEPZLXVQLYGVOOVCCREDJZJOMCSCFFKEIEAVCTPUZOWNOLJHGBJHJFBFFORGXOXXFOCAGBWEFCIDEKDLB
PTXSUINQAJURNFQPMMSPLZTQAHCIOFJUEFFZGIHTSJNIEXQLLHRQUXXLLORJEHGQJOXSLIAVFPEJNGMMVAXDDMPXLOSTRLLFLYRM
JQNCLENGTROIKDWBMXRNJYPGZRQOREPJJPTXKVVKPYYZENEOIQKZOPXAYGFXORXRIDGATHMZFDJIOIOKVDJBHSXQMYCBYFGXWHLH
CITGTILGPGBHZMNWWHXEFPGDPJUVFBJKAQWACZHPRPJYCOLGZTBDCVHNRSUAJUQAWAPMQJDQIFPZQZEONWHIYKMXDZOMVETEFJRB
RDOTIDCFEESOKYPYCGQQKOGPMGJRITSVTKOKDSXLRLJRRHNFRFXCMDNQMCEGZFJWHZOAFBQXXPXNBSWTSUYPAWQRHAUGLNPBRSJT
HOWRIUGMOQTUYIHDWJRFBWWKWYKCICSVBVKTBIIWGFSVIFCTUKIHHUUISCOTEOYRWQXTAEBXQQOLLMOALNIYVCCHNSWIKHMYYNZO
OFRIYYXPPSRTPAYMUJSSDILKIZAYSEIOLANQIAOVKARDPGVFCSYBSNHAPGTIKLAWTTKOEADWRLAACAAFYTBTNSGFTYLYUHJXBMMA
NJFTMLUIBKDPWBXQOMBVQXCZOIREHRSZCSJOIVBXWQIBUTYBQNTZRVROHGOIZYAJWXLEATLOZJIKJMIHSLGSVTCXJWIOOGWSERRQ
DBQJNGBLRIYFIKHBEYOZQBOAGGNIZKFDHWXCFNJLBQXVLHIQNIBZSDLTTRERHNWCMLJCVBBGGAQTPUQHIRABXPQSYGSDVMBNNDFG
KPLFUYXHYGOCZPPXMWCZYNKCYBCRZVKFBHQXPGPBZFTTGEPQTJMOFHAYSQQZDMQECGXOXADYHNNXUKNBXZBYHBOULXNBJZKIZREF
LVHAMSNXJOCVRPVGJUWXFVOCUCLCZDXRPBBDRLRAVVNLOZWOHWMXYSNMXAKJYWYGILNGUJGIPKAUDVANZLFWKUWWUSQYBRCBVDIJ
QCXPLOTPPGXCUZOUSSTXHVMLHVMJTUSSOPLRKEBQSGWNGVHKANVZWYQHSHLIPWSYCPKTUKPMWPLVFLLAHXZQANFXHFNYHIQVIOYN
ZPTJJCBHXPSUPOMNRVCKXSUFCNRCRNCPTPGIDQOEQUDFNUNMJPOEKVIMUJAJZOUKMAFSLDWYMCHTSNJYUDJAHQOIXPYSRHVAFFCR
DCGMEEWXWMNOSSJNIZCINRHENPPPCYVFWYCONOPKXMFZXXIHNXIGAHAMHSBRESOETGVXWDNQLGCEOUDDJXHQIVCHRNKBFFEWILGY
SOAIQNALXRBSGAQIDQVMVDKVZCPMJNXKXRXPFZAUVQPBHHQKTPDSQROLQTUGMFQRWGVEWCYPDYDZGNNNUFKJUEHJKPLIQNRQYXHU
GKGWUCJXUKAEHLRLNDFUQPSJAZTVJRXWXQVBMRJXULEMJJPDCVTOWVFDBVLSBHZRRQUVMUQYKTJCLSGGHGCPHPHMWYAECLJIZUWV
QQNKPQRJMSOCEAYDNKPHVEGKAGCKAPDXTGVXULHUXHJPDXCSKQTCJENVTZTMRUENCSWHBEORALSREBWAJEMQDXMRKGHJGICDHKHY
YNSDSWDRLBBFUFVVICMGUCGBSVDLJNXGKXNFGVLKAVBJRRRUHKRXTPBJAKIEBAVMDIOJLIUDABCGNPNJIYBCXMOOWKRPHPYSWRDC
BORWTNBISSLTVKBRTLWKRNCEDCNEGCIYJIPDICFAVNOISYAHWBLGMNFKXZYTTWJOBEPNMSJEJMHXVPGOJOLQQQVXFGEULANQIAOD
OQETOJHCZXGTUKIWGMEVVMXCURISUOFQSAWZWDMZWVYHZMPEIMWKJDGERODVVUXYRTYLCRGYQQOIOFZSSZRAIESWBQOAIQNALJNR
HEYWHPLLPCUEOCBAOWGAYEJZQJHLVNMVQNSQQGGUBOIMDPFLOVSQGBLYAMBRYJDVOXOQINLJAVYALAKHPKOYNKGXIISSJNGKHYMS
IQVRYKXCUFIRNENEXFJTMOTJWYXSMTDHHPRHWIXETWVVIXZELKLLWRWQYGBCGJNYSUQEFCOUDNIJMLJNLAWSYJGULKBCFPYVSSMW
WQHGWRQFWFOTGPBBSJBDUKOMBXNRPIMCGPGVZFADWTBVIEMVTBXVAFQDDMJALCOMZTXUFFKBQQZDFAMTFWEXTHBKNWRLUVITQXLN
OPPJQKNGHWWPENVQIABJCQNKXNPWOWRFEOKQPQLANQIAORGGOLAYCEGZBHZVLPBERWYIJNJUNXKULUQOJLTNRDZDEYWEMYCHJLLB
LJISOAQLXJEFXVTOZSICOLQIJEXUANJWIFSIMGUQWHBXUDWOEILYFUZTGDZDSPLZPDPXBLFAXLEFQFEPDSJQWEQMXKKHCXHMSATM
UMUJENPBYKZLWAJAXJKDIYCBREBPOETQHMRHLKSEZUIPRGWIZDDQLSJAPKPBWMJMPZWLNFLFCQOCDBMLIHIYCXUJLFLPZVGWBKMY
WHZJLKEWUPETVUREKVKCLBNYFLWCERVIPUDINNWGQTUHWXCTDVTMYATYUZLMVLOHKBOGIZCQDOWFBCWJAVUXYUEVRKPOXCKHAWZC
RPLNLCUHJRADHJNSDPZXIKXGUKEJZCFJQASVUBSNLXCJXVCJZXGMRYRLOBCNGPDUJQVEFKMYHNZGZOAIQNALQDHTBWJXPKJLFXJY
MKCEZEDAFGSOCORWJGMOKWPVVBVDYZDZHPXFWJBDELHPGOQHMBAHUUUJMGXAEKZCTQTBXNVYUIQUVZGXSKQXJWRUPSFIJDYIAORC
GKFKQNXPJWOPPBTUKTHUBIROSYOVFEMJBRREWICJPCIOSTWPAUSKTRQULXPWRSXHSRYBCWYCYOTCTPFSQLDIILIGMEVZKYSOYRPH
SFDSCSMLLNARCCGCBJOGZAEQTGNGSFAQIXLPDBSWZDTYVASYYPVBRFBTIAGGWONGSVKCJDBBLYKAIOXUATGMALZXFOHZFTXALCFU
CUSSTLCRYPDTFSFJFENKJWTEBOBEPLSNXLALQWCKSLVMZQDJITHZKVCCQXTEXOSVAUFYAZXJUOAPPVEEWOIIMOSZZMCOQBRUXWKG
PDOFSCKKJJTRYRWGLEZODQTJSIMXIAOLNMLPHBAYLPTTLPYWILSEIIQVSXNHIJEORVCNJHYXRBIZZJTADGMRTSXVRXYGVQQNUEIC
IHNJOQXUXTXFPALCHOELNVMWDWQTEARUKPIFWXJSMWZLMNLAODUTKNZDYRFRLGBLIBGIBXJBOYMLYLANQIAORORYKSJPOOOAMVRN
IWIUHLYJKTQGVJBDPROSRGZUFITDIBCDPICNEFIGHWGSROWBYKUCLCQYLJXLHLXSCTJWKDLHHMLDBZCVDKPXYYASHUUMUJMVSXAD
GXOYXQFEBFIEJJLHBNGSYALOUXNQBXXZAAZJXENJJVVGFVHOTKSLEGLJVSJCQHSSZFEIOGBOGWSPIRENQAAWRQFBEFEXBKGMSTRC
PYIANSGMNKBCDPHWDUPKICQEUDNZPNGRUJYSZIRLXGXXITAFBCANGDLVAQLDPVTJNSAUZMBBNOBBOERSHQIOLBVTSPPJKVCMXUBS
IKMDIYSNCJZKJKJQMTIKEPRUNAHJUSWJHSLWIVWHYAYLOIOGSZVWKQWXZDBPHWZRAIPMXDJHBIISVJWVEVZAEGAKCYYMNZARBZPC
DLDFVQDFDMVHYVOWEKMFKWUXLTPWIVKPRZZXOLMDAPAIQEKJHCHYAGJDBOFWDGNEGQGOOKWSKLTLREMGGTVJFHAIBCQKNZVRCZYS
FBQASGNCCBBGNKJHCDBTGBIIWKMPHDABKEWDEPYEAVKNMPATUZZUOEHGUGAZNECSGUCIIJPMMRAMTVADMTCRJCBWDLWWFNFOWMVZ
XFJFBGDAVGGAIZHAUIYENDZTRUWHPQUFWCHOXNCWYNAWVPLBLNQKQDTKQQKXNFXCTBGRWUZFHNRBDNLNKQVOLLGBBJQIYOBCEIKO
CURAGWXMLYBSIZLAXFONZZMQMRNNSRQKRHQGFGZUTLONAYRKSSOWAMKZBSGOOYQDPTBHGPBNQEDCZHRTOXREOFJEKJVIZXZBCJPN
KGYBZTZRKOGBETJRUWRNUCIFKIMCZGYTZLCZYGCGKVZRJIFZQIQPTCPPUHYWIXBOFFGSGSAIMNGKKUUROAVNJUQQNSWJRZIZEHAF
DDAOBVCPOVODVJFLSNPJXHWQBHILWZAHQQMTQASNADZLZNXJLJMFCOUWOZJCMVVTYCKTUBABWLCEBNYWAMOLNBQQYBRUJCQCZALE
TVVRPMYFIKINHIUEJBDLTCUMMUWICIUVCZNIQIUEWVAHLANQIAONMEYJWPDAFXVNOSOFDOCESSLGZPTJINBUAFWWWMPTYALZIGVD
DCZGKILMBFXIQQFEKJBIUDEMIFCANVGNYZAYSQFMNNQFEPZFUUVGTBKSMDXITBLANQIAOQUKTPNYPOWSQQYWWMJHSDYVFDJYXBAF
VGYXAMDRRZWVIHNQPZZWRNWBTROOJOLNUGXBILZKQEGIQSYGKZGODPWBJSCMRRWSSQURUFIAFQGEZLGZNOEQMNQEYUKPEQPPVAMO
SYSFUAJFKIPUJVQSZRWQCJYAUMLDDNOKODDXIEQIFLANQIAOZFUNKUBVDBLMJOAUTVCZVLKJRQIORQPGAVCEYVNYUZHXILHERYEC
GJEKWEKIJNIWUXZNVIWIAANHIOSOLATSQFSSCTAKESUTSPPYFHEHLVLIBJZEEBCOWMNHFTZMAPKFUPNFLTFFJQRVJHAKDVMGGUIX
KAKXXNKSOAIQNALLWKWGVACYWBQEVTFSEUCYRORQTHWFUJFLQHONWZEKPLSNPRPBOMOFFCPMKXFZBKIERBKDYFKYUEYVYRPMOAQI
WNICDLQKZXGTKDLIEFBGELGJOAIQNALXZLGGDQIBVEULDPBWUJNTYOKFBPGMAWRRUJPPIGYCNYURNOSQRIRBAZAGWWDUHAAZQWPT
KFXZQXRMKSBUXWOUVVHSJWTLKZELGXMMAIDSJIWGCJPCBWZIEKMNUPUAFHTUMOZKJWVTIAQNOHELEMWGKJHKPNJVSRVHAUFXBUOU
XOWCZJYQLXJRUOOYSKDLDXKWTTJBYBTLKSWRUYPOYTPBGUJXBMRWNELBWADCSZDAEEFGPVRHNNLBFDDXNPDXLKQUSJAZDEUDBMBD
QIKYEKMVUHGGWZDKXFVQQNECZOAWCFUBHQMEPEPKEFSDBAYJQOSGAIHRBRAUKLQRANKMTTIOJDDXAEWTQHIYSGRRMEFTNNWCLZSI
ZFUQAQCSFNVUQMKUQWBWFQIEQVVXPOSVIDTUOBLLTGHQKEMSUWWHWRISLGRDPPQPZBANSGDWXKNYTKMWECPMPDYSCJZXPUKPWGYI
CNGVLBSCBHRLJARWSRENGHYYQDKRATERCPEAOPAJZUMOYIDHVPDMQPKKHCBAMRBGEIEXXJALMCXKPUGXYVINRORFYURXAMOJCBZQ
YJHHAWESCLMDIHVYMLAJZQSYTDEURWYPOLJCAKIKSATGVIALBLWPPKDEGSPMRLDBQNVPPCLQXKUQLQJERMYFGAETUATEBQZUMGUN
NBWUBVXYDFPLPJYLIDFVTVKKGFWMXVINLJUDUPABTSBJAJENZSXIMUJQWPEZTAVDMBBHFYTJKYFXIXQTBTTQIKQXQDPWYNMXRQDJ
OGWLZQUBJJHAQNPVRGHGPNMMJPIDGANYEEDWYPOLKLNEPYSRTQYCJLSWFRJRRGGSNSDHIXYYSNAKKBWQDDGYYMOGPUXQEUSAPSOU
CLLSELRVFZUFYVTJQKCQHNICMERWQFQNPVRPIIYKHZWJYJAFCLNSZXUHSPOZWQUMJHLKKYJENVZOCSWCTPYWIZONUUCLSUROGAYS
AZGNIMXPLPCEPULRRBHHQOBELHJZPUQAMWUASVKDXVEWAOFMAYSJFXHCNEUXUQWUESFBRUFZQLKKWHCHKOPLECCBYSLECAEZIMMI
TUUEOCEBAUKWLTSYJJPLZTIARAOZXKYYWIOXBBTZZCSAULKNEJWVQXIKUWBIWVHGNTHVBAWAVPGLHSDJDLPVHHHUNVSFKXARXLVQ
EMVDFSLANQIAOPTLFLFRKGNUZCTXWCAXHECTZFHWUFENRGQICHTYLSHZWIEGLNVDJZOMTKAAUWOHVOVOCTUKOSINSAYIAEUYORNA
VGPRMLCAQZIPRFQOZMEFTQZYVOTVFNVOIQSJCIPPQXQKJIXICUIGMHAJJMSXENCBQFIJHNZXIQMWACKDKQSEWWKMLOAUPFHAZGRY
SQWQMRSQBGGKYKGWEZYRIHWGNXRPOUMFSFGTYDLUDWPWAVQORTMQUXWKUQVNMDPWQFIZPOIHCJATODRQGZDMQXZVNXXVEJNGWZOM
PVBGZSQPCELDIWDHOQWAUHILGLPYRIICTLFSOYKQZYZOCIZPTECSWOODGGBDTSGIMYGMVPJPRPEVWOOKYFWRGXHWUCRQNYJEMSYL
XWOFXFVDXPTHYTCEGMODCILAHYBREZVVHOUPZKCNHUEVPMKHUBNRPFMWXVQACVZCALZLYMZSBLCEASPMIEFOTGKMPGWYQADSNDPR
QPHAVLZDZLKIEISFLLVWXAVBZLZIJRHGROUVGXRDLUJAXNHBBZYNCVERJGSKLWZEKGJBCWMSMLYIHZFFMIOGVIMZQBSRHQWAADYN
MNXEGTDXCDKIUDOISQXEUJWETPELKBCYFSDNJQWNNBPYMWBUPQBAAINMYZOYCEGNLFNNHZFEMSQVXJJGWBCRAVKZFWFBKMBRVBFD
HKACSZIUWUXLWKFPKOCUQJEPQDZCMUJFLVCLIOQQRVKSWFIAKNHMRLNJTKGVNTGLCVPVMBLJANOBCXUGVWBJYSIXZQVAVFWILWFB
QWNLTPMCYHRSKVHXLONRANWKWXUTHYQLIOFKGDBMSWDRCYRKVSAGGRJMWQYQFLMUIGGCLAUQAACTYLPZEOJBHMWRKHCRXGTGRMUP
CPQKJRBLYDNPUGHCRBVYBAIRVCAWLBWVWCMKNBIRKJOUGYQEBQRHDSTWXDIWGRVMLIJFBWHLHCDAAVUDLZSCGQNOUXVUIVIZZZMD
NMHGYPFUUDWKQGTAKKGCDFJFYJFNRZVXDPGZEAMWQVQZODKTXHIYFVKJSSAWVHYCUCZMLLBPXTILDYJQEMWDRUFKISOUVPUDTYPB
FDAQUBXHUJYTAYNWVIJNUSQDTQDEMUAPWXRYUWONTBDZCHZOUEGPMWEZTQWWSHAYOBWVTDIMZYNVNZKUHOFCQKPHJXWNRCGUJEKO
WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFRSZIOGWNTYAJYLQCGEOWY
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
char
a
[
100
][
100
];
ifstream
fin
(
"1.txt"
);
//我把那些字符放在了1.txt里,读取它
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
100
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
100
;
j
++
)
{
fin
>>
a
[
i
][
j
];
}
}
fin
.
close
();
//关闭读取文件
int
sum
,
i
,
j
;
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
105
;
i
++
)
//把Q放在前面,分成八个方向分别判断是否成为LANQIAO。
{
for
(
j
=
0
;
j
<
105
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
==
'Q'
&&
j
>=
3
&&
j
<
97
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
-
3
]
==
'L'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
-
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
3
]
==
'O'
)
sum
++
;
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
-
3
]
==
'O'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
-
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
][
j
+
3
]
==
'L'
)
sum
++
;
}
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
==
'Q'
&&
i
>=
3
&&
i
<
97
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
]
==
'L'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
]
==
'O'
)
sum
++
;
if
(
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
]
==
'O'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
]
==
'L'
)
sum
++
;
}
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
==
'Q'
&&
i
>=
3
&&
i
<
97
&&
j
>=
3
&&
j
<
97
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
-
3
]
==
'L'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
+
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
+
3
]
==
'O'
)
sum
++
;
if
(
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
-
3
]
==
'O'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
+
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
+
3
]
==
'L'
)
sum
++
;
if
(
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
-
3
]
==
'L'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
-
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
+
3
]
==
'O'
)
sum
++
;
if
(
a
[
i
+
3
][
j
-
3
]
==
'O'
&&
a
[
i
+
2
][
j
-
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
+
1
][
j
-
1
]
==
'I'
&&
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
]
==
'N'
&&
a
[
i
-
2
][
j
+
2
]
==
'A'
&&
a
[
i
-
3
][
j
+
3
]
==
'L'
)
sum
++
;
}
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
sum
);
}
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"f1f09e2a086b4304a9f3df41413c566e"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/11.字母阵列/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 字母阵列
仔细寻找,会发现:在下面的8x8的方阵中,隐藏着字母序列:“LANQIAO”。
```
SLANQIAO
ZOEXCCGB
MOAYWKHI
BCCIPLJQ
SLANQIAO
RSFWFNYA
XIFZVWAL
COAIQNAL
```
我们约定: 序列可以水平,垂直,或者是斜向;并且走向不限(实际上就是有一共8种方向)。
上面一共有4个满足要求的串。
下面有一个更大的(100x100)的字母方阵。
你能算出其中隐藏了多少个“LANQIAO”吗?
我就把这些东西放在了txt文件里
```
FOAIQNALWIKEGNICJWAOSXDHTHZPOLGYELORAUHOHCZIERPTOOJUITQJCFNIYYQHSBEABBQZPNGYQTCLSKZFCYWDGOAIADKLSNGJ
GSOZTQKCCSDWGUWAUOZKNILGVNLMCLXQVBJENIHIVLRPVVXXFTHQUXUAVZZOFFJHYLMGTLANQIAOQQILCDCJERJASNCTLYGRMHGF
TSDFYTLVIBHKLJVVJUDMKGJZGNNSTPVLCKTOFMUEUFSVQIAUVHNVFTGBDDARPKYNNCUOYUAZXQJNOEEYKLFRMOEMHUKJTPETHLES
FKVINSLWEVGAGMKVFVIUBMYOIAFHLVNKNTYKTZWVXQWRWIGPENFXYDTKRVPKRTHMGHVYOCLDCKMEKRLGEKBYUCLOLYPAKPFSOREH
KWPUOLOVMOFBIXYACWRDYBINTMPASPCEOKHXQIGBQQMCEOIVULIEOPFSCSIHENAJCVDPJDOIWIIULFDNOZOFVAMCABVGKAKCOZMG
XWMYRTAFGFOCNHLBGNGOXPJSTWLZUNNAGIRETGXFWAQSSJPFTQAXMTQWMZWYVEPQERKSWTSCHSQOOBGXAQTBCHOEGBDVKGWJIFTG
ZWWJEIISPLMXIMGHOOGDRZFTGNDDWDWMNUFWJYJGULPHNUFSAQNNIUVAAFZIAZKFXXNWCEABGJAUMGYEIEFVQXVHHHEDYUITRCQB
XZHDPZQTOBECJVBZLACVXACZEDYOGVAVQRNWEOWGRAQYUEUESTEDQTYJUTEFOOITSHDDZHONJGBRCWNEQLZUTBNQIADKNFIOMWZR
EBFKCVNLURZSNPOLTISRPDTNUMCDGKTYRGIOVEPTUTSBAWQKWWEUWIWHAANUZUADGZEATZOQICWFUJTWNZDBKLQNELWVTBNDLNFH
PESISEATZNCDFRMXBQUKBFTIGYSFCWVHPMSUSDKPSCOMVLDOHYQVFHAJKRDTAVLIMNZBZSMLMRTLRPSLAHXDBASDMWAAYBPYVJZF
SCCWYHLQOUKBMCEYENQNJXFOMOOJMTKDSHJJOHDKEGATFZHGWJJAZJROWHAZUFGEQKPYXLCAAXHHQBDALPYUDWZQHBASBBCFGQCQ
ZKNXUBRYZVSPQHOVLAEUAUITMPWXNXJQVIBJVBCSVXKWFAFRPRWOLYVSDVTGGOFFMNQJZOBUDJLFHJTCYMPNOBHQJHGKLIKLZMLA
POCKVEQXUAVHERIAQLGJHYOOVOMTXQFRTBFSETOZICPCHZHFBWNESVJJLSVSVOOGYYABFESWNWDNYBGBNAKRCFQMTCUMIFTESVIN
JCAULIQRYUMAMAOVVWSEUTMECXSDTONRMMROQUISYEURSAYNZUVOPXLIFBDOHPXMABBLEQZGLJXQJOEYYRRRCFTEZQAOIWKRJQDL
ZNUUDWZXZZURPMHGXQGNQBIQWWNERZWULSAPIBODBFFQQIHEQKCKLJYQNXQUTAAYGRBXSLLQNOQPZJEWHETQHPXJANMJFOHINWOW
KJGAWWFSVIZHFNUWBLWYVPIWAEICCAHOEIWRADSLOZGPSVGPUBUUQAVYCHOIGINKYKJABWAQCZCXOBKTNJZQRHLUFKQLACAAOIWJ
SIKWLXQHKDFJVGBVXWDWJKUSFRQRTDJYQMNFOQQALHRLMHSDMCFLAOVKDMTKMTPVTLAZLYJNJXZCFRHHSDIXYUUSVIMIICLUJHFW
JHWUSMCFYHPIXHAPBBSHYDQCKVGQFTENLVERFVOVDCLSTQFUSEPUMTFODLZLYQXDOXAEPONIQWTDWSAWBNSZYACGSJQSHAUMIKXT
MVBNFXMFNPAYSODPXEAYNRKTEZJWMUACSIUYPIORUFPMXAOZZJPJXPFLNSKNIAMETMOVULZPQIJJIRCSYQXOEVRHCNACSBRHKYNW
KGKBTBHGWKVJYZCOVNSKUREKZEIWVLOHAMUAYKLUGHEUESICBZAHURNTJAECTHRNKSIJQFIPVZANSZYSPJWHPKHCAPEYWNXUYQSD
RRRFYQFIQSWYRQTSNGNUFOBMSLGAFWPJGYEHGASFKTJCCZPXFIQLSXNKNWCYVTETOAPCOZJNHEWOCCAWVDEZUQCLLAVUQJJTQCKJ
NMBKMUENVGXXVMQCLXPJDQIQCFWYADIFDSGINGZDJYHPUPXVRMWDIPJRWPNRYOFGYYPEAVKDEMLYRRRMNCRQXPTDSQIVKKGJWDEF
SBAEKIFZCKDOMIQKBDWVQGBYWPDIBOLQUGAQRXLJDAZMXVZXYSNWEWTNZKYREMBEUHOTFOCKEJSXCMUBCKXNGQXTQJRCRCLWJTOI
YXBFBIBRAAFNPKBLTSMCFERZURZNWHMOEHIHNQTBWXNPJGIDYDPRGEWACCBULJRACOFLANQIAOIHMYCNQHVKXSIGAMWAHUSNBBTD
QDGPTRONXHAZWOUPNBFJFEWAMFZUQZFDKAPNJUBQPWBPYGPZHKUDZZDLCCWHGAUKJCSLLFWGPYJKJQBNLCZESOGXXSQCVVKVRVAW
NXPGQOUEFLUZHHSAODIWEPZLXVQLYGVOOVCCREDJZJOMCSCFFKEIEAVCTPUZOWNOLJHGBJHJFBFFORGXOXXFOCAGBWEFCIDEKDLB
PTXSUINQAJURNFQPMMSPLZTQAHCIOFJUEFFZGIHTSJNIEXQLLHRQUXXLLORJEHGQJOXSLIAVFPEJNGMMVAXDDMPXLOSTRLLFLYRM
JQNCLENGTROIKDWBMXRNJYPGZRQOREPJJPTXKVVKPYYZENEOIQKZOPXAYGFXORXRIDGATHMZFDJIOIOKVDJBHSXQMYCBYFGXWHLH
CITGTILGPGBHZMNWWHXEFPGDPJUVFBJKAQWACZHPRPJYCOLGZTBDCVHNRSUAJUQAWAPMQJDQIFPZQZEONWHIYKMXDZOMVETEFJRB
RDOTIDCFEESOKYPYCGQQKOGPMGJRITSVTKOKDSXLRLJRRHNFRFXCMDNQMCEGZFJWHZOAFBQXXPXNBSWTSUYPAWQRHAUGLNPBRSJT
HOWRIUGMOQTUYIHDWJRFBWWKWYKCICSVBVKTBIIWGFSVIFCTUKIHHUUISCOTEOYRWQXTAEBXQQOLLMOALNIYVCCHNSWIKHMYYNZO
OFRIYYXPPSRTPAYMUJSSDILKIZAYSEIOLANQIAOVKARDPGVFCSYBSNHAPGTIKLAWTTKOEADWRLAACAAFYTBTNSGFTYLYUHJXBMMA
NJFTMLUIBKDPWBXQOMBVQXCZOIREHRSZCSJOIVBXWQIBUTYBQNTZRVROHGOIZYAJWXLEATLOZJIKJMIHSLGSVTCXJWIOOGWSERRQ
DBQJNGBLRIYFIKHBEYOZQBOAGGNIZKFDHWXCFNJLBQXVLHIQNIBZSDLTTRERHNWCMLJCVBBGGAQTPUQHIRABXPQSYGSDVMBNNDFG
KPLFUYXHYGOCZPPXMWCZYNKCYBCRZVKFBHQXPGPBZFTTGEPQTJMOFHAYSQQZDMQECGXOXADYHNNXUKNBXZBYHBOULXNBJZKIZREF
LVHAMSNXJOCVRPVGJUWXFVOCUCLCZDXRPBBDRLRAVVNLOZWOHWMXYSNMXAKJYWYGILNGUJGIPKAUDVANZLFWKUWWUSQYBRCBVDIJ
QCXPLOTPPGXCUZOUSSTXHVMLHVMJTUSSOPLRKEBQSGWNGVHKANVZWYQHSHLIPWSYCPKTUKPMWPLVFLLAHXZQANFXHFNYHIQVIOYN
ZPTJJCBHXPSUPOMNRVCKXSUFCNRCRNCPTPGIDQOEQUDFNUNMJPOEKVIMUJAJZOUKMAFSLDWYMCHTSNJYUDJAHQOIXPYSRHVAFFCR
DCGMEEWXWMNOSSJNIZCINRHENPPPCYVFWYCONOPKXMFZXXIHNXIGAHAMHSBRESOETGVXWDNQLGCEOUDDJXHQIVCHRNKBFFEWILGY
SOAIQNALXRBSGAQIDQVMVDKVZCPMJNXKXRXPFZAUVQPBHHQKTPDSQROLQTUGMFQRWGVEWCYPDYDZGNNNUFKJUEHJKPLIQNRQYXHU
GKGWUCJXUKAEHLRLNDFUQPSJAZTVJRXWXQVBMRJXULEMJJPDCVTOWVFDBVLSBHZRRQUVMUQYKTJCLSGGHGCPHPHMWYAECLJIZUWV
QQNKPQRJMSOCEAYDNKPHVEGKAGCKAPDXTGVXULHUXHJPDXCSKQTCJENVTZTMRUENCSWHBEORALSREBWAJEMQDXMRKGHJGICDHKHY
YNSDSWDRLBBFUFVVICMGUCGBSVDLJNXGKXNFGVLKAVBJRRRUHKRXTPBJAKIEBAVMDIOJLIUDABCGNPNJIYBCXMOOWKRPHPYSWRDC
BORWTNBISSLTVKBRTLWKRNCEDCNEGCIYJIPDICFAVNOISYAHWBLGMNFKXZYTTWJOBEPNMSJEJMHXVPGOJOLQQQVXFGEULANQIAOD
OQETOJHCZXGTUKIWGMEVVMXCURISUOFQSAWZWDMZWVYHZMPEIMWKJDGERODVVUXYRTYLCRGYQQOIOFZSSZRAIESWBQOAIQNALJNR
HEYWHPLLPCUEOCBAOWGAYEJZQJHLVNMVQNSQQGGUBOIMDPFLOVSQGBLYAMBRYJDVOXOQINLJAVYALAKHPKOYNKGXIISSJNGKHYMS
IQVRYKXCUFIRNENEXFJTMOTJWYXSMTDHHPRHWIXETWVVIXZELKLLWRWQYGBCGJNYSUQEFCOUDNIJMLJNLAWSYJGULKBCFPYVSSMW
WQHGWRQFWFOTGPBBSJBDUKOMBXNRPIMCGPGVZFADWTBVIEMVTBXVAFQDDMJALCOMZTXUFFKBQQZDFAMTFWEXTHBKNWRLUVITQXLN
OPPJQKNGHWWPENVQIABJCQNKXNPWOWRFEOKQPQLANQIAORGGOLAYCEGZBHZVLPBERWYIJNJUNXKULUQOJLTNRDZDEYWEMYCHJLLB
LJISOAQLXJEFXVTOZSICOLQIJEXUANJWIFSIMGUQWHBXUDWOEILYFUZTGDZDSPLZPDPXBLFAXLEFQFEPDSJQWEQMXKKHCXHMSATM
UMUJENPBYKZLWAJAXJKDIYCBREBPOETQHMRHLKSEZUIPRGWIZDDQLSJAPKPBWMJMPZWLNFLFCQOCDBMLIHIYCXUJLFLPZVGWBKMY
WHZJLKEWUPETVUREKVKCLBNYFLWCERVIPUDINNWGQTUHWXCTDVTMYATYUZLMVLOHKBOGIZCQDOWFBCWJAVUXYUEVRKPOXCKHAWZC
RPLNLCUHJRADHJNSDPZXIKXGUKEJZCFJQASVUBSNLXCJXVCJZXGMRYRLOBCNGPDUJQVEFKMYHNZGZOAIQNALQDHTBWJXPKJLFXJY
MKCEZEDAFGSOCORWJGMOKWPVVBVDYZDZHPXFWJBDELHPGOQHMBAHUUUJMGXAEKZCTQTBXNVYUIQUVZGXSKQXJWRUPSFIJDYIAORC
GKFKQNXPJWOPPBTUKTHUBIROSYOVFEMJBRREWICJPCIOSTWPAUSKTRQULXPWRSXHSRYBCWYCYOTCTPFSQLDIILIGMEVZKYSOYRPH
SFDSCSMLLNARCCGCBJOGZAEQTGNGSFAQIXLPDBSWZDTYVASYYPVBRFBTIAGGWONGSVKCJDBBLYKAIOXUATGMALZXFOHZFTXALCFU
CUSSTLCRYPDTFSFJFENKJWTEBOBEPLSNXLALQWCKSLVMZQDJITHZKVCCQXTEXOSVAUFYAZXJUOAPPVEEWOIIMOSZZMCOQBRUXWKG
PDOFSCKKJJTRYRWGLEZODQTJSIMXIAOLNMLPHBAYLPTTLPYWILSEIIQVSXNHIJEORVCNJHYXRBIZZJTADGMRTSXVRXYGVQQNUEIC
IHNJOQXUXTXFPALCHOELNVMWDWQTEARUKPIFWXJSMWZLMNLAODUTKNZDYRFRLGBLIBGIBXJBOYMLYLANQIAORORYKSJPOOOAMVRN
IWIUHLYJKTQGVJBDPROSRGZUFITDIBCDPICNEFIGHWGSROWBYKUCLCQYLJXLHLXSCTJWKDLHHMLDBZCVDKPXYYASHUUMUJMVSXAD
GXOYXQFEBFIEJJLHBNGSYALOUXNQBXXZAAZJXENJJVVGFVHOTKSLEGLJVSJCQHSSZFEIOGBOGWSPIRENQAAWRQFBEFEXBKGMSTRC
PYIANSGMNKBCDPHWDUPKICQEUDNZPNGRUJYSZIRLXGXXITAFBCANGDLVAQLDPVTJNSAUZMBBNOBBOERSHQIOLBVTSPPJKVCMXUBS
IKMDIYSNCJZKJKJQMTIKEPRUNAHJUSWJHSLWIVWHYAYLOIOGSZVWKQWXZDBPHWZRAIPMXDJHBIISVJWVEVZAEGAKCYYMNZARBZPC
DLDFVQDFDMVHYVOWEKMFKWUXLTPWIVKPRZZXOLMDAPAIQEKJHCHYAGJDBOFWDGNEGQGOOKWSKLTLREMGGTVJFHAIBCQKNZVRCZYS
FBQASGNCCBBGNKJHCDBTGBIIWKMPHDABKEWDEPYEAVKNMPATUZZUOEHGUGAZNECSGUCIIJPMMRAMTVADMTCRJCBWDLWWFNFOWMVZ
XFJFBGDAVGGAIZHAUIYENDZTRUWHPQUFWCHOXNCWYNAWVPLBLNQKQDTKQQKXNFXCTBGRWUZFHNRBDNLNKQVOLLGBBJQIYOBCEIKO
CURAGWXMLYBSIZLAXFONZZMQMRNNSRQKRHQGFGZUTLONAYRKSSOWAMKZBSGOOYQDPTBHGPBNQEDCZHRTOXREOFJEKJVIZXZBCJPN
KGYBZTZRKOGBETJRUWRNUCIFKIMCZGYTZLCZYGCGKVZRJIFZQIQPTCPPUHYWIXBOFFGSGSAIMNGKKUUROAVNJUQQNSWJRZIZEHAF
DDAOBVCPOVODVJFLSNPJXHWQBHILWZAHQQMTQASNADZLZNXJLJMFCOUWOZJCMVVTYCKTUBABWLCEBNYWAMOLNBQQYBRUJCQCZALE
TVVRPMYFIKINHIUEJBDLTCUMMUWICIUVCZNIQIUEWVAHLANQIAONMEYJWPDAFXVNOSOFDOCESSLGZPTJINBUAFWWWMPTYALZIGVD
DCZGKILMBFXIQQFEKJBIUDEMIFCANVGNYZAYSQFMNNQFEPZFUUVGTBKSMDXITBLANQIAOQUKTPNYPOWSQQYWWMJHSDYVFDJYXBAF
VGYXAMDRRZWVIHNQPZZWRNWBTROOJOLNUGXBILZKQEGIQSYGKZGODPWBJSCMRRWSSQURUFIAFQGEZLGZNOEQMNQEYUKPEQPPVAMO
SYSFUAJFKIPUJVQSZRWQCJYAUMLDDNOKODDXIEQIFLANQIAOZFUNKUBVDBLMJOAUTVCZVLKJRQIORQPGAVCEYVNYUZHXILHERYEC
GJEKWEKIJNIWUXZNVIWIAANHIOSOLATSQFSSCTAKESUTSPPYFHEHLVLIBJZEEBCOWMNHFTZMAPKFUPNFLTFFJQRVJHAKDVMGGUIX
KAKXXNKSOAIQNALLWKWGVACYWBQEVTFSEUCYRORQTHWFUJFLQHONWZEKPLSNPRPBOMOFFCPMKXFZBKIERBKDYFKYUEYVYRPMOAQI
WNICDLQKZXGTKDLIEFBGELGJOAIQNALXZLGGDQIBVEULDPBWUJNTYOKFBPGMAWRRUJPPIGYCNYURNOSQRIRBAZAGWWDUHAAZQWPT
KFXZQXRMKSBUXWOUVVHSJWTLKZELGXMMAIDSJIWGCJPCBWZIEKMNUPUAFHTUMOZKJWVTIAQNOHELEMWGKJHKPNJVSRVHAUFXBUOU
XOWCZJYQLXJRUOOYSKDLDXKWTTJBYBTLKSWRUYPOYTPBGUJXBMRWNELBWADCSZDAEEFGPVRHNNLBFDDXNPDXLKQUSJAZDEUDBMBD
QIKYEKMVUHGGWZDKXFVQQNECZOAWCFUBHQMEPEPKEFSDBAYJQOSGAIHRBRAUKLQRANKMTTIOJDDXAEWTQHIYSGRRMEFTNNWCLZSI
ZFUQAQCSFNVUQMKUQWBWFQIEQVVXPOSVIDTUOBLLTGHQKEMSUWWHWRISLGRDPPQPZBANSGDWXKNYTKMWECPMPDYSCJZXPUKPWGYI
CNGVLBSCBHRLJARWSRENGHYYQDKRATERCPEAOPAJZUMOYIDHVPDMQPKKHCBAMRBGEIEXXJALMCXKPUGXYVINRORFYURXAMOJCBZQ
YJHHAWESCLMDIHVYMLAJZQSYTDEURWYPOLJCAKIKSATGVIALBLWPPKDEGSPMRLDBQNVPPCLQXKUQLQJERMYFGAETUATEBQZUMGUN
NBWUBVXYDFPLPJYLIDFVTVKKGFWMXVINLJUDUPABTSBJAJENZSXIMUJQWPEZTAVDMBBHFYTJKYFXIXQTBTTQIKQXQDPWYNMXRQDJ
OGWLZQUBJJHAQNPVRGHGPNMMJPIDGANYEEDWYPOLKLNEPYSRTQYCJLSWFRJRRGGSNSDHIXYYSNAKKBWQDDGYYMOGPUXQEUSAPSOU
CLLSELRVFZUFYVTJQKCQHNICMERWQFQNPVRPIIYKHZWJYJAFCLNSZXUHSPOZWQUMJHLKKYJENVZOCSWCTPYWIZONUUCLSUROGAYS
AZGNIMXPLPCEPULRRBHHQOBELHJZPUQAMWUASVKDXVEWAOFMAYSJFXHCNEUXUQWUESFBRUFZQLKKWHCHKOPLECCBYSLECAEZIMMI
TUUEOCEBAUKWLTSYJJPLZTIARAOZXKYYWIOXBBTZZCSAULKNEJWVQXIKUWBIWVHGNTHVBAWAVPGLHSDJDLPVHHHUNVSFKXARXLVQ
EMVDFSLANQIAOPTLFLFRKGNUZCTXWCAXHECTZFHWUFENRGQICHTYLSHZWIEGLNVDJZOMTKAAUWOHVOVOCTUKOSINSAYIAEUYORNA
VGPRMLCAQZIPRFQOZMEFTQZYVOTVFNVOIQSJCIPPQXQKJIXICUIGMHAJJMSXENCBQFIJHNZXIQMWACKDKQSEWWKMLOAUPFHAZGRY
SQWQMRSQBGGKYKGWEZYRIHWGNXRPOUMFSFGTYDLUDWPWAVQORTMQUXWKUQVNMDPWQFIZPOIHCJATODRQGZDMQXZVNXXVEJNGWZOM
PVBGZSQPCELDIWDHOQWAUHILGLPYRIICTLFSOYKQZYZOCIZPTECSWOODGGBDTSGIMYGMVPJPRPEVWOOKYFWRGXHWUCRQNYJEMSYL
XWOFXFVDXPTHYTCEGMODCILAHYBREZVVHOUPZKCNHUEVPMKHUBNRPFMWXVQACVZCALZLYMZSBLCEASPMIEFOTGKMPGWYQADSNDPR
QPHAVLZDZLKIEISFLLVWXAVBZLZIJRHGROUVGXRDLUJAXNHBBZYNCVERJGSKLWZEKGJBCWMSMLYIHZFFMIOGVIMZQBSRHQWAADYN
MNXEGTDXCDKIUDOISQXEUJWETPELKBCYFSDNJQWNNBPYMWBUPQBAAINMYZOYCEGNLFNNHZFEMSQVXJJGWBCRAVKZFWFBKMBRVBFD
HKACSZIUWUXLWKFPKOCUQJEPQDZCMUJFLVCLIOQQRVKSWFIAKNHMRLNJTKGVNTGLCVPVMBLJANOBCXUGVWBJYSIXZQVAVFWILWFB
QWNLTPMCYHRSKVHXLONRANWKWXUTHYQLIOFKGDBMSWDRCYRKVSAGGRJMWQYQFLMUIGGCLAUQAACTYLPZEOJBHMWRKHCRXGTGRMUP
CPQKJRBLYDNPUGHCRBVYBAIRVCAWLBWVWCMKNBIRKJOUGYQEBQRHDSTWXDIWGRVMLIJFBWHLHCDAAVUDLZSCGQNOUXVUIVIZZZMD
NMHGYPFUUDWKQGTAKKGCDFJFYJFNRZVXDPGZEAMWQVQZODKTXHIYFVKJSSAWVHYCUCZMLLBPXTILDYJQEMWDRUFKISOUVPUDTYPB
FDAQUBXHUJYTAYNWVIJNUSQDTQDEMUAPWXRYUWONTBDZCHZOUEGPMWEZTQWWSHAYOBWVTDIMZYNVNZKUHOFCQKPHJXWNRCGUJEKO
WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFRSZIOGWNTYAJYLQCGEOWY
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
41
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
38
```
### B
```
cpp
39
```
### C
```
cpp
40
```
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-d27bd096aa7a423bac3d435800cc8501"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"字符串编码"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
小明发明了一种给由全大写字母组成的字符串编码的方法。
对于每一个大写字母,小明将它转换成它在 26 个英文字母中序号,即 A → 1, B → 2, … Z →26。
这样一个字符串就能被转化成一个数字序列:比如 ABCXYZ → 123242526。
现在给定一个转换后的数字序列,小明想还原出原本的字符串。
当然这样的还原有可能存在多个符合条件的字符串。
小明希望找出其中字典序最大的字符串。
#### 输入格式
一个数字序列。
#### 输出格式
一个只包含大写字母的字符串,代表答案
#### 样例输入
```
123242526
```
#### 样例输出
```
LCXYZ
```
#### 数据范围
```
对于 20% 的评测用例,输入的长度不超过 20。
对于所有评测用例,输入的长度不超过 200000。
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
200010
;
char
op
[
27
]
=
{
'0'
,
'A'
,
'B'
,
'C'
,
'D'
,
'E'
,
'F'
,
'G'
,
'H'
,
'I'
,
'J'
,
'K'
,
'L'
,
'M'
,
'N'
,
'O'
,
'P'
,
'Q'
,
'R'
,
'S'
,
'T'
,
'U'
,
'V'
,
'W'
,
'X'
,
'Y'
,
'Z'
};
int
main
()
{
string
s
;
cin
>>
s
;
string
ans
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
s
.
size
();
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
+
1
<
s
.
size
())
{
int
t
=
(
s
[
i
]
-
'0'
)
*
10
+
(
s
[
i
+
1
]
-
'0'
);
if
(
t
<=
26
)
{
ans
+=
op
[
t
];
i
++
;
}
else
ans
+=
op
[
s
[
i
]
-
'0'
];
}
else
ans
+=
op
[
s
[
i
]
-
'0'
];
}
cout
<<
ans
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"eefc0335733a482fa5ef4c6b6747f414"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/12.字符串编码/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 字符串编码
**问题描述**
小明发明了一种给由全大写字母组成的字符串编码的方法。
对于每一个大写字母,小明将它转换成它在 26 个英文字母中序号,即 A → 1, B → 2, … Z →26。
这样一个字符串就能被转化成一个数字序列:比如 ABCXYZ → 123242526。
现在给定一个转换后的数字序列,小明想还原出原本的字符串。
当然这样的还原有可能存在多个符合条件的字符串。
小明希望找出其中字典序最大的字符串。
**输入格式**
一个数字序列。
**输出格式**
一个只包含大写字母的字符串,代表答案
**样例输入**
```
123242526
```
**样例输出**
```
LCXYZ
```
**数据范围**
```
对于 20% 的评测用例,输入的长度不超过 20。
对于所有评测用例,输入的长度不超过 200000。
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
string
in
;
string
re
=
""
;
cin
>>
in
;
int
len
=
in
.
length
();
in
=
in
+
'Z'
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
len
;)
{
int
temp
=
int
(
in
[
i
]
-
'0'
)
*
10
+
int
(
in
[
i
+
1
]
-
'0'
);
if
(
temp
>
26
)
{
re
=
re
+
char
(
in
[
i
]
-
'0'
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
++
;
}
else
{
__________________
}
}
cout
<<
re
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
+=
2
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
+=
1
;
```
### B
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
);
i
+=
1
;
```
### C
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
);
i
+=
2
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-af235ccf483e404a8ab217aead930d8c"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"格子中输出"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串。 要求字符串在水平、垂直两个方向上都居中。 如果字符串太长,就截断。 如果不能恰好居中,可以稍稍偏左或者偏上一点。
输出:

\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void
StringInGrid
(
int
width
,
int
height
,
const
char
*
s
)
{
int
i
,
k
;
char
buf
[
1000
];
strcpy
(
buf
,
s
);
if
(
strlen
(
s
)
>
width
-
2
)
buf
[
width
-
2
]
=
0
;
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
1
;
k
<
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"|"
);
printf
(
"%*s%s%*s"
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
+
1
;
k
<
height
-
1
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
StringInGrid
(
20
,
6
,
"abcd1234"
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"9b7ed564233642b4a3be0a822719234e"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/8.格子中输出/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 格子中输出
StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串。 要求字符串在水平、垂直两个方向上都居中。 如果字符串太长,就截断。 如果不能恰好居中,可以稍稍偏左或者偏上一点。
输出:

以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void
StringInGrid
(
int
width
,
int
height
,
const
char
*
s
)
{
int
i
,
k
;
char
buf
[
1000
];
strcpy
(
buf
,
s
);
if
(
strlen
(
s
)
>
width
-
2
)
buf
[
width
-
2
]
=
0
;
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
1
;
k
<
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"|"
);
printf
(
"%*s%s%*s"
,
__________________
;
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
+
1
;
k
<
height
-
1
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
StringInGrid
(
20
,
6
,
"abcd1234"
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
1
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
1
)
/
2
,
""
```
### B
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
+
1
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
+
1
)
/
2
,
""
```
### C
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
),
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
),
""
```
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-068d044e1db44935ab46bcfc3020fd41"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"最大公共子串"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
最大公共子串长度问题就是:
求两个串的所有子串中能够匹配上的最大长度是多少。
比如:“abcdkkk” 和 “baabcdadabc”,
可以找到的最长的公共子串是"abcd",所以最大公共子串长度为4。
下面的程序是采用矩阵法进行求解的,这对串的规模不大的情况还是比较有效的解法。
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 256
int
f
(
const
char
*
s1
,
const
char
*
s2
)
{
int
a
[
N
][
N
];
int
len1
=
strlen
(
s1
);
int
len2
=
strlen
(
s2
);
int
i
,
j
;
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
int
)
*
N
*
N
);
int
max
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
len1
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
len2
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
s1
[
i
-
1
]
==
s2
[
j
-
1
])
{
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
]
+
1
;
//填空
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
>
max
)
max
=
a
[
i
][
j
];
}
}
}
return
max
;
}
int
main
()
{
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
f
(
"abcdkkk"
,
"baabcdadabc"
));
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"6be1237b0e294a2f92408c026803ce22"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/9.最大公共子串/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 最大公共子串
最大公共子串长度问题就是:
求两个串的所有子串中能够匹配上的最大长度是多少。
比如:“abcdkkk” 和 “baabcdadabc”,
可以找到的最长的公共子串是"abcd",所以最大公共子串长度为4。
下面的程序是采用矩阵法进行求解的,这对串的规模不大的情况还是比较有效的解法。
请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 256
int
f
(
const
char
*
s1
,
const
char
*
s2
)
{
int
a
[
N
][
N
];
int
len1
=
strlen
(
s1
);
int
len2
=
strlen
(
s2
);
int
i
,
j
;
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
int
)
*
N
*
N
);
int
max
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
len1
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
len2
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
s1
[
i
-
1
]
==
s2
[
j
-
1
])
{
__________________
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
>
max
)
max
=
a
[
i
][
j
];
}
}
}
return
max
;
}
int
main
()
{
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
f
(
"abcdkkk"
,
"baabcdadabc"
));
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
]
+
1
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
];
```
### B
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
1
;
```
### C
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
][
j
-
1
]
+
1
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-260e61bb6bbf44e1a55b0a439e14f7ee"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"振兴中华"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
小明参加了学校的趣味运动会,其中的一个项目是:跳格子。
地上画着一些格子,每个格子里写一个字,如下所示:
```
从我做起振
我做起振兴
做起振兴中
起振兴中华
```
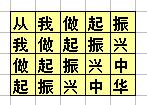
比赛时,先站在左上角的写着“从”字的格子里,可以横向或纵向跳到相邻的格子里,但不能跳到对角的格子或其它位置。一直要跳到“华”字结束。
要求跳过的路线刚好构成“从我做起振兴中华”这句话。
请你帮助小明算一算他一共有多少种可能的跳跃路线呢?
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
a
[
4
][
5
];
int
sum
;
void
dfs
(
int
row
,
int
col
,
int
index
)
{
if
(
a
[
row
][
col
]
==
index
&&
index
==
7
)
sum
++
;
else
{
if
(
row
+
1
<
4
)
dfs
(
row
+
1
,
col
,
index
+
1
);
if
(
col
+
1
<
5
)
dfs
(
row
,
col
+
1
,
index
+
1
);
}
}
int
main
()
{
int
row
,
col
;
for
(
row
=
0
;
row
<
4
;
row
++
)
for
(
col
=
0
;
col
<
5
;
col
++
)
a
[
row
][
col
]
=
row
+
col
;
dfs
(
0
,
0
,
0
);
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"6d38c0f384384c6ea184f94b091f9544"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/9.振兴中华/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 振兴中华
小明参加了学校的趣味运动会,其中的一个项目是:跳格子。
地上画着一些格子,每个格子里写一个字,如下所示:
```
从我做起振
我做起振兴
做起振兴中
起振兴中华
```

比赛时,先站在左上角的写着“从”字的格子里,可以横向或纵向跳到相邻的格子里,但不能跳到对角的格子或其它位置。一直要跳到“华”字结束。
要求跳过的路线刚好构成“从我做起振兴中华”这句话。
请你帮助小明算一算他一共有多少种可能的跳跃路线呢?
以下代码实现了这一功能,请你填补空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
int
f
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
if
(
x
==
3
||
y
==
4
)
return
1
;
__________________
}
int
main
()
{
cout
<<
f
(
0
,
0
)
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
+
1
);
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
-
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
-
1
);
```
### B
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
-
1
);
```
### C
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
+
1
)
+
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
+
1
);
```
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-1402245808fb4c3c962a23d6498eb593"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"幸运数"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
幸运数是波兰数学家乌拉姆命名的。它采用与生成素数类似的“筛法”生成。
首先从1开始写出自然数1,2,3,4,5,6,…
1 就是第一个幸运数。
我们从2这个数开始。把所有序号能被2整除的项删除,变为:
1 _ 3 _ 5 _ 7 _ 9 …
把它们缩紧,重新记序,为:
1 3 5 7 9 … 。
这时,3为第2个幸运数,然后把所有能被3整除的序号位置的数删去。注意,是序号位置,不是那个数本身能否被3整除!! 删除的应该是5,11, 17, …
此时7为第3个幸运数,然后再删去序号位置能被7整除的(19,39,…)
最后剩下的序列类似:
```
1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 15, 21, 25, 31, 33, 37, 43, 49, 51, 63, 67, 69, 73, 75, 79, …
```
#### 输入格式
输入两个正整数m n, 用空格分开 (m < n < 1000
*
1000)
#### 输出格式
程序输出 位于m和n之间的幸运数的个数(不包含m和n)。
#### 样例输入1
```
1 20
```
#### 样例输出1
```
5
```
#### 样例输入2
```
30 69
```
#### 样例输出2
```
8
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
int
a
[
500005
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
k
=
1
;
//k表示a数组大小
int
m
,
n
,
sum
=
0
;
//sum表示幸运数个数
int
temp
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1000000
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
k
++
]
=
i
;
}
temp
=
2
;
//当前幸运数所处的序号位置
while
(
temp
<=
1000
)
{
int
b
[
500005
],
t
=
1
;
//b记录幸运数
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
k
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
%
a
[
temp
]
!=
0
)
//如果序号位置i不能被某一个幸运数整除,则将其存储到b数组
b
[
t
++
]
=
a
[
i
];
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
t
;
i
++
)
a
[
i
]
=
b
[
i
];
temp
++
;
k
=
t
;
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
m
&&
a
[
i
]
<
n
)
//注意幸运数的区间(不包含m和n)
{
sum
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"c204cf8ad83e49e7acea61c70e64926c"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/2.幸运数/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 幸运数
**问题描述**
幸运数是波兰数学家乌拉姆命名的。它采用与生成素数类似的“筛法”生成。
首先从1开始写出自然数1,2,3,4,5,6,…
1 就是第一个幸运数。
我们从2这个数开始。把所有序号能被2整除的项删除,变为:
1 _ 3 _ 5 _ 7 _ 9 …
把它们缩紧,重新记序,为:
1 3 5 7 9 … 。
这时,3为第2个幸运数,然后把所有能被3整除的序号位置的数删去。注意,是序号位置,不是那个数本身能否被3整除!! 删除的应该是5,11, 17, …
此时7为第3个幸运数,然后再删去序号位置能被7整除的(19,39,…)
最后剩下的序列类似:
```
1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 15, 21, 25, 31, 33, 37, 43, 49, 51, 63, 67, 69, 73, 75, 79, …
```
**输入格式**
输入两个正整数m n, 用空格分开 (m < n < 1000
*
1000)
**输出格式**
程序输出 位于m和n之间的幸运数的个数(不包含m和n)。
**样例输入1**
```
1 20
```
**样例输出1**
```
5
```
**样例输入2**
```
30 69
```
**样例输出2**
```
8
```
以下
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的一项是?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
int
m
,
n
;
int
len
=
0
;
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d %d"
,
&
m
,
&
n
);
vector
<
int
>
vc
(
n
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
vc
[
i
]
=
2
*
i
-
1
;
int
divided
=
2
;
len
=
n
;
for
(
int
select
=
1
;;
++
select
)
{
divided
=
vc
[
select
-
1
];
int
num
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
len
;
i
++
)
if
(
i
%
divided
!=
0
)
vc
[
num
++
]
=
vc
[
i
];
len
=
num
;
if
(
vc
[
select
]
>
n
)
break
;
}
int
count
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
vc
[
i
]
>=
n
)
break
;
if
(
vc
[
i
]
<
n
&&
vc
[
i
]
>
m
)
{
++
count
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
count
);
return
0
;
}
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
vector
<
int
>
a
;
a
.
push_back
(
0
);
int
i
,
m
,
n
,
start
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
2
*
i
-
1
>=
n
)
break
;
a
.
push_back
(
2
*
i
-
1
);
}
start
=
2
;
int
k
;
vector
<
int
>
old
;
do
{
old
.
push_back
(
0
);
if
(
start
>
a
.
size
()
-
1
)
break
;
k
=
a
[
start
++
];
if
(
k
>
a
.
size
())
break
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
a
.
size
();
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
%
k
)
old
.
push_back
(
a
[
i
]);
}
a
.
clear
();
a
.
assign
(
old
.
begin
(),
old
.
end
());
old
.
clear
();
}
while
(
true
);
int
sum
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
a
.
size
();
i
++
)
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
m
)
{
sum
=
sum
+
1
;
}
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
### B
```
cpp
int
a
[
500005
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
k
=
1
;
int
m
,
n
,
sum
=
0
;
int
temp
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1000000
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
k
++
]
=
i
;
}
temp
=
2
;
while
(
temp
<=
1000
)
{
int
b
[
500005
],
t
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
k
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
%
a
[
temp
]
!=
0
)
b
[
t
++
]
=
a
[
i
];
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
t
;
i
++
)
a
[
i
]
=
b
[
i
];
temp
++
;
k
=
t
;
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
m
&&
a
[
i
]
<
n
)
{
sum
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
### C
```
cpp
struct
num
{
int
order
;
int
value
;
};
int
main
()
{
int
m
,
n
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
vector
<
num
>
numbers
;
int
count
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
num
tempNum
;
tempNum
.
order
=
count
;
tempNum
.
value
=
i
;
numbers
.
push_back
(
tempNum
);
count
++
;
}
int
index
=
1
,
tempCount
=
1
,
value
=
numbers
[
index
].
value
;
while
(
index
<=
tempCount
)
{
int
j
,
tempValue
=
-
1
;
tempCount
=
1
;
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
j
].
order
!=
-
1
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
j
].
order
%
value
==
0
)
{
numbers
[
j
].
order
=
-
1
;
}
else
{
tempCount
++
;
numbers
[
j
].
order
=
tempCount
;
if
(
tempCount
==
index
+
1
)
{
tempValue
=
numbers
[
j
].
value
;
}
}
}
}
index
++
;
value
=
tempValue
;
}
int
numCount
=
0
;
for
(
int
t
=
0
;
t
<
n
;
t
++
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
t
].
order
!=
-
1
&&
numbers
[
t
].
value
>
m
&&
numbers
[
t
].
value
<
n
)
{
numCount
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
numCount
;
return
0
;
}
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-719cc75a00de4222a1007a86652c72d5"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"小朋友排队"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 题目描述
n 个小朋友站成一排。
现在要把他们按身高从低到高的顺序排列,但是每次只能交换位置相邻的两个小朋友。
每个小朋友都有一个不高兴的程度。
开始的时候,所有小朋友的不高兴程度都是 0。
如果某个小朋友第一次被要求交换,则他的不高兴程度增加 1,如果第二次要求他交换,则他的不高兴程度增加 2(即不高兴程度为 3),依次类推。当要求某个小朋友第 k 次交换时,他的不高兴程度增加 k。
请问,要让所有小朋友按从低到高排队,他们的不高兴程度之和最小是多少。
如果有两个小朋友身高一样,则他们谁站在谁前面是没有关系的。
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n,表示小朋友的个数。
第二行包含 n 个整数 H1,H2,…,Hn,分别表示每个小朋友的身高。
#### 输出格式
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示小朋友的不高兴程度和的最小值。
#### 数据范围
```
1≤n≤100000,
0≤Hi≤1000000
```
#### 输入样例:
```
3
3 2 1
```
#### 输出样例:
```
9
```
#### 样例解释
首先交换身高为3和2的小朋友,再交换身高为3和1的小朋友,再交换身高为2和1的小朋友,每个小朋友的不高兴程度都是3,总和为9。
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
N
=
1e6
+
10
;
int
h
[
N
],
s
[
N
],
tr
[
N
];
//h高,s多少个大于h[i]和小于h[i]的人,tr树状数组
int
n
;
int
lowbit
(
int
x
)
{
return
x
&
-
x
;
}
int
add
(
int
x
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
<
N
;
i
+=
lowbit
(
i
))
tr
[
i
]
++
;
}
//这里不是添加值,支持计算次数,所以自增1
int
q
(
int
x
)
{
int
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
;
i
-=
lowbit
(
i
))
res
+=
tr
[
i
];
return
res
;
}
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
h
[
i
],
h
[
i
]
++
;
//树状数组必须从1开始
s
[
i
]
=
q
(
N
-
1
)
-
q
(
h
[
i
]);
//比i大的数
add
(
h
[
i
]);
}
memset
(
tr
,
0
,
sizeof
tr
);
//tr清零重复使用
for
(
int
i
=
n
-
1
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
s
[
i
]
+=
q
(
h
[
i
]
-
1
),
add
(
h
[
i
]);
//逆序比较//比h[i]小的数
LL
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
res
+=
(
LL
)
s
[
i
]
*
(
s
[
i
]
+
1
)
/
2
;
//公式计算 累加 因为过大所以用LL
cout
<<
res
;
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"9f57f79e642d4087b95544e7e02b0299"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/12.小朋友排队/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 小朋友排队
**题目描述**
n 个小朋友站成一排。
现在要把他们按身高从低到高的顺序排列,但是每次只能交换位置相邻的两个小朋友。
每个小朋友都有一个不高兴的程度。
开始的时候,所有小朋友的不高兴程度都是 0。
如果某个小朋友第一次被要求交换,则他的不高兴程度增加 1,如果第二次要求他交换,则他的不高兴程度增加 2(即不高兴程度为 3),依次类推。当要求某个小朋友第 k 次交换时,他的不高兴程度增加 k。
请问,要让所有小朋友按从低到高排队,他们的不高兴程度之和最小是多少。
如果有两个小朋友身高一样,则他们谁站在谁前面是没有关系的。
**输入格式**
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n,表示小朋友的个数。
第二行包含 n 个整数 H1,H2,…,Hn,分别表示每个小朋友的身高。
**输出格式**
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示小朋友的不高兴程度和的最小值。
**数据范围**
```
1≤n≤100000,
0≤Hi≤1000000
```
**输入样例:**
```
3
3 2 1
```
**输出样例:**
```
9
```
**样例解释**
首先交换身高为3和2的小朋友,再交换身高为3和1的小朋友,再交换身高为2和1的小朋友,每个小朋友的不高兴程度都是3,总和为9。
以下
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的一项是?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
#define ll long long
using
namespace
std
;
int
const
MAX
=
1e5
+
5
;
ll
cnt
[
MAX
],
ans
;
int
n
;
struct
DATA
{
int
idx
;
ll
num
;
}
d
[
MAX
];
bool
cmp
(
DATA
a
,
DATA
b
)
{
return
a
.
num
<
b
.
num
;
}
void
Solve
(
int
l
,
int
mid
,
int
r
)
{
int
i
=
l
,
j
=
mid
+
1
;
while
(
i
<=
mid
&&
j
<=
r
)
{
if
(
d
[
i
].
num
<=
d
[
j
].
num
)
i
++
;
else
{
cnt
[
d
[
j
].
idx
]
+=
(
ll
)(
mid
-
i
+
1
);
j
++
;
}
}
i
=
mid
,
j
=
r
;
while
(
i
>=
l
&&
j
>=
mid
+
1
)
{
if
(
d
[
i
].
num
>
d
[
j
].
num
)
{
cnt
[
d
[
i
].
idx
]
+=
(
ll
)(
j
-
mid
);
i
--
;
}
else
j
--
;
}
sort
(
d
+
l
,
d
+
r
+
1
,
cmp
);
return
;
}
void
Div
(
int
l
,
int
r
)
{
if
(
l
>=
r
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
l
+
r
)
>>
1
;
Div
(
l
,
mid
);
Div
(
mid
+
1
,
r
);
Solve
(
l
,
mid
,
r
);
}
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
d
[
i
].
num
);
d
[
i
].
idx
=
i
;
}
ans
=
0
;
Div
(
0
,
n
-
1
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
ans
+=
cnt
[
i
]
*
cnt
[
i
]
/
2
;
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
ans
);
}
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
N
=
1e6
+
10
;
int
h
[
N
],
s
[
N
],
tr
[
N
];
int
n
;
int
lowbit
(
int
x
)
{
return
x
&
-
x
;
}
int
add
(
int
x
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
<
N
;
i
+=
lowbit
(
i
))
tr
[
i
]
++
;
}
int
q
(
int
x
)
{
int
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
;
i
-=
lowbit
(
i
))
res
+=
tr
[
i
];
return
res
;
}
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
h
[
i
],
h
[
i
]
++
;
s
[
i
]
=
q
(
N
-
1
)
-
q
(
h
[
i
]);
add
(
h
[
i
]);
}
memset
(
tr
,
0
,
sizeof
tr
);
for
(
int
i
=
n
-
1
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
s
[
i
]
+=
q
(
h
[
i
]
-
1
),
add
(
h
[
i
]);
LL
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
res
+=
(
LL
)
s
[
i
]
*
(
s
[
i
]
+
1
)
/
2
;
cout
<<
res
;
return
0
;
}
```
### B
```
cpp
struct
childInfo
{
int
location
;
int
valueNum
;
};
int
cnt
[
100005
];
void
Merge_sort1
(
vector
<
childInfo
>
&
tempChild
,
int
left
,
int
right
)
{
if
(
left
>=
right
-
1
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
left
+
right
)
/
2
;
Merge_sort1
(
tempChild
,
left
,
mid
);
Merge_sort1
(
tempChild
,
mid
,
right
);
int
i
=
left
,
j
=
mid
,
t
=
0
;
childInfo
*
temp
=
new
childInfo
[
right
-
left
];
while
(
i
<
mid
||
j
<
right
)
{
if
(
j
>=
right
||
i
<
mid
&&
tempChild
[
i
].
valueNum
<=
tempChild
[
j
].
valueNum
)
temp
[
t
++
]
=
tempChild
[
i
++
];
else
{
cnt
[
tempChild
[
j
].
location
]
+=
mid
-
i
;
temp
[
t
++
]
=
tempChild
[
j
++
];
}
}
t
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
left
;
k
<
right
;
k
++
)
tempChild
[
k
]
=
temp
[
t
++
];
delete
[]
temp
;
}
void
Merge_sort2
(
vector
<
childInfo
>
&
tempChild
,
int
left
,
int
right
)
{
if
(
left
>=
right
-
1
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
left
+
right
)
/
2
;
Merge_sort2
(
tempChild
,
left
,
mid
);
Merge_sort2
(
tempChild
,
mid
,
right
);
childInfo
*
temp
=
new
childInfo
[
right
-
left
];
int
i
=
mid
-
1
,
j
=
right
-
1
,
t
=
right
-
left
-
1
;
while
(
i
>=
left
||
j
>=
mid
)
{
if
(
i
<
left
||
j
>=
mid
&&
tempChild
[
i
].
valueNum
<=
tempChild
[
j
].
valueNum
)
temp
[
t
--
]
=
tempChild
[
j
--
];
else
{
cnt
[
tempChild
[
i
].
location
]
+=
j
-
mid
+
1
;
temp
[
t
--
]
=
tempChild
[
i
--
];
}
}
t
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
left
;
i
<
right
;
i
++
)
tempChild
[
i
]
=
temp
[
t
++
];
delete
[]
temp
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
childInfo
tempChild
;
tempChild
.
location
=
i
;
cin
>>
tempChild
.
valueNum
;
childLists
.
push_back
(
tempChild
);
}
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists1
(
childLists
.
begin
(),
childLists
.
end
());
Merge_sort1
(
childLists
,
0
,
childLists
.
size
());
Merge_sort2
(
childLists1
,
0
,
childLists1
.
size
());
long
long
sum
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
childLists
.
size
();
i
++
)
sum
+=
1ll
*
(
1
+
cnt
[
i
])
*
cnt
[
i
]
/
2
;
cout
<<
sum
;
return
0
;
}
```
### C
```
cpp
struct
childInfo
{
int
location
;
int
valueNum
;
};
bool
lowCompare
(
childInfo
temp1
,
childInfo
temp2
)
{
return
temp1
.
valueNum
>
temp2
.
valueNum
;
}
bool
upCompare
(
childInfo
temp1
,
childInfo
temp2
)
{
return
temp1
.
valueNum
<
temp2
.
valueNum
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
childNums
;
cin
>>
childNums
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists1
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists2
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
childNums
;
i
++
)
{
childInfo
tempInfo
;
tempInfo
.
location
=
i
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
tempInfo
.
valueNum
);
childLists
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
childLists1
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
childLists2
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
}
sort
(
childLists1
.
begin
(),
childLists1
.
end
(),
lowCompare
);
sort
(
childLists2
.
begin
(),
childLists2
.
end
(),
upCompare
);
long
long
int
count
=
0
;
for
(
int
m
=
0
;
m
<
childNums
;
m
++
)
{
int
sadNum
=
0
;
long
long
int
count1
=
0
,
count2
=
0
;
int
compareNum
=
childLists
[
m
].
valueNum
,
compareLoc
=
childLists
[
m
].
location
;
for
(
int
n
=
0
;
n
<
childNums
;
n
++
)
{
if
(
compareNum
<
childLists1
[
n
].
valueNum
)
{
if
(
compareLoc
>
childLists1
[
n
].
location
)
{
sadNum
++
;
count1
+=
sadNum
;
}
}
else
{
break
;
}
}
for
(
int
n
=
0
;
n
<
childNums
;
n
++
)
{
if
(
compareNum
>
childLists2
[
n
].
valueNum
)
{
if
(
compareLoc
<
childLists2
[
n
].
location
)
{
sadNum
++
;
count2
+=
sadNum
;
}
}
else
{
break
;
}
}
count
+=
count1
+
count2
;
}
cout
<<
count
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-c9f679acc8a84a21aa6a4fbd0638df41"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"灵能传输"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 题目背景
在游戏《星际争霸 II》中,高阶圣堂武士作为星灵的重要 AOE 单位,在游戏的中后期发挥着重要的作用,其技能”灵能风暴“可以消耗大量的灵能对一片区域内的敌军造成毁灭性的伤害。经常用于对抗人类的生化部队和虫族的
刺蛇飞龙等低血量单位。
#### 问题描述
你控制着 n 名高阶圣堂武士,方便起见标为 1,2,··· ,n。每名高阶圣堂武士需要一定的灵能来战斗,每个人有一个灵能值$a_i$表示其拥有的灵能的多少($a_i$非负表示这名高阶圣堂武士比在最佳状态下多余了$a_i$点灵能,$a_i$为负则表示这名高阶圣堂武士还需要$-a_i$点灵能才能到达最佳战斗状态) 。现在系统赋予了你的高阶圣堂武士一个能力,传递灵能,每次你可以选择一个$ i ∈ [2,n − 1]$,若$a_i ≥ 0 $则其两旁的高阶圣堂武士,也就是$ i − 1、i + 1 $这两名高阶圣堂武士会从i 这名高阶圣堂武士这里各抽取$ a_i $点灵能;若$ a_i < 0 $则其两旁的高阶圣堂武士,也就是$ i−1,i+1 $这两名高阶圣堂武士会给 i 这名高阶圣堂武士$ −a_i $点灵能。形式化来讲就是$ a_{i-1} + = a_i ,a_{i+1} + = a_i ,a_i − = 2a_i $。
灵能是非常高效的作战工具,同时也非常危险且不稳定,一位高阶圣堂武士拥有的灵能过多或者过少都不好,定义一组高阶圣堂武士的不稳定度为$max^n_{i=1} |a_i|$,请你通过不限次数的传递灵能操作使得你控制的这一组高阶圣堂武士的不稳定度最小。
#### 输入格式
本题包含多组询问。输入的第一行包含一个正整数 T 表示询问组数。
接下来依次输入每一组询问。
每组询问的第一行包含一个正整数 n,表示高阶圣堂武士的数量。
接下来一行包含 n 个数 $a_1 ,a_2 ,··· ,a_n $。
#### 输出格式
输出 T 行。每行一个整数依次表示每组询问的答案。
#### 样例输入
```
3
3
5 -2 3
4
0 0 0 0
3
1 2 3
```
#### 样例输出
```
3
0
3
```
#### 样例说明
```
对于第一组询问:
对 2 号高阶圣堂武士进行传输操作后 a 1 = 3,a 2 = 2,a 3 = 1。答案为 3。
对于第二组询问:
这一组高阶圣堂武士拥有的灵能都正好可以让他们达到最佳战斗状态。
```
#### 样例输入
```
3
4
-1 -2 -3 7
4
2 3 4 -8
5
-1 -1 6 -1 -1
```
#### 样例输出
```
5
7
4
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
N
=
300010
;
int
n
;
LL
sum
[
N
],
a
[
N
],
s0
,
sn
;
bool
st
[
N
];
int
main
()
{
int
T
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
T
);
while
(
T
--
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
sum
[
0
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
sum
[
i
]);
sum
[
i
]
+=
sum
[
i
-
1
];
}
s0
=
sum
[
0
],
sn
=
sum
[
n
];
if
(
s0
>
sn
)
swap
(
s0
,
sn
);
sort
(
sum
,
sum
+
n
+
1
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
if
(
s0
==
sum
[
i
])
{
s0
=
i
;
break
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
n
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
if
(
sn
==
sum
[
i
])
{
sn
=
i
;
break
;
}
memset
(
st
,
0
,
sizeof
st
);
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
s0
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
{
a
[
l
++
]
=
sum
[
i
];
st
[
i
]
=
true
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
sn
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
r
--
]
=
sum
[
i
];
st
[
i
]
=
true
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
if
(
!
st
[
i
])
{
a
[
l
++
]
=
sum
[
i
];
}
LL
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
res
=
max
(
res
,
abs
(
a
[
i
]
-
a
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
res
);
}
return
0
;
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"a7672a561bd14ce5ba8bca21c4074683"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/13.灵能传输/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 灵能传输
**题目背景**
在游戏《星际争霸 II》中,高阶圣堂武士作为星灵的重要 AOE 单位,在游戏的中后期发挥着重要的作用,其技能”灵能风暴“可以消耗大量的灵能对一片区域内的敌军造成毁灭性的伤害。经常用于对抗人类的生化部队和虫族的
刺蛇飞龙等低血量单位。
**问题描述**
你控制着 n 名高阶圣堂武士,方便起见标为 1,2,··· ,n。每名高阶圣堂武士需要一定的灵能来战斗,每个人有一个灵能值$a_i$表示其拥有的灵能的多少($a_i$非负表示这名高阶圣堂武士比在最佳状态下多余了$a_i$点灵能,$a_i$为负则表示这名高阶圣堂武士还需要$-a_i$点灵能才能到达最佳战斗状态) 。现在系统赋予了你的高阶圣堂武士一个能力,传递灵能,每次你可以选择一个$ i ∈ [2,n − 1]$,若$a_i ≥ 0 $则其两旁的高阶圣堂武士,也就是$ i − 1、i + 1 $这两名高阶圣堂武士会从i 这名高阶圣堂武士这里各抽取$ a_i $点灵能;若$ a_i < 0 $则其两旁的高阶圣堂武士,也就是$ i−1,i+1 $这两名高阶圣堂武士会给 i 这名高阶圣堂武士$ −a_i $点灵能。形式化来讲就是$ a_{i-1} + = a_i ,a_{i+1} + = a_i ,a_i − = 2a_i $。
灵能是非常高效的作战工具,同时也非常危险且不稳定,一位高阶圣堂武士拥有的灵能过多或者过少都不好,定义一组高阶圣堂武士的不稳定度为$max^n_{i=1} |a_i|$,请你通过不限次数的传递灵能操作使得你控制的这一组高阶圣堂武士的不稳定度最小。
**输入格式**
本题包含多组询问。输入的第一行包含一个正整数 T 表示询问组数。
接下来依次输入每一组询问。
每组询问的第一行包含一个正整数 n,表示高阶圣堂武士的数量。
接下来一行包含 n 个数 $a_1 ,a_2 ,··· ,a_n $。
**输出格式**
输出 T 行。每行一个整数依次表示每组询问的答案。
**样例输入**
```
3
3
5 -2 3
4
0 0 0 0
3
1 2 3
```
**样例输出**
```
3
0
3
```
**样例说明**
```
对于第一组询问:
对 2 号高阶圣堂武士进行传输操作后 a 1 = 3,a 2 = 2,a 3 = 1。答案为 3。
对于第二组询问:
这一组高阶圣堂武士拥有的灵能都正好可以让他们达到最佳战斗状态。
```
**样例输入**
```
3
4
-1 -2 -3 7
4
2 3 4 -8
5
-1 -1 6 -1 -1
```
**样例输出**
```
5
7
4
```
以下选项
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的是?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
ll
;
#define int ll
#define rep(i, a, n) for (int i = a; i < (int)n; i++)
#define per(i, a, n) for (int i = (int)n - 1; i >= a; i--)
const
int
maxn
=
3e5
+
10
;
inline
int
read
()
{
int
x
=
0
,
f
=
1
;
char
ch
=
getchar
();
while
(
!
isdigit
(
ch
))
{
if
(
ch
==
'-'
)
f
=
-
1
;
ch
=
getchar
();
}
while
(
isdigit
(
ch
))
{
x
=
(
x
<<
3
)
+
(
x
<<
1
)
+
ch
-
48
;
ch
=
getchar
();
}
return
x
*
f
;
}
int
s
[
maxn
],
a
[
maxn
];
bool
vis
[
maxn
];
inline
void
cf
()
{
int
t
=
read
();
while
(
t
--
)
{
int
n
=
read
();
s
[
0
]
=
0
;
rep
(
i
,
1
,
n
+
1
)
{
int
x
=
read
();
s
[
i
]
=
s
[
i
+
1
]
+
x
;
}
int
s0
=
0
,
sn
=
s
[
n
];
if
(
s0
>
sn
)
swap
(
s0
,
sn
);
sort
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
);
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
s
[
i
]
==
s0
)
{
s0
=
i
;
break
;
}
per
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
s
[
i
]
==
sn
)
{
sn
=
i
;
break
;
}
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
vis
[
i
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
s0
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
sn
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
a
[
r
--
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
];
int
ans
=
0
;
rep
(
i
,
1
,
n
+
1
)
ans
=
max
(
ans
,
abs
(
a
[
i
]
-
a
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
ans
);
}
return
;
}
signed
main
()
{
cf
();
return
0
;
}
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
#define ll long long
const
int
N
=
3e5
;
ll
a
[
N
],
s
[
N
];
bool
vis
[
N
];
int
n
;
int
main
()
{
int
T
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
T
);
while
(
T
--
)
{
memset
(
vis
,
0
,
sizeof
(
vis
));
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
s
[
0
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
s
[
i
]);
s
[
i
]
+=
s
[
i
-
1
];
}
ll
s0
=
0
,
sn
=
s
[
n
];
if
(
s0
>
sn
)
swap
(
s0
,
sn
);
sort
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
);
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
lower_bound
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
,
s0
)
-
s
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
{
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
lower_bound
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
,
sn
)
-
s
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
r
--
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
{
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
];
}
ll
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
res
=
max
(
res
,
abs
(
a
[
i
]
-
a
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
res
);
}
return
0
;
}
```
### B
```
cpp
const
int
MAXN
=
300010
;
int
nums
[
MAXN
];
bool
judgeYi
(
int
a
,
int
b
)
{
return
a
>
0
&&
b
<
0
||
a
<
0
&&
b
>
0
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
T
,
n
;
cin
>>
T
;
while
(
T
--
)
{
cin
>>
n
;
bool
hasNe
=
false
,
hasPo
=
false
;
int
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
nums
[
i
]);
if
(
nums
[
i
]
<
0
)
{
hasNe
=
true
;
}
else
if
(
nums
[
i
]
>
0
)
{
hasPo
=
true
;
}
}
if
(
hasNe
&&
hasPo
)
{
bool
canNext
;
do
{
canNext
=
false
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
-
1
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
],
nums
[
i
-
1
])
||
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
(
nums
[
i
]
>
0
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
-
1
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
((
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
0
&&
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
])
>
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+
nums
[
i
])
||
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
0
&&
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
])
>
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+
nums
[
i
]))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
else
{
if
(
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
])
>
nums
[
i
]
||
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
])
>
nums
[
i
])
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
}
else
if
(
nums
[
i
]
<
0
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
-
1
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
((
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
0
&&
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+
nums
[
i
]))
||
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
0
&&
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+
nums
[
i
])))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
else
{
if
(
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
])
||
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
]))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
}
}
}
}
while
(
canNext
);
}
int
t
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
res
=
max
(
res
,
abs
(
nums
[
i
]));
}
cout
<<
res
<<
endl
;
}
return
0
;
}
```
### C
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
INF
=
0x3f3f3f3f
;
const
double
Pi
=
acos
(
-
1
);
namespace
{
template
<
typename
T
>
inline
void
read
(
T
&
x
)
{
x
=
0
;
T
f
=
1
;
char
s
=
getchar
();
for
(;
!
isdigit
(
s
);
s
=
getchar
())
if
(
s
==
'-'
)
f
=
-
1
;
for
(;
isdigit
(
s
);
s
=
getchar
())
x
=
(
x
<<
3
)
+
(
x
<<
1
)
+
(
s
^
48
);
x
*=
f
;
}
}
#define fio \
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); \
cin.tie(0); \
cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define _srep(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i >= (m); i--)
#define _sfor(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i > (m); i--)
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define lowbit(x) x &(-x)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define fi first
#define se second
const
int
N
=
1e6
+
5
;
LL
a
[
N
];
LL
ans
[
N
];
bool
vis
[
N
];
LL
Abs
(
LL
x
)
{
return
x
<
0
?
-
x
:
x
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
t
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
t
);
while
(
t
--
)
{
int
n
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
a
[
0
]
=
0
;
_rep
(
1
,
n
,
i
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
a
+
i
);
a
[
i
]
+=
a
[
i
-
1
];
}
LL
a0
=
0
,
an
=
a
[
n
],
Max
=
0
;
int
A0
,
AN
;
sort
(
a
,
a
+
n
+
1
);
memset
(
vis
,
0
,
sizeof
vis
);
if
(
a0
>
an
)
swap
(
a0
,
an
);
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
a0
==
a
[
i
])
{
A0
=
i
;
break
;
}
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
an
==
a
[
i
])
{
AN
=
i
;
break
;
}
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
A0
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
ans
[
l
++
]
=
a
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
AN
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
ans
[
r
--
]
=
a
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
ans
[
l
++
]
=
a
[
i
];
_rep
(
1
,
n
,
i
)
Max
=
max
(
Max
,
Abs
(
ans
[
i
]
-
ans
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
Max
);
}
}
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-1eaf5bb9038240d29dfa4596f55e66d6"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"压缩变换"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
小明最近在研究压缩算法。
他知道,压缩的时候如果能够使得数值很小,就能通过熵编码得到较高的压缩比。
然而,要使数值很小是一个挑战。
最近,小明需要压缩一些正整数的序列,这些序列的特点是,后面出现的数字很大可能是刚出现过不久的数字。对于这种特殊的序列,小明准备对序列做一个变换来减小数字的值。
变换的过程如下:
从左到右枚举序列,每枚举到一个数字,如果这个数字没有出现过,刚将数字变换成它的相反数,如果数字出现过,则看它在原序列中最后的一次出现后面(且在当前数前面)出现了几种数字,用这个种类数替换原来的数字。
比如,序列(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5)=(1, 2, 2, 1, 2)在变换过程为:
a1: 1未出现过,所以a1变为-1;
a2: 2未出现过,所以a2变为-2;
a3: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a2,在a2后、a3前有0种数字,所以a3变为0;
a4: 1出现过,最后一次为原序列的a1,在a1后、a4前有1种数字,所以a4变为1;
a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字,所以a5变为1。
现在,给出原序列,请问,按这种变换规则变换后的序列是什么。
#### 输入
输入第一行包含一个整数n,表示序列的长度。
第二行包含n个正整数,表示输入序列。
#### 输出
输出一行,包含n个数,表示变换后的序列。
#### 输入例子 1
```
5
1 2 2 1 2
```
#### 输出例子 1
```
-1 -2 0 1 1
```
#### 输入例子 2
```
12
```
#### 输出例子 2
```
-1 0 -2 -3 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
maxn
=
1e6
+
5
;
int
a
[
maxn
],
tree
[
maxn
<<
2
];
// 假设层数 M = log 2 (n - 1), 树节点数就要开2倍了
// 循环中遍历最后一个结点的的子节点(虽然不存在) 需要 2n * 2的数组大小
int
n
,
maxpoint
;
void
init
()
{
maxpoint
=
1
;
while
(
maxpoint
<
n
)
maxpoint
<<=
1
;
//比最后一个结点大的2的倍数个结点
memset
(
tree
,
0
,
sizeof
(
tree
));
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
a
));
}
void
update
(
int
k
,
int
addnum
)
{
// addnum 在出现前边时更新所有子节点 + 1, 出现后边时 所有子节点都 - 1
k
+=
maxpoint
-
1
;
// 每个节点都当作根节点一样遍历子节点
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
while
(
k
)
{
k
=
(
k
-
1
)
>>
1
;
// 访问父节点直到根结点
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
}
}
int
query
(
int
a
,
int
b
,
int
k
,
int
l
,
int
r
)
{
if
(
a
==
b
||
(
r
<=
a
||
l
>=
b
))
return
0
;
// 不符合查询条件 返回 0
if
(
a
<=
l
&&
r
<=
b
)
return
tree
[
k
];
// 子区域就直接返回
else
{
int
mid
=
(
l
+
r
)
>>
1
;
return
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
<<
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
<<
1
,
mid
,
r
);
}
}
int
main
()
{
int
temp
;
map
<
int
,
int
>
mp
;
cin
>>
n
;
init
();
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
temp
;
if
(
mp
.
count
(
temp
))
{
int
pre
=
mp
[
temp
];
a
[
i
]
=
query
(
pre
+
1
,
i
,
0
,
0
,
maxpoint
);
update
(
pre
,
-
1
);
}
else
{
a
[
i
]
=
-
temp
;
}
mp
[
temp
]
=
i
;
update
(
i
,
1
);
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
cout
<<
a
[
i
]
<<
" "
;
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"937e94612cba4743b2dcf248fc21a179"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.压缩变换/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 压缩变换
**问题描述**
小明最近在研究压缩算法。
他知道,压缩的时候如果能够使得数值很小,就能通过熵编码得到较高的压缩比。
然而,要使数值很小是一个挑战。
最近,小明需要压缩一些正整数的序列,这些序列的特点是,后面出现的数字很大可能是刚出现过不久的数字。对于这种特殊的序列,小明准备对序列做一个变换来减小数字的值。
变换的过程如下:
从左到右枚举序列,每枚举到一个数字,如果这个数字没有出现过,刚将数字变换成它的相反数,如果数字出现过,则看它在原序列中最后的一次出现后面(且在当前数前面)出现了几种数字,用这个种类数替换原来的数字。
比如,序列(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5)=(1, 2, 2, 1, 2)在变换过程为:
a1: 1未出现过,所以a1变为-1;
a2: 2未出现过,所以a2变为-2;
a3: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a2,在a2后、a3前有0种数字,所以a3变为0;
a4: 1出现过,最后一次为原序列的a1,在a1后、a4前有1种数字,所以a4变为1;
a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字,所以a5变为1。
现在,给出原序列,请问,按这种变换规则变换后的序列是什么。
**输入**
输入第一行包含一个整数n,表示序列的长度。
第二行包含n个正整数,表示输入序列。
**输出**
输出一行,包含n个数,表示变换后的序列。
**输入例子 1**
```
5
1 2 2 1 2
```
**输出例子 1**
```
-1 -2 0 1 1
```
**输入例子 2**
```
12
```
**输出例子 2**
```
-1 0 -2 -3 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
maxn
=
1e6
+
5
;
int
a
[
maxn
],
tree
[
maxn
<<
2
];
int
n
,
maxpoint
;
void
init
()
{
maxpoint
=
1
;
while
(
maxpoint
<
n
)
maxpoint
<<=
1
;
memset
(
tree
,
0
,
sizeof
(
tree
));
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
a
));
}
void
update
(
int
k
,
int
addnum
)
{
k
+=
maxpoint
-
1
;
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
while
(
k
)
{
k
=
(
k
-
1
)
>>
1
;
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
}
}
int
query
(
int
a
,
int
b
,
int
k
,
int
l
,
int
r
)
{
if
(
a
==
b
||
(
r
<=
a
||
l
>=
b
))
return
0
;
if
(
a
<=
l
&&
r
<=
b
)
return
tree
[
k
];
else
{
int
mid
=
(
l
+
r
)
>>
1
;
return
__________________
;
}
}
int
main
()
{
int
temp
;
map
<
int
,
int
>
mp
;
cin
>>
n
;
init
();
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
temp
;
if
(
mp
.
count
(
temp
))
{
int
pre
=
mp
[
temp
];
a
[
i
]
=
query
(
pre
+
1
,
i
,
0
,
0
,
maxpoint
);
update
(
pre
,
-
1
);
}
else
{
a
[
i
]
=
-
temp
;
}
mp
[
temp
]
=
i
;
update
(
i
,
1
);
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
cout
<<
a
[
i
]
<<
" "
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
<<
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
<<
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
>>
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
>>
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
### B
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
k
<<
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
k
<<
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
### C
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
<<
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
>>
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-627cd47f835d4067a9c95c0b8f982470"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"明码"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
汉字的字形存在于字库中,即便在今天,16点阵的字库也仍然使用广泛。
16点阵的字库把每个汉字看成是16x16个像素信息。并把这些信息记录在字节中。
一个字节可以存储8位信息,用32个字节就可以存一个汉字的字形了。
把每个字节转为2进制表示,1表示墨迹,0表示底色。
每行2个字节,一共16行,布局是:
第1字节,第2字节
第3字节,第4字节
…
第31字节, 第32字节
这道题目是给你一段多个汉字组成的信息,每个汉字用32个字节表示,这里给出了字节作为有符号整数的值。
题目的要求隐藏在这些信息中。你的任务是复原这些汉字的字形,从中看出题目的要求,并根据要求填写答案。
这段信息是(一共10个汉字):
```
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
16 64 16 64 34 68 127 126 66 -124 67 4 66 4 66 -124 126 100 66 36 66 4 66 4 66 4 126 4 66 40 0 16
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
0 -128 64 -128 48 -128 17 8 1 -4 2 8 8 80 16 64 32 64 -32 64 32 -96 32 -96 33 16 34 8 36 14 40 4
4 0 3 0 1 0 0 4 -1 -2 4 0 4 16 7 -8 4 16 4 16 4 16 8 16 8 16 16 16 32 -96 64 64
16 64 20 72 62 -4 73 32 5 16 1 0 63 -8 1 0 -1 -2 0 64 0 80 63 -8 8 64 4 64 1 64 0 -128
0 16 63 -8 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 4 -1 -2 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 5 0 2 0
2 0 2 0 7 -16 8 32 24 64 37 -128 2 -128 12 -128 113 -4 2 8 12 16 18 32 33 -64 1 0 14 0 112 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 9 32 9 16 17 12 17 4 33 16 65 16 1 32 1 64 0 -128 1 0 2 0 12 0 112 0
0 0 0 0 7 -16 24 24 48 12 56 12 0 56 0 -32 0 -64 0 -128 0 0 0 0 1 -128 3 -64 1 -128 0 0
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <bits/stdc++.h> //万能头文件
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
15
;
void
code
(
int
x
)
{
int
std
[
N
],
flag
=
0
;
if
(
x
<
0
)
flag
=
1
,
x
=
-
x
;
//小于0求其绝对值
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
8
;
++
i
)
{
//转换2进制
std
[
i
]
=
x
%
2
;
x
/=
2
;
}
if
(
flag
)
// 如果是负数要求补码
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
8
;
++
i
)
//对8位二进制遍历
if
(
std
[
i
]
==
1
&&
i
<
7
)
{
//找到不为0的第一位
for
(
int
j
=
i
+
1
;
j
<
8
;
++
j
)
std
[
j
]
=
1
-
std
[
j
];
//从第不为零的一位开始取反
break
;
//跳出第一重for循环
}
for
(
int
i
=
7
;
i
>=
0
;
--
i
)
{
//逆序输出
if
(
std
[
i
]
==
0
)
printf
(
" "
);
//0输出空格
else
printf
(
"*"
);
//1输出*
}
}
int
main
()
{
int
i
=
10
;
while
(
i
--
)
{
//对10行数码遍历
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<
17
;
++
j
)
{
//一行32个数,每次读取两个,所以循环16次
int
p
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
p
);
code
(
p
);
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
p
);
code
(
p
);
printf
(
"
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"
\n\n\n
"
);
//输出完成一个字后换行
}
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"4b3866651eef41919f698e1adb5bea18"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/15.明码/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 明码
汉字的字形存在于字库中,即便在今天,16点阵的字库也仍然使用广泛。
16点阵的字库把每个汉字看成是16x16个像素信息。并把这些信息记录在字节中。
一个字节可以存储8位信息,用32个字节就可以存一个汉字的字形了。
把每个字节转为2进制表示,1表示墨迹,0表示底色。
每行2个字节,一共16行,布局是:
第1字节,第2字节
第3字节,第4字节
…
第31字节, 第32字节
这道题目是给你一段多个汉字组成的信息,每个汉字用32个字节表示,这里给出了字节作为有符号整数的值。
题目的要求隐藏在这些信息中。你的任务是复原这些汉字的字形,从中看出题目的要求,并根据要求填写答案。
这段信息是(一共10个汉字):
```
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
16 64 16 64 34 68 127 126 66 -124 67 4 66 4 66 -124 126 100 66 36 66 4 66 4 66 4 126 4 66 40 0 16
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
0 -128 64 -128 48 -128 17 8 1 -4 2 8 8 80 16 64 32 64 -32 64 32 -96 32 -96 33 16 34 8 36 14 40 4
4 0 3 0 1 0 0 4 -1 -2 4 0 4 16 7 -8 4 16 4 16 4 16 8 16 8 16 16 16 32 -96 64 64
16 64 20 72 62 -4 73 32 5 16 1 0 63 -8 1 0 -1 -2 0 64 0 80 63 -8 8 64 4 64 1 64 0 -128
0 16 63 -8 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 4 -1 -2 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 5 0 2 0
2 0 2 0 7 -16 8 32 24 64 37 -128 2 -128 12 -128 113 -4 2 8 12 16 18 32 33 -64 1 0 14 0 112 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 9 32 9 16 17 12 17 4 33 16 65 16 1 32 1 64 0 -128 1 0 2 0 12 0 112 0
0 0 0 0 7 -16 24 24 48 12 56 12 0 56 0 -32 0 -64 0 -128 0 0 0 0 1 -128 3 -64 1 -128 0 0
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
387420489
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
10000000000
```
### B
```
cpp
16777216
```
### C
```
cpp
43046721
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-dfa89f3b35aa42cf86e0ad71d43060fe"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"三体攻击"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 题目描述
三体人将对地球发起攻击。为了抵御攻击,地球人派出了 A × B × C 艘战舰,在太空中排成一个 A 层 B 行 C 列的立方体。其中,第 i 层第 j 行第 k 列的战舰(记为战舰 (i, j, k))的生命值为 d(i, j, k)。
三体人将会对地球发起 m 轮“立方体攻击”,每次攻击会对一个小立方体中的所有战舰都造成相同的伤害。具体地,第 t 轮攻击用 7 个参数 $la_t, ra_t, lb_t, rb_t, lc_t, rc_t, h_t $描述;
所有满足$ i ∈ [la_t, ra_t],j ∈ [lb_t, rb_t],k ∈ [lc_t, rc_t] $的战舰 (i, j, k) 会受到 $h_t$ 的伤害。如果一个战舰累计受到的总伤害超过其防御力,那么这个战舰会爆炸。
地球指挥官希望你能告诉他,第一艘爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。
#### 输入格式
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 4 个正整数 A, B, C, m;
第二行包含 A × B × C 个整数,其中第 ((i − 1)×B + (j − 1)) × C + (k − 1)+1 个数为 d(i, j, k);
第 3 到第 m + 2 行中,第 (t − 2) 行包含 7 个正整数 $la_t, ra_t, lb_t, rb_t, lc_t, rc_t, h_t$。
#### 输出格式
输出到标准输出。
输出第一个爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。保证一定存在这样的战舰。
#### 样例输入
```
2 2 2 3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 2 1 2 1 1 1
1 1 1 2 1 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 2
```
#### 样例输出
```
2
```
#### 样例解释
在第 2 轮攻击后,战舰 (1,1,1) 总共受到了 2 点伤害,超出其防御力导致爆炸。
#### 数据约定
```
对于 10% 的数据,B = C = 1;
对于 20% 的数据,C = 1;
对于 40% 的数据,A × B × C, m ≤ 10, 000;
对于 70% 的数据,A, B, C ≤ 200;
对于所有数据,A × B × C ≤ 10^6, m ≤ 10^6, 0 ≤ d(i, j, k), ht ≤ 10^9。
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
2000010
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
int
A
,
B
,
C
,
m
;
LL
s
[
N
],
b
[
N
],
bp
[
N
];
int
op
[
N
/
2
][
7
];
const
int
d
[
8
][
4
]
=
{
{
0
,
0
,
0
,
1
},
{
0
,
0
,
1
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
0
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
1
,
-
1
}};
int
get
(
int
i
,
int
j
,
int
k
)
{
return
(
i
*
B
+
j
)
*
C
+
k
;
}
bool
check
(
int
mid
)
{
memcpy
(
b
,
bp
,
sizeof
bp
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
mid
;
i
++
)
{
int
x1
=
op
[
i
][
0
],
x2
=
op
[
i
][
1
],
y1
=
op
[
i
][
2
],
y2
=
op
[
i
][
3
],
z1
=
op
[
i
][
4
],
z2
=
op
[
i
][
5
],
h
=
op
[
i
][
6
];
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
}
memset
(
s
,
0
,
sizeof
s
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
{
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
b
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)];
for
(
int
u
=
1
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
-=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
}
if
(
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
<
0
)
return
true
;
}
return
false
;
}
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d%d%d%d"
,
&
A
,
&
B
,
&
C
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
for
(
int
u
=
0
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
+=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
m
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
7
;
j
++
)
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
op
[
i
][
j
]);
int
l
=
1
,
r
=
m
;
while
(
l
<
r
)
{
int
mid
=
l
+
r
>>
1
;
if
(
check
(
mid
))
r
=
mid
;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
r
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"4db03bcefa5649d19f4dd5fe293221ab"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/16.三体攻击/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 三体攻击
**题目描述**
三体人将对地球发起攻击。为了抵御攻击,地球人派出了 A × B × C 艘战舰,在太空中排成一个 A 层 B 行 C 列的立方体。其中,第 i 层第 j 行第 k 列的战舰(记为战舰 (i, j, k))的生命值为 d(i, j, k)。
三体人将会对地球发起 m 轮“立方体攻击”,每次攻击会对一个小立方体中的所有战舰都造成相同的伤害。具体地,第 t 轮攻击用 7 个参数 $la_t, ra_t, lb_t, rb_t, lc_t, rc_t, h_t $描述;
所有满足$ i ∈ [la_t, ra_t],j ∈ [lb_t, rb_t],k ∈ [lc_t, rc_t] $的战舰 (i, j, k) 会受到 $h_t$ 的伤害。如果一个战舰累计受到的总伤害超过其防御力,那么这个战舰会爆炸。
地球指挥官希望你能告诉他,第一艘爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。
**输入格式**
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 4 个正整数 A, B, C, m;
第二行包含 A × B × C 个整数,其中第 ((i − 1)×B + (j − 1)) × C + (k − 1)+1 个数为 d(i, j, k);
第 3 到第 m + 2 行中,第 (t − 2) 行包含 7 个正整数 $la_t, ra_t, lb_t, rb_t, lc_t, rc_t, h_t$。
**输出格式**
输出到标准输出。
输出第一个爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。保证一定存在这样的战舰。
**样例输入**
```
2 2 2 3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 2 1 2 1 1 1
1 1 1 2 1 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 2
```
**样例输出**
```
2
```
**样例解释**
在第 2 轮攻击后,战舰 (1,1,1) 总共受到了 2 点伤害,超出其防御力导致爆炸。
**数据约定**
```
对于 10% 的数据,B = C = 1;
对于 20% 的数据,C = 1;
对于 40% 的数据,A × B × C, m ≤ 10, 000;
对于 70% 的数据,A, B, C ≤ 200;
对于所有数据,A × B × C ≤ 10^6, m ≤ 10^6, 0 ≤ d(i, j, k), ht ≤ 10^9。
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
2000010
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
int
A
,
B
,
C
,
m
;
LL
s
[
N
],
b
[
N
],
bp
[
N
];
int
op
[
N
/
2
][
7
];
const
int
d
[
8
][
4
]
=
{
{
0
,
0
,
0
,
1
},
{
0
,
0
,
1
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
0
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
1
,
-
1
}};
int
get
(
int
i
,
int
j
,
int
k
)
{
return
(
i
*
B
+
j
)
*
C
+
k
;
}
bool
check
(
int
mid
)
{
memcpy
(
b
,
bp
,
sizeof
bp
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
mid
;
i
++
)
{
int
x1
=
op
[
i
][
0
],
x2
=
op
[
i
][
1
],
y1
=
op
[
i
][
2
],
y2
=
op
[
i
][
3
],
z1
=
op
[
i
][
4
],
z2
=
op
[
i
][
5
],
h
=
op
[
i
][
6
];
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
}
memset
(
s
,
0
,
sizeof
s
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
{
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
b
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)];
for
(
int
u
=
1
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
-=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
}
if
(
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
<
0
)
return
true
;
}
return
false
;
}
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d%d%d%d"
,
&
A
,
&
B
,
&
C
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
for
(
int
u
=
0
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
__________________
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
m
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
7
;
j
++
)
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
op
[
i
][
j
]);
int
l
=
1
,
r
=
m
;
while
(
l
<
r
)
{
int
mid
=
l
+
r
>>
1
;
if
(
check
(
mid
))
r
=
mid
;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
r
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
+=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
### B
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
*=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
### C
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
+
t
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-8ad88f17b5e2460abe964d49ffae23eb"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"兰顿蚂蚁"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
问题描述

兰顿蚂蚁,是于1986年,由克里斯·兰顿提出来的,属于细胞自动机的一种。
平面上的正方形格子被填上黑色或白色。在其中一格正方形内有一只“蚂蚁”。
蚂蚁的头部朝向为:上下左右其中一方。
蚂蚁的移动规则十分简单:
若蚂蚁在黑格,右转90度,将该格改为白格,并向前移一格;
若蚂蚁在白格,左转90度,将该格改为黑格,并向前移一格。
规则虽然简单,蚂蚁的行为却十分复杂。刚刚开始时留下的路线都会有接近对称,像是会重复,但不论起始状态如何,蚂蚁经过漫长的混乱活动后,会开辟出一条规则的“高速公路”。
蚂蚁的路线是很难事先预测的。
你的任务是根据初始状态,用计算机模拟兰顿蚂蚁在第n步行走后所处的位置。
#### 输入格式
输入数据的第一行是 m n 两个整数(3 < m, n < 100),表示正方形格子的行数和列数。
接下来是 m 行数据。
每行数据为 n 个被空格分开的数字。0 表示白格,1 表示黑格。
接下来是一行数据:x y s k, 其中x y为整数,表示蚂蚁所在行号和列号(行号从上到下增长,列号从左到右增长,都是从0开始编号)。s 是一个大写字母,表示蚂蚁头的朝向,我们约定:上下左右分别用:UDLR表示。k 表示蚂蚁走的步数。
#### 输出格式
输出数据为两个空格分开的整数 p q, 分别表示蚂蚁在k步后,所处格子的行号和列号。
#### 样例输入
```
5 6
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
2 3 L 5
```
#### 样例输出
```
1 3
```
#### 样例输入
```
3 3
0 0 0
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 U 6
```
#### 样例输出
```
0 0
```
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using
namespace
std
;
int
a
[
105
][
105
];
//定义一个二维数组存储格子颜色
int
main
()
{
int
m
,
n
;
int
x
,
y
,
k
;
char
s
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
cin
>>
a
[
i
][
j
];
}
}
scanf
(
"%d %d %c %d"
,
&
x
,
&
y
,
&
s
,
&
k
);
while
(
k
--
)
{
if
(
a
[
x
][
y
]
==
1
)
//蚂蚁在黑格
{
a
[
x
][
y
]
=
0
;
if
(
s
==
'U'
)
{
y
++
;
s
=
'R'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'D'
)
{
y
--
;
s
=
'L'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'L'
)
{
x
--
;
s
=
'U'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'R'
)
{
x
++
;
s
=
'D'
;
}
}
else
//蚂蚁在白格
{
a
[
x
][
y
]
=
1
;
if
(
s
==
'U'
)
{
y
--
;
s
=
'L'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'D'
)
{
y
++
;
s
=
'R'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'L'
)
{
x
++
;
s
=
'D'
;
}
else
if
(
s
==
'R'
)
{
x
--
;
s
=
'U'
;
}
}
}
printf
(
"%d %d
\n
"
,
x
,
y
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"802f2c1b8c8b43b7bcc3880221a7fd63"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/5.蓝桥杯-模拟/17.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 兰顿蚂蚁
问题描述

兰顿蚂蚁,是于1986年,由克里斯·兰顿提出来的,属于细胞自动机的一种。
平面上的正方形格子被填上黑色或白色。在其中一格正方形内有一只“蚂蚁”。
蚂蚁的头部朝向为:上下左右其中一方。
蚂蚁的移动规则十分简单:
若蚂蚁在黑格,右转90度,将该格改为白格,并向前移一格;
若蚂蚁在白格,左转90度,将该格改为黑格,并向前移一格。
规则虽然简单,蚂蚁的行为却十分复杂。刚刚开始时留下的路线都会有接近对称,像是会重复,但不论起始状态如何,蚂蚁经过漫长的混乱活动后,会开辟出一条规则的“高速公路”。
蚂蚁的路线是很难事先预测的。
你的任务是根据初始状态,用计算机模拟兰顿蚂蚁在第n步行走后所处的位置。
**输入格式**
输入数据的第一行是 m n 两个整数(3 < m, n < 100),表示正方形格子的行数和列数。
接下来是 m 行数据。
每行数据为 n 个被空格分开的数字。0 表示白格,1 表示黑格。
接下来是一行数据:x y s k, 其中x y为整数,表示蚂蚁所在行号和列号(行号从上到下增长,列号从左到右增长,都是从0开始编号)。s 是一个大写字母,表示蚂蚁头的朝向,我们约定:上下左右分别用:UDLR表示。k 表示蚂蚁走的步数。
**输出格式**
输出数据为两个空格分开的整数 p q, 分别表示蚂蚁在k步后,所处格子的行号和列号。
**样例输入**
```
5 6
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
2 3 L 5
```
**样例输出**
```
1 3
```
**样例输入**
```
3 3
0 0 0
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 U 6
```
**样例输出**
```
0 0
```
以下程序实现了该功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
enum
_direction
{
Dup
,
Dright
,
Ddown
,
Dleft
}
Direction
;
void
SolveNextDirection
(
Direction
direction
,
int
**
arr
,
int
nRow
,
int
nCol
,
int
move
)
{
int
n
=
0
;
while
(
n
<
move
)
{
if
(
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
==
1
)
{
if
(
direction
==
Dleft
)
{
direction
=
Dup
;
}
else
direction
=
(
Direction
)(
direction
+
1
);
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
=
0
;
}
else
{
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
{
direction
=
Dleft
;
}
else
direction
=
(
Direction
)(
direction
-
1
);
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
=
1
;
}
__________________
++
n
;
}
cout
<<
nRow
<<
" "
<<
nCol
<<
endl
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
m
,
n
;
int
nRow
,
nCol
,
move
;
char
Dre
;
Direction
direction
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
int
**
arr
=
new
int
*
[
m
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
arr
[
i
]
=
new
int
[
n
];
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
n
;
++
j
)
{
cin
>>
arr
[
i
][
j
];
}
cin
>>
nRow
>>
nCol
>>
Dre
>>
move
;
if
(
Dre
==
'U'
)
{
direction
=
Dup
;
}
else
if
(
Dre
==
'R'
)
{
direction
=
Dright
;
}
else
if
(
Dre
==
'D'
)
{
direction
=
Ddown
;
}
else
direction
=
Dleft
;
SolveNextDirection
(
direction
,
arr
,
nRow
,
nCol
,
move
);
delete
[]
arr
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
nCol
-=
1
;
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
nCol
-=
1
;
++
n
;
```
### B
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
nCol
+=
1
;
```
### C
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
nCol
+=
1
;
```
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-4b2e60353629424a8de36420863aec94"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"字串排序"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#### 问题描述
小蓝最近学习了一些排序算法,其中冒泡排序让他印象深刻。
在冒泡排序中,每次只能交换相邻的两个元素。小蓝发现,如果对一个字符串中的字符排序,只允许交换相邻的两个字符,则在所有可能的排序方案中,冒泡排序的总交换次数是最少的。
例如,对于字符串 lan 排序,只需要 1 次交换。对于字符串 qiao 排序,总共需要 4 次交换。
小蓝找到了很多字符串试图排序,他恰巧碰到一个字符串,需要 V 次交换,可是他忘了把这个字符串记下来,现在找不到了。
请帮助小蓝找一个只包含小写英文字母且没有字母重复出现的字符串,对该串的字符排序,正好需要 V 次交换。如果可能找到多个,请告诉小蓝最短的那个。如果最短的仍然有多个,请告诉小蓝字典序最小的那个。请注意字符串中可以包含相同的字符。
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数V,小蓝的幸运数字。
#### 输出格式
题面要求的一行字符串。
#### 样例输入
```
4
```
#### 样例输出
```
bbaa
```
#### 样例输入
```
100
```
#### 样例输出
```
jihgfeeddccbbaa
```
#### 评测用例规模与约定
```
对于 30% 的评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 20。
对于 50% 的评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 100。
对于所有评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 10000。
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
1e5
+
5
;
char
str
[
N
];
int
main
()
{
//字母只有26个,数大了就会超,剩下的还要分情况
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(false);
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
int
r
=
0
;
while
(
r
*
(
r
+
1
)
/
2
<
n
)
r
++
;
r
++
;
// cout<<r<<endl;
int
t
=
(
r
-
1
)
*
r
/
2
-
n
;
// cout<<t<<endl;
str
[
r
-
1
]
=
'a'
;
for
(
int
i
=
r
-
2
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
{
if
(
t
>
r
/
2
)
{
str
[
i
]
=
str
[
i
+
1
];
i
--
;
str
[
i
]
=
str
[
i
+
1
];
i
--
;
t
-=
3
;
}
else
if
(
t
>
0
)
{
str
[
i
]
=
str
[
i
+
1
];
i
--
;
t
--
;
}
if
(
i
>=
0
)
str
[
i
]
=
str
[
i
+
1
]
+
1
;
}
puts
(
str
);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"156e715e2a744a2eb5a0548a19a4541e"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-搜索/13.字串排序/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 字串排序
**问题描述**
小蓝最近学习了一些排序算法,其中冒泡排序让他印象深刻。
在冒泡排序中,每次只能交换相邻的两个元素。小蓝发现,如果对一个字符串中的字符排序,只允许交换相邻的两个字符,则在所有可能的排序方案中,冒泡排序的总交换次数是最少的。
例如,对于字符串 lan 排序,只需要 1 次交换。对于字符串 qiao 排序,总共需要 4 次交换。
小蓝找到了很多字符串试图排序,他恰巧碰到一个字符串,需要 V 次交换,可是他忘了把这个字符串记下来,现在找不到了。
请帮助小蓝找一个只包含小写英文字母且没有字母重复出现的字符串,对该串的字符排序,正好需要 V 次交换。如果可能找到多个,请告诉小蓝最短的那个。如果最短的仍然有多个,请告诉小蓝字典序最小的那个。请注意字符串中可以包含相同的字符。
**输入格式**
输入的第一行包含一个整数V,小蓝的幸运数字。
**输出格式**
题面要求的一行字符串。
**样例输入**
```
4
```
**样例输出**
```
bbaa
```
**样例输入**
```
100
```
**样例输出**
```
jihgfeeddccbbaa
```
**评测用例规模与约定**
```
对于 30% 的评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 20。
对于 50% 的评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 100。
对于所有评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 10000。
```
下面的程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
maxn
=
1e6
+
5
;
const
int
mod
=
1e9
+
7
;
int
dp
[
152
][
26
][
152
];
int
dfs
(
int
pre
,
int
x
,
int
aft
)
{
int
&
d
=
dp
[
pre
][
x
][
aft
];
if
(
~
d
)
return
d
;
if
(
x
==
1
)
return
d
=
pre
*
aft
;
if
(
aft
==
0
)
{
if
(
x
!=
0
)
return
-
1e9
;
return
0
;
}
int
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
aft
;
i
++
)
{
int
res
=
dfs
(
pre
+
i
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
i
)
+
i
*
pre
;
if
(
ans
<
res
)
{
ans
=
res
;
}
}
return
d
=
ans
;
}
void
dfs2
(
int
pre
,
int
x
,
int
aft
,
int
rest
,
string
&
res
)
{
if
(
x
==
1
)
{
res
+=
string
(
aft
,
'a'
);
return
;
}
int
len
=
1e9
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
aft
;
i
++
)
{
int
d
=
dfs
(
pre
+
i
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
i
)
+
i
*
pre
;
if
(
d
>=
rest
)
{
len
=
i
;
break
;
}
}
res
+=
string
(
len
,
'a'
+
x
-
1
);
rest
-=
len
*
pre
;
__________________
return
;
}
int
calc
(
string
a
)
{
int
n
=
a
.
size
();
int
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
i
+
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
a
[
j
])
ans
++
;
}
}
return
ans
;
}
void
solve
(
int
v
)
{
memset
(
dp
,
-
1
,
sizeof
dp
);
int
len
=
1e9
,
x
=
1e9
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
150
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
26
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
dfs
(
0ll
,
j
,
i
)
>=
v
)
{
if
(
len
>
i
)
{
len
=
i
,
x
=
j
;
}
else
if
(
len
==
i
)
{
x
=
min
(
x
,
j
);
}
}
}
}
string
ans
;
dfs2
(
0
,
x
,
len
,
v
,
ans
);
cout
<<
ans
<<
endl
;
return
;
}
int
main
()
{
ios
::
sync_with_stdio
(
false
);
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
solve
(
n
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
len
,
rest
,
res
);
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
,
aft
-
len
,
rest
,
res
);
```
### B
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
1
,
rest
,
res
);
```
### C
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
,
rest
,
res
);
```
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/6.糖果/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@
...
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@
2
2
```
```
以下
错误
的一项是?
以下
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的一项是?
## aop
## aop
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-d70bc24ce5604f50ad73e70e07d4ace6"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"矩阵"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
把 1 ∼ 2020 放在 2 × 1010 的矩阵里。
要求同一行中右边的比左边大,同一列中下边的比上边的大。一共有多少种方案?
答案很大,你只需要给出方案数除以 2020 的余数即可。
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <stdio.h>
int
DP
[
1011
][
1011
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
j
;
DP
[
1
][
0
]
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
DP
[
i
][
0
]
=
1
;
//初始化
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
i
==
j
)
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
];
else
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
])
%
2020
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
DP
[
1010
][
1010
]);
return
0
;
}
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"483bdaab5a5a4b239c9ae9064f112ad3"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/7.矩阵/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 矩阵
把 1 ∼ 2020 放在 2 × 1010 的矩阵里。
要求同一行中右边的比左边大,同一列中下边的比上边的大。一共有多少种方案?
答案很大,你只需要给出方案数除以 2020 的余数即可。
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int
DP
[
1011
][
1011
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
j
;
DP
[
1
][
0
]
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
DP
[
i
][
0
]
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
i
==
j
)
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
];
else
__________________
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
DP
[
1010
][
1010
]);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
### before
```
cpp
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
])
%
2020
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
]
+
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
])
%
2020
```
### B
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
])
%
2020
```
### C
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
])
%
2020
```
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/config.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"node_id"
:
"algorithm-f6ca94b72dae4b929f58d1ac0f903b5a"
,
"keywords"
:
[
"蓝桥杯"
,
"垒骰子"
],
"children"
:
[],
"export"
:
[]
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/desc.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
赌圣atm晚年迷恋上了垒骰子,就是把骰子一个垒在另一个上边,不能歪歪扭扭,要垒成方柱体。
经过长期观察,atm 发现了稳定骰子的奥秘:有些数字的面贴着会互相排斥!
我们先来规范一下骰子:1 的对面是 4,2 的对面是 5,3 的对面是 6。
假设有 m 组互斥现象,每组中的那两个数字的面紧贴在一起,骰子就不能稳定的垒起来。
atm想计算一下有多少种不同的可能的垒骰子方式。
两种垒骰子方式相同,当且仅当这两种方式中对应高度的骰子的对应数字的朝向都相同。
由于方案数可能过多,请输出模 $10^9 + 7$ 的结果。
不要小看了 atm 的骰子数量哦~
#### 输入格式
第一行两个整数 n m
n表示骰子数目
接下来 m 行,每行两个整数 a b ,表示 a 和 b 数字不能紧贴在一起。
#### 输出格式
一行一个数,表示答案模 10^9 + 7 的结果。
#### 样例输入
```
2 1
1 2
```
#### 样例输出
```
544
```
#### 数据范围
```
对于 30% 的数据:n <= 5
对于 60% 的数据:n <= 100
对于 100% 的数据:0 < n <= 10^9, m <= 36
```
#### 资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.cpp
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using
namespace
std
;
vector
<
int
>
can
[
7
];
//存can[i]能和哪些点挨着
int
up
[
7
]
=
{
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
};
int
temp
[
7
]
=
{
1
};
int
k
=
4
;
const
int
MOD
=
1000000007
;
void
init
()
//初始化都可挨着
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
6
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
j
++
)
can
[
i
].
push_back
(
j
);
}
void
dele
(
int
side1
,
int
side2
)
//删除不可挨着的点
{
for
(
vector
<
int
>::
iterator
it
=
can
[
side1
].
begin
();
it
!=
can
[
side1
].
end
();
it
++
)
if
(
*
it
==
side2
)
{
can
[
side1
].
erase
(
it
);
break
;
}
for
(
vector
<
int
>::
iterator
it
=
can
[
side2
].
begin
();
it
!=
can
[
side2
].
end
();
it
++
)
if
(
*
it
==
side1
)
{
can
[
side2
].
erase
(
it
);
break
;
}
}
void
fun
(
int
n
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
2
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
//计算出第i层骰子每种底面的可能次数
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
j
++
)
{
temp
[
j
]
=
0
;
for
(
vector
<
int
>::
iterator
it
=
can
[
j
].
begin
();
it
!=
can
[
j
].
end
();
it
++
)
temp
[
j
]
+=
up
[
*
it
];
}
//转化为第i层骰子顶面的可能次数
up
[
1
]
=
temp
[
4
]
%
MOD
;
up
[
2
]
=
temp
[
5
]
%
MOD
;
up
[
3
]
=
temp
[
6
]
%
MOD
;
up
[
4
]
=
temp
[
1
]
%
MOD
;
up
[
5
]
=
temp
[
2
]
%
MOD
;
up
[
6
]
=
temp
[
3
]
%
MOD
;
//4^n
k
=
k
*
4
;
k
=
k
%
MOD
;
}
int
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
j
++
)
ans
+=
up
[
j
];
cout
<<
(
ans
*
k
)
%
MOD
;
}
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
{
init
();
int
n
,
m
;
cin
>>
n
>>
m
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
int
side1
,
side2
;
cin
>>
side1
>>
side2
;
dele
(
side1
,
side2
);
}
fun
(
n
);
return
0
;
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.java
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.json
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
{
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
"author"
:
"CSDN.net"
,
"source"
:
"solution.md"
,
"exercise_id"
:
"6b4b68a3ead544a2a9640d9ca6f008b1"
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-动态规划/8.垒骰子/solution.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
987907e1
# 垒骰子
赌圣atm晚年迷恋上了垒骰子,就是把骰子一个垒在另一个上边,不能歪歪扭扭,要垒成方柱体。
经过长期观察,atm 发现了稳定骰子的奥秘:有些数字的面贴着会互相排斥!
我们先来规范一下骰子:1 的对面是 4,2 的对面是 5,3 的对面是 6。
假设有 m 组互斥现象,每组中的那两个数字的面紧贴在一起,骰子就不能稳定的垒起来。
atm想计算一下有多少种不同的可能的垒骰子方式。
两种垒骰子方式相同,当且仅当这两种方式中对应高度的骰子的对应数字的朝向都相同。
由于方案数可能过多,请输出模 $10^9 + 7$ 的结果。
不要小看了 atm 的骰子数量哦~
**输入格式**
第一行两个整数 n m
n表示骰子数目
接下来 m 行,每行两个整数 a b ,表示 a 和 b 数字不能紧贴在一起。
**输出格式**
一行一个数,表示答案模 $10^9 + 7$ 的结果。
**样例输入**
```
2 1
1 2
```
**样例输出 **
```
544
```
**数据范围**
```
对于 30% 的数据:n <= 5
对于 60% 的数据:n <= 100
对于 100% 的数据:0 < n <= 10^9, m <= 36
```
**资源约定:**
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
以下选项
<span
style=
"color:red"
>
错误
</span>
的是?
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
### after
```
cpp
```
## 答案
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
using
namespace
std
;
int
points
[
7
]
=
{
0
,
4
,
5
,
6
,
1
,
2
,
3
};
int
n
,
m
;
int
ban
[
36
][
2
];
long
long
result
;
bool
judge
(
int
point1
,
int
point2
)
{
bool
flag
=
true
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
int
point3
=
points
[
point2
];
if
(
point1
==
ban
[
i
][
0
]
&&
point3
==
ban
[
i
][
1
])
{
flag
=
false
;
break
;
}
if
(
point1
==
ban
[
i
][
1
]
&&
point3
==
ban
[
i
][
0
])
{
flag
=
false
;
break
;
}
}
return
flag
;
}
void
dfs
(
int
cnt
,
int
point
)
{
if
(
cnt
==
n
)
{
result
++
;
return
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
6
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
judge
(
point
,
i
))
{
cnt
++
;
dfs
(
cnt
,
i
);
cnt
--
;
}
}
}
long
long
quickpow
(
int
x
,
int
N
)
{
int
reg
=
x
;
int
sum
=
1
;
while
(
N
)
{
if
(
N
&
1
)
{
sum
=
sum
*
reg
;
}
reg
*=
reg
;
N
=
N
>>
1
;
}
return
sum
;
}
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
>>
m
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
ban
[
i
][
0
]
>>
ban
[
i
][
1
];
}
dfs
(
0
,
0
);
long
long
temp
=
quickpow
(
4
,
n
);
cout
<<
result
*
temp
%
MOD
;
return
0
;
}
```
## 选项
### A
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
typedef
long
long
LL
;
LL
dp
[
2
][
7
];
int
n
,
m
;
bool
conflict
[
7
][
7
];
map
<
int
,
int
>
op
;
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
struct
M
{
LL
a
[
6
][
6
];
M
()
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
1
;
}
}
}
};
M
mMultiply
(
M
m1
,
M
m2
)
{
M
ans
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
0
;
k
<
6
;
++
k
)
{
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
+
m1
.
a
[
i
][
k
]
*
m2
.
a
[
k
][
j
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
}
return
ans
;
}
M
mPow
(
M
m
,
int
k
)
{
M
ans
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
if
(
i
==
j
)
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
1
;
else
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
0
;
}
}
while
(
k
)
{
if
(
k
&
1
)
{
ans
=
mMultiply
(
ans
,
m
);
}
m
=
mMultiply
(
m
,
m
);
k
>>=
1
;
}
return
ans
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
M
cMatrix
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
a
,
b
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
a
,
&
b
);
cMatrix
.
a
[
op
[
a
]
-
1
][
b
-
1
]
=
0
;
cMatrix
.
a
[
op
[
b
]
-
1
][
a
-
1
]
=
0
;
}
M
cMatrix_n_1
=
mPow
(
cMatrix
,
n
-
1
);
LL
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
ans
=
(
ans
+
cMatrix_n_1
.
a
[
i
][
j
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
LL
t
=
1
;
LL
tmp
=
4
;
LL
p
=
n
;
while
(
p
)
{
if
(
p
&
1
)
{
t
=
t
*
tmp
%
MOD
;
}
tmp
=
tmp
*
tmp
%
MOD
;
p
>>=
1
;
}
printf
(
"%lld"
,
ans
*
t
%
MOD
);
return
0
;
}
```
### B
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
typedef
long
long
LL
;
LL
dp
[
2
][
7
];
int
n
,
m
;
bool
conflict
[
7
][
7
];
map
<
int
,
int
>
op
;
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
a
,
b
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
a
,
&
b
);
conflict
[
a
][
b
]
=
true
;
conflict
[
b
][
a
]
=
true
;
}
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
++
j
)
{
dp
[
0
][
j
]
=
1
;
}
int
cur
=
0
;
for
(
int
level
=
2
;
level
<=
n
;
++
level
)
{
cur
=
1
-
cur
;
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
++
j
)
{
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
6
;
++
i
)
{
if
(
conflict
[
op
[
j
]][
i
])
continue
;
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
=
(
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
+
dp
[
1
-
cur
][
i
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
}
LL
sum
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
6
;
++
k
)
{
sum
=
(
sum
+
dp
[
cur
][
k
])
%
MOD
;
}
LL
ans
=
1
;
LL
tmp
=
4
;
LL
p
=
n
;
while
(
p
)
{
if
(
p
&
1
)
ans
=
(
ans
*
tmp
)
%
MOD
;
tmp
=
(
tmp
*
tmp
)
%
MOD
;
p
>>=
1
;
}
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
(
sum
*
ans
)
%
MOD
);
return
0
;
}
```
### C
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
int
op
[
7
];
bool
confilct
[
7
][
7
];
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
int
n
,
m
;
long
long
int
f
(
int
up
,
int
count
)
{
if
(
count
==
0
)
return
4
;
long
long
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
upp
=
1
;
upp
<=
6
;
++
upp
)
{
if
(
confilct
[
op
[
up
]][
upp
])
continue
;
ans
=
(
ans
+
f
(
upp
,
count
-
1
))
%
MOD
;
}
return
ans
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
x
,
y
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
x
,
&
y
);
confilct
[
y
][
x
]
=
true
;
confilct
[
x
][
y
]
=
true
;
}
long
long
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
up
=
1
;
up
<=
6
;
++
up
)
{
ans
=
(
ans
+
4
*
f
(
up
,
n
-
1
))
%
MOD
;
}
printf
(
"%lli
\n
"
,
ans
);
return
0
;
}
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/170.幸运数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@
...
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@
这时,3为第2个幸运数,然后把所有能被3整除的序号位置的数删去。注意,是序号位置,不是那个数本身能否被3整除!! 删除的应该是5,11, 17, …
这时,3为第2个幸运数,然后把所有能被3整除的序号位置的数删去。注意,是序号位置,不是那个数本身能否被3整除!! 删除的应该是5,11, 17, …
此时7为第3个幸运数,然后再删去序号位置能被7整除的(19,39,…)
此时7为第3个幸运数,然后再删去序号位置能被7整除的(19,39,…)
最后剩下的序列类似:
最后剩下的序列类似:
```
```
1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 15, 21, 25, 31, 33, 37, 43, 49, 51, 63, 67, 69, 73, 75, 79, …
1, 3, 7, 9, 13, 15, 21, 25, 31, 33, 37, 43, 49, 51, 63, 67, 69, 73, 75, 79, …
```
```
...
@@ -50,12 +51,15 @@
...
@@ -50,12 +51,15 @@
8
8
```
```
以下错误的一项是?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
...
@@ -67,7 +71,44 @@
...
@@ -67,7 +71,44 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
m
,
n
;
int
len
=
0
;
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d %d"
,
&
m
,
&
n
);
vector
<
int
>
vc
(
n
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
vc
[
i
]
=
2
*
i
-
1
;
int
divided
=
2
;
len
=
n
;
for
(
int
select
=
1
;;
++
select
)
{
divided
=
vc
[
select
-
1
];
int
num
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
len
;
i
++
)
if
(
i
%
divided
!=
0
)
vc
[
num
++
]
=
vc
[
i
];
len
=
num
;
if
(
vc
[
select
]
>
n
)
break
;
}
int
count
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
vc
[
i
]
>=
n
)
break
;
if
(
vc
[
i
]
<
n
&&
vc
[
i
]
>
m
)
{
++
count
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
count
);
return
0
;
}
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -75,17 +116,160 @@
...
@@ -75,17 +116,160 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
vector
<
int
>
a
;
a
.
push_back
(
0
);
int
i
,
m
,
n
,
start
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
2
*
i
-
1
>=
n
)
break
;
a
.
push_back
(
2
*
i
-
1
);
}
start
=
2
;
int
k
;
vector
<
int
>
old
;
do
{
old
.
push_back
(
0
);
if
(
start
>
a
.
size
()
-
1
)
break
;
k
=
a
[
start
++
];
if
(
k
>
a
.
size
())
break
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
a
.
size
();
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
%
k
)
old
.
push_back
(
a
[
i
]);
}
a
.
clear
();
a
.
assign
(
old
.
begin
(),
old
.
end
());
old
.
clear
();
}
while
(
true
);
int
sum
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
a
.
size
();
i
++
)
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
m
)
{
sum
=
sum
+
1
;
}
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
a
[
500005
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
k
=
1
;
int
m
,
n
,
sum
=
0
;
int
temp
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1000000
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
k
++
]
=
i
;
}
temp
=
2
;
while
(
temp
<=
1000
)
{
int
b
[
500005
],
t
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
k
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
i
%
a
[
temp
]
!=
0
)
b
[
t
++
]
=
a
[
i
];
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<
t
;
i
++
)
a
[
i
]
=
b
[
i
];
temp
++
;
k
=
t
;
}
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
m
&&
a
[
i
]
<
n
)
{
sum
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
sum
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
struct
num
{
int
order
;
int
value
;
};
int
main
()
{
int
m
,
n
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
vector
<
num
>
numbers
;
int
count
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
num
tempNum
;
tempNum
.
order
=
count
;
tempNum
.
value
=
i
;
numbers
.
push_back
(
tempNum
);
count
++
;
}
int
index
=
1
,
tempCount
=
1
,
value
=
numbers
[
index
].
value
;
while
(
index
<=
tempCount
)
{
int
j
,
tempValue
=
-
1
;
tempCount
=
1
;
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
j
].
order
!=
-
1
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
j
].
order
%
value
==
0
)
{
numbers
[
j
].
order
=
-
1
;
}
else
{
tempCount
++
;
numbers
[
j
].
order
=
tempCount
;
if
(
tempCount
==
index
+
1
)
{
tempValue
=
numbers
[
j
].
value
;
}
}
}
}
index
++
;
value
=
tempValue
;
}
int
numCount
=
0
;
for
(
int
t
=
0
;
t
<
n
;
t
++
)
{
if
(
numbers
[
t
].
order
!=
-
1
&&
numbers
[
t
].
value
>
m
&&
numbers
[
t
].
value
<
n
)
{
numCount
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
numCount
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/38.小朋友排队/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -54,12 +54,15 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
...
@@ -54,12 +54,15 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
首先交换身高为3和2的小朋友,再交换身高为3和1的小朋友,再交换身高为2和1的小朋友,每个小朋友的不高兴程度都是3,总和为9。
首先交换身高为3和2的小朋友,再交换身高为3和1的小朋友,再交换身高为2和1的小朋友,每个小朋友的不高兴程度都是3,总和为9。
以下错误的一项是?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
...
@@ -71,7 +74,77 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
...
@@ -71,7 +74,77 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define ll long long
using
namespace
std
;
int
const
MAX
=
1e5
+
5
;
ll
cnt
[
MAX
],
ans
;
int
n
;
struct
DATA
{
int
idx
;
ll
num
;
}
d
[
MAX
];
bool
cmp
(
DATA
a
,
DATA
b
)
{
return
a
.
num
<
b
.
num
;
}
void
Solve
(
int
l
,
int
mid
,
int
r
)
{
int
i
=
l
,
j
=
mid
+
1
;
while
(
i
<=
mid
&&
j
<=
r
)
{
if
(
d
[
i
].
num
<=
d
[
j
].
num
)
i
++
;
else
{
cnt
[
d
[
j
].
idx
]
+=
(
ll
)(
mid
-
i
+
1
);
j
++
;
}
}
i
=
mid
,
j
=
r
;
while
(
i
>=
l
&&
j
>=
mid
+
1
)
{
if
(
d
[
i
].
num
>
d
[
j
].
num
)
{
cnt
[
d
[
i
].
idx
]
+=
(
ll
)(
j
-
mid
);
i
--
;
}
else
j
--
;
}
sort
(
d
+
l
,
d
+
r
+
1
,
cmp
);
return
;
}
void
Div
(
int
l
,
int
r
)
{
if
(
l
>=
r
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
l
+
r
)
>>
1
;
Div
(
l
,
mid
);
Div
(
mid
+
1
,
r
);
Solve
(
l
,
mid
,
r
);
}
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
d
[
i
].
num
);
d
[
i
].
idx
=
i
;
}
ans
=
0
;
Div
(
0
,
n
-
1
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
ans
+=
cnt
[
i
]
*
cnt
[
i
]
/
2
;
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
ans
);
}
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -79,17 +152,211 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
...
@@ -79,17 +152,211 @@ n 个小朋友站成一排。
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
N
=
1e6
+
10
;
int
h
[
N
],
s
[
N
],
tr
[
N
];
int
n
;
int
lowbit
(
int
x
)
{
return
x
&
-
x
;
}
int
add
(
int
x
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
<
N
;
i
+=
lowbit
(
i
))
tr
[
i
]
++
;
}
int
q
(
int
x
)
{
int
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
x
;
i
;
i
-=
lowbit
(
i
))
res
+=
tr
[
i
];
return
res
;
}
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
h
[
i
],
h
[
i
]
++
;
s
[
i
]
=
q
(
N
-
1
)
-
q
(
h
[
i
]);
add
(
h
[
i
]);
}
memset
(
tr
,
0
,
sizeof
tr
);
for
(
int
i
=
n
-
1
;
i
>=
0
;
i
--
)
s
[
i
]
+=
q
(
h
[
i
]
-
1
),
add
(
h
[
i
]);
LL
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
res
+=
(
LL
)
s
[
i
]
*
(
s
[
i
]
+
1
)
/
2
;
cout
<<
res
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
struct
childInfo
{
int
location
;
int
valueNum
;
};
int
cnt
[
100005
];
void
Merge_sort1
(
vector
<
childInfo
>
&
tempChild
,
int
left
,
int
right
)
{
if
(
left
>=
right
-
1
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
left
+
right
)
/
2
;
Merge_sort1
(
tempChild
,
left
,
mid
);
Merge_sort1
(
tempChild
,
mid
,
right
);
int
i
=
left
,
j
=
mid
,
t
=
0
;
childInfo
*
temp
=
new
childInfo
[
right
-
left
];
while
(
i
<
mid
||
j
<
right
)
{
if
(
j
>=
right
||
i
<
mid
&&
tempChild
[
i
].
valueNum
<=
tempChild
[
j
].
valueNum
)
temp
[
t
++
]
=
tempChild
[
i
++
];
else
{
cnt
[
tempChild
[
j
].
location
]
+=
mid
-
i
;
temp
[
t
++
]
=
tempChild
[
j
++
];
}
}
t
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
left
;
k
<
right
;
k
++
)
tempChild
[
k
]
=
temp
[
t
++
];
delete
[]
temp
;
}
void
Merge_sort2
(
vector
<
childInfo
>
&
tempChild
,
int
left
,
int
right
)
{
if
(
left
>=
right
-
1
)
return
;
int
mid
=
(
left
+
right
)
/
2
;
Merge_sort2
(
tempChild
,
left
,
mid
);
Merge_sort2
(
tempChild
,
mid
,
right
);
childInfo
*
temp
=
new
childInfo
[
right
-
left
];
int
i
=
mid
-
1
,
j
=
right
-
1
,
t
=
right
-
left
-
1
;
while
(
i
>=
left
||
j
>=
mid
)
{
if
(
i
<
left
||
j
>=
mid
&&
tempChild
[
i
].
valueNum
<=
tempChild
[
j
].
valueNum
)
temp
[
t
--
]
=
tempChild
[
j
--
];
else
{
cnt
[
tempChild
[
i
].
location
]
+=
j
-
mid
+
1
;
temp
[
t
--
]
=
tempChild
[
i
--
];
}
}
t
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
left
;
i
<
right
;
i
++
)
tempChild
[
i
]
=
temp
[
t
++
];
delete
[]
temp
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
childInfo
tempChild
;
tempChild
.
location
=
i
;
cin
>>
tempChild
.
valueNum
;
childLists
.
push_back
(
tempChild
);
}
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists1
(
childLists
.
begin
(),
childLists
.
end
());
Merge_sort1
(
childLists
,
0
,
childLists
.
size
());
Merge_sort2
(
childLists1
,
0
,
childLists1
.
size
());
long
long
sum
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
childLists
.
size
();
i
++
)
sum
+=
1ll
*
(
1
+
cnt
[
i
])
*
cnt
[
i
]
/
2
;
cout
<<
sum
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
struct
childInfo
{
int
location
;
int
valueNum
;
};
bool
lowCompare
(
childInfo
temp1
,
childInfo
temp2
)
{
return
temp1
.
valueNum
>
temp2
.
valueNum
;
}
bool
upCompare
(
childInfo
temp1
,
childInfo
temp2
)
{
return
temp1
.
valueNum
<
temp2
.
valueNum
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
childNums
;
cin
>>
childNums
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists1
;
vector
<
childInfo
>
childLists2
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
childNums
;
i
++
)
{
childInfo
tempInfo
;
tempInfo
.
location
=
i
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
tempInfo
.
valueNum
);
childLists
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
childLists1
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
childLists2
.
push_back
(
tempInfo
);
}
sort
(
childLists1
.
begin
(),
childLists1
.
end
(),
lowCompare
);
sort
(
childLists2
.
begin
(),
childLists2
.
end
(),
upCompare
);
long
long
int
count
=
0
;
for
(
int
m
=
0
;
m
<
childNums
;
m
++
)
{
int
sadNum
=
0
;
long
long
int
count1
=
0
,
count2
=
0
;
int
compareNum
=
childLists
[
m
].
valueNum
,
compareLoc
=
childLists
[
m
].
location
;
for
(
int
n
=
0
;
n
<
childNums
;
n
++
)
{
if
(
compareNum
<
childLists1
[
n
].
valueNum
)
{
if
(
compareLoc
>
childLists1
[
n
].
location
)
{
sadNum
++
;
count1
+=
sadNum
;
}
}
else
{
break
;
}
}
for
(
int
n
=
0
;
n
<
childNums
;
n
++
)
{
if
(
compareNum
>
childLists2
[
n
].
valueNum
)
{
if
(
compareLoc
<
childLists2
[
n
].
location
)
{
sadNum
++
;
count2
+=
sadNum
;
}
}
else
{
break
;
}
}
count
+=
count1
+
count2
;
}
cout
<<
count
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/39.灵能传输/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -72,12 +72,15 @@
...
@@ -72,12 +72,15 @@
4
4
```
```
以下选项错误的是?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
...
@@ -89,7 +92,74 @@
...
@@ -89,7 +92,74 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
ll
;
#define int ll
#define rep(i, a, n) for (int i = a; i < (int)n; i++)
#define per(i, a, n) for (int i = (int)n - 1; i >= a; i--)
const
int
maxn
=
3e5
+
10
;
inline
int
read
()
{
int
x
=
0
,
f
=
1
;
char
ch
=
getchar
();
while
(
!
isdigit
(
ch
))
{
if
(
ch
==
'-'
)
f
=
-
1
;
ch
=
getchar
();
}
while
(
isdigit
(
ch
))
{
x
=
(
x
<<
3
)
+
(
x
<<
1
)
+
ch
-
48
;
ch
=
getchar
();
}
return
x
*
f
;
}
int
s
[
maxn
],
a
[
maxn
];
bool
vis
[
maxn
];
inline
void
cf
()
{
int
t
=
read
();
while
(
t
--
)
{
int
n
=
read
();
s
[
0
]
=
0
;
rep
(
i
,
1
,
n
+
1
)
{
int
x
=
read
();
s
[
i
]
=
s
[
i
+
1
]
+
x
;
}
int
s0
=
0
,
sn
=
s
[
n
];
if
(
s0
>
sn
)
swap
(
s0
,
sn
);
sort
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
);
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
s
[
i
]
==
s0
)
{
s0
=
i
;
break
;
}
per
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
s
[
i
]
==
sn
)
{
sn
=
i
;
break
;
}
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
vis
[
i
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
s0
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
sn
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
a
[
r
--
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
rep
(
i
,
0
,
n
+
1
)
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
];
int
ans
=
0
;
rep
(
i
,
1
,
n
+
1
)
ans
=
max
(
ans
,
abs
(
a
[
i
]
-
a
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
ans
);
}
return
;
}
signed
main
()
{
cf
();
return
0
;
}
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -97,17 +167,246 @@
...
@@ -97,17 +167,246 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define ll long long
const
int
N
=
3e5
;
ll
a
[
N
],
s
[
N
];
bool
vis
[
N
];
int
n
;
int
main
()
{
int
T
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
T
);
while
(
T
--
)
{
memset
(
vis
,
0
,
sizeof
(
vis
));
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
s
[
0
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
s
[
i
]);
s
[
i
]
+=
s
[
i
-
1
];
}
ll
s0
=
0
,
sn
=
s
[
n
];
if
(
s0
>
sn
)
swap
(
s0
,
sn
);
sort
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
);
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
lower_bound
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
,
s0
)
-
s
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
{
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
lower_bound
(
s
,
s
+
n
+
1
,
sn
)
-
s
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
{
a
[
r
--
]
=
s
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
{
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
a
[
l
++
]
=
s
[
i
];
}
ll
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
++
i
)
res
=
max
(
res
,
abs
(
a
[
i
]
-
a
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
res
);
}
return
0
;
}
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
const
int
MAXN
=
300010
;
int
nums
[
MAXN
];
bool
judgeYi
(
int
a
,
int
b
)
{
return
a
>
0
&&
b
<
0
||
a
<
0
&&
b
>
0
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
T
,
n
;
cin
>>
T
;
while
(
T
--
)
{
cin
>>
n
;
bool
hasNe
=
false
,
hasPo
=
false
;
int
res
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
nums
[
i
]);
if
(
nums
[
i
]
<
0
)
{
hasNe
=
true
;
}
else
if
(
nums
[
i
]
>
0
)
{
hasPo
=
true
;
}
}
if
(
hasNe
&&
hasPo
)
{
bool
canNext
;
do
{
canNext
=
false
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
-
1
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
],
nums
[
i
-
1
])
||
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
(
nums
[
i
]
>
0
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
-
1
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
((
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
0
&&
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
])
>
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+
nums
[
i
])
||
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
0
&&
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
])
>
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+
nums
[
i
]))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
else
{
if
(
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
])
>
nums
[
i
]
||
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
])
>
nums
[
i
])
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
}
else
if
(
nums
[
i
]
<
0
)
{
if
(
judgeYi
(
nums
[
i
-
1
],
nums
[
i
+
1
]))
{
if
((
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
0
&&
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+
nums
[
i
]))
||
(
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
0
&&
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+
nums
[
i
])))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
else
{
if
(
nums
[
i
-
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
])
||
nums
[
i
+
1
]
>
abs
(
nums
[
i
]))
{
nums
[
i
+
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
-
1
]
+=
nums
[
i
];
nums
[
i
]
=
-
nums
[
i
];
canNext
=
true
;
}
}
}
}
}
}
while
(
canNext
);
}
int
t
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
res
=
max
(
res
,
abs
(
nums
[
i
]));
}
cout
<<
res
<<
endl
;
}
return
0
;
}
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
INF
=
0x3f3f3f3f
;
const
double
Pi
=
acos
(
-
1
);
namespace
{
template
<
typename
T
>
inline
void
read
(
T
&
x
)
{
x
=
0
;
T
f
=
1
;
char
s
=
getchar
();
for
(;
!
isdigit
(
s
);
s
=
getchar
())
if
(
s
==
'-'
)
f
=
-
1
;
for
(;
isdigit
(
s
);
s
=
getchar
())
x
=
(
x
<<
3
)
+
(
x
<<
1
)
+
(
s
^
48
);
x
*=
f
;
}
}
#define fio \
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); \
cin.tie(0); \
cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define _srep(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i >= (m); i--)
#define _sfor(n, m, i) for (register int i = (n); i > (m); i--)
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define lowbit(x) x &(-x)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define fi first
#define se second
const
int
N
=
1e6
+
5
;
LL
a
[
N
];
LL
ans
[
N
];
bool
vis
[
N
];
LL
Abs
(
LL
x
)
{
return
x
<
0
?
-
x
:
x
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
t
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
t
);
while
(
t
--
)
{
int
n
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
a
[
0
]
=
0
;
_rep
(
1
,
n
,
i
)
{
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
a
+
i
);
a
[
i
]
+=
a
[
i
-
1
];
}
LL
a0
=
0
,
an
=
a
[
n
],
Max
=
0
;
int
A0
,
AN
;
sort
(
a
,
a
+
n
+
1
);
memset
(
vis
,
0
,
sizeof
vis
);
if
(
a0
>
an
)
swap
(
a0
,
an
);
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
a0
==
a
[
i
])
{
A0
=
i
;
break
;
}
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
an
==
a
[
i
])
{
AN
=
i
;
break
;
}
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
A0
;
i
>=
0
;
i
-=
2
)
ans
[
l
++
]
=
a
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
for
(
int
i
=
AN
;
i
<=
n
;
i
+=
2
)
ans
[
r
--
]
=
a
[
i
],
vis
[
i
]
=
1
;
_rep
(
0
,
n
,
i
)
if
(
!
vis
[
i
])
ans
[
l
++
]
=
a
[
i
];
_rep
(
1
,
n
,
i
)
Max
=
max
(
Max
,
Abs
(
ans
[
i
]
-
ans
[
i
-
1
]));
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
Max
);
}
}
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/42.振兴中华/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -16,6 +16,25 @@
...
@@ -16,6 +16,25 @@
请你帮助小明算一算他一共有多少种可能的跳跃路线呢?
请你帮助小明算一算他一共有多少种可能的跳跃路线呢?
以下代码实现了这一功能,请你填补空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
int
f
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
if
(
x
==
3
||
y
==
4
)
return
1
;
__________________
}
int
main
()
{
cout
<<
f
(
0
,
0
)
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -33,7 +52,7 @@
...
@@ -33,7 +52,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
+
1
);
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -41,17 +60,17 @@
...
@@ -41,17 +60,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
-
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
-
1
);
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
)
+
f
(
x
,
y
-
1
);
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
return
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
+
1
)
+
f
(
x
+
1
,
y
+
1
);
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/43.格子中输出/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -5,6 +5,52 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串
...
@@ -5,6 +5,52 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串


以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void
StringInGrid
(
int
width
,
int
height
,
const
char
*
s
)
{
int
i
,
k
;
char
buf
[
1000
];
strcpy
(
buf
,
s
);
if
(
strlen
(
s
)
>
width
-
2
)
buf
[
width
-
2
]
=
0
;
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
1
;
k
<
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"|"
);
printf
(
"%*s%s%*s"
,
__________________
;
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
for
(
k
=
(
height
-
1
)
/
2
+
1
;
k
<
height
-
1
;
k
++
)
{
printf
(
"|"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
" "
);
printf
(
"|
\n
"
);
}
printf
(
"+"
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
width
-
2
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"-"
);
printf
(
"+
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
StringInGrid
(
20
,
6
,
"abcd1234"
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -22,7 +68,7 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串
...
@@ -22,7 +68,7 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
)
/
2
,
""
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -30,17 +76,17 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串
...
@@ -30,17 +76,17 @@ StringInGrid函数会在一个指定大小的格子中打印指定的字符串
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
1
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
1
)
/
2
,
""
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
+
1
)
/
2
,
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
+
1
)
/
2
,
""
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
),
""
,
buf
,
(
width
-
strlen
(
buf
)
-
2
),
""
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/44.最大公共子串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -10,6 +10,43 @@
...
@@ -10,6 +10,43 @@
下面的程序是采用矩阵法进行求解的,这对串的规模不大的情况还是比较有效的解法。
下面的程序是采用矩阵法进行求解的,这对串的规模不大的情况还是比较有效的解法。
请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 256
int
f
(
const
char
*
s1
,
const
char
*
s2
)
{
int
a
[
N
][
N
];
int
len1
=
strlen
(
s1
);
int
len2
=
strlen
(
s2
);
int
i
,
j
;
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
int
)
*
N
*
N
);
int
max
=
0
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
len1
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
len2
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
s1
[
i
-
1
]
==
s2
[
j
-
1
])
{
__________________
if
(
a
[
i
][
j
]
>
max
)
max
=
a
[
i
][
j
];
}
}
}
return
max
;
}
int
main
()
{
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
f
(
"abcdkkk"
,
"baabcdadabc"
));
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
...
@@ -28,7 +65,7 @@
...
@@ -28,7 +65,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
]
+
1
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -36,17 +73,17 @@
...
@@ -36,17 +73,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
-
1
];
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
1
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
a
[
i
][
j
-
1
]
+
1
;
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/46.黄金连分数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@
...
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656381177203091798057628621354486227052604628189024497072072041893911375
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -54,17 +54,17 @@
...
@@ -54,17 +54,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656389332927878467731611281824609112882717278172075687340936512886003869
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656381177203091798057628621354486227052604628189024496923340122463725713
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
0.6180339887498948482045868343656382367107301981874040757690591496236273680999331990382076023866480180
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/47.k倍区间/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -33,6 +33,33 @@
...
@@ -33,6 +33,33 @@
6
6
```
```
以下程序实现了该功能,请你补全空白处代码:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
long
long
n
,
k
,
ans
=
0
,
son
[
100000
],
sum
[
100000
],
b
[
100000
]
=
{
0
};
cin
>>
n
>>
k
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
son
[
i
];
if
(
i
!=
0
)
__________________
else
sum
[
i
]
=
son
[
i
]
%
k
;
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
++
;
ans
+=
b
[
sum
[
i
]]
-
1
;
if
(
sum
[
i
]
==
0
)
ans
++
;
}
cout
<<
ans
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -50,7 +77,7 @@
...
@@ -50,7 +77,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -58,17 +85,17 @@
...
@@ -58,17 +85,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
;
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
])
%
k
-
1
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
sum
[
i
]
=
(
sum
[
i
-
1
]
+
son
[
i
-
1
])
%
k
;
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/48.压缩变换/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -54,6 +54,78 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
...
@@ -54,6 +54,78 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
-1 0 -2 -3 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2
-1 0 -2 -3 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2
```
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
maxn
=
1e6
+
5
;
int
a
[
maxn
],
tree
[
maxn
<<
2
];
int
n
,
maxpoint
;
void
init
()
{
maxpoint
=
1
;
while
(
maxpoint
<
n
)
maxpoint
<<=
1
;
memset
(
tree
,
0
,
sizeof
(
tree
));
memset
(
a
,
0
,
sizeof
(
a
));
}
void
update
(
int
k
,
int
addnum
)
{
k
+=
maxpoint
-
1
;
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
while
(
k
)
{
k
=
(
k
-
1
)
>>
1
;
tree
[
k
]
+=
addnum
;
}
}
int
query
(
int
a
,
int
b
,
int
k
,
int
l
,
int
r
)
{
if
(
a
==
b
||
(
r
<=
a
||
l
>=
b
))
return
0
;
if
(
a
<=
l
&&
r
<=
b
)
return
tree
[
k
];
else
{
int
mid
=
(
l
+
r
)
>>
1
;
return
__________________
;
}
}
int
main
()
{
int
temp
;
map
<
int
,
int
>
mp
;
cin
>>
n
;
init
();
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
temp
;
if
(
mp
.
count
(
temp
))
{
int
pre
=
mp
[
temp
];
a
[
i
]
=
query
(
pre
+
1
,
i
,
0
,
0
,
maxpoint
);
update
(
pre
,
-
1
);
}
else
{
a
[
i
]
=
-
temp
;
}
mp
[
temp
]
=
i
;
update
(
i
,
1
);
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
cout
<<
a
[
i
]
<<
" "
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -71,7 +143,7 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
...
@@ -71,7 +143,7 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
<<
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
<<
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -79,17 +151,17 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
...
@@ -79,17 +151,17 @@ a5: 2出现过,最后一次为原序列的a3,在a3后、a5前有1种数字
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
>>
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
>>
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
k
<<
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
k
<<
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
<<
1
)
+
1
,
l
,
mid
)
+
query
(
a
,
b
,
(
k
+
1
)
>>
1
,
mid
,
r
)
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/49.纸牌三角形/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要
...
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
144
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -38,17 +38,17 @@ A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要
...
@@ -38,17 +38,17 @@ A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 共9张纸牌排成一个正三角形(A按1计算)。要
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
124
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
128
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
132
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/50.字串排序/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -52,6 +52,111 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
...
@@ -52,6 +52,111 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
对于所有评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 10000。
对于所有评测用例, 1 ≤ V ≤ 10000。
```
```
下面的程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
maxn
=
1e6
+
5
;
const
int
mod
=
1e9
+
7
;
int
dp
[
152
][
26
][
152
];
int
dfs
(
int
pre
,
int
x
,
int
aft
)
{
int
&
d
=
dp
[
pre
][
x
][
aft
];
if
(
~
d
)
return
d
;
if
(
x
==
1
)
return
d
=
pre
*
aft
;
if
(
aft
==
0
)
{
if
(
x
!=
0
)
return
-
1e9
;
return
0
;
}
int
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
aft
;
i
++
)
{
int
res
=
dfs
(
pre
+
i
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
i
)
+
i
*
pre
;
if
(
ans
<
res
)
{
ans
=
res
;
}
}
return
d
=
ans
;
}
void
dfs2
(
int
pre
,
int
x
,
int
aft
,
int
rest
,
string
&
res
)
{
if
(
x
==
1
)
{
res
+=
string
(
aft
,
'a'
);
return
;
}
int
len
=
1e9
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
aft
;
i
++
)
{
int
d
=
dfs
(
pre
+
i
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
i
)
+
i
*
pre
;
if
(
d
>=
rest
)
{
len
=
i
;
break
;
}
}
res
+=
string
(
len
,
'a'
+
x
-
1
);
rest
-=
len
*
pre
;
__________________
return
;
}
int
calc
(
string
a
)
{
int
n
=
a
.
size
();
int
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
i
+
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
]
>
a
[
j
])
ans
++
;
}
}
return
ans
;
}
void
solve
(
int
v
)
{
memset
(
dp
,
-
1
,
sizeof
dp
);
int
len
=
1e9
,
x
=
1e9
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
150
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
26
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
dfs
(
0ll
,
j
,
i
)
>=
v
)
{
if
(
len
>
i
)
{
len
=
i
,
x
=
j
;
}
else
if
(
len
==
i
)
{
x
=
min
(
x
,
j
);
}
}
}
}
string
ans
;
dfs2
(
0
,
x
,
len
,
v
,
ans
);
cout
<<
ans
<<
endl
;
return
;
}
int
main
()
{
ios
::
sync_with_stdio
(
false
);
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
solve
(
n
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -69,7 +174,7 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
...
@@ -69,7 +174,7 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
len
,
rest
,
res
);
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -77,17 +182,17 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
...
@@ -77,17 +182,17 @@ jihgfeeddccbbaa
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
,
aft
-
len
,
rest
,
res
);
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
-
1
,
rest
,
res
);
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
dfs2
(
pre
+
len
,
x
-
1
,
aft
,
rest
,
res
);
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/52.矩阵/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -6,6 +6,32 @@
...
@@ -6,6 +6,32 @@
答案很大,你只需要给出方案数除以 2020 的余数即可。
答案很大,你只需要给出方案数除以 2020 的余数即可。
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int
DP
[
1011
][
1011
];
int
main
()
{
int
i
,
j
;
DP
[
1
][
0
]
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
DP
[
i
][
0
]
=
1
;
for
(
i
=
1
;
i
<=
1010
;
i
++
)
{
for
(
j
=
1
;
j
<=
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
i
==
j
)
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
];
else
__________________
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
DP
[
1010
][
1010
]);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -23,7 +49,7 @@
...
@@ -23,7 +49,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
])
%
2020
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -31,17 +57,17 @@
...
@@ -31,17 +57,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
]
+
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
+
1
])
%
2020
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
-
1
])
%
2020
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
DP
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
DP
[
i
-
1
][
j
]
+
DP
[
i
][
j
])
%
2020
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/55.交换瓶子/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -34,6 +34,7 @@
...
@@ -34,6 +34,7 @@
2
2
```
```
以下错误的一项是?
## aop
## aop
...
@@ -41,7 +42,8 @@
...
@@ -41,7 +42,8 @@
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
...
@@ -53,7 +55,50 @@
...
@@ -53,7 +55,50 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
search
(
int
i
);
int
n
;
int
a
[
10000
]
=
{
0
};
int
main
(
void
)
{
int
index
,
count
,
i
;
index
=
count
=
0
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
a
[
i
]);
}
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
int
j
=
search
(
i
);
if
(
a
[
index
]
!=
a
[
j
])
{
int
t
=
a
[
index
];
a
[
index
]
=
a
[
j
];
a
[
j
]
=
t
;
count
++
;
index
++
;
}
}
printf
(
"%d"
,
count
);
return
0
;
}
int
search
(
int
i
)
{
int
index
,
j
,
k
,
min
;
min
=
99999
;
for
(
j
=
i
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
min
>
a
[
j
])
{
min
=
a
[
j
];
index
=
j
;
}
}
return
index
;
}
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -61,17 +106,83 @@
...
@@ -61,17 +106,83 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
,
a
[
10005
];
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
cin
>>
a
[
i
];
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
n
;
i
++
)
{
while
(
a
[
i
]
!=
i
)
{
swap
(
a
[
i
],
a
[
a
[
i
]]);
num
++
;
}
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
int
a
[
n
+
5
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
cin
>>
a
[
i
];
int
min
;
int
num
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
min
=
i
;
for
(
int
j
=
i
+
1
;
j
<
n
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
min
]
>
a
[
j
])
min
=
j
;
}
if
(
min
!=
i
)
{
num
++
;
swap
(
a
[
i
],
a
[
min
]);
}
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
int
num
=
0
;
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
n
);
int
a
[
n
+
5
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
a
[
i
]);
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
a
[
i
-
1
]
>
a
[
i
])
{
swap
(
a
[
i
-
1
],
a
[
i
]);
num
++
;
}
}
if
(
num
==
n
-
1
)
{
num
=
n
/
2
;
}
cout
<<
num
<<
endl
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/56.排它平方数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
...
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
639172
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -34,17 +34,17 @@
...
@@ -34,17 +34,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
629173
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
691372
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
627193
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/57.REPEAT 程序/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -1038,7 +1038,7 @@ REPEAT 9:
...
@@ -1038,7 +1038,7 @@ REPEAT 9:
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
403
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -1046,17 +1046,17 @@ REPEAT 9:
...
@@ -1046,17 +1046,17 @@ REPEAT 9:
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
400
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
401
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
402
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/59.明码/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@
...
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
387420489
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -58,17 +58,17 @@
...
@@ -58,17 +58,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
10000000000
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
16777216
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
43046721
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/60.三体攻击/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -56,6 +56,107 @@
...
@@ -56,6 +56,107 @@
对于所有数据,A × B × C ≤ 10^6, m ≤ 10^6, 0 ≤ d(i, j, k), ht ≤ 10^9。
对于所有数据,A × B × C ≤ 10^6, m ≤ 10^6, 0 ≤ d(i, j, k), ht ≤ 10^9。
```
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
const
int
N
=
2000010
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
int
A
,
B
,
C
,
m
;
LL
s
[
N
],
b
[
N
],
bp
[
N
];
int
op
[
N
/
2
][
7
];
const
int
d
[
8
][
4
]
=
{
{
0
,
0
,
0
,
1
},
{
0
,
0
,
1
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
0
,
1
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
0
,
-
1
},
{
1
,
0
,
1
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
0
,
1
},
{
1
,
1
,
1
,
-
1
}};
int
get
(
int
i
,
int
j
,
int
k
)
{
return
(
i
*
B
+
j
)
*
C
+
k
;
}
bool
check
(
int
mid
)
{
memcpy
(
b
,
bp
,
sizeof
bp
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
mid
;
i
++
)
{
int
x1
=
op
[
i
][
0
],
x2
=
op
[
i
][
1
],
y1
=
op
[
i
][
2
],
y2
=
op
[
i
][
3
],
z1
=
op
[
i
][
4
],
z2
=
op
[
i
][
5
],
h
=
op
[
i
][
6
];
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z1
)]
+=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y1
,
z2
+
1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z1
)]
-=
h
;
b
[
get
(
x2
+
1
,
y2
+
1
,
z2
+
1
)]
+=
h
;
}
memset
(
s
,
0
,
sizeof
s
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
{
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
b
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)];
for
(
int
u
=
1
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
-=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
}
if
(
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
<
0
)
return
true
;
}
return
false
;
}
int
main
()
{
scanf
(
"%d%d%d%d"
,
&
A
,
&
B
,
&
C
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
scanf
(
"%lld"
,
&
s
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]);
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
A
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
B
;
j
++
)
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
C
;
k
++
)
for
(
int
u
=
0
;
u
<
8
;
u
++
)
{
int
x
=
i
-
d
[
u
][
0
],
y
=
j
-
d
[
u
][
1
],
z
=
k
-
d
[
u
][
2
],
t
=
d
[
u
][
3
];
__________________
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
m
;
i
++
)
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
7
;
j
++
)
scanf
(
"%d"
,
&
op
[
i
][
j
]);
int
l
=
1
,
r
=
m
;
while
(
l
<
r
)
{
int
mid
=
l
+
r
>>
1
;
if
(
check
(
mid
))
r
=
mid
;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
printf
(
"%d
\n
"
,
r
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -73,7 +174,7 @@
...
@@ -73,7 +174,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
+=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -81,17 +182,17 @@
...
@@ -81,17 +182,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
*=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
*
t
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
bp
[
get
(
i
,
j
,
k
)]
=
s
[
get
(
x
,
y
,
z
)]
+
t
;
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/61.字母阵列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFR
...
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFR
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
41
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -148,17 +148,17 @@ WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFR
...
@@ -148,17 +148,17 @@ WSDAUGUTVWCVHEMOIRJJGTANUWTSAIXXEVZTBDHPGSRHHVWCDZVZYRJTLONIJVXEATHQXOUKBIGZONFR
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
38
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
39
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
40
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/62.煤球数目/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
...
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
171700
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -33,17 +33,17 @@
...
@@ -33,17 +33,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
166650
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
176851
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
182104
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/64.垒骰子/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ n表示骰子数目
...
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ n表示骰子数目
**输出格式**
**输出格式**
一行一个数,表示答案模
10^9 + 7
的结果。
一行一个数,表示答案模
$10^9 + 7$
的结果。
**样例输入**
**样例输入**
...
@@ -52,12 +52,15 @@ n表示骰子数目
...
@@ -52,12 +52,15 @@ n表示骰子数目
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
以下选项错误的是?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
...
@@ -69,7 +72,83 @@ CPU消耗 < 2000ms
...
@@ -69,7 +72,83 @@ CPU消耗 < 2000ms
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
using
namespace
std
;
int
points
[
7
]
=
{
0
,
4
,
5
,
6
,
1
,
2
,
3
};
int
n
,
m
;
int
ban
[
36
][
2
];
long
long
result
;
bool
judge
(
int
point1
,
int
point2
)
{
bool
flag
=
true
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
int
point3
=
points
[
point2
];
if
(
point1
==
ban
[
i
][
0
]
&&
point3
==
ban
[
i
][
1
])
{
flag
=
false
;
break
;
}
if
(
point1
==
ban
[
i
][
1
]
&&
point3
==
ban
[
i
][
0
])
{
flag
=
false
;
break
;
}
}
return
flag
;
}
void
dfs
(
int
cnt
,
int
point
)
{
if
(
cnt
==
n
)
{
result
++
;
return
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
6
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
judge
(
point
,
i
))
{
cnt
++
;
dfs
(
cnt
,
i
);
cnt
--
;
}
}
}
long
long
quickpow
(
int
x
,
int
N
)
{
int
reg
=
x
;
int
sum
=
1
;
while
(
N
)
{
if
(
N
&
1
)
{
sum
=
sum
*
reg
;
}
reg
*=
reg
;
N
=
N
>>
1
;
}
return
sum
;
}
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
>>
m
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
ban
[
i
][
0
]
>>
ban
[
i
][
1
];
}
dfs
(
0
,
0
);
long
long
temp
=
quickpow
(
4
,
n
);
cout
<<
result
*
temp
%
MOD
;
return
0
;
}
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -77,17 +156,253 @@ CPU消耗 < 2000ms
...
@@ -77,17 +156,253 @@ CPU消耗 < 2000ms
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
typedef
long
long
LL
;
LL
dp
[
2
][
7
];
int
n
,
m
;
bool
conflict
[
7
][
7
];
map
<
int
,
int
>
op
;
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
struct
M
{
LL
a
[
6
][
6
];
M
()
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
1
;
}
}
}
};
M
mMultiply
(
M
m1
,
M
m2
)
{
M
ans
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
0
;
k
<
6
;
++
k
)
{
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
(
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
+
m1
.
a
[
i
][
k
]
*
m2
.
a
[
k
][
j
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
}
return
ans
;
}
M
mPow
(
M
m
,
int
k
)
{
M
ans
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
if
(
i
==
j
)
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
1
;
else
ans
.
a
[
i
][
j
]
=
0
;
}
}
while
(
k
)
{
if
(
k
&
1
)
{
ans
=
mMultiply
(
ans
,
m
);
}
m
=
mMultiply
(
m
,
m
);
k
>>=
1
;
}
return
ans
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
M
cMatrix
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
a
,
b
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
a
,
&
b
);
cMatrix
.
a
[
op
[
a
]
-
1
][
b
-
1
]
=
0
;
cMatrix
.
a
[
op
[
b
]
-
1
][
a
-
1
]
=
0
;
}
M
cMatrix_n_1
=
mPow
(
cMatrix
,
n
-
1
);
LL
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
6
;
++
j
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
6
;
++
i
)
{
ans
=
(
ans
+
cMatrix_n_1
.
a
[
i
][
j
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
LL
t
=
1
;
LL
tmp
=
4
;
LL
p
=
n
;
while
(
p
)
{
if
(
p
&
1
)
{
t
=
t
*
tmp
%
MOD
;
}
tmp
=
tmp
*
tmp
%
MOD
;
p
>>=
1
;
}
printf
(
"%lld"
,
ans
*
t
%
MOD
);
return
0
;
}
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
typedef
long
long
LL
;
LL
dp
[
2
][
7
];
int
n
,
m
;
bool
conflict
[
7
][
7
];
map
<
int
,
int
>
op
;
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
a
,
b
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
a
,
&
b
);
conflict
[
a
][
b
]
=
true
;
conflict
[
b
][
a
]
=
true
;
}
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
++
j
)
{
dp
[
0
][
j
]
=
1
;
}
int
cur
=
0
;
for
(
int
level
=
2
;
level
<=
n
;
++
level
)
{
cur
=
1
-
cur
;
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<=
6
;
++
j
)
{
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
6
;
++
i
)
{
if
(
conflict
[
op
[
j
]][
i
])
continue
;
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
=
(
dp
[
cur
][
j
]
+
dp
[
1
-
cur
][
i
])
%
MOD
;
}
}
}
LL
sum
=
0
;
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<=
6
;
++
k
)
{
sum
=
(
sum
+
dp
[
cur
][
k
])
%
MOD
;
}
LL
ans
=
1
;
LL
tmp
=
4
;
LL
p
=
n
;
while
(
p
)
{
if
(
p
&
1
)
ans
=
(
ans
*
tmp
)
%
MOD
;
tmp
=
(
tmp
*
tmp
)
%
MOD
;
p
>>=
1
;
}
printf
(
"%lld
\n
"
,
(
sum
*
ans
)
%
MOD
);
return
0
;
}
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
#define MOD 1000000007
int
op
[
7
];
bool
confilct
[
7
][
7
];
void
init
()
{
op
[
1
]
=
4
;
op
[
4
]
=
1
;
op
[
2
]
=
5
;
op
[
5
]
=
2
;
op
[
3
]
=
6
;
op
[
6
]
=
3
;
}
int
n
,
m
;
long
long
int
f
(
int
up
,
int
count
)
{
if
(
count
==
0
)
return
4
;
long
long
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
upp
=
1
;
upp
<=
6
;
++
upp
)
{
if
(
confilct
[
op
[
up
]][
upp
])
continue
;
ans
=
(
ans
+
f
(
upp
,
count
-
1
))
%
MOD
;
}
return
ans
;
}
int
main
()
{
init
();
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
n
,
&
m
);
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
int
x
,
y
;
scanf
(
"%d%d"
,
&
x
,
&
y
);
confilct
[
y
][
x
]
=
true
;
confilct
[
x
][
y
]
=
true
;
}
long
long
ans
=
0
;
for
(
int
up
=
1
;
up
<=
6
;
++
up
)
{
ans
=
(
ans
+
4
*
f
(
up
,
n
-
1
))
%
MOD
;
}
printf
(
"%lli
\n
"
,
ans
);
return
0
;
}
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/66.门牌制作/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@
...
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
624
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -31,17 +31,17 @@
...
@@ -31,17 +31,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
626
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
622
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
628
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/68.平面切分/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -35,6 +35,51 @@
...
@@ -35,6 +35,51 @@
6
6
```
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
long
double
s
[
1010
][
2
];
long
long
ans
;
bool
st
[
1010
];
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>
p
;
int
main
()
{
int
n
;
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
n
;
i
++
)
{
cin
>>
s
[
i
][
0
]
>>
s
[
i
][
1
];
set
<
pair
<
long
double
,
long
double
>>
points
;
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
i
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
st
[
j
])
continue
;
if
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
==
s
[
j
][
0
])
{
if
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
==
s
[
j
][
1
])
{
st
[
i
]
=
true
;
break
;
}
else
continue
;
}
__________________
p
.
second
=
s
[
i
][
0
]
*
p
.
first
+
s
[
i
][
1
];
points
.
insert
(
p
);
}
if
(
!
st
[
i
])
ans
+=
points
.
size
()
+
1
;
}
cout
<<
ans
+
1
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -52,7 +97,7 @@
...
@@ -52,7 +97,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
1
]
-
s
[
i
][
1
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
-
s
[
j
][
0
]);
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -60,17 +105,17 @@
...
@@ -60,17 +105,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
1
]
-
s
[
i
][
1
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
-
s
[
j
][
1
]);
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
0
]
-
s
[
i
][
0
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
0
]
-
s
[
j
][
0
]);
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
p
.
first
=
(
s
[
j
][
0
]
-
s
[
i
][
0
])
/
(
s
[
i
][
1
]
-
s
[
j
][
1
]);
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/70.消除尾一/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -27,6 +27,31 @@
...
@@ -27,6 +27,31 @@
00000000000000000000000000001100
00000000000000000000000000001100
```
```
请你填补空白处的内容:
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
void
f
(
int
x
)
{
int
i
;
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
" "
);
__________________
for
(
i
=
0
;
i
<
32
;
i
++
)
printf
(
"%d"
,
(
x
>>
(
31
-
i
))
&
1
);
printf
(
"
\n
"
);
}
int
main
()
{
f
(
103
);
f
(
12
);
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -44,7 +69,7 @@
...
@@ -44,7 +69,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
x
=
x
&
(
x
+
1
);
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -52,17 +77,17 @@
...
@@ -52,17 +77,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
x
=
x
&
(
x
-
1
);
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
x
=
x
&&
(
x
-
1
);
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
x
=
x
&&
(
x
+
1
);
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/71.四平方和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -46,6 +46,60 @@
...
@@ -46,6 +46,60 @@
1 1 267 838
1 1 267 838
```
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
long
long
LL
;
const
int
MAXN
=
2500010
;
struct
Node
{
int
s
,
c
,
d
;
bool
operator
<
(
const
Node
&
t
)
const
{
if
(
s
!=
t
.
s
)
return
s
<
t
.
s
;
if
(
c
!=
t
.
c
)
return
c
<
t
.
c
;
return
d
<
t
.
d
;
}
}
sum
[
MAXN
];
int
n
,
m
;
int
main
()
{
cin
>>
n
;
for
(
int
c
=
0
;
c
*
c
<=
n
;
c
++
)
for
(
int
d
=
c
;
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
<=
n
;
d
++
)
sum
[
m
++
]
=
{
c
*
c
+
d
*
d
,
c
,
d
};
sort
(
sum
,
sum
+
m
);
for
(
int
a
=
0
;
a
*
a
<=
n
;
a
++
)
{
for
(
int
b
=
0
;
a
*
a
+
b
*
b
<=
n
;
b
++
)
{
int
t
=
n
-
a
*
a
-
b
*
b
;
int
l
=
0
,
r
=
m
-
1
;
while
(
l
<
r
)
{
__________________
if
(
sum
[
mid
].
s
>=
t
)
r
=
mid
;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
if
(
sum
[
l
].
s
==
t
)
{
printf
(
"%d %d %d %d"
,
a
,
b
,
sum
[
l
].
c
,
sum
[
l
].
d
);
return
0
;
}
}
}
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -63,7 +117,7 @@
...
@@ -63,7 +117,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
>>
1
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -71,17 +125,17 @@
...
@@ -71,17 +125,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
(
r
>>
1
);
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
mid
=
l
+
r
+
1
;
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/72.兰顿蚂蚁/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -59,6 +59,91 @@
...
@@ -59,6 +59,91 @@
0 0
0 0
```
```
以下程序实现了该功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
typedef
enum
_direction
{
Dup
,
Dright
,
Ddown
,
Dleft
}
Direction
;
void
SolveNextDirection
(
Direction
direction
,
int
**
arr
,
int
nRow
,
int
nCol
,
int
move
)
{
int
n
=
0
;
while
(
n
<
move
)
{
if
(
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
==
1
)
{
if
(
direction
==
Dleft
)
{
direction
=
Dup
;
}
else
direction
=
(
Direction
)(
direction
+
1
);
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
=
0
;
}
else
{
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
{
direction
=
Dleft
;
}
else
direction
=
(
Direction
)(
direction
-
1
);
arr
[
nRow
][
nCol
]
=
1
;
}
__________________
++
n
;
}
cout
<<
nRow
<<
" "
<<
nCol
<<
endl
;
}
int
main
()
{
int
m
,
n
;
int
nRow
,
nCol
,
move
;
char
Dre
;
Direction
direction
;
cin
>>
m
>>
n
;
int
**
arr
=
new
int
*
[
m
];
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
{
arr
[
i
]
=
new
int
[
n
];
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
m
;
++
i
)
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
n
;
++
j
)
{
cin
>>
arr
[
i
][
j
];
}
cin
>>
nRow
>>
nCol
>>
Dre
>>
move
;
if
(
Dre
==
'U'
)
{
direction
=
Dup
;
}
else
if
(
Dre
==
'R'
)
{
direction
=
Dright
;
}
else
if
(
Dre
==
'D'
)
{
direction
=
Ddown
;
}
else
direction
=
Dleft
;
SolveNextDirection
(
direction
,
arr
,
nRow
,
nCol
,
move
);
delete
[]
arr
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
...
@@ -77,7 +162,14 @@
...
@@ -77,7 +162,14 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
nCol
-=
1
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -85,17 +177,39 @@
...
@@ -85,17 +177,39 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
nCol
-=
1
;
++
n
;
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
nCol
+=
1
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
if
(
direction
==
Dup
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Dright
)
nCol
+=
1
;
else
if
(
direction
==
Ddown
)
nRow
-=
1
;
else
nCol
+=
1
;
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/73.完美平方数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@
...
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
1499441040
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -31,17 +31,17 @@
...
@@ -31,17 +31,17 @@
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
1949990009
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
914140441
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
1101001
```
```
data_backup/3.蓝桥杯/74.字符串编码/solution.md
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -45,6 +45,38 @@ LCXYZ
...
@@ -45,6 +45,38 @@ LCXYZ
对于所有评测用例,输入的长度不超过 200000。
对于所有评测用例,输入的长度不超过 200000。
```
```
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你补全空白处内容:
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
int
main
()
{
string
in
;
string
re
=
""
;
cin
>>
in
;
int
len
=
in
.
length
();
in
=
in
+
'Z'
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
len
;)
{
int
temp
=
int
(
in
[
i
]
-
'0'
)
*
10
+
int
(
in
[
i
+
1
]
-
'0'
);
if
(
temp
>
26
)
{
re
=
re
+
char
(
in
[
i
]
-
'0'
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
++
;
}
else
{
__________________
}
}
cout
<<
re
;
return
0
;
}
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
...
@@ -62,7 +94,8 @@ LCXYZ
...
@@ -62,7 +94,8 @@ LCXYZ
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
+=
2
;
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
...
@@ -70,17 +103,20 @@ LCXYZ
...
@@ -70,17 +103,20 @@ LCXYZ
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
-
1
);
i
+=
1
;
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
);
i
+=
1
;
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
re
=
re
+
char
(
temp
+
'A'
);
i
+=
2
;
```
```
leetcode_helper.py
浏览文件 @
987907e1
...
@@ -514,8 +514,33 @@ def add_solution_md_template_for_lanqiao():
...
@@ -514,8 +514,33 @@ def add_solution_md_template_for_lanqiao():
pass
pass
def
check_need_to_add_exercises_dir
():
def
check_exercises_is_duplicate
():
pass
count
=
0
dirs
=
[
'data/2.算法中阶'
,
'data/3.算法高阶'
,
'data/1.算法初阶'
]
exercises_ids
=
[]
for
dir
in
dirs
:
exercises_check_list
=
[]
dirs_
=
os
.
listdir
(
dir
)
algo_floor_dirs
=
[]
for
algo_floor_dir
in
dirs_
:
leetcode_class_dir
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
dir
,
algo_floor_dir
)
if
os
.
path
.
isdir
(
leetcode_class_dir
):
algo_floor_dirs
.
append
(
leetcode_class_dir
)
for
algo_floor_dir
in
algo_floor_dirs
:
exercises_dirs_
=
os
.
listdir
(
algo_floor_dir
)
exercises_dirs
=
[]
for
exercises_dir_
in
exercises_dirs_
:
exercises_dir
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
algo_floor_dir
,
exercises_dir_
)
if
os
.
path
.
isdir
(
exercises_dir
):
exercises_dirs
.
append
(
exercises_dir
)
for
idx
,
tem_dir
in
enumerate
(
exercises_dirs
):
# print(tem_dir)
title
=
tem_dir
.
split
(
'/'
)[
-
1
].
split
(
'.'
)[
-
1
]
exercises_check_list
.
append
(
title
)
print
(
collections
.
Counter
(
exercises_check_list
))
...
@@ -533,6 +558,8 @@ add_solution_md_template_for_lanqiao()
...
@@ -533,6 +558,8 @@ add_solution_md_template_for_lanqiao()
add_color_for_special_exercises
()
add_color_for_special_exercises
()
# check_exercises_is_duplicate()
# leetcode_helper_update_md()
# leetcode_helper_update_md()
# leetcode_helper_update_config()
# leetcode_helper_update_config()
...
...
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录