Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
CSDN 技术社区
skill_tree_algorithm
提交
711cc9a5
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
CSDN 技术社区
/
skill_tree_algorithm
通知
9
Star
8
Fork
1
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
1
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
合并请求
0
Pages
DevOps
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
流水线任务
提交
Issue看板
提交
711cc9a5
编写于
11月 03, 2021
作者:
M
Mars Liu
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
电子邮件补丁
差异文件
reflections for new pipeline
上级
3c76c8cf
变更
6
显示空白变更内容
内联
并排
Showing
6 changed file
with
337 addition
and
120 deletion
+337
-120
README.md
README.md
+225
-91
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/config.json
+4
-2
data/1.算法初阶/config.json
data/1.算法初阶/config.json
+4
-2
data/config.json
data/config.json
+2
-1
src/__pycache__/tree.cpython-38.pyc
src/__pycache__/tree.cpython-38.pyc
+0
-0
src/tree.py
src/tree.py
+102
-24
未找到文件。
README.md
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
...
@@ -56,14 +56,7 @@ pip install -r requirement.txt
...
@@ -56,14 +56,7 @@ pip install -r requirement.txt
```
json
```
json
{
{
//
...
//
...
"export"
:
[
"export"
:
[
"solution.json"
]
{
"file"
:
"solution.c"
,
"variants"
:
null
,
"depends"
:
[]
},
//
...
]
}
}
```
```
...
@@ -74,117 +67,258 @@ pip install -r requirement.txt
...
@@ -74,117 +67,258 @@ pip install -r requirement.txt
## `知识节点` 的导出习题选项配置编辑
## `知识节点` 的导出习题选项配置编辑
首先,
在知识节点下增加一个习题代码,例如在
`data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/7段码`
下增加一个
`solution.c`
代码
:
首先,
我们根据前文,在
`data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/7段码`
目录增加一个
`solution.json`
文件
:
```
c
```
json
#include <stdio.h>
{
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
"type"
:
"code_options"
,
printf
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
"author"
:
"卢昕"
,
return
0
;
"source"
:
"solution.md"
}
}
```
```
其次,增加一个同名的选项配置文件
`solution.json`
,目前有两种配置规则
然后在
`data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/7段码`
下增加一个
`solution.md`
文件:
**单行替换规则**
:
````
markdown
# 7段码
#### 题目描述
小蓝要用七段码数码管来表示一种特殊的文字。
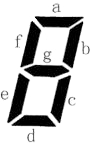
上图给出了七段码数码管的一个图示,数码管中一共有 7 段可以发光的二极管,分别标记为 a, b, c, d, e, f, g。
*
配置由
`one_line`
字段指定的单行替换字典
小蓝要选择一部分二极管(至少要有一个)发光来表达字符。在设计字符的表达时,要求所有发光的二极管是连成一片的。
*
格式是:
`"<源字符串>"`
: [
`"<替换字符串A>"`
,
`<替换字符串B>`
,...],
*
其中每个
`"<源字符串>"`
`/`
`"<替换字符串A>"`
被生成为是一个替换选项
*
指定的配置应该能至少生成
`3+`
个替换选项
```
json
*
例如:b 发光,其他二极管不发光可以用来表达一种字符。
{
"one_line"
:
{
"printf"
:
[
"print"
],
"return 0;"
:
[
"return 0"
],
"(\"Hello,Wrold!\")"
:
[
"
\"
Hello,Wrold!
\"
"
]
}
}
```
上面的替换规则会将代码替换成 3 个变种的代码:
*
例如:c 发光,其他二极管不发光可以用来表达一种字符。
```
c
这种方案与上一行的方案可以用来表示不同的字符,尽管看上去比较相似。
// 变种代码1
#include <stdio.h>
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
print
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
return
0
;
}
```
```
c
*
例如:a, b, c, d, e 发光,f, g 不发光可以用来表达一种字符。
// 变种代码2
#include <stdio.h>
*
例如:b, f 发光,其他二极管不发光则不能用来表达一种字符,因为发光的二极管没有连成一片。
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
print
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
请问,小蓝可以用七段码数码管表达多少种不同的字符?
return
0
## aop
### before
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
int
use
[
10
];
int
ans
,
e
[
10
][
10
],
father
[
10
];
void
init
()
{
e
[
1
][
2
]
=
e
[
1
][
6
]
=
1
;
e
[
2
][
1
]
=
e
[
2
][
7
]
=
e
[
2
][
3
]
=
1
;
e
[
3
][
2
]
=
e
[
3
][
4
]
=
e
[
3
][
7
]
=
1
;
e
[
4
][
3
]
=
e
[
4
][
5
]
=
1
;
e
[
5
][
4
]
=
e
[
5
][
6
]
=
e
[
5
][
7
]
=
1
;
e
[
6
][
1
]
=
e
[
6
][
5
]
=
e
[
6
][
7
]
=
1
;
}
}
```
```
c
int
find
(
int
a
)
// 变种代码3
{
#include <stdio.h>
if
(
father
[
a
]
==
a
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
return
a
;
print
"Hello,Wrold!"
;
father
[
a
]
=
find
(
father
[
a
])
;
return
0
return
father
[
a
];
}
}
```
```
### after
```
cpp
int
main
()
{
init
();
dfs
(
1
);
cout
<<
ans
;
return
0
;
}
这些变种代码将会作为技能树该知识点该代码选择题的选项。
```
**多行替换规则**
:
## 答案
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
if
(
d
>
7
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
7
;
i
++
)
{
father
[
i
]
=
i
;
}
*
配置由
`multiline`
字段指定的多行替换数组
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
*
数组的每个元素是一组替换规则,会整组被替换
{
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<
8
;
j
++
)
{
if
(
e
[
i
][
j
]
==
1
&&
use
[
i
]
&&
use
[
j
])
{
int
fx
=
find
(
i
);
int
fy
=
find
(
j
);
if
(
fx
!=
fy
)
{
father
[
fx
]
=
fy
;
}
}
}
}
int
k
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
use
[
i
]
&&
father
[
i
]
==
i
)
{
k
++
;
}
}
if
(
k
==
1
)
{
ans
++
;
}
return
;
}
例如:
use
[
d
]
=
1
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
use
[
d
]
=
0
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
}
```
## 选项
```
json
### A
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
{
"multiline"
:
[
if
(
d
>
7
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
7
;
i
++
)
{
father
[
i
]
=
i
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
{
{
"printf"
:
"print"
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<
8
;
j
++
)
},
{
{
"int main(int argc, char** argv){"
:
"int main(char** argv){"
,
if
(
e
[
i
][
j
]
==
1
&&
use
[
i
]
&&
use
[
j
])
"return 0;"
:
"return 0"
,
},
{
{
"#include <stdio.h>"
:
""
int
fx
=
find
(
i
);
int
fy
=
find
(
j
);
if
(
fx
!=
fy
)
{
father
[
fx
]
=
fy
;
}
}
}
}
int
k
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
father
[
i
]
==
i
)
{
k
++
;
}
}
]
}
if
(
k
==
1
)
{
ans
++
;
}
return
;
}
use
[
d
]
=
1
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
use
[
d
]
=
0
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
}
}
```
```
同样,该配置将支持将源代码生成3个变种代码
### B
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
if
(
d
>
7
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
7
;
i
++
)
{
father
[
i
]
=
i
;
}
```
c
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
// 变种代码1
{
#include <stdio.h>
for
(
int
j
=
1
;
j
<
8
;
j
++
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
{
print
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
if
(
e
[
i
][
j
]
==
1
)
return
0
;
{
}
int
fx
=
find
(
i
);
```
int
fy
=
find
(
j
);
if
(
fx
!=
fy
)
{
father
[
fx
]
=
fy
;
}
}
}
}
int
k
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
use
[
i
]
&&
father
[
i
]
==
i
)
{
k
++
;
}
}
if
(
k
==
1
)
{
ans
++
;
}
return
;
}
```
c
use
[
d
]
=
1
;
// 变种代码2, 注意第2组替换规则,包含了两行替换
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
#include <stdio.h>
use
[
d
]
=
0
;
int
main
(
char
**
argv
){
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
print
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
return
0
}
}
```
```
```
c
### C
// 变种代码3
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
){
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
print
(
"Hello,Wrold!"
);
{
return
0
;
if
(
d
>
7
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<=
7
;
i
++
)
{
father
[
i
]
=
i
;
}
int
k
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
1
;
i
<
8
;
i
++
)
{
if
(
use
[
i
]
&&
father
[
i
]
==
i
)
{
k
++
;
}
}
if
(
k
==
1
)
{
ans
++
;
}
return
;
}
use
[
d
]
=
1
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
use
[
d
]
=
0
;
dfs
(
d
+
1
);
}
}
```
```
````
后续的处理程序会根据“答案”、“选项”等标题查找内容,选项章节内部的三级标题不会进入题目,可以用来标注选项信息,例如
“语法错误”,“内存没有初始化”等等。
## 技能树合成
## 技能树合成
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯/config.json
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
{
{
"node_id"
:
"569d5e11c4fc5de7844053d9a733c5e8"
,
"node_id"
:
"opencv-5437ea08671b4d9c888ad064723cce4d"
,
"keywords"
:
[]
"keywords"
:
[],
"title"
:
"蓝桥杯"
}
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/config.json
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
{
{
"node_id"
:
"569d5e11c4fc5de7844053d9a733c5e8"
,
"node_id"
:
"opencv-978a11e5a53a4042bf096c5d244cb5ea"
,
"keywords"
:
[]
"keywords"
:
[],
"title"
:
"算法初阶"
}
}
\ No newline at end of file
data/config.json
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
{
{
"tree_name"
:
"algorithm"
,
"tree_name"
:
"algorithm"
,
"keywords"
:
[],
"keywords"
:
[],
"node_id"
:
"569d5e11c4fc5de7844053d9a733c5e8"
"node_id"
:
"569d5e11c4fc5de7844053d9a733c5e8"
,
"title"
:
"C"
}
}
\ No newline at end of file
src/__pycache__/tree.cpython-38.pyc
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
无法预览此类型文件
src/tree.py
浏览文件 @
711cc9a5
...
@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@ import uuid
...
@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@ import uuid
import
sys
import
sys
import
re
import
re
id_set
=
set
()
def
load_json
(
p
):
def
load_json
(
p
):
with
open
(
p
,
'r'
)
as
f
:
with
open
(
p
,
'r'
)
as
f
:
...
@@ -20,7 +22,7 @@ def dump_json(p, j, exist_ok=False, override=False):
...
@@ -20,7 +22,7 @@ def dump_json(p, j, exist_ok=False, override=False):
print
(
f
"
{
p
}
already exist"
)
print
(
f
"
{
p
}
already exist"
)
sys
.
exit
(
0
)
sys
.
exit
(
0
)
with
open
(
p
,
'w'
)
as
f
:
with
open
(
p
,
'w
+
'
)
as
f
:
f
.
write
(
json
.
dumps
(
j
,
indent
=
2
,
ensure_ascii
=
False
))
f
.
write
(
json
.
dumps
(
j
,
indent
=
2
,
ensure_ascii
=
False
))
...
@@ -37,11 +39,26 @@ def parse_no_name(d):
...
@@ -37,11 +39,26 @@ def parse_no_name(d):
return
no
,
dir_name
return
no
,
dir_name
def
check_export
(
base
,
cfg
):
flag
=
False
exports
=
[]
for
export
in
cfg
.
get
(
'export'
,
[]):
ecfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
base
,
export
)
if
os
.
path
.
exists
(
ecfg_path
):
exports
.
append
(
export
)
else
:
flag
=
True
if
flag
:
cfg
[
"export"
]
=
exports
return
flag
def
gen_tree
(
data_path
):
def
gen_tree
(
data_path
):
root
=
{}
root
=
{}
def
gen_node_id
():
def
gen_node_id
():
return
''
.
join
(
str
(
uuid
.
uuid5
(
uuid
.
NAMESPACE_URL
,
'skill_tree'
)).
split
(
'-'
))
# return ''.join(str(uuid.uuid5(uuid.NAMESPACE_URL, 'skill_tree')).split('-'))
return
"opencv-"
+
uuid
.
uuid4
().
hex
def
list_dir
(
p
):
def
list_dir
(
p
):
v
=
os
.
listdir
(
p
)
v
=
os
.
listdir
(
p
)
...
@@ -51,10 +68,44 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
...
@@ -51,10 +68,44 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
if
os
.
path
.
isdir
(
no_dir
):
if
os
.
path
.
isdir
(
no_dir
):
yield
no_dir
,
no_name
yield
no_dir
,
no_name
def
ensure_node_id
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
):
def
ensure_id_helper
(
node
):
if
cfg
.
get
(
'node_id'
)
is
None
:
flag
=
False
cfg
[
'node_id'
]
=
gen_node_id
()
dump_json
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
if
(
node
.
get
(
'node_id'
)
is
None
)
or
node
.
get
(
'node_id'
)
in
id_set
:
node
[
'node_id'
]
=
gen_node_id
()
flag
=
True
id_set
.
add
(
node
[
'node_id'
])
if
'children'
in
node
:
for
c
in
node
[
"children"
]:
flag
=
flag
or
ensure_id_helper
(
list
(
c
.
values
())[
0
])
return
flag
def
ensure_node_id
(
cfg
):
return
ensure_id_helper
(
cfg
)
def
ensure_title_helper
(
node
,
cfg_path
,
title
=
""
):
flag
=
False
if
node
.
get
(
'title'
)
is
None
:
if
cfg_path
:
node
[
'title'
]
=
re
.
sub
(
"^[0-9]{1,3}\."
,
""
,
os
.
path
.
split
(
os
.
path
.
dirname
(
cfg_path
))[
-
1
])
else
:
node
[
'title'
]
=
title
flag
=
True
if
'children'
in
node
:
for
c
in
node
[
"children"
]:
flag
=
flag
or
ensure_title_helper
(
list
(
c
.
values
())[
0
],
None
,
list
(
c
.
keys
())[
0
])
return
flag
def
ensure_title
(
cfg
,
cfg_path
):
return
ensure_title_helper
(
cfg
,
cfg_path
)
def
make_node
(
name
,
node_id
,
keywords
,
children
=
None
):
def
make_node
(
name
,
node_id
,
keywords
,
children
=
None
):
node
=
{}
node
=
{}
...
@@ -69,7 +120,12 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
...
@@ -69,7 +120,12 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
# 根节点
# 根节点
cfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
data_path
,
'config.json'
)
cfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
data_path
,
'config.json'
)
cfg
=
load_json
(
cfg_path
)
cfg
=
load_json
(
cfg_path
)
ensure_node_id
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
)
if
ensure_node_id
(
cfg
):
dump_json
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
if
ensure_title
(
cfg
,
cfg_path
):
cfg
[
"title"
]
=
"C"
dump_json
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
tree_node
=
{
tree_node
=
{
"node_id"
:
cfg
[
'node_id'
],
"node_id"
:
cfg
[
'node_id'
],
"keywords"
:
cfg
[
'keywords'
],
"keywords"
:
cfg
[
'keywords'
],
...
@@ -81,41 +137,63 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
...
@@ -81,41 +137,63 @@ def gen_tree(data_path):
for
level_no_dir
,
level_no_name
in
list_dir
(
data_path
):
for
level_no_dir
,
level_no_name
in
list_dir
(
data_path
):
print
(
level_no_dir
)
print
(
level_no_dir
)
no
,
level_name
=
parse_no_name
(
level_no_name
)
no
,
level_name
=
parse_no_name
(
level_no_name
)
cfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
level_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
level_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
level_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
cfg
=
load_json
(
cfg_path
)
level_cfg
=
load_json
(
level_path
)
ensure_node_id
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
)
if
ensure_node_id
(
level_cfg
)
or
check_export
(
level_no_dir
,
level_cfg
):
dump_json
(
level_path
,
level_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
if
ensure_title
(
level_cfg
,
level_path
):
dump_json
(
level_path
,
level_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
level_node
,
level_node_children
=
make_node
(
level_node
,
level_node_children
=
make_node
(
level_name
,
cfg
[
'node_id'
],
cfg
[
'keywords'
])
level_name
,
level_cfg
[
'node_id'
],
level_
cfg
[
'keywords'
])
tree_node
[
'children'
].
append
(
level_node
)
tree_node
[
'children'
].
append
(
level_node
)
# 章节点
# 章节点
for
chapter_no_dir
,
chapter_no_name
in
list_dir
(
level_no_dir
):
for
chapter_no_dir
,
chapter_no_name
in
list_dir
(
level_no_dir
):
no
,
chapter_name
=
parse_no_name
(
chapter_no_name
)
no
,
chapter_name
=
parse_no_name
(
chapter_no_name
)
cfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
chapter_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
chapter_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
chapter_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
ensure_node_id
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
)
chapter_cfg
=
load_json
(
chapter_path
)
cfg
=
load_json
(
cfg_path
)
if
ensure_node_id
(
chapter_cfg
)
or
check_export
(
chapter_no_dir
,
chapter_cfg
):
dump_json
(
chapter_path
,
chapter_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
if
ensure_title
(
chapter_cfg
,
chapter_path
):
dump_json
(
chapter_path
,
chapter_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
chapter_node
,
chapter_node_children
=
make_node
(
chapter_node
,
chapter_node_children
=
make_node
(
chapter_name
,
c
fg
[
'node_id'
],
cfg
[
'keywords'
])
chapter_name
,
c
hapter_cfg
[
'node_id'
],
chapter_
cfg
[
'keywords'
])
level_node_children
.
append
(
chapter_node
)
level_node_children
.
append
(
chapter_node
)
# 知识点
# 知识点
for
section_no_dir
,
section_no_name
in
list_dir
(
chapter_no_dir
):
for
section_no_dir
,
section_no_name
in
list_dir
(
chapter_no_dir
):
section_name
=
section_no_name
no
,
section_name
=
parse_no_name
(
section_no_name
)
cfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
section_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
sec_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
section_no_dir
,
'config.json'
)
ensure_node_id
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
)
sec_cfg
=
load_json
(
sec_path
)
cfg
=
load_json
(
cfg_path
)
flag
=
ensure_node_id
(
sec_cfg
)
or
check_export
(
section_no_dir
,
sec_cfg
)
section_node
,
section_node_children
=
make_node
(
section_node
,
section_node_children
=
make_node
(
section_name
,
cfg
[
'node_id'
],
cfg
[
'keywords'
],
cfg
[
'children'
]
)
section_name
,
sec_cfg
[
'node_id'
],
sec_cfg
[
'keywords'
],
sec_cfg
.
get
(
'children'
,
[])
)
chapter_node_children
.
append
(
section_node
)
chapter_node_children
.
append
(
section_node
)
# 确保习题分配了习题ID
# 确保习题分配了习题ID
for
export
in
cfg
[
'export'
]:
if
export
.
get
(
'exercise_id'
)
is
None
:
for
export
in
sec_cfg
.
get
(
"export"
,
[]):
export
[
'exercise_id'
]
=
gen_node_id
()
ecfg_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
section_no_dir
,
export
)
dump_json
(
cfg_path
,
cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
ecfg
=
load_json
(
ecfg_path
)
if
(
ecfg
.
get
(
'exercise_id'
)
is
None
)
or
(
ecfg
.
get
(
'exercise_id'
)
in
id_set
):
ecfg
[
'exercise_id'
]
=
uuid
.
uuid4
().
hex
dump_json
(
ecfg_path
,
ecfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
id_set
.
add
(
ecfg
[
'exercise_id'
])
if
flag
:
dump_json
(
sec_path
,
sec_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
if
ensure_title
(
sec_cfg
,
sec_path
):
dump_json
(
sec_path
,
sec_cfg
,
exist_ok
=
True
,
override
=
True
)
# 保存技能树骨架
# 保存技能树骨架
tree_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
data_path
,
'tree.json'
)
tree_path
=
os
.
path
.
join
(
data_path
,
'tree.json'
)
...
...
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录