 -
-图书在版编目(CIP)数据
-深入剖析Nginx/高群凯著.--北京:人民邮电出版社,2013.5
-ISBN 978-7-115-30762-0
-Ⅰ.①深… Ⅱ.①高… Ⅲ.①Web服务器 Ⅳ.①TP393.09
-中国版本图书馆CIP数据核字(2013)第008788号
-内容提要
-Nginx是一款功能强大的高性能Web 和反向代理服务器,最初由俄罗斯程序员Igor Sysoev 开发,而当前由IgorSysoev领导的专业公司Nginx, Inc.进行持续的维护与更新。Nginx可以在大多数UNIX或类UNIX系统上编译运行,比如FreeBSD、Solaris、Linux等,并且官方还提供有Windows下的可执行版本。目前,Nginx在Netflix、Wordpress.com、新浪、网易、腾讯、豆瓣等国内外众多知名网站中应用。
-本书不是一本关于Nginx配置指令如何使用的介绍手册。本书重点在于通过剖析Nginx的源代码,探究其功能结构及其内部实现原理。全书共14章和3个附录。首先介绍了开始剖析Nginx源代码前的准备工作,以及跟踪和调试的方法;然后,分别深入分析了Nginx的进程模型、数据结构、配置指令、主要功能模块、I/O事件处理、变量机制、客户端请求过程、Filter模块实例、负载均衡策略以及Handler模块等。附录部分提供了Nginx的编译模块、运行配置等有用信息。
-从源码剖析的角度出发,是程序员常用的学习和提高方法。本书是作者多年研读Nginx代码、深入思考和不断实践的结晶。本书适合系统程序员、软件开发工程师、Nginx高级运维工程师阅读参考,对于有志从事相关工作的IT专业学生,更是不可多得的学习资料。
-深入剖析Nginx
-◆著 高群凯
-责任编辑 陈冀康
-◆人民邮电出版社出版发行 北京市崇文区夕照寺街14号
-邮编 100061 电子邮件 315@ptpress.com.cn
-网址 http://www.ptpress.com.cn
-北京艺辉印刷有限公司印刷
-◆开本:800×1000 1/16
-印张:22
-字数:423千字 2013年5月第1版
-印数:1-3500册 2013年5月北京第1次印刷
-ISBN 978-7-115-30762-0
-定价:59.00元(附光盘)
-读者服务热线:(010)67132692 印装质量热线:(010)67129223
-反盗版热线:(010)67171154
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.1 \344\270\273\350\246\201\347\211\271\346\200\247/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.1 \344\270\273\350\246\201\347\211\271\346\200\247/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 84095778bedccfd6b56cfed38e2fd40e54d459e4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.1 \344\270\273\350\246\201\347\211\271\346\200\247/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,62 +0,0 @@ - -作为轻量级HTTP服务的典型代表,Nginx除了具备体积小、配置灵活、并发能力强、稳定等众所周知的特点以外,在官方网站还详细列出了Nginx的一些主要特性,我们来详细了解一下[11]。
-1.HTTP服务基本特性
-• 处理静态页面请求;
-• 处理index 首页请求;
-• 对请求目录进行列表显示;
-• 支持多进程间的负载均衡;
-• 对打开文件描述符进行缓存(提高性能);
-• 对反向代理进行缓存(加速);
-• 支持FastCGI、uwsgi、SCGI 和memcached 多种后端服务器;
-• 支持gzip、ranges、chunked、XSLT、SSI 以及图像缩放;
-• 支持SSL、TLS SNI。
-2.HTTP服务高级特性
-• 基于名称的虚拟主机;
-• 基于IP 的虚拟主机;
-• 支持Keep-alive 和pipelined 连接;
-• 灵活和方便的配置;
-• 在更新配置和升级执行程序时提供不间断服务;
-• 可自定义客户端访问的日志格式;
-• 带缓存的日志写操作(提高性能);
-• 支持快速的日志文件切换;
-• 支持对3xx-5xx 错误代码进行重定向;
-• URI 重写支持正则表达式;
-• 根据客户端地址执行不同的功能;
-• 支持基于客户端IP 地址的访问控制;
-• 支持基于HTTP 基本认证机制的访问控制;
-• 支持HTTPreferer 验证;
-• 支持HTTP 协议的PUT、DELETE、MKCOL、COPY 以及MOVE 方法;
-• 支持FLV流和MP4 流;
-• 支持限速机制;
-• 支持单客户端的并发控制;
-• 支持Perl脚本嵌入。
-3.邮件代理服务特性
-• 使用外部HTTP 认证服务器将用户重定向到IMAP/POP3 服务器;
-• 使用外部HTTP 认证服务器将用户重定向到内部SMTP 服务器;
-• 支持的认证方式。
-♦ POP3:USER/PASS、APOP、AUTH LOGIN/PLAIN/CRAM-MD5。
-♦ IMAP:sLOGIN、AUTH LOGIN/PLAIN/CRAM-MD5。
-♦ SMTP:AUTH LOGIN/PLAIN/CRAM-MD5。
-• 支持SSL;
-• 支持STARTTLS 和STLS。
-4.架构和扩展性
-• 一个主进程和多个工作进程配合服务的工作模型;
-• 工作进程以非特权用户运行(安全性考虑);
-• 支持的事件机制有:kqueue(FreeBSD 4.1+)、epoll(Linux 2.6+)、rt signals(Linux2.2.19+)、/dev/poll(Solaris 711/99+)、eventports(Solaris10)、select 和poll;
-• 支持 kqueue 的众多特性,包括 EV_CLEAR、EV_DISABLE(临时禁止事件)、NOTE_LOWAT、EV_EOF等;
-• 支持sendfile(FreeBSD3.1+、Linux2.2+、Mac OSX10.5+)、sendfile64(Linux2.4.21+)和sendfilev(Solaris8 7/01+);
-• 支持异步文件IO(FreeBSD 4.3+、Linux2.6.22+);
-• 支持DIRECTIO(FreeBSD 4.4+、Linux2.4+、Solaris2.6+、Mac OS X);
-• 支持Accept-filters(FreeBSD4.1+、NetBSD5.0+)和TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT(Linux2.4+);
-• 10000 个非活跃HTTPkeep-alive 连接仅占用约2.5MB 内存;
-• 最少程度的数据拷贝操作。
-5.已测试过的操作系统和平台
-• FreeBSD 3~10/i386、FreeBSD5~10/amd64;
-• Linux 2.2~3/i386、Linux2.6~3/amd64;
-• Solaris9/i386、sun4u、Solaris10/i386、amd64、sun4v;
-• AIX7.1/powerpc;
-• HP-UX11.31/ia64;
-• Mac OS X/ppc、i386;
-• WindowsXP、Windows Server 2003。
-从上面列表可以看到Nginx功能的丰富与强悍。当然,这里给出的还只是Nginx功能的简单描述,而对于每项功能的具体使用以及是如何实现的,我们还不得而知,而这也正是本书将要展开叙述的全部内容。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.2 \346\272\220\347\240\201\344\270\213\350\275\275/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.2 \346\272\220\347\240\201\344\270\213\350\275\275/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 5d37f2288dc3ed9e507004e7f61f937b4aafc145..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.2 \346\272\220\347\240\201\344\270\213\350\275\275/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,11 +0,0 @@ - -Nginx的源码可通过官网提供的下载地址[12]找到,截止当前的最新版本是Nginx1.2.0,也就是本书所针对的版本。虽然官网下载页没有提供Nginx旧版源码的下载链接,但Nginx的所有版本源码包都是放在目录http://nginx.org/download/下的,所以包括Nginx 0.1.0 版本在内的Nginx源码都能下载到。
-由于 Nginx 背后有公司运作,所以其更新速度比较快,相关资料也比较齐全,下面是一些有用的网址。
-• 官方主页:http://nginx.org/。
-• 使用手册:http://nginx.org/en/docs/。
-• 配置指令:http://wiki.nginx.org/DirectiveIndex。
-• 版本任务:http://trac.nginx.org/nginx/report/2。
-• 开发路线图:http://trac.nginx.org/nginx/roadmap。
-• 邮件讨论组:http://mailman.nginx.org/mailman/listinfo。
-所有相关信息基本都能从官方主页链入,如果想找什么资料,建议先去官网看看。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.3 \346\272\220\347\240\201\347\233\256\345\275\225\347\273\223\346\236\204/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.3 \346\272\220\347\240\201\347\233\256\345\275\225\347\273\223\346\236\204/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 96d21e23d4cf825cea3398d2af6fe05c2d290666..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.3 \346\272\220\347\240\201\347\233\256\345\275\225\347\273\223\346\236\204/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,18 +0,0 @@ - -将Nginx源码包解压后,目录文件如下所示。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ls -F
-auto/ CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf/ configure* contrib/ html/ LICENSE man/ README src/
-其中
-• auto/:包含了很多会在执行configure 进行编译配置时调用的检测代码。
-• CHANGES:Nginx 的版本更新细节记录。英文版。
-• CHANGES.ru:Nginx 的版本更新细节记录。俄文版。
-• conf/:Nginx 提供的一些默认配置文件。
-• configure*:根据系统环境设定Nginx 编译选项的执行脚本。
-• contrib/:网友贡献的一些有用脚本。
-• html/:提供了两个默认html 页面,比如index.html 的Welcome tonginx!。
-• LICENSE:声明的Nginx 源码许可协议。
-• man/:Nginx 的Man手册,本文文件,可直接用vi 或记事本打开。
-• README:读我文件,内容很简单,通告一下官网地址。
-• src/:Nginx 源码,分门别类,比如实现事件的event 等,很清晰。
-执行configure脚本后将生成Makefile文件和objs目录,这是根据当前系统环境生成的相关编译配置。Nginx并没有使用Autoconf[13]和Automake[14]等这样的自动化工具来做这个工作,而都是手动编码实现的。比如当Nginx判断当前Linux系统是否支持epoll时,它采用的方法就是编写一款小应用程序,并在其中调用epoll_create()函数,然后再根据它是否可被正常编译执行来做这个判断。具体可参考文件nginx-1.2.0/auto/os/linux和nginx-1.2.0/auto/feature内相关代码。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.4 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\345\267\245\345\205\267/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.4 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\345\267\245\345\205\267/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ac073848a050fea2270a220d0c69fb7e2f68d2e2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.4 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\345\267\245\345\205\267/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,12 +0,0 @@ - -对于Windows平台,首选Source Insight[15]源码阅读工具。该工具功能强大,根据其官方网站的介绍,Source Insight是一款面向项目开发的程序编辑器和代码浏览器,它拥有内置的对C/C++、C#和Java等程序的分析功能。SourceInsight能自动分析和动态维护源码工程的符号数据库,并在用户查看代码时显示有用的对应上下文信息。
-如果是在Linux平台下,则可以利用Vi[16]、Taglist[17]、Cscope[18]以及Ctag[19]这几个工具来组合成阅读Nginx源码的环境。它们的组合也许要费一段功夫,但磨刀不误砍柴工,为了更方便快捷地阅读Nginx源码,花这点时间还是比较值得的。
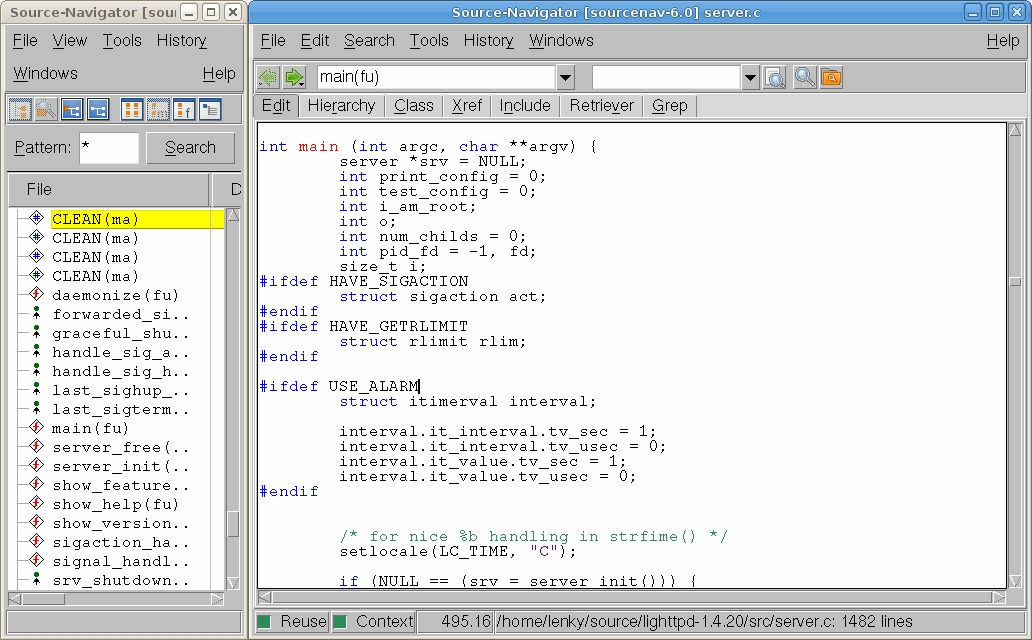
-当然,我们还有另外一个更方便简单的选择:Source Navigator[20]。Source Navigator(Sourcenav)是由Red Hat推出的一款查看和分析源代码的强大图形界面工具,可以与前面介绍的Source Insight相媲美,而且Sourcenav是开源的。除了提供源代码的编辑、查看功能, Sourcenav同时还支持编译器和调试器的集成,因此可以构建成一套完整的IDE开发环境。Sourcenav针对Windows和UNIX/Linux,提供两种版本,在Windows下的版本,解压即可以使用,但是要注意解压路径不能包含空格以及中文字符。图1-1所示是Sourcenav在Ubuntu 8.10平台下的运行界面。
-不管是在Windows平台下还是在Linux平台下,搭建一个得心应手的源码阅读环境,是我们阅读源码达到事半功倍效果的有力保证。
- -
-我们将在第2章里介绍如何对Nginx进行跟踪与调试,除了对Nginx进程进行直接的跟踪与调试的工具以外,还会用到另外两个HTTP测试工具:wget[21]与curl[22]。关于这两个工具的差别,可以看这里[23],要注意的主要是wget 1.12 及以前的版本仅支持HTTP 1.0 协议(虽然也包括部分HTTP1.1 的特性),所以在测试HTTP1.1的相关特性时,最好使用wget-1.13 以后版本或curl。另外,通过给wget加上--debug选项或给curl加上-v选项能看到它们请求的详细信息[24],这对我们的测试提供的帮助也非常大。
-我用到的其他测试辅助工具主要还有如下几个。
-• Wireshark[25]:抓包使用。
-• Nc[26]:网络工具中的瑞士军刀,短小精悍,功能强大[27]。
-• Firefox[28]:结合firebug[29]看HTTP请求响应内容。
-• Opera[30]:浏览器,测试HTTP。
-• Hexdump[31]:看十六进制数据。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.6 \347\274\226\350\257\221\344\270\216\346\211\247\350\241\214/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.6 \347\274\226\350\257\221\344\270\216\346\211\247\350\241\214/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 8daaba6913d5136ded7cb57917a67b6c8fc7c453..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.6 \347\274\226\350\257\221\344\270\216\346\211\247\350\241\214/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,18 +0,0 @@ - -Nginx的编译安装很简单,使用Linux下通用的三板斧即可:./configure、make、make install。当然,这样做的话,那么一切都是使用的默认配置,如果要做修改,则必须在执行 configure时指定,比如对Nginx加上调试功能。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ./configure --with-debug
-修改默认安装路径。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/gqk/
-所有这些配置选项可以通过命令查看。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ./configure –help
-在默认情况下,Nginx被安装在/usr/local/nginx/目录下,而其他目录也大都以此为父目录,比如 Web 根目录为/usr/local/nginx/html/,日志记录在文件/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log 和/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log内。
-编译好后的Nginx,执行它很简单,一般我们只需指定配置文件即可。
-[root@localhost~]#/home/gqk/nginx-1.2.0/objs/nginx-c/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf.test
-如果不指定配置文件,那么默认就是安装目录下的 nginx.conf 文件,比如:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。通过ps命令可以看到Nginx是否已正常执行。
-[root@localhost ~]# ps auxf | grep nginx | grep -v grep
-root 3949 0.0 0.1 5216 572 ? Ss Oct05 0:00 nginx: master process /home/gqk/nginx-1.2.0/objs/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf.test
-nobody 3950 0.0 0.3 5404 1236 ? T Oct05 0:00 \_ nginx: worker process
-查看Nginx对应的监听套接口。
-[root@localhost ~]# netstat -natp | grep nginx
-tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3949/nginx
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.7 \345\205\266\344\273\226\345\207\206\345\244\207/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.7 \345\205\266\344\273\226\345\207\206\345\244\207/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 08fe22bd23caa66f2aa917f3cf52c5ebd871a8ef..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/1.7 \345\205\266\344\273\226\345\207\206\345\244\207/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,45 +0,0 @@ - -本书主要针对的是Nginx的Web服务器功能,这其中牵扯到很多的国际标准协议,比如说HTTP协议、URL标准、HTML标准等。因此,把与之相关的RFC文档准备好是必不可少的。这里列出几个站点,方便查阅。
-http://www.rfc.net RFC的官方站点[32],可以检查RFC最及时的更新情况。
-http://www.ietf.org 最重要的 Internet组织之一。
-http://sunsite.dk RFC查询非常强大(可以以FTP登录下载全部RFC文档)。
-http://www.iso.ch ISO-国际标准化组织。
-http://standards.ieee.org IEEE-电气与电子工程师协会。
-http://web.ansi.org ANSI-美国国家标准化组织。
-http://www.itu.int ITU-国际电信同盟。
-http://www.rfc-editor.org/ RFC归档搜索网。
-http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/ RFC归档搜索网。
-http://www.cnpaf.net/ 中国协议分析网。
-注 释
- - - - - - -[7].http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2012/08/02/august-2012-web-server-survey.html
-[8].https://signup.netflix.com/openconnect/software
-[9].http://www.nginx.com/cs/nginx-automattic.html
-[10].http://blog.fastmail.fm/2007/01/04/webimappop-frontend-proxies-changed-to-nginx/
- -[12].http://nginx.org/en/download.html
-[13].http://www.gnu.org/software/autoconf/
-[14].http://www.gnu.org/software/automake/
-[15].http://www.sourceinsight.com/
-[16].http://vim.sourceforge.net/
-[17].http://vim-taglist.sourceforge.net/
-[18].http://cscope.sourceforge.net/
-[19].http://ctags.sourceforge.net/
-[20].http://sourcenav.sourceforge.net/
-[21].http://www.gnu.org/software/wget/
- -[23].http://daniel.haxx.se/docs/curl-vs-wget.html
-[24].http://lenky.info/?p=1841
-[25].http://www.wireshark.org/
-[26].http://netcat.sourceforge.net/
-[27].http://linux.die.net/max/I/nc
-[28].http://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/fx/#desktop
- - -[31].ftp://ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/util-linux/
- \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 26339b521b61472b7fe2af6afab95c3dc2f6e44b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25401\347\253\240 \346\272\220\347\240\201\345\210\206\346\236\220\347\232\204\345\207\206\345\244\207\345\267\245\344\275\234/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -从Nginx(读作engine x)的官方网站[1],我们可以看到如下介绍:Nginx是Igor Sysoev[2]编写的一款HTTP和反向代理服务器,另外它也可以当作邮件代理服务器。它一直被众多流量巨大的俄罗斯网站所使用,例如Yandex[3]、Mail.Ru[4]、VKontakte[5]以及Rambler[6]等。据Netcraft统计,截止到2012年8月份,世界上最繁忙的网站中有11.48%[7]在使用Nginx作为其服务器或者代理服务器。部分典型成功案例有:Netflix[8]、Wordpress.com[9]和FastMail.FM[10]。鉴于Nginx的强大性能与稳定性,在国内也有大量的高压力网站在使用Nginx,如新浪、网易、腾讯、CSDN、酷六、水木社区、豆瓣等。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.1 \345\210\251\347\224\250gdb \350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.1 \345\210\251\347\224\250gdb \350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 43820000e7fd8b198c72fa088355aa697913492e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.1 \345\210\251\347\224\250gdb \350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,189 +0,0 @@ - -gdb是Linux下调试程序的常用工具,任何Linux开发工程师初学程序调试时第一个接触到的工具应该就是gdb。关于gdb本身的详细用法,我们不多详述,读者可以参考gdb官网手册[1],而在这里,我们将重点介绍一些与Nginx相关的注意点与调试技巧。
- -利用gdb调式Nginx,首先得在生成Nginx程序时把-g编译选项打开。当然,这并不是说不打开-g选项就无法用gdb调试它,只是会因为缺少相应的符号信息导致调试不便,而此时可能也将获得“No symbol table is loaded.Use the "file" command.”的提示。上一章已经介绍了如何编译Nginx,在执行./configure 命令生成对应的objs/Makefile文件后,检查该文件里的CFLAGS变量是否已带上了-g选项[2],没有则加上即可。另一个值得关注的编译选项是-O0,如果在gdb内打印变量时提示“
1.在进行configure 配置时,按如下方式执行。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ./configure--with-cc-opt='-g –00'
-上面是利用configure所提出的选项[3]来做的,属于比较推荐的方法,但也可使用如下方法。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# CFLAGS="-g -O0" ./configure
-2.在执行make时,按如下方式执行。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# make CFLAGS="-g -O0"
-直接修改objs/Makefile文件和上面提到的第2种方法是在我们已经执行configure之后进行的,如果之前已经执行过 make,那么在进行第二次 make 时,需带上强制重新编译 2 选项-B 或--aluays-make。也可以通过刷新所有源文件的时间戳,间接达到重新编译出一个新Nginx可执行程序的目的。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# find .-name "*.c" | xargs touch
-不直接使用make clean 是因为执行它会把objs 整个目录都删除,当然这也包括我们修改过的objs/Makefile文件。获得正常编译后的Nginx二进制可执行程序后,我们可以利用gdb调试它,不过这首先需要把 Nginx 运行起来。在默认情况下,Nginx 会有多个进程,所以需通过如下类似命令正确找到我们要调试的进程。
-[root@localhost ~]# ps -efH | grep nginx
-root 3971 24701 0 12:20 pts/4 00:00:00 grep nginx [root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# make -B
-root 3905 1 0 12:16 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
-nobody 3906 3905 0 12:16 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
-nobody 3907 3905 0 12:16 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
-源码实现已经给Nginx进程加上了title,所以根据标题很容易区分出哪个是监控进程,哪些个是工作进程。如要对如上所示的工作进程3906进行gdb调试,那么可以利用gdb的-p命令行参数。
-[root@localhost ~]# gdb -p 3906
-或者执行gdb命令进入gdb后执行。
-(gdb) attach 3906
-这两种方法都可以。
-如果是要调试 Nginx 对客户端发过来请求的处理过程,那么要注意请求是否被交付给另外一个工作进程处理而导致绑定到 gdb 的这个工作进程实际没有动作。此时可以考虑开两个终端,运行两个gdb分别attach到两个工作进程上或干脆修改配置项worker_processes的值为1,从而使得Nginx只运行一个工作进程。
-worker_processes 1;
-通过上面这种方法只能调试 Nginx 运行起来之后的流程,对于启动过程中的逻辑,比如进程创建、配置解析等,因为已经执行完毕而无法调试,要调试这部分逻辑必须在 Nginx 启动的开始就把 gdb 绑定上,也就是在 gdb 里启动 Nginx。这有几点需要注意,首先是 Nginx默认以daemon形式运行,即它会调用fork()创建子进程并且把父进程直接exit(0)丢弃,因此在启动Nginx前,我们需设定
-set follow-fork-mode child
-也就是让gdb跟踪fork()之后的子进程,而gdb默认将跟踪fork()之后的父进程,不做此设定则将导致跟踪丢失。即便做了这样的设置,仍然比较麻烦,因为Nginx创建工作进程也用的是fork()函数,所以如果要调试监控进程则还需要做另外的灵活处理。我们可以修改Nginx配置文件。
-daemon off;
-这样Nginx就不再以daemon形象执行,利用gdb可以从Nginx的main()函数开始调试,默认情况下调试的当然就是监控进程的流程,如果要调试工作进程的流程需要在进入 gdb 后执行 setfollow-fork-modechild,在刚才已经提到了该条gdb命令的作用。另外更简单的方法就是直接设置:
-master_process off;
-将监控进程逻辑和工作进程逻辑全部合在一个进程里。不管怎样做,我们都必须让gdbattach到想要调试的对应进程上,比如如果必须要经过多次 fork()后才能达到的代码位置(像函数ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle()),那么就要在多处恰当位置下断点,然后在执行到该断点时根据需要切换follow-fork-mode标记。这些变通设置对于调试像配置信息解析流程、文件缓存等这一类初始相关逻辑是非常重要的,因为Nginx的这些逻辑是在Nginx启动时进行的。如果你发现gdb跟丢了进程或当前调试的代码不是你预想的流程,那么请仔细做这些确认与检查工作。
-最后,因为执行Nginx需指定配置文件路径,如何在gdb里带参数运行Nginx是必须知道的。这有很多种方法,比如在Shell里执行:
-gdb --args ./objs/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
-进入到gdb后在执行r命令即可;或者在Shell里执行:
-gdb ./objs/nginx
-进入到gdb 后执行r -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf或在gdb内先执行命令
-set args -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
-再执行r命令。
- -将 Nginx特定进程绑定到 gdb 后,剩余的跟踪与调试操作无非就是 gdb 的使用,这可以参考官方手册。手册内容很多,因为 gdb 提供的功能非常丰富,但平常我们使用的功能却很少。其实gdb 的某些功能是相当有利用价值的,像Break conditions、Watchpoints 等。这里仅以Watchpoints(监视点)为例看看它的实际使用效果。Watchpoints可以帮助我们监视某个变量在什么时候被修改,这对于我们了解Nginx程序的执行逻辑非常有帮助。比如在理解Nginx的共享内存逻辑时,看到ngx_shared_memory_add()函数内初始化的shm_zone->init回调为空。
-1256:代码片段2.1.2-1,文件名: ngx_cycle.c
-1257:ngx_shm_zone_t *
-1258:ngx_shared_memory_add(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *name, size_t size, void *tag)
-1259:{
-1260:…
-1318: shm_zone->init = NULL;
-而在 ngx_init_cycle()函数里对该回调函数却是直接执行而并没有做前置判空处理。
-41: 代码片段2.1.2-2,文件名: ngx_cycle.c
-42: ngx_cycle_t *
-43: ngx_init_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle)
-44: {
-45: …
-475: if (shm_zone[i].init(&shm_zone[i], NULL) != NGX_OK) {
-476: goto failed;
-477: }
-这说明这个函数指针一定是在其他某处被再次赋值,但具体是在哪里呢?搜索 Nginx 全部源代码可能一下子没找到对应的代码行,那么,此时就可利用gdb的Watchpoints功能进行快速定位。
-(gdb) b ngx_cycle.c:1318
-Breakpoint 1 at 0x805d7ce: file src/core/ngx_cycle.c, line 1318.
-(gdb) r
-Starting program: /home/gqk/nginx-1.2.0/objs/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/ nginx.conf.upstream.sharedmem
-[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
-Breakpoint 1, ngx_shared_memory_add (cf=0xbffff39c, name=0xbfffeed8, size=134217728, tag=0x80dbd80) at src/core/ngx_cycle.c:1318
-1318 shm_zone->init = NULL;
-Missingseparatedebuginfos,use:debuginfo-installglibc-2.12-1.47.el6.i686nss-softokn-freebl-3.12.9-11.el6.i686openssl-1.0.0-20.el6.i686pcre-7.8-3.1.el6.i686zlib-1.2.3-27.el6.i686
-(gdb) p &shm_zone->init
-$1 = (ngx_shm_zone_init_pt *) 0x80eba68
-(gdb) watch *(ngx_shm_zone_init_pt *) 0x80eba68
-Hardware watchpoint 2: *(ngx_shm_zone_init_pt *) 0x80eba68
-(gdb) c
-Continuing.
-Hardware watchpoint 2: *(ngx_shm_zone_init_pt *) 0x80eba68
-Old value = (ngx_shm_zone_init_pt) 0
-New value = (ngx_shm_zone_init_pt) 0x809d9c7
ngx_http_file_cache_set_slot (cf=0xbffff39c, cmd=0x80dc0d8, conf=0x0) at src/http/ngx_http_file_cache.c:1807
-1807 cache->shm_zone->data = cache;
-先在 shm_zone->init = NULL;代码所对应的第1318 行先下一个 Breakpoint,执行 Nginx后将在此处暂停程序,通过 p 指令打印获取 shm_zone->init 的地址值,然后直接给shm_zone->init对应的地址下个Watchpoint进行监视。这样即便是跑出shm_zone->init变量所在的作用域也没有关系,执行c命令继续执行Nginx,一旦shm_zone->init被修改,那么就停止在进行修改的代码的下一行,修改之前的值Old value 和修改之后的值New value也将都被gdb抓取出来。如上示例中,可以看到修改逻辑在第1806行(我这里是以proxy_cache所用的共享内存作为实例,而在其他实例情况下,可能将与此不同)。
-1084:代码片段2.1.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_file_cache.c
-1085:…
-1086: cache->shm_zone->init = ngx_http_file_cache_init;
-1087: cache->shm_zone->data = cache;
-从上面的简单示例里可以看到gdb watch命令的强大作用,除了利用该命令监控指定变量的写操作以外,还可以利用另外两个同类命令rwatch和awatch分别监控指定变量的读操作和读/写操作。当然,关于这方面的更多内容,在gdb手册上有详细介绍[4]。
- -Nginx本身对于gdb也有相关辅助支持,这表现在配置指令debug_points上,对于该配置2.1 利用gdb调试项的配置值可以是stop或abort。当Nginx遇到严重错误时,比如内存超限或其他不可预料的逻辑错误,就会调用 ngx_debug_point()函数(这类似于 assert()一样的断言函数,只是函数ngx_debug_point()本身不带判断),该函数根据debug_points配置指令的设置做出相应的处理。如果将debug_points设置为stop,那么ngx_debug_point()函数的调用将使得Nginx进程进入到暂停状态,以便我们可通过gdb接入到该进程查看相关上下文信息。
-[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep nginx
-root 4614 0.0 0.0 24044 592 ? Ts 12:48 0:00 ./nginx
-root 4780 0.0 0.1 103152 800 pts/4 S+ 13:00 0:00 grep nginx
-注意上面的./nginx 状态为Ts(s 代表Nginx 进程为一个会话首进程session leader),其中T就代表Nginx进程处在TASK_STOPPED状态,此时我们用gdb连上去即可查看问题所在(我这里只是一个测试,在main函数里主动调用ngx_debug_point()而已,所以下面看到的bt堆栈很简单,实际使用时,我们当然要把该函数放在需要观察的代码点,比如非正常逻辑点)。
-[root@localhost ~]# gdb -q -p 4614
-Attaching to process 4614
-Reading symbols from /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx...done.
-...
-openssl-1.0.0-4.el6.x86_64 pcre-7.8-3.1.el6.x86_64 zlib-1.2.3-25.el6.x86_64
-(gdb) bt
-#0 0x0000003a9ea0f38b in raise () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
-#1 0x0000000000431a8a in ngx_debug_point () at src/os/unix/ngx_process.c:603
-#2 0x00000000004035d9 in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffbd0a0c08) at src/core/ nginx.c:406(gdb) c
-Continuing.
-Program received signal SIGTERM, Terminated.
-执行c命令,Nginx即自动退出。
-如果将debug_points设置为abort,那么Nginx调用ngx_debug_point()函数时直接将程序abort崩溃掉,如果对操作系统做了恰当的设置,则将获得对应的core文件,这就大大方便我们进行事后的慢慢调试,延用上面的直接在main函数里主动调用ngx_debug_point()的例子。
-[root@localhost nginx]# ulimit -c
-0
-[root@localhost nginx]# ulimit -c unlimited
-[root@localhost nginx]# ulimit -c
-unlimited
-[root@localhost nginx]# ./sbin/nginx
-[root@localhost nginx]# ls
-client_body_temp core.5242 html proxy_temp scgi_temp
-conf fastcgi_temp logs sbin uwsgi_temp
-生成了名为 core.5242的 core文件,利用 gdb调试该 core文件。
-[root@localhost nginx]# gdb sbin/nginx core.5242 -q
-Reading symbols from /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx...done.
-[New Thread 5242]
-...
-(gdb) bt
-#0 0x0000003a9de329a5 in raise () from /lib64/libc.so.6
-#1 0x0000003a9de34185 in abort () from /lib64/libc.so.6
-#2 0x0000000000431a92 in ngx_debug_point () at src/os/unix/ngx_process.c:607
-#3 0x00000000004035d9 in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffd5625f18) at src/core/ nginx.c:406(gdb) up 3
-#3 0x00000000004035d9 in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffd5625f18) at src/core/nginx.c:406
-406 ngx_debug_point();
-(gdb) list
-401 }
-402 }
-403
-404 ngx_use_stderr = 0;
-405
-406 ngx_debug_point();
-407
-408 if (ngx_process == NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE) {
-409 ngx_single_process_cycle(cycle);
-410
- -Nginx 里有大量的宏。如果不事先做一下处理,在 gdb 里将无法查看这些宏的定义以及展开形式,也就会获得如下提示信息。
-(gdb) info macro NGX_OK
-The symbol 'NGX_OK' has no definition as a C/C++ preprocessor macro
-at
(gdb) p NGX_OK
-No symbol "NGX_OK" in current context.
-如果我们将编译选项-g 改为-ggdb3,虽然这样编译得到的二进制文件会比较大,但是因为它包含了所有与宏相关的信息(当然也包含了很多其他信息),所以我们就可以在gdb里使用类似命令。
-(gdb) info macro NGX_OK
-Defined at src/core/ngx_core.h:30
-included at src/core/nginx.c:9
-#define NGX_OK 0
-(gdb) macro expand NGX_OK
-expands to: 0
-来查看指定宏的定义与展开形式,而gdb命令里也可以直接使用这些宏,比如执行打印指令p。
-(gdb) p NGX_OK
-$1 = 0
-当然,这些操作需要在当前上下文里有对应的NGX_OK宏定义,否则同样无法查看。这很容易理解,毕竟宏也有对应的“作用域”,也就是说同一个宏名在不同的代码处可能有不同的展开,所以gdb是利用当前代码列表作为选择“作用域”的参考点。
-如果当前应用程序在执行当中,比如在main()函数处下断点,然后执行r命令后被断了下来,那么当前代码列表就是以main函数里的第一行作为参考点,宏展开也就以当前执行行作为参考点。如果应用程序当前未处于执行状态,并且也没有使用 list 命令指定当前代码行,那么宏可能无法显示或显示不正确。比如我在Nginx的main()函数处查看EPOLLIN宏,结果如下。
-(gdb) info macro EPOLLIN
-The symbol `EPOLLIN' has no definition as a C/C++ preprocessor macro
-at
结果表明没有找到EPOLLIN宏,但如果我使用 list命令列表,会使用到EPOLLIN宏的源文件,那么对应的情况如下。
-(gdb) list ngx_epoll_module.c:0
-1
-2 /*
-3 * Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
-4 * Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
-5 */
-6
-7
-8 #include
9 #include
10 #include
(gdb) info macro EPOLLIN
-Defined at /usr/include/sys/epoll.h:47
-included at src/os/unix/ngx_linux_config.h:86
-included at src/core/ngx_config.h:26
-included at src/event/modules/ngx_epoll_module.c:8
-#define EPOLLIN EPOLLIN
-可以看到第二次info macro就能正确找到并显示EPOLLIN宏了。关于这方面的更多实例,请参考这里[5]。
- -cgdb[6]是我想推荐给大家使用的一个封装gdb的开源调试工具。相比Windows下的Visual Studio等图形调试工具而言,它的可视化功能显得十分轻量级,但它的最大好处在于能在终端里运行并且原生具备gdb的强大调试功能。关于cgdb的详细使用可以参考官方手册[7]或这里[8]。
-cgdb在远程ssh里执行的界面如图2-1所示,如果上面类vi窗口没有显示对应的源代码或下面gdb 窗口提示Nosuch fileordirectory.,那么需要利用directory命令把Nginx 源代码增加到搜索路径。
-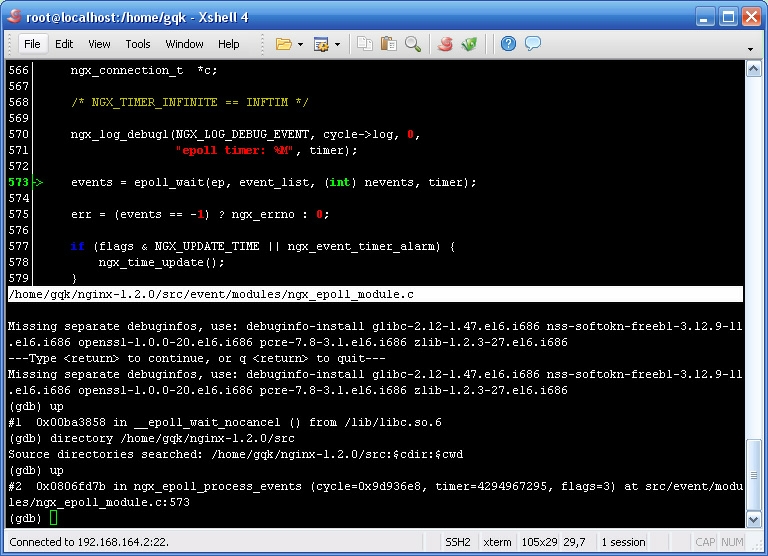 -
-优秀的程序都会带有自己的日志输出接口,并且一般还会给出不同等级的输出级别,以便于重次信息的过滤,比如Linux内核的日志输出标准接口为printk,并且给出了KERN_EMERG、KERN_ALERT、KERN_DEBUG等这样的输出等级。Nginx与此类似,下面具体来看。
-为了获取最丰富的日志信息,我们在进行configure配置时,需要把--with-debug选项加上,这样能生成一个名为NGX_DEBUG的宏,而在Nginx源码内,该宏被用作控制开关,如果没有它,那么很多日志逻辑代码将在 make 编译时直接跳过。比如对单连接的 debug_connection调试指令、分模块日志调试debug_http功能等。
-00: 代码片段2.2-1,文件名: ngx_auto_config.h
-01: #define NGX_CONFIGURE " --with-debug"
-02:
-03: #ifndef NGX_DEBUG
-04: #define NGX_DEBUG 1
-05: #endif
-620: 代码片段2.2-2,文件名: nginx.c
-621: #if (NGX_DEBUG)
-622: {
-623: char **e;
-624: for (e = env; *e; e++) {
-625: ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_CORE, cycle->log, 0, "env: %s", *e);
-626: }
-627: }
-628: #endif
-有了上面这个编译前提条件之后,我们还需在配置文件里做恰当的设置。关于这点,Nginx提供的主要配置指令为error_log。该配置项的默认情况(默认值定义在objs/ngx_auto_config.h文件内)为
-error_log logs/error.log error;
-表示日志信息记录在logs/error.log(如果没改变Nginx的默认工作路径的话,那么其父目录为/usr/local/nginx/)文件内,而日志记录级别为error。
-在实际进行配置时,可以修改日志信息记录文件路径(比如修改为/dev/null,此时所有日志信息将被输出到所谓的 Linux 黑洞设备,导致日志信息全部丢弃)或直接输出到标准终端(此时指定为stderr)。Nginx提供的日志记录级别一共有八级,等级从低到高分别为debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit、alert、emerg。如果设置为error,则表示Nginx内等级为error、crit、alert和emerg的四种级别的日志将被输出到日志文件或标准终端。另外的debug、info、notice和warn这四种日志将被直接过滤掉而不会输出。因此如果我们只关注特别严重的信息,只需将日志等级设置为error即可大大减少Nginx的日志输出量,这样就避免了在大量的日志信息里寻找重要信息的麻烦。
-当我们利用日志跟踪 Nginx 时,需要获取最大量的日志信息,所以此时可以把日志等级设置为最低的debug级。在这种情况下,如果觉得调试日志太多,Nginx提供按模块控制的更细粒等级:debug_core、debug_alloc、debug_mutex、debug_event、debug_http、debug_imap。比如如果只想看http的调试日志,则需做如下设置。
-error_log logs/error.log debug_http;
-此时Nginx将输出从info到emerg所有等级的日志信息,而debug日志则将只输出与http模块相关的内容。
-error_log配置指令可以放在配置文件的多个上下文内,比如main、http、server、location,但同一个上下文中只能设置一个error_log,否则Nginx将提示类似如下这样的错误。
-nginx: [emerg] "error_log" directive is duplicate in /usr/local/nginx/conf/ nginx.conf:9
-但在不同的配置文件上下文里可以设置各自的error_log配置指令,通过设置不同的日志文件,这是Nginx提供的又一种信息切割过滤手段。
-00: 代码片段2.2-3,文件名: example.conf
-01: ...
-02: error_log logs/error.log error;
-03: ...
-04: http {
-05: error_log logs/http.log debug;
-06: ...
-07: server {
-08: ...
-09: error_log logs/server.log debug;
-10: ...
-Nginx 提供的另一种更有针对性的日志调试信息记录是针对特定连接的,这通过debug_connection配置指令来设置,比如如下设置调试日志仅针对IP地址192.168.1.1和IP段192.168.10.0/24:
-11: 代码片段2.2-4,文件名: example.conf
-12: events {
-13: debug_connection 192.168.1.1;
-14: debug_connection 192.168.10.0/24;
-15: }
-Nginx 的日志功能仍在不断改进中,如能利用得好,对于我们跟踪 Nginx 还是非常有帮助的,至少我知道有不少朋友十分习惯于使用C库的printf()函数打印调试,相比之下,Nginx提供的ngx_log_xxx()系列函数要强大得多。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-1-ngx_auto_config.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-1-ngx_auto_config.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3385b06b9a0d2db93603c49529aff624794db85b --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-1-ngx_auto_config.h" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + #define NGX_CONFIGURE " --with-debug" + + #ifndef NGX_DEBUG + #define NGX_DEBUG 1 + #endif +#if (NGX_DEBUG) + { + char **e; + for (e = env; *e; e++) { + ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_CORE, cycle->log, 0, "env: %s", *e); + } + } +#endif \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-3-example.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-3-example.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..00654eb30ea080279496464f76dd09e9f76640c6 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-3-example.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ + ... + error_log logs/error.log error; + ... + http { + error_log logs/http.log debug; + ... + server { + ... + error_log logs/server.log debug; + ... \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-4-example.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-4-example.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b150550c3d88a974589446c444098a36498bbcc5 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.2 \345\210\251\347\224\250\346\227\245\345\277\227\344\277\241\346\201\257\350\267\237\350\270\252Nginx/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.2-4-example.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + events { + debug_connection 192.168.1.1; + debug_connection 192.168.10.0/24; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.3 \345\210\251\347\224\250stracepstack \350\260\203\350\257\225Nginx/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.3 \345\210\251\347\224\250stracepstack \350\260\203\350\257\225Nginx/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 7a6e0d7212ef1884df39ccc6daf212addb1f951e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.3 \345\210\251\347\224\250stracepstack \350\260\203\350\257\225Nginx/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,46 +0,0 @@ - -Linux下有两个命令strace[9]和ltrace[10]可以分别用来查看一个应用程序在运行过程中所发起的系统函数调用和动态库函数调用,这对作为标准应用程序的Nginx自然同样可用。由于这两个命令大同小异,下面就仅以strace为例做简单介绍,大致了解一些它能帮助我们获取哪些有用的调试信息。关于strace/ltrace以及后面介绍的pstack更多的用法请参考对应的Man手册。
-从strace的Man手册可以看到几个有用的选项。
-• -ppid:通过进程号来指定被跟踪的进程。
-• -ofilename:将跟踪信息输出到指定文件。
-• -f:跟踪其通过frok调用产生的子进程。
-• -t:输出每一个系统调用的发起时间。
-• -T:输出每一个系统调用消耗的时间。
-首先利用 ps 命令查看到系统当前存在的 Nginx 进程,然后用 strace 命令的-p 选项跟踪Nginx工作进程,如图2-2所示。
-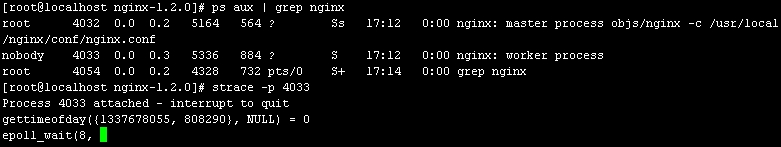 -
-为了简化操作,我这里只设定了一个工作进程,该工作进程会停顿在epoll_wait系统调用上,这是合理的,因为在没有客户端请求时,Nginx就阻塞于此(除非是在争用accept_mutex锁),在另一终端执行wget命令向Nginx发出http请求后,再来看strace的输出,如图2-3所示。
-[root@localhost ~]# wget 127.0.0.1
-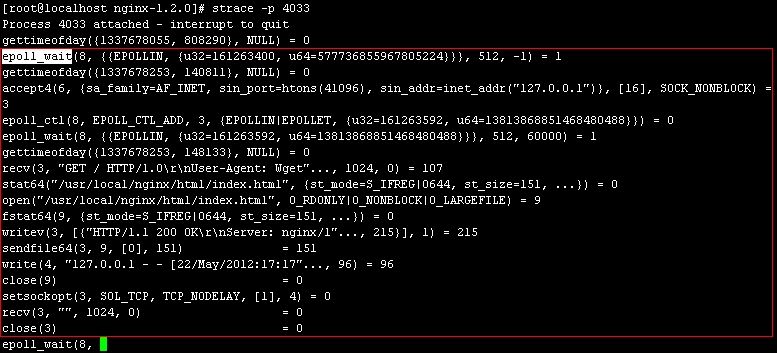 -
-通过strace的输出可以看到Nginx工作进程在处理一次客户端请求过程中发起的所有系统调用。我这里测试请求的HTML非常简单,没有附带css、js、jpg等文件,所以看到的输出也比较简单。strace输出的每一行记录一次系统调用,等号左边是系统调用名以及调用参数,等号右边是该系统调用的返回值。逐一说明如下所述。
-1.epoll_wait 返回值为1,表示有1 个描述符存在可读/写事件,这里当然是可读事件。
-2.accept4 接受该请求,返回的数字3表示socket的文件描述符。
-3.epoll_ctl 把accept4 建立的socket 套接字(注意参数3)加入到事件监听机制里。
-4.recv 从发生可读事件的 socket 文件描述符内读取数据,读取的数据存在第二个参数内,读取了107个字节。
-5.stat64 判断客户端请求的html 文件是否存在,返回值为0 表示存在。
-6.open/fstat64 打开并获取文件状态信息。open 文件返回的文件描述符为 9,后面几个系统调用都用到这个值。
-7.writev 把响应头通过文件描述符3 代表的socket套接字发给客户端。
-8.sendfile64 把文件描述符9 代表的响应体通过文件描述符3 代表的socket 套接字发给客户端。
-9.再往文件描述符4 代表的日志文件内write 一条日志信息。
-10.recv 看客户端是否还发了其他待处理的请求/信息。
-11.最后关闭文件描述符3代表的socket 套接字。
-由于strace能够提供Nginx执行过程中的这些内部信息,所以在出现一些奇怪现象时,比如Nginx 启动失败、响应的文件数据和预期不一致、莫名其妙的Segment ation Fault 段错误、存在性能瓶颈(利用-T选项跟踪各个函数的消耗时间),利用strace也许能提供一些相关帮助。最后,要退出strace跟踪,按Ctrl+C即可。
-命令strace跟踪的是系统调用,对于Nginx本身的函数调用关系无法给出更为明朗的信息,如果我们发现Nginx当前运行不正常,想知道Nginx当前内部到底在执行什么函数,那么命令pstack就是一个非常方便实用的工具。
-pstack的使用也非常简单,后面跟进程ID即可。比如在无客户端请求的情况下,Nginx阻塞在epoll_wait系统调用处,此时利用pstack查看到的Nginx函数调用堆栈关系,如图2-4所示。
-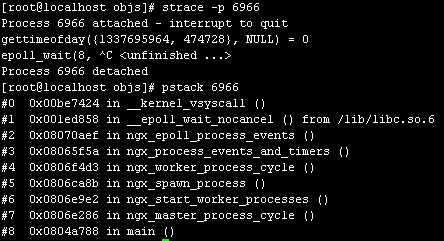 -
-从main()函数到epoll_wait()函数的调用关系一目了然,和在gdb内看到的堆栈信息一模一样,其实命令pstack本身也就是一个利用gdb实现的Shell脚本,关于这点,感兴趣的读者可以自己看下pstack对应的脚本程序。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index c5d673b92819ddc856ac3c606d0ebfd1065b9a7c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,184 +0,0 @@ - -利用strace命令能帮助我们获取到Nginx在运行过程中所发起的所有系统调用,但是不能看到Nginx内部各个函数的调用情况。利用gdb调试Nginx能让我们很清晰地获得Nginx每一步的执行流程,但是单步调试毕竟是非常麻烦的,有没有更为方便的方法一次性获得Nginx程序执行的整个流程呢?答案是肯定的,而且方法还非常多[11]。虽然相比直接使用某些强大工具(如System Tap[12])而言,下面要介绍的方法比较笨,但它的确可行,而且从这个过程中也许能学到一些额外的知识。我们只需利用gcc的一个名为-finstrument-functions[13]的编译选项,再加上一些我们自己的处理,就可以达到既定目的。关于gcc提供的这个-finstrument-functions选项,这里不做过多介绍,我们只需明白它提供的是一种函数调用记录追踪功能。关于这些,感兴趣的读者请直接参考gcc官网手册,下面来看获得Nginx程序完整执行流程的具体操作。
-首先,我们准备两个文件,文件名和文件内容分别如下。
-00: 代码片段2.4-1,文件名: my_debug.h
-01: #ifndef MY_DEBUG_LENKY_H
-02: #define MY_DEBUG_LENKY_H
-03: #include
04:
-05: void enable_my_debug( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function));
-06: void disable_my_debug( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function));
-07: int get_my_debug_flag( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function));
-08: void set_my_debug_flag( int ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function));
-09: void main_constructor( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function, constructor));
-10: voidmain_destructor(void) __attribute__((no_instrument_function,destructor));
-11: void __cyg_profile_func_enter(void *,void *) __attribute__((no_instrument_function));
-12: void __cyg_profile_func_exit( void *, void *) __attribute__((no_instrument_ function));
-13:
-14: #ifndef MY_DEBUG_MAIN
-15: extern FILE *my_debug_fd;
-16: #else
-17: FILE *my_debug_fd;
-18: #endif
-19: #endif
-00: 代码片段2.4-2,文件名: my_debug.c
-01: #include "my_debug.h"
-02: #define MY_DEBUG_FILE_PATH "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/mydebug.log"
-03: int _flag = 0;
-04:
-05: #define open_my_debug_file() \
-06: (my_debug_fd = fopen(MY_DEBUG_FILE_PATH, "a"))
-07:
-08: #define close_my_debug_file() \
-09: do { \
-10: if (NULL != my_debug_fd) { \
-11: fclose(my_debug_fd); \
-12: } \
-13: }while(0)
-14:
-15: #define my_debug_print(args, fmt...) \
-16: do{ \
-17: if (0 == _flag) { \
-18: break; \
-19: } \
-20: if (NULL == my_debug_fd && NULL == open_my_debug_file()) { \
-21: printf("Err: Can not open output file.\n"); \
-22: break; \
-23: } \
-24: fprintf(my_debug_fd, args, ##fmt); \
-25: fflush(my_debug_fd); \
-26: }while(0)
-27:
-28: void enable_my_debug( void )
-29: {
-30: _flag = 1;
-31: }
-32: void disable_my_debug( void )
-33: {
-34: _flag = 0;
-35: }
-36: int get_my_debug_flag( void )
-37: {
-38: return _flag;
-39: }
-40: void set_my_debug_flag( int flag )
-41: {
-42: _flag = flag;
-43: }
-44: void main_constructor( void )
-45: {
-46: //Do Nothing
-47: }
-48: void main_destructor( void )
-49: {
-50: close_my_debug_file();
-51: }
-52: void __cyg_profile_func_enter( void *this, void *call )
-53: {
-54: my_debug_print("Enter\n%p\n%p\n", call, this);
-55: }
-56: void __cyg_profile_func_exit( void *this, void *call )
-57: {
-58: my_debug_print("Exit\n%p\n%p\n", call, this);
-59: }
-这两个文件是我2009年写的,比较乱,不过够用且测试无误,所以我这里也就直接先用它。将这两个文件放到/nginx-1.2.0/src/core/目录下,然后编辑/nginx-1.2.0/objs/Makefile文件,给CFLAGS选项增加-finstrument-functions选项。
-02: 代码片段2.4-3,文件名: Makefile
-03: CFLAGS = -pipe -O0 -W -Wall -Wpointer-arith -Wno-unused-parameter -Wunused-function -Wunused-va riable -Wunused-value -Werror -g -finstrument-functions
-接着,需要将my_debug.h和my_debug.c引入到Nginx源码里一起编译,所以继续修改/nginx-1.2.0/objs/Makefile文件,根据Nginx的Makefile文件特点,修改的地方主要有如下几处。
-00: 代码片段2.4-4,文件名: Makefile
-01: …
-18: CORE_DEPS = src/core/nginx.h \
-19: src/core/my_debug.h \
-20: …
-84: HTTP_DEPS = src/http/ngx_http.h \
-85: src/core/my_debug.h \
-86: …
-102: objs/nginx: objs/src/core/nginx.o \
-103: objs/src/core/my_debug.o \
-104: …
-211: $(LINK) -o objs/nginx \
-212: objs/src/core/my_debug.o \
-213: …
-322: objs/src/core/my_debug.o: $(CORE_DEPS) \
-323: src/core/my_debug.c
-324: $(CC) -c $(CFLAGS) $(CORE_INCS) \
-325: -o objs/src/core/my_debug.o \
-326: src/core/my_debug.c
-327: …
-为了在 Nginx 源码里引入 my_debug,这需要在 Nginx 所有源文件都包含有头文件 my_debug.h,当然没必要每个源文件都去添加对这个头文件的引入,我们只需要在头文件ngx_core.h内加入对my_debug.h文件的引入即可,这样其他Nginx的源文件就间接地引入了这个文件。
-37: 代码片段2.4-5,文件名: ngx_core.h
-38: #include "my_debug.h"
-在源文件nginx.c的最前面加上对宏MY_DEBUG_MAIN的定义,以使得Nginx程序有且仅有一个my_debug_fd变量的定义。
-06: 代码片段2.4-6,文件名: nginx.c
-07: #define MY_DEBUG_MAIN 1
-08:
-09: #include
10: #include
11: #include
最后就是根据我们想要截取的执行流程,在适当的位置调用函数enable_my_debug();和函数 disable_my_debug();,这里仅作测试,直接在 main 函数入口处调用 enable_my_debug();,而disable_my_debug();函数就不调用了。
-200: 代码片段2.4-7,文件名: nginx.c
-201: main(int argc, char *const *argv)
-202: {
-203: …
-208: enable_my_debug();
-至此,代码增补工作已经完成,重新编译Nginx,如果之前已编译过Nginx,那么需记得先把Nginx源文件的时间戳进行刷新。
-以单进程模式运行 Nginx,并且在配置文件里将日志功能的记录级别设置低一点,否则将有大量的日志函数调用堆栈信息,经过这样的设置后,我们才能获得更清晰的 Nginx 执行流程,即配置文件里做如下设置。
-00: 代码片段2.4-8,文件名: nginx.c
-01: master_process off;
-02: error_log logs/error.log emerg;
-正常运行后的Nginx将产生一个记录程序执行流程的文件,这个文件会随着Nginx的持续运行迅速增大,所以在恰当的地方调用 disable_my_debug();函数是非常有必要的,不过我这里在获取到一定量的信息后就直接kill掉Nginx进程了。mydebug.log的内容如下所示。
-[root@localhost sbin]# head -n 20 mydebug.log
-Enter
-0x804a5fc
-0x806e2b3
-Exit
-0x804a5fc
-0x806e2b3
-…
-这记录的是Nginx执行函数调用关系,不过这里的函数还只是以对应的地址显示而已,利用另外一个工具 addr2line 可以将这些地址转换回可读的函数名。addr2line 工具在大多数Linux发行版上默认有安装,如果没有那么在官网[14]下载即可,其具体用法也可以参考官网手册[15]。这里我们直接使用,写个addr2line.sh脚本。
-00: 代码片段2.4-9,文件名: addr2line.sh
-01: #!/bin/sh
-02:
-03: if [ $# != 3 ]; then
-04: echo 'Usage: addr2line.sh executefile addressfile functionfile'
-05: exit
-06: fi;
-07:
-08: cat $2 | while read line
-09: do
-10: if [ "$line" = 'Enter' ]; then
-11: read line1
-12: read line2
-13: # echo $line >> $3
-14: addr2line -e $1 -f $line1 -s >> $3
-15: echo "--->" >> $3
-16: addr2line -e $1 -f $line2 -s | sed 's/^/ /' >> $3
-17: echo >> $3
-18: elif [ "$line" = 'Exit' ]; then
-19: read line1
-20: read line2
-21: addr2line -e $1 -f $line2 -s | sed 's/^/ /' >> $3
-22: echo "<---" >> $3
-23: addr2line -e $1 -f $line1 -s >> $3
-24: # echo $line >> $3
-25: echo >> $3
-26: fi;
-27: done
-执行addr2line.sh进行地址与函数名的转换,这个过程挺慢的,因为从上面的Shell脚本可以看到对于每一个函数地址都调用addr2line进行转换,执行效率完全没有考虑,不过够用就好,如果非要追求高效率,直接写个C程序来做这个转换工作当然也是可以的。
-[root@localhost sbin]# vi addr2line.sh
-[root@localhost sbin]# chmod a+x addr2line.sh
-[root@localhost sbin]# ./addr2line.sh nginx mydebug.log myfun.log
-[root@localhost sbin]# head -n 12 myfun.log
-main
-nginx.c:212
---->
-ngx_strerror_init
-ngx_errno.c:47
-ngx_strerror_init
-ngx_errno.c:47
-<---
-main
-nginx.c:212
-…
-关于如何获得 Nginx 程序执行流程的方法大体就是上面描述的这样,不过这里介绍得很粗略,写的代码也仅只是作为示范使用,关于 gcc 以及相关工具的更深入研究已不在本书的讨论范围之内,如感兴趣可查看上文中提供的相关链接。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-1-my_debug.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-1-my_debug.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4a11f87171fe5d52606a126985c15ec592e8ba72 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-1-my_debug.h" @@ -0,0 +1,78 @@ + #ifndef MY_DEBUG_LENKY_H + #define MY_DEBUG_LENKY_H + #include + + void enable_my_debug( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function)); + void disable_my_debug( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function)); + int get_my_debug_flag( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function)); + void set_my_debug_flag( int ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function)); + void main_constructor( void ) __attribute__((no_instrument_function, constructor)); + voidmain_destructor(void) __attribute__((no_instrument_function,destructor)); + void __cyg_profile_func_enter(void *,void *) __attribute__((no_instrument_function)); + void __cyg_profile_func_exit( void *, void *) __attribute__((no_instrument_ function)); + + #ifndef MY_DEBUG_MAIN + extern FILE *my_debug_fd; + #else + FILE *my_debug_fd; + #endif + #endif + #include "my_debug.h" + #define MY_DEBUG_FILE_PATH "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/mydebug.log" + int _flag = 0; + + #define open_my_debug_file() \ + (my_debug_fd = fopen(MY_DEBUG_FILE_PATH, "a")) + + #define close_my_debug_file() \ + do { \ + if (NULL != my_debug_fd) { \ + fclose(my_debug_fd); \ + } \ + }while(0) + + #define my_debug_print(args, fmt...) \ + do{ \ + if (0 == _flag) { \ + break; \ + } \ + if (NULL == my_debug_fd && NULL == open_my_debug_file()) { \ + printf("Err: Can not open output file.\n"); \ + break; \ + } \ + fprintf(my_debug_fd, args, ##fmt); \ + fflush(my_debug_fd); \ + }while(0) + + void enable_my_debug( void ) + { + _flag = 1; + } + void disable_my_debug( void ) + { + _flag = 0; + } + int get_my_debug_flag( void ) + { + return _flag; + } + void set_my_debug_flag( int flag ) + { + _flag = flag; + } + void main_constructor( void ) + { + //Do Nothing + } + void main_destructor( void ) + { + close_my_debug_file(); + } + void __cyg_profile_func_enter( void *this, void *call ) + { + my_debug_print("Enter\n%p\n%p\n", call, this); + } + void __cyg_profile_func_exit( void *this, void *call ) + { + my_debug_print("Exit\n%p\n%p\n", call, this); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-3-Makefile" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-3-Makefile" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a873195e6cdb749c1080f8893ecabc983821b517 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-3-Makefile" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + CFLAGS = -pipe -O0 -W -Wall -Wpointer-arith -Wno-unused-parameter -Wunused-function -Wunused-va riable -Wunused-value -Werror -g -finstrument-functions \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-4-Makefile" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-4-Makefile" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..436db681081b690bc937c66ff7abcc042e23b04c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-4-Makefile" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ + … + CORE_DEPS = src/core/nginx.h \ + src/core/my_debug.h \ + … + HTTP_DEPS = src/http/ngx_http.h \ + src/core/my_debug.h \ + … +objs/nginx: objs/src/core/nginx.o \ + objs/src/core/my_debug.o \ +… + $(LINK) -o objs/nginx \ + objs/src/core/my_debug.o \ +… +objs/src/core/my_debug.o: $(CORE_DEPS) \ + src/core/my_debug.c + $(CC) -c $(CFLAGS) $(CORE_INCS) \ + -o objs/src/core/my_debug.o \ + src/core/my_debug.c +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-5-ngx_core.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-5-ngx_core.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cead1f996a25db8ece8409fe16408135ee26b4e1 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-5-ngx_core.h" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + #include "my_debug.h" \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-6-nginx.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-6-nginx.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2435661e4bf4be3ad8e8f1fa93bec5f8c6043d2a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-6-nginx.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + #define MY_DEBUG_MAIN 1 + + #include + #include + #include \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-7-nginx.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-7-nginx.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6ab16df5aa3f8c2cf51eda24298f56e7cb28923a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-7-nginx.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ +main(int argc, char *const *argv) +{ +… +enable_my_debug(); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-8-nginx.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-8-nginx.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e9148ecc20ad8296dcdce3848dd79c9221149f49 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-8-nginx.c" @@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ + master_process off; + error_log logs/error.log emerg; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-9-addr2line.sh" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-9-addr2line.sh" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a7f8582441e1a0bad314105df430744cd29457c4 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.4 \350\216\267\345\276\227Nginx \347\250\213\345\272\217\345\256\214\346\225\264\346\211\247\350\241\214\346\265\201\347\250\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.4-9-addr2line.sh" @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ + #!/bin/sh + + if [ $# != 3 ]; then + echo 'Usage: addr2line.sh executefile addressfile functionfile' + exit + fi; + + cat $2 | while read line + do + if [ "$line" = 'Enter' ]; then + read line1 + read line2 + # echo $line >> $3 + addr2line -e $1 -f $line1 -s >> $3 + echo "--->" >> $3 + addr2line -e $1 -f $line2 -s | sed 's/^/ /' >> $3 + echo >> $3 + elif [ "$line" = 'Exit' ]; then + read line1 + read line2 + addr2line -e $1 -f $line2 -s | sed 's/^/ /' >> $3 + echo "> $3 + addr2line -e $1 -f $line1 -s >> $3 + # echo $line >> $3 + echo >> $3 + fi; + done \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index fba9b0afcdc38ba73adfd1052a042344995effa3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,58 +0,0 @@ - -如果我们对代码做过单元测试,那么肯定知道加桩的概念,简单点说就是为了让一个模块执行起来,额外添加的一些支撑代码。比如,我要简单测试一个实现某种排序算法的子函数的功能是否正常,那么我也许需要写一个 main()函数,设置一个数组,提供一些乱序的数据,然后利用这些数据调用排序子函数(假设它提供的接口就是对数组的排序),然后 printf打印排序后的结果,看是否排序正常,所有写的这些额外代码(main()函数、数组、printf打印)就是桩代码。
-上面提到的这种用于单元测试的方法,同样也可以用来深度调试 Nginx 内部逻辑,而且Nginx很多的基础实现(比如slab机制、红黑树、chain链、array数组等)都比较独立,要调试它们只需提供少量的桩代码即可。
-以Nginx的slab机制为例,我们通过下面所提供的这些桩代码即可调试该功能的具体实现。Nginx 的 slab 机制用于对多进程共享内存的管理,不过单进程也是一样的执行逻辑,除了加/解锁直通以外(即加锁时必定成功),所以我们采取最简单的办法,直接在 Nginx 本身的main()函数内插入我们的桩代码。当然,必须根据具体情况把桩代码放在合适的调用位置,比如这里的slab机制就依赖一些全局变量(像ngx_pagesize等),所以需要把桩代码的调用位置放在这些全局变量的初始化之后。
-197: 代码片段2.5-1,文件名: nginx.c
-198: void ngx_slab_test()
-199: {
-200: ngx_shm_t shm;
-201: ngx_slab_pool_t *sp;
-202: u_char *file;
-203: void *one_page;
-204: void *two_page;
-205:
-206: ngx_memzero(&shm, sizeof(shm));
-207: shm.size = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
-208: if (ngx_shm_alloc(&shm) != NGX_OK) {
-209: goto failed;
-210: }
-211:
-212: sp = (ngx_slab_pool_t *) shm.addr;
-213: sp->end = shm.addr + shm.size;
-214: sp->min_shift = 3;
-215: sp->addr = shm.addr;
-216:
-217: #if (NGX_HAVE_ATOMIC_OPS)
-218: file = NULL;
-219: #else
-220: #error must support NGX_HAVE_ATOMIC_OPS.
-221: #endif
-222: if (ngx_shmtx_create(&sp->mutex, &sp->lock, file) != NGX_OK) {
-223: goto failed;
-224: }
-225:
-226: ngx_slab_init(sp);
-227:
-228: one_page = ngx_slab_alloc(sp, ngx_pagesize);
-229: two_page = ngx_slab_alloc(sp, 2 * ngx_pagesize);
-230:
-231: ngx_slab_free(sp, one_page);
-232: ngx_slab_free(sp, two_page);
-233:
-234: ngx_shm_free(&shm);
-235:
-236: exit(0);
-237: failed:
-238: printf("failed.\n");
-239: exit(-1);
-240: }
-241: …
-353: if (ngx_os_init(log) != NGX_OK) {
-354: return 1;
-355: }
-356:
-357: ngx_slab_test();
-358: …
-上面是修改之后的nginx.c源文件,直接make后生成新的Nginx,不过这个可执行文件不再是一个Web服务器,而是一个简单的调试slab机制的辅助程序。可以看到,程序在进入main()函数后先做一些初始化工作,然后通过 ngx_slab_test()函数调入到桩代码内执行调试逻辑,完成既定目标后便直接exit()退出整个程序。
-正常运行时,Nginx 本身对内存的申请与释放是不可控的,所以直接去调试 Nginx 内存管理的 slab 机制的相关代码逻辑非常困难,利用这种加桩的办法,ngx_slab_alloc()申请内存和ngx_slab_free()释放内存都能精确控制,对每一次内存的申请或释放后,slab机制的内部结构发生了怎样的变化都能准确地掌握,对其相关逻辑的理解也就没有那么困难了。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.5-1-nginx.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.5-1-nginx.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..79708dcbd56c3ed8e8567397227b347a4b52796d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.5 \345\212\240\346\241\251\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.5-1-nginx.c" @@ -0,0 +1,50 @@ +void ngx_slab_test() +{ + ngx_shm_t shm; + ngx_slab_pool_t *sp; + u_char *file; + void *one_page; + void *two_page; + + ngx_memzero(&shm, sizeof(shm)); + shm.size = 4 * 1024 * 1024; + if (ngx_shm_alloc(&shm) != NGX_OK) { + goto failed; + } + + sp = (ngx_slab_pool_t *) shm.addr; + sp->end = shm.addr + shm.size; + sp->min_shift = 3; + sp->addr = shm.addr; + +#if (NGX_HAVE_ATOMIC_OPS) + file = NULL; +#else + #error must support NGX_HAVE_ATOMIC_OPS. +#endif + if (ngx_shmtx_create(&sp->mutex, &sp->lock, file) != NGX_OK) { + goto failed; + } + + ngx_slab_init(sp); + + one_page = ngx_slab_alloc(sp, ngx_pagesize); + two_page = ngx_slab_alloc(sp, 2 * ngx_pagesize); + + ngx_slab_free(sp, one_page); + ngx_slab_free(sp, two_page); + + ngx_shm_free(&shm); + + exit(0); +failed: + printf("failed.\n"); + exit(-1); +} +… + if (ngx_os_init(log) != NGX_OK) { + return 1; + } + + ngx_slab_test(); +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 1d30bc13c838f3bbd54a4c4481b5ec2ab49339f6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,107 +0,0 @@ - -前面所讲的调试方法都是针对 Nginx 本身很容易跑到的逻辑,而对于某些只有在特定情况下才会被执行到的代码,又该怎样去调试呢?举个例子,我们知道 Nginx 里有大量的超时处理,比如,如果读取客户端请求头部数据超时,Nginx 就将执行对应的超时处理函数,假设我想通过单步执行的方式来了解这部分相关逻辑,无疑就得让 Nginx 的执行逻辑走到这条路径上来。由于此时影响 Nginx 行为的决定因素是客户端所发送的请求头部数据,我们就必须在客户端做动作来构造出这种场景。一般的浏览器,如IE、Firefox等发出请求的行为基本已经固定,而常用的命令行工具,比如 curl、wget 的源代码又略显复杂,定制它们的请求动作和改变环境来构造所需的场景相对较为麻烦,所以一种更便利的方法就是我们自己写个socket通信的客户端即可,而这并不需要多少代码。
-下面给出一个测试示例用代码,为了简单,所以服务器IP和端口都是固定在代码里的,用于发送数据的函数write()调用也未做返回值判断等(后续还有其他类似测试代码也是如此,这点请注意)。
-00: 代码片段2.6-1,文件名: request_timeout.c
-01: /**
-02: * gcc -Wall -g -o request_timeout request_timeout.c
-03: */
-04: #include
05: #include
06: #include
07: #include
08: #include
09: #include
10: #include
11: #include
12: #include
13:
-14: //charreq_header[]="GET/HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent:curl/7.19.7\r\nHost:127.0.0.1\r\nAccept: */*\r\n\r\n";
-15: char req_header[] = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent: curl/7.19.7\r\n";
-16:
-17: int main(int argc, char *const *argv)
-18: {
-19: int sockfd;
-20: struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
-21:
-22: if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
-23: fprintf (stderr, "Socket error,%s\r\n", strerror (errno));
-24: return -1;
-25: }
-26:
-27: bzero (&server_addr, sizeof (server_addr));
-28: server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
-29: server_addr.sin_port = htons (80);
-30:
-31: if(!inet_aton("192.168.1.1", &server_addr.sin_addr)) {
-32: fprintf (stderr, "Bad address:%s\r\n", strerror (errno));
-33: close (sockfd);
-34: return -1;
-35: }
-36:
-37: if (connect (sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) (&server_addr),
-38: sizeof (struct sockaddr)) == -1) {
-39: fprintf (stderr, "Connect Error:%s\r\n", strerror (errno));
-40: close (sockfd);
-41: return -1;
-42: }
-43:
-44: write (sockfd, req_header, strlen(req_header));
-45:
-46: close (sockfd);
-47: return 0;
-48: }
-该程序的代码比较简单,变量req_header存储的是http请求头部数据,被注释掉的是正常的请求头,而我这里使用的请求头是不完整的(正常请求头可以用wget、curl或wireshark[16]等工具获得,异常请求头必须根据自己所预期场景来进行构造,比如在这里,其他异常情况的请求头可能导致Nginx以其他错误方式返回而不是进行超时监控),所以这会使得Nginx在接收到该请求后,持续等待进一步的头部数据,直到超时。编译这个源代码得到应用程序request_timeout。
-将接受http请求的Nginx工作进程绑定到gdb,然后在超时函数ngx_event_expire_timers()内的第149行下断点并按c继续。
-75: 代码片段2.6-2,文件名: ngx_event_timer.c
-76: void
-77: ngx_event_expire_timers(void)
-78: {
-79: …
-147: ev->timedout = 1;
-148:
-149: ev->handler(ev);
-这个断点是Nginx已经捕获到超时事件,设置其超时旗标并调用对应的回调函数进行处理。在另一个gdb内执行request_timeout,当然,我们需要让它停止在第47行[17],避免程序退出,导致它与Nginx工作进程之间的连接断开。等待约 60 秒(Nginx读取请求头部数据的默认超时时间为60秒,可通过配置指令client_header_timeout修改)后,attach到Nginx工作进程的gdb就会断下来,按s跟进函数,再顺着执行路径而下就会发现此时Nginx将执行到这个逻辑里。
-955: 代码片段2.6-3,文件名: ngx_event_timer.c
-956: static void
-957: ngx_http_process_request_headers(ngx_event_t *rev)
-958: {
-959: …
-976: if (rev->timedout) {
-977: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out");
-978: c->timedout = 1;
-979: ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT);
-980: return;
-981: }
-将执行到第976行的if判断内部,即连接超时,我们看到对于在读取请求头部数据超时的情况下,Nginx 工作进程最后所做的几步主要工作,即日志记录、关闭请求并返回。通过这样一个实例,我们也就了解了如何去调试这样的特殊应用逻辑,不仅仅只是针对客户端,对于后端应用服务器也能如此进行模拟构造。
-上面演示的环境构造步骤,虽然比较简单且能真实模拟,但毕竟需要我们了解它的细节,也就是需知道触发这种情况的前提条件,如果前提条件比较多,那么模拟起来可能还是比较麻烦,其实,如果我们只是了解一下 Nginx 如果这样执行会怎么样,那么完全可以通过利用gdb的p命令或set命令修改对应条件变量的值来达到目的。比如在前面的例子里,在一般情况下,rev->timedout为0,即不超时而无法执行第977-980行代码,但我又想看一下执行这几条语句的情况会怎么样,那么就可以像下面这样做。
-Breakpoint 1, ngx_http_process_request_headers (rev=0x94a6bfc) at src/http/ ngx_http_request.c:976
-976 if (rev->timedout) {
-(gdb) p rev->timedout
-$1 = 0
-(gdb) p rev->timedout=1
-$2 = 1
-(gdb) n
-977 ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out");
-(gdb) set rev->timedout=0
-(gdb) p rev->timedout
-$3 = 0
-(gdb)
-通过执行“prev->timedout=1”把变量rev->timedout的值改为1,这样就执行到第977 行了,当然,如上所示,set命令也可以改变Nginx执行变量的值。值得特别注意的是,这样做仅仅只是因为改变了条件判断的变量值而使得 Nginx 程序执行路径发生变化,但是其在新的路径上,可能由于使用的某些变量值不是原本所期望的情况而导致执行异常。
-注 释
-[1].http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/。
- -[3].执行命令".lconfigure--help"可以看到所有参数选项。
-[4].http://sourceware.org/gdb/current/onlinedocs/gdb/Set-Watchpoints.html#Set-Watchpoints
- - -[7].http://cgdb.github.com/docs/index.html
- -[9].http://sourceforge.net/projects/strace/
- -[11].http://lenky.info/?p=2202
-[12].http://sourceware.org/sysemtop/
-[13].http://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Code-Gen-Options.html#Code-Gen-Options
-[14].http://sourceware.org/binutils/
-[15].http://sourceware.org/binutils/docs/binutils/addr2line.html。
-[16].http://www.wireshark.org/。
-[17].在此行加个gdb断点进行暂停或在该行后利用sleep()函数进行暂停都可以。
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-1-request_timeout.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-1-request_timeout.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f116277690c431bb84333243d42fa37acf7433bd --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-1-request_timeout.c" @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ + /** + * gcc -Wall -g -o request_timeout request_timeout.c + */ + #include + #include + #include + #include + #include + #include + #include + #include + #include + + //charreq_header[]="GET/HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent:curl/7.19.7\r\nHost:127.0.0.1\r\nAccept: */*\r\n\r\n"; + char req_header[] = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent: curl/7.19.7\r\n"; + + int main(int argc, char *const *argv) + { + int sockfd; + struct sockaddr_in server_addr; + + if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) { + fprintf (stderr, "Socket error,%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); + return -1; + } + + bzero (&server_addr, sizeof (server_addr)); + server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; + server_addr.sin_port = htons (80); + + if(!inet_aton("192.168.1.1", &server_addr.sin_addr)) { + fprintf (stderr, "Bad address:%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); + close (sockfd); + return -1; + } + + if (connect (sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) (&server_addr), + sizeof (struct sockaddr)) == -1) { + fprintf (stderr, "Connect Error:%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); + close (sockfd); + return -1; + } + + write (sockfd, req_header, strlen(req_header)); + + close (sockfd); + return 0; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-2-ngx_event_timer.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-2-ngx_event_timer.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..19a857f8c41bf199df694de1e38bfbc29fbc69a7 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-2-ngx_event_timer.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ + void + ngx_event_expire_timers(void) + { + … + ev->timedout = 1; + + ev->handler(ev); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-3-ngx_event_timer.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-3-ngx_event_timer.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a25d0fdccc61a42bd756454c2fad5fc0420a084a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/2.6 \347\211\271\346\256\212\345\272\224\347\224\250\351\200\273\350\276\221\347\232\204\350\260\203\350\257\225/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2652.6-3-ngx_event_timer.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +static void +ngx_http_process_request_headers(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + if (rev->timedout) { + ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out"); + c->timedout = 1; + ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index e97ee16e60e5c8755f94de468b9b5d71af21a9f2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25402\347\253\240 \350\267\237\350\270\252\344\270\216\350\260\203\350\257\225/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -跟踪与调试,不仅是我们解决程序Bug的有力途径,也是帮助我们理解现有代码的有效方法。通过跟踪程序执行的过程,我们可以清楚地了解程序的内部逻辑,对于不明就里的实现细节,调试查看程序内部变量也能更好地帮助我们做出正确的理解。本章将介绍一些跟踪与调试程序的方法,除了最基本的gdb调试,我还将结合个人经验,介绍一些相对高级的应用技巧。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.1 \346\225\264\344\275\223\346\236\266\346\236\204/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.1 \346\225\264\344\275\223\346\236\266\346\236\204/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index f44363ab14c831dcba5a42ed62a29051de7e954e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.1 \346\225\264\344\275\223\346\236\266\346\236\204/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,9 +0,0 @@ - -如前面介绍的那样,正常执行起来后的Nginx会有多个进程,最基本的有master_process(即监控进程,也叫主进程)和worker_process(即工作进程),还可能会有Cache相关进程。这些进程之间会相互进行通信,以传递一些信息(主要是监控进程往工作进程传递)。除了自身进程之间的相互通信,Nginx还凭借强悍的功能模块与外界四通八达,比如通过upstream与后端Web服务器通信、依靠fastcgi与后端应用服务器通信等。一个较为完整的整体框架结构如图3-1所示。
-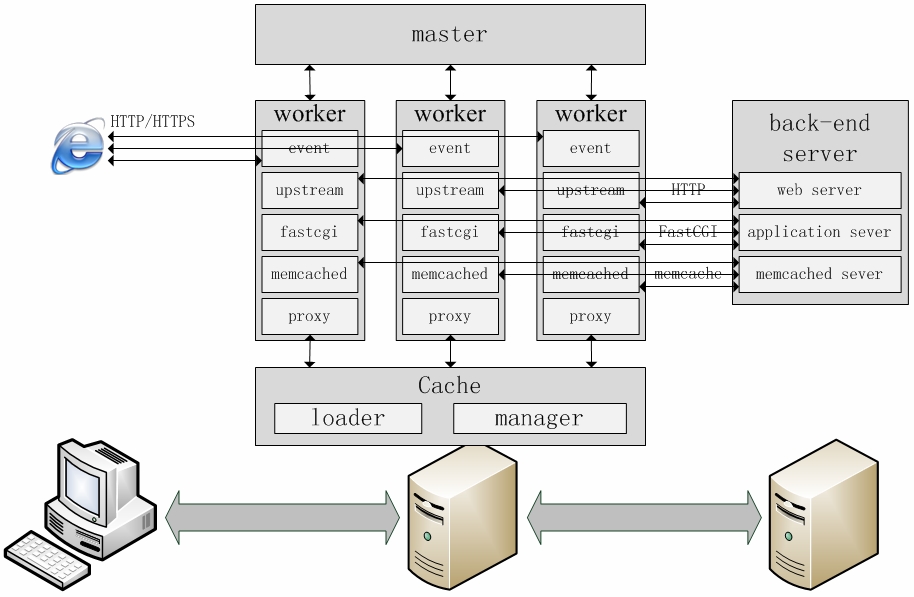 -
-Nginx的进程模型和现在大多数后台服务程序一样,按职责将进程分成监控进程和工作进程两类,启动Nginx的主进程将充当监控进程,而由主进程fork()出来的子进程则充当工作进程。工作进程的任务自然是完成具体的业务逻辑,而监控进程充当整个进程组与用户的交互接口,同时对工作进程进行监护,比如如果某工作进程意外退出,监控进程将重新fork()生成一个新的工作进程。Nginx也可以单进程模型执行,在这种进程模型下,主进程就是工作进程,此时没有监控进程,单进程模型比较简单且官方建议[1]仅供开发与测试使用,所以下面主要分析多进程模型。
-分析Nginx多进程模型的入口为主进程的ngx_master_process_cycle()函数,在该函数做完信号处理设置等之后就会调用一个名为 ngx_start_worker_processes()的函数用于 fork()产生出子进程(子进程数目通过函数调用的第二个实参指定),子进程作为一个新的实体开始充当工作进程的角色执行ngx_worker_process_cycle()函数,该函数主体为一个无限for ( ;; )循环,持续不断地处理客户端的服务请求,而主进程继续执行 ngx_master_process_cycle()函数,也就是作为监控进程执行主体for ( ;; )循环,这自然也是一个无限循环,直到进程终止才退出。服务进程基本都是这种写法,所以不用详述,下面先看看图3-2所示的这个模型。
-图3-2 表现得很清晰,监控进程和每个工作进程各有一个无限for ( ;; )循环,以便进程持续的等待和处理自己负责的事务,直到进程退出。
- -监控进程的无限for ( ;; )循环内有一个关键的sigsuspend()函数调用,该函数的调用使得监控进程的大部分时间都处于挂起等待状态,直到监控进程接收到信号为止。当监控进程接收到信号时,信号处理函数 ngx_signal_handler()就会被执行。我们知道信号处理函数一般都要求足够简单,所以在该函数内执行的动作主要也就是根据当前信号值对相应的旗标变量做设置,而实际的处理逻辑必须放在主体代码里来进行,所以该for ( ;; )循环接下来的代码就是判断有哪些旗标变量被设置而需要处理的,比如 ngx_reap(有子进程退出?)、ngx_quit 或ngx_terminate(进行要退出或终止?值得注意的是,虽然两个旗标都是表示结束Nginx,不过ngx_quit 的结束更优雅,它会让 Nginx 监控进程做一些清理工作且等待子进程也完全清理并退出之后才终止,而ngx_terminate更为粗暴,不过它通过使用SIGKILL信号能保证在一段时间后必定被结束掉)、ngx_reconfigure(重新加载配置)等。当所有信号都处理完时又挂起在函数sigsuspend()调用处继续等待新的信号,如此反复,构成监控进程的主要执行体。
-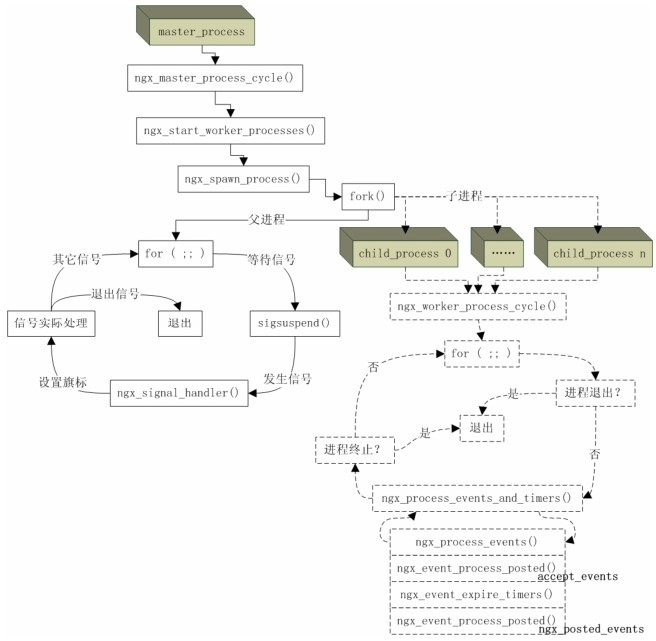 -
-82: 代码片段3.2.1-1,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-83: void
-84: ngx_master_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
-85: {
-86: …
-146: for ( ;; ) {
-147: …
-170: sigsuspend(&set);
-171: …
-177: if (ngx_reap) {
-178: …
-184: if (!live && (ngx_terminate || ngx_quit)) {
-185: …
-188: if (ngx_terminate) {
-189: …
-210: if (ngx_quit) {
-211: …
-212: }
-213: …
- -工作进程的执行主体与监控进程类似,不过工作进程既然名为工作进程,那么它的主要关注点就是与客户端或后端真实服务器(此时Nginx作为中间代理)之间的数据可读/可写等I/O交互事件,而不是进程信号,所以工作进程的阻塞点是在像select()、epoll_wait()等这样的I/O 多路复用函数调用处,以等待发生数据可读/可写事件,当然,也可能被新收到的进程信号中断。关于I/O多路复用的更多细节,后续章节会详细讲解。
-721: 代码片段3.2.2-1,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-722: static void
-723: ngx_worker_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *data)
-724: {
-725: …
-780: for ( ;; ) {
-781:
-782: if (ngx_exiting) {
-783: …
-806: ngx_process_events_and_timers(cycle);
-807:
-808: if (ngx_terminate) {
-809: …
-810: }
-811: …
-在代码片段3.2.2-1中,通过函数ngx_process_events_and_timers()调到对应的事件监控阻塞点,即(以epoll_wait()为例)
-ngx_process_events_and_timers() -> ngx_process_events()/ngx_epoll_process_ events() ->epoll_wait()
-函数epoll_wait()会阻塞等待,一旦有事件发生或收到信号就会立即返回,工作进程也就开始对发生的事件进行逐个处理,关于这部分的具体逻辑,我们暂且不说,等到第7章再看。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a29e7d1e1792bd4e3e3761424f21391067761809 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ + void + ngx_master_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) + { + … + for ( ;; ) { + … + sigsuspend(&set); + … + if (ngx_reap) { + … + if (!live && (ngx_terminate || ngx_quit)) { + … + if (ngx_terminate) { + … + if (ngx_quit) { + … + } +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b13d32ca4db109661bd6611ec035aac40f8290f7 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.2 \346\240\270\345\277\203\350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.2.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ +static void +ngx_worker_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *data) +{ +… + for ( ;; ) { + + if (ngx_exiting) { + … + ngx_process_events_and_timers(cycle); + + if (ngx_terminate) { + … + } +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 587e11ddcd40237b628426899e02b51be4d4bbf7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,136 +0,0 @@ - -如果Nginx 开启了缓存功能,比如ProxyCache,那么Nginx 还将创建另外两个Cache 相关进程。编写类似如下的Nginx配置文件。
-17: 代码片段3.3-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: worker_processes 1;
-19:
-20: http {
-21: …
-22: proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels=1:2 keys_zone=one:10m;
-23:
-24: server {
-25: listen 80;
-26: location / {
-27: proxy_cache one;
-28: proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
-29: proxy_pass http://load_balance;
-30: }
-31: }
-以该配置文件启动Nginx后,我们就能看到如下4个进程。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ps auxf | grep nginx | grep -v grep
-root 16126 0.0 0.1 15460 576 ? Ss 18:42 0:00 nginx: master process objs/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
-nobody 16127 0.0 0.2 15636 928 ? S 18:42 0:00 \_ nginx: worker process
-nobody 16128 0.0 0.2 15612 912 ? S 18:42 0:00 \_ nginx: cache manager process
-nobody 16129 0.0 0.2 15612 804 ? S 18:42 0:00 \_ nginx: cache loader process
-从前面的介绍中,我们已经知道master process和worker process各自的功能和内部逻辑,而cache manager process(Cache 管理进程)与cache loader process(Cache加载进程)则是与Cache缓存机制相关的进程。它们也是由主进程创建,对应的模型框图如图3-3所示。
-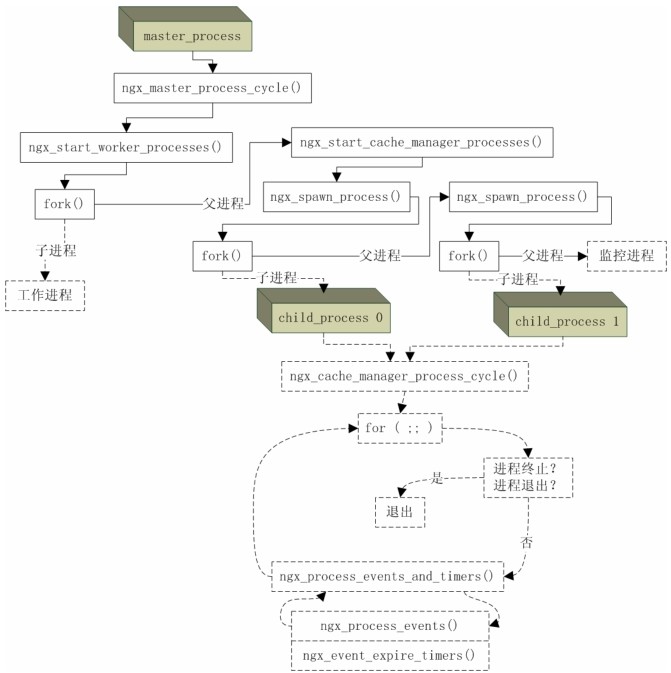 -
-Cache 进程不处理客户端请求,也就没有监控的 I/O 事件,而其处理的是超时事件,在ngx_process_events_and_timers()函数内执行的事件处理函数只有ngx_event_expire_timers()函数。
- -Cache管理进程与Cache加载进程的主流程都是ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle()函数,但是它们附带的参数不同。管理进程执行到函数ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle()内时,传递的data为ngx_cache_manager_ctx。
-68: 代码片段3.3.1-1,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-69: static ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t ngx_cache_manager_ctx = {
-70: ngx_cache_manager_process_handler, "cache manager process", 0
-71: };
-结构体 ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t的定义如下。
-29: 代码片段3.3.1-2,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.h
-30: typedef struct {
-31: ngx_event_handler_pt handler;
-32: char *name;
-33: ngx_msec_t delay;
-34: } ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t;
-再看函数 ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle()的具体代码。
-1282:代码片段3.3.1-3,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-1283:static void
-1284:ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *data)
-1285:{
-1286: ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t *ctx = data;
-1287:
-1288: void *ident[4];
-1289: ngx_event_t ev;
-1290:…
-1297: ngx_close_listening_sockets(cycle);
-1298:
-1299: ngx_memzero(&ev, sizeof(ngx_event_t));
-1300: ev.handler = ctx->handler;
-1301: ev.data = ident;
-1302: ev.log = cycle->log;
-1303: ident[3] = (void *) -1;
-1304:…
-1309: ngx_add_timer(&ev, ctx->delay);
-Cache管理进程不接收客户端请求,所以在代码第1297行关闭了监听套接口。其他代码创建了一个事件对象并设置了对应的超时事件。注意两点。第一,代码第1303行并没有特别的设定功能,仅只是因为事件对象的data字段一般挂载的是connect对象,此处设置为−1刚好是把 connect 对象的 fd 字段设置为−1,以避免在其他代码里走到异常逻辑。第二,此处ctx->delay为0,因此立即超时,执行对应的函数。
-ngx_process_events_and_timers() -> ngx_event_expire_timers() -> ngx_cache_ manager_process_handler()
-函数ngx_cache_manager_process_handler()的处理很简单,它会调用每一个磁盘缓存管理对象的manager()函数,然后重新设置事件对象的下一次超时时刻后返回。
-1328:代码片段3.3.1-4,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-1329:static void
-1330:ngx_cache_manager_process_handler(ngx_event_t *ev)
-1331:{
-1332:…
-1338: path = ngx_cycle->pathes.elts;
-1339: for (i = 0; i < ngx_cycle->pathes.nelts; i++) {
-1340:
-1341: if (path[i]->manager) {
-1342: n = path[i]->manager(path[i]->data);
-1343:…
-1347: }
-1348: }
-1349:…
-1354: ngx_add_timer(ev, next * 1000);
-1355:}
-对于我们这里的示例,对应的manager()函数为ngx_http_file_cache_manager()函数,这是Nginx在调用函数ngx_http_file_cache_set_slot()解析配置指令proxy_cache_path时设置的回调值。函数 ngx_http_file_cache_manager()做了两件事情,首先删除已过期的缓存文件,然后检查缓存文件总大小是否超限,如果超限则进行强制删除。代码如下。
-1312:代码片段3.3.1-5,文件名: ngx_http_file_cache.c
-1313:static time_t
-1314:ngx_http_file_cache_manager(void *data)
-1315:{
-1316:…
-1321: next = ngx_http_file_cache_expire(cache);
-1322:…
-1326: for ( ;; ) {
-1327:…
-1336: size = cache->sh->size;
-1337:…
-1336: if (size < cache->max_size) {
-1337: return next;
-1338: }
-1339:
-1340: wait = ngx_http_file_cache_forced_expire(cache);
-1341:
-1342: if (wait > 0) {
-1343: return wait;
-1344: }
-1345:…
-1349: }
-1350:}
-代码逻辑容易理解,代码第1342行的判断为真则表示当前缓存文件(如果存在)都在使用中,所以需直接返回等待,避免CPU 空旋for ( ;; )循序导致CPU 计算能力的浪费。
-总结来说,Cache 管理进程的任务就是清理超时缓存文件,限制缓存文件总大小,这个过程反反复复,直到Nginx整个进程退出为止。
- -以3.3-1配置代码执行的Nginx在一开始会有4个进程,但在一段时间后,Cache加载进程将消失,这是因为Cache加载进程的功能是在Nginx正常启动后(具体是60秒)将磁盘中上次缓存的对象加载到内存中。可以看到,这个过程是一次性的,所以当 Cache 加载进程完成它的加载任务后也就自动退出了。
-Cache加载进程执行的到ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle()为止的上层函数调用与Cache管理进程一致,但在该函数内设置的事件对象回调函数为ngx_cache_loader_process_handler()。
-72: 代码片段3.3.2-1,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-73: static ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t ngx_cache_loader_ctx = {
-74: ngx_cache_loader_process_handler, "cache loader process", 60000
-75: };
-事件对象的超时时间为 60000毫秒。函数 ngx_cache_loader_process_handler()执行的是每一个磁盘缓存管理对象的 loader()回调函数。
-1357:代码片段3.3.2-2,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-1358:static void
-1359:ngx_cache_loader_process_handler(ngx_event_t *ev)
-1360:{
-1361:…
-1367: path = cycle->pathes.elts;
-1368: for (i = 0; i < cycle->pathes.nelts; i++) {
-1369:…
-1374: if (path[i]->loader) {
-1375: path[i]->loader(path[i]->data);
-1376: ngx_time_update();
-1377: }
-1378: }
-1379:
-1380: exit(0);
-1381:}
-注意代码第1380行的exit(0)函数调用,可见Cache加载进程的执行逻辑是一次性的。同样的设置流程,对于我们这里的示例,对应的 loader()函数被设置为 ngx_http_file_cache_loader()函数,该函数给磁盘缓存管理对象对应路径下已有的缓存文件建立对应的红黑树,从而让Nginx可以继续使用上次缓存的文件。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..095679de0213bfd0f80b519108d24e308930b744 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ + worker_processes 1; + + http { + … + proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels=1:2 keys_zone=one:10m; + + server { + listen 80; + location / { + proxy_cache one; + proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m; + proxy_pass http://load_balance; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6732e40ce4a4d3b0349208d9074ede6dd0fadae9 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + static ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t ngx_cache_manager_ctx = { + ngx_cache_manager_process_handler, "cache manager process", 0 + }; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-2-ngx_process_cycle.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-2-ngx_process_cycle.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..688837b0fac1f30128aa4463e1fbb4d6ac73cc8d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-2-ngx_process_cycle.h" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + typedef struct { + ngx_event_handler_pt handler; + char *name; + ngx_msec_t delay; + } ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d9fafc4a4570b7554fe45a85f33702f1d85aa542 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +static void +ngx_cache_manager_process_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *data) +{ + ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t *ctx = data; + + void *ident[4]; + ngx_event_t ev; +… + ngx_close_listening_sockets(cycle); + + ngx_memzero(&ev, sizeof(ngx_event_t)); + ev.handler = ctx->handler; + ev.data = ident; + ev.log = cycle->log; + ident[3] = (void *) -1; +… + ngx_add_timer(&ev, ctx->delay); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..03d9ba964f2545f4e0442ea9e67baebef6185954 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +static void +ngx_cache_manager_process_handler(ngx_event_t *ev) +{ +… + path = ngx_cycle->pathes.elts; + for (i = 0; i < ngx_cycle->pathes.nelts; i++) { + + if (path[i]->manager) { + n = path[i]->manager(path[i]->data); +… + } + } +… + ngx_add_timer(ev, next * 1000); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-5-ngx_http_file_cache.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-5-ngx_http_file_cache.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..679a1c45d4e497511324dd110c25d17e39c2e2b8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.1-5-ngx_http_file_cache.c" @@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ +static time_t +ngx_http_file_cache_manager(void *data) +{ +… + next = ngx_http_file_cache_expire(cache); +… + for ( ;; ) { +… + size = cache->sh->size; +… + if (size < cache->max_size) { + return next; + } + + wait = ngx_http_file_cache_forced_expire(cache); + + if (wait > 0) { + return wait; + } +… + } +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..43dd35d12b5615e240aac13bed522665bc050974 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-1-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + static ngx_cache_manager_ctx_t ngx_cache_loader_ctx = { + ngx_cache_loader_process_handler, "cache loader process", 60000 + }; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f4c6e97c700bdf73b91baa447c20f0d006c0acf1 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.3 Cache \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.3.2-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +static void +ngx_cache_loader_process_handler(ngx_event_t *ev) +{ +… + path = cycle->pathes.elts; + for (i = 0; i < cycle->pathes.nelts; i++) { +… + if (path[i]->loader) { + path[i]->loader(path[i]->data); + ngx_time_update(); + } + } + + exit(0); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 83227a5f73a6928afe8b4c97085d300e1fe88020..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,84 +0,0 @@ - -运行在多进程模型的Nginx在正常工作时,自然就会有多个进程实例,例如,图3-4是在配置worker_processes 4;情况下的显示,Nginx 设置的进程title 能很好地帮助我们区分监控进程与工作进程,不过带上选项f的ps命令以树目录的形式打印各个进程信息也能帮助我们做这个区分。多进程联合工作必定要牵扯到进程之间的通信问题,下面就来看看 Nginx 是如何做的(仅关注监控进程与工作进程)。
- -
-采用socketpair()函数创造一对未命名的UNIX域套接字来进行Linux下具有亲缘关系的进程之间的双向通信是一个非常不错的解决方案。Nginx就是这么做的,先看fork()生成新工作进程的ngx_spawn_process()函数以及相关代码。
-21: 代码片段3.4-1,文件名: ngx_process.h
-22: typedef struct {
-23: ngx_pid_t pid;
-24: int status;
-25: ngx_socket_t channel[2];
-26: …
-27: } ngx_process_t;
-28: …
-47: #define NGX_MAX_PROCESSES 1024
-35: 代码片段3.4-2,文件名: ngx_process.c
-36: ngx_process_t ngx_processes[NGX_MAX_PROCESSES];
-37:
-86: ngx_pid_t
-87: ngx_spawn_process(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_spawn_proc_pt proc, void *data,
-88: char *name, ngx_int_t respawn)
-89: {
-90: …
-117: if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, ngx_processes[s].channel) == -1)
-118: …
-186: pid = fork();
-187: …
-在该函数进行 fork()之前,先调用了 socketpair()创建一对 socket 描述符存放在变量 ngx_processes[s].channel内(其中s标志在ngx_processes数组内第一个可用元素的下标,比如最开始产生第一个工作进程时,可用元素的下标s为0),而在fork()之后,由于子进程继承了父进程的资源,那么父子进程就都有了这一对socket描述符,而Nginx将channel[0]给父进程使用,channel[1]给子进程使用,这样分别错开地使用不同socket描述符,即可实现父子进程之间的双向通信。
- -
-除此之外,对于各个子进程之间,也可以进行双向通信。如前面所述,父子进程的通信channel设定是自然而然的事情,而子进程之间的通信 channel 设定就涉及进程之间文件描述符(socket描述符也属于文件描述符)的传递,因为虽然在后生成的子进程通过继承的 channel[0]能够往在前生成的子进程发送信息,但在前生成的子进程无法获知在后生成子进程的channel[0]而不能发送信息,所以在后生成的子进程必须利用已知的在前生成子进程的channel[0]进行主动告知。
-在子进程的启动初始化函数 ngx_worker_process_init()里,会把 ngx_channel (也就是channel[1])加入到读事件监听集里,对应的回调处理函数为ngx_channel_handler()。
-834: 代码片段3.4-3,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-835: static void
-836: ngx_worker_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_uint_t priority)
-837: {
-838: …
-994: if (ngx_add_channel_event(cycle, ngx_channel, NGX_READ_EVENT,
-995: ngx_channel_handler)
-996: == NGX_ERROR)
-997: {
-998: …
-而在父进程fork()生成一个新子进程后,就会立即通过ngx_pass_open_channel()函数把这个子进程的相关信息告知给其前面已生成的子进程。
-430: 代码片段3.4-4,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-431: static void
-432: ngx_pass_open_channel(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_channel_t *ch)
-433: {
-434:
-436: for (i = 0; i < ngx_last_process; i++) {
-437: …
-453: ngx_write_channel(ngx_processes[i].channel[0],
-454: ch, sizeof(ngx_channel_t), cycle->log);
-455: }
-456: }
-其中参数ch里包含了刚创建的新子进程(假定为A)的pid、进程信息在全局数组里存储下标、socket描述符channel[0]等信息,这里通过for循环遍历所有存活的其他子进程,然后调用函数ngx_write_channel()通过继承的channel[0]描述符进行信息主动告知,而收到这些消息的子进程将执行设置好的回调函数 ngx_channel_handler(),把接收到的新子进程 A 的相关信息存储在全局变量ngx_processes内。
-1066:代码片段3.4-5,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-1067:static void
-1068:ngx_channel_handler(ngx_event_t *ev)
-1069:{
-1070:…
-1126: case NGX_CMD_OPEN_CHANNEL:
-1127:…
-1132: ngx_processes[ch.slot].pid = ch.pid;
-1133: ngx_processes[ch.slot].channel[0] = ch.fd;
-1134: break;
-1135:…
-这样,前后子进程都有了对方的相关信息,相互通信也就没有问题了。这其中有一些具体实现细节没有提到,这里也不打算详说[2],直接看一下表3-1中的实例,就以上面显示的各个父子进程为例。
-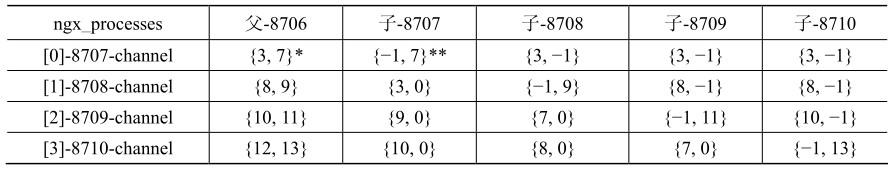 -
-表3-1 中,{a, b}分别表示channel[0]和channel[1]的值,−1 表示这之前是描述符,但在其后被主动close()掉了,0表示这一直都无对应的描述符,其他数字表示对应的描述符值。每一列数据都表示该列所对应进程与其它进程进行通信的描述符,如果当前列所对应进程为父进程,那么它与其它进程进行通信的描述符都为channel[0];如果当前列所对应进程为子进程,那么它与父进程进行通信的描述符为channel[1],与其它子进程进行通信的描述符都为channel[0]。比如,带*的{3, 7}表示如果父进程8706 向子进程8707 发送消息,需使用channel[0],即描述符3,它的channel[1]为7,没有被close()关闭掉,但一直也都没有被使用,所以没有影响,不过按道理应该关闭才是。而带**的{−1, 7}表示如果子进程8707 向父进程8706发送消息(注意该数据所处的行位置,如果是子进程8709与父进程8706进行通信,那么使用的描述符将是带#3 的{−1, 11}所对应的 channel[1],即描述符 11),需使用channel[1],即描述符7,它的channel[0]为−1表示已经close()关闭掉了(Nginx某些地方调用 close()时并没有设置对应变量为−1,我这里为了更好说明,将已经 close()掉的描述符全部标记为−1了)。
-越是后生成的子进程,其channel[0]与父进程的对应channel[0]值相同的越多,因为基本都是继承而来,但前面生成的子进程的 channel[0]是通过传递获得的,所以与父进程的对应channel[0]不一定相等。比如如果子进程8707向子进程8710发送消息,需使用channel[0],即描述符10,而对应的父进程channel[0]却是12。虽然它们在各自进程里表现为不同的整型数字,但在内核里表示同一个描述符结构,即不管是子进程8707往描述符10写数据还是父进程8706往描述符12写数据,子进程8710都能通过描述符13正确读取到这些数据,至于子进程8710怎么识别它读到的数据是来自子进程8707还是父进程8706,就得靠其收到的数据特征(比如pid字段)来做标记区分。
-最后,就目前 Nginx 代码来看,子进程并没有往父进程发送任何消息,子进程之间也没有相互通信的逻辑。也许是因为 Nginx 有其他一些更好的进程通信方式,比如共享内存等,所以这种 channel 通信目前仅做为父进程往子进程发送消息使用。但由于有这个基础在这,如果未来要使用channel做这样的事情,的确是可以的。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-1-ngx_process.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-1-ngx_process.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b229a2e5c8ff831e6504b617340e883ab963952c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-1-ngx_process.h" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ + typedef struct { + ngx_pid_t pid; + int status; + ngx_socket_t channel[2]; + … + } ngx_process_t; + … + #define NGX_MAX_PROCESSES 1024 + ngx_process_t ngx_processes[NGX_MAX_PROCESSES]; + + ngx_pid_t + ngx_spawn_process(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_spawn_proc_pt proc, void *data, + char *name, ngx_int_t respawn) + { + … + if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, ngx_processes[s].channel) == -1) +… + pid = fork(); +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7c6fd2a51ed1a158a24f79c6ac9ac4067f7ae1f6 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-3-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +static void +ngx_worker_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_uint_t priority) +{ +… + if (ngx_add_channel_event(cycle, ngx_channel, NGX_READ_EVENT, + ngx_channel_handler) + == NGX_ERROR) + { +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6786c0a43c53e1be9765e5533f7361a1cf247268 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-4-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +static void +ngx_pass_open_channel(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_channel_t *ch) +{ + + for (i = 0; i < ngx_last_process; i++) { +… + ngx_write_channel(ngx_processes[i].channel[0], + ch, sizeof(ngx_channel_t), cycle->log); + } +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-5-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-5-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2b2d6bf72dc8d1ff646b293ae869ef854ea64f1d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.4 \350\277\233\347\250\213\351\200\232\344\277\241/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.4-5-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +static void +ngx_channel_handler(ngx_event_t *ev) +{ +… + case NGX_CMD_OPEN_CHANNEL: +… + ngx_processes[ch.slot].pid = ch.pid; + ngx_processes[ch.slot].channel[0] = ch.fd; + break; +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.5 \345\205\261\344\272\253\345\206\205\345\255\230/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.5 \345\205\261\344\272\253\345\206\205\345\255\230/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 60ff1d7474e5f449547dfc0a537be0959f5be640..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.5 \345\205\261\344\272\253\345\206\205\345\255\230/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,62 +0,0 @@ - -共享内存是Linux下进程之间进行数据通信的最有效方式之一,而Nginx就为我们提供了统一的操作接口来使用共享内存。
-在Nginx里,一块完整的共享内存以结构体ngx_shm_zone_t来封装表示,其中包括的字段有共享内存的名称( shm_zone[i].shm.name )、大小( shm_zone[i].shm.size )、标签( shm_zone[i].tag )、分配内存的起始地址( shm_zone[i].shm.addr )以及初始回调函数(shm_zone[i].init)等。
-24: 代码片段3.5-1,文件名: ngx_cycle.h
-25: typedef struct ngx_shm_zone_s ngx_shm_zone_t;
-26: …
-27: struct ngx_shm_zone_s {
-28: void *data;
-29: ngx_shm_t shm;
-30: ngx_shm_zone_init_pt init;
-31: void *tag;
-32: };
-这些字段大都容易理解,只有tag字段需要解释一下,因为看上去它和name字段有点重复,而事实上,name字段主要用作共享内存的唯一标识,它能让Nginx知道我想使用哪个共享内存,但它没法让 Nginx 区分我到底是想新创建一个共享内存,还是使用那个已存在的旧的共享内存。举个例子,模块A创建了共享内存sa,模块A或另外一个模块B再以同样的名称sa去获取共享内存,那么此时Nginx是返回模块A已创建的那个共享内存sa给模块A/模块B,还是直接以共享内存名重复提示模块A/模块B出错呢?不管Nginx采用哪种做法都有另外一种情况出错,所以新增一个 tag 字段做冲突标识,该字段一般也就指向当前模块的ngx_module_t变量即可。这样在上面的例子中,通过tag字段的帮助,如果模块A/模块B再以同样的名称sa去获取模块A已创建的共享内存sa,模块A将获得它之前创建的共享内存的引用(因为模块A前后两次请求的tag相同),而模块B则将获得共享内存已做他用的错误提示(因为模块B请求的tag与之前模块A请求时的tag不同)。
-当我们要使用一个共享内存时,总会在配置文件里加上该共享内存的相关配置信息,而Nginx 在进行配置解析的过程中,根据这些配置信息就会创建对应的共享内存,不过此时的创建仅仅只是代表共享内存的结构体 ngx_shm_zone_t 变量的创建,这具体实现在函数shared_memory_add()内。另外从这个函数中,我们也可以看到Nginx使用的所有共享内存都以list链表的形式组织在全局变量cf->cycle->shared_memory下,在创建新的共享内存之前会先对该链表进行遍历查找以及冲突检测,对于已经存在且不存在冲突的共享内存可直接返回引用。以ngx_http_limit_req_module模块为例,它需要的共享内存在配置文件里以limit_req_zone配置项出现。
-limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s;
-Nginx 在进行配置解析时,遇到 limit_req_zone 配置项则调用其对应的处理函数 ngx_http_limit_req_zone() ,而在该函数内又将继续调用函数 shared_memory_add()创建对应的ngx_shm_zone_t结构体变量并加入到全局链表内。
-ngx_http_limit_req_zone() -> ngx_shared_memory_add() -> ngx_list_push()
-共享内存的真正创建是在配置文件全部解析完后,所有代表共享内存的结构体ngx_shm_zone_t变量以链表的形式挂接在全局变量cf->cycle->shared_memory下,Nginx此时遍历该链表并逐个进行实际创建,即分配内存、管理机制(比如锁、slab)初始化等。
-398: 代码片段3.5-2,文件名: ngx_cycle.c
-399: /* create shared memory */
-400:
-401: part = &cycle->shared_memory.part;
-402: shm_zone = part->elts;
-403:
-404: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) {
-405: …
-467: if (ngx_shm_alloc(&shm_zone[i].shm) != NGX_OK) {
-468: …
-471: if (ngx_init_zone_pool(cycle, &shm_zone[i]) != NGX_OK) {
-472: …
-475: if (shm_zone[i].init(&shm_zone[i], NULL) != NGX_OK) {
-476: ...
-477: }
-其中函数 ngx_shm_alloc()是共享内存的实际分配,针对当前系统可提供接口,可以是mmap或shmget等。而ngx_init_zone_pool()函数是共享内存管理机制的初始化,因为共享内存的使用涉及到另外两个主题:第一,既然是共享内存,那么必然是多进程共同使用,所以必须考虑互斥问题;第二,Nginx 既以性能著称,那么对于共享内存自然也有其独特的使用方式,虽然我们可以不用(在马上要介绍到的init回调函数里做覆盖处理即可),但在这里也默认都会以这种slab的高效访问机制进行初始化。关于这两点,这里暂且略过,待后续再做讨论。
-回调函数 shm_zone[i].init()是各个共享内存所特定的,根据使用方的自身需求不同而不同,这也是我们在使用共享内存时需特别注意的函数。继续看实例ngx_http_limit_req_module模块的init函数ngx_http_limit_req_init_zone()。
-398: 代码片段3.5-3,文件名: ngx_http_limit_req_module.c
-399: static ngx_int_t
-400: ngx_http_limit_req_init_zone(ngx_shm_zone_t *shm_zone, void *data)
-401: {
-402: ngx_http_limit_req_ctx_t *octx = data;
-403: …
-398: if (octx) {
-399: …
-608: ctx->shpool = octx->shpool;
-609: …
-608: return NGX_OK;
-609: }
-610:
-611: ctx->shpool = (ngx_slab_pool_t *) shm_zone->shm.addr;
-612: …
-608: ctx->sh = ngx_slab_alloc(ctx->shpool, sizeof(ngx_http_limit_req_ shctx_t));
-609: …
-函数ngx_http_limit_req_init_zone()的第二个参数data表示“旧”数据,在进行重新加载配置时(即Nginx收到SIGHUP信号)该值将不为空。如果旧数据可继续使用,那么可直接返回 NGX_OK;否则,需根据自身模块逻辑对共享内存的使用做相关初始化,比如ngx_http_limit_req_module模块,在第634、642行直接使用默认已初始化好的slab机制,进行内存的分配等。当函数 ngx_http_limit_req_init_zone()正确执行结束,一个完整的共享内存就已创建并初始完成,接着要做的就是共享内存的使用,这即回到前面提到的两个主题:互斥与slab。
-要解决互斥问题,无非就是利用锁机制,强制同一时刻只能有一个进程在访问共享内存,其基本原理就是利用共享的简单资源(比如最简单的原子变量)来代表复杂资源,一个进程在需要操作复杂资源之前先获得对简单资源的使用权限。因为简单资源足够简单,对它的使用权限的获取往往只有一步或几步,所以更容易避免冲突。这个应该是容易理解的,比如一个需要100步的操作肯定比一个只需要3步的操作更容易发生冲突(每一步需要的复杂度相同),因为前一种情况可能会发生一个进程在进行了 99 步后却因另外一个进程发出动作而失败的情况,而后一种情况的进程执行完3步后就已经获得完全使用权限了。
-要讲清楚 Nginx 互斥锁的实现,如果不结合具体的代码恐怕是不行的,因为都是一些细节上的考量,比如根据各种不同的CPU架构选择不同的汇编指令、使用不同的共享简单资源(原子变量或文件描述符),并没有什么特别难以理解的地方,查 CPU 手册和系统 Man 手册很容易懂,所以具体实现这里暂且不讲。Nginx 互斥锁的使用非常简单,提供的接口函数以及含义如表3-2。
-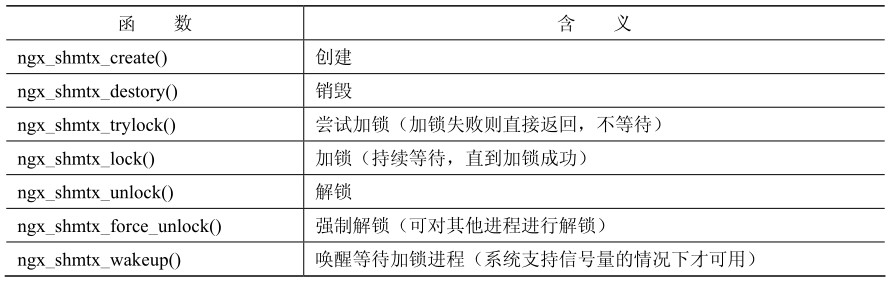 -
-Nginx的slab机制与Linux的slab机制在基本原理上并没有什么特别大的不同(当然,相比而言,Linux的slab机制要复杂得多),简单来说也就是基于两点:缓存与对齐。缓存意味着预分配,即提前申请好内存并对内存做好划分形成内存池,当我们需要使用一块内存空间时, Nginx就直接从已经申请并划分好的内存池里取出一块合适大小的内存即可,而内存的释放也是把内存返还给Nginx的内存池,而不是操作系统;对齐则意味着内存的申请与分配总是按2的幂次方进行,即内存大小总是为8、16、32、64等,比如,虽然只申请33个字节的内存,但也将获得实际64字节可用大小的内存,这的确存在一些内存浪费,但对于内存性能的提升是显著的[3],更重要的是把内部碎片也掌握在可控的范围内。
-Nginx的slab机制主要是和共享内存一起使用,前面提到对于共享内存,Nginx在解析完配置文件,把即将使用的共享内存全部以 list 链表的形式组织在全局变量 cf->cycle->shared_memory下之后,就会统一进行实际的内存分配,而Nginx的slab机制要做的就是对这些共享内存进行进一步的内部划分与管理。关于这点,从函数ngx_slab_init()的逻辑即可初见端倪。不过在此之前,先看看ngx_init_zone_pool()函数对它的调用。
-916: 代码片段3.6-1,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-917: static ngx_int_t
-918: ngx_init_zone_pool(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_shm_zone_t *zn)
-919: {
-920: u_char *file;
-921: ngx_slab_pool_t *sp;
-922:
-923: sp = (ngx_slab_pool_t *) zn->shm.addr;
-924: …
-937: sp->end = zn->shm.addr + zn->shm.size;
-938: sp->min_shift = 3;
-939: sp->addr = zn->shm.addr;
-940: …
-960: ngx_slab_init(sp);
-961: …
-函数 ngx_init_zone_pool()是在共享内存分配好后进行的初始化调用,而该函数内又调用了本节介绍的重点对象slab的初始化函数ngx_slab_init();,此时的情况如图3-6所示。
-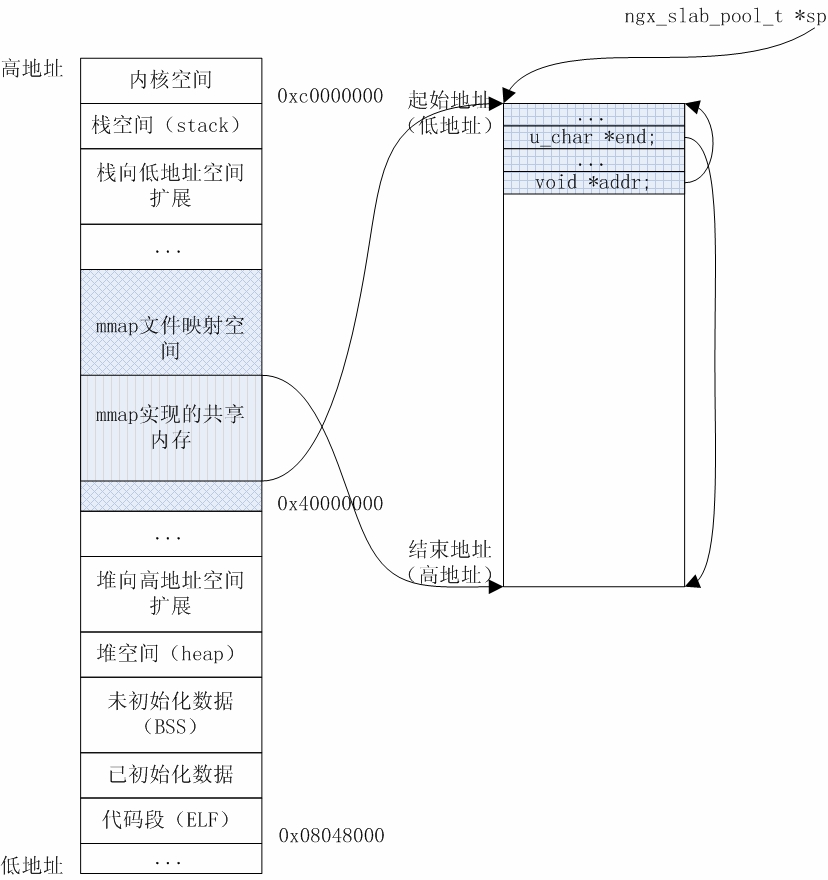 -
-可以看到此时共享内存的开始部分内存已经被用作结构体ngx_slab_pool_t的存储空间,这相当于是slab机制的额外开销(overhead),后面还会看到其他额外开销,任何一种管理机制都有自己的一些控制信息需要存储,所以这些内存使用是无法避免的。共享内存剩下的部分才是被管理的主体,slab 机制对这部分内存进行两级管理,首先是 page 页,然后是 page页内的slab块(通过slot对相等大小的slab块进行管理,为了区分slab机制,下面以slot块来指代这些slab块),也就是说slot块是在page页内存的再一次管理。
-在继续对slab机制分析之前,先看看下面这个表格里记录的一些变量以及其对应的值,因为它们可以帮助我们对后面内容的理解。这些变量会根据系统环境的不同而不同,但一旦系统环境确定,那么这些值也就将都是一些常量值,表3-3 基于的系统环境在本书最开始有统一介绍,这里不再赘述。
-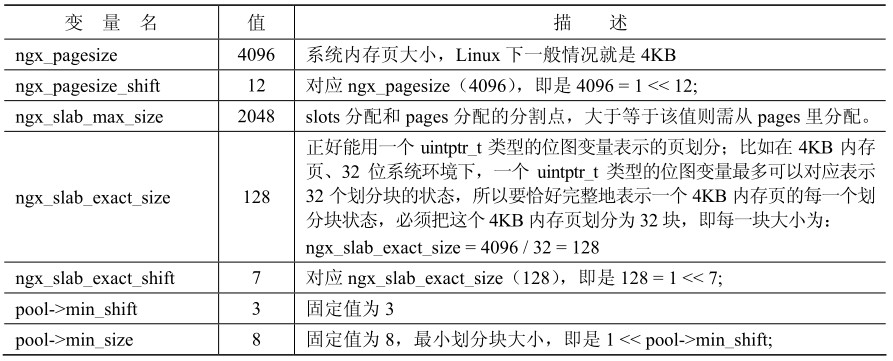 -
-再来看slab机制对page页的管理,初始结构示意图如图3-7所示。
- -
-slab 机制对page 页的静态管理主要体现在ngx_slab_page_t[K]和page[N] 这两个数组上,需要解释几点。
-第一,虽然是一个页管理结构(即ngx_slab_page_t元素)与一个page内存页相对应,但因为有对齐消耗以及slot块管理结构体的占用(图中的ngx_slab_page_t[n]数组),所以实际上页管理结构体数目比page页内存数目要多,即图中的ngx_slab_page_t[N]到ngx_slab_page_t[K-1],这些结构体完全被忽视,我们也不用去管它们,只是需要知道有这些东西的存在。
-第二,如何根据页管理结构page获得对应内存页的起始地址p?计算方法如下。
-384: 代码片段3.6-2,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-385: p = (page - pool->pages) << ngx_pagesize_shift;
-386: p += (uintptr_t) pool->start;
-对照前面图示来看这很明显,无需过多解释;相反,根据内存页的起始地址 p 也能计算出其对应的页管理结构page。
-第三,对齐是指实际 page 内存页按 ngx_pagesize 大小对齐,从图中看就是原本的 start是那个虚线箭头所指的位置,对齐后就是实线箭头所指的位置,对齐能提高对内存页的访问速度,但这有一些内存浪费,并且末尾可能因为不够一个 page 内存页而被浪费掉,所以在ngx_slab_init()函数的最末尾有一次最终可用内存页的准确调整。
-75: 代码片段3.6-3,文件名: ngx_cycle.c
-76: void
-77: ngx_slab_init(ngx_slab_pool_t *pool)
-78: {
-79: …
-130: m = pages - (pool->end - pool->start) / ngx_pagesize;
-131: if (m > 0) {
-132: pages -= m;
-133: pool->pages->slab = pages;
-134: }
-135: …
-代码第130行计算的m值如果大于0,说明对齐等操作导致实际可用内存页数减少,所以后面的if语句进行判断调整。
-page页的静态管理结构基本就是如此了,再来看page页的动态管理,即page页的申请与释放,这就稍微麻烦一点,因为一旦page页被申请或释放,那么就有了相应的状态:使用或空闲。先看空闲页的管理,Nginx对空闲page页进行链式管理,链表的头节点pool->free,初始状态下的链表情况如图3-8所示。
- -
-这是一个有点特别的链表,它的节点可以是一个数组,比如图3-8中的ngx_slab_page_t[N]数组就是一个链表节点,这个数组通过第0号数组元素,即ngx_slab_page_t[0],接入到这个空闲page页链表内,并且整个数组的元素个数也记录在这个第0号数组元素的slab字段内。
-如果经历如下几步内存操作:子进程1从共享内存中申请1页,子进程2接着申请了2页,然后子进程1又释放掉刚申请的1页,那么空闲链表各是一个什么状态呢?逐步来看。
-子进程1从共享内存中申请1页,如图3-9所示。
- -
-子进程2接着申请了2页,如图3-10所示。
-然后子进程1又释放掉刚申请的1页,如图3-11所示。
-释放的page页被插入到链表头部,如果子进程2接着释放其拥有的那2页内存,那么空闲链表结构将如图3-12所示。
-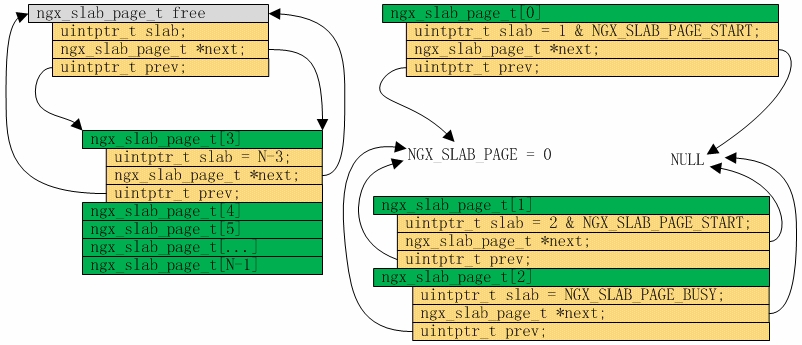 -
-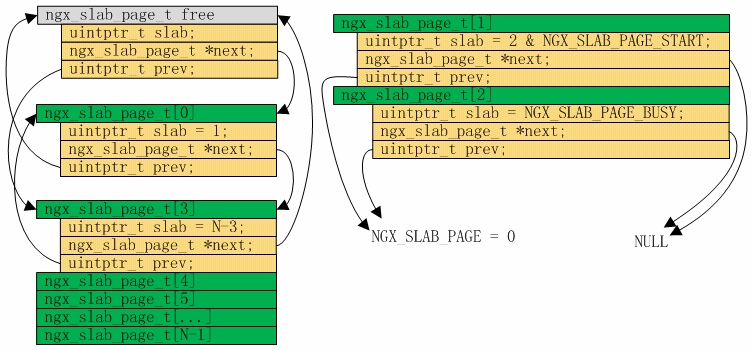 -
-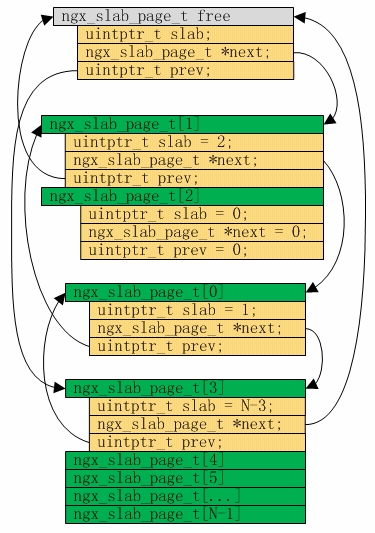 -
-可以看到,Nginx对空闲page页的链式管理不会进行节点合并,不过关系不大,毕竟page页既不是slab机制的最小管理单元,也不是其主要分配单元。对处于使用状态中的page页,也是采用的链式管理,在介绍其详细之前,需先来看看 slab 机制的第二级管理机制,即 slot块,这样便于前后的连贯理解。
-slot块是对每一页page内存的内部管理,它将page页划分成很多小块,各个page页的slot块大小可以不相等,但同一个page页的slot块大小一定相等。page页的状态通过其所在的链表即可辨明,而page页内各个slot块的状态却需要一个额外的标记,在Nginx的具体实现里采用的是位图方式,即一个bit位标记一个对应slot块的状态,1为使用,0为空闲。
-根据slot块的大小不同,一个page页可划分的slot块数也不同,从而需要的位图大小也不一样。前面提到过,每一个page页对应一个名为ngx_slab_page_t的管理结构,该结构体有一个uintptr_t类型的slab字段。在32位平台上(也就是本书讨论的设定平台),uintptr_t类型占4个字节,即slab字段有32个bit位。如果page页划分的slot块数小于等于32,那么Nginx直接利用该字段充当位图,这在Nginx内叫exact划分,每个slot块的大小保存在全局变量ngx_slab_exact_size以及ngx_slab_exact_shift内。比如,1个4KB的page页,如果每个slot块大小为128字节,那么恰好可划分成32块。图3-13是这种划分下的一种可能的中间情况。
-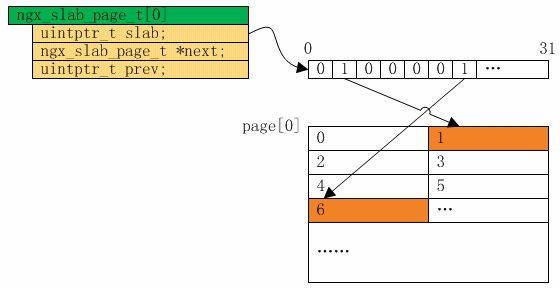 -
-如果划分的每个slot块比ngx_slab_exact_size还大,那意味着一个page页划分的slot块数更少,此时当然也是使用 ngx_slab_page_t 结构体的 slab 字段作为位图。由于比ngx_slab_exact_size大的划分可以有很多种,所以需要把其具体的大小也记录下来,这个值同样也记录在 slab 字段里。这样做是可行的,由于划分总是按 2 次幂增长,所以比ngx_slab_exact_size还大的划分至少要减少一半的slot块数,因此利用slab字段的一半bit位即可完整表示所有slot块的状态。具体点说就是:slab字段的高端bit用作位图,低端bit用于存储slot块大小(仅存其对应的移位数)。代码如下。
-378: 代码片段3.6-4: ngx_slab.c
-379: page->slab = ((uintptr_t) 1 << NGX_SLAB_MAP_SHIFT) | shift;
-如果申请的内存大于等于ngx_slab_max_size,Nginx直接返回一个page整页,此时已经不在slot块管理里,所有无需讨论。下面来看小于ngx_slab_exact_size的情况,此时slot块数目已经超出了slab字段可表示的容量。比如假设按8字节划分,那么1个4KB的page页将被划分为512块,表示各个slot块状态的位图也就需要512个bit位,一个slab字段明显是不足够的,所以需要为位图另找存储空间,而slab字段仅用于存储slot块大小(仅存其对应的移位数)。
-另找的位图存储空间就落在page页内,具体点说是其划分的前面几个slot块内。接着刚才说的例子,512个bit位的位图,即64个字节,而一个slot块有8个字节,所以就需要占用page页的前8个slot块用作位图。一个按8字节划分slot块的page页初始情况如图3-14所示。
-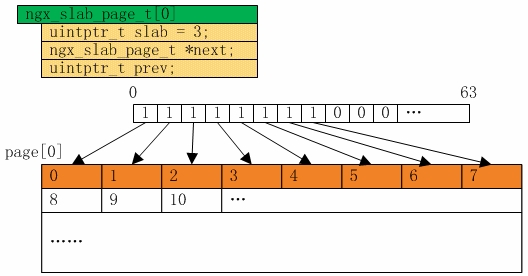 -
-由于前几个slot块一开始就被用作位图空间,所以必须把它们对应的bit位设置为1,表示其状态为使用。
-不论哪种情况,都有了slot块的大小以及状态,那对slot块的分配与释放就水到渠成了。下面回到slab机制的最后一个话题,即对处于使用状态中的page页的链式管理。其实很简单,首先,根据每页划分的slot块大小,将各个page页加入到不同的链表内。在我们这里设定的平台上,也就是按8、16、32、64、128、256、512、1024、2048一共9条链表,在ngx_slab_init()函数里有其初始化。
-102: 代码片段3.6-5,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-103: n = ngx_pagesize_shift - pool->min_shift;
-104:
-105: for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
-106: slots[i].slab = 0;
-107: slots[i].next = &slots[i];
-108: slots[i].prev = 0;
-109: }
-假设申请一块 8字节的内存,那么 slab机制将一共分配 page那么多页,将它按 8字节做slot划分,并且接入到链表slots[0]内,相关示例(表示这只是其中一处实现)代码如下。
-352: 代码片段3.6-6,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-353: page->slab = shift;
-354: page->next = &slots[slot];
-355: page->prev = (uintptr_t) &slots[slot] | NGX_SLAB_SMALL;
-356:
-357: slots[slot].next = page;
-page->prev按4字节对齐,所以末尾两位可以用做他用,这里用于标记当前slot划分类型为NGX_SLAB_SMALL,如图3-15所示。
- -
-继续申请8字节的内存不会分配新的page页,除非刚才那页page(暂且称之为页A)被全是使用完,一旦页A被使用完,它会被拆除出链表,相关示例代码如下。
-232: 代码片段3.6-7,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-233: prev = (ngx_slab_page_t *)
-234: (page->prev & ~NGX_SLAB_PAGE_MASK);
-235: prev->next = page->next;
-236: page->next->prev = page->prev;
-237:
-238: page->next = NULL;
-239: page->prev = NGX_SLAB_SMALL;
-第234行是过滤掉末尾的标记位,以获得正确的前一节点的地址,如图3-16所示。
- -
-如果仍然继续申请8字节的内存,那么Nginx的slab机制必须分配新的page页(暂且称之为页B),类似于前面介绍的那样,页B会被加入到链表内,此时链表中只有一个节点,但如果此时页A释放了某个slot块,它又会被加入到链表中,终于形成了具有两个节点的链表,相关示例代码(变量page指向页A)如下,如图3-17所示。
-455: 代码片段3.6-8,文件名: ngx_slab.c
-456: page->next = slots[slot].next;
-457: slots[slot].next = page;
-458:
-459: page->prev = (uintptr_t) &slots[slot] | NGX_SLAB_SMALL;
-460: page->next->prev = (uintptr_t) page | NGX_SLAB_SMALL;
- -
-通过对signal信号的处理,使得Nginx支持与用户进行信息交互,从而实现某些特定功能,比如在不中止Nginx服务的情况下更新配置。在前面曾简单提到过Nginx各类进程对信号的处理,下面详细来看。
- -Nginx对所有发往其自身的信号进行了统一管理,其封装了一个对应的ngx_signal_t结构体来描述一个信号。
-13: 代码片段3.7.1-1,文件名: ngx_process.c
-14: typedef struct {
-15: int signo;
-16: char *signame;
-17: char *name;
-18: void (*handler)(int signo);
-19: } ngx_signal_t;
-其中字段signo也就是对应的信号值,比如SIGHUP、SIGINT等,当然这是宏,其具体在库头文件signal.h内有定义,比如宏SIGHUP就是数值1[4]。
-[root@localhost ~]# grep SIGHUP /usr/include/*/signal.h
-/usr/include/asm-generic/signal.h:#define SIGHUP 1
-/usr/include/asm/signal.h:#define SIGHUP 1
-字段signame为信号名,信号值所对应宏的字符串,比如"SIGHUP"。字段name和信号名不一样,名称表明该信号的自定义作用,即 Nginx 根据自身对该信号的使用功能而设定的一个字符串,比如SIGHUP用于实现“在不中止Nginx服务的情况下更新配置”的功能,所以对应的该字段为"reload"。字段handler,处理信号的回调函数指针,未直接忽略的信号,其处理函数全部为函数ngx_signal_handler()。
-有了描述单个信号的结构体后,Nginx 定义了一个 ngx_signal_t 数组类型的全局变量signals,把它将要处理的信号全部罗列在其中,看其中的几个元素示例。
-38: 代码片段3.7.1-2,文件名: ngx_process.c
-39: ngx_signal_t signals[] = {
-40: { ngx_signal_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL),
-41: "SIG" ngx_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL),
-42: "reload",
-43: ngx_signal_handler },
-44: …
-80: { SIGPIPE, "SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN", "", SIG_IGN },
-81:
-82: { 0, NULL, "", NULL }
-83: };
-ngx_signal_value()、ngx_value()等几个都是宏,虽然展开后也很简单,但是它用到了一点额外的知识,如表3-4所示。另外,在C语言代码中,以空格隔开的连续的多个字符串会自动连接,比如两个字符串"SIG""HUP"将自动组合为"SIGHUP"。
-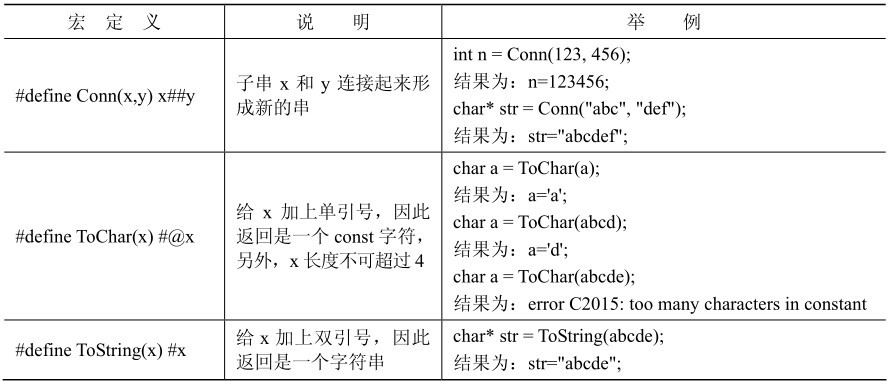 -
-有了上面这些介绍,那么对于如下所示的signals[0]的各个字段值就很容易理解了。
-{1, "SIGHUP", "reload", ngx_signal_handler}
-对于signals数组的后面几个元素,其回调函数为SIG_IGN,表示忽略该信号,这和不做设置是不一样的。如果不做设置,那么将按系统默认的处理进行,而这里主动设置为忽略,也是对其的一种处理方式。数组最后一个元素的各个字段为0或NULL,这是把它当末尾哨兵使用,这是不定数组的惯用手法,以便后续能方便地对它做遍历(因为结束条件的判断就由哨兵把持即可)。
- -做好了准备工作,接下来就要对它们进行设置以便生效,进而在 Nginx 收到信号时能调用对应的回调函数进行处理。
-在Nginx的启动流程里,有一个下面这样的函数调用。
-main() -> ngx_init_signals()
-即由函数ngx_init_signals()完成信号的设置工作。
-282: 代码片段3.7.2-1,文件名: ngx_process.c
-283: ngx_int_t
-284: ngx_init_signals(ngx_log_t *log)
-285: {
-286: ngx_signal_t *sig;
-287: struct sigaction sa;
-288:
-289: for (sig = signals; sig->signo != 0; sig++) {
-290: ngx_memzero(&sa, sizeof(struct sigaction));
-291: sa.sa_handler = sig->handler;
-292: sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
-293: if (sigaction(sig->signo, &sa, NULL) == -1) {
-294: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno,
-295: "sigaction(%s) failed", sig->signame);
-296: return NGX_ERROR;
-297: }
-298: }
-299:
-300: return NGX_OK;
-301: }
-了解API函数sigaction()的话,上面代码很容易看懂,在这里我们也看到了signals数组末尾哨兵的功能。
-对信号进行设置并生效是在 fork()函数调用之前进行的,所以工作进程等都能受此作用。当然,一般情况下,我们不会向工作进程等子进程发送控制信息,而主要是向监控进程父进程发送,父进程收到信号做相应处理后,再根据情况看是否要把信号再通知到其他所有子进程。
- -本小节以惯用的“在不间断Nginx服务的情况下更新Nginx使用配置”为例,来看下Nginx的整个处理过程。
-我们知道,在一般情况下,Nginx主进程总是阻塞在sigsuspend()函数调用点,以等待接收信号,通过pstack命令可以验证这一情况(注意:命令后半句的前后并不是单引号字符,而是反引号)。
-[root@localhost ~]# pstack `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
-#0 0x00fe6424 in __kernel_vsyscall ()
-#1 0x00af0ec7 in sigsuspend () from /lib/libc.so.6
-#2 0x08070b29 in ngx_master_process_cycle ()
-#3 0x0804b81f in main ()
-如果Nginx主进程被直接kill-9掉了,那么函数sigsuspend()将得不到返回[5],此时Nginx相关子进程也无法获得主进程发送的信号(因为主进程根本就没机会做这个动作),我们这里不考虑这种情况。如果Nginx主进程收到并捕获了信号,比如用户通过kill命令进行信号发送。
-[root@localhost ~]# kill -s SIGHUP 'cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid'
-那么函数sigsuspend()将在对应的信号处理函数执行完之后才返回继续处理,这点很重要,看Nginx的信号处理回调函数ngx_signal_handler()。
-349: 代码片段3.7.3-1,文件名: ngx_process.c
-350: case ngx_signal_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL):
-351: ngx_reconfigure = 1;
-352: action = ", reconfiguring";
-353: break;
-对信号的处理非常的简单,仅根据其收到的信号对相应的全局变量进行置位操作,这符合信号处理函数要求简单快速的一般特点。
-函数ngx_signal_handler()处理完后返回,进而函数sigsuspend()返回,从而主进程可以执行后面的代码。
-145: 代码片段3.7.3-2,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c
-146: for ( ;; ) {
-147: …
-170: sigsuspend(&set);
-171: …
-227: if (ngx_reconfigure) {
-228: ngx_reconfigure = 0;
-229: …
-260: }
-261: …
-284: if (ngx_noaccept) {
-285: ngx_noaccept = 0;
-286: ngx_noaccepting = 1;
-287: ngx_signal_worker_processes(cycle,
-288: ngx_signal_value(NGX_SHUTDOWN_SIGNAL));
-289: }
-290: }
-第170行的函数sigsuspend()返回后,后面对全局变量进行判断,发现置位了,那么就开始处理,当然,在处理前先把该全局变量复位,以免下次重复进入。如代码第287 行所示,如果有必要,会利用函数 ngx_signal_worker_processes()再把信号值发送给子进程,而子进程收到信号的处理也大致类似,这无需多说。
-这里要注意一下信号发送函数 ngx_signal_worker_processes(),它首先通过父子进之间的channel调用函数ngx_write_channel()进行信号传递,当这种方法失败时才利用kill()函数,相关代码逻辑也比较简单,略过不提。
-另外,除了通过kill命令向Nginx发送信号外,Nginx本身封装了几个对信号的发送工作,这主要是通过Nginx的命令行参数选项提供的,比如stop,quit,reopen,reload,而其内部实现也是通过读取当前正在执行的Nginx进程所对应的nginx.pid文件,获得它对应的pid,然后调用kill()函数进行信号发送,对应的函数调用流程为
-main() -> ngx_signal_process() -> ngx_os_signal_process()
-由于nginx.pid文件路径可以通过配置指令pid指定。如果当前执行的Nginx进程与准备发送信号的Nginx程序使用的是不同的配置,并且配置文件中指定的nginx.pid文件路径不同,那么将可能出现发送失败的情况。比如,当前正在执行的 Nginx 进程使用的配置是nginx.conf.old,指定的pid路径为pid /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.pid.old;,而此时用默认配置执行nginx -s reload 将获得如下错误。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# objs/nginx -s reload
-nginx: [error] open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file ordirectory)
-注 释
-[1].http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#master_process。
-[2].感兴趣的读者请以关键字“进程之间文件描述符传递”搜索互联网相应资源。
-[3].关于内存对齐对性能的影响,可以参考:http://lenky.info/?p=310。
-[4].Man手册的第7节也可以看到:man 7 signal或http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?signal+7。
- \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-1-ngx_process.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-1-ngx_process.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fc0d65e3e0eeb57ff24e1e7b8e744dcf3ea9a04d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-1-ngx_process.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + typedef struct { + int signo; + char *signame; + char *name; + void (*handler)(int signo); + } ngx_signal_t; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-2-ngx_process.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-2-ngx_process.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d296cc69ef321166533fe15d54faa2e42d670e8c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.1-2-ngx_process.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ + ngx_signal_t signals[] = { + { ngx_signal_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL), + "SIG" ngx_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL), + "reload", + ngx_signal_handler }, + … + { SIGPIPE, "SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN", "", SIG_IGN }, + + { 0, NULL, "", NULL } + }; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.2-1-ngx_process.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.2-1-ngx_process.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7721738ef88da8634c06c083324f63ed69a67a8d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.2-1-ngx_process.c" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +ngx_int_t +ngx_init_signals(ngx_log_t *log) +{ + ngx_signal_t *sig; + struct sigaction sa; + + for (sig = signals; sig->signo != 0; sig++) { + ngx_memzero(&sa, sizeof(struct sigaction)); + sa.sa_handler = sig->handler; + sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask); + if (sigaction(sig->signo, &sa, NULL) == -1) { + ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno, + "sigaction(%s) failed", sig->signame); + return NGX_ERROR; + } + } + + return NGX_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-1-ngx_process.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-1-ngx_process.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9e6e2d8263111d46d2c65d7a7dc2c700a6dba338 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-1-ngx_process.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + case ngx_signal_value(NGX_RECONFIGURE_SIGNAL): + ngx_reconfigure = 1; + action = ", reconfiguring"; + break; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7134b548f4a680f5a98046a1e913a888353fc197 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/3.7 \344\277\241\345\217\267\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2653.7.3-2-ngx_process_cycle.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ + for ( ;; ) { +… + sigsuspend(&set); +… + if (ngx_reconfigure) { + ngx_reconfigure = 0; +… + } +… + if (ngx_noaccept) { + ngx_noaccept = 0; + ngx_noaccepting = 1; + ngx_signal_worker_processes(cycle, + ngx_signal_value(NGX_SHUTDOWN_SIGNAL)); + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ed42529dfe883f5288f4fc6e8bb127534d70cf31..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25403\347\253\240 \350\277\233\347\250\213\346\250\241\345\236\213/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -一般情况下,在启动Nginx后系统将出现多个Nginx进程,每个进程各司其责共同完成对客户端请求处理响应的任务。这些进程各自负责哪些业务逻辑、它们之间是否有交互以及如何交互等是本章将要介绍的内容。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 8824bce828d9fd724cd472ae916c02040cae4081..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,117 +0,0 @@ - -对于任何一个应用程序,在执行具体逻辑的时候必定要使用到内存资源,Nginx 也不例外,而针对自身业务的特点,Nginx 封装了一个名为 ngx_pool_t 类型的内存池,下面就先来看看这个内存池的相关信息。不过在此之前,额外多说几句个人经验:对于C代码里的一个复杂数据结构,我们应该怎样去开始着手分析和理解?其实,和看其他代码一样,先要找到入口,比如应用程序从 main()函数入手,数据结构当然没有 main()函数,不过它可能有类似于C++类一样的初始函数(在C++类中,也就是构造函数),一般被命名为init()、create()等,所以对于Nginx内存池,我们也先来看它的初始函数ngx_create_pool()。
-15: 代码片段4.1-1,文件名: ngx_palloc.c
-16: ngx_pool_t *
-17: ngx_create_pool(size_t size, ngx_log_t *log)
-18: {
-19: ngx_pool_t *p;
-20:
-21: p = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, size, log);
-22: …
-26: p->d.last = (u_char *) p + sizeof(ngx_pool_t);
-27: p->d.end = (u_char *) p + size;
-28: …
-31: size = size - sizeof(ngx_pool_t);
-32: p->max = (size < NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL) ? size : NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL;
-33:
-34: p->current = p;
-35: …
-40: return p;
-41: }
-19: 代码片段4.1-2,文件名: ngx_palloc.h
-20: #define NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL (ngx_pagesize - 1)
-21: …
-24: #define NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT 16
-一些给ngx_pool_t结构体字段赋值为NULL或0的语句被我去掉了,代码片段4.1-1的第21行是进行 16 字节的内存对齐分配,对齐处理一般是为了从性能上做考虑。而另一个值得关注的赋值语句是代码第32行,可以看到max最大值为4095(假设一页大小为4KB),在后面会看到这个字段的应用。一个完整的代表当前状况的图如图4-1所示(max的值可能为size,当然,从代码片段4.1-1的第32行可以看出,max的值还可能是NGX_MAX_ALLOL_FROM_POOL)。
- -
-创建的内存池被结构体ngx_pool_t占去开头一部分(即额外开销overhead),Nginx实际从该内存池里分配空间的起始位置从p->d.last开始,随着内存池空间的对外分配,这个字段的指向会向后移动。其他字段为空,不过既然设置有这些字段,那肯定是有作用的,但可以暂且不管, 分析到后面自然会遇到,所以直接来看如何从这个内存池里分配内存空间。接口函数挺多,有如下这些。
-void *ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-void *ngx_pnalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-void *ngx_pmemalign(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size, size_t alignment)
-void *ngx_pcalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-static void *ngx_palloc_block(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-static void *ngx_palloc_large(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-后面两个接口被static修饰,初步猜想这是内调函数,不会被外部使用,而事实上也的确如此,所以真正对外的内存分配接口只有前面四个,逐一来看。
-函数ngx_palloc()尝试从pool内存池里分配size大小的内存空间。这有两种情况。第一种,如果size小于等于pool->max(我们称之为小块内存分配),即小于等于内存池总大小或1页内存(4K-1),那么就可以从内存池里分配,这个分配的内存不一定是来之当前内存池节点(为什么说是节点?马上会解释),因为有可能当前内存池节点里可用的内存空间大小已经小于size,如果是这样的话,就需调用函数ngx_palloc_block()申请一个新的等同大小的内存池节点,然后从这个新内存池节点里分配出size大小的内存空间。除此之外,函数ngx_palloc_block()还会做另外两件事情。首先,把新内存池节点连接到上一个内存池节点的p->d.next字段下形成单链表,如图4-2所示。
- -
-既然有链表,那么就有链表节点,所以我前面说是内存池节点也就是基于这个原因,新链表节点的加入是在链表尾进行的。另外可以看到新建立的内存池节点的 overhead 都只有结构体ngx_pool_data_t了,这是当然的,一个内存池没有必要有多个ngx_pool_t描述结构,内存能省就省。
-函数 ngx_palloc_block()做的另一件事情是根据需要移动内存池描述结构 ngx_pool_t 的current 字段,这个字段记录了后续从该内存池分配内存的起始内存池节点,即从这个字段指向的内存池节点开始搜索可分配的内存。current 字段的变动是根据统计来做的,如果从当前内存池节点分配内存总失败次数(记录在字段p->d.failed内)大于等于6次(这是一个经验值,具体判断是“if (p->d.failed++> 4) {”,由于p->d.failed 初始值为0,所以当这个判断为真时,至少已经分配失败6 次了),就将current字段移到下一个内存池节点,如果下一个内存池节点的failed统计数也大于等于6次,再下一个,依次如此,如果直到最后仍然是failed统计数大于等于6次,那么current字段则指向刚新分配的内存池节点。
-在函数ngx_palloc()内,实现小块内存分配逻辑的相关代码如下所示。
-123: 代码片段4.1-3,文件名: ngx_palloc.c
-124: p = pool->current;
-125:
-126: do {
-127: m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT);
-128:
-129: if ((size_t) (p->d.end - m) >= size) {
-130: p->d.last = m + size;
-131:
-132: return m;
-133: }
-134:
-135: p = p->d.next;
-136:
-137: } while (p);
-138:
-139: return ngx_palloc_block(pool, size);
-pool->current 字段的变动是基于性能的考虑,如果从前面的内存池节点里分配内存总是失败,那在下次再进行内存分配时,当然就没有必要再去搜索这些内存池节点,把pool->current指向后移,也就是直接跳过它们。
-再来看size大于pool->max的情况(即分配大块内存),此时函数ngx_palloc()直接“return ngx_palloc_large(pool, size);”,函数 ngx_palloc_large()只能调用系统 API 接口 malloc()向操作系统申请内存,申请的内存块被挂接在内存池字段p->large->alloc下(会有对应的管理头结构ngx_pool_large_t),如图4-3所示。
-如果继续分配大块内存,那么从系统新分配的内存块就以单链表的形式继续挂载在内存池字段p->large->alloc下,不过这是一种链头插入(和之前的另一个链表有点不同),如图4-4所示。
-在内存池的使用过程中,由于大块内存可能会被释放(通过函数ngx_pfree()),此时将空出其对应的头结构体变量ngx_pool_large_t,所以在进行实际的链头插入操作前,会去搜索当前是否有这种情况存在(如图4-5所示)。
- -
-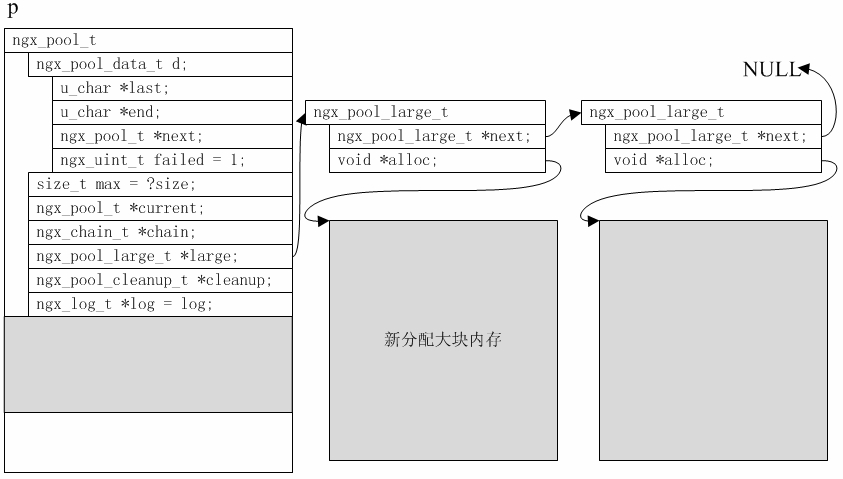 -
-如果有,则直接把新分配的内存块设置在其alloc指针字段下,综合平衡考虑,这种搜索也只是对前面几个链表节点进行。
-两种情况都分析完后,ngx_palloc()函数的介绍就算到此结束了。不过,有个细节问题,为什么要将 pool->max 字段的最大值限制在一页内存?从前面的分析可知,这个字段是区分小块内存与大块内存的临界,所以这里的原因也就在于只有当分配的内存空间小于一页时才有缓存的必要(即向Nginx内存池申请),否则的话,还不如直接利用系统接口malloc()向操作系统申请。这可以认为是一种经验,比如很多有内核编程经验的人都知道,在 32 位 Linux系统环境里,一般情况下,如果申请的内存空间大于一页,此时就没有必要使用kmalloc()函数,而使用vmalloc()函数就好,道理与此类似。
- -
-回过头来看另外几个内存分配函数,ngx_pnalloc()函数与刚才介绍的 ngx_palloc()函数实现基本一致,但是它取得的内存起始地址没有做对齐处理(典型代码对比情况)。
-116: 代码片段4.1-4,文件名: ngx_palloc.c
-117: ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-118: …
-127: m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT);
-128:
-147: ngx_pnalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
-148: …
-157: m = p->d.last;
- -
-函数ngx_pcalloc()是在ngx_palloc()上的封装,但它在返回分配的内存之前会对这些内存做清零操作。
-函数 ngx_pmemalign()不管 size 大小如何,都直接向操作系统申请内存,然后挂接在p->large->alloc字段下。当然,根据名称就可以看出,申请的内存额外的有对齐处理。
-Nginx另外还提供的一套函数接口ngx_pool_cleanup_add()、ngx_pool_run_cleanup_file()、ngx_pool_cleanup_file()、ngx_pool_delete_file()用于对内存与其他资源的关联管理,也就是说从内存池里申请一块内存时,可能外部会附带一些其他资源(比如说打开的文件),这些资源的使用和申请的内存是绑定在一起的,那么在进行资源释放的时候,当然也就希望这些资源的释放能放置在和内存池释放时一起进行(通过handler()回调函数),既能避免无意的资源泄露,又省得单独执行资源释放的麻烦。具体代码逻辑不多赘述,如图4-7所示。
- -
-最后,来看内存池的释放问题,从代码中不难看出 Nginx 仅提供对大块内存的释放(通过接口ngx_pfree()),而没有提供对小块内存的释放,这意味着从内存池里分配出去的内存不会再回收到内存池里来,而只有在销毁整个内存池时,所有这些内存才会回收到系统内存里,这是Nginx内存池一个很重要的特点,前面介绍的很多内存池设计与处理也都是基于这个特点。Nginx内存池这样设计的原因在于Web Server应用的特殊性,即阶段与时效,对于其处理的业务逻辑分有明确的阶段,而对每一个阶段又有明确的时效,因此Nginx可针对阶段来分配内存池,针对时效来销毁内存池。比如,当一个阶段(比如request处理)开始(或其过程中)就创建对应所需的内存池,而当这个阶段结束时就销毁其对应的内存池,由于这个阶段有严格的时效性,即在一段时间后,其必定会因正常处理、异常错误或超时等而结束,所以不会出现Nginx长时间占据大量无用内存池的情况,既然如此,在其阶段过程中回收不用的小块内存自然也就是不必要的,等待一会再一起回收岂不更简单方便?关于内存池的释放,具体实现在函数ngx_destroy_pool()与ngx_reset_pool()内,这两者逻辑都比较简单明朗,无需多说。
-毫无疑问,内存池的使用给Nginx带来了诸多好处,比如内存使用的便利、逻辑代码的简化以及程序性能的提升,但另一方面,它对我们在使用相关内存诊断工具(比如Valgrind[1])进行问题排查时产生了一定程度上的负面干扰,导致我们可能无法正确的捕获到相关内存异常问题。因此,在进行Nginx二次开发过程中,如遇到诡异的内存问题无法顺利排查时,不妨试试一些第三方补丁[2],其通过禁用Nginx的内存池,即采用malloc/free接口直接使用系统内存的方式来避免内存池的负面干扰,方便Valgrind工具的使用,以提高解决问题的正确率和效率。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-1-ngx_palloc.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-1-ngx_palloc.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..510c1e8223217ffa33265a6d1671eb9ae7ef89d2 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-1-ngx_palloc.c" @@ -0,0 +1,20 @@ + ngx_pool_t * + ngx_create_pool(size_t size, ngx_log_t *log) + { + ngx_pool_t *p; + + p = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, size, log); + … + p->d.last = (u_char *) p + sizeof(ngx_pool_t); + p->d.end = (u_char *) p + size; + … + size = size - sizeof(ngx_pool_t); + p->max = (size < NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL) ? size : NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL; + + p->current = p; + … + return p; + } + #define NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL (ngx_pagesize - 1) + … + #define NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT 16 \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-3-ngx_palloc.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-3-ngx_palloc.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9b07bd1268a3997845e7156ac43789753e631ea9 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-3-ngx_palloc.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ + p = pool->current; + + do { + m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT); + + if ((size_t) (p->d.end - m) >= size) { + p->d.last = m + size; + + return m; + } + + p = p->d.next; + + } while (p); + + return ngx_palloc_block(pool, size); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-4-ngx_palloc.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-4-ngx_palloc.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6cce018782b65f2f89f9e1f04ce1a403e61fdfd7 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.1 \345\206\205\345\255\230\346\261\240/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2654.1-4-ngx_palloc.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size) +… + m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT); + +ngx_pnalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size) +… + m = p->d.last; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.2 Hash/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.2 Hash/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 23d31c90156d43310f66c8687215edef868d03a2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25404\347\253\240 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204/4.2 Hash/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,106 +0,0 @@ - -Nginx Hash数据结构的创建过程有点复杂,这从其初始函数ngx_hash_init()就占去200 多行可知一二,但这种复杂是源于Nginx对高效率的极致追求。我们知道影响Hash数据结构查找效率的最大因素是哈希冲突[3]的平均次数,如果没有冲突,那么每一次查找都是一次完成,效率自然很高。如何减少平均冲突次数,一方面是选择好的映射函数,另一方面是扩大Hash内存空间。Nginx的哈希映射函数可以认为是两重,先是计算哈希键值key(这是一个字符串)的哈希码hashcode,然后对hashcode做一个按实际Hash内存空间大小取模运算就得到其在这个内存空间里的具体位置,这部分比较简单无需多说。另一个重点就是Hash内存空间大小的选择,虽然说越大的内存空间冲突自然也就越少,但也不能无限制的大,因此以时间换取空间也是必要的,这是一个选择中间平衡的过程,也是函数ngx_hash_init()的主要逻辑。下面就开始依附实例来逐步解析Nginx Hash数据结构的内部实现。
-Nginx对虚拟主机的管理使用到了Hash数据结构,比如假设配置文件里有如下这样的配置。
-23: 代码片段4.2-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-24: server {
-25: listen 192.168.1.1:80;
-26: server_name www.web_test2.com blog.web_test2.com;
-27: …
-41: server {
-42: listen 192.168.1.1:80;
-43: server_name www.web_test1.com bbs.web_test1.com;
-44: …
-当Nginx以此配置文件正常启动后,如果来了一个客户端请求到192.168.1.1的80端口,那么Nginx肯定就要做一个查找,看当前请求该使用哪个Server配置。为了提高查找效率,所以在启动开始后,Nginx就将根据这些server_name建立起一个Hash数据结构。
-1512:代码片段4.2-2,文件名: ngx_http.c
-1513: hash.key = ngx_hash_key_lc;
-1514: hash.max_size = cmcf->server_names_hash_max_size;
-1515: hash.bucket_size = cmcf->server_names_hash_bucket_size;
-1516: hash.name = "server_names_hash";
-1517: hash.pool = cf->pool;
-1518:
-1519: if (ha.keys.nelts) {
-1520: hash.hash = &addr->hash;
-1521: hash.temp_pool = NULL;
-1522:
-1523: if (ngx_hash_init(&hash, ha.keys.elts, ha.keys.nelts) != NGX_OK) {
-代码第1523行调用初始函数ngx_hash_init()开始创建这个对应的Hash数据结构,看看此时的已准备数据(对于ngx_hash_keys_arrays_t结构体,这里只关注与此相关的keys字段以及已构建成的数据内容,之前它的其他字段以及它的数据是如何构建的,比较简单,所以在这里不做讲解)。
-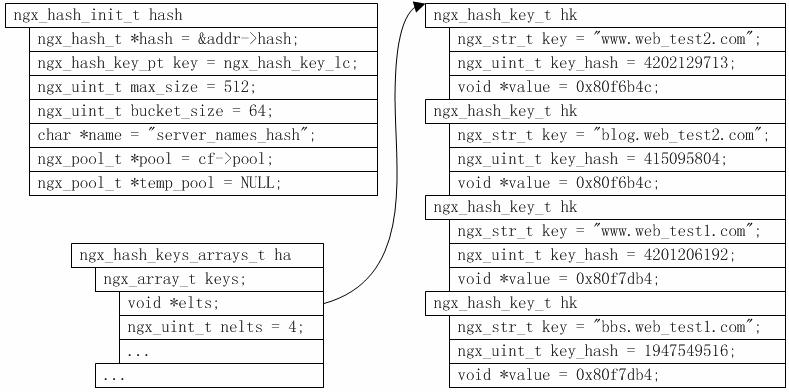 -
-ngx_hash_init()函数的第二和第三个参数指示了创建这个 Hash 的原始来源数据(后续称之为实际元素),这无需多说,但是另外一个值得注意的是通过第一个参数传入的 hash.hash其实是一个输出参数,如果我们还注意到给该字段赋的值,表明最后生成的Hash数据结构会存放在addr->hash内,从而后面才可以引用并使用到这个Hash,而它的结构非常简单:
-22: 代码片段4.2-3,文件名: ngx_hash.h
-23: typedef struct {
-24: ngx_hash_elt_t **buckets;
-25: ngx_uint_t size;
-26: } ngx_hash_t;
-这是由Nginx提供的Hash数据结构的特点所决定的,即创建之后就不可再修改,只供高效查找,所以相关字段自然是相当简洁。我们不妨先来看看生成之后的Hash是怎样一个结构。
-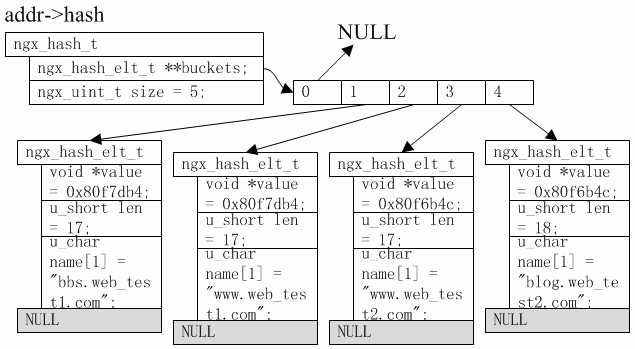 -
-上图中,字段buckets指向的就是Hash节点所对应的存储空间,不过这里具体实现时用的是二级指针,那么*buckets本身是一个数组,每一个数组元素用来存储映射到此的Hash节点。由于可能有多个实际元素映射到同一个Hash节点(即发生冲突),所以对实际元素再次进行数组形式的组织存储在一个bucket内,这个数组的结束以哨兵元素NULL作为标记,而前面的每一个ngx_hash_elt_t结构对应一个实际元素的存储。这里的实例,整体上也就形成上面所示那样的结构图。对于图中name字段的长度为 1,却保存了那么多数据,是不是会有问题?这也是具体实现上的技巧,类似于gcc的0长度数组[4]。
-对于包含4个实际元素的Hash数据结构却只有5个Hash节点(为什么是5呢?在后面马上会讲到),并且没有冲突(即同一个Hash节点下只有一个实际元素),是不是很惊讶Nginx是怎么做到的?它为什么知道只要5个Hash节点的内存空间就足够了呢?这就是实现在函数ngx_hash_init()前面部分的相关测试代码所做的功劳。
-247: 代码片段4.2-4,文件名: ngx_hash.c
-248: #define NGX_HASH_ELT_SIZE(name) \
-249: (sizeof(void *) + ngx_align((name)->key.len + 2, sizeof(void *)))
-250:
-251: ngx_int_t
-252: ngx_hash_init(ngx_hash_init_t *hinit, ngx_hash_key_t *names, ngx_uint_t nelts)253: {
-254: …
-260: for (n = 0; n < nelts; n++) {
-261: if (hinit->bucket_size 262: … 267: return NGX_ERROR; 代码第261行的这个判断是确保一个bucket至少能存放一个实际元素以及结束哨兵,如果有任意一个实际元素(比如其name 字段特别的长)无法存放到bucket 内则报错返回。具体实现来看,NGX_HASH_ELT_SIZE(&names[n])是该实际元素names[n]所需的内存空间(有对齐处理),而sizeof(void *)自然就是结束哨兵的所需内存空间,hinit->bucket_size 记录了一个bucket的内存空间大小,所以拿它们做比较即可。 接下来开始测试针对当前传入的所有实际元素,测试分配多少个Hash节点(也就是多少bucket)会比较好,即能省内存又能少冲突,否则的话,直接把Hash节点数目设置为最大值hinit->max_size即可。看看这个测试的具体过程(也就是前面那个数值5是怎么得来的)。 270: 代码片段4.2-5,文件名: ngx_hash.c 271: test = ngx_alloc(hinit->max_size * sizeof(u_short), hinit->pool->log); 272: … 276: bucket_size = hinit->bucket_size - sizeof(void *); 277: 278: start = nelts / (bucket_size / (2 * sizeof(void *))); 279: start = start ? start : 1; 280: 281: if (hinit->max_size > 10000 && nelts && hinit->max_size / nelts < 100) { 282: start = hinit->max_size - 1000; 283: } 代码第276行代码是计算一个bucket除去结束哨兵所占空间后的实际可用空间大小。代码第278~279行代码计算所需bucket的最小个数,注意到存储一个实际元素所需的内存空间的最小值也就是(2 * sizeof(void *))(即宏 NGX_HASH_ELT_SIZE 的对齐处理),所以一个bucket 可以存储的最大实际元素个数就为bucket_size /(2* sizeof(void *)),然后总实际元素个数nelts除以这个值也就是最少所需要的bucket个数。第281及以后的代码处理另外一种特殊情况,这是一种经验值,如果这个if条件成立,意味着实际元素个数非常多,那么有必要直接把start起始值调高,否则在后面的循环里要执行过多的无用测试。 284: 代码片段4.2-6,文件名: ngx_hash.c 285: for (size = start; size < hinit->max_size; size++) { 286: 287: ngx_memzero(test, size * sizeof(u_short)); 288: 289: for (n = 0; n < nelts; n++) { 290: if (names[n].key.data == NULL) { 291: continue; 292: } 293: 294: key = names[n].key_hash % size; 295: test[key] = (u_short) (test[key] + NGX_HASH_ELT_SIZE(&names[n])); 296: … 303: if (test[key] > (u_short) bucket_size) { 304: goto next; 305: } 306: } 307: 308: goto found; 309: 310: next: 311: 312: continue; 313: } 上面的代码就是获取Hash结构最终节点数目的逻辑,其实也非常的简单,就是逐步增加Hash节点数目(那么对应的bucket数目同步增加),然后把所有的实际元素往这些bucket里添放,这有可能发生冲突,但只要冲突的次数可以容忍,即任意一个bucket都还没满,那么就继续填,如果发生有任何一个bucket满溢了(即第303行代码为真,test[key]记录了key这个hash节点所对应的bucket内存储实际元素后的总大小,如果它大于一个bucket可用的最大空间bucket_size,自然也就是满溢了),那么就必须增加Hash节点、增加bucket。如果所有实际元素都填完后没有发生满溢,那么当前的size值就是最终的节点数目值。 找到需创建的Hash节点数目值,接下来就是实际的Hash结构创建工作,这部分逻辑比较简单,但是其对内存的使用有点技巧,直接点说就是所有buckets所占的内存空间是连接在一起的,并且是按需分配(即某个bucket需多少内存存储实际元素就分配多少内存,不多也不少,当然,除了额外的对齐处理),如图4-10所示。 对创建好的Nginxhash数据结构,唯一的可执行操作就是查找,实现在函数ngx_hash_find()内,逻辑非常的简单,先对key值取模得到对应的Hash节点,然后在该Hash节点所对应的bucket里逐个(实现类似数组,结束有哨兵保证)对比元素名称(比如"www.web_test1.com")来找到唯一的那个实际元素,最后返回其value值(比如,如果在addr->hash结构里找到对应的实际元素,返回value就是其ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t配置)。当然,这是一切OK的情况,否则的话就是没找到,返回NULL。 基树(Radixtree),是一种基于二进制表示键值的二叉查找树,正是由于其键值的这个特点,所以只有在特定的情况下才会使用,典型的应用场景有文件系统、路由表等。关于基树的理论知识,在一些数据结构或算法书籍上有详细描述,所以这里直接来看 Nginx 基树的具体实现。 按惯例,从其初始函数 ngx_radix_tree_create()开始分析,代码首先分配了基树描述结构ngx_radix_tree_t的内存,然后创建了一个只有根节点的基树,如图4-11所示。 在ngx_radix_tree_t结构体中,除root以外的几个字段都是为了对该基树所使用的内存进行管理所做的设计,free 字段下挂载的是当前空闲的树节点(即从树里删除出来而没被使用的废弃节点,这个节点所占内存空间既没有返还给内存池,也没有返还给系统)。这些节点以单链表的形式组织起来(把节点描述结构ngx_radix_node_t的right字段当链表的next字段使用),所以在节点申请函数 ngx_radix_alloc()里,会先去这个空闲链表查找是否有废弃节点可用。如果有的话,就直接取链头节点返回;否则就要申请(如果之前没申请过页内存或者上次剩余内存不足一个基树节点)一页内存(ngx_pagesize大小,有对齐处理),然后先从中分出一个待分配的基树节点,剩下内存的起始地址和大小分布记录在tree->start和tree->size字段里,以便下次分配基树节点时,可从该剩余内存里直接获取。读者会有个疑问,对于申请的页内存,基树相关代码里怎么没有释放,并且如果申请第二块内存页则第一块内存页的起始地址都搞丢了,这会不会导致内存泄露?当然不会,这些基树内存的最终回收会在 Nginx内存池里处理,所以不用担心。 关于基树对内存的管理与使用,上面就介绍完了,下面再来专心看基树本身的相关逻辑。在函数 ngx_radix_tree_create()创建完只有根节点的基树后,还会根据参数 preallocate 进行树节点的创建。如果该值指定为0,表示不需预创建而直接返回;如果preallocate为正数n,则表示要预创建的基树(预创建的是一颗满二叉树,即,除了叶子节点,其他节点的子节点都有左右两个子节点)深度(假定根节点的层次为 0,树深度定义为最大的叶结点层次,也就是说如果preallocate值为1,那么树深度为1,接下来将创建2个树节点;如果preallocate指定为2,那么树深度为2,那么接下来将一共创建6个树节点);如果preallocate为−1,则表示要选择一个默认深度,这根据平台的不同而不同。如果为其他负数,那这就是一个未被函数 ngx_radix_tree_create()所处理的异常输入,比如如果为−2,那么将几乎创建无数多个树节点而必定由于内存不足而失败,所以调用函数ngx_radix_tree_create()时需特别小心。 根据平台的不同选择默认深度的代码也有bug[5],不过这是一个“笔误”,在计算一页内存可以存放多少树节点时用错了结构体。 61: 代码片段4.3-1,文件名: ngx_radix_tree.c 62: if (preallocate == -1) { 63: switch (ngx_pagesize / sizeof(ngx_radix_tree_t)) { 代码第63行的代码sizeof(ngx_radix_tree_t)应该为sizeof(ngx_radix_node_t),这个bug不算严重,仅影响默认预创建的节点个数,所以会稍微影响一下性能(或者说没有其原本的期望目标性能那么好)。如何选择默认深度是从性能上来考虑的,认为默认预分配的节点所占内存总大小为一页即为最佳(这只是Nginx代码作者的一种经验看法),这样认识是否恰当我们不做评论,按此计算,在x86 32 位平台上,一个节点大小为16 字节,所以一页4KB 内存可以创建256个节点,那么代表树的深度的preallocate值也就是7(即总节点数=2^(树深度+1)–1,因为这里预创建的是一颗满二叉树)。其他的平台情况类似计算即可。 接下来正式进行树节点创建,相关逻辑如下。 14: 代码片段4.3-2,文件名: ngx_radix_tree.c 15: ngx_radix_tree_t * 16: ngx_radix_tree_create(ngx_pool_t *pool, ngx_int_t preallocate) 17: { 18: … 81: mask = 0; 82: inc = 0x80000000; 83: 84: while (preallocate--) { 85: 86: key = 0; 87: mask >>= 1; 88: mask |= 0x80000000; 89: 90: do { 91: if (ngx_radix32tree_insert(tree, key, mask, NGX_RADIX_NO_VALUE) 92: != NGX_OK) 93: { 94: return NULL; 95: } 96: 97: key += inc; 98: 99: } while (key); 100: 101: inc >>= 1; 102: } 在讲解这代码之前需要先补充几点背景知识。首先,Nginx提供的这个基树仅被geo模块使用,这个模块使用基树来处理IP地址的匹配查找;其次,在nginx-1.2.0版本内,geo模块仅支持IPv4,这意味着这颗基树支持的最大深度为32就足够用了,所以这里的几个变量key、mask、inc 都为 uint32_t 类型;再次,key 与节点的对应是从高位向低位逐步匹配的,比如图4-12中节点d所对应的key是0x40000000,节点f所对应的key是0xC0000000,等。为什么要这样对应呢?这是因为 geo 模块里真正使用的 IP 网络地址,比如 192.168.0.0/16、10.10.0.0/16等,它们前面bit 位才是有效区分位,如果从后往前位匹配,那么会有大量的bit 0,导致基本任何一个IP网络地址插入到该基树都会达到32层。 最后,在基树的两个节点操作函数ngx_radix32tree_insert()和ngx_radix32tree_delete()中,有了参数key,为什么还有一个参数mask。 38: 代码片段4.3-3,文件名: ngx_radix_tree.h 39: ngx_int_t ngx_radix32tree_insert(ngx_radix_tree_t *tree, 40: uint32_t key, uint32_t mask, uintptr_t value); 41: ngx_int_t ngx_radix32tree_delete(ngx_radix_tree_t *tree, 42: uint32_t key, uint32_t mask); 43: uintptr_t ngx_radix32tree_find(ngx_radix_tree_t *tree, uint32_t key); 它是做什么用的?其实,这还是跟 Nginx 内基树的应用有关。刚才已经说过,基树只被geo模块使用,而geo模块存储的IP网络地址大多只有前面bit位有效,比如192.168.0.0/16只有前 16 位有效,那么参数 mask 就是用于告诉函数 ngx_radix32tree_insert() ,插入“192.168.0.0/16”所对应的树节点,只要到16位(也就是前16层)就可以了,否则的话,就要到32位而白白浪费内存,更糟糕的是还无法区分“192.168.0.0/16”与“192.168.0.0/24”这两种不同情况,而加了参数mask就能解决这个问题。函数ngx_radix32tree_delete()的道理与此类似。而另一个重点函数ngx_radix32tree_find()不需要参数mask的原因在于它是最长匹配,而且利用key值一直往下匹配时,遇到空节点会自然停止。 另外,值得注意的是,这里预创建的是一颗满二叉(基)树,这在前面提到过。有了这些背景知识,我们再来看代码:第82行的inc赋值0x80000000以及第88行的初始mask值(第一次循环时),即最高位为1,对应1层节点(根节点对应第0层);第90行到第99的代码用于创建这一层的所有节点。比如,在第1 层时,key首先为0,创建的左节点a,当key+=inc 后,即key等于0x80000000,此时创建的是右节点b。再执行key += inc后,由于溢出导致key为0,从而do(…)while (key)循环退出。 当第二次进入while (preallocate--){}循环(假设此时为真,即预创建的树深度超过1)后, mask 值等于0x C0000000,对应2 层节点。在内部do(…)while (key)循环内,key值依次是:0x0、0x40000000、0x80000000、0xC0000000、0x0(因为溢出而得到该值),前面4次分别创建c、d、e、f4 个节点,第5 次时循环退出。 其他层次节点的创建情况与上类似而无需再讲,整个基树的解析到此结束。因为理解了函数 ngx_radix_tree_create(),另外的几个未提及具体实现的函数接口也就很容易懂了,值得注意的是基树并不要求是满二叉树,仅仅只是在函数 ngx_radix_tree_create()里设定预创建为满二叉树,但是在其他地方调用函数ngx_radix32tree_insert()进行节点插入时,是哪个位置的树节点就从根开始创建到哪个位置,并不会让这颗基树时时刻刻都保持为满二叉树。 注 释 [2].https://github.com/shrimp/no-pool-nginx [4].http://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Zero-Length.html。 [5].http://forum.nginx.org/read.php?2,229884。 为了自身使用的方便,Nginx 封装了很多非常有用的数据结构,其中包括一些很简单的封装,比如字符串ngx_str_t结构体。 15: 代码片段4-1,文件名: ngx_string.h 16: typedef struct { 17: size_t len; 18: u_char *data; 19: } ngx_str_t; 我们可以很容易读懂每个字段的含义,还有一些比如ngx_list_t、ngx_array_t、ngx_queue_t等也都较为简单,所以本章不打算介绍这些基础数据结构,而把重点放在那些稍微复杂一点的数据结构,比如内存池、哈希等的封装与实现上。 Nginx的配置文件格式是其作者Igor Sysoev自己定义的,并没有采用像语法分析生成器LEMON[2]那种经典复杂的LALR(1)语法来描述配置信息,而是采用一种近似于key-value对的形式,当然,这只是从配置文件内容静态格式上的直观简单描述。事实上,Nginx配置文件可以认为是一种上下文相关的,高度可扩展的,有作用域以及可自定义变量等诸多高级语言特性的脚本语言。本小节暂只介绍配置文件的静态格式,对于更进一步的内容留待后面章节详细阐述。 对于这种自定义格式的配置文件,好处就是自由、灵活,而坏处就是对于 Nginx 的每一项配置信息都必须做针对性的解析和设置,因此我们很容易看到 Nginx 源码里有大量篇幅的配置信息解析与赋值代码。 Nginx配置文件是由多个配置项组成的,每一个配置项都有一个项目名和对应的项目值,项目名又称为指令(Directive),而项目值可能是简单的字符串(以分号结尾),也可能是由简单字符串和多个配置项组合而成配置块的复合结构(以大括号}结尾),我们可以将配置项归纳为两种:简单配置项和复杂配置项[3]。 上图只是一个示例,而实际的简单配置项与复杂配置项会更多样化。要区分简单配置项与复杂配置项很简单,不带大括号的就是简单配置项,反之则反,比如 error_log /var/log/nginx.error_log info; 因为它不带大括号,所以是一个简单配置项。而 location ~ \.php$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:1025; } 带大括号,所以这是一个复杂配置项。为什么要做这种看似毫无意义的区分?因为后面会看到对于复杂配置项而言,Nginx并不做具体的解析与赋值操作,一般只是申请对应的内容空间、切换解析状态,然后递归调用(因为复杂配置项本身含有递归的思想)解析函数,而真正将用户配置信息转换为Nginx内控制变量的值,还是依靠那些简单配置项所对应的处理函数来做。 不管是简单配置项还是复杂配置项,它们的项目名和项目值都是由标记(token:这里是指一个配置文件字符串内容中被空格、引号、分号、tab号、括号,比如‘{’、换行符等分割开来的字符子串)组成的,配置项目名就是一个token,而配置项目值可以是一个、两个和多个token组成。 比如简单配置项 daemon off; 其项目名daemon为一个token,项目值off也是一个token。简单配置项: error_page 404 /404.html; 其项目值就包含有两个token,分别为404和/404.html。 对于复杂配置项 location /gqk { index index.html index.htm index.php; try_files $uri $uri/ @gqk; } 其项目名location为一个token,项目值是一个token(/gqk)和多条简单配置项(通过大括号)组成的复合结构(后续称之为配置块)。上面几个例子中的taken都是被空格分割出来的,事实上下面这样的配置也是正确的。 "daemon" "off"; 'daemon' 'off'; daemon 'off'; "daemon" off; 当然,一般情况下没必要画蛇添足似地去加些引号,除非我们需要在 token 内包含空格而又不想使用转义字符(\)的话就可以利用引号,比如 log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $status ' '"$request" $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; 但是像下面这种格式就会有问题,这对于我们来说很容易理解,不多赘述。 "daemon "off"; 最后值得提一下的是,Nginx配置文件里的注释信息以井号(#)作为开头标记。 直观上看到的配置文件格式大概就是上面介绍的这些,但根据 Nginx 应用本身的特定,我们可以对配置文件做上下文识别和区分,或者说是配置项的作用域。因为虽然某项配置项在同一个上下文里只能设置一次,但却可以在不同的上下文里设置多次,以便达到更细粒的控制。比如配置项error_log就是如此,在不同的server上下文里可以设置不同的日志输出级别和输出文件路径。就http应用而言,目前Nginx预定义的配置上下文主要包括main、http、server、location4 种(还有其他几种,比如event、upstream、if、mail 等)。图5-2 是一个http服务器示例配置的上下文情况。 前面提到对于配置文件里的每一项配置,程序都必须针对性地解析并转化为内部控制变量的值,因此对于所有可能出现的配置项,Nginx 都会提供对应的代码做它的解析转换工作,如果配置文件内出现了Nginx无法解析的配置项,那么Nginx将报错并直接退出程序。 举例来说,对于配置项daemon,在模块ngx_core_module的配置项目解析数组内的第一元素就是保存的对该配置项进行解析所需要的信息,比如daemon配置项的类型,执行实际解析操作的回调函数,解析出来的配置项值所存放的地址等。 32: 代码片段5.2-1,文件名: nginx.c 33: static ngx_command_t ngx_core_commands[] = { 34: 35: { ngx_string("daemon"), 36: NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_DIRECT_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG, 37: ngx_conf_set_flag_slot, 38: 0, 39: offsetof(ngx_core_conf_t, daemon), 40: NULL }, 而如果我在配置文件中加入如下配置内容。 lenky on; Nginx 启动后将直接返回如下提示错误,这是因为对于“lenky on”这个配置项,Nginx根本就没有对应的代码去解析它。 [emerg]: unknown directive "lenky" in /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:2 如果读者在使用 Nginx 的过程中也遇到类似的错误提示,那么应立即检查配置文件是否不小心敲错了字符或配置指令在当前执行版本的Nginx里尚不支持等。 为了统一配置项目的解析,Nginx利用ngx_command_s数据类型对所有的Nginx配置项进行了统一的描述。 77: 代码片段5.2-2,文件名: ngx_conf_file.h 78: struct ngx_command_s { 79: ngx_str_t name; 80: ngx_uint_t type; 81: char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf); 82: ngx_uint_t conf; 83: ngx_uint_t offset; 84: void *post; 85: }; 这是一个结构体数据类型,它包含多个字段,其中几个主要字段的含义为:字段 name指定与其对应的配置项目的名称,字段set指向配置指令处理回调函数,而字段offset指定转换后控制值的存放位置。 以上面的daemon配置项目为例,当遇到配置文件里的daemon项目名时,Nginx就调用ngx_conf_set_flag_slot()回调函数对其项目值进行解析,并根据其是 on 还是 off 把 ngx_core_conf_t的daemon字段置为1或者0,这样就完成了从配置项目信息到Nginx内部实际值的转换过程。当然,这还有其他一些细节未说,下面再具体来看看。 ngx_command_s结构体的type字段指定该配置项的多种相关信息。 1.该配置的类型:NGX_CONF_FLAG 表示该配置项目有一个布尔类型的值,例如daemon就是一个布尔类型的配置项目,其值为on或者off;NGX_CONF_BLOCK表示该配置项目为复杂配置项,因此其有一个由大括号组织起来的多值块,比如配置项http、events等。 2.该配置项目的配置值的token 个数:NGX_CONF_NOARGS、NGX_CONF_TAKE1、NGX_CONF_TAKE2……NGX_CONF_TAKE7 ,分别表示该配置项的配置值没有token、一个、两个……七个token;NGX_CONF_TAKE12、NGX_CONF_TAKE123、NGX_CONF_1MORE等这些表示该配置项的配置值的token个数不定,分别为1个或2个、1个或2个或3个、1个以上。 3.该配置项目可处在的上下文:NGX_MAIN_CONF(配置文件最外层,不包含其内的类似于 http 这样的配置块内部,即不向内延伸,其他上下文都有这个特性)、NGX_EVENT_CONF(event 配置块)、NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF(http 配置块)、NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF(http的server指令配置块)、NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF(http的location指令配置块)、NGX_HTTP_SIF_CONF(http的在server配置块内的if指令配置块)、NGX_HTTP_LIF_CONF(http的在location配置块内的if指令配置块)、NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF(http的limit_except指令配置块)、NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF ( http 的 upstream 指令配置块)、NGX_MAIL_MAIN_CONF ( mail 配置块)、NGX_MAIL_SRV_CONF(mail的server指令配置块)、等等。 字段 conf 主要由 NGX_HTTP_MODULE 类型模块所使用,其指定当前配置项所在的大致位置,取值为 NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET、NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET、NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET三者之一、其他模块基本不用该字段,直接指定为0。 字段offset指定该配置项值的精确存放位置,一般指定为某一个结构体变量的字段偏移(利用offsetof宏)。对于复杂配置项目,例如server,它不用保存配置项值,或者说它本身无法保存,也可以说是因为它的值被分得更细小而被单个保存起来,此时字段offset指定为0即可。 字段post在大多数情况下都为NULL,但在某些特殊配置项中也会指定其值,而且多为回调函数指针,例如auth_basic、connection_pool_size、request_pool_size、optimize_host_names、client_body_in_file_only等配置项。 每个模块都把自己所需要的配置项目的对应ngx_command_s结构体变量组成一个数组,并以ngx_xxx_xxx_commands的形式命名,该数组以元素ngx_null_command作为结束哨兵。 下面开始对Nginx配置信息的整个解析流程进行描述。假设我们以命令 nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 启动Nginx,而配置文件nginx.conf也比较简单,如下所示。 00: 代码片段5.3-1,文件名: nginx.conf 01: worker_processes 2; 02: error_log logs/error.log debug; 03: events { 04: use epoll; 05: worker_connections 1024; 06: } 07: http { 08: include mime.types; 09: default_type application/octet-stream; 10: server { 11: listen 8888; 12: server_name localhost; 13: location / { 14: root html; 15: index index.html index.htm; 16: } 17: error_page 404 /404.html; 18: error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 19: location = /50x.html { 20: root html; 21: } 22: } 23: } 00: 代码片段5.3-2,文件名: mime.types 01: types { 02: text/html html htm shtml; 03: text/css css; 04: text/xml xml; 05: image/gif gif; 06: image/jpeg jpeg jpg; 07: application/x-javascript js; 08: … 09: } 首先,抹掉一些前枝末节,我们直接跟着 Nginx 的启动流程进入到与配置信息相关的函数调用处。 main() -> ngx_init_cycle() -> ngx_conf_parse(): 267: 代码片段5.3-3,文件名: ngx_cycle.c 268: if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 269: environ = senv; 270: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf); 271: return NULL; 272: } 此处调用ngx_conf_parse()函数传入了两个参数,第一个参数为ngx_conf_s变量,关于这个变量我们在他处再讲,而第二个参数就是保存的配置文件路径的字符串/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。ngx_conf_parse()函数是执行配置文件解析的关键函数,其原型声明如下。 char *ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename); 它是一个间接递归函数,也就是说虽然我们在该函数体内看不到直接的对其本身的调用,但是它执行的一些其他函数(比如ngx_conf_handler())内又会调用到ngx_conf_parse()函数,从而形成递归。这一般在处理复杂配置项和一些特殊配置指令时发生,比如指令 include、events、http、server、location等。 ngx_conf_parse()函数体代码量不算太多,但是它照样也将配置内容的解析过程分得很清楚,总体来看分成以下三个步骤。 1.判断当前解析状态。 2.读取配置标记token。 3.当读取了合适数量的标记 token 后对其进行实际的处理,也就是将配置值转换为Nginx内对应控制变量的值。 当进入到ngx_conf_parse()函数时,首先做的第一步是判断当前解析过程处在一个什么样的状态,这有三种可能。 1.正要开始解析一个配置文件:此时的参数filename指向一个配置文件路径字符串,需要函数ngx_conf_parse()打开该文件并获取相关的文件信息(比如文件描述符等)以便下面代码读取文件内容并进行解析。除了在上面介绍的Nginx启动时开始配置文件解析属于这种情况以外,还有当遇到include指令时也将以这种状态调用ngx_conf_parse()函数,因为include指令表示一个新的配置文件要开始解析。状态标记为type=parse_file;。 2.正要开始解析一个复杂配置项值:此时配置文件已经打开并且也已经对文件进行了部分解析,当遇到复杂配置项比如events、http等时,这些复杂配置项的处理函数又会递归调用 ngx_conf_parse()函数,此时解析的内容还是来自当前的配置文件,因此无需再次打开它,状态标记为type= parse_block;。 3.正要开始解析命令行参数配置项值,在对用户通过命令行-g参数输入的配置信息进行解析时处于这种状态,如nginx-g'daemonon;',Nginx在调用ngx_conf_parse()函数对命令行参数配置信息'daemonon;'进行解析时就是这种状态,状态标记为type=parse_param;。 在判断好当前解析状态之后就开始读取配置文件内容,前面已经提到配置文件都是由一个个token组成的,因此接下来就是循环从配置文件里读取token,而ngx_conf_read_token()函数就是用来做这个事情的。 rc = ngx_conf_read_token(cf); 函数ngx_conf_read_token()对配置文件进行逐个字符扫描并解析出单个的token。当然,该函数并不会频繁的去读取配置文件,它每次将从文件内读取足够多的内容以填满一个大小为 NGX_CONF_BUFFER(4096)的缓存区(除了最后一次,即配置文件剩余内容本来就不够了),这个缓存区在函数ngx_conf_parse()内申请并保存引用到变量cf->conf_file->buffer内,函数ngx_conf_read_token()反复使用该缓存区,该缓存区可能有如下一些状态。 初始状态,即函数ngx_conf_parse()内申请缓存区后的初始状态,如图5-3所示。 处理过程中的中间状态,有一部分配置内容已经被解析为一个个 token 并保存起来,而有一部分内容正要被组合成token,还有一部分内容等待处理,如图5-4所示 已解析字符和已扫描字符都属于已处理字符,但它们又是不同的:已解析字符表示这些字符已经被作为token额外保存起来了,所以这些字符已经完全没用了;而已扫描字符表示这些字符还未组成一个完整的token,所以它们还不能被丢弃。 当缓存区里的字符都处理完时,需要继续从打开的配置文件中读取新的内容到缓存区,此时的临界状态为,如图5-5所示。 前面图示说过,已解析字符已经没用了,因此我们可以将已扫描但还未组成token的字符移动到缓存区的前面,然后从配置文件内读取内容填满缓存区剩余的空间,情况如图5-6所示。 如果最后一次读取配置文件内容不够,那么情况如图5-7所示。 函数ngx_conf_read_token()在读取了合适数量的标记token之后就开始下一步骤,即对这些标记进行实际的处理,那多少才算是读取了合适数量的标记呢?区别对待,对于简单配置项,读取其全部的标记,也就是遇到配置项结束标记分号;为止,此时一条简单配置项的所有标记都已经被读取并存放在cf->args数组内,因此可以开始下一步骤,即执行回调函数进行实际的解析处理;对于复杂配置项则是读完其配置块前的所有标记,即遇到大括号{为止,此时复杂配置项处理函数所需要的标记都已读取到,而对于配置块{}内的标记将在接下来的函数ngx_conf_parse()递归调用中继续处理,这可能是一个反复的过程。当然,ngx_conf_read_token()函数也可能在其他情况下提前返回,比如配置文件格式出错、文件处理完(遇到文件结束)、块配置处理完(遇到大括号}),这几种返回情况的处理都很简单,不再赘述。 ngx_conf_read_token()函数如何识别并将token缓存在cf->args数组中的逻辑还是比较简单的。首先是对配置文件临时缓存区内容的调整(如有必要),这对应前面几个图示的缓存区状态。接着通过缓存区从前往后的扫描整个配置文件的内容,对每一个字符与前面已扫描字符的组合进行有效性检查并进行一些状态旗标切换,比如d_quoted旗标置1则表示当前处于双引号字符串后,last_space 旗标置 1 则表示前一个字符为空白字符(包括空格、回车、tab等)……这些旗标能大大方便接下来的字符有效性组合检查,比如前面的 nginx.conf 配置文件的第5行末尾多加了个分号(即有2个分号),那么启动Nginx将报错。 nginx: [emerg] unexpected ";" in /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:5 再接下来就是判断当前已扫描字符是否能够组成一个 token 标记,两个双引号、两个单引号、两个空白字符之间的字符就能够组成一个token标记,此时在cf->args数组内申请对应的存储空间并进行token标记字符串拷贝,从而完成一个token标记的解析与读取工作。此时根据情况要么继续进行下一个token标记的解析与读取,要么返回到ngx_conf_parse()函数内进行实际的处理。 表5-1列出了ngx_conf_parse()函数在解析nginx.conf配置文件时每次调用ngx_conf_read_token()函数后的cf->args里存储的内容是什么(这通过gdb调试Nginx时在ngx_conf_file.c:185处加断点就很容易看到这些信息),这会大大帮助对后续内容的理解。 ngx_conf_read_token()函数的返回值决定了ngx_conf_parse()函数接下来的进一步处理,参见表5-2。 讨论情况3,我们知道此时解析转换所需要token都已经保存到cf->args内,那么接下来就是要将这些token转换为Nginx内控制变量的值,执行此逻辑的主要是ngx_conf_handler()函数,不过在此之前会首先判断cf->handler回调函数是否存在,该回调函数存在的目的是针对类似于“text/html html htm shtml;”和“text/css css;”这样的types 配置项或geo 模块里“192.168.0.0/16 local”这样的不定配置项。这些配置项的主要特点是众多且变化不定(一般可被用户自由配置),但格式又基本统一,往往以key/values的形式存在,更重要的是对于这些配置项, Nginx的处理也很简单,只是拷贝到对应的变量内,所以这时一般会提供一个统一的cf->handler回调函数来做这个工作。比如types指令的处理函数ngx_http_core_types()就将cf->handler赋值为ngx_http_core_type(),从而使得mime.types的转换与设置全部由该函数统一处理。 配置转换核心函数ngx_conf_handler()的调用被传入了两个参数,ngx_conf_t类型的cf包含有不少重要的信息,比如转换所需要token就保存在cf->args内,而第二个参数无需多说,记录的是最近一次token解析函数ngx_conf_read_token()的返回值。 前面说过Nginx的每一个配置指令都对应一个ngx_command_s数据类型变量,记录着该配置指令的解析回调函数、转换值存储位置等,而每一个模块又都把自身所相关的所有指令以数组的形式组织起来,所以函数 ngx_conf_handler()首先做的就是查找当前指令所对应的ngx_command_s变量,这通过循环遍历各个模块的指令数组即可。由于Nginx的所有模块也是以数组的形式组织起来的,所有在 ngx_conf_handler()函数体内我们可以看到有两个 for 循环的遍历查找。 279: 代码片段5.3-4,文件名: ngx_conf_file.c 280: static ngx_int_t 281: ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last) 282: { 283: … 293: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) { 294: … 303: cmd = ngx_modules[i]->commands; 304: … 308: for ( /* void */ ; cmd->name.len; cmd++) { 两个for循环的结束判断之所以可以这样写,是因为这些数组都带有对应的末尾哨兵。具体代码里面还有一些有效性判断(比如当前模块类型、指令名称、项目值个数、指令位置)等操作,虽然繁琐但并没有难点所以忽略不讲,直接看里面的函数调用。 393: 代码片段5.3-5,文件名: ngx_conf_file.c 394: rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf); 当代码执行到这里,则Nginx已经查找到配置指令所对应的ngx_command_s变量cmd,所以这里就开始调用回调函数进行处理,以配置项目“worker_processes 2;”为例,对应的ngx_command_s变量为 69: 代码片段5.3-6,文件名: nginx.c 70: { ngx_string("worker_processes"), 71: NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_DIRECT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1, 72: ngx_conf_set_num_slot, 73: 0, 74: offsetof(ngx_core_conf_t, worker_processes), 75: NULL }, 那么其回调函数为ngx_conf_set_num_slot()。这是一个比较公共的配置项处理函数,也就是那种数字的配置项目都可以使用该函数进行转换。该函数的内部逻辑非常简单,首先找到转换后值的存储位置,然后利用ngx_atoi()函数把字符串的数字转换为整型的数字,存储到对应位置。这就完成了从配置文件里的“worker_processes 2;”到Nginx 里 ngx_core_conf_t 结构体类型变量conf的worker_processes字段控制值的转换。 worker_processes指令的回调处理函数比较简单,对于复杂配置项,比如server指令的回调处理函数ngx_http_core_server()就要复杂得多,比如它会申请内存空间(以便存储其包含的简单配置项的控制值)、会再次调用ngx_conf_parse()等,这些留在后续需要的时候再做详解。 对于Nginx配置文件的解析流程基本就是如此,上面的介绍忽略了很多细节,前面也说过,事实上,对于每个具体配置信息解析的代码(即各种各样的回调函数cmd->set的具体实现)占去了Nginx大量的源代码,而我们这里却没有做过多的分析,仅例举了worker_processes配置指令的简单解析过程。虽然对于不同的配置项,解析代码会根据自身应用不同而不同,但基本框架大致就是这样了。最后,看一个Nginx配置文件解析的流程图,如图5-8所示。 这里讲的配置信息已不再是配置文件里的内容(比如daemonoff;),而是指在Nginx 的执行环境里作为特定变量值的存在(比如 ngx_flag_t daemon;)。虽然前面已经描述了从各个配置项到特定变量值的转换过程,但并没有详细阐明这些控制变量的整体组织结构,下面就尝试描述这部分内容。 Nginx内部对配置信息的组织首先是根据上下级别来区分的,也就是所谓的配置上下文。以http服务为例,最外层是main上下文、http指令的block块内为http上下文、接着是server上下文、location 上下文,之所以说是按上下级别来区分是因为 main、http、server、location之间存在严格的包含与被包含关系,比如http包含server、server包含location,这个无需赘述。配置信息的组织还是按模块来划分的,这体现在每一平行级别上,也就是说对于所有main上下文里的配置,是根据模块来划分组织的,这是自然而然的事情,因为 Nginx 代码本身也进行了模块化划分,而用户传递进来的配置信息说到底要被这些模块代码使用,为了让模块更方便地找到与自己相关的配置信息,那么直接根据模块来组织配置信息是合理的。会不会出现多个模块共用一个配置值的情况呢?按理不会,如果出现这种情况就说明模块的划分不恰当导致模块之间耦合性太强。看具体实现,首先是 187: 代码片段5.4-1,文件名: ngx_cycle.c 188: cycle->conf_ctx = ngx_pcalloc(pool, ngx_max_module * sizeof(void *)); 189: … 215: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) { 216: if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) { 217: continue; 218: } 219: 220: module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx; 221: 222: if (module->create_conf) { 223: rv = module->create_conf(cycle); 224: if (rv == NULL) { 225: ngx_destroy_pool(pool); 226: return NULL; 227: } 228: cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index] = rv; 229: } 230: } 231: … 251: conf.ctx = cycle->conf_ctx; 252: … 262: if (ngx_conf_param(&conf) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 263: ... 268: if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 269: ... 代码第188 行用于申请存储模块配置信息的内存空间,可以看到这是一个指针数组,数组元素的个数为ngx_max_module,刚好一个指针元素可以对应一个模块,后续这些指针就指向其对应模块配置信息的具体存储位置。 代码第215行的for循环主要是为了调用核心模块的create_conf()函数,创建实际的配置信息存储空间。为什么先只处理核心模块呢?因为核心模块才是基本模块,它们的配置空间必须首先创建,以便作为其他非核心模块的支撑。对于 for 循环内两个 if 判断的理解,是因为不是所有的模块都是核心模块,也不是所有的核心模块都有create_conf()函数,比如虽然模块ngx_http_module和模块ngx_mail_module都是核心模块,但它们却并没有create_conf()函数,因为这两个模块是否真正使用依赖于具体的配置文件。如果配置文件里并没有配置http,但Nginx代码却先在这里把http的配置信息存储空间申请出来而后面又完全不用,那岂不是多此一举?所以,这两个核心模块的配置信息存储空间会在配置文件的解析过程中根据需要申请。第223行的存储空间若创建成功,那么第228行就把它赋值给对应的指针元素,完成前面所说的那样,即指针指向其对应模块配置信息的具体存储位置。 以核心模块 ngx_core_module 为例,从名字就可以看出这是一个特别基础且重要的核心模块,模块序号index为0,而create_conf回调指针指向函数ngx_core_module_create_conf()。 924: 代码片段5.4-2,文件名: nginx.c 925: static void * 926: ngx_core_module_create_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) 927: { 928: ngx_core_conf_t *ccf; 929: 930: ccf = ngx_pcalloc(cycle->pool, sizeof(ngx_core_conf_t)); 931: … 945: ccf->daemon = NGX_CONF_UNSET; 946: ccf->master = NGX_CONF_UNSET; 947: … 970: return ccf; 971: } 这个函数主要做了一件事情,申请内存空间、初始内存空间并返回内存空间的指针引用。注意类似于NGX_CONF_UNSET这样的初始赋值,这很重要,根据名称就能猜出这些值可用来判断用户是否有在配置文件里对这些配置项做过设置,因为这些值都是特殊值-1(用户的合法设置不会有-1的情况),所以如果用户没做设置,那么在配置文件解析完后,对应的字段值仍然为-1,如果此时在其他配置设定下,正常运行 Nginx 需要这些字段,那么就需给这些字段设置对应的默认值。设置默认值的处理在模块的回调函数init_conf()内,在配置文件解析完(有的只是对应的配置块解析完,比如http、events配置块,前面提到的create_conf()函数也是如此,比如 http 配置块的 create_main_conf()、init_main_conf()等,但默认值的设定肯定是在对应的依赖配置内容已经全部解析完后才进行的)后就会调用该函数。 278: 代码片段5.4-3,文件名: ngx_cycle.c 279: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) { 280: … 286: if (module->init_conf) { 287: if (module->init_conf(cycle, cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules [i]->index]) 288: == NGX_CONF_ERROR) 289: … 看看核心模块 ngx_core_module的默认值设置 ngx_core_module_init_conf()函数。 973: 代码片段5.4-4,文件名: nginx.c 974: static char * 975: ngx_core_module_init_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf) 976: { 977: ngx_core_conf_t *ccf = conf; 978: 979: ngx_conf_init_value(ccf->daemon, 1); 980: ngx_conf_init_value(ccf->master, 1); 981: … 229: 代码片段5.4-5,文件名: ngx_conf_file.h 230: #define ngx_conf_init_value(conf, default) \ 231: if (conf == NGX_CONF_UNSET) { \ 232: conf = default; \ 233: } 前后一连贯,这部分逻辑就应该很容易懂了,比如如果用户没有对daemon做设置,那么它的值就还是NGX_CONF_UNSET,进而就需把它设置为default默认值,也就是1。其他字段的默认值处理也与此类似。 回过头来接着看,前面提到的两段相关源码执行完之后,我们目前所了解的配置信息最基本的组织结构将如图5-9所示。 可以看到只有两个核心模块ngx_core_module和ngx_regex_module有对应的create_conf回调函数,申请的配置存储空间“挂载”在对应的数组元素下。当然,这只是我这里的Nginx模块情况(请参考附录 A),也许你那因为 configure 编译设置不同而有所不同,不过可以肯定基本结构都是这样。 再来看代码片段5.4-1的第251行和第268行(第262行是对通过Nginx命令行传过来的配置信息的处理,和第268 行将执行的逻辑一样,而且应该更简单一点,所以略过),因为cycle->conf_ctx 是唯一能正确找到配置存储空间的指针,不能把它弄乱,所以把它赋值给conf.ctx 供后续使用,conf.ctx 也就是类似于一个临时变量,不管后续代码怎样修改它(这个值会随着配置文件的解析、配置上下文的切换而变化),我们的 cycle->conf_ctx 不变,如第268行所看到的那样,ngx_conf_parse()的第一个参数就是conf的引用,该函数再通过函数调用,把conf又传递到函数ngx_conf_handler()内。 101: 代码片段5.4-6,文件名: ngx_conf_file.c 102: char * 103: ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename) 104: { 105: … 244: rc = ngx_conf_handler(cf, rc); 277: } 278: 279: 280: static ngx_int_t 281: ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last) 282: { 283: … 376: /* set up the directive's configuration context */ 377: 378: conf = NULL; 379: 380: if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) { 381: conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[ngx_modules[i]->index]; 382: 383: } else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) { 384: conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[ngx_modules[i]->index]); 385: 386: } else if (cf->ctx) { 387: confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf); 388: 389: if (confp) { 390: conf = confp[ngx_modules[i]->ctx_index]; 391: } 392: } 393: 394: rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf); 395: … 431: } 第378~392行的代码是我们关注的重点。看第380行的if判断,什么样的配置项类型是NGX_DIRECT_CONF的?搜索一下Nginx的所有源代码,发现只有核心模块的配置项才可能是这个类型,比如ngx_core_module模块的daemon和master_process等,ngx_openssl_module模块的ssl_engine、ngx_regex_module模块的pcre_jit。 从前面分析,我们知道这些核心模块的配置存储空间已经申请了,所有其配置项的转换后值也就已有存储的地方。看第381行给conf赋值语句,以ngx_core_module模块为例,那么conf指针的当前指向如图5-10所示。 41: 代码片段5.4-7,文件名: nginx.c 42: { ngx_string("master_process"), 43: NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_DIRECT_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG, 44: ngx_conf_set_flag_slot, 45: 0, 46: offsetof(ngx_core_conf_t, master), 47: NULL }, 1041:代码片段5.4-8,文件名: ngx_conf_file.c 1042:char * 1043:ngx_conf_set_flag_slot(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 1044:{ 1045: char *p = conf; 1046:… 1048: ngx_flag_t *fp; 1049:… 1051: fp = (ngx_flag_t *) (p + cmd->offset); 1052:… 1059: if (ngx_strcasecmp(value[1].data, (u_char *) "on") == 0) { 1060: *fp = 1; 1061: 1062: } else if (ngx_strcasecmp(value[1].data, (u_char *) "off") == 0) { 1063: *fp = 0; 1064:… 上面两段代码显示了配置项master_process的转换与存储过程,第1045与1051行结合起来找到master_process转换后值的存储位置,而1059到1063完成转换(on为1,off为0)与存储。 接着看代码片段5.4-6的第383行,有哪些配置项被打了NGX_MAIN_CONF标签而又不是 NGX_DIRECT_CONF 的?http、mail、events、error_log 等,其中前面三个的处理比较类似,以http配置项的处理为例,我们知道ngx_http_module虽然是核心模块,但是其配置存储空间还没有实际申请,所以看第384行给conf进行赋值的语句右值是数组元素的地址,由于ngx_http_module模块对应7号数组元素,所以conf指针的当前指向如图5-11所示。 83: 代码片段5.4-8,文件名: ngx_http.c 84: { ngx_string("http"), 85: NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS, 86: ngx_http_block, 87: 0, 88: 0, 89: NULL }, 90: … 118: static char * 119: ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 120: { 121: … 125: ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx; 126: … 132: ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t)); 133: … 137: *(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t **) conf = ctx; 138: 代码第132行申请了内存空间,而第137行通过conf参数间接地把这块内存空间“挂载”在 7 号数组元素下。对于多级指针,大多数人都容易搞混乱,如果没有理解,请仔细思考一下上面的指针操作。经过ngx_http_block()函数的处理,我们能看到的配置信息最基本的组织结构如图5-12所示。 对于ngx_http_module模块的内部配置,除了main_conf配置外,为什么还有srv_conf、loc_conf是因为这两个字段里存储的配置信息是针对server、location应用的http全局配置。这些配置信息在结构上的组织和 cycle->conf_ctx 类似,仍然是根据模块来划分,当然只是NGX_HTTP_MODULE类型的模块,如图5-13所示。 NGX_HTTP_MODULE类型模块具有哪种范围域的配置信息就将申请的内存空间“挂载”在对应的数组元素下。虽然大多数模块都只有一种,比如ngx_http_auth_basic_module模块只有loc_conf配置项,但ngx_http_charset_filter_module模块却有main_conf和loc_conf两类配置项,如图5-13所示(在整个NGX_HTTP_MODULE类型模块中排序,ngx_http_auth_basic_module模块序号为6、ngx_http_charset_filter_module模块序号为31,图5-13只画出了两个示例模块的情况)。继续看ngx_http_block函数的处理。 117: 代码片段5.4-9,文件名: ngx_http.c 118: static char * 119: ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 120: { 121: … 218: pcf = *cf; 219: cf->ctx = ctx; 220: … 235: /* parse inside the http{} block */ 236: 237: cf->module_type = NGX_HTTP_MODULE; 238: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF; 239: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); 240: … 325: *cf = pcf; 326: … 代码片段5.4-9第218行把cf值(注意指针取值符号*,所以这里是进行的结构体赋值操作)保存起来,而第325行进行恢复,前面曾说过在配置文件解析的过程中,cf->ctx会随着上下文的切换而改变,第219行就可以看到这点。第239行调入到ngx_conf_parse()后,当前配置上下文环境就从main切换到http,如果在接下来的解析过程中遇到server指令,其指令处理函数ngx_http_core_server(),类似于http指令的处理,对于server上下文这一同级别的所有配置同样也是按照模块划分来组织的,如图5-14所示。 在server上下文里不再有http全局配置,所以其main_conf字段直接指向http上下文的main_conf即可。另外,在http上下文里,可以有多个server配置指令,所以需通过数组来进行管理。 2700:代码片段5.4-10,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 2701:static char * 2702:ngx_http_core_server(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *dummy) 2703:{ 2704:… 2780: /* parse inside server{} */ 2781: 2782: pcf = *cf; 2783: cf->ctx = ctx; 2784: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF; 2785: 2786: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); 2787: 2788: *cf = pcf; 2789:… 第2786行调入到ngx_conf_parse()后,当前配置上下文环境就从http切换到server,如果在接下来的解析过程中遇到location指令,其指令处理函数ngx_http_core_location(),类似于http指令、server指令的处理,对于location上下文这一同级别的所有配置同样也是按照模块划分来组织,如图5-15所示。 在 server 上下文里,可以有多个 location 配置指令,通过队列来对它们进行统一管理。location的处理函数ngx_http_core_location()依旧是进行上下文的切换(第3007和3008行),然后调用ngx_conf_parse()函数继续处理。 2824:代码片段5.4-11,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 2825:static char * 2826:ngx_http_core_location(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *dummy) 2827:{ 2828:… 3007: save = *cf; 3008: cf->ctx = ctx; 3009: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF; 3010: 3011: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); 3012: 3013: *cf = save; 3014:… 由于location可以出现在location以内,所以对于location上下文而言,本身就可以一直向下延伸,图5-16 显示的是LocationA配置块内又有Location B 的情况(注意:队列形式管理的多个location仅限于当前上下文里的,对于location里的location,不在当前管理范围内)。 当然,location 可以无限嵌套使用只是一种理论情况,而在实际使用中,很少会有人让location指令嵌套三层以上。但总得来说,不管是http上下文还是server上下文、location上下文,调入到ngx_conf_parse()函数内后,cf->ctx指向的都是一个ngx_http_conf_ctx_t结构体,如果此时从 ngx_conf_parse()函数再调入到 ngx_conf_handler()函数,情况是怎么样呢?回过头来看代码片段5.4-6的第386行,这是第三种情况,在前面两个if都不匹配的情况下再来进行这个判断,通过查看http模块配置项的type字段发现这些配置项的ngx_conf_handler()函数处理都会进入到这个判断里,看下面这个实例。 138: 代码片段5.4-12,文件名: ngx_http_charset_filter_module.c 139: { ngx_string("charset"), 140: NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF|NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF 141: |NGX_HTTP_LIF_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1, 142: ngx_http_set_charset_slot, 143: NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET, 144: offsetof(ngx_http_charset_loc_conf_t, charset), 145: NULL }, 配置项charset的type既不包含NGX_DIRECT_CONF旗标又不包含NGX_MAIN_CONF旗标,所以进入到第386行的判断里。 385: 代码片段5.4-13,文件名: ngx_conf_file.c 386: } else if (cf->ctx) { 387: confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf); 388: 389: if (confp) { 390: conf = confp[ngx_modules[i]->ctx_index]; 391: } 392: } 从配置项charset的type字段里看出它可以在多个上下文里使用,但如前所述,不管当前是在哪个上下文里,cf->ctx指向的都是一个ngx_http_conf_ctx_t结构体,配置项charset的conf字段为NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,也就是 51: 代码片段5.4-14,文件名: ngx_http_config.h 52: #define NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET offsetof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t, loc_conf) 即取ngx_http_conf_ctx_t结构体的字段loc_conf偏移量,那么第387行代码也就是获取指针字段loc_conf所指向的数组,再由第390行根据模块序号获取对应的数组元素,这就和本节最开始讲述的情况统一起来了。 在上一小节中,我们已经看到Nginx配置信息的层次组织结构,也就是main、http、server以及location,而对于location还可以继续包含location,对于用户在某个层次没有设置的配置选项,那么它的值应该来自上一层,也就是所谓的配置信息的继承。当然,如果其上一层没有该配置选项,那么就使用默认值。比如listen指令就只能用在server上下文,所以如果某个server没有配置listen选项,那么将使用它的默认值,因为其无法从http或main上下文里继承过来。 再举一个继承的示例,比如配置指令direct_test可以应用在任何上下文里,因此如果用户在某个location里没有设置direct_test,那么该location上下文里direct_test的值就将继承之它的上一层,也就是server上下文(假定该location是直接处在server配置块内)。如果server配置块里也没有设置direct_test,那么server上下里direct_test的值就继续继承之它的上一层,即http上下文。如果http配置块里也没有设置direct_test,那么Nginx就会直接把main上下文里的配置值(如果存在)作为默认值或给它的direct_test设置一个默认值。反正不管怎样, direct_test的值都将逐步继承下去,直到某一个层次自己设置了该选项,这时就用它自己设置的值。当然,这是最理想的情况,Nginx 在实际实现时会有细节上的差别,但思想大致与此类似。 实现配置信息继承功能的入口代码在函数ngx_http_block()里,在整个http配置块解析完后即开始做配置从上往下的继承处理。 252: 代码片段5.5-1,文件名: ngx_http.c 253: for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { 254: if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { 255: continue; 256: … 263: if (module->init_main_conf) { 264: rv = module->init_main_conf(cf, ctx->main_conf[mi]); 265: … 270: rv = ngx_http_merge_servers(cf, cmcf, module, mi); 271: … 274: } 每个模块对自己拥有的配置项负责,所以上面的处理也是循环处理每个http模块,调用(如果存在,有的模块可能没有配置项或配置项不能用于 http 上下文)它们的回调函数init_main_conf(),比如http核心模块ngx_http_core_module的ngx_http_core_init_main_conf()回调函数。这处理的是http上下文里的配置项,而且它们所做的主要工作是初始化,比如分配内存或给用户没有主动设置的配置项赋初始值等。Nginx 对客户端请求的处理,主要是依赖server和location上下文,所以实际做继承处理的主要是这两个。如果它们从http上下文里没有继承到对应的配置值,则直接从main上下里继承,而不再经过http上下文进行一次过渡。在后面的配置指令error_log实例里可以看到这点的具体情况。 那么,实际做继承处理的代码在代码片段5.5-1的第270行,即函数ngx_http_merge_servers()的调用。该函数循环处理http下的所有sever,而对每一个server,除了做server层次的配置项继承处理外(即从上一层次 http 继承配置值到当前层次 server 内),还会通过调用函数ngx_http_merge_locations()循环处理其下的每一个location(即从上一层次server继承配置值到当前层次location内),而在处理完每一个location后又递归调用函数ngx_http_merge_locations()继续处理当前 location 下的每一个 location(即从上一层次 location 继承配置值到当前层次location内)。整个这个处理过程虽然繁琐(每个Nginx模块都非常清楚地知道自己会使用哪些配置项,但每个配置项是否能够从上一层继承或会有什么样的默认值等情况都各不相同,因此在关注某个特定的配置项时需查看具体的代码才能确保万无一失)。这逻辑清晰简单并没有什么特别难以理解之处,如图5-17所示。 先对http上下文做初始化,然后server继承http、location继承server、location继承location处理下去。在继承的过程中,如果上一级没有,该配置项可以出现在最顶层的main上下文(注意:如果上一层没有对应的配置值,那么上上一层也不会有,因为我们的继承处理是从上往下进行的,具体点说是从server层往下推进),那么会直接把main上下文里的值赋值过来,即前面描述过的不再经过http上下文进行过渡,但同样也是统一继承。 具体相关代码就不加以分析了,看几个实例。首先是配置指令 error_log,它可以使用于任何上下文环境,在进行配置的继承处理过程中,由函数ngx_http_core_merge_loc_conf()处理该指令的继承过程,其中有这么一段相关代码,如下所示。 3553:代码片段5.5-2,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 3554: if (conf->error_log == NULL) { 3555: if (prev->error_log) { 3556: conf->error_log = prev->error_log; 3557: } else { 3558: conf->error_log = &cf->cycle->new_log; 3559: } 3560: } 如果当前层次的error_log配置值为空(第3554行为真),那么需要做继承处理;如果上一层次存在error_log配置值(第3555行为真),那么就将它的值继承下来(第3556行);否则,直接使用最顶层(即main上下文)的配置值。 如果在main上下文配置了error_log指令,那么将在对应的回调处理ngx_error_log()函数(该函数属于ngx_errlog_module模块)里设置配置值cf->cycle->new_log;如果在main上下文里也没有配置error_log指令,那么此时将使用默认值。 38: 代码片段5.5-3,文件名: ngx_cycle.c 39: static ngx_str_t error_log = ngx_string(NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH); 40: … 342: if (cycle->new_log.file == NULL) { 343: cycle->new_log.file = ngx_conf_open_file(cycle, &error_log); 344: if (cycle->new_log.file == NULL) { 345: goto failed; 346: } 347: } 另一个示例是root 指令,它可以用在http、server、location(包括if in location)上下文里,它的继承和默认值采用都实现在函数ngx_http_core_merge_loc_conf()内。 3459:代码片段5.5-4,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 3460: if (conf->root.data == NULL) { 3461: 3462: conf->alias = prev->alias; 3463: conf->root = prev->root; 3464: conf->root_lengths = prev->root_lengths; 3465: conf->root_values = prev->root_values; 3466: 3467: if (prev->root.data == NULL) { 3468: ngx_str_set(&conf->root, "html"); 上面代码简单明了,第3463行表示继承使用上一层的配置值,第3467和3468行表示使用默认值,即root为指定配置路径(宏NGX_PREFIX)下的"html"文件夹。 通过这样的配置信息继承设计,对 Nginx 的配置就变得非常方便。比如,如果想把所有server的error_log信息都输出到一块,那么只需在main或http里设置一次即可或不设置而使用统一默认值,如果更进一步,想把某一个server的error_log信息单独出来,那么只需在该server里设置error_log配置值即可。 注 释 [1].http://wiki.nginx.org/DirectiveIndex。 [2].http://www.hwaci.com/sw/lemon/。 [3].这仅仅只是我个人的归纳,并没有任何官方说明,而且把它们简单的归纳为key-value模型可能显得比较粗糙与生硬,如果大家有更好的模型来描述Nginx配置文件的静态格式,欢迎发邮件给我。 配置指令是提供给用户自定义Nginx具体行为的外部接口,也是一种十分便利且通用有效的方案,几乎所有比较灵活的程序或系统都会给用户提供相应的可配置选项,以便用户能根据自己的需求做出最佳的设定。Nginx提供的配置指令非常多,在官网[1]能找到大部分配置指令的功能描述与使用方法,但限于文档更新与源码并不是完全实时同步,对一些配置指令的描述并不那么全面,所以只有通过查看源代码才能了解这些配置指令,而本章介绍的是Nginx配置指令解析的全过程,通过对这个过程的完全理解,读者就能自行查阅每个Nginx配置选项的具体功能与内部实现细节,从而真正做到把Nginx源代码本身变成一本配置使用手册。 对于客户端 http 请求的处理,为了获得更强的控制能力,Nginx 将整个过程细分为多个阶段,每一个阶段可以有零个或多个回调函数进行专门处理,当我们在编写自己的 Handlers类型模块时,必须把模块功能处理函数挂载在正确的阶段点上,如前面所述的模块ngx_http_static_module 就将自己的模块功能处理函数 ngx_http_static_handler()挂载在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段。这在提供很大灵活性的同时,也极大地增加了编写自定义模块的困难,不过在详细了解每一个处理阶段之后,这种困难也许没有想象中那么大。 http请求的整个处理过程一共被分为11个阶段,每一个阶段对应的处理功能都比较单一,这样能尽量让Nginx模块代码更为内聚。这11个阶段是Nginx处理客户端请求的核心所在,在实际的处理过程中,因等待事件或内部跳转或子请求等会导致这些阶段被反复执行,但在任意时刻,对某个指定的客户端请求而言,对应的request对象总是处于某个确切的阶段,在后文中,将request对象在各个阶段之间的切换统一描述称之为“请求处理状态机”的转动,参见表6-2。 对于表6-2 中给出的每一个阶段,大部分都能根据名称来猜测其在整个处理过程中所占的位置(或地位)以及所要起的作用,但有的阶段却不是那么容易理解,由于Handler模块是实现Nginx功能的主要逻辑,下面就逐一详细介绍。 NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE阶段,这很容易理解,当Nginx成功接收到一个客户端请求后(即函数 accept()正确返回对应的套接口描述符,连接建立),针对该请求所做的第一个实际工作就是读取客户端发过来的请求头内容,如果在这个阶段挂上对应的回调函数,那么在Nginx读取并解析完客户端请求头内容后(阶段名称里的POST有在…之后的含义),就会执行这些回调函数。 NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE 阶段,和第3 阶段 NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE都属于地址重写,也都是针对rewrite模块而设定的阶段,前者用于server上下文里的地址重写,而后者用于location上下文里的地址重写。为什么要设置两个地址重写阶段,原因在于rewrite模块的相关指令(比如rewrite、if、set等)既可用于server上下文,又可用于location上下文。在客户端请求被Nginx接收后,首先做server查找与定位,在定位到server(如果没查找到就是默认server)后执行NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE阶段上的回调函数,然后再进入到下一个阶段:NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE 阶段。当然,NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE阶段在NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE阶段之后,所以具体的先后顺序如图6-1所示。 NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE阶段上不能挂载任何回调函数,因为它们永远也不会被执行,该阶段完成的是Nginx的特定任务,即进行Location定位。只有把当前请求的对应location找到了,才能从该location上下文中取出更多精确的用户配置值,做后续的进一步请求处理。 经过上一个阶段后, Nginx 已经正确定位到当前请求的对应 location ,于是进入到NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE阶段进行地址重写,这和第1阶段的地址重写没什么特别,而唯一差别在于,定义在location里的地址重写规则只对被定位到当前location的请求才生效,用编程语言的说法就是,它们各自的作用域不一样。 NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE阶段,根据名称,该阶段是指在进行地址重写之后,当然,根据前面的列表来看,具体是在location请求地址重写阶段之后。这个阶段不会执行任何回调函数,它本身也是为了完成 Nginx 的特定任务,即检查当前请求是否做了过多的内部跳转(比如地址重写、redirect等),我们不能让对一个请求的处理在Nginx内部跳转很多次甚至是死循环(包括在 server上下文或是在 location上下文所进行的跳转),毕竟跳转一次,基本所有流程就得重新走一遍,这是非常消耗性能的。如果跳转次数超过限定值NGX_HTTP_MAX_ URI_CHANGES(宏定义为10),那么就直接返回状态码500 给客户端,提示当前发生服务器内部错误。其实,如果出现这种情况,多半是因为 Nginx 配置文件写得有问题。 接下来的三个阶段:NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE、NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE、NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE,很好理解,做访问权限检查的前期、中期、后期工作,其中后期工作是固定的,判断前面访问权限检查的结果(状态码存放在字段 r->access_code内),如果当前请求没有访问权限,那么直接返回状态403错误,所以这个阶段也无法去挂载额外的回调函数。 NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE阶段是针对配置项try_files的特定处理阶段,后面章节会详细介绍;而NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE阶段,也无需多说,是专门针对日志模块所设定的处理阶段。 在一般条件下,我们的自定义模块回调函数都挂载在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段,毕竟大部分的业务需求都是修改 http 响应数据,Nginx 自身的产生响应内容的模块,像ngx_http_static_module、ngx_http_random_index_module、ngx_http_index_module、ngx_http_gzip_static_module、ngx_http_dav_module等也都挂载在这个阶段。 大多数情况下,功能模块会在其对应配置解析完后的回调函数,也就是ngx_http_module_t结构体的postconfiguration字段指向的函数内将当前模块的回调功能函数挂载到这11个阶段的其中一个上。看下面这个示例。 16: 代码片段6.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_static_module.c 17: ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_static_module_ctx = { 18: NULL, /* preconfiguration */ 19: ngx_http_static_init, /* postconfiguration */ 20: … 270: static ngx_int_t 271: ngx_http_static_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) 272: { 273: ngx_http_handler_pt *h; 274: ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf; 275: 276: cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); 277: 278: h=ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers); 279: if (h == NULL) { 280: return NGX_ERROR; 281: } 282: 283: *h = ngx_http_static_handler; 284: 285: return NGX_OK; 286: } 在模块 ngx_http_static_module 的 postconfiguration 回调函数 ngx_http_static_init()内,将ngx_http_static_module模块的核心功能函数ngx_http_static_handler()挂载在http请求处理流程中的NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段。这样,当一个客户端的http静态页面请求发送到Nginx服务器,Nginx就能够调用到我们这里注册的ngx_http_static_handler()函数,具体怎么做呢?接着看。 各个功能模块将其自身的功能函数挂载在cmcf->phases后,内部的情况如图6-2所示。 回调函数会根据选用模块的不同而不同,图6-2中显示的是在如附录A所示的模块选用下的情况。这些回调函数的调用是有条件的,调用后也要做一些根据返回值的结果处理,比如某次处理能否进入到阶段NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE的回调函数中处理,这需要一个事前判断,所以在函数 ngx_http_init_phase_handlers()里对所有这些回调函数进行一次重组,结果将如图6-3所示。 这里不过多描述 ngx_http_init_phase_handlers()函数如何对这些回调函数进行重组,因为对照图6-3并利用gdb跟踪一下也就清楚了,但从图6-3中可以看到,该函数只把有回调函数的处理阶段给提取了出来,同时利用 ngx_http_phase_handler_t 结构体数组对这些回调函数进行重组,不仅加上了进入回调函数的条件判断checker函数,而且通过next字段的使用,把原本的二维数组实现转化为可直接在一维函数数组内部跳动。一般来讲,二维数组的遍历需要两层循环,而遍历一维函数数组只需一层循环,所以加上 next 字段也并非无的放矢。 再来看对http请求进行分阶段处理核心函数ngx_http_core_run_phases。 863: 代码片段6.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 864: void 865: ngx_http_core_run_phases(ngx_http_request_t *r) 866: { 867: ngx_int_t rc; 868: ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph; 869: ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf; 870: 871: cmcf = ngx_http_get_module_main_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); 872: 873: ph = cmcf->phase_engine.handlers; 874: 875: while (ph[r->phase_handler].checker) { 876: 877: rc = ph[r->phase_handler].checker(r, &ph[r->phase_handler]); 878: 879: if (rc == NGX_OK) { 880: return; 881: } 882: } 883: } 注意 while 循环代码并结合前面的分析,可以看到这是一个超简单的遍历处理。r->phase_handler标志当前处理的序号,对一个客户端请求处理的最开始时刻,该值当然就是0了,while循环判断如果存在checker函数(末尾数组元素的checker函数为NULL),那么就调用该checker函数并有可能进而调用对应的回调函数,以NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE阶段的ngx_http_core_access_phase()函数为例。 1087:代码片段6.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 1088:ngx_int_t 1089:ngx_http_core_access_phase(ngx_http_request_t*r,ngx_http_phase_handler_t*ph) 1090:{ 1091:… 1094: if (r != r->main) { 1095: r->phase_handler = ph->next; 1096: return NGX_AGAIN; 1097: } 1098:… 1102: rc = ph->handler(r); 1103: 1104: if (rc == NGX_DECLINED) { 1105: r->phase_handler++; 1106: return NGX_AGAIN; 1107: } 1108: 1109: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN || rc == NGX_DONE) { 1110: return NGX_OK; 1111: } 1112: 1113:… 1142: /* rc == NGX_ERROR || rc == NGX_HTTP_... */ 1143: 1144: ngx_http_finalize_request(r, rc); 1145: return NGX_OK; 1146:} 代码片段6.1-3的第1094行是一个回调函数准入判断,如果当前不是主请求,那么当然无需进行访问权限检测,所以第1095 行代码让状态机直接进入到下一个处理阶段;第1102行进行回调处理,也就是执行功能模块的功能函数,如果第1104行判断成功则表示当前回调拒绝处理或者说是不符合它的处理条件,那么第1105行将处理移到下一回调函数(注意:处理阶段可能会发生迁移,比如当前回调函数已经是当前阶段的最后一个回调函数,那么调用下一个回调函数时就进入到下一个阶段);如果第1109 行判断成功则表示当前回调需要再次调用或已经成功处理,但此处与前两处返回不同,首先,并没有进行自增phase_handler变量,其次,这里返回NGX_OK导致ngx_http_core_run_phases()函数里的循环处理会退出,这表示状态机的继续处理需要等待更进一步的事件发生,这可以是子请求结束、socket 描述符变得可写、超时发生等,并且再进入到状态机处理函数时,仍将从当前回调开始;第1142行后表示发生错误(比如NGX_ERROR、NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN、NGX_HTTP_ UNAUTHORIZED等)后的处理流程。 可以看到,一个功能模块的handler函数可以返回多种类型的值,并且这些值有其固有的含义,参见表6-3。 值得说明的是,表6-3 只是一般情况下的含义,针对具体的阶段,我们最好仔细对照它的checker函数,看checker函数内对回调函数返回值的具体处理是怎样的。 由于回调函数的返回值会影响到同一阶段的后续回调函数的处理与否,而 Nginx 又采用先进后出的方案,即先注册的模块,其回调函数反而后执行,所以回调函数或者说模块的前后顺序非常重要。以 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段的三个回调函数为例,在附录 A显示的模块列表里可以看到三个相关模块的注册顺序是 ngx_http_static_module、ngx_http_autoindex_module、ngx_http_index_module,而从前面的图中看到回调函数顺序却是ngx_http_index_handler、ngx_http_autoindex_handler、ngx_http_static_handler。这个顺序是合理的。当我们打开Nginx服务器时,如果直接访问的是一个目录,那么Nginx先是查看当前目录下是否存在 index..html/index.htm/index.php 等这样的默认显示页面,这是回调函数 ngx_http_index_handler()的工作。如果不存在默认显示页面,那么就看是否允许生成如图6-4所示的列表页面。这又是属于ngx_http_autoindex_handler()函数的工作,而ngx_http_static_handler()回调函数则是根据客户端静态页面请求查找对应的页面文件并组成待响应内容。可以看到这三个回调函数虽然都挂载在 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段,但各自实现的功能本身存在先后关系,如果函数ngx_http_autoindex_handler()在ngx_http_index_handler()函数之前,那么对于本就存在默认显示页面的目录进行列表显示,就是非常明显的逻辑错误。 对于http请求处理handlers产生的响应内容,在输出到客户端之前需要做过滤处理,这些过滤处理对于完成功能的增强实现与性能的提升是非常有必要的。比如如果没有过滤模块ngx_http_chunked_filter_module,那么就无法支持完整的 HTTP 1.1 协议的 chunk 功能。如果没有 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module 过滤模块,那么就无法让客户端使用本地缓存来提高性能。诸如这些都需要过滤模块的支持。由于响应数据包括响应头和响应体,所以与此相对应,任一 Filter 模块必须提供处理响应头的 header 过滤功能函数(比如ngx_http_not_modified_ filter_module 模块提供的 ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter()函数)或处理响应体的 body 过滤功能函数(比如 ngx_http_copy_filter_module 模块提供的ngx_http_copy_filter()函数),或两者皆有(比如 ngx_http_chunked_filter_module 模块提供的ngx_http_chunked_header_filter()函数和ngx_http_chunked_body_filter()函数)。 所有的header过滤功能函数和body过滤功能函数会分别组成各自的两条过滤链,如图6-5所示(使用附录A所列模块)。 这两条过滤链是怎么形成的呢?在源文件 ngx_http.c 里,可以看到定义了这样的两个函数指针变量。 71: 代码片段6.2-1,文件名: ngx_http.c 72: ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_top_header_filter) (ngx_http_request_t *r); 73: ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_top_body_filter) (ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *ch); 这是整个Nginx范围内可见的全局变量。然后在每一个Filter模块内,我们还会看到类似于这样的定义(如果当前模块只有header过滤功能函数或只有body过滤功能函数,那么如下定义也就只有相应的那个变量)。 52: 代码片段6.2-2,文件名: ngx_http.c 53: static ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt ngx_http_next_header_filter; 54: static ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt ngx_http_next_body_filter; 注意到static修饰符,也就是说这两个变量是属于模块范围内可见的局部变量。有了这些函数指针变量,再在各个Filter模块的postconfiguration回调函数(该函数会在其对应配置解析完后被调用做一些设置工作,前面已经描述过)内,全局变量与局部变量的巧妙赋值使得最终行成了两条过滤链。以header过滤链为例,通过附录A的模块列表ngx_modules变量,可以看到ngx_http_header_filter_module是具有header过滤功能函数的序号最小的过滤模块,其postconfiguration回调函数如下。 616: 代码片段6.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_header_filter_module.c 617: static ngx_int_t 618: ngx_http_header_filter_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) 619: { 620: ngx_http_top_header_filter = ngx_http_header_filter; 621: 622: return NGX_OK; 623: } ngx_http_top_header_filter指向其header过滤功能函数ngx_http_header_filter,此时header过滤链表现如图6-6所示。 接着 Nginx 初始化再继续执行到下一序号的带有 header 过滤功能函数的过滤模块的postconfiguration回调函数。 231: 代码片段6.2-4,文件名: ngx_http_chunked_filter_module.c 232: static ngx_int_t 233: ngx_http_chunked_filter_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) 234: { 235: ngx_http_next_header_filter = ngx_http_top_header_filter; 236: ngx_http_top_header_filter = ngx_http_chunked_header_filter; 237: … 无需对上面两行代码做过多解释,此时header过滤链表现如图6-7所示。 其他过滤模块类似加入,逐步形成最终的完整header过滤链。当然,body过滤链的形成过程也与此类似。两条过滤链形成后,其对应的调用入口分别在函数 ngx_http_send_header()和函数ngx_http_output_filter()内。 1888:代码片段6.2-5,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 1889:ngx_int_t 1890:ngx_http_send_header(ngx_http_request_t *r) 1891:{ 1892:… 1897: return ngx_http_top_header_filter(r); 1898:} 1899: 1901:ngx_int_t 1902:ngx_http_output_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) 1903:{ 1904:… 1912: rc = ngx_http_top_body_filter(r, in); 1913:… 1919: return rc; 1920:} 这两个函数非常简单,主要是通过过滤链的链头函数指针全局变量进入到两条过滤链内,进而依次执行链上的各个函数。比如这里 ngx_http_top_header_filter 指向的是 ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter()函数,因此进入到该函数内执行,而在该函数的执行过程中又会根据情况,继续通过当前模块内的函数指针局部变量 ngx_http_next_header_filter 间接地调用到header 过滤链的下一个过滤函数。这对保证过滤链的前后承接是非常必要的,除非我们遇到无法继续处理的错误,此时只有返回NGX_ERROR这样的值。 51: 代码片段6.2-6,文件名: ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c 52: static ngx_int_t 53: ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) 54: { 55: … 70: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); 71: } 根据 HTTP 协议具备的响应头影响或决定响应体内容的特点,一般是先对响应头进行过滤,根据头过滤处理返回值再对响应体进行过滤处理,如果在响应头过滤处理中出错或某些特定情况下,响应体过滤处理可以不用再进行。 Upstream模块与具体的协议无关,其除了支持HTTP以外,还支持包括FASTCGI、SCGI、UWSGI、MEMCACHED等在内的多种协议。 Upstream模块的典型应用是反向代理,这里就以ngx_http_proxy_module模块为例。假定我们有如下的实例环境,客户端对服务器80 端口的请求都被Nginx Proxy Server转发到另外两个真实的NginxWeb Server实例上进行处理(图6-8 是实验环境,Web Server 和Proxy Server都只是Nginx进程,并且运行在同一台服务器)。 那么,NginxProxyServer的核心配置多半是像下面这样。 00: 代码片段6.3-1,文件名: nginx.conf.upstream 01: … 02: http { 03: … 04: upstream load_balance { 05: server localhost:8001; 06: server localhost:8002; 07: } 08: 09: server { 10: listen 80; 11: location / { 12: proxy_buffering off; 13: proxy_pass http://load_balance; 14: } 15: } 16: } 上面的proxy_buffering off;配置是为了禁用Nginx 反向代理的缓存功能,保证客户端的每次请求都被转发到后端真实服务器,以便我们这里每次跟踪分析的 Nginx 执行流程更加简单且完整。另外两个配置指令upstream和proxy_pass在此处显得特别重要,其中upstream配置指令的回调处理函数为ngx_http_upstream(),该函数除了申请内存、设置初始值等之外,最主要的动作就是切换配置上下文并调用ngx_conf_parse()函数继续进行配置解析。 4160:代码片段6.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c 4161: pcf = *cf; 4162: cf->ctx = ctx; 4163: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF; 4164: 4165: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); 4166:… 4173: if (uscf->servers == NULL) { 进入 upstream 配置块,最主要的配置指令也就是 server ,其对应的处理函数为ngx_http_upstream_server()。对于每一个后端真实服务器,除了其uri地址外,还有诸如down、weight、max_fails、fail_timeout、backup这样的可选参数,所有这些都需要ngx_http_upstream_server()函数来处理。 在ngx_http_upstream.c的第4173行下个断点,我们可以看到图6-9给出示例的解析结果。 另外一个重要配置指令 proxy_pass 主要出现在 location 配置上下文中,其对应的处理函数为ngx_http_proxy_pass()。抹去该函数内的众多细节,我们重点关注两个赋值语句。 3336:代码片段6.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_proxy_module.c 3337:static char * 3338:ngx_http_proxy_pass(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 3339:{ 3340:… 3356: clcf->handler = ngx_http_proxy_handler; 3357:… 3425: plcf->upstream.upstream = ngx_http_upstream_add(cf, &u, 0); 上面片段代码里的第一个赋值语句给当前 location 的 http 处理设置回调函数,而第二个赋值语句则是查找(没有找到则会创建,比如如果配置文件中upstream指令出现在proxy_pass指令的后面)其对应的upstream配置,我们这里就一个名为load_balance的upstream,所以找到的配置就是它了,如图6-10所示。 前面曾提到, Nginx 将对客户端的 http 请求处理分为多个阶段,而其中有个 NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE阶段主要就是做配置查找处理,如果当前请求location设置了upstream,即回调函数指针clcf->handler不为空,则表示对该location的请求需要后端真实服务器来处理(注意代码第1519~1520行)。 949: 代码片段6.3-4,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 950: ngx_int_t 951: ngx_http_core_find_config_phase(ngx_http_request_t *r, 952: ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph) 953: { 954: … 981: ngx_http_update_location_config(r); 982: … 1439: void 1440: ngx_http_update_location_config(ngx_http_request_t *r) 1441: { 1442: … 1519: if (clcf->handler) { 1520: r->content_handler = clcf->handler; 1521: } 1522: } 在其他location更新的情况下,比如redirect重定向location或named命名location或if条件location等,此时也会调用ngx_http_update_location_config()函数进行location配置更新。我们知道Upstream模块的主要功能是产生响应数据,而这些响应数据来自后端真实服务器,所以在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段的checker函数ngx_http_core_content_phase()内,我们可以看到在r->content_handler不为空的情况下会优先对r->content_handler函数指针进行回调。 1385:代码片段6.3-5,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 1386:ngx_int_t 1387:ngx_http_core_content_phase(ngx_http_request_t *r, 1388: ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph) 1389:{ 1390:… 1394: if (r->content_handler) { 1395: r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler; 1396: ngx_http_finalize_request(r, r->content_handler(r)); 1397: return NGX_OK; 1398: } 1399:… 第1394 行,如果 r->content_handler 不为空,即存在 upstream,那么进入处理,注意第1397行直接返回NGX_OK,也即不再调用挂在该阶段的其他模块回调函数,所以说Upstream模块的优先级是最高的。根据前面的回调赋值,调用r->content_handler()指针函数,实质上就是执行函数ngx_http_proxy_handler(),直到这里,我们才真正走进Upstream代理模块的处理逻辑里。 对于任何一个Upstream模块而言,最核心的实现主要是7个回调函数,Upstream代理模块自然也不例外,它实现并注册了7个回调函数如表6-4所示。 上表格中前面5个函数执行的先后次序如下图所示,由于在Client/Proxy/Server之间,一次请求/响应数据可以发送多次(下图中只画出一次就发送完毕的情况),所以下图中对应的函数也可能被执行多次。不过一般情况下,这5个函数执行的先后次序就是这样,如图6-11所示。 这些回调函数如何夹杂到Nginx中被调用并不需要完全搞清楚,要写一个Upstream模块,我们只要实现上面提到的这7个函数即可。当然,可以看到最主要的也就是create_request、process_header和input_filter这三个回调,它们实现从HTTP协议到Nginx与后端服务器之间交互协议的来回转换,使得在用户看来,他访问的就是一台功能完整的Web服务器,而也许事实上,显示在他面前的数据来自Memcache或别的什么服务器。 Load-balance 模块可以称为辅助模块,与前面介绍的以处理请求/响应数据为目标的三种模块完全不同,它主要为Upstream模块服务,目标明确且单一,即如何从多台后端服务器中选择出一台合适的服务器来处理当前请求。 要实现一个具体的Load-balance模块,只需实现如下4个回调函数即可,参见表6-5。 Nginx默认采用round_robin加权算法,如果要选择其他负载均衡算法,必须在upstream的配置上下文中明确指定。比如采用IP_hash算法的upstream配置如下所示。 00: 代码片段6.4-1,文件名: nginx.conf 01: … 20: upstream load_balance { 21: ip_hash; 22: server localhost:8001; 23: … 后面 server 的解析判断,对前面选用哪种负载均衡算法存在一定的依赖关系,所以配置指令ip_hash;最好放在所有server指令的前面。 在配置项 ip_hash 的处理函数里,会给 uscf->peer.init_upstream 函数指针赋值上 IP_hash模块提供的回调函数,这样在Nginx后续处理过程中才能调到IP_hash模块的功能逻辑里。 注 释 [1].这意味着当前所指的filters其实为output filters,而在未来,不排除Nginx官方可能会引入input filters来满足某些特定需求。 Nginx 的模块非常之多,可以认为所有代码都是以模块的形式组织的,包括核心模块和功能模块。针对不同的应用场合,并非所有的功能模块都要被用到,附录 A 给出的是默认configure(即简单的http服务器应用)下被编译连接的模块。这里虽说是模块连接,但Nginx不会像Apache或Lighttpd那样在编译时生成so动态库,然后在程序执行时再进行动态加载, Nginx 模块源文件会在生成 Nginx 时就直接被编译到其二进制执行文件中,所以,如果要选用不同的功能模块,必须对 Nginx 做重新配置和编译。对于功能模块的选择,如果要修改默认值,需要在进行configure时主动指定,比如新增http_flv功能模块(默认是没有这个功能的,各个选项的默认值可以在文件auto/options内看到)。 [root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ./configure --with-http_flv_module 执行后,生成的objs/ngx_modules.c源文件内就会包含对ngx_http_flv_module模块的引用,要再去掉http_flv功能模块,则需要重新configure,即不带--with-http_flv_module配置后再编译生成新的Nginx二进制程序。通过执行./configure--help,我们可以看到更多的配置选项,包括各种可选模块。 虽然 Nginx 模块有很多,并且每个模块实现的功能各不相同,但是根据模块的主要功能性质,大体可以将它们分为四个类别。 1.handlers:协同完成客户端请求的处理、产生响应数据,比如ngx_http_rewrite_module模块,用于处理客户端请求的地址重写,ngx_http_static_module模块,负责处理客户端的静态页面请求,ngx_http_log_module模块,负责记录请求访问日志。 2.filters:对handlers产生的响应数据[1]做各种过滤处理(即增/删/改),比如模块ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module,对待响应数据进行过滤检测,如果通过时间戳判断出前后两次请求的响应数据没有发生任何实质改变,那么可以直接响应“304 Not Modified”状态标识,让客户端使用本地缓存即可,而原本待发送的响应数据将被清除掉。 3.upstream:如果存在后端真实服务器,Nginx 可利用 upstream 模块充当反向代理(Reverse Proxy)的角色,对客户端发起的请求只负责进行转发(当然也包括对后端真实服务器响应数据的回转),比如ngx_http_proxy_module就为标准的upstream模块。 4.load-balance:在Nginx 充当中间代理角色时,由于后端真实服务器往往多于一个,对于某一次客户端的请求,如何选择对应的后端真实服务器来进行处理,有类似于ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module这样的loadbalance模块来实现不同的负载均衡算法。 对于这几类模块,我们会分别进行详细介绍并分析各自典型代表模块,不过在此之前先从Nginx模块源码上进行直观认识。前面讲过Nginx的所有代码都是以模块的形式进行组织,而封装Nginx模块的结构体为ngx_module_s,定义如下。 110: 代码片段6-1,文件名: ngx_conf_file.h 111: struct ngx_module_s { 112: ngx_uint_t ctx_index; //当前模块在同类模块中的序号 113: ngx_uint_t index; //当前模块在所有模块中的序号 114: … 120: ngx_uint_t version; //当前模块版本号 121: 122: void *ctx; //指向当前模块特有的数据 123: ngx_command_t *commands; //指向当前模块配置项解析数组 124: ngx_uint_t type; //模块类型 125: //以下为模块回调函数,回调时机可根据函数名看出 126: ngx_int_t (*init_master)(ngx_log_t *log); 127: … 128: }; 11: 代码片段6-2,文件名: ngx_core.h 12: typedef struct ngx_module_s ngx_module_t; 结构体ngx_module_s值得关注的几个字段分别为ctx、commands和type,其中commands字段表示当前模块可以解析的配置项目,这在配置文件解析一章做过详细描述。表示模块类型的type只有5种可能的值,而同一类型模块的ctx指向的数据类型也相同,参见表6-1。 表6-1 中第三列里的数据类型非常重要,它们的字段基本都是一些回调函数,这些回调函数会在其模块对应的配置文件解析过程前/中/后适时地被调用,做一些内存准备、初始化、配置值检查、初始值填充与合并、回调函数挂载等初始工作。以 ngx_http_core_module 模块为例,该模块type类型为NGX_HTTP_MODULE,ctx指向的ngx_http_module_t结构体变量ngx_http_core_module_ctx。 785: 代码片段6-3,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 786: static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_core_module_ctx = { 787: ngx_http_core_preconfiguration, /* preconfiguration */ 788: NULL, /* postconfiguration */ 789: 790: ngx_http_core_create_main_conf, /* create main configuration */ 791: ngx_http_core_init_main_conf, /* init main configuration */ 792: 793: ngx_http_core_create_srv_conf, /* create server configuration */ 794: ngx_http_core_merge_srv_conf, /* merge server configuration */ 795: 796: ngx_http_core_create_loc_conf, /* create location configuration */ 797: ngx_http_core_merge_loc_conf /* merge location configuration */ 798: }; 根据上面代码的英文注释,可以很明显地看出各个回调函数的回调时机,比如函数ngx_http_core_preconfiguration()将在进行 http 块配置解析前被调用,所以在 ngx_http_block()函数里可以看到下面这样的代码。 117: 代码片段6-4,文件名: ngx_http.c 118: static char * 119: ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 120: … 228: if (module->preconfiguration) { 229: if (module->preconfiguration(cf) != NGX_OK) { 230: return NGX_CONF_ERROR; 231: } 232: } 233: … 239: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); 240: … 309: if (module->postconfiguration) { 310: if (module->postconfiguration(cf) != NGX_OK) { 311: return NGX_CONF_ERROR; 312: } 313: } 314: … 至于这些回调函数内的具体逻辑,如前所述一般是一些初始或默认值填充工作,但也有回调函数挂载的设置,比如 ngx_http_static_module 模块的 postconfiguration 字段回调函数ngx_http_static_init()就是将自己的处理函数 ngx_http_static_handler()挂载在 http 处理状态机上,总体来看这毕竟都只是一些简单的初始准备工作,不多赘述。 各种操作系统平台下支持的各种I/O事件处理机制在Nginx内部都被进行了统一封装,这样不论Nginx被用在何种平台都能以最高效的方式运行,表7-1列出了Nginx对各种I/O事件处理机制的具体支持情况。 表7-1给出的8种I/O事件处理机制中,前6种属于本节将介绍的I/O多路复用模型,而后两种机制,实时信号和异步I/O[2]比较特殊,在此不做过多的描述,本书其他地方也暂不做考虑。 不论哪种 I/O 多路复用模型,基本的原理是相同的,它们都能让应用程序可以同时对多个 I/O 端口进行监控以判断其上的操作是否可以进行,达到时间复用的目的。举个例子,如果要监控来自 10 根不同地方的水管(I/O 端口)是否有水流到达(即是否可读),那么需要10个人(即10个线程或10处代码)来做这件事情。如果利用某种技术(比如摄像头)把这10根水管的状态情况统一传达到某个点,那么就只需要1个人在那个点进行监控就行了,而类似于select或epoll这样的多路I/O复用机制就好比是摄像头的功能,它们能够把多个I/O端口的状况反馈到同一处,比如某个特定的文件描述符上,这样,应用程序只需利用对应的select()或epoll_wait()系统调用阻塞关注这一处即可。 不同的平台有支持不同的I/O多路复用模型,在下一节会重点介绍一下epoll模型(其他复用模型请自行查阅Man手册或进行Google搜索),这里我们直接来看Nginx对这些I/O多路复用模型的封装与使用。在 Nginx 源码里, I/O 多路复用模型被封装在一个名为ngx_event_actions_t的结构体里,该结构体包含的字段主要就是回调函数,将各个I/O多路复用模型的功能接口进行统一,参见表7-2。 由于I/O多路复用模型各自具体实现的不同,表7-2列出的一些回调接口,在Nginx的各个 I/O 多路复用处理模块里可能并没有对应的处理,但几个最基本的接口,比如add/del/process_events肯定都会有实现。为了方便使用任何一种事件处理机制,Nginx定义了一个类型为ngx_event_actions_t的全局变量ngx_event_actions,并且还定义了几个宏。 44: 代码片段7.1-1,文件名: ngx_event.c 45: ngx_event_actions_t ngx_event_actions; 447: 代码片段7.1-2,文件名: ngx_event.h 448: #define ngx_process_changes ngx_event_actions.process_changes 449: #define ngx_process_events ngx_event_actions.process_events 450: #define ngx_done_events ngx_event_actions.done 451: 452: #define ngx_add_event ngx_event_actions.add 453: #define ngx_del_event ngx_event_actions.del 454: #define ngx_add_conn ngx_event_actions.add_conn 455: #define ngx_del_conn ngx_event_actions.del_conn 这样,Nginx要将某个事件添加到多路复用监控里,只需调用ngx_add_event()函数即可,至于这个函数对应到哪个具体的I/O多路复用处理模块上,在这里可以毫不关心。 当然,我们做分析还是要知道 ngx_add_event()函数是怎么关联到具体的 I/O 多路复用处理模块的,而不难看出,关键点是全局变量 ngx_event_actions 的值。给全局变量ngx_event_actions进行赋值出现在各个事件处理模块的初始化函数内,比如epoll模块。 147: 代码片段7.1-3,文件名: ngx_epoll_module.c 148: ngx_event_module_t ngx_epoll_module_ctx = { 149: &epoll_name, 150: ngx_epoll_create_conf, /* create configuration */ 151: ngx_epoll_init_conf, /* init configuration */ 152: 153: { 154: ngx_epoll_add_event, /* add an event */ 155: ngx_epoll_del_event, /* delete an event */ 156: ngx_epoll_add_event, /* enable an event */ 157: ngx_epoll_del_event, /* disable an event */ 158: ngx_epoll_add_connection, /* add an connection */ 159: ngx_epoll_del_connection, /* delete an connection */ 160: NULL, /* process the changes */ 161: ngx_epoll_process_events, /* process the events */ 162: ngx_epoll_init, /* init the events */ 163: ngx_epoll_done, /* done the events */ 164: } 165: }; 166: … 288: static ngx_int_t 289: ngx_epoll_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_msec_t timer) 290: { 291: … 327: ngx_event_actions = ngx_epoll_module_ctx.actions; 注意到代码片段7.1-3的第327行就是epoll模块的ngx_event_actions赋值,而在其他事件处理模块的初始化函数内也可以找到这样的赋值语句,所以一旦设定Nginx使用某个事件处理模块,经过事件处理模块的初始化后,就把全局变量ngx_event_actions指向了它的封装。比如从上面epoll模块的源代码来看,调用ngx_add_event()函数对应执行的就是ngx_epoll_add_event()函数。 设定Nginx使用哪个事件处理机制是通过在event块里使用use指令来指定的。该配置指令对应的处理函数为 ngx_event_use(),在经过相关验证(比如重复指定、对应的事件处理模块是否存在等)后,就会把对应的事件处理模块序号记录在配置变量 ecf->use 内。如果不进行主动指定,那么 Nginx 会根据当前系统平台选择一个合适的事件处理模块,并且同样把其模块序号记录在配置变量ecf->use内,其相关逻辑实现在函数ngx_event_core_init_conf()内。 在工作进程的初始化函数 ngx_worker_process_init()内会调用事件核心模块的初始化函数ngx_event_process_init(),而在该函数内,根据配置变量ecf->use记录的值,进而调用到对应事件处理模块的初始化函数,比如epoll模块的ngx_epoll_init()函数。 582: 代码片段7.1-4,文件名: ngx_event.c 583: static ngx_int_t 584: ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) 585: { 586: … 617: for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { 618: if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) { 619: continue; 620: } 621: 622: if (ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index != ecf->use) { 623: continue; 624: } 625: 626: module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; 627: 628: if (module->actions.init(cycle, ngx_timer_resolution) != NGX_OK) { 629: /* fatal */ 630: exit(2); 631: } 632: 633: break; 634: } 至此,Nginx内对I/O多路复用模型的整体封装,前后才真正衔接起来,这个整体封装的一个粗略的框图,如图7-1所示。 epoll接口作为poll接口的变体在Linux内核2.5中被引入[3]。相比于select实现的多路复用I/O模型,epoll模型最大的好处在于它不会随着被监控描述符数目的增长而导致效率急速下降。具体来说,select模型是采用遍历扫描来判断每个描述符是否有事件发生。当监控的描述符数目越多,自然耗时越大,而且由于受系统默认限制(依赖的__FD_SETSIZE宏被定义为1024[4]),select模型最多只能同时监控1024个描述符。相反,epoll模型就没有这些缺点,首先基于poll的epoll原生的具有poll的优点,即同时监控的描述符个数不受限制(其实是受进程可打开文件描述符个数限制,但这个数值一般比较大,通过执行命令“cat/proc/sys/fs/file-max”可看到该值,比如我这里是22883);其次,epoll模型对事件的响应是触发式的,也即无需对整个监控描述符列表做扫描,而只需对有事件发生的描述符做处理即可;还有一些其他详细差别,可以看select/epoll的源码分析,这里不多描述。 epoll提供了三个系统调用接口,分别如下所示。 #include int epoll_create(int size); int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event); int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout); int epoll_pwait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout, const sigset_t *sigmask); 系统调用epoll_create()创建一个epoll的句柄(epoll模型专用的文件描述符),size用来告诉内核监听的描述符数目的最大值,请求内核为存储事件分配空间,并返回一个描述符(在epoll使用完后,必须调用close()关闭这个描述符,否则可能导致系统描述符被耗尽)。 函数epoll_ctl()用来向内核注册、删除或修改事件,其第一个参数epfd是函数epoll_create()的返回值;第二个参数op表示动作,可以为EPOLL_CTL_ADD(注册新的fd到epfd中)、EPOLL_CTL_MOD(修改已经注册的fd的监听事件)以及EPOLL_CTL_DEL(从epfd中删除一个fd);第三个参数fd表示需要监听的描述符;第四个参数event是epoll_event结构体类型,用于告诉内核需要监听什么事件,其中结构体 epoll_event 的字段 events 可能取值有EPOLLIN(普通数据可读)、EPOLLOUT(普通数据可写)、EPOLLPRI(高优先级数据可读)、EPOLLERR(发生错误)、EPOLLHUP(发生挂起)、EPOLLET(将epoll设为边缘触发(EdgeTriggered)模式,这是相对于水平触发(Level Triggered,默认触发方式)来说的)。该函数执行成功返回0;发生错误返回-1,同时设置错误标志errno。相关数据结构定义如下。 80: 代码片段7.2-1,文件名: /usr/include/sys/epoll.h 81: typedef union epoll_data 82: { 83: void *ptr; 84: int fd; 85: uint32_t u32; 86: uint64_t u64; 87: } epoll_data_t; 88: 89: struct epoll_event 90: { 91: uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */ 92: epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */ 93: }; 函数epoll_wait()用来等待事件发生,其第一个参数epfd仍然是函数epoll_create()的返回值;第二个参数events用来从内核接收发生事件的集合;第三个参数maxevents指定一次获取的最大事件数目,其值不能大于之前函数 epoll_create()调用时的参数 size,但同时也必须大于 0;第四个参数timeout指定epoll_wait()函数调用等待多久(单位为毫秒),取值为−1则无限等待(这是指超时时间无限长,一旦有事件或信号发生,等待自然终止);为0则立即返回(即仅查询一下当前是否有事件发生,有则获取,没有也不进行阻塞等待);大于0则等待指定时间段。该函数执行成功将返回发生事件的描述符数目,当超时仍没有事件发生时返回0;发生错误返回−1,同时设置错误标志errno。 函数 epoll_pwait()和函数 epoll_wait()的差别在于其可以通过最后一个参数设置阻塞过程中的信号屏蔽字,即 ready = epoll_pwait(epfd, &events, maxevents, timeout, &sigmask); 等价于 sigset_t origmask; sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigmask, &origmask); ready = epoll_wait(epfd, &events, maxevents, timeout); sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &origmask, NULL); 关于这些API接口的详细使用信息,请参考最新的Man手册,因为它们可能会跟随内核的更新而发生变化[5]。 下面重点来看epoll 模型的两种触发方式,水平触发与边缘触发。LT(leveltriggered,水平触发)是默认的工作方式,同时支持block和no-block I/O。在这种工作方式下,当描述符从未就绪变为就绪时,内核通过epoll告诉进程该描述符有事件发生,之后如果进程一直不对这个就绪状态做出任何操作,则内核会持续通知,直到事件处理完成。而ET(edge-triggered,边缘触发)是高速工作方式,只支持no-block I/O。在这种工作方式下,当描述符从未就绪变为就绪时,内核通过epoll告诉进程该描述符有事件发生,之后就算进程一直不对这个就绪状态做出任何操作,内核也不会再发送更多的通知(当然,除非是该I/O上又来了新的事件),也就是说内核仅在 I/O 描述符状态发生变化的那个突变边缘对进程做出一次通知。举个例子,假设在进程A和进程B之间通过某个pipe P 进行通信,那么可能有如下这样的场景。 1.进程A将P的读端描述符rfd以ET方式加入到自己epoll监控里,并调用epoll_wait()函数阻塞。 2.进程B 往P的写端写入2KB 数据。 3.进程A的描述符rfd 上触发可读事件,因此epoll_wait())函数调用返回。 4.进程A从描述符rfd 上读取1KB 数据。 5.进程A调用epoll_wait()函数。 根据ET方式的特点,在第5 步中,进程A调用epoll_wait()函数后会阻塞而不会触发可读事件,即便我们知道当前pipe P里还有1KB的数据可读。如果此时进程B又在等待进程A读完全部数据后给出的响应,而没有写出新的数据,从而导致一个类似ABBA deadlock[6]的“假死锁”异常状态。假设进程B不管进程A是否已读完全部数据,进行第6步。 6.进程B 往P的写端又写入2KB 数据。 此时进程A的epoll_wait()函数会捕获描述符rfd上的可读事件而返回么?这个在Man手册上未提到,但是我们可自己动手直接利用Nginx做下实验。我们知道,客户端向Nginx发送请求时肯定发送了相关的数据,而 Nginx 会执行监听套接口上对应的回调函数ngx_event_accept(),Nginx的监听套接口是以水平方式加入到epoll模型的(后面章节会讲到详情)。要验证很简单,在ngx_event_accept()函数内加这么一句。 17: 代码片段7.2-2,文件名: ngx_event_accept.c 18: void 19: ngx_event_accept(ngx_event_t *ev) 20: { 21: … 49: return; 50: do { 51: socklen = NGX_SOCKADDRLEN; 即让该函数不执行后面的accept()函数,也就是不读取客户端发送的相关请求数据,重新编译并执行Nginx,利用gdb attach 到工作进程(可以在配置文件里设置工作进程数目为1)后,在ngx_event_accept()下断点,最后模拟客户端发起一个请求(利用IE浏览器也好,wget命令也好),可以看到gdb被断了下来,按c后又马上被断下来,不管按多少遍都是如此,这说明因为ngx_event_accept()函数被直接返回导致监听描述符上的数据没有被读走,所以使得系统反复通知Nginx可读事件。如果我们在gdb里主动执行accept()读走数据。 (gdb) p accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen) $1 = 3 此时按c后,gdb才不再被断下(除非又有新的客户端请求到达),这就是epoll模型的水平触发方式的特性。要测试边缘触发方式的特性,需要把监听套接口以边缘触发的方式加入到Nginx的epoll模型里,修改ngx_epoll_add_event()函数即可。 378: 代码片段7.2-3,文件名: ngx_epoll_module.c 379: static ngx_int_t 380: ngx_epoll_add_event(ngx_event_t *ev, ngx_int_t event, ngx_uint_t flags) 381: { 382: … 415: ee.events = events | (uint32_t) flags | EPOLLET; 416: ee.data.ptr = (void *) ((uintptr_t) c | ev->instance); 全部带上EPOLLET标记,即都以边缘触发方式加入,和前面一样,重新编译执行Nginx并利用gdb attach,模拟客户端发起一个请求,gdb 被断了下来。按c 后情况就不一样了,gdb没有被马上断下来,说明Nginx工作进程被阻塞在epoll_wait()处。这体现了前面提到的边缘触发方式的特点:一个事件仅通知一次,数据不读走也不会再重复通知。再验证另一个重点问题:如果此时又有客户端发出请求,即监听套接口上又有新数据到达,此时会怎么样?我的实际操作告诉我,gdb 被断了下来,也就是说在监听套接口上触发了可读事件,此时主动去accept()可以获得两个“数据”(即便是前一个客户端已经关闭了)。 (gdb) p accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen) $1 = 3 (gdb) p accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen) $2 = 10 (gdb) p accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen) $3 = -1 到此,我们已经验证了在进程B(客户端,比如wget进程)往进程A(Nginx)的监听套接口上写了数据而没有被进程A读取,此时如果进程C(客户端,另一个wget进程)继续往进程A的监听套接口上写数据,结果是进程A的epoll_wait()函数会捕获该监听套接口上的可读事件而返回。那么回到前面的提问,如果进程B往P的写端又写入2KB数据,进程A的 epoll_wait()函数会捕获描述符 rfd 上的可读事件而返回吗?根据刚才的验证能类推得到其答案么?答案是会。下面给出验证的测试代码。 00: 代码片段7.2-4,文件名: epoll_test.c 01: /** 02: * gcc -Wall -g -o epoll_test epoll_test.c 03: */ 04: #include 05: #include 06: #include 07: #include 08: #include 09: #include 10: #include 11: #include 12: #include 13: 14: int main(int argc, char *const *argv) 15: { 16: int sockfd; 17: struct sockaddr_in server_addr; 18: 19: if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) { 20: fprintf (stderr, "Socket error,%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); 21: return -1; 22: } 23: 24: bzero (&server_addr, sizeof (server_addr)); 25: server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; 26: server_addr.sin_port = htons (80); 27: 28: if(!inet_aton("192.168.1.1", &server_addr.sin_addr)) { 29: fprintf (stderr, "Bad address:%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); 30: close (sockfd); 31: return -1; 32: } 33: 34: if (connect (sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) (&server_addr), 35: sizeof (struct sockaddr)) == -1) { 36: fprintf (stderr, "Connect Error:%s\r\n", strerror (errno)); 37: close (sockfd); 38: return -1; 39: } 40: 41: write (sockfd, "test1", sizeof("test1")); 42: write (sockfd, "test2", sizeof("test2")); 43: 44: close (sockfd); 45: return 0; 46: } 修改Nginx的ngx_http_read_request_header()函数,在开头加入语句“returnNGX_AGAIN;”,这样让Nginx不读走数据。在gdb里单步执行epoll_test,会发现虽然41行写出的数据没有被Nginx读走,但是在执行到第42行再写出数据时,会触发Nginx再次捕获可读事件。 相关验证到此结束,根据边缘触发方式的特性,epoll模型工作在此方式时必须使用非阻塞文件描述符,以避免由于一个文件描述符的阻塞读/写操作而导致需处理的其他多个文件描述符任务给“饿死”。总的来说,使用边缘触发方式的epoll模型,推荐的步骤如下。 1.基于非阻塞文件描述符:即把待加入到epoll 模型里的描述符都设置为no-block。 2.只有当read()或write()返回EAGAIN(对于面向包/令牌的文件,比如数据包套接口、规范模式的终端)或是read()/write()读到/写出的数据长度小于请求的数据长度(对于面向流的文件,比如 pipe、FIFO、流套接口)时才需要挂起等待下一个事件,否则可能会出现意想不到的逻辑异常。 一般而言,在大并发的系统中,从性能上讲,边缘触发模式会比水平触发模式更有优势,但是对程序员的要求也更高。 Nginx内事件封装所对应的结构体为ngx_event_t,在该结构体内可以看到很多位域字段,凭经验即可知道它们都是用作旗标,即标记事件当前是否处在某种状态。除去这些旗标字段,与事件本身联系更为紧密的是回调接口handler字段,该字段直接指定了当事件发生时,Nginx该如何进行处理。 我们所关注的事件基本都是依附在socket描述符上的,而随着处理流程的不断变化,在socket描述符上所关注的事件也会发生改变。比如,对于一个新建连接socket,一开始必定是关注其可读事件,以便从客户端获取请求信息,当读取完所有请求信息并且被 Nginx 正常处理后,又将关注该socket的可写事件,从而可以将对应的响应信息顺利发送给客户端。即便是关注的同一个事件,根据当前处理阶段的不同,其事件处理回调函数也可能不同,这很容易理解,比如同是新建连接socket的可读事件,但处理客户端请求头的回调函数与处理客户端请求体的回调函数肯定不是同一个。下面分析一个客户端请求/服务端响应的完整流程,看在这个过程中,关注事件如何变化,回调函数又如何变化,如图7-1所示。 这是一个非常简单的流程,客户端浏览器(比如IE)发送请求(请求某静态页面)到服务器,服务器也就是 Nginx 程序,Nginx 从磁盘文件系统读取静态文件发送给客户端,流程结束,如图7-2所示。 当客户端浏览器发送请求到 Nginx 时,Nginx 就将调用监听套接口对应的事件处理函数ngx_event_accept(),在该函数内将创建一个新的关联当前请求连接的套接口。在这个套接口上,Nginx关注的事件以及回调函数列表(通过gdb的watch指令抓取或利用systemtap工具探测获取)参见表7-3。 accept()新建的套接口最先关注的当然是读事件,以便从客户端获取请求信息,其回调函数为ngx_http_init_request(),一旦读到客户端请求信息就开始进行初始化等准备工作。此时不关注写事件,所以写事件的回调函数为 ngx_http_empty_handler(),即什么也不做,仅打印一条日志。接下来对请求头、请求头处理依次进行,一旦处理结束就开始关注写事件,此时的写事件回调函数同为ngx_http_request_handler(),将响应数据全部发回给客户端后,将写事件的回调函数又置为 ngx_http_empty_handler()。最后,关注读事件等待客户端的下一个请求,此时的回调处理函数为 ngx_http_keepalive_handler(),表示当前是在与客户端保持 keepalive状态。如果客户端有新的请求数据发到,那么在ngx_http_keepalive_handler()函数内将读到对应的数据,并且调用ngx_http_init_request()做初始化,开始一个新的请求处理。如果此时客户端关闭了连接,那么Nginx同样也将获得一个可读事件,调用ngx_http_keepalive_handler()函数处理却读取不到数据,于是关闭连接、回收资源,函数返回。这部分相关逻辑如下所示。 2662:代码片段7.3-1,文件名: ngx_event.c 2663:static void 2664:ngx_http_keepalive_handler(ngx_event_t *rev) 2665:{ 2666:… 2730: n = c->recv(c, b->last, size); 2731:… 2743: if (n == 0) { 2744: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, ngx_socket_errno, 2745: "client %V closed keepalive connection", &c->addr_text); 2746: ngx_http_close_connection(c); 2747: return; 2748: } 2749:… 2767: ngx_http_init_request(rev); 2768:} Nginx 对事件的处理耦合性太强,对上一步骤、当前处理步骤以及下一步骤都必须仔细把握,否则回调设置错了,一切就乱了。当然,这也可以说它灵活,只要你乐意,插入几个自编的模块到处理步骤里也是一件非常简单的事情。 在一般情况下,配置 Nginx 执行时,工作进程都会有多个,由于各个工作进程相互独立的接收客户端请求、处理、响应,所以就可能会出现负载不均衡的情况,比如极端情况可能会是1个工作进程当前有3000个请求等待处理;而另1个进程当前却只有300个请求等待处理,Nginx采取了哪些均衡措施来避免这种情况就是本节将要讨论的内容。 我们已经知道,Nginx工作进程的主要任务就是处理事件,而事件的最初源头来自监听套接口,所以一旦某个工作进程独自拥有了某个监听套接口,那么所有来自该监听套接口的客户端请求都将被这个工作进程处理。当然,如果是多个工作进程同时拥有某个监听套接口,那么一旦该监听套接口出现某客户端请求,此时就将引发所有拥有该监听套接口的工作进程去争抢这个请求,能争抢到的肯定只有某一个工作进程,而其他工作进程注定要无获而返,这种现象即为惊群[7][8](thunderingherd)。关于惊群问题是否已经被Linux内核所解决,这里不做讨论,但可以肯定的是,要进行负载均衡,最基本的着手点也就是监听套接口,Nginx是不是这样做的呢?来看下面。 在Nginx源码里能看到这样一个名为ngx_use_accept_mutex的全局变量,可以说它就是Nginx均衡措施的根本所在。该变量是整型类型,具体定义如下。 53: 代码片段7.4.1-1,文件名: ngx_event.c 54: ngx_uint_t ngx_use_accept_mutex; 该变量的赋值语句在函数ngx_event_process_init()内,也就是每个工作进程开始时的初始化函数,前后调用关系如下。 ngx_worker_process_cycle() -> ngx_worker_process_init() -> ngx_event_process_init() 在函数ngx_event_process_init()内,可以看到只有多进程模型下,并且工作进程数目大于1、用户配置开启负载均衡的情况下才设置该变量为1,否则为0。 596: 代码片段7.4.1-2,文件名: ngx_event.c 597: if (ccf->master && ccf->worker_processes > 1 && ecf->accept_mutex) { 598: ngx_use_accept_mutex = 1; 599: ngx_accept_mutex_held = 0; 600: ngx_accept_mutex_delay = ecf->accept_mutex_delay; 601: 602: } else { 603: ngx_use_accept_mutex = 0; 604: } 前两个条件很容易理解,只有多个进程才有均衡的概念,而对于ecf->accept_mutex字段的判断主要是提供用户便利,可以关闭该功能,因为既然均衡策略也有相应的代码逻辑,难保不会在某些情况下因其本身的消耗而得不偿失。当然,该字段默认为 1,在配置初始化函数ngx_event_core_init_conf()内,有这么一句: ngx_conf_init_value(ecf->accept_mutex, 1); 一旦变量ngx_use_accept_mutex值为1,也就开启了Nginx负载均衡策略,此时在每个工作进程的初始化函数 ngx_event_process_init()内,所有监听套接口都不会被加入到其事件监控机制里,如下所示,第828行和第829行的代码跳过了后面第838行将监听套接口加入到事件监控机制里。 745: 代码片段7.4.1-3,文件名: ngx_event.c 746: for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) { 747: … 828: if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) { 829: continue; 830: } 831: … 838: if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT,0) == NGX_ERROR) { 839: return NGX_ERROR; 840: } 841: … 845: } 真正将监听套接口加入到事件监控机制是在函数ngx_process_events_ and_timers()里。在前面的进程模型一节,曾提到工作进程的主要执行体是一个无限for循序,而在该循环内最重要的函数调用就是 ngx_process_events_and_timers(),所以可以想象在该函数内动态添加或删除监听套接口是一种很灵活的方式。如果当前工作进程负载比较小,就将监听套接口加入到自身的事件监控机制里,从而带来新的客户端请求;而如果当前工作进程负载比较大,就将监听套接口从自身的事件监控机制里删除,避免引入新的客户端请求而带来更大的负载。当然,并不是想加就加、想删就删,这需要利用锁机制来做互斥与同步,既避免监听套接口被同时加入到多个进程的事件监控机制里,又避免监听套接口在某一时刻没有被任何一个进程监控。 看函数ngx_process_events_and_timers()源码,这里有一段至关重要的代码。 222: 代码片段7.4.1-4,文件名: ngx_event.c 223: if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) { 224: if (ngx_accept_disabled > 0) { 225: ngx_accept_disabled--; 226: 227: } else { 228: if (ngx_trylock_accept_mutex(cycle) == NGX_ERROR) { 229: return; 230: } 231: 232: if (ngx_accept_mutex_held) { 233: flags |= NGX_POST_EVENTS; 234: 235: } else { 236: if (timer == NGX_TIMER_INFINITE 237: || timer > ngx_accept_mutex_delay) 238: { 239: timer = ngx_accept_mutex_delay; 240: } 241: } 242: } 243: } 可以看到这段代码只有在开启负载均衡(即ngx_use_accept_mutex =1;)后才生效。在该逻辑内,首先通过检测变量ngx_accept_disabled值是否大于0来判断当前进程是否已经过载,为什么可以这样判断需要理解变量ngx_accept_disabled值的含义,这在accept()接受新连接请求的处理函数ngx_event_accept()内可以看到。 17: 代码片段7.4.1-5,文件名: ngx_event_accept.c 18: void 19: ngx_event_accept(ngx_event_t *ev) 20: { 21: … 107: ngx_accept_disabled = ngx_cycle->connection_n / 8 108: - ngx_cycle->free_connection_n; 其中ngx_cycle->connection_n表示一个工作进程的最大可承受连接数,可以通过worker_connections指令配置,其默认值为512。在工作进程配置初始化函数ngx_event_core_init_conf()内有这样的语句。 12: 代码片段7.4.1-6,文件名: ngx_event.c 13: #define DEFAULT_CONNECTIONS 512 1244: ngx_conf_init_uint_value(ecf->connections, DEFAULT_CONNECTIONS); 1245: cycle->connection_n = ecf->connections; 另外一个变量 ngx_cycle->free_connection_n 则表示当前可用连接数,假设当前活动连接数为x,那么该值为ngx_cycle->connection_n-x;,故此ngx_accept_disabled 的值为 ngx_accept_disabled = x - ngx_cycle->connection_n * 7 / 8; 也就是说如果当前活动连接数(x)超过最大可承受连接数的 7/8,则表示发生过载,变量ngx_accept_disabled值将大于0,并且该值越大表示过载越大,当前进程的负载越重。 回过头来看函数 ngx_process_events_and_timers()内的代码,当进程处于过载状态时,所做的工作仅仅只是对变量ngx_accept_disabled自减1(第225行),这表示既然经过了一轮事件处理,那么负载肯定有所减小,所以也要相应的调整变量 ngx_accept_disabled 的值。经过一段时间,ngx_accept_disabled又会降到0以下,便可争用锁获取新的请求连接。所以,可以看出最大可承受连接数的 7/8 是一个负载均衡点,当某工作进程的负载达到这个临界点时,它就不会去尝试获取互斥锁,从而让新增负载均衡到其他工作进程上。 如果进程并没有处于过载状态,那么就会去争用锁(第228行),当然,实际上是争用监听套接口的监控权,争锁成功就会把所有监听套接口(注意:是所有的监听套接口,它们总是作为一个整体被加入或删除,下同)加入到自身的事件监控机制里(如果原本不在);争锁失败就会把监听套接口从自身的事件监控机制里删除(如果原本就在)。从函数ngx_trylock_ accept_mutex()的内部实现可以看到这一点,代码非常容易理解,画个流程图表示(剔除了异常流程),如图7-3所示。 变量 ngx_accept_mutex_held 的值用于标识当前是否拥有锁,注意这一点很重要,因为接着看第232~241 行的代码就是针对这一点处理的。如果当前拥有锁,则给 flags 变量打个NGX_POST_EVENTS 标记,这表示所有发生的事件都将延后处理(POST 有表示在…之后的意思)。这是任何架构设计都必须遵守的一个约定,即持锁者必须尽量缩短自身持锁的时间,Nginx的设计也不得例外,所以照此把大部分事件延迟到释放锁之后再去处理,把锁尽快释放,缩短自身持锁的时间能让其他进程尽可能的有机会获取到锁。如果当前进程没有拥有锁,那么就把事件监控机制阻塞点(比如 epoll_wait() )的超时时间限制在一个比较短的范围内(即ngx_accept_mutex_delay,可通过指令accept_mutex_delay配置,默认值为500毫秒),超时更快,那么也就更频繁地从阻塞中跳出来,也就有更多的机会去争抢到互斥锁。 没有拥有锁的进程接下来的操作与无负载均衡情况没有什么不同,所以下面开始重点介绍,拥有锁的进程对事件的处理,这也就是前面提到的延迟处理。当一个事件发生时,一般处理(即不做延迟)会立即调用事件对应的回调函数,而延迟处理则会将该事件以链表的形式缓存起来,可以看epoll模型里的代码作为示例。 556: 代码片段7.4.1-7,文件名: ngx_epoll_module.c 557: static ngx_int_t 558: ngx_epoll_process_events(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, ngx_msec_t timer, ngx_uint_t flags) 559: { 560: … 672: if (flags & NGX_POST_EVENTS) { 673: queue = (ngx_event_t **) (rev->accept ? 674: &ngx_posted_accept_events : &ngx_posted_events); 675: 676: ngx_locked_post_event(rev, queue); 677: 678: } else { 679: rev->handler(rev); 680: } 681: … 706: if (flags & NGX_POST_EVENTS) { 707: ngx_locked_post_event(wev, &ngx_posted_events); 708: 709: } else { 710: wev->handler(wev); 711: } 第679行和第710行是直接调用事件回调函数进行处理,而另外的代码是进行事件缓存,即加到ngx_posted_accept_events链表(新建连接事件,也就是监听套接口上的发生的可读事件)或ngx_posted_events链表。 回到我们讨论的最初函数ngx_process_events_and_timers(),看最后一点相关内容。 199: 代码片段7.4.1-8,文件名: ngx_event.c 200: void 201: ngx_process_events_and_timers(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) 202: { 203: … 247: (void) ngx_process_events(cycle, timer, flags); 248: … 254: if (ngx_posted_accept_events) { 255: ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_accept_events); 256: } 257: 258: if (ngx_accept_mutex_held) { 259: ngx_shmtx_unlock(&ngx_accept_mutex); 260: } 261: … 269: if (ngx_posted_events) { 270: … 274: ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_events); 275: … 276: } 在 ngx_process_events()函数调用里已经将所有事件缓存起来,接下来先处理新建连接缓存事件 ngx_posted_accept_events,此时还不能释放锁,因为我们还在处理监听套接口上的事件,还要读取上面的请求数据,所以必须独占,一旦缓存的新建连接事件全部被处理完就必须马上释放持有的锁了,因为连接套接口只可能被某一个进程自始至终的占有,不会出现多进程之间的相互冲突,所以对于连接套接口上事件ngx_posted_events的处理可以在释放锁之后进行,虽然对于它们的具体处理与响应是最消耗时间的,不过在此之前已经释放了持有的锁,所以即使慢一点也不会影响到其他进程。 补充两点。第一,如果在处理新建连接事件的过程中,在监听套接口上又来了新的请求会怎么样?这没有关系,当前进程只处理已缓存的事件,新的请求将被阻塞在监听套接口上,而前面曾提到监听套接口是以水平方式加入到事件监控机制里的,所以等到下一轮被哪个进程争取到锁并加到事件监控机制里时才会触发而被抓取出来。第二,第259行只是释放锁而并没有将监听套接口从事件监控机制里删除,所以有可能在接下来处理ngx_posted_events缓存事件的过程中,互斥锁被另外一个进程争抢到并且把所有监听套接口加入到它的事件监控机制里。因此严格来说,在同一时刻,监听套接口可能被多个进程拥有,但是,在同一时刻,监听套接口只可能被一个进程监控(也就是epoll_wait()这种),因此进程在处理完ngx_posted_events缓存事件后去争用锁,发现锁被其他进程占有而争用失败,会把所有监听套接口从自身的事件监控机制里删除,然后才进行事件监控。在同一时刻,监听套接口只可能被一个进程监控,这也就意味着Nginx根本不会受到惊群的影响,而不论Linux内核是否已经解决惊群问题。 关于多核平台的优化,说起来内容比较多,但最核心的思路就是per-cpu化处理,小到程序内部变量,大到架构设计都是如此,只有这样才有可能做到性能按CPU线性扩展。 Nginx在多核平台上针对负载均衡和优化所做的工作,就是提供有worker_cpu_affinity配置指令,利用该指令可以将各个工作进程固定在指定的CPU核上执行。可以看到,这也是一种per-cpu 化处理,对于此有个较为通俗的名称叫做CPU affinity,即CPU 亲和性。 CPU亲和性,简单点说就是让某一段代码/数据尽量在指定的某一个或几个CPU核心上长时间运行/计算的机制。Nginx 把工作进程绑定到指定CPU 是CPU affinity的其中一种应用,另外一种典型应用就是网卡收发包时硬中断的多CPU绑定等,这样做的最直观好处就是能够大大提高CPU cache 的命中率,提高性能。 关于CPU亲和性的使用介绍以及CPU cache对性能的影响,请参考相应的Man手册或这里[10]。下面仅看一下Nginx内CPU亲和性的使用配置,其实非常简单,首先根据系统CPU个数设定工作进程数目,我这里只有两个核,所以就指定2个工作进程(也可以指定4、6、8等,除非是有其他特别的原因,否则在一般情况下,进程数与系统CPU数一致即可,太多反而可能会导致进程切换频繁,使得整体性能下降),并且要让工作进程0运行在0号CPU上,工作进程1运行在1号CPU上(都是从0开始编号)。 00: 代码片段7.4.2-1,文件名: nginx.conf 01: worker_processes 2; 02: worker_cpu_affinity 01 10; worker_cpu_affinity指令的配置值是位图表示法,从前往后分别是0号工作进程、1号工作进程…n号工作进程的CPU二进制掩码(各个掩码之间用空格隔开),所以这里0号工作进程的CPU掩码为01,表示其使用0号CPU,1号工作进程的CPU掩码为10,表示其使用1号CPU;如果哪个工作进程的CPU掩码为11,则表示其既使用0号CPU,又使用1号CPU。 使用这个配置文件来执行Nginx,利用ps的-F选项查看,如图7-4所示。 PSR列对应的就是进程所在CPU号,可以看到0号工作进程(即2224)的CPU号为0,而1号工作进程(即2225)的CPU号为1。 将配置修改一下:worker_cpu_affinity1001;。重启Nginx 再看,如图7-5所示。 事件超时意味着等待的事件没有在指定的时间内到达,Nginx有必要对这些可能发生超时的事件(下面统称为超时事件对象)进行统一管理,并在发生事件超时时做出相应的处理,比如回收资源,返回错误等。举个具体例子来说,当客户端对Nginx发出请求连接后,Nginx就会accept()并建立对应的连接对象 connection、读取客户端请求的头部信息。而读取这个头部信息显然是要求在一定的时间内完成,如果在一个有限的时间内没有读取到头部信息或读取的头部信息不完整,那么Nginx就无法进行正常处理,并且应该认为这是一个错误/非法的请求,直接返回错误信息("Requesttimeout"(408))并释放相应的资源,如果Nginx不这样做,那么针对如此的恶意攻击就很容易实施。当然,其他需要进行事件超时监控的地方还有很多,比如读取客户端请求体数据、回写响应数据、管道通信等,下面就看Nginx是如何对这些超时事件对象进行统一超时管理的。 对于超时管理,无非要解决两个问题:第一,超时事件对象的组织,Nginx 采用的是红黑树(本节如无特殊说明,提到红黑树就是指这颗树);第二,超时事件对象的超时检测。Nginx提供了两种方案。一种是定时检测机制,通过设置定时器,争取在每过一定的时间就对红黑树管理的所有超时事件对象进行一次超时扫描检测。另一种方案是先计算出距离当前最快发生超时的时间是多久,假设时间为t秒,那么就等待t秒(通过设定事件处理模型所对应的接口,比如epoll_wait()最长阻塞t秒)后去进行一次超时检测。 先看超时事件对象的组织结构红黑树,我们知道 Nginx 把事件封装在一个名为ngx_event_s的结构体内,而该结构体有几个字段与Nginx的超时管理联系紧密。 37: 代码片段7.5-1,文件名: ngx_event.h 38: struct ngx_event_s { 39: … 67: unsigned timedout:1; 68: unsigned timer_set:1; 69: … 134: ngx_rbtree_node_t timer; 其中 timedout 域字段用于标识当前事件是否已经超时,0 为没有超时;timer_set 域字段用于标识当前事件是否已经加入到红黑树管理,需要对其是否超时做监控,0 为没有加入;而timer字段,很容易看出它属于红黑树节点类型变量,红黑树就是通过该字段来组织所有的超时事件对象。 Nginx设置了两个全局变量以便在程序的任何地方都能快速地访问到这颗红黑树。 17: 代码片段7.5-2,文件名: ngx_event_timer.c 18: ngx_thread_volatile ngx_rbtree_t ngx_event_timer_rbtree; 19: static ngx_rbtree_node_t ngx_event_timer_sentinel; ngx_event_timer_rbtree封装了整棵红黑树结构,而ngx_event_timer_sentinel属于红黑树节点类型变量,在红黑树的操作过程中被当作哨兵节点[11]使用,同时注意到它是static的,所以作用域仅局限于ngx_event_timer.c源文件内。 红黑树的初始化函数 ngx_event_timer_init()是在 ngx_event_process_init()函数内被调用,所以每个工作进程都会在自身的初始化时建立这颗红黑树,如图7-6所示。 当需要对某个事件进行超时监控时,就会把它加入到这个红黑树内。仍以之前的例子来说,在Nginx调用accept()接受到客户端请求并建立对应的连接对象connection后,在连接对象的初始化函数ngx_http_init_connection()内,可以找到这么一行代码。 224: 代码片段7.5-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c 225: ngx_add_timer(rev, c->listening->post_accept_timeout); 这也就是将 rev 事件(触发该事件即表示客户端传来请求头等信息)对象加入到红黑树内进行超时管理,同时给它指定的超时时限为c->listening->post_accept_timeout(该变量的值可由用户通过client_header_timeout指令进行配置,默认情况下是60000毫秒)。 函数ngx_add_timer()完成将一个超时事件对象加入到红黑树的具体逻辑,代码非常简单,首先在对应树节点的 key 字段里记录超时时刻(在后续进行超时检测扫描时就需要该字段来进行时刻的先后比较),然后判断该超时事件对象是否已经加入到红黑树,如果是的话则需要先调用函数ngx_del_timer()将它从红黑树里移除,最后再调用ngx_rbtree_insert()函数将超时事件对象真正加入到红黑树。另外可以看到,这种加入是间接性的,根据前面的介绍可知,每个事件对象封装结构体都有一个timer字段,其为ngx_rbtree_node_t类型变量,加入到红黑树的就是这个字段,而非事件对象结构体本身。当然,可以通过利用offsetof宏来根据该timer字段快速方便地找到其所在的对应事件对象结构体,所以并不用为这种设计而担心。 具有四个节点的红黑树描述如图7-7所示。从该图中可以看到两点:第一,可以通过全局变量 ngx_event_timer_rbtree.root 快速定位到该红黑树的根节点;第二,从该红黑树根节点从左或从右遍历下去,最后都将到达全局变量 ngx_event_timer_sentinel 指定的末端树节点,这也是前面称ngx_event_timer_sentinel为哨兵节点的原因所在。 通过红黑树,Nginx对那些需要关注其是否超时的事件对象就有了统一的管理,Nginx可以选择在合适的时机对事件计时红黑树管理的事件进行一次超时检测,对于超时了的事件对象进行相应的处理。在前面曾提到过Nginx的超时检测方案有两种,下面就来分别介绍。 Nginx具体使用哪种超时检测方案主要取决于一个配置指令timer_resolution,比如 03: 代码片段7.5-4,文件名: nginx.conf 04: timer_resolution 100ms; 反映到Nginx代码逻辑内,也就是全局变量ngx_timer_resolution的值为100,再接下来分析,就又得看工作进程的核心处理函数ngx_process_events_and_timers()。 199: 代码片段7.5-5,文件名: ngx_event.c 200: void 201: ngx_process_events_and_timers(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) 202: { 203: … 206: if (ngx_timer_resolution) { 207: timer = NGX_TIMER_INFINITE; 208: flags = 0; 209: 210: } else { 211: timer = ngx_event_find_timer(); 212: flags = NGX_UPDATE_TIME; 213: … 247: (void) ngx_process_events(cycle, timer, flags); 可以看到ngx_timer_resolution变量是否为0主要影响了两个变量的值:timer和flags。先看非0情况,也就是超时检测方案1,此时flags值为0,可以认为这表示对其他地方代码逻辑无附加影响,而timer 为无限大(即#defineNGX_TIMER_INFINITE (ngx_msec_t) -1),而该值在 ngx_process_events()函数内将被用作事件处理机制被阻塞的最长时间,那么将 timer设置为无限大是否会使得工作进程在事件处理机制里“无限”等待而导致超时事件得不到及时处理呢?当然不会,先不说正常情况下,事件处理机制肯定会监控到某些I/O事件的发生,即便是因为服务器太空闲,没有任何 I/O 事件发生,工作进程也不会无限等待,因为工作进程在一开始就设置好了一个定时器,这实现在初始化函数ngx_event_process_init()内,关于这个函数前面曾多次提到,所以下面直接看相关代码。 642: 代码片段7.5-6,文件名: ngx_event.c 643: sa.sa_handler = ngx_timer_signal_handler; 644: … 652: itv.it_interval.tv_sec = ngx_timer_resolution / 1000; 653: itv.it_interval.tv_usec = (ngx_timer_resolution % 1000) * 1000; 654: itv.it_value.tv_sec = ngx_timer_resolution / 1000; 655: itv.it_value.tv_usec = (ngx_timer_resolution % 1000 ) * 1000; 656: 657: if (setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &itv, NULL) == -1) { 通过setitimer()函数设置的定时器会自动循环,所以每隔ngx_timer_resolution毫秒,工作进程就将收到一个定时事件,将其从事件处理机制的阻塞等待里唤醒出来(如果它正处于阻塞状态)。定时事件的回调函数为 ngx_timer_signal_handler(),该函数简单明了,仅设置一下标记:ngx_event_timer_alarm= 1;,如前所述,这非常符合信号中断处理函数的一般特点。 只有在ngx_event_timer_alarm为1的情况下,工作进程才会更新它的时间,也就是工作进程的时间粒度为ngx_timer_resolution。 573: 代码片段7.5-7,文件名: ngx_epoll_module.c 574: events = epoll_wait(ep, event_list, (int) nevents, timer); 575: 576: err = (events == -1) ? ngx_errno : 0; 577: 578: if (flags & NGX_UPDATE_TIME || ngx_event_timer_alarm) { 579: ngx_time_update(); 580: } 从上面代码可以看到,就算工作进程被 I/O 事件唤醒而执行到第578 行,但只要ngx_event_timer_alarm不为1就不会(从前面可知,在这里讨论的超时检测方案1下,第578行前半句判断为假)执行时间更新函数ngx_time_update(),从而导致下面的第262行也为假,超时检测函数ngx_event_expire_timers()也就不会执行到。 244: 代码片段7.5-8,文件名: ngx_event.c 245: delta = ngx_current_msec; 246: 247: (void) ngx_process_events(cycle, timer, flags); 248: 249: delta = ngx_current_msec - delta; 250: … 262: if (delta) { 263: ngx_event_expire_timers(); 264: } 如果经过了ngx_timer_resolution毫秒,执行了定时函数ngx_timer_signal_handler(),设置了ngx_event_timer_alarm值为1,又更新了时间,那么第263行的超时检测函数ngx_event_expire_timers()自然会被执行到,这无需多说,下面再来看ngx_timer_resolution为0的情况,即超时检测方案2。 在超时检测方案2里,timer的值设置为最快发生超时的事件对象的超时时刻与当前时刻的时间差。举个例子来说,比如红黑树管理着三个事件a、b、c,它们分别将在5000、6000、7000毫秒后超时,那么距离当前最快发生超时的就是事件a,而事件a的超时时刻与当前时刻的时间差为5000毫秒,因此变量timer的值就将被设置5000。timer值的具体计算实现在函数ngx_event_find_timer()内,该函数从红黑树内找到key值最小(key值记录的就是事件的超时时刻,那么该值最小的节点表示的也就是距离当前最快发生超时的事件)的节点,然后用该节点的key值减去当前时刻(ngx_current_msec,事实上由于该值并不是完全实时的,所以和精确的当前时刻会有一些偏差,不过不影响)即得到预期的timer值。预期的timer值可能为负数,这表示已经有事件超时了,因此直接将timer值设置为0,那么事件处理机制在开始监控I/O事件时会立即返回,以便能马上处理这些超时事件。另一个变量flags被标记为NGX_UPDATE_TIME,从前面第578行代码可以看到函数ngx_time_update()将被执行,时间被更新,也就是说事件处理机制每次返回都会更新时间,如果I/O事件比较多(比如客户端请求非常多),那么将会导致比较频繁地调用gettimeofday()系统函数[12],这也可以说是超时检测方案2对性能影响的最大缺点[13]。 回过头来看超时检测方案 1,简单直观、容易理解,但有可能导致一些超时事件得不到及时的处理,不过这并不会造成多大问题,如果不放心则可以根据应用环境通过配置指令timer_resolution适当地调整一下ngx_timer_resolution变量值即可。 来看最后一个需要讨论的问题,即对超时事件对象是否超时需进行的扫描检测以及对已超时事件对象的处理。由于工作进程利用红黑树来组织管理超时事件对象,因此检测是否有事件对象超时并不需要遍历扫描所有的超时事件对象,而直接找到最近的即将超时的超时事件对象,判断其是否超时,如果超时则将其移出红黑树、设置其超时标记(即将ev->timedout置为 1)并调用该事件对应的回调处理函数进行处理,处理完了再判断第二近的即将超时的超时事件对象,如此反复,直到遇到某个超时事件对象还未超时或所有超时事件对象都已超时并处理完毕就结束检测。这整个逻辑具体实现都在函数 ngx_event_expire_timers()内,流程图如图7-8所示。 注 释 [1].也有一些特别的流程是由Nginx在某些逻辑点上主动执行的,比如后面章节将介绍的子请求。 [2].http://lenky.info/tag/aio/ [3].http://www.xmailserver.org/linux-patches/nio-improve.html。 [4].定义在头文件/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h内,如果没有找到,则可以用命令“grep __FD_SETSIZE -R/usr/include/”搜索。 [5].https://lwn.net/Articles/520012/和https://lwn.net/Articles/520198/ [6].http://www.makelinux.net/books/lkd2/ch08lev1sec3 [7].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thundering_herd_problem [8].http://lenky.info/tag/thundering-herd-problem/ [9].本小节内容比较独立,与本章主题的关系不大,但因全书都没有特别合适的位置,而它又与负载均衡同为对工作进程的优化手段,所以也就放在这里了。 [10].http://lenky.info/?p=1262 和http://lenky.info/?p=310 [11].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sentinel_node [12].通过函数ngx_time_update()间接调用。 Nginx是以事件驱动的,也就是说Nginx内部流程的向前推进基本[1]都是靠各种事件的触发来驱动,否则Nginx将一直阻塞在函数epoll_wait()或sigsuspend()这样的系统调用上。Nginx工作进程内关注的事件主要有两类:I/O事件与定时器事件。比如,一个客户端请求到达后,当前拥有监听套接口的工作进程就将获得对应的可读事件,从而执行对应的回调函数,开始一个请求的处理与响应。本章将介绍Nginx如何对这些事件进行管理的相关机制。 前面已经讲过Nginx配置文件的解析过程,也就是Nginx如何在启动的过程中对用户设定的配置文件进行解析,并将配置文件中的各个配置项与配置值转换为对应的 Nginx 内部变量值,从而能让Nginx按照用户预想的情况去运行。 如果只是一些比较简单并且确定的功能配置需求,那么 Nginx 用户能够很方便地做出相应的设定,比如用户想要设置工作进程数为2个,那么配置文件中这样写即可。 worker_processes 2; 与此同理,Nginx 也很容易做到按用户的配置要求去执行,比如这里 Nginx 主进程也就只需执行且仅执行2次fork()函数来生成工作进程即可,具体实现可利用for循环并通过控制上限值来做到。 360: 代码片段8.1-1,文件名: ngx_process_cycle.c 361: for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { 362: … 365: ngx_spawn_process(cycle, ngx_worker_process_cycle, NULL, 366: "worker process", type); 在上面的源代码里,for循环的条件判断上限值n(也就是ccf->worker_processes)即为2,它是通过解析配置项worker_processes时根据用户的具体设定而赋值的。 如果是更高级一点的功能配置,比如当请求连接的客户端是IE浏览器时,Nginx能自动将请求文件重定向到/msie目录下,那么Nginx用户在配置文件里又该如何去表达这个逻辑呢?熟悉Nginx的用户肯定知道要实现这个需求,我们可以做如下配置[1]。 49: 代码片段8.1-2,文件名: nginx.conf 50: if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) { 51: rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break; 52: } 这样,我们用非IE浏览器访问该Web站点时,请求的文件来之其根目录,而用IE浏览器访问该Web站点时,请求的文件却来自其根目录下的msie文件夹(事实上,如果用IE浏览器做目录访问,即后面不带文件名,如果Nginx配置了index模块,那么访问可能会出现这样的错误:2012/05/25 11:19:25 [error] 4274#0: *3 open() "/usr/local/nginx/web/msie//msie//index.html" failed (2: No such file or directory), client: 192.168.164.1, server: localhost, request:"GET/ HTTP/1.1", host:"192.168.164.2"。可以看到是因为被映射了两次,即首先根目录匹配,由/映射为/msie/,然后被index模块改为/msie//index.html后重定向,又匹配到if条件被再次映射为/msie//msie//index.html 而导致路径错乱。关于这个错误以及官方提到的可以考虑用try_files替代if等暂不做过多讨论,本节仅以此作为示例讨论Nginx变量)。 从上面的配置内容来看,对于稍懂一点编程知识的人来说,直观上并没有什么难以理解的地方,首先判断客户端是否为IE浏览器,是则将URI重定向到msie文件夹,否则继续原URI 的操作,这看似非常简单的逻辑却至少需要一个东西的支撑,也就是必须要有一个符号(或别的什么)来代表客户端浏览器,Nginx用户才能在配置文件里表达类似“当‘客户端浏览器’是什么,Nginx就该怎么样,如果不是,Nginx又该怎么样”这样的语义,而这个符号也就是本节将要重点介绍的Nginx变量,如上面示例配置中的$http_user_agent就是一个Nginx变量。 对于Nginx而言,变量是指配置文件中以$开头的标识符(本章整个都不涉及SSI模块的变量,因为其比较独特),这和编程语言PHP里的变量命名要求基本一致,当然,Nginx变量的功能等各个方面肯定相对简单得多,这是不言而喻的,够用就好,毕竟 Nginx 的主要功能不在这里。 和其他编程语言里的变量意义一致,Nginx 的变量也同样是指明有一块内存空间,存放会根据情况发生变化的动态值。比如,对于变量$http_user_agent所代表的一块内存空间而言,客户端用IE浏览器访问时,其内存放的值为MSIE,用非IE浏览器访问时,其内存放的值也许就变化为Opera或Safari等(根据客户端具体浏览器类型而定),但肯定就不是MSIE了,否则上下文中的if判断逻辑将失去它的作用,用户的设置也将失效。 不像PHP或C语言那样拥有众多的变量类型,Nginx只有一种变量类型,即字符串,而且既然变量是用在配置文件中,那么根据曾在配置解析一章的讲解,变量值字符串加或者不加引号,加双引号或单引号都没有什么影响,除非字符串内包含有空格,需要利用引号或用转义字符(\)将它前后的字符连成一个字符串。 Nginx 变量所代表的内存里存放的字符串当然不是凭空生成的,就像是在C语言里,我们定义一个变量后总会直接或间接的给它赋值,否则读取出来的就是垃圾数据,所以 Nginx变量也会被赋值。不过这种赋值大部分情况下是自动的,并且是延后的。 自动赋值的意思很简单,比如在上面的示例中,在整个配置文件内,我们都没有对变量$http_user_agent 进行赋值操作,但是却可以直接拿它来用,因为我们知道在每一个客户端请求连接里,这个变量都会自动地被Nginx赋值,要么为MSIE,或Opera、或Safari等,当然,大家都知道原因,因为它是 Nginx 内部变量。其实,我们实际使用中,大部分情况也就是使用内部变量,一方面在于 Nginx 提供的内部变量非常多,基本考虑了大多数的使用场景,另一方面,如果你使用外部变量(或称之为自定义变量),那么就得给它赋值,如果是将一个确定的值(或内部变量)赋值给它,那么在使用这个变量的地方用这个确定的值(或内部变量)就行了,何必多此一举。当然,除非是要根据特殊逻辑组织多个不同的确定值和(或)内部变量在一起成一个新的变量,不过这种情况一般也都比较少。 延后赋值,专业术语叫惰性求值(Lazy Evaluation),其实说清楚了也容易懂,它是从性能上的考虑。Nginx光内部变量就有好几十个,如果每一个客户端请求,Nginx都去给它们赋好值,但是配置文件里却又根本没用到,这岂不是大大的性能浪费?所以,对于大部分变量,只有在真正去读它的值时,Nginx才会临时执行一段代码先给它赋上相应的值,然后再将结果返回(当然还有其他细节,比如如果之前Nginx已经给它赋好了值并且有效,就不用做第二次赋值,直接返回即可),这种优化与编程中的另一种常见技术,即写时复制(Copy On Write[2])有异曲同工之妙。 内部变量意味着变量名是预先定义好的,Nginx目前具体提供有哪些预定义好的内部变量以及每个变量的含义在官方wiki文档[3]上可以查看,也可以通过源代码(检索关键字:ngx_http_variable_t )根据变量名的英文单词猜测其代表的大致含义。除了http核心模块ngx_http_core_module提供了大量的内部变量之外,其他模块比如ngx_http_fastcgi_module、ngx_http_geoip_module等也有一些内部变量,如果我们自己开发Nginx模块,自然也可以提供类似这样的内部变量供用户在Nginx配置文件里使用。 除了内部变量之外,与之相对的就是外部变量(或称为自定义变量)。外部变量是Nginx用户在配置文件里定义的变量,因此变量名可由用户随意设定,当然也是要以$开头,并且得注意不要覆盖内部变量名。目前Nginx主要是通过ngx_http_rewrite_module模块的set指令来添加外部变量,当然也有其他模块比如ngx_http_geo_module来新增外部变量,这些在后面小节的分析中会看到其具体的实现。 任意一个变量都有其变量名和变量值, Nginx 与此对应的封装分别为结构体ngx_http_variable_s和ngx_variable_value_t。 16: 代码片段8.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_variables.h 17: typedef ngx_variable_value_t ngx_http_variable_value_t; 35: struct ngx_http_variable_s { 36: ngx_str_t name; /* must be first to build the hash */ 37: ngx_http_set_variable_pt set_handler; 38: ngx_http_get_variable_pt get_handler; 39: uintptr_t data; 40: ngx_uint_t flags; 41: ngx_uint_t index; 42: }; 27: 代码片段8.2-2,文件名: ngx_string.h 28: typedef struct { 29: unsigned len:28; 30: 31: unsigned valid:1; 32: unsigned no_cacheable:1; 33: unsigned not_found:1; 34: unsigned escape:1; 35: 36: u_char *data; 37: } ngx_variable_value_t; 可以看到这两个结构体并非只是简单地包含其名与值,还有其他相关的辅助字段,甚至结构体ngx_http_variable_s本身就包含一个data 字段,看似是用来存放变量值的地方,那为什么又还要一个专门的ngx_variable_value_t结构体来封装Nginx变量值呢?关于这个问题,在本节后面的讲解中会逐步清晰,这里暂且不讲。 在进行配置解析之前,Nginx 会统计其支持的所有内部变量,即在每个模块的回调函数module->preconfiguration 内,将模块自身支持的内部变量统一加入到 http 核心配置ngx_http_core_main_conf_t的variables_keys字段内。 149: 代码片段8.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_core.module.h 150: typedef struct { 151: … 157: ngx_hash_t variables_hash; 158: 159: ngx_array_t variables; /* ngx_http_variable_t */ 160: … 168: ngx_hash_keys_arrays_t *variables_keys; 169: … 175: } ngx_http_core_main_conf_t; 就以 http 核心模块 ngx_http_core_module 为例,其模块的 preconfiguration 回调函数为ngx_http_core_preconfiguration(),该函数就一条语句:调用ngx_http_variables_add_core_vars()函数,从而将自身支持的所有内部变量(组织在 ngx_http_core_variables 数组内)加入到cmcf->variables_keys变量内。 2014:代码片段8.2-4,文件名: ngx_http_variables.c 2015:ngx_int_t 2016:ngx_http_variables_add_core_vars(ngx_conf_t *cf) 2017:{ 2018:… 2022: cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); 2023: 2024: cmcf->variables_keys = ngx_pcalloc(cf->temp_pool, 2025: sizeof(ngx_hash_keys_arrays_t)); 2026:… 2039: for (v = ngx_http_core_variables; v->name.len; v++) { 2040: rc = ngx_hash_add_key(cmcf->variables_keys, &v->name, v, 2041: NGX_HASH_READONLY_KEY); 2042:… 上面代码中,函数ngx_hash_add_key()是实际执行往变量cmcf->variables_keys内进行新增操作的函数,除了http 核心模块ngx_http_core_module以外,其他模块都会这么直接或间接地把自身支持的内部变量加到cmcf->variables_keys内,再比如ngx_http_proxy_module模块,其相关执行过程如下。 ngx_http_proxy_add_variables() -> ngx_http_add_variable() -> ngx_hash_add_key() 其中ngx_http_proxy_add_variables()是ngx_http_proxy_module模块的preconfiguration回调函数。不仅是内部变量,用户自定义的外部变量在配置文件的解析过程中也会被添加到cmcf->variables_keys内,这从外部变量的主要设置指令set的回调函数ngx_http_rewrite_set()的内部实现即可看出。 ngx_http_rewrite_set() -> ngx_http_add_variable() -> ngx_hash_add_key() 总之,当Nginx解析配置正常结束时,所有的变量都被集中在cmcf->variables_keys内,那这有什么作用呢?继续来看。 Nginx 在配置文件的解析过程中会遇到用户使用变量的情况,如最前面的配置示例中使用了变量$http_user_agent ,所有这些被用户在配置文件里使用的变量都会先通过ngx_http_get_variable_index()函数而添加到cmcf->variables 内。如果配置文件中出现:set $filet_a;,在这里这个$file变量既是定义,又是使用,先定义它,然后把字符串"t_a"赋值给它,这也是一种使用,所以它会被加入到cmcf->variables内,可以简单地认为Nginx在解析配置文件的过程中遇到的所有变量都会被加入到 cmcf->variables 内。有些变量虽然没有出现在配置文件内,但是以Nginx默认设置的形式出现在源代码里,比如ngx_http_log_module模块内的ngx_http_combined_fmt全局静态变量里就出现了一些Nginx变量。 189: 代码片段8.2-5,文件名: ngx_http_log_module.c 190: static ngx_str_t ngx_http_combined_fmt = 191: ngx_string("$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] " 192: "\"$request\" $status $body_bytes_sent " 193: "\"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\""); 它们同样也会被加入到 cmcf->variables 中。另外,有些变量是模块自身特有的,比如ngx_http_log_module模块内的$time_local变量,其模块自身具有专有逻辑来独自处理,从而没有加入到 cmcf->variables 内(可以看到,Nginx 的哲学是怎么高效就怎么做,除非是对代码框架影响特别大,这也是我们在看源代码的过程中要注意的,所以我的描述也只能针对大多数情况,即便是我在叙述的过程中使用了“全”、“都”这样的字词也不代表就是绝对如此)。这些和我前面描述的一致,虽然 Nginx 默认提供的变量有很多,但只需把我们在配置文件里真正用到了的变量给挑出来,当配置文件解析完后,所有用到的变量也被集中起来了。另外,所有这些变量需要检查其是否合法,因为 Nginx 不能让用户在配置文件里使用一个非法的变量,这就需要cmcf->variables_keys的帮忙。 这个合法性检测逻辑很简单,实现在函数ngx_http_variables_init_vars()内,其遍历cmcf->variables内收集的所有已使用变量,逐个去已定义变量cmcf->variables_keys集合里查找。如果找到则表示用户使用无误,如果没找到,则需要注意,这还只能说明它可能是一个非法变量。有一点之前一直没讲,那就是有一部分变量虽然没有包含在cmcf->variables_key内,但是它们却合法。这部分变量是以"http_"、"sent_http_"、"upstream_ http_"、"cookie_"、"arg_"开头的五类变量。这些变量庞大并且不可预知,不可能提前定义并收集到cmcf->variables_keys内,比如以"arg_"开头代表的参数类变量会根据客户端请求URI时附带的参数不同而不同,一个类似于“http://192.168.164.2/?pageid=2”这样的请求会自动生成变量$arg_pageid。因此还需判断用户在配置文件里使用的变量是否在这五类变量里,具体来说就是检测用户使用的变量名前面几个字符是否与它们一致(这也间接说明,用户自定义变量时最好不要以这些字符开头)。当然,如果用户在配置文件里使用了变量$arg_pageid,而客户端请求时却并没有带上pageid参数,此时变量$arg_pageid值为空,但它总还算是合法的,但如果提示类似如下这样的错误,请需检查配置文件内变量名是否书写正确。 nginx: [emerg] unknown "x_var_test" variable 函数ngx_http_variables_init_vars()在对已使用变量进行合法性检测的同时,对于合法的使用变量会将其对应的三个主要字段设置好,即 get_handler()回调、data 数据、flags 旗标。从前面给出的结构体ngx_http_variable_s定义来看,name存储的是变量名字符串,index存储的是该变量在cmcf->variables内的下标(通过函数ngx_http_get_variable_index()获得),这两个都是不变的,而set_handlerr()回调目前只在使用set配置指令构造脚本引擎时才会用到,而那里直接使用 cmcf->variables_keys 里对应变量的该字段,并且一旦配置文件解析完毕, set_handlerr()回调也就用不上了,所以只有剩下的三个字段才需要做赋值操作,即从cmcf->variables_keys 里对应变量的对应字段拷贝过来,或是另外五类变量就根据不同类别进行固定的赋值。 先看 flags 旗标字段,这里涉及到的旗标主要是两个。一个为 NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE,表示该变量可重复添加,该标记影响的逻辑主要是变量添加函数 ngx_http_add_variable()。比如如下配置不会出错,因为 set 指令新增的变量都是 NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE的。 6,文件名: nginx.conf49: 代码片段8.2- 50: set $file t_a; 51: set $file t_b; 此时,set指令会重复添加变量$file(其实,第51行并不会新增变量$file,因为在新增的过程中发现已经有该变量了,并且是NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE的,所以就返回该变量使用),并且其最终值将为t_b。如果新增一个不是NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE的变量$t_var,那么Nginx 将提示theduplicate"t_var" variable 后退出执行。 另一个标记为NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE,表示该变量不可缓存。我们都知道,所有这些变量基本都是跟随客户端请求的每个连接而变的,比如变量$http_user_agent 会随着客户端使用浏览器的不同而不同,但是在客户端的同一个连接里,这个变量肯定不会发生改变,即不可能一个连接前半个是IE浏览器而后半个是Opera浏览器,所以这个变量是可缓存的,在处理这个客户端连接的整个过程中,变量$http_user_agent 值计算一次就行了,后续使用可直接使用其缓存。然而,有一些变量,因为 Nginx 本身的内部处理会发生改变,比如变量$uri,虽然客户端发过来的请求连接URI是/thread-3760675-2-1.html,但通过rewrite一转换却变成了/thread.php?id=3760675&page=2&floor=1,也即是变量$uri发生了改变,所以对于变量$uri,每次使用都必须进行主动计算(即调用回调 get_handler()函数),该标记影响的逻辑主要是变量取值函数ngx_http_get_flushed_variable()。当然,如果我们明确知道当前的细节情况,此时从性能上考虑,也不一定就非要重新计算获取值,比如刚刚通过主动计算获取了变量$uri的值,接着马上又去获取变量$uri的值(这种情况当然有,例如连续将$uri变量的值赋值给另外两个不同变量),此时可使用另外一个取值函数 ngx_http_get_indexed_variable(),直接取值而不考虑是否可缓存标记。 再来看 data 数据字段,这个字段指向存放该变量值的地方,具体点说是指向结构体ngx_httpr_equest_t变量r中的某个字段。我们知道(或者将要知道,下文会讲到)一个Nginx变量总是与具体的 http 请求绑定在一起的,一个 http 请求总有一个与之对应的ngx_http_request_t变量r,该变量r内存放有大量的与当前http请求相关的信息,而大部分Nginx变量的值又是与http请求相关的,简而言之,Nginx内置变量的值大部分直接或间接的来之变量r的某些字段内。举个例子,Nginx内部变量$args表示的是客户端GET请求时uri里的参数,熟悉结构体ngx_http_request_t定义的人知道该结构体有一个ngx_str_t类型字段为args,其内存放的就是GET请求参数,所以内部变量$args的这个data字段就是指向变量r里的args字段,表示其数据来之这里。这是直接的情况,那么间接的情况呢?看Nginx内部变量$remote_port,这个变量表示客户端端口号,这个值在结构体ngx_http_request_t内没有直接的字段对应,但是肯定同样也是来自ngx_http_request_t变量r里,怎么去获取就看get_handler()函数的实现,此时data数据字段没什么作用,值为0。 最后来看 get_handler()回调字段,这个字段主要实现获取变量值的功能。前面讲了Nginx内置变量的值都是有默认来源的,如果是简单地直接存放在某个地方(上面讲的内部变量$args情况),那么不要这个get_handler()回调函数倒还可以,通过data字段指向的地址读取。但是如果比较复杂,虽然知道这个值存放在哪儿,但是却需要比较复杂的逻辑获取(上面讲的内部变量$remote_port情况),此时就必须靠回调函数get_handler()来执行这部分逻辑。总之,不管简单或复杂,回调函数 get_handler()帮我们去在合适的地方通过合适的方式,获取到该内部变量的值,这也是为什么我们并没有给Nginx内部变量赋值,却又能读到值,因为有这个回调函数的存在。来看看这两个示例变量的 data 字段与get_handler()回调字段情况。 191: 代码片段8.2-7,文件名: ngx_http_variables.c 192: { ngx_string("args"), 193: ngx_http_variable_request_set, 194: ngx_http_variable_request, 195: offsetof(ngx_http_request_t s),, arg 196: NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE|NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE,0}, 197: … 555: static ngx_int_t 556: ngx_http_variable_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_variable_value_t *v, 557: uintptr_t data) 558: { 559: … 561: s = (ngx_str_t *) ((char *) r + data); 562: 563: if (s->data) { 564: … 568: v->data = s->data; 因为data字段的帮助,变量$args的get_handler()回调函数ngx_http_variable_request()的实现非常简单。 155: 代码片段8.2-8,文件名: ngx_http_variables.c 156: { ngx_string("remote_port"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_remote_port, 0, 0, 0 }, 157: ... 1039:static ngx_int_t 1040:ngx_http_variable_remote_port(ngx_http_request_t *r, 1041: ngx_http_variable_value_t *v, uintptr_t data) 1042:{ 1043: ngx_uint_t port; 1044:… 1059: kaddr->sa_family) {switch (r->connection->soc 1060: if (NGX_HAVE_INET6)1061:# 1062: case AF_INET6: 1063: sin6 = (struct sockaddr_in6 *) r->connection->sockaddr; 1064: port = ntohs(sin6->sin6_port); 1065: break; 1066:#endif 1067:… 1074: if (port > 0 && port < 65536) { 1075: v->len = ngx_sprintf(v->data, "%ui", port) - v->data; 1076: } 再看变量$remote_port的get_handler()回调函数ngx_http_variable_remote_port()的处理就比较麻烦了,上面只给出了部分代码,它根据不同的情况做不同的处理,此时 data 字段也没用了。另外,可以看到两个变量的回调函数都是通过传出参数 v 来将获取到的变量值返回。 一并再来看下set_handler(),这个回调目前只被使用在set指令里,组成脚本引擎的一个步骤,提供给用户在配置文件里可以修改内置变量的值,带有set_handler()接口的变量非常少,如变量$args、$limit_rate,且这类变量一定会带上 NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE 标记,否则这个接口毫无意义,因为既然不能修改,何必提供修改接口?也会带上 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE标记,因为既然会被修改,自然也是不可缓存的。下面看看变量$args的set_handler()接口函数ngx_http_variable_request_set()。 577: 代码片段8.2-9,文件名: ngx_http_variables.c 578: static void 579: ngx_http_variable_request_set(ngx_http_request_t *r, 580: ngx_http_variable_value_t *v, uintptr_t data) 581: { 582: ngx_str_t *s; 583: 584: s = (ngx_str_t *) ((char *) r + data); 585: 586: s->len = v->len; 587: s->data = v->data; 588: } 直接修改了结构体ngx_http_request_t变量r里的args字段(因为data会指向那里)。由此可以看到,不管从哪方面来讲,data字段都只是一个辅助get_handler()、set_handler()回调处理的指示字段,在调用这两个回调函数时,会把data指定传递进来,以明确指定变量值来源的地方,简化和统一这两个回调函数的逻辑,所以能看到大多数变量的get_handler()回调字段都是指向ngx_http_variable_header()、ngx_http_variable_request()这样的通用函数。其实,如果有必要,data 字段完全可以设置其他值以便传到 get_handler()、set_handler()这两个回调处理函数里,这就回答了前面的疑问:为什么结构体ngx_http_variable_s里已经包含有一个data字段了,Nginx还要弄一个专门的ngx_variable_value_t结构体封装来Nginx变量值,因为这两个data字段各自原本的作用就是不同的。 是否可以把ngx_variable_value_t结构体的所有字段都移到结构体ngx_http_variable_s内,将变量值和变量名组织在一起呢?非要这样做(假设合并而成的结构体为ngx_http_variable_name_value_t,有些重复字段要改一下,比如ngx_variable_value_t里的data改为value_data等),当然可以,但是如果那样设计的话,以现在的代码逻辑,在Nginx里使用Nginx变量名时,所有ngx_variable_value_t这些字段是否都会浪费(即它们用不上)?而当使用Nginx变量值时,那所有的ngx_http_variable_s那些字段又是多余(因为,此时那些字段也用不上)?举个例子,合并之后,对于变量$args,就有个对应的结构体变量 ngx_http_variable_name_value_t来统一描述它的名称和值,而我们知道变量是与请求相关联的,这也就是说Nginx工作进程当前有多少个客户端请求正在被处理,就有多少份$args变量,假设当前有 3 个客户端请求正在被处理,从而变量$args 也就有三份,对应结构体 ngx_http_variable_name_value_t 里的关于对变量名的描述就有三份,这岂不是大大浪费内存?这也违背高性能程序设计里同一份数据只存一份的一般性原则(因为存放多份一样的冗余数据,不管是生成、更新、维护都麻烦。当然,除非是有其他需求,比如稳定性或数据安全等)。按照现在Nginx对变量的设计,三个请求的$args变量如图8-1所示,可以看到$args变量名只存一份,而$args变量值根据每个请求而存三份,虚线箭头是指各个$args变量值根据$args变量名的data字段与http请求对象的args字段关联起来(调用get_handler()、set_handler()回调函数时,会把当前http请求对象r传递进去)。 如果合二结构体为一个,那么就是如图8-2所示的情况,相比现在的设计,多次保存$args变量名就是对内存的一种浪费。 现在,我们知道在 Nginx 内部,对于多个变量,其变量名只会保存一次,那么怎么把变量名和变量值对应起来呢?也就是说,比如要读取变量的值,该利用哪个变量名的get_handler()回调函数呢?关键点就在变量名里的index字段,关于这个字段在前面说过,它的值来自将变量添加cmcf->variables内时所对应的数组下标,比如假定cmcf->variables数组内当前已有6个Nginx变量,如果此时再新增一个使用变量$a,那么$a的index就是6(注意下标的序号是从0开始)。当然,在这里,为什么说index字段很关键,下面继续来看就会理解了。 继续来看函数 ngx_http_variables_init_vars()后面的逻辑,可以看到 cmcf->variables_keys变量指NULL,其原本实际所占的内存空间因为在cf->temp_pool内(函数ngx_http_variables_add_core_vars()的第2024行),所以在初始化基本结束后也会被释放掉(函数ngx_init_cycle()的第717行)。 41: 代码片段8.2-10,文件名: ngx_cycle.c 42: ngx_cycle_t * 43: ngx_init_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle) 44: { 45: … 717: ngx_destroy_pool(conf.temp_pool); 因此,关于Nginx变量,到最后,我们就剩下了一个cmcf->variables数组,里面存放了用户所有用到的变量,但是要清楚 cmcf->variables 数组存放的只是有可能被用到的变量,因为在实际处理客户端请求的过程中,根据请求的不同(比如请求地址、传递参数等)执行的具体路径也不相同,所以实际用到的变量也不相同。另外,刚刚讲了,cmcf->variables 数组存放的只是各个变量名(以及相关属性、回调字段),其变量值是通过另外一个结构体ngx_variable_value_t 变量来存储的,所以必须为这个变量申请对应的内存空间。这在 Nginx处理每一个客户端请求时的初始化函数ngx_http_init_request()内创建了这个存储空间。 236: 代码片段8.2-11,文件名: ngx_http_request.c 237: static void 238: ngx_http_init_request(ngx_event_t *rev) 239: { 240: … 478: r->variables = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, cmcf->variables.nelts 479: * sizeof(ngx_http_variable_value_t)); 这个变量和cmcf->variables是一一对应的,形成var_name与var_value对,所以两个数组里的同一个下标位置元素刚好就是相互对应的变量名和变量值,而我们在使用某个变量时总会先通过函数ngx_http_get_variable_index()获得它在变量名数组里的index下标,也就是变量名里的index字段值,然后利用这个index下标进而去变量值数组里取对应的值,这就解释了前面所提到的疑问。 对于子请求,虽然有独立的ngx_http_request_t对象r,但是却没有额的外创建r->variables,和父请求(或者说主请求)是共享的,这在ngx_http_subrequest()函数里可以看到相应的代码。 2365:代码片段8.2-12,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c 2366:ngx_int_t 2367:ngx_http_subrequest(ngx_http_request_t *r, 2368: ngx_str_t *uri, ngx_str_t *args, ngx_http_request_t **psr, 2369: ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *ps, ngx_uint_t flags) 2370:{ 2371:… 2373: ngx_http_request_t *sr; 2374:… 2386: sr = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t)); 2387:… 2455: sr->variables = r->variables; 针对子请求,虽然重新创建了 ngx_http_request_t 变量 sr,但子请求的 Nginx 变量值数组sr->variables 却是直接指向父请求的 r->variables。其实这并不难理解,因为父子请求的大部分变量值都是一样的,当然没必要申请另外的空间,而对于那些父子请求之间可能会有不同变量值的变量,又有NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE标记的存在,所以也不会有什么问题。比如变量$args,在父请求里去访问该变量值时,发现该变量是不可缓存的,于是就调用get_handler()函数从main_req对象的args字段(即r->args)里去取,此时得到的值可能是page=9999。而在子请求里去访问该变量值时,发现该变量是不可缓存的,于是也调用get_handler()函数从sub_req对象的args字段(即sr->args,注意对象sr与r之间是分隔开的)里去取,此时得到的值就可能是id=12。因而,在获取父子请求之间可变变量的值时,并不会相互干扰,如图8-3所示。 关于 Nginx 变量的基本支撑机制大概就是上面介绍的这些,另外值得说明的是,函数ngx_http_variables_init_vars()里还有一些没提到的代码以及相关逻辑,这包括旗标NGX_HTTP_VAR_INDEXED、NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOHASH、变量cmcf->variables_hash以及取值函数ngx_http_get_variable()等,它们都是为SSI模块实现而设计的,所以本章暂且不讲,否则夹杂在一起反而容易搞混,这里仅提醒注意一下。 有了对变量支撑机制的了解,下面就直接进入脚本引擎的主题,可通过“set $file t_a;”这个非常简单的实例来描述脚本引擎的大致情况。该实例虽然简单,但已包含脚本引擎处理的基本过程,更复杂一点的情况无非也就是回调处理多几重、相关数据多一点而已。 Nginx 在解析配置文件时遇到“set$file t_a;”这句配置项就会执行set 指令相应的回调函数ngx_http_rewrite_set(),下面开始逐步分析。 首先,value字符串数组(其实它本身只是一个字符串指针,但因为它指向的是数组变量cf->args的elts字段,所以可以认为它是一个数组。类似于这种细节,后面不再一一解释,请根据上下文环境自行理解)包含有三个元素,分别为set、$file、t_a,其中set是指令符号,抛开不管,所以第一个被处理的字符串为$file。我们知道set是用来设置自定义变量的,所以先判断变量名是否合法(即第一个字符是否为$符号),合法则利用函数ngx_http_add_variable()将它加入到变量集cmcf->variables_keys里,同时利用函数ngx_http_get_variable_index()将它也加入到已使用变量集cmcf->variables内并获取它的对应下标index,以便后续使用它。这些都是准备工作,其相关代码如下。 891: 代码片段8.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c 892: static char * 893: ngx_http_rewrite_set(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 894: { 895: … 905: if (value[1].data[0] != '$') { 906: … 914: v = ngx_http_add_variable(cf, &value[1], NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE); 915: … 919: index = ngx_http_get_variable_index(cf, &value[1]); 接下来就是构建“set $file t_a;”所对应的脚本引擎。脚本引擎是一系列的回调函数以及相关数据(它们被组织成 ngx_http_script_xxx_code_t 这样的结构体,代表各种不同功能的操作步骤),被保存在变量lcf->codes数组内,而ngx_http_rewrite_loc_conf_t类型变量lcf是与当前location相关联的,所以这个脚本引擎只有当客户端请求访问当前这个location时才会被启动执行。如下配置中,“set $filet_a;”构建的脚本引擎只有当客户端请求访问/t 目录时才会被触发,如果当客户端请求访问根目录时则与它毫无关系。 13: 代码片段8.3-2,文件名: nginx.conf 14: location / { 15: root web; 16: } 17: location /t { 18: set $file t_a; 19: } 这也可以说是 Nginx 变量惰性求值特性的根本来源,没触发脚本引擎或没执行到的脚本引擎路径,自然不会去计算其相关变量的值。 在函数 ngx_http_rewrite_set()接下来的逻辑里就是如何去构建相对应的脚本引擎,“set$filet_a;”配置语句比较简单,略去过多无关重要的细节,仅关注与其相关的关键执行代码路径,第一个重点关注逻辑在函数ngx_http_rewrite_value()内。 在代码片段8.3-4第933行可以看到该函数具体被调用时的上下文环境,这里直接看它的核心实现: 963: 代码片段8.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c 964: static char * 965: ngx_http_rewrite_value(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_rewrite_loc_conf_t *lcf, 966: ngx_str_t *value) 967: { 968: … 976: val = ngx_http_script_start_code(cf->pool, &lcf->codes, 977: sizeof(ngx_http_script_value_code_t)); 978: … 988: val->code = ngx_http_script_value_code; 989: val->value = (uintptr_t) n; 990: val->text_len = (uintptr_t) value->len; 991: val->text_data = (uintptr_t) value->data; 函数 ngx_http_script_start_code()利用 ngx_array_push_n()在 lcf->codes 数组内申请了sizeof(ngx_http_script_value_code_t)个元素,注意每个元素的大小为一个字节,所以其实也就是为ngx_http_script_value_code_t类型变量val申请存储空间(很棒的技巧)。接着第988行开始保存回调函数指针以及相关数据。 第二个重点关注的逻辑在函数 ngx_http_rewrite_set()内,其继续保存 ngx_http_script_xxx_code_t类结构体变量 891: 代码片段8.3-4,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c 892: static char * 893: ngx_http_rewrite_set(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) 894: { 895: … 933: if (ngx_http_rewrite_value(cf, lcf, &value[2]) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 934: … 951: vcode = ngx_http_script_start_code(cf->pool, &lcf->codes, 952: sizeof(ngx_http_script_var_code_t)); 953: … 957: vcode->code = ngx_http_script_set_var_code; 958: vcode->index = (uintptr_t) index; 逻辑很简单,利用函数ngx_http_script_start_code()为ngx_http_script_var_code_t类型变量vcode申请存储空间,然后保存回调函数以及相关数据。 根据“set $file t_a;”配置,其他未能执行到的代码路径被我略去了,总之,结果如图8-4所示,Nginx创建了两个结构体变量,并且设置好了字段值。 可以看到这两个结构体变量在地址空间上是连续存储的(图中,我特意把每个结构体字段的地址给标了出来),这一点非常重要,因为在脚本引擎实际执行时,回调函数前后的依次调用就靠这个来保证。到这里,对于配置项目“set$filet_a;”而言,整个set 指令就已完成了它原本的功能,对应的回调函数 ngx_http_rewrite_set()构建了这么一个脚本引擎的基础结构(每一个结构体变量代表脚本引擎的一个步骤),但这个脚本引擎还没“跑”起来。要让这个脚本引擎跑起来,我们把这个配置项目放到配置文件的某一个 location 下,然后去请求这个location,此时Nginx就会要执行这个配置语句,对应的脚本引擎自然也就“跑”起来了。 为了判断脚本引擎“跑”起来后的效果,我们需要查看变量$file的值,这可以借助互联网上提供的第三方开源模块,比如echo模块[4]。不过我们这里可以灵活利用一下rewrite指令即可,在配置文件里设定如下配置项。 13: 代码片段8.3-5,文件名: nginx.conf 14: location / { 15: root web; 16: } 17: location /t { 18: set $file t_a; 19: rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html?$file redirect; 20: root html; 21: } 这样,任何对 t 目录的访问都被无条件地重定向到根目录,并且将变量$file 的内容(这里也就是"t_a")以参数的形式带过去。由于redirect指令会以http状态码302来指示浏览器重新请求新的URI,因此我们能在浏览器地址栏里间接看到$file的值,比如wget看到的情况如图8-5所示。 前面章节曾讲过,Nginx将对客户端的连接请求响应处理分成11个阶段,每一个阶段可以有零个或多个回调函数进行专门处理,而在这里,当客户端对/t目录进行请求访问时,Nginx执行到NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE阶段的回调函数ngx_http_rewrite_handler(),就会触发该location上脚本引擎的执行。 135: 代码片段8.3-6,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c 136: static ngx_int_t 137: ngx_http_rewrite_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) 138: { 139: … 166: e->sp = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, 167: rlcf->stack_size * sizeof(ngx_http_variable_value_t)); 168: … 172: e->ip = rlcf->codes->elts; 173: … 178: while (*(uintptr_t *) e->ip) { 179: code = *(ngx_http_script_code_pt *) e->ip; 180: code(e); 181: } 代码第178~181行代表脚本引擎的执行,可以看到其逻辑也非常简单,因为刚提到脚本引擎各步骤在内存逻辑地址空间上连续,所以前一步骤的回调执行完后,指针偏移到下一步,然后判断是否有效,有效则接着执行,如此反复。由于每个步骤自身占据多大空间只有自己清楚,因此回调指针的偏移操作是由各个步骤自己来处理的。以这里的实例来看,第一个步骤对应的是结构体 ngx_http_script_value_code_t 变量,回调函数为 ngx_http_script_value_code()。 1650:代码片段8.3-7,文件名: ngx_http_script.c 1651:void 1652:ngx_http_script_value_code(ngx_http_script_engine_t *e) 1653:{ 1654: ngx_http_script_value_code_t *code; 1655: 1656: code = (ngx_http_script_value_code_t *) e->ip; 1657: 1658: e->ip += sizeof(ngx_http_script_value_code_t); 1659: 1660: e->sp->len = code->text_len; 1661: e->sp->data = (u_char *) code->text_data; 1662:… 1666: e->sp++; 1667:} 很容易看出来,上面代码中的第1658 行就是做回调指针偏移操作,加上当前结构体ngx_http_script_value_code_t 变量大小即可。另外,这也隐含默认所有的 ngx_http_script_xxx_code_t结构体第一个字段必定为回调函数指针,如果我们添加自己的脚本引擎功能步骤,这点就需要注意。 第一步骤的回调函数 ngx_http_script_value_code()处理完后,转到 ngx_http_rewrite_handler()函数的第178行判断,为真,所以接着执行结构体ngx_http_script_var_code_t变量的回调函数ngx_http_script_set_var_code(),同样做相应的偏移,再判断就会进入到rewrite指令所对应的处理步骤里。先不管后面步骤,只看与set指令相关的两个步骤,我们知道set指令是让Nginx 用户给变量赋值,这里“set $file t_a;”即是将字符串"t_a"赋值给变量$file,所以这个逻辑也就是实现在刚才的那两个步骤里,具体来说是两个函数 ngx_http_script_value_code()与ngx_http_script_set_var_code()。 在继续分析之前,需要先提一个变量e->sp,它是一个数组,在ngx_http_rewrite_handler()函数的第166 行申请空间,通过它来在脚本引擎的各个步骤之间进行数据的传递。对于它的使用,与数据结构中栈的操作一致,存入传递值就压栈,取传递值就退栈。比如看上面ngx_http_script_value_code()函数的实现代码,它将用户设定的值(用户在配置文件里设定的字符串"t_a"以及长度在Nginx解析配置文件时存在了ngx_http_script_value_code_t结构体变量的相关字段内)存起来,所以在第1660、1661以及1666行的代码,就是转存用户设定值并压栈(注意栈顶数据为空)。而函数ngx_http_script_set_var_code()就是取值退栈。 1669:代码片段8.3-8,文件名: ngx_http_script.c 1670:void 1671:ngx_http_script_set_var_code(ngx_http_script_engine_t *e) 1672:{ 1673:… 1676: code = (ngx_http_script_var_code_t *) e->ip; 1677: 1678: e->ip += sizeof(ngx_http_script_var_code_t); 1679:… 1682: e->sp--; 1683: 1684: r->variables[code->index].len = e->sp->len; 1685:… 1688: r->variables[code->index].data = e->sp->data; 变量code->index表示Nginx变量$file在cmcf->variables数组内的下标,对应每个请求的变量值存储空间就为 r->variables[code->index],这里从栈中取出数据并进行 C 语言变量普通意义上的赋值。 基本过程就是,利用ngx_http_script_value_code()函数将"t_a"存储到临时空间(e->sp栈),然后利用函数ngx_http_script_set_var_code()从临时空间(e->sp栈)取值放到变量$file内,整个set指令的逻辑工作得以完成。 更复杂一点的 Nginx 配置被解析后生成的脚本引擎及其执行,与上面的介绍并无特别大的差异,只是在脚本引擎的具体生成过程中可能会涉及到正则式的处理,比如 # rewrite /download/*/mp3/*.any_ext to /download/*/mp3/*.mp3 rewrite ^/(download/.*)/mp3/(.*)\..*$ /$1/mp3/$2.mp3 break; 前面的“^/(download/.*)/mp3/(.*)\..*$”就是一个正则匹配,^表示开头,$表示结尾, (download/.*)与(.*)分别对应后面的变量$1 ,$2 ,像这个路径:/download/20120805/mp3/sample.txt,其对应的变量$1的值为download/20120805,变量$2的值为sample,所以rewrite后的路径为/download/20120805/mp3/sample.mp3。关于这方面的更多内容不过多介绍,对于复杂脚本引擎感兴趣的或遇到实际问题的,可自行查看 Nginx相关源代码或Man 手册,我相信有了前面介绍的基础知识,那不会太难理解,无非是细节代码繁琐一点。 关于 Nginx 变量(或者说是其所在的脚本引擎)的执行顺序,是一个值得关注的话题,因为不理解它的内在原理,就容易让人在 Nginx 配置文件里实际使用变量时出现困惑。但对于Nginx本身来说,这也是自然而然的事情,在前面的模块解析一章曾描述过Nginx将对客户端请求的处理分成11个阶段,每一个阶段前后按序执行,那么与此对应的Nginx变量也将受此影响,而出现貌似不合常理的异常情况。举个实例来说,假设在 Nginx 配置文件里有这么一段配置(这段配置在实际使用中毫无用处,这里仅作问题描述)。 49: 代码片段8.4-1,文件名: nginx.conf 50: location / { 51: root web; 52: set $file index1.html; 53: index $file; 54: … 65: set $file index2.html; 66: … 第52行设置变量$file的值为index1.html,第53行再通过index配置指令来指定根目录的首页文件为变量$file(也就是index1.html),这是我们原本的意图。在接下来的配置里,变量$file的值又被修改作为他用,比如也许被修改为logs/root_access.log,然后用户access_log配置指令来指定根目录的访问日志文件。这里为了对比演示,我们直接把它设置为index2.html,并且index1.html和index2.html的文件内容也非常简单,分别为 [root@localhost web]# cat index1.html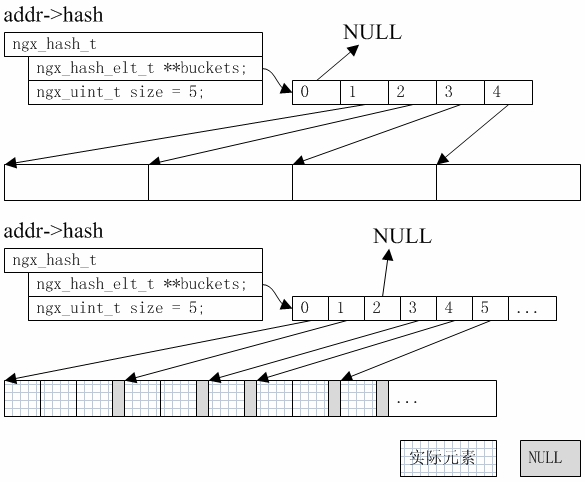 -
-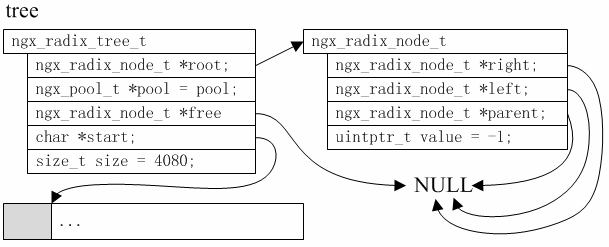 -
-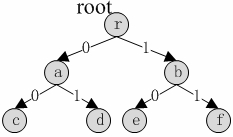 -
-第4章 数据结构
-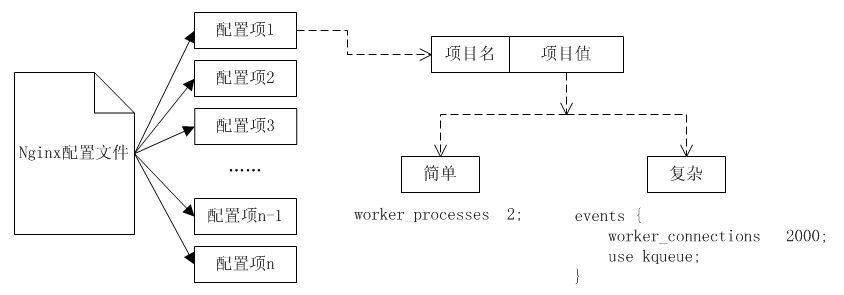 -
-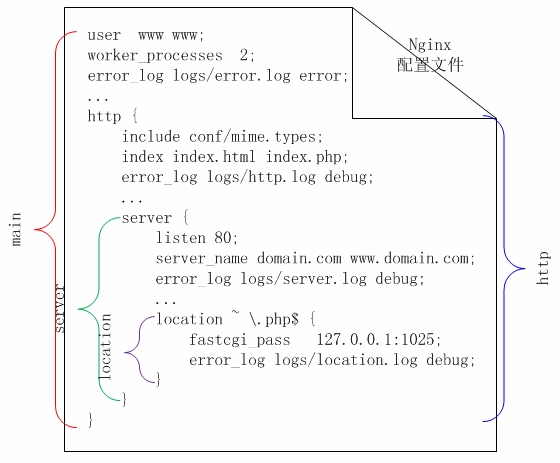 -
-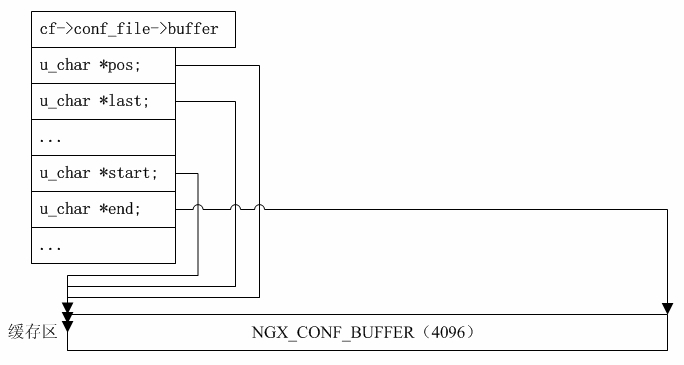 -
-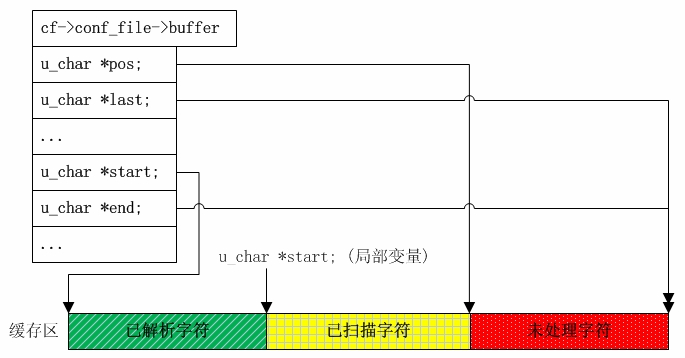 -
-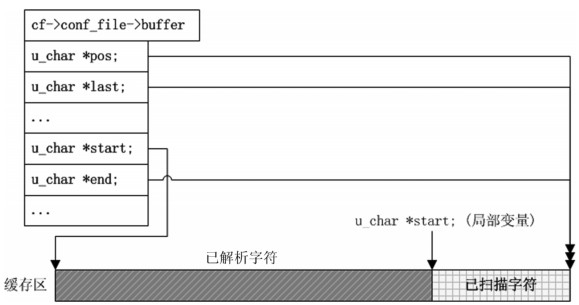 -
-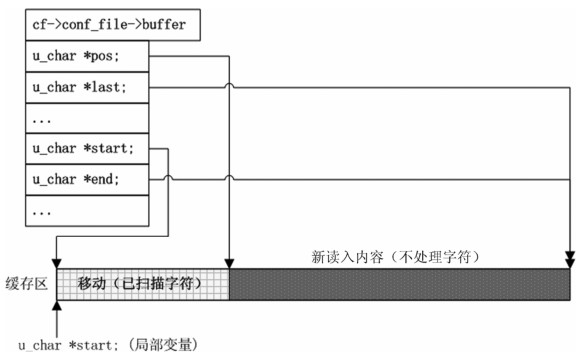 -
-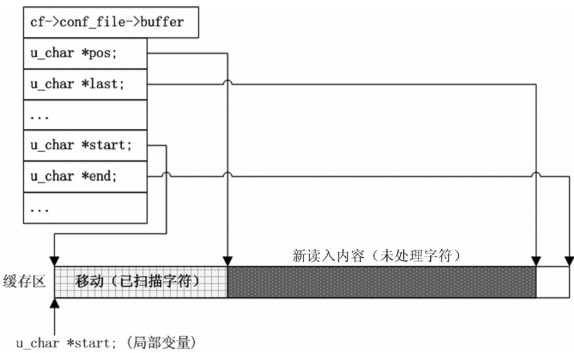 -
-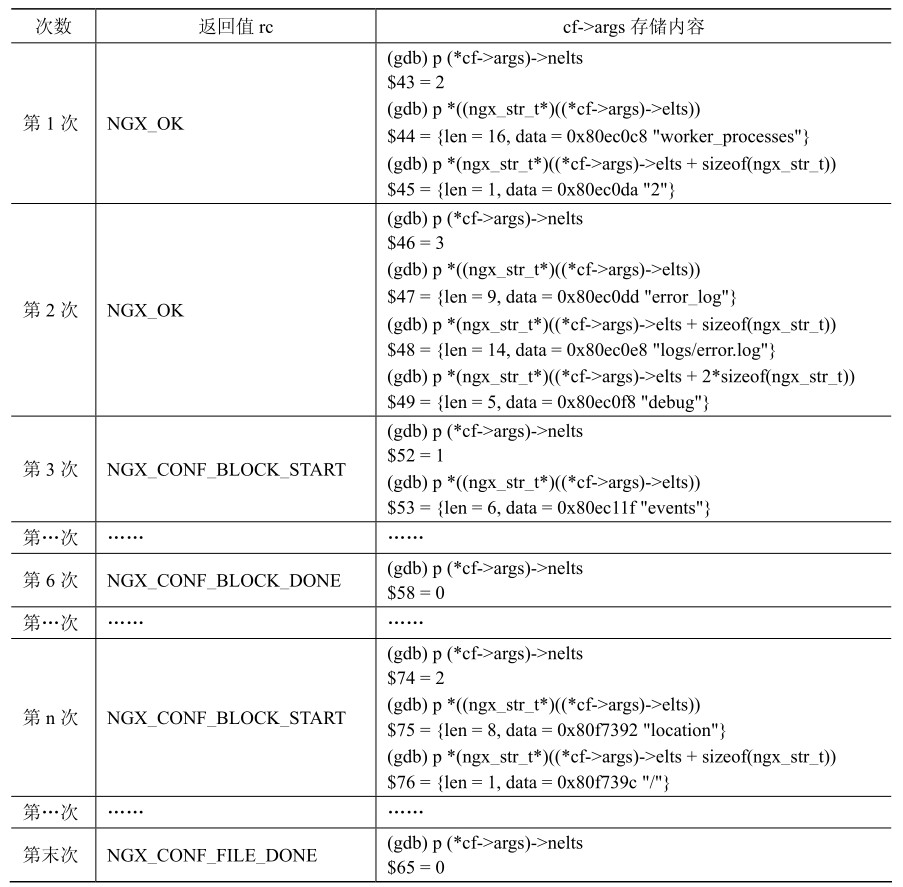 -
-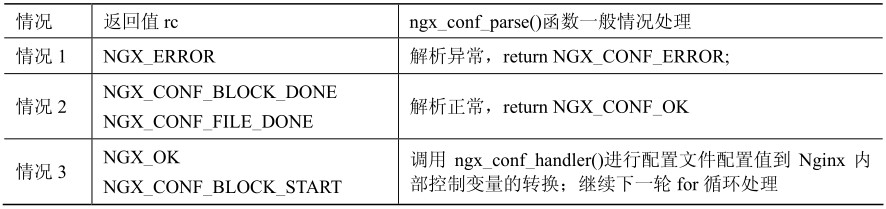 -
-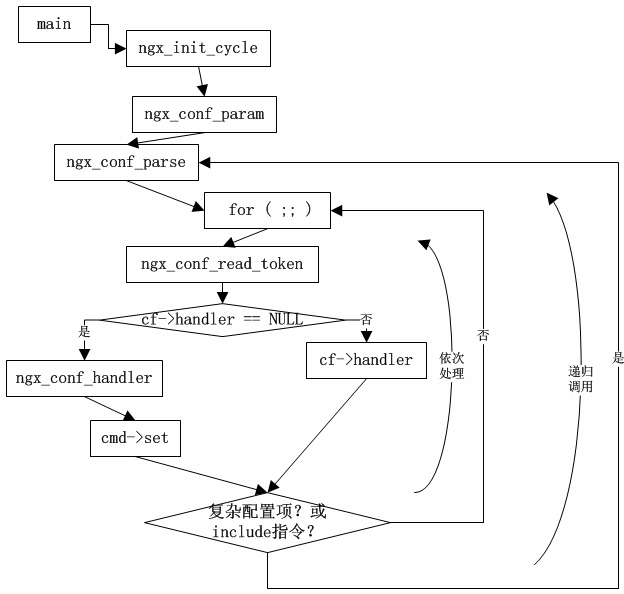 -
-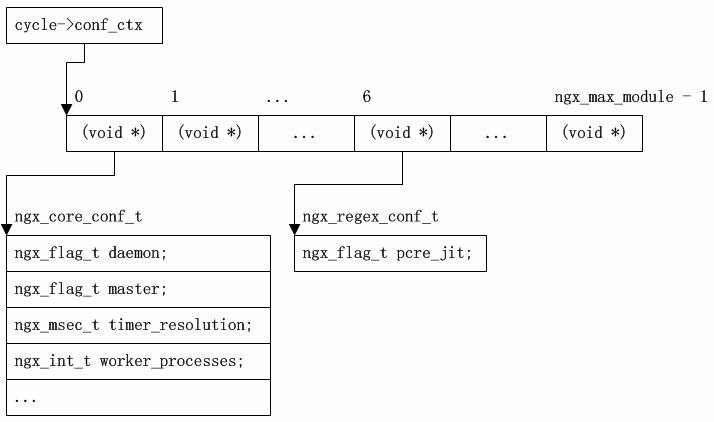 -
-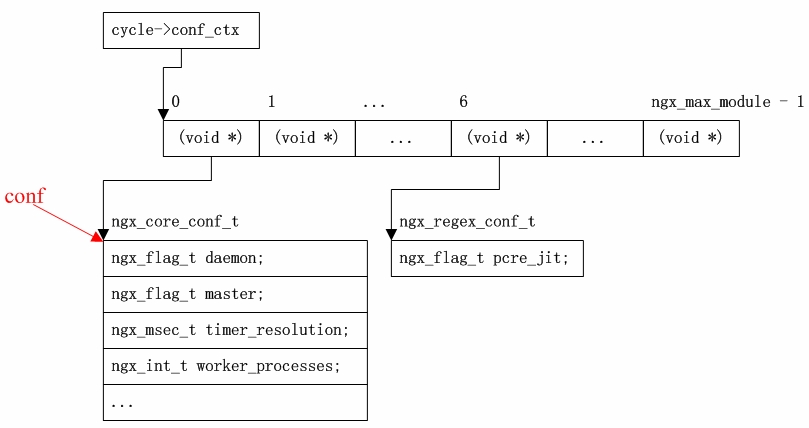 -
- -
- -
- -
-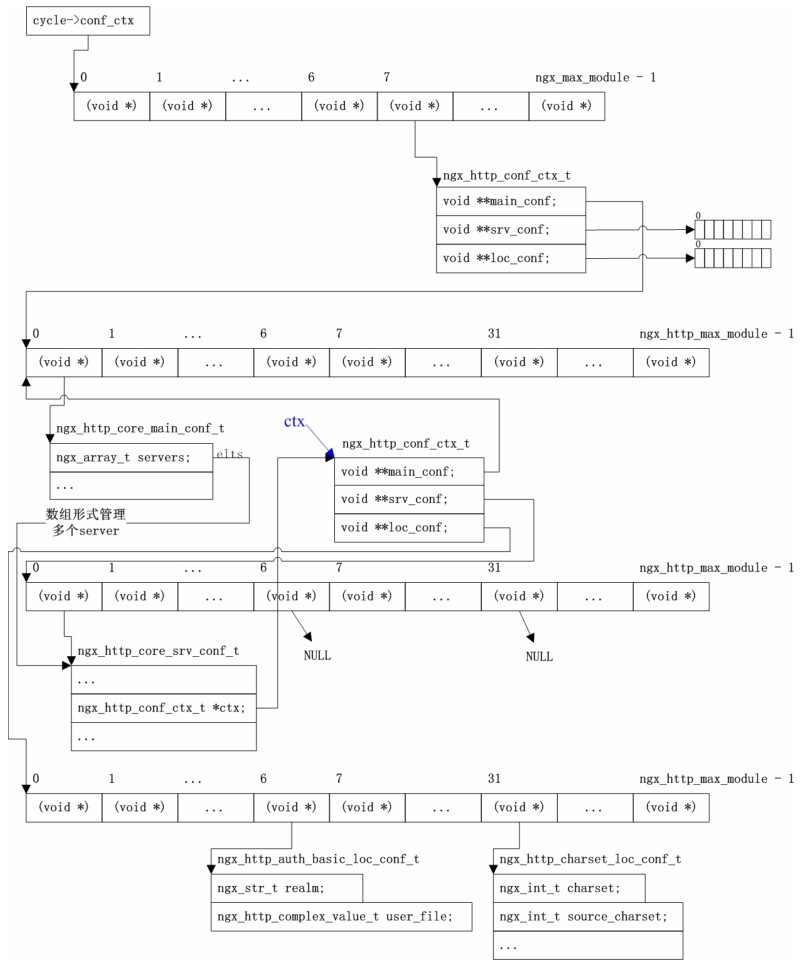 -
-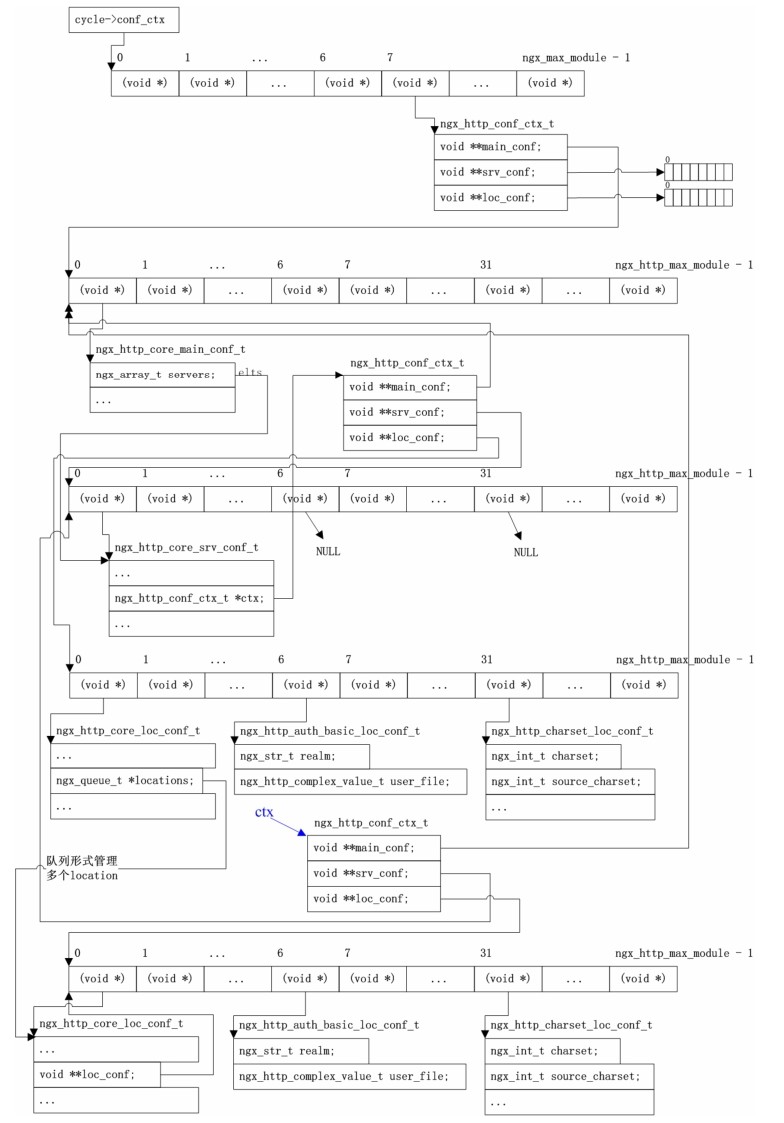 -
-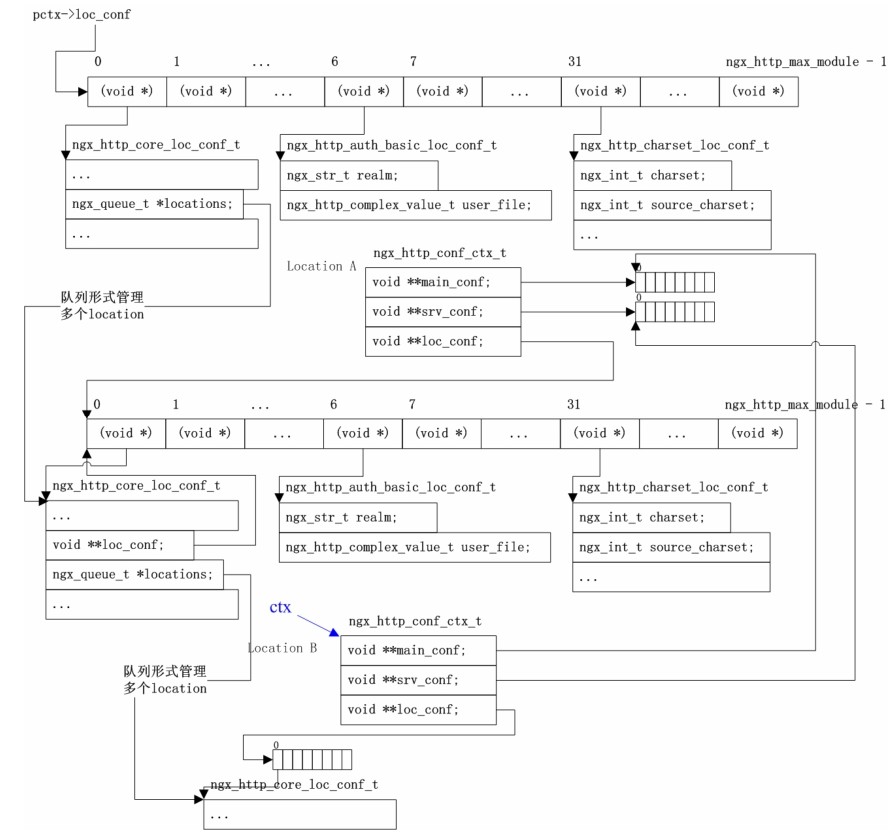 -
- -
-第5章 配置解析
-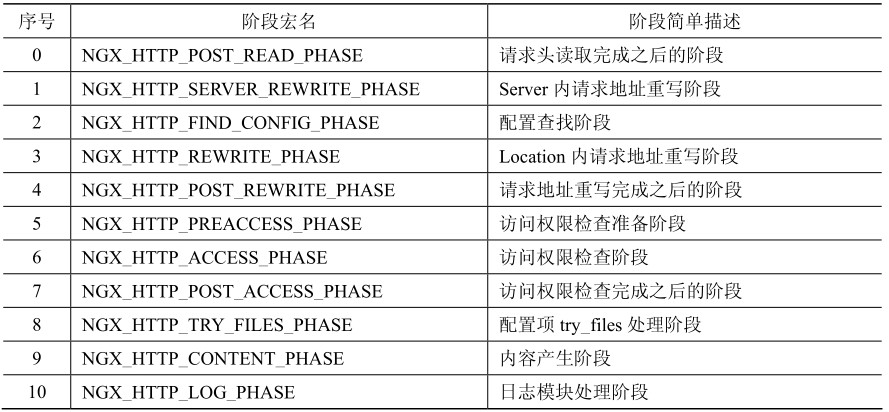 -
-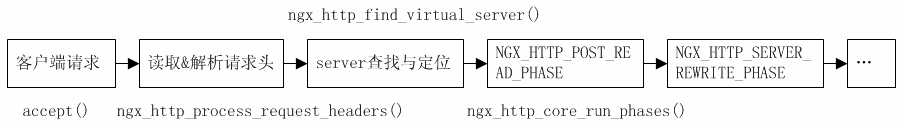 -
-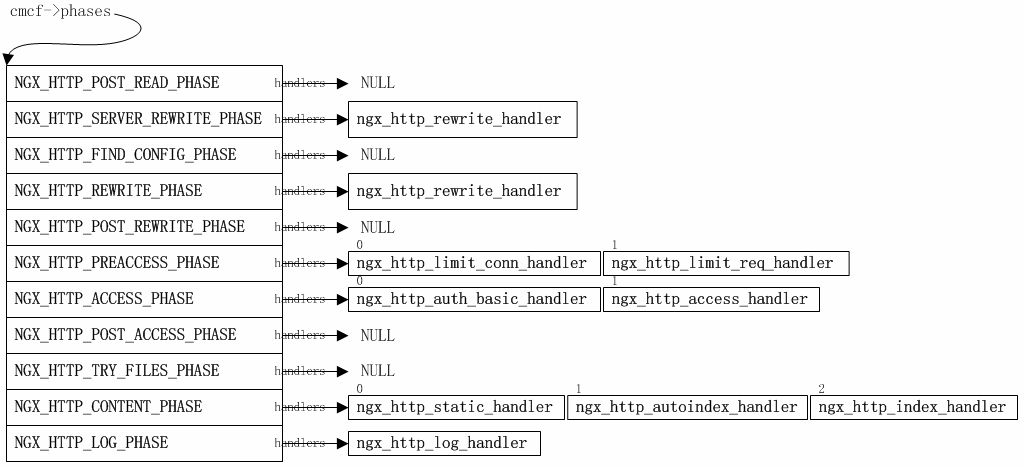 -
- -
-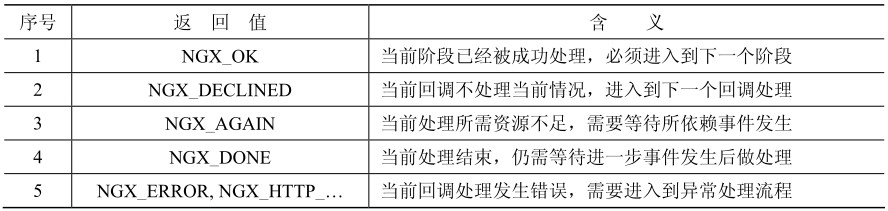 -
- -
-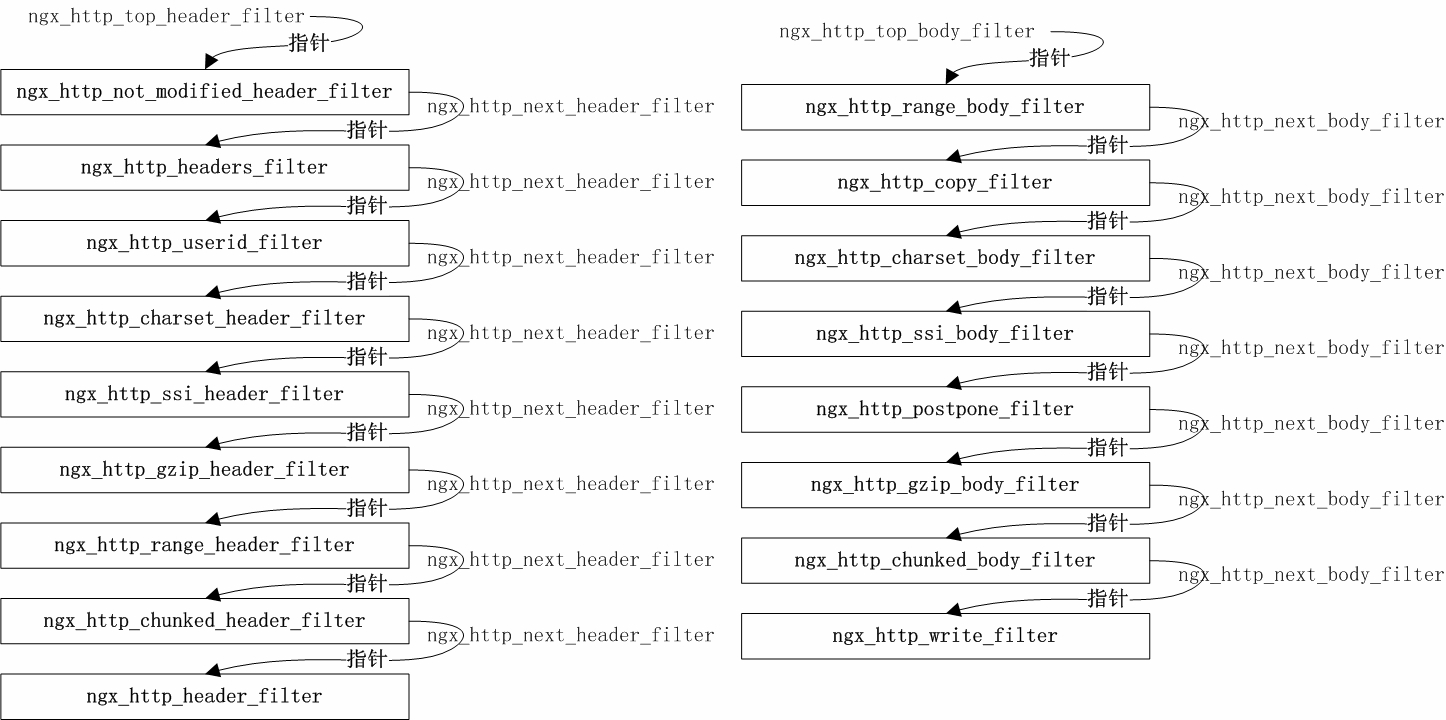 -
-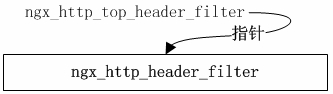 -
-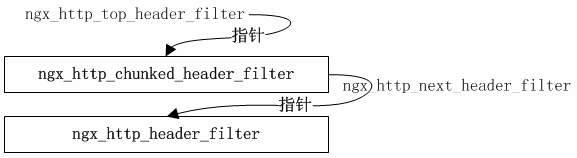 -
-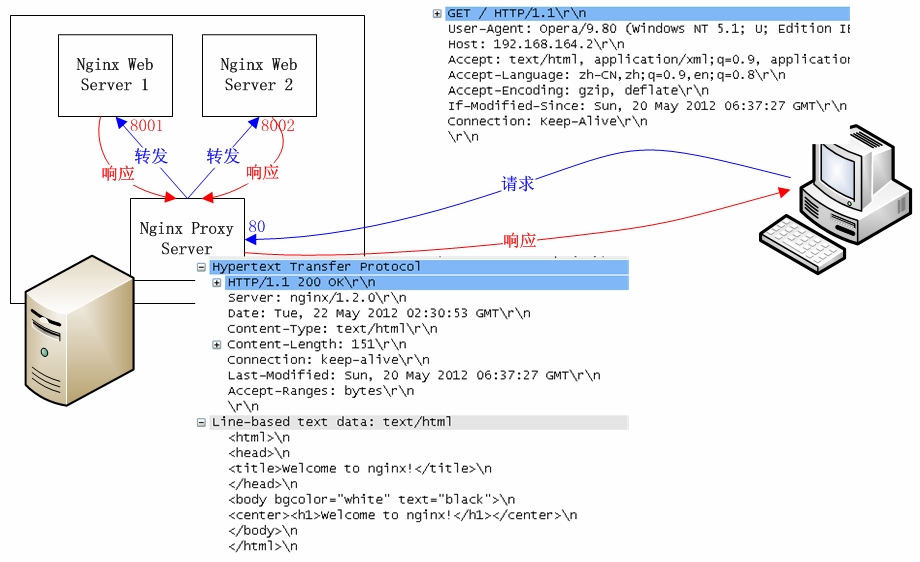 -
-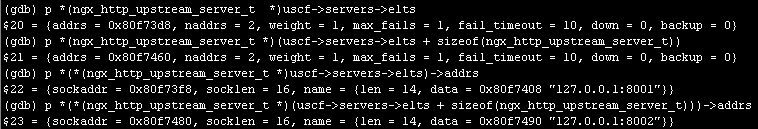 -
- -
-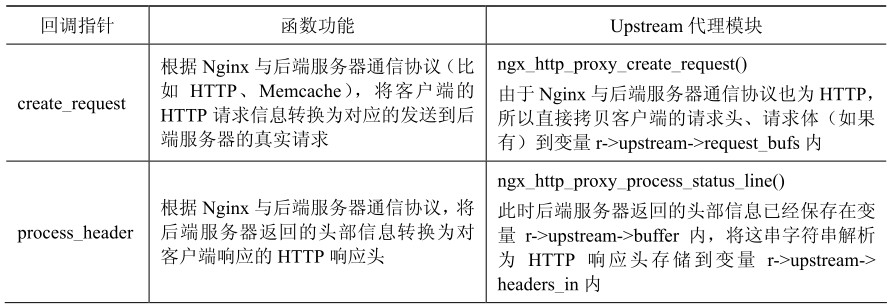 -
-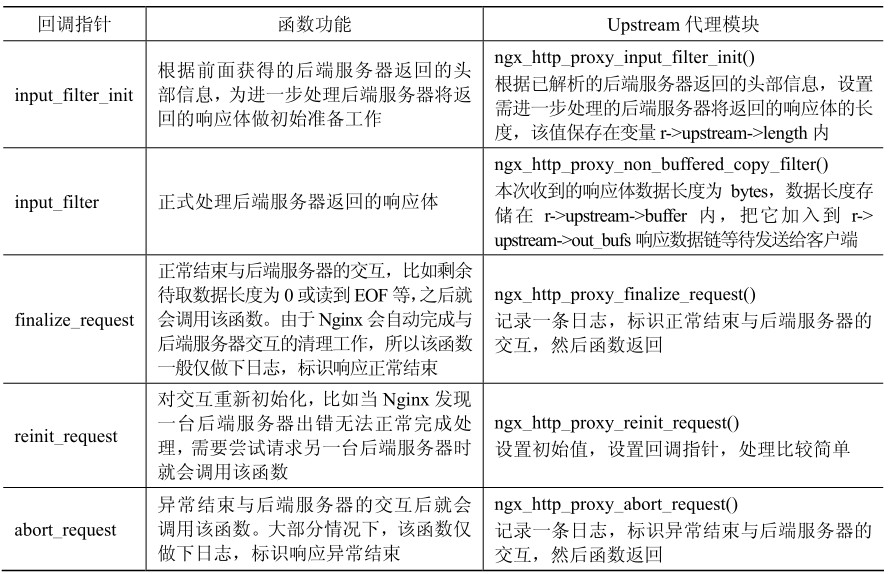 -
-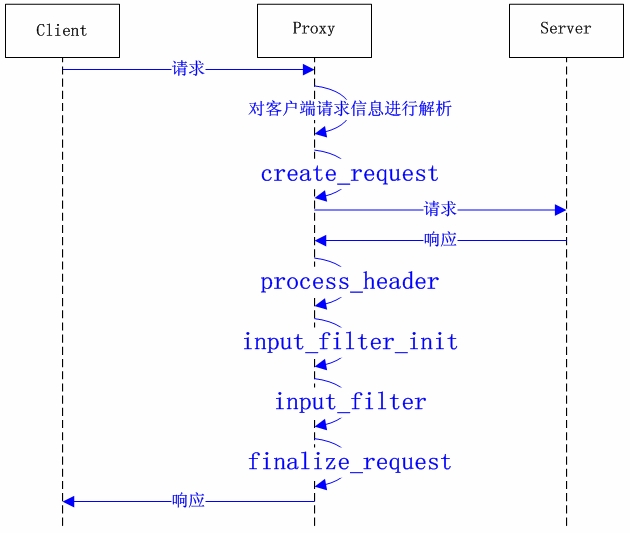 -
-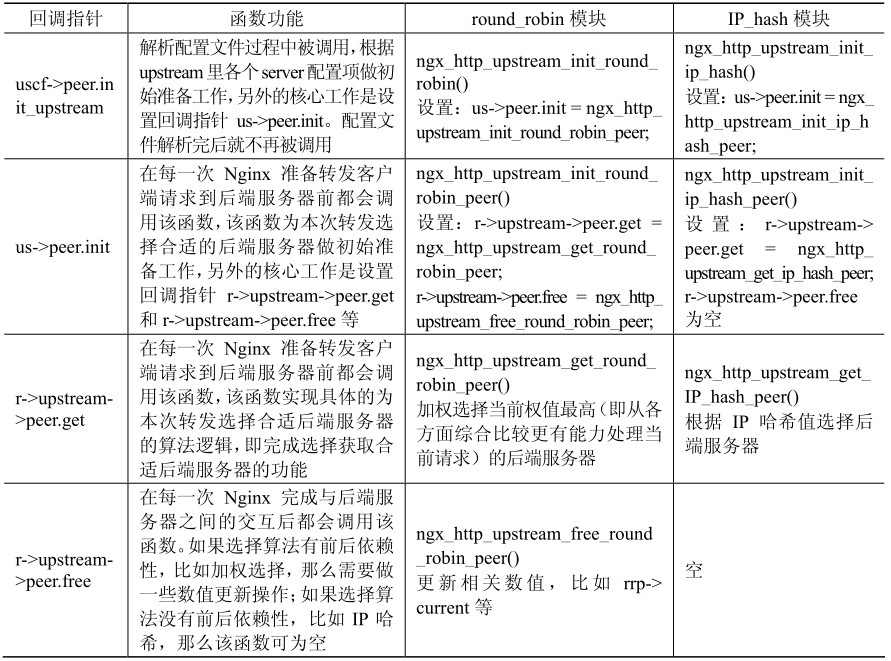 -
-第6章 模块综述
-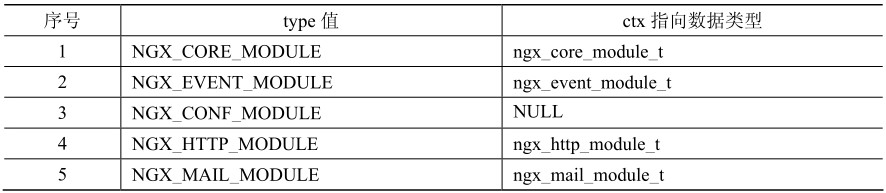 -
-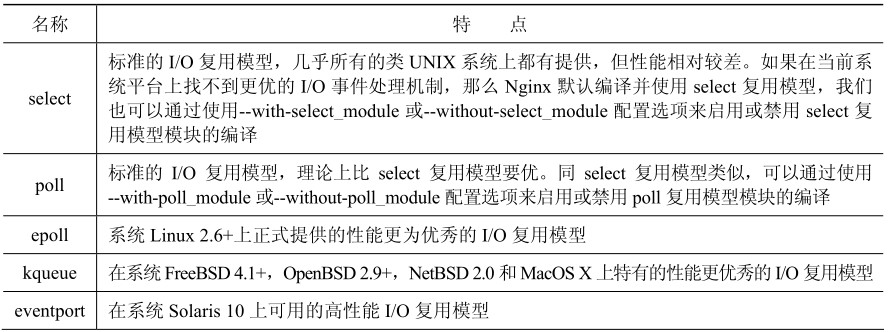 -
- -
-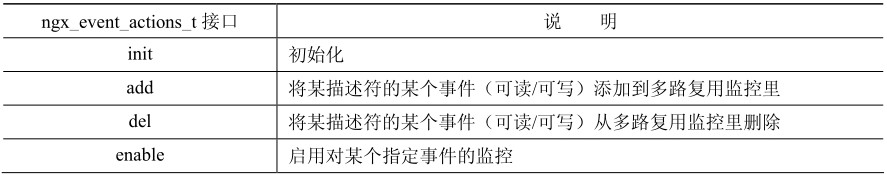 -
-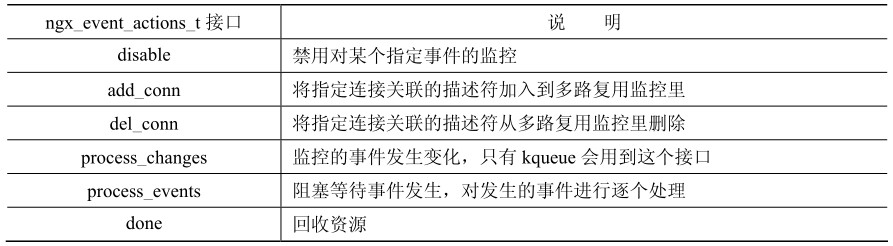 -
-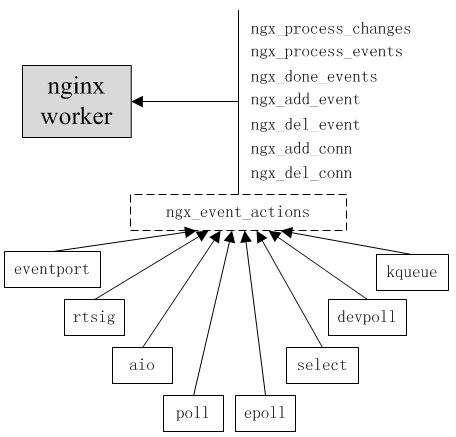 -
-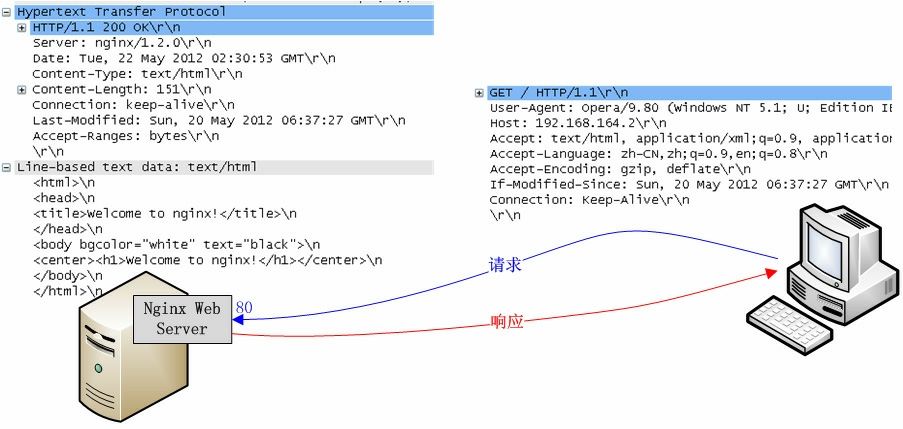 -
-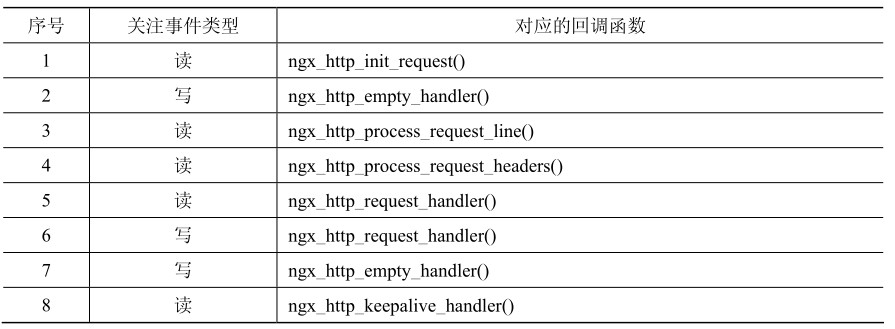 -
-7.4.1 客户端请求均衡
-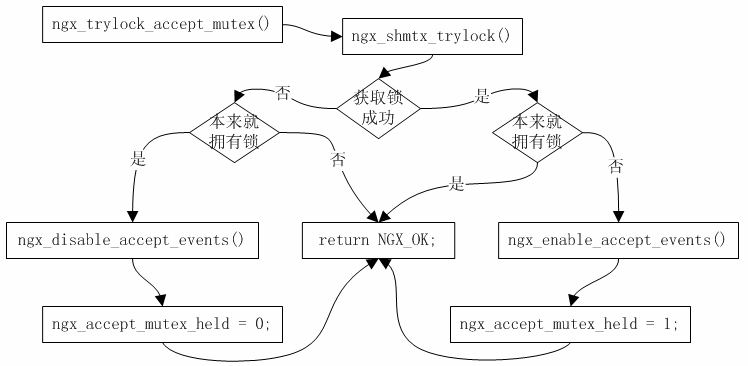 -
-7.4.2 多核绑定[9]
-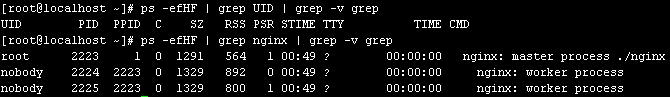 -
- -
- -
- -
-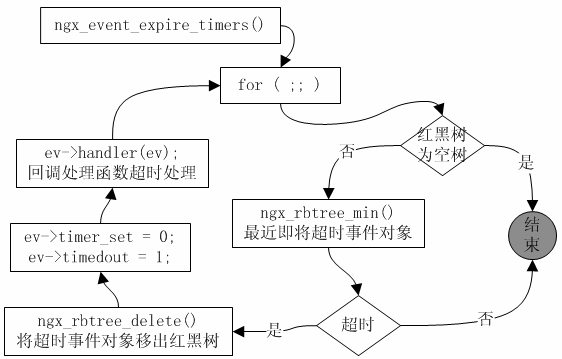 -
-第7章 事件管理机制
- -
- -
- -
- -
-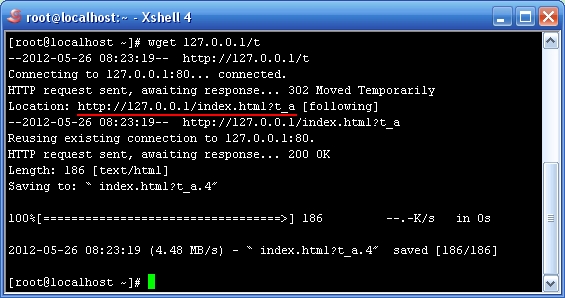 -
-1
[root@localhost web]# cat index2.html
-利用这个配置文件执行Nginx后,通过curl命令来请求访问该根目录,结果如图8-6所示。
- -
-奇怪的是,Nginx 返回的内容来自文件 index2.html,完全超出我们原本的设想,这是不是Nginx的bug呢?当然不是,其真实原因正是由于受到变量执行顺序的影响。
-Nginx 对客户端的请求是分阶段处理的,配置文件里使用到的 Nginx 变量会跟随处理阶段的向前推进而逐个被执行到,而与它在配置文件里的具体前后位置并没有关系(当然,必须都在本次会执行到的路径上),也就是说是以请求处理 11 阶段的先后顺序为主导。由于在Nginx 启动阶段,通过对配置文件的逐行解析,会把属于同一阶段的变量集中在一起。如在上面的实例中,虽然两条set指令使用的$file变量跨越了index指令使用的$file变量,但在配置文件解析后,其效果变成了类似于图8-7所示的样子。
- -
-当一个客户端请求过来时,在REWRITE_PHASE阶段,将依次执行“set$fileindex1.html;”、“set$fileindex2.html;”,再到CONTENT_PHASE阶段执行ngx_http_index_module模块的逻辑时,$file变量的值已经是index2.html,所以Nginx返回给客户端的才是文件index2.html的内容。
-上面给出的只是一个非常简单的例子,但是也较为清楚地说明了 Nginx 变量的执行顺序及其内在原因。如果继续举例没有太大必要,毕竟原理就这么简单,我们在实际进行 Nginx配置时,也就要特别注意配置文件里都使用了哪些Nginx变量,每个Nginx变量都使用在哪些配置指令里,避免出现受变量执行顺序的隐含影响而导致Nginx工作不正常的情况。
-注 释
-[1].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpRewriteModule#if。
-[2].http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copy-on-write。
-[3].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#Variables。
-[4].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpEchoModule。
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/8.4 \346\211\247\350\241\214\351\241\272\345\272\217/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2658.4-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/8.4 \346\211\247\350\241\214\351\241\272\345\272\217/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2658.4-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4d8970d0d5cea1f80a2ecf523b6d01b54a33b274 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/8.4 \346\211\247\350\241\214\351\241\272\345\272\217/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2658.4-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ + location / { + root web; + set $file index1.html; + index $file; + … + set $file index2.html; + … \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 309ff787f6bdf035653d12c6d3a5d674fada186b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25408\347\253\240 \345\217\230\351\207\217\346\234\272\345\210\266/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -本章提到的变量是指Nginx配置文件里所使用的可变符号,对于早已使用过Nginx的读者来说,这肯定并不陌生,但对于 Nginx 是如何实现配置变量可能会感到好奇,本章就将尝试介绍这部分内容,并且还包括更高级的脚本引擎。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ef122dc0a61c86ccdfa7eff01357e51a924a98d2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,106 +0,0 @@ - -创建哪些监听套接口当然是由用户来指定的,Nginx提供的配置指令为listen[1],该指令功能非常丰富,不过在大部分情况下,我们都用得比较简单,一般是指定监听IP和端口号(因为HTTP协议是基于TCP的,所以这里自然也就是TCP端口),比如:
-listen 192.168.1.1:80;,
-这表示Nginx仅监听目的IP是192.168.1.1且端口是80的http请求。如果主机上还有一个192.168.1.2的IP地址,那么客户端对该地址的80端口访问将被拒绝,要让该地址也能正常访问需同样把它加入监听:listen192.168.1.2:80;。如果有更多IP,这样逐个加入比较麻烦,因而另一种更偷懒的配置方法是只指定端口号:listen 80;,那么此时任意目的IP 都可以访问到。不过,这两种不同的配置方式会影响到Nginx创建监听套接口的数目,对于前一种方式, Nginx 会对应地创建多个监听套接口,而后一种方式,由于listen 80;包含了所有的目标IP,所以创建一个监听套接口就完全足够,即便是配置文件里还有其他类似listen 192.168.1.1:80;这样的配置。
-看看实例,感性地认识一下。
-00: 代码片段9.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-15: server {
-16: listen 80;
-17: ...
-34: server {
-35: listen 192.168.1.1:80;
-36:
-上面配置中有两个server,第一个配置listen的目标IP为任意(只要是本地主机有的),第二个配置listen的目标IP为192.168.1.1,但是Nginx在创建监听套接口时却只创建了一个。
-[root@localhost html]# netstat -ntap | grep nginx
-tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13040/nginx
-如果将第16行配置改为listen192.168.1.2:80;,那么此时的Nginx将创建两个监听套接口。
-[root@localhost nginx]# netstat -ntpa | grep nginx
-tcp 0 0 192.168.1.1:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13145/nginx
-tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13145/nginx
-再来看Nginx代码的具体实现,配置指令listen的使用上下文为server,其对应的处理函数为ngx_http_core_listen()。该函数本身的功能比较单一,主要是解析listen指令并将对应的结果存到变量lsopt(可能有人注意到这是一个局部变量,不过没关系,在后面的函数调用里会通过结构体赋值的方式,将它的值全部复制给另外一个变量addr->opt)内,最后调用函数ngx_http_add_listen(),这才是此处需要关注的核心函数,它将所有的 listen 配置以[port,addr]的形式组织在http核心配置ngx_http_core_main_conf_t下的ports数组字段内。另外,如果有一个server内没有配置监听端口,那么Nginx会自动创建一个变量lsopt并给出一些默认值,然后调用函数ngx_http_add_listen()将其组织到ports数组字段内,这在server块配置的回调函数ngx_http_core_server()最后可以看到。
-2700:代码片段9.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-2701:static char *
-2702:ngx_http_core_server(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *dummy)
-2703:{
-2704:…
-2790: if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK && !cscf->listen) {
-2791: ngx_memzero(&lsopt, sizeof(ngx_http_listen_opt_t));
-2792:…
-2795: sin->sin_family = AF_INET;
-2796:…
-2799: sin->sin_port = htons((getuid() == 0) ? 80 : 8000);
-2800:#endif
-2801: sin->sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
-2802:…
-2816: if (ngx_http_add_listen(cf, cscf, &lsopt) != NGX_OK) {
-2817:…
-默认的设置是IPv4协议族、80或8000端口、任意目的IP,所以不管怎么样,一个server配置至少有一个监听套接口。回过头来看 ngx_http_add_listen()函数以及相关逻辑,具体代码并没有什么难以理解的地方,我们直接看一个实例以及对应的图示,这样更直观且能把握全局。仍接着前面的实例,再加一个server配置。
-00: 代码片段9.1-3,文件名: nginx.conf
-15: server {
-16: listen 80;
-17: server_name www.other_all.com;
-18: ...
-34: server {
-35: listen 192.168.1.1:80;
-36: server_name www.web_test1.com;
-37: …
-53: server {
-54: listen 192.168.1.2:8000;
-55: server_name www.web_test2.com;
-56: …
-当Nginx的http配置块全部解析完后,所有的监听套接口信息(包括用户主动listen配置或Nginx默认添加)都已被收集起来,先按port端口分类形成数组存储在cmcf->ports内,然后再在每一个port内按IP地址分类形成数组存储在port->addrs内,这也就是一个[port, addr]的二维划分,如图9-1所示。附带说一下,其实一个[port, addr]可以对应有多个server配置块,但这里的实例中 server 配置块只有一个,所以也就是默认配置块 default_server;对应 server配置块的多少并不会影响到监听套接口的创建逻辑,因为创建监听套接口依赖的是[port, addr]本身,而非它对应的 server 配置块。回到刚才的思路上,在 http 配置指令对应的回调函数ngx_http_block() 的最后,也就是http配置块全部解析完后,将调用函数ngx_http_optimize_servers()“创建”对应的监听套接口。之所以打上引号是因为这里还只是名义上的创建,也就只是创建了每个监听套接口所对应的结构体变量ngx_listening_s,并以数组的形式组织在全局变量cycle->listening内。具体的函数调用关系如下。
-ngx_http_optimize_servers() -> ngx_http_init_listening() -> ngx_http_add_listening()-> ngx_create_listening()
-先关注两点。第一,如果某端口上有任意目的IP的listen配置,那么在该端口上只会创建一个结构体变量ngx_listening_s,不管是否还有其他IP在该端口上的listen配置,在后面创建监听套接口描述符时也会只创建一个,这在前面的演示实例里验证过这种情况,相关逻辑代码实现在函数ngx_http_init_listening()内,比如局部变量bind_wildcard,也包括前面函数中对IP地址排序的准备工作等。第二,ngx_listening_s结构体变量ls的回调字段handler被设置为 ngx_http_init_connection(),注意到这点可以帮助我们在理解后面的逻辑时,如果看到对handler()的回调,心中就能清楚地知道它实际执行的是这个函数。
-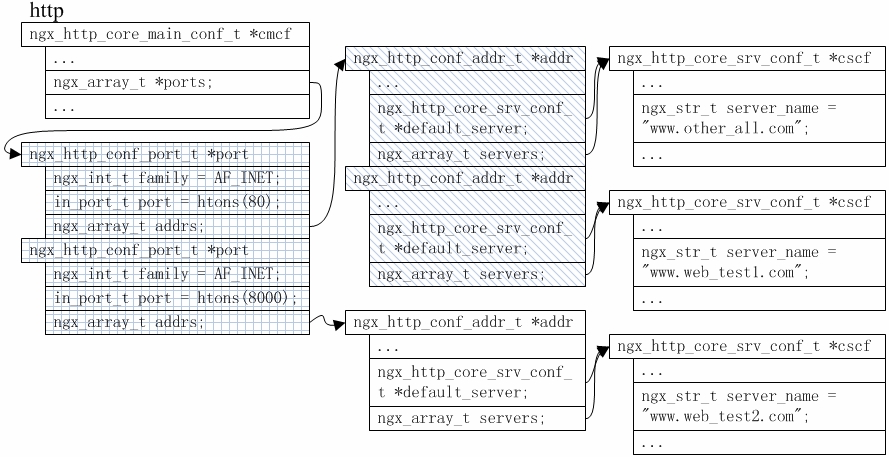 -
-另外要关注的是监听套接口与 server 配置块的关联,这是必须的,因为当监听套接口上一个客户端请求到达时,Nginx必须知道它对应的server配置才能做进一步的处理。这部分逻辑主要在函数ngx_http_add_addrs()内(以IPv4为例),调用关系如下。
-ngx_http_optimize_servers() -> ngx_http_init_listening() -> ngx_http_add_addrs()
-至此,在上面所举示例里,所有等待创建的监听套接口以及相关数据组织结构如图9-2所示("www.web_test1.com"排到了"www.other_all.com"的前面,是因为ngx_sort()排序的缘故)。
-在所有配置解析完并且做了一些其他初始化工作以后,就开始真正进行监听套接口描述符创建以及套接口选项设置操作,也就是调用诸如 socket()、setsockopt()、bind()、listen()等这样的系统函数,相关逻辑实现在函数ngx_open_listening_sockets()和ngx_configure_listening_sockets()内,而这两个函数是在 Nginx 主进程初始化函数 ngx_init_cycle()内靠结尾处被调用。从函数ngx_open_listening_sockets()内的代码实现,可以看到就是遍历 cycle->listening 数组内每一个ls元素并进行逐个创建,而ngx_configure_listening_sockets()内的描述符特性设置也是如此。
-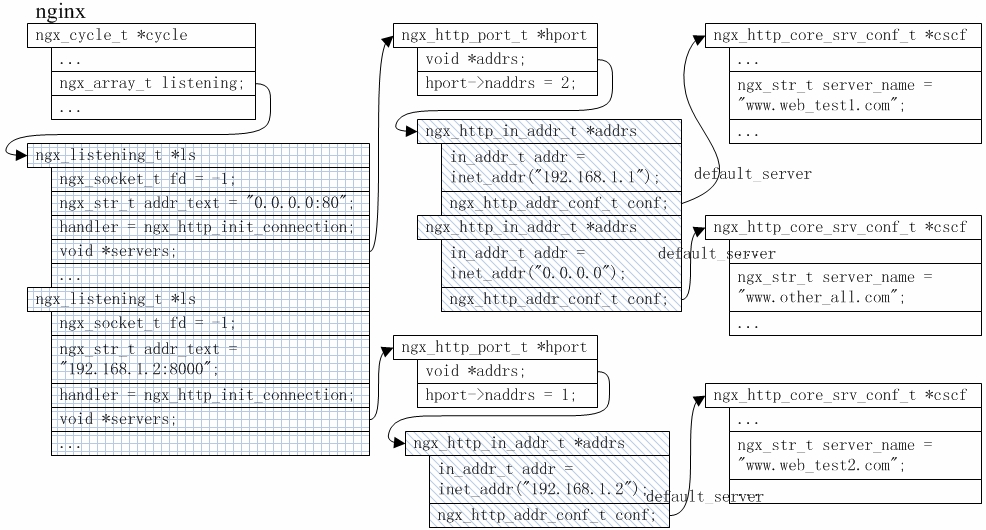 -
-267: 代码片段9.1-4,文件名: ngx_connection.c
-268: ngx_int_t
-269: ngx_open_listening_sockets(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
-270: {
-271: …
-292: ls = cycle->listening.elts;
-293: for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {
-294: …
-312: s = ngx_socket(ls[i].sockaddr->sa_family, ls[i].type, 0);
-313: …
-在这两个函数执行完之后,cycle->listening数组的每一个ls元素,其fd就不再是-1,而是一个可用的监听套接口描述符,并且该描述符根据用户配置而赋予了不同的默认特性,比如收包缓存区大小,发包缓存区大小等。
-关于监听套接口,Nginx主进程的工作就做完了,接下来主进程通过fork()函数创建子进程,也就是工作进程,它们将全部继承这些已初始化好的监听套接口。在每个工作进程的事件初始化函数ngx_event_process_init()内,对每一个监听套接口创建对应的connection连接对象(为什么不直接用一个event事件对象呢?主要是考虑到可以传递更多信息到函数ngx_event_accept()内,并且这个连接对象虽然没有对应的客户端,但可以与 accept()创建的连接套接口统一起来,因为连接套接口对应的是connection连接对象,所以可以简化相关逻辑的代码实现而无需做复杂的判断与区分),并利用该connection的read事件对象(因为在监听套接口上触发的肯定是读事件)。
-582: 代码片段9.1-5,文件名: ngx_event.c
-583: static ngx_int_t
-584: ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
-585: {
-586: …
-745: ls = cycle->listening.elts;
-746: for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {
-747:
-748: c = ngx_get_connection(ls[i].fd, cycle->log);
-749: …
-759: rev = c->read;
-760: …
-762: rev->accept = 1;
-763: …
-826: rev->handler = ngx_event_accept;
-read事件对象的回调处理函数为ngx_event_accept(),请记住它。一切都准备就绪,接下来就是对 rev 事件对象进行监控,即将监听套接口所对应的事件对象加入到 Nginx 的事件监控机制里,那什么时候加入呢?如果没有启动accept_mutex,那么在函数ngx_event_process_init()末尾会通过ngx_add_event()将它加入到事件监控机制内。
-837: 代码片段9.1-6,文件名: ngx_event.c
-838: if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
-否则就需要在核心执行函数 ngx_process_events_and_timers()内进行竞争,只有抢占到accept_mutex锁,进程才会把它加入到自己的事件监控机制内。
-353: 代码片段9.1-7,文件名: ngx_event_accept.c
-354: if (ngx_add_event(c->read, NGX_READ_EVENT,0)==NGX_ERROR){
-在事件管理机制一章的负载均衡一节有对这两方面的详细描述,而在这里我们需特别注意的是,这些事件对象是以水平触发的方式加入到事件监控机制内的,这意味着一个进程一次没有处理完的客户端连接请求可以再次被自己或另外的进程捕获到。
-举个例子,我们知道在默认情况下,Nginx一次只accept()一个请求(即multi_accept为off),如果某个监听套接口 A 上同时来了两个客户端连接请求,触发可读事件被工作进程捕获,工作进程accept()处理了一个请求后,重新阻塞(假定当前进程争抢到accept_mutex锁,即还是拥有监听套接口A;当然,如果是其他进程争抢到accept_mutex锁也是类此)在事件机制监控处(比如 epoll_wait()),但事实上,监听套接口 A 上还有一个客户端连接请求没有被处理,如果监听套接口A不是以水平触发而是以边缘触发加入到事件监控机制,此时监听套接口A虽然可读却无法触发可读事件而让epoll_wait()返回。除非监听套接口A上又来了新的请求重新触发可读事件,但这无疑会导致连接请求得不到及时处理并逐渐累积,最后该监听套接口A彻底失效。理解这个例子需要对epoll事件模型的水平触发LT与边缘触发ET两种模式特性有一定的了解,这在前面章节都已经讲过。
-另外,可以看到 Nginx 主进程在创建完工作进程后并没有关闭这些监听套接口,但主进程却又没有进行accept()客户端连接请求,那么是否会导致一些客户端请求失败呢?答案当然是否定的,虽然主进程也拥有那些监听套接口,并且它也的确能收到客户端的请求,但是主进程并没有监控这些监听套接口上的事件,没有去读取客户端的请求数据。既然主进程没有去读监听套接口上的数据,那么数据就阻塞在那里,等待任意一个工作进程捕获到对应的可读事件后,进而去处理并响应客户端请求。至于主进程为什么要保留(不关闭)那些监听套接口,是因为在后续再创建新工作进程(比如某工作进程异常退出,主进程收到 SIGCHLD信号)时,还要把这些监听套接口传承过去。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..256a99e35676e19a8777ebf586844df80d943250 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + server { + listen 80; + ... + server { + listen 192.168.1.1:80; diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fd38f85dfcbcbf88e677e26489852e3b1012be00 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_core_server(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *dummy) +{ +… + if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK && !cscf->listen) { + ngx_memzero(&lsopt, sizeof(ngx_http_listen_opt_t)); +… + sin->sin_family = AF_INET; +… + sin->sin_port = htons((getuid() == 0) ? 80 : 8000); +#endif + sin->sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; +… + if (ngx_http_add_listen(cf, cscf, &lsopt) != NGX_OK) { +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-3-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-3-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ccb62006d2525e0ecd13d446eae17aa139b3ad1f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-3-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,12 @@ + server { + listen 80; + server_name www.other_all.com; + ... + server { + listen 192.168.1.1:80; + server_name www.web_test1.com; + … + server { + listen 192.168.1.2:8000; + server_name www.web_test2.com; + … \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-4-ngx_connection.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-4-ngx_connection.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1f11b62a8e4b02f75f0e126bb919d19eb971042f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-4-ngx_connection.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +ngx_int_t +ngx_open_listening_sockets(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) +{ +… + ls = cycle->listening.elts; + for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) { + … + s = ngx_socket(ls[i].sockaddr->sa_family, ls[i].type, 0); +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-5-ngx_event.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-5-ngx_event.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9a4c1d0253c66920cc119d41b1974d998a22f409 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-5-ngx_event.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) +{ +… + ls = cycle->listening.elts; + for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) { + + c = ngx_get_connection(ls[i].fd, cycle->log); + … + rev = c->read; + … + rev->accept = 1; + … + rev->handler = ngx_event_accept; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-6-ngx_event.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-6-ngx_event.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..09b19eb1bb91097b5ab53df729dbf0319fda4184 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-6-ngx_event.c" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) { \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-7-ngx_event_accept.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-7-ngx_event_accept.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2c5e7cf94deff7e6122faf772f0a579b832f9852 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.1 \345\210\233\345\273\272\347\233\221\345\220\254\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.1-7-ngx_event_accept.c" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + if (ngx_add_event(c->read, NGX_READ_EVENT,0)==NGX_ERROR){ \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 71197b11f4ed29165a8d5c17720be94293f6387d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,64 +0,0 @@ - -当有客户端发起连接请求,监控监听套接口的事件管理机制就会捕获到可读事件,工作进程便执行对应的回调函数ngx_event_accept(),从而开始连接套接口的创建工作。
-函数ngx_event_accept()的整体逻辑都比较简单,但是有两个需要注意的地方。首先是每次调用 accept()函数接受客户端请求的次数,默认情况下调用 accept()函数一次,即工作进程每次捕获到监听套接口上的可读事件后,只接受一个客户端请求,如果同时收到多个客户端请求,那么除第一个以外的请求需等到再一次触发事件才能被accept()接受。但是,如果用户配置有 multi_accept on;,那么工作进程每次捕获到监听套接口上的可读事件后,将反复调用accept()函数,即一次接受当前所有到达的客户端连接请求。这样看起来,似乎“一次接受当前所有到达的客户端连接请求”更高效,可为什么它却不是默认配置呢?
-举个例子就懂了,假设两个工作进程A和B相互争用监听套接口并对其上的客户端连接请求进行处理,假定两者争用成功的概率都为 50%,但是进程 A 的运气有点差,亦或者说运气有点好,反正不管怎么说,每次进程A拥有这些监听套接口时,总是同时有很多个客户端请求到达,而进程B却每次只有少数的几个请求到达,这样几个循环下来,进程A就非常繁忙了,工作进程之间的负载没有得到较好的均衡,所以在默认情况下,工作进程一次只 accept()接受一个客户端连接请求,这样的粒度更细,多工作进程之间的负载更容易得到均衡。相关的逻辑代码如下所示(系统调用accept4()与accept()差别不大,具体可查Man手册,下面代码以使用accept()为例)。
-17: 代码片段9.2-1,文件名: ngx_event_accept.c
-18: void
-19: ngx_event_accept(ngx_event_t *ev)
-20: {
-21: …
-40: ev->available = ecf->multi_accept;
-41: …
-50: do {
-51: …
-61: s = accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen);
-62: …
-64: if (s == -1) {
-65: …
-70: return;
-71: …
-290: } while (ev->available);
-当配置文件中有 multi_accept on;时,对应的解析值 ecf->multi_accept 为 1,从而ev->available值为1,所以这个do{}while是一个死循环,直到accept()接受不到客户端请求时,即返回值s等于−1时,循环才得以退出。在未配置multi_accept或multi_accept为off的情况下,ev->available值为0,此时循环主体自然也就只执行一次,也就是工作进程一次只accept()一个客户端连接请求。
-调用函数accept()成功接受客户端连接请求后,就通过函数ngx_get_connection()申请对应的连接对象,做一些初始赋值等,简单明了而无需多说,但有一个需要解释的处理是deferred_accept,相关代码如下。
-204: 代码片段9.2-2,文件名: ngx_event_accept.c
-205: if (ev->deferred_accept) {
-206: rev->ready = 1;
-207: …
-284: ls->handler(c);
-ev->deferred_accept值的最初设置是在listen配置的附属项目里,前面曾讲过listen配置项非常复杂,有大量的附属项目提供用户来指定这个监听套接口的相关属性,而deferred就是其中的一个,带有该附属项目的对应监听套接口描述符会被设置TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT特性,并且对应到这里的ev->deferred_accept值为 1(前后是怎样的转换与逐步赋值略过不讲,翻下代码很容易理解)。TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT[2]特性意味当工作进程accept()接受这个监听套接口上的客户端连接请求时,请求的具体数据内容已经到达了,所以这里第206行直接将rev->ready值设置为 1 ,表示数据准备就绪。最后执行的ls->handler回调也就是函数ngx_http_init_connection(),这是在很早之前赋值(还记得么?上一节曾提到过)的。
-181: 代码片段9.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-182: void
-183: ngx_http_init_connection(ngx_connection_t *c)
-184: {
-185: …
-206: rev->handler = ngx_http_init_request;
-207: …
-213: if (rev->ready) {
-214: /* the deferred accept(), rtsig, aio, iocp */
-215:
-216: if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) {
-217: ngx_post_event(rev, &ngx_posted_events);
-218: return;
-219: }
-220:
-221: ngx_http_init_request(rev);
-222: return;
-223: }
-224:
-225: ngx_add_timer(rev, c->listening->post_accept_timeout);
-226:
-227: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-228: …
-函数ngx_http_init_connection()很简单,但注意到rev->ready,如果它为0,则将事件对象rev分别加入到超时管理机制和事件监控机制,等待超时或请求数据到达。如果rev->ready为1,也就是监听套接口描述符使用刚才讲到的TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT特性,accept()接受服务请求后,请求数据已经准备好了,当然是开始着手处理。第216行的if判断为真则意味着有加锁,所以先把该事件对象加到ngx_posted_events链表,函数返回解锁后再进行实际处理,否则在第221 行就开始处理。这部分逻辑结合事件管理机制一章的描述应该容易理解,不过需注意在rev->ready为1的处理情况下,到此时为止,我们新建连接对象都还没有被加入到事件监控机制里,因为当前我们是知道有数据可读,如果运气好,需要的所有请求数据都已经全部到达了,读取数据处理请求然后响应即可,没有必要把连接对象加到事件监控机制里,否则就可能出现“什么作用都没起到却又要把它从事件监控机制里删除”的无用功。只有当进行数据读取时,发现所需要的请求数据没有全部到达,此时才需要将连接对象加到事件监控机制里,以便等待进一步数据到达时获得事件通知,所以在后面的ngx_http_read_request_header()等类似函数内会看到 ngx_handle_read_event()这样的函数调用也就是因为这个原因:
-1139:代码片段9.2-4,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1140:static ssize_t
-1141:ngx_http_read_request_header(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-1142:{
-1143:…
-1164: if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1165:…
-1167: ngx_add_timer(rev, cscf->client_header_timeout);
-1168:…
-1170: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-如上所示,在读到NGX_AGAIN时,也就是需要的请求数据没有全部到达,将事件对象rev加入到超时管理机制和事件监控机制,以等待后续数据可读事件或超时事件。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-1-ngx_event_accept.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-1-ngx_event_accept.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4ad92c5ec6c41bcc974bc05b1d7c3e37ebc6ca2f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-1-ngx_event_accept.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ + void + ngx_event_accept(ngx_event_t *ev) + { + … + ev->available = ecf->multi_accept; + … + do { + … + s = accept(lc->fd, (struct sockaddr *) sa, &socklen); + … + if (s == -1) { + … + return; + … + } while (ev->available); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-2-ngx_event_accept.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-2-ngx_event_accept.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1d992cee2226eef51c1bfc08651ab2170e99b680 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-2-ngx_event_accept.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + if (ev->deferred_accept) { + rev->ready = 1; +… + ls->handler(c); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f006865eda54e9d768d9eebf96f8666f2da4346f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ +void +ngx_http_init_connection(ngx_connection_t *c) +{ +… + rev->handler = ngx_http_init_request; +… + if (rev->ready) { + /* the deferred accept(), rtsig, aio, iocp */ + + if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) { + ngx_post_event(rev, &ngx_posted_events); + return; + } + + ngx_http_init_request(rev); + return; + } + + ngx_add_timer(rev, c->listening->post_accept_timeout); + + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) { +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5441b4a286a9f26f24064267305d994228bcf47d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.2 \345\210\233\345\273\272\350\277\236\346\216\245\345\245\227\346\216\245\345\217\243/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +static ssize_t +ngx_http_read_request_header(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (n == NGX_AGAIN) { +… + ngx_add_timer(rev, cscf->client_header_timeout); +… + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) { \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 2d131cedb1568650ea9b54089887bf8d6054330e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,137 +0,0 @@ - -函数ngx_http_init_request(),正式开始对一个客户端服务请求进行处理与响应工作。该函数的主要功能仍然只是做处理准备:建立http连接对象ngx_http_connection_t、http请求对象ngx_http_request_t、找到对应的server配置default_server、大量的初始化赋值操作,最后执行回调函数ngx_http_process_request_line(),进入到http请求头的处理中。
-236: 代码片段9.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-237: static void
-238: ngx_http_init_request(ngx_event_t *rev)
-239: {
-240: …
-276: hc = ngx_pcalloc(c->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_connection_t));
-277: …
-295: r = ngx_pcalloc(c->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t));
-296: …
-380: addr = port->addrs;
-381: addr_conf = &addr[0].conf;
-382: …
-388: /* the default server configuration for the address:port */
-389: cscf = addr_conf->default_server;
-390: …
-395: rev->handler = ngx_http_process_request_line;
-396: …
-519: rev->handler(rev);
-520: }
-查找当前请求对应属于到端口上的哪个服务 IP 地址是通过对比目的 IP 来进行的(前面讲过,如果某端口上设置有任意IP监听,比如*:80,那么即便还有其他指定IP的监听,比如192.168.1.1:80,也只会创建一个监听套接口,所以对于该套接口上接收到的连接请求首先要进行目的IP地址匹配),这部分代码很容易理解,就是一个for循环遍历查找。要注意的是由于IPv4的地址只有32位可以直接比较,但IPv6的地址有128位,所以需采用memcmp()比较。上面没有显示这部分代码,给出的第380、381 行代码是监听套接口上只有一个目的 IP的情况,此时直接使用它,并且第389行取用该地址上的默认server配置。如果客户端请求对应的 server 不是这个默认的会怎么样?不用当心这种情况,因为在后面还会有其他处理,比如ngx_http_find_virtual_server()函数。来进行查找与定位,而在此之前,当然只能使用默认server配置。这部分内容在后面第10章10.3小节还会做更详细的介绍。
-在继续下面的内容讲解前,有必要先介绍一下HTTP协议。当然,关于HTTP协议方面的内容,如果展开来说一时半会说不完,而且也有专门的书籍可以参考,比如《HTTP Pocket Reference》(O'Reilly)[3]、《HTTPThe Definitive Guide》(O'Reilly)[4]、《HTTP Developers Handbook》(Sams)[5]等,所以这里仅以RFC 2616[6]为依据简单介绍一下http请求响应数据的格式,以便继续后面的Nginx内容讲解。
-根据RFC 2616 内容可知,http请求消息(也包括响应消息。消息,即message,简单认为就是上面提到的请求响应数据的学术名称,我说数据是笼统说法,请勿拘泥这些名词概念)是利用RFC 822[7]定义的常用消息格式来传输实体(消息的负载,即真正有价值的数据)。这种常用消息格式就是由开始行(start-line),零个或多个头域(经常被称作“头”)、一个指示头域结束的空行(一个仅包含CRLF的“空”行)以及一个可有可无的消息主体(message-body)。当然,RFC2616文档里对http请求响应消息格式描叙得更具体一点,其中请求消息格式的BNF[8](巴科斯诺尔范式)表示如下。
-Request = Request-Line ; Section 5.1
-*(( general-header ; Section 4.5
-| request-header ; Section 5.3
-| entity-header ) CRLF) ; Section 7.1
-CRLF
-[ message-body ] ; Section 4.3
-Request-Line = Method SP Request-URI SP HTTP-Version CRLF
-Method = "OPTIONS" ; Section 9.2
-| "GET" ; Section 9.3
-| "HEAD" ; Section 9.4
-| "POST" ; Section 9.5
-| "PUT" ; Section 9.6
-| "DELETE" ; Section 9.7
-| "TRACE" ; Section 9.8
-| "CONNECT" ; Section 9.9
-| extension-method
-extension-method = token
-Request-URI = "*" | absoluteURI | abs_path | authority
-可以看到,工作进程收到的客户端请求头部数据以Request-Line开始(GET/HTTP/1.0\r\n),接着是不定数的请求头部(User-Agent: Wget/1.12 (linux-gnu)\r\nAccept:*/*\r\nHost: www.web_test2.com\r\nConnection:Keep-Alive\r\n),最后以一个空行结束(\r\n)。
-而函数ngx_http_process_request_line()处理的数据就是客户端发送过来的http请求头中的Request-Line。这个过程可分为三步:读取 Request-Line 数据、解析 Request-Line、存储解析结果并设置相关值。当然,这个过程实际执行时可能重复多次(比如 Request-Line 数据分多次到达监听套接口),所以函数内的实现是一个for ( ;; )循环。下面逐一简单来看下各个步骤。
-第一步,读取Request-Line数据。通过函数ngx_http_read_request_header()将数据读到缓存区r->header_in内。比如执行wget www.web_test2.com[9]请求时,用gdb调试Nginx对应的工作进程,打印数据[10]如下。
-(gdb) p r->header_in->pos
-$8=(u_char *)0x98bdef8"GET/HTTP/1.0\r\nUser-Agent:Wget/1.12(linux-gnu)\r\nAccept:*/*\r\nHost: www.web_test2.com\r\nConnection: Keep-Alive\r\n\r\n"
-一次就把整个请求的头部数据读到了,当然也就包括完整的Request-Line数据(即GET /HTTP/1.0\r\n)。另外说一句,可以看到我这里的wget命令默认是以HTTP1.0协议发送的请求,不过不影响(下面仍以它的数据为例),因为Nginx也支持HTTP1.0 协议,也可以用curl命令curlwww.web_test2.com进行请求。
-(gdb) p r->header_in->pos
-$9=(u_char *)0x98bdef8"GET/HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent:curl/7.19.7(i686-pc-linux-gnu)libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.12.7.0 zlib/1.2.3 libidn/1.18 libssh2/ 1.2.2\r\nHost: www.web_test2.com\r\nAccept: */*\r\n\r\n"
-刚才提到,由于客户端请求头部数据可能分多次到达,所以缓存区r->header_in内可能还有一些上一次没解析完的头部数据,所以会存在数据的移动等操作。不过都比较简单,这里仅提示读者注意而具体内容略过不讲。
-第二步,解析 Request-Line。对读取到的 Request-Line 数据进行解析的工作实现在函数ngx_http_parse_request_line()内。由于Request-Line数据有严格的BNF对应,所以其解析过程虽然繁琐,但并无不好理解的地方。
-第三步,存储解析结果并设置相关值。在Request-Line的解析过程中会有一些赋值操作,但更多的是在成功解析后,ngx_http_request_t对象r内的相关字段值都将被设置,比如uri(/)、method_name(GET)、http_protocol(HTTP/1.0)等。
-Request-Line解析成功,即函数ngx_http_parse_request_line()返回NGX_OK,意味着这初步算是一个合法的 http 客户端请求。接下来就开始解析其他请求头( general-header、request-header、entity-header)。
-706: 代码片段9.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-707: static void
-708: ngx_http_process_request_line(ngx_event_t *rev)
-709: {
-710: …
-732: for ( ;; ) {
-733: …
-735: n = ngx_http_read_request_header(r);
-736: …
-742: rc = ngx_http_parse_request_line(r, r->header_in);
-743:
-744: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-745: …
-896: if (ngx_list_init(&r->headers_in.headers, r->pool, 20,
-897: sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t))
-898: …
-915: rev->handler = ngx_http_process_request_headers;
-916: ngx_http_process_request_headers(rev);
-函数ngx_http_process_request_headers()对每一个请求头的处理步骤与函数ngx_http_process_request_line()处理 Request-Line 的情况类似,也是分为三步:读取数据(对应函数 ngx_http_read_request_header(),如果数据已经从监听套接口描述符读到缓存区了,那么无需再读)、解析数据(对应函数ngx_http_parse_header_line())、存储解析结果。
-在第二步骤中,函数 ngx_http_parse_header_line()解析的每一个请求头都会放到r->headers_in.headers内,看看gdb断点后捕获到的实例数据:
-(gdb) p r->headers_in.headers.part
-$34 = {elts = 0x98be5d4, nelts = 4, next = 0x0}
-(gdb) p *(ngx_table_elt_t *)r->headers_in.headers.part.elts
-$35 = {hash = 486342275, key = {len = 10, data = 0x98bdf08 "User-Agent"}, value = {len =21, data = 0x98bdf14 "Wget/1.12 (linux-gnu)"}, ...}
-(gdb) p *(ngx_table_elt_t *)(r->headers_in.headers.part.elts+sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t) * 1)
-$36 = {hash = 2871506184, key = {len = 6, data = 0x98bdf2b "Accept"}, value = {len =3, data = 0x98bdf33 "*/*"}, ...}
-(gdb) p *(ngx_table_elt_t *)(r->headers_in.headers.part.elts+sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t) * 2)
-$37 = {hash = 3208616, key = {len = 4, data = 0x98bdf38 "Host"}, value = {len = 17,data = 0x98bdf3e "www.web_test2.com"}, ...}
-(gdb) p *(ngx_table_elt_t *)(r->headers_in.headers.part.elts+sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t) * 3)
-$38 = {hash = 3519315678, key = {len = 10, data = 0x98bdf51 "Connection"}, value = {len =10, data = 0x98bdf5d "Keep-Alive"}, ...}
-如果请求头有对应的回调处理函数,还会做进一步处理,所有可以被 Nginx 识别并处理的请求头定义在数组ngx_http_headers_in内,比如
-80: 代码片段9.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-81: ngx_http_header_t ngx_http_headers_in[] = {
-82: { ngx_string("Host"), offsetof(ngx_http_headers_in_t, host),
-83: ngx_http_process_host },
-84:
-85: { ngx_string("Connection"), offsetof(ngx_http_headers_in_t, connection),
-86: ngx_http_process_connection },
-87: …
-而在函数ngx_http_process_request_headers()内的具体实现如下。
-955: 代码片段9.3-4,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-956: static void
-957: ngx_http_process_request_headers(ngx_event_t *rev)
-958: {
-959: …
-1038: rc = ngx_http_parse_header_line(r, r->header_in,
-1039: cscf->underscores_ in_headers);
-1040:
-1041: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-1042:..
-1056: h = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_in.headers);
-1057:…
-1085: hh = ngx_hash_find(&cmcf->headers_in_hash, h->hash,
-1086: h->lowcase_key, h->key.len);
-1087:…
-1088: if (hh && hh->handler(r, h, hh->offset) != NGX_OK) {
-1089:…
-第1041 行为真则表示一个请求头被成功解析,在第1056 行先把它加入到 r->headers_in.headers内,然后在cmcf->headers_in_hash(该变量对应ngx_http_headers_in变量)内查找该请求头能否被Nginx处理,比如"Host"请求头就能够被Nginx处理,从而调用其对应的处理函数ngx_http_process_host()。
-当函数ngx_http_parse_header_line()返回NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE时,表示所有的请求头都已经处理完成(最后一个被处理的请求头为 entity-header),客户端的具体请求已经基本被理解(可能还有请求体,比如POST请求时),Nginx开始进入到内部处理,即开始执行各种模块 Handler。不过在此之前,通过调用 ngx_http_process_request_header()函数先做一个简单的检查。
-1099:代码片段9.3-5,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1100: if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) {
-1101:…
-1110: rc = ngx_http_process_request_header(r);
-1111:
-1112: if (rc != NGX_OK) {
-1113: return;
-1114:…
-1116: ngx_http_process_request(r);
-函数ngx_http_process_request_header()的检查比较简单,比如:如果客户端使用HTTP 1.1协议发送请求却没有带上"Host"请求头,直接返回错误(HTTP1.1协议明确要求必须有"Host"请求头[11]);客户端发送TRACE请求则也返回错误(TRACE请求用于调试跟踪,Nginx不支持);等等。
-调用函数ngx_http_process_request()即开始执行各个模块Handler,调用关系如下。
-ngx_http_process_request() -> ngx_http_handler() -> ngx_http_core_run_phases()
-也就是那个在前面章节曾提到过的“状态机”。
-874: 代码片段9.3-6,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-875: while (ph[r->phase_handler].checker) {
-876:
-877: rc = ph[r->phase_handler].checker(r, &ph[r->phase_handler]);
-878:
-879: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-880: return;
-881: }
-882: }
-对一个客户端请求的处理,终于衔接到Nginx的Handler模块来了,各个Handler模块的处理在前面章节已经描述过,所以这里不再多讲。对于一个访问静态页面的GET类型请求,最终会被 ngx_http_static_module 模块的 ngx_http_static_handler()函数捕获,该函数组织待响应的数据,然后调用ngx_http_output_filter()经过Nginx过滤链后将数据发送到客户端,此时一个请求的处理与响应也就完成,所以当回到ngx_http_process_request()函数的最末,调用到函数 ngx_http_run_posted_requests()内时,因为 c->destroyed 为真而直接退出。下一节就具体来看http数据响应的内部逻辑过程。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..187daf90c4d44c6c497e13984b9b9ec053e24eba --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +static void +ngx_http_init_request(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + hc = ngx_pcalloc(c->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_connection_t)); +… + r = ngx_pcalloc(c->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t)); +… + addr = port->addrs; + addr_conf = &addr[0].conf; +… + /* the default server configuration for the address:port */ + cscf = addr_conf->default_server; +… + rev->handler = ngx_http_process_request_line; +… + rev->handler(rev); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f4b31ffc073ef9d2d53670734c3d20d522bb086a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +static void +ngx_http_process_request_line(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + for ( ;; ) { +… + n = ngx_http_read_request_header(r); +… + rc = ngx_http_parse_request_line(r, r->header_in); + + if (rc == NGX_OK) { +… + if (ngx_list_init(&r->headers_in.headers, r->pool, 20, + sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t)) +… + rev->handler = ngx_http_process_request_headers; + ngx_http_process_request_headers(rev); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1218f3cf23f298640fac737ecf0bbb44e73d0409 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ + ngx_http_header_t ngx_http_headers_in[] = { + { ngx_string("Host"), offsetof(ngx_http_headers_in_t, host), + ngx_http_process_host }, + + { ngx_string("Connection"), offsetof(ngx_http_headers_in_t, connection), + ngx_http_process_connection }, + … \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-4-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-4-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..10a34da35abb56a8a15d71327466b5f7e27c2714 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-4-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +static void +ngx_http_process_request_headers(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + rc = ngx_http_parse_header_line(r, r->header_in, + cscf->underscores_ in_headers); + + if (rc == NGX_OK) { +.. + h = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_in.headers); +… + hh = ngx_hash_find(&cmcf->headers_in_hash, h->hash, + h->lowcase_key, h->key.len); +… + if (hh && hh->handler(r, h, hh->offset) != NGX_OK) { +… \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-5-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-5-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..16532b251d43222c4ca0a362dc7645770973a2d6 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-5-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) { +… + rc = ngx_http_process_request_header(r); + + if (rc != NGX_OK) { + return; +… + ngx_http_process_request(r); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..afb606c3a9a84193b0a870d9752d58090e4188c2 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.3-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + while (ph[r->phase_handler].checker) { + + rc = ph[r->phase_handler].checker(r, &ph[r->phase_handler]); + + if (rc == NGX_OK) { + return; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 4be5c06a3daa5204cc860a610d97a0c81a5d368d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,92 +0,0 @@ - -http响应消息也分为head头部和body主体,和请求消息一致,也是头部信息先发送,然后才是主体信息。本节仍以简单的GET请求静态页面为例,来看看Nginx如何对客户端做出数据响应。
-前面提到,简单的GET请求静态页面最终会被ngx_http_static_module模块实际处理,执行的函数为ngx_http_static_handler()。该函数首先要做的当然是找到请求静态页面所对应的磁盘文件,通过组合当前location配置的根目录与GET请求里的绝对URI即可得到该磁盘文件的绝对路径[12]。
-接着通过绝对路径打开该磁盘文件,并且通过文件属性来设置相关响应头,比如:通过文件大小来设置 Content-Length 响应头(这里还只是设置对应的字段值,并非创建实际的响应头,下同),告诉客户端接收数据的长度;通过文件修改时间来设置Last-Modified响应头,那么客户端下次再请求该静态文件时可带上该时间戳,那时Nginx就有可能直接返回304状态码,让客户端直接使用本地缓存,从而提高性能;等等。发送响应体需要一些内存资源,这会在发送响应头以前分配好,因为如果内存申请失败可提前异常返回,避免可能出现响应头已经发送出去后却发现发送响应体需要的内存资源没法成功申请的情况。当然,发送响应头还需要经过Nginx的过滤链,这是通过函数
-ngx_http_send_header() -> ngx_http_top_header_filter()
-逐步顺链调用下去,过滤链上的回调函数可能会对响应头数据进行检测、截获、新增、修改和删除等操作,不管怎样,一般情况下,执行流程会走到过滤链最末端的两个函数内。
-ngx_http_header_filter() -> ngx_http_write_filter()
-其中函数ngx_http_header_filter()完成响应头字符串数据的组织工作。该函数申请一个buf缓存块,然后根据最初设置以及经过过滤链的修改后的相关响应头字段值,组织响应头数据以字符串的形式存储在该缓存块内。下面是在该函数接近末尾的地方,用gdb捕获到的数据。
-152: 代码片段9.4-1,文件名: ngx_http_header_filter_module.c
-153: static ngx_int_t
-154: ngx_http_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-155: {
-156: …
-161: ngx_chain_t out;
-162: …
-610: out.buf = b;
-611: out.next = NULL;
-612:
-613: return ngx_http_write_filter(r, &out);
-614: }
-(gdb) p b->pos
-$39 = (u_char *) 0x98be920 "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nServer: nginx/1.2.0\r\nDate: Sun, 27May 2012 13:58:31 GMT\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 219\r\nLast-Modified:Fri, 25 May 2012 15:20:11 GMT\r\nConnection:keep-alive\ r\nAccept-Ranges: bytes\r\n\r\n"
-该缓存块被接入到发送链变量 out (注意这是一个局部变量)内,之后进入到函数ngx_http_write_filter()进行“写出”操作,打上引号是因为此处只有在满足某些条件的情况下才会执行实际的数据写出。
-46: 代码片段9.4-2,文件名: ngx_http_write_filter_module.c
-47: ngx_int_t
-48: ngx_http_write_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
-49: {
-50: …
-172: /*
-173: * avoid the output if there are no last buf, no flush point,
-174: * there are the incoming bufs and the size of all bufs
-175: * is smaller than "postpone_output" directive
-176: */
-177:
-178: if (!last && !flush && in && size < (off_t) clcf->postpone_output) {
-179: return NGX_OK;
-180: }
-可以看到如果没有带最后一个缓存块(last),没有要求强制写出(flush),当前有新加缓存块(in为真)并且当前缓存块总数据大小小于设定值(clcf->postpone_output),此时可直接返回NGX_OK,这意味着会有数据马上跟来(该if语句为什么会有对in 是否为真的判断就是因为这个原因,如果当前都没有新加入数据,那么也不要期待下一步会马上有数据加入,因此基于这种思路,从时延上考虑,就需要立即写出,从而整个if判断为假),所以此次可以不写。之所以这么做,当然还是从性能上考虑,不管是用哪种读/写方式,总还是要进行用户空间与内核空间的切换,性能损耗比较大,所以读/写操作能省一次就一次。
-在我们的示例里,或者说是客户端访问服务器静态页面的这种情况下,此时一般就是从第179 行退出返回了,但是在该函数前面的逻辑里,我们的待发送缓存块(即包含响应头数据的字符串数据)已经被连接到 r->out 链内。这样做是必须的,毕竟传入进来的 out 发送链(对应参数in)是个局部变量(但是out发送链内存储数据的buf缓存块在函数退出时并没有被释放,这点要注意)。此时的情况如图9-3所示。
-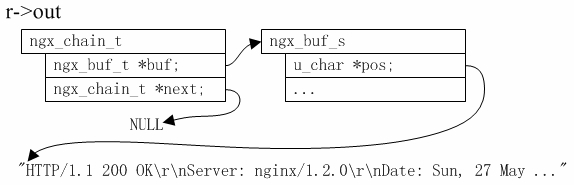 -
-函数依次返回后到函数ngx_http_static_handler()内继续执行,看一下相关的完整代码。
-47: 代码片段9.4-3,文件名: ngx_http_static_module.c
-48: static ngx_int_t
-49: ngx_http_static_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-50: {
-51: …
-235: b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
-236: …
-240: b->file = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_file_t));
-241: …
-245: rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
-246: …
-255: b->last_buf = (r == r->main) ? 1: 0;
-256: …
-258: b->file->fd = of.fd;
-259: b->file->name = path;
-260: …
-266: return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
-267: }
-代码第235、240、245行在前面已经描述过了,第255行的last_buf会被置1,即由于当前请求就是主请求,第258、259行在后面实现将静态文件写出到客户端时会要用到,第266行开始进入到body过滤链,最后也进入到函数ngx_http_write_filter()内。同样,该函数的前面逻辑把这个新缓存块也加入到r->out链内,但是在判断是否要实际写出的if判断时,由于last标记为真,所以此时的确需要做数据写出操作。此时的r->out链情况如图9-4所示。
-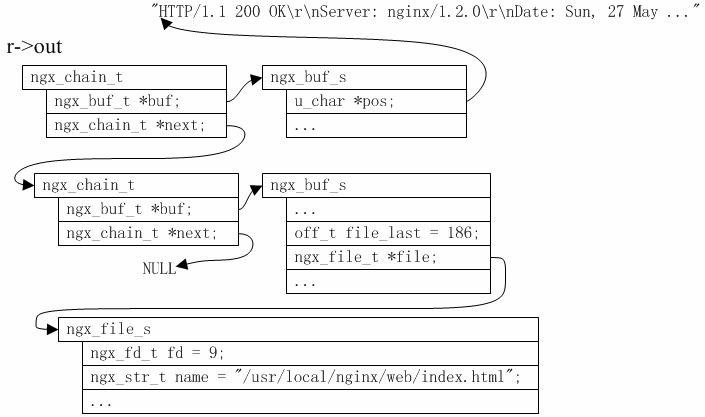 -
-在进行实际的数据写出操作时,会有一些其他与本节无关的细节,比如限速、一次没完全写完等原因导致需设置定时器再写,撇开这些而关注我们的重点函数。
-241: 代码片段9.4-4,文件名: ngx_http_write_filter_module.c
-242: chain = c->send_chain(c, r->out, limit);
-回调指针send_chain根据系统环境的不同而指向不同的函数,比如在我这里的环境下,指向的是ngx_linux_sendfile_chain()函数,该函数遍历r->out链上的每一个缓存块,根据缓存块里的数据类型调用不同的系统接口函数将数据写出到客户端。比如这里,对于第一个缓存块,其内数据是存放在内存中的字符串数据(响应头),所以调用系统接口函数writev()将其写出。对于第二个缓存块,其相关联数据是磁盘上文件系统内某个文件(该文件已被打开,对应文件描述符存放在buf->file->fd内)的内容,对于这些数据的写出采用的是系统调用sendfile()。相关代码如下。
-36: 代码片段9.4-5,文件名: ngx_linux_sendfile_chain.c
-37: ngx_chain_t *
-38: ngx_linux_sendfile_chain(ngx_connection_t *c, ngx_chain_t *in, off_t limit)
-39: {
-40: …
-78: for ( ;; ) {
-79: …
-92: for (cl = in; cl && send < limit; cl = cl->next) {
-93: …
-248: if (file) {
-249: …
-264: rc = sendfile(c->fd, file->file->fd, &offset, file_size);
-265: …
-293: } else {
-294: rc = writev(c->fd, header.elts, header.nelts);
-客户端需要的数据都发送出去了,那么剩下的工作也就是进行连接关闭和一些连接相关资源的清理。当然,如果需要与客户端进行keepalive,那么执行函数ngx_http_set_keepalive()保留一些可重用的资源,这样在同一个客户端新的请求到达时,处理能更快速。关于这些的详细信息,请继续看本章后面小节的内容。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-1-ngx_http_header_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-1-ngx_http_header_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6bec73f6431484b09137525e8921a1a66489c843 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-1-ngx_http_header_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + ngx_chain_t out; +… + out.buf = b; + out.next = NULL; + + return ngx_http_write_filter(r, &out); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-2-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-2-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e156e498362a519aef05f640086a8780533e93df --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-2-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + ngx_int_t + ngx_http_write_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) + { + … + /* + * avoid the output if there are no last buf, no flush point, + * there are the incoming bufs and the size of all bufs + * is smaller than "postpone_output" directive + */ + + if (!last && !flush && in && size < (off_t) clcf->postpone_output) { + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-3-ngx_http_static_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-3-ngx_http_static_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..026cdbbe783e77603c9c5909ddec21b289c27988 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-3-ngx_http_static_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_static_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) + { + … + b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t)); +… + b->file = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_file_t)); +… + rc = ngx_http_send_header(r); +… + b->last_buf = (r == r->main) ? 1: 0; +… + b->file->fd = of.fd; + b->file->name = path; +… + return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-4-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-4-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..976a31ea10c0706b51dd149d29684e33899852f8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-4-ngx_http_write_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + chain = c->send_chain(c, r->out, limit); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-5-ngx_linux_sendfile_chain.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-5-ngx_linux_sendfile_chain.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..90b9d1dd84144b0a793041b5f77a5ce712bdc512 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.4-5-ngx_linux_sendfile_chain.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ + ngx_chain_t * + ngx_linux_sendfile_chain(ngx_connection_t *c, ngx_chain_t *in, off_t limit) + { + … + for ( ;; ) { + … + for (cl = in; cl && send < limit; cl = cl->next) { + … + if (file) { +… + rc = sendfile(c->fd, file->file->fd, &offset, file_size); +… + } else { + rc = writev(c->fd, header.elts, header.nelts); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 41fc0422331970f5d32d2a7691894980d85c7f62..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,292 +0,0 @@ - -在进一步描述http连接关闭流程之前,有必要先介绍一下Nginx的子请求(sub request)概念,因为它的出现导致了http连接关闭流程的复杂化。所谓子请求,并不是由客户端直接发起的,它是由于Nginx在处理客户端的请求时,根据自身逻辑而内建的新请求,如图9-5所示。
-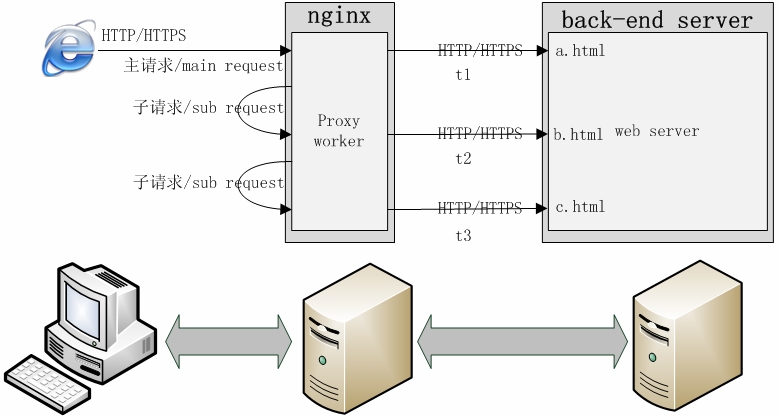 -
-子请求几乎具有主请求的所有特征(比如有对应完整的ngx_http_request_t结构体对象),并且子请求本身也可以发起新的子请求,即这是一个可以嵌套的概念。在默认情况下,在对一个客户端请求(即主请求)的处理过程中,可以发起的总子请求数目(即包括子请求、孙子请求等)大约为200个(由宏NGX_HTTP_MAX_SUBREQUESTS限定),这在一般情况下,已经足够了。
-子请求并非HTTP标准里的概念,可以说是Nginx所特有的设计,为什么需要有子请求?一般认为这主要是为了提高Nginx内部对单个客户端请求处理的并发能力,进一步提高效率。如果客户端的某个主请求访问了多处资源(比如通过 SSI 功能包含了 a.html、b.html、c.html三个资源),那么针对每一处资源访问建立一个子请求并让它们同时进行,效率自然会更高。不过需注意的是,从进程级的微观上而言,一个客户端请求总是只有一个进程处理,所以,针对一个主请求,不论建立多少个子请求,在同一时刻能被进程处理的只有其中的一个。但是,如果对其中某一处资源进行访问的子请求被阻塞(比如等待的事件未到达)时,进程转而可以处理其他子请求,因此从请求级的宏观上而言,达到了“同时进行”的并发处理。这样,对整个请求处理的理论最短时间可能就不再是对各处资源请求访问时间的总和(t1+t2+t3),而可能是约等于最长的请求访问某处资源所消耗的时间(max(t1, t2,t3))。当然,这只有在最理想最特殊的情况下才会发生。在实际处理过程中,如果对每一处资源的请求访问都没有阻塞等待,那么子请求的实际作用就没有发挥出来,此时从性能上来讲,还不如不使用子请求,因为子请求的创建、最终同步、处理流程的重复进行等额外的逻辑,可能会导致服务器压力的增大,从而对整个请求处理的时间反而增大。不过有了子请求机制后,Nginx在处理某些复杂输出逻辑时就比较方便了,比如SSI功能模块。
-发起某个子请求的请求被称为该子请求的父请求。从理论上讲,子请求可以在 Nginx 处理父请求逻辑的任何阶段发起,但从各个父/子请求之间数据同步上的考虑,目前官方所提供的 Nginx 模块代码仅在 filter 阶段(即仅模块 ngx_http_addition_filter_module 和模块ngx_http_ssi_filter_module用到了子请求)发起子请求,而此时父请求的结果数据已经产生,注意到这点很重要,因为它能帮助我们理解后面的数据同步部分。对于其他第三方模块在handler阶段发起子请求,由于此时父请求的结果数据还未产生,所以在数据同步方面需要做进一步的针对处理。本节仅关注在filter阶段发起子请求的情况。
-父请求被记录在子请求的 parent 字段内,而直接关联客户端的主请求仍然是重点关注对象,因此它被记录在每一个请求的main字段内。看一个ngx_http_addition_filter_module模块(该模块需要通过“./configure --with-http_addition_module”主动加入到Nginx 内)使用子请求的实例,假定有如下Nginx配置。
-26: 代码片段9.5-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-27: location / {
-28: root html;
-29: index index.html index.htm;
-30: add_before_body /before.html;
-31: add_after_body /after.html;
-32: }
-使用该配置启动Nginx,然后通过wget向该路径发起请求,看到的数据如下。
-[root@localhost test]# wget 127.0.0.1
-[root@localhost test]# cat index.html
-before
-index
-after
-这三行数据分别为 Nginx 站点根目录下文件 before.html、index.html、after.html 的内容,也就是说当我们通过 wget 向 Nginx 发起 http请求后,Nginx 在内部的处理过程中分别访问了三处文件资源,并且把它们各自的内容进行恰当的组合合并后当作响应数据发回给wget。可以看到,整个过程涉及到两个至关重要的问题,即分别访问与组合合并。其中分别访问不算难以处理,子请求本身就是为此而设计的,在任何时刻,如果需要发起新的资源访问,新建新的子请求即可;真正困难的地方在于对各个主/子请求处理完成后所得数据的组合与合并,因为各个请求在什么时候结束是不可预知的,后发起的子请求有可能比先发起的子请求更早结束,所以就涉及到同步问题。比如在上面的示例中,必须按照before.html、index.html、after.html这样的次序来组织各个请求的结果,才能将它当作最终的响应数据发回给客户端,否则的话,客户端请求所获得的数据可能就不是原本正确的结果。
-根据发起子请求的特征,即子请求可以递归发起子请求(树结构)以及同一个子请求可以发起多个子请求(链表结构),按照树加链表的形式对它们进行组织是自然而然的事情。而在结构体ngx_http_request_t内提供有两个与此相对应的字段。
-325: 代码片段9.5-2,文件名: ngx_http_request.h
-326: typedef struct ngx_http_postponed_request_s ngx_http_postponed_request_t;
-327:
-328: struct ngx_http_postponed_request_s {
-329: ngx_http_request_t *request;
-330: ngx_chain_t *out;
-331: ngx_http_postponed_request_t *next;
-332: };
-333: …
-347: struct ngx_http_request_s {
-348: …
-394: ngx_http_request_t *parent;
-395: ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed;
-通过字段 parent 组织成树,通过 postponed 组织成链表。注意到 ngx_http_postponed_request_s结构体内还有一个ngx_chain_t类型的out字段,它做何用?其实,它用于临时保存当前请求处理后的结果数据,也就是为了组织最终的响应数据而设计。我们这里,对于某个请求的所有子请求,它们处理后的数据将按照各自发起的先后顺序进行组合排列,但是,对于该主请求本身所产生的数据如何插入到这个组合里呢?这可能是在所有子请求产生的数据之前,或之中,或之后,所以Nginx干脆就封装了一个ngx_chain_t来与子请求融合到一起。至于具体怎么融合,马上就会讲到,对于刚才的wget实例,某一时刻的可能情况如图9-6所示。
-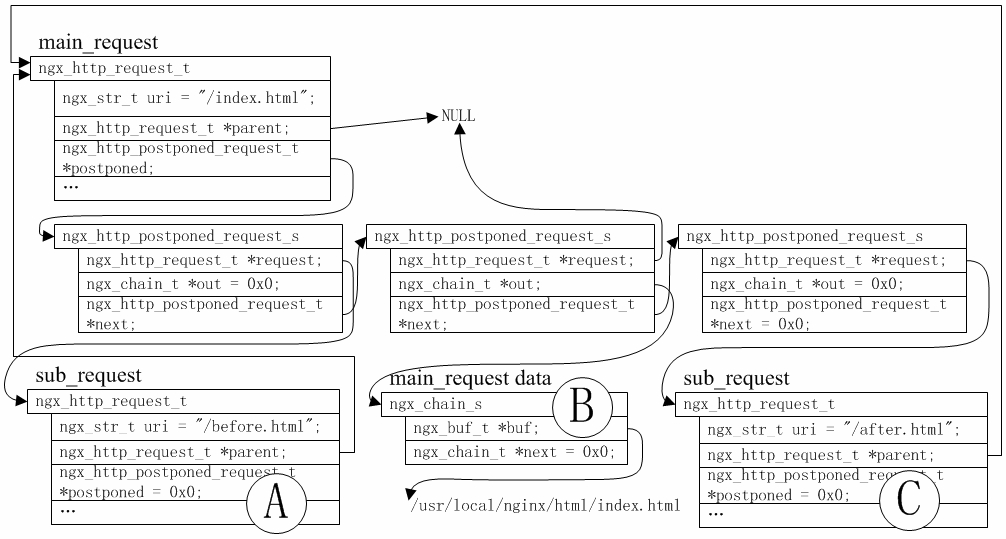 -
-上面讲述的是子请求的静态组织,与此相对的是动态执行,这用到了结构体ngx_http_request_t里的另外两个字段。
-316: 代码片段9.5-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.h
-317: typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-318: void *data, ngx_int_t rc);
-319:
-320: typedef struct {
-321: ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt handler;
-322: void *data;
-323: } ngx_http_post_subrequest_t;
-324: …
-335: typedef struct ngx_http_posted_request_s ngx_http_posted_request_t;
-336:
-337: struct ngx_http_posted_request_s {
-338: ngx_http_request_t *request;
-339: ngx_http_posted_request_t *next;
-340: };
-341: …
-347: struct ngx_http_request_s {
-348: …
-396: ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest;
-397: ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests;
-字段 post_subrequest 记录的主要是一个回调函数以及可传递给该回调函数的数据,回调函数在当前子请求结束时被调用,因此可以做进一步的自定义处理。
-1915:代码片段9.5-4,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1916:void
-1917:ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
-1918:{
-1919:…
-1946: if (r != r->main && r->post_subrequest) {
-1947: rc = r->post_subrequest->handler(r, r->post_subrequest->data, rc);
-1948: }
-函数ngx_http_finalize_request()在后面会详细提到,这里根据其命名就可以看出它是在做请求处理的结束工作,字段post_subrequest记录的回调函数也就是在此处被执行。
-另一个字段 posted_requests 是 Nginx 对子请求进行逐个处理的关键所在。虽然每一个ngx_http_request_t 结构体都有该字段,但只有主请求所对应的 ngx_http_request_t 结构体的posted_requests字段有效。在该字段内挂载的是一个链表,记录了当前所有需要被执行的子请求,在恰当的时机,Nginx 就会调用函数 ngx_http_run_posted_requests()遍历处理所有的子请求。正是由于字段posted_requests和函数ngx_http_run_posted_requests()的存在,才使得整个请求处理过程能向前推进。
-说了这么多,还未提到子请求是如何创建以及怎样与主请求并行执行的,下面就继续以ngx_http_addition_filter_module模块功能为示例,从头来详细了解子请求的整个处理过程。在这个实例里,因为ngx_http_addition_filter_module属于Filter模块,所以Nginx在处理客户端wget发出的主请求的过程中,直到走进该模块都还只有一个请求对象,并且到此时已经获得了对应的处理结果。原本走完这一层层Filter模块后,就可把结果数据实际发送给wget客户端,但因为我们的用户配置,Nginx在ngx_http_addition_filter_module模块内需要给整体响应数据再新增before_body数据和after_body数据。
-128: 代码片段9.5-5,文件名: ngx_http_addition_filter_module.c
-129: static ngx_int_t
-130: ngx_http_addition_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
-131: {
-132: …
-154: if (conf->before_body.len) {
-155: if(ngx_http_subrequest(r, &conf->before_body, NULL, &sr, NULL, 0)
-156: != NGX_OK)
-157: …
-178: rc = ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
-179: …
-184: if (ngx_http_subrequest(r, &conf->after_body, NULL, &sr, NULL, 0)
-185: != NGX_OK)
-186: {
-根据配置文件的设置,在代码第155和184行分别调用函数ngx_http_subrequest()创建了两个子请求(图9-6中的A和C)以获取对应的before_body数据和after_body数据,而代码第178行继续原来的body处理。显然,在继续原来的body处理时,这些body数据不能发送出去,因为至少要等before_body数据先发送,这也就是前面提到的次序问题。为了实现这一点, Nginx 提供了另外一个 Filter 模块 ngx_http_postpone_filter_module ,它创建一个ngx_http_postponed_request_t对象并把数据缓存(图9-6中的B)在其内,然后挂接到当前请求的postponed 链表内。由于所有请求都会经过这个 Filter 模块,什么时候需要缓存而什么时候又不需要缓存得有一个判断,以 Nginx 在结构体 ngx_connection_t 内设置了一个 data字段(该字段的初始值也就是主请求,在函数ngx_http_init_request()里能看到对应的设置:c->data = r;),记录当前排序在最前面的请求对象,也就是当前可以往客户端发送数据的请求对象(注意:只是说可以发,也就是按照最终响应数据的先后次序来看,该请求产生的数据已经可以组织到最终的out chain 链里了,但并不一定就会立即被Nginx 发送到网络上,在9.4小节讲述过这个问题)。如果当前请求对象不是排序在最前面,那么就需要做缓存,反之则反。那么,综合来看,对于子请求的整体组织,在 Nginx 内部可能出现的情况如图9-7所示。
-关于子请求,Nginx 内大量的逻辑都是针对最前请求的切换处理,因为它是保证最终响应数据正确的主要手段,后续的进一步分析也是针对如此。逐一来看,先是实现创建子请求的函数ngx_http_subrequest(),它的具体声明如下。
-492: 代码片段9.5-6,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.h
-493: ngx_int_t ngx_http_subrequest(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-494: ngx_str_t *uri, ngx_str_t *args, ngx_http_request_t **sr,
-495: ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *psr, ngx_uint_t flags);
-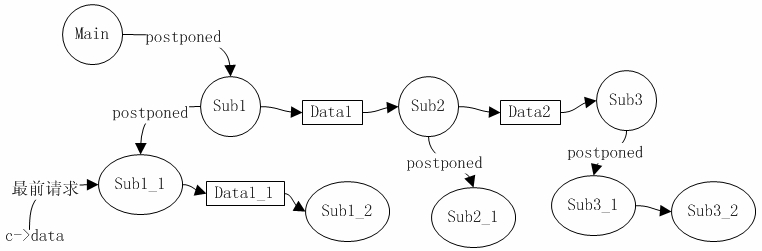 -
-各个参数的含义分别为:r 表示当前创建子请求的请求对象,也就是父请求;uri 和 args表示子请求的 uri 地址与 get 参数;psr 是一个传出参数,通过二级指针可以将 ngx_http_subrequest()新创建的子请求导出;ps指定子请求的回调处理函数;flags为旗标值,目前可取值NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_IN_MEMORY或NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_WAITED,分别表示结果数据是否可存放于内存中和先结束的子请求是否需等待前面子请求的结束才设置done标记(主要用于SSI功能模块)。
-函数ngx_http_subrequest()创建子请求的过程主要是初始化,把父请求的相关数据复制过来,包括main_conf、srv_conf、loc_conf等这样的配置。看另外几个关注重点。
-2422:代码片段9.5-7,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-2423: sr->method = NGX_HTTP_GET;
-2424:…
-2427: sr->uri = *uri;
-2428:
-2429: if (args) {
-2430: sr->args = *args;
-2431:…
-2445: sr->main = r->main;
-2446: sr->parent = r;
-2447: sr->post_subrequest = ps;
-2448: sr->read_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler;
-2449: sr->write_event_handler = ngx_http_handler;
-2450:
-2451: if (c->data == r && r->postponed == NULL) {
-2452: c->data = sr;
-2453: }
-子请求的method只能是GET(代码第2423行),所有请求对象的main字段都指向主请求(代码第2445行),把传入的参数复制到对应的字段(代码第2427~2430、2446~2447行)。值得重点关注的是代码第2449行,回调函数被设置为ngx_http_handler()意味着对该子请求的处理将完全重走一遍处理逻辑。而在一开始,当然无需关注读事件,所以读回调被设置为空函数ngx_http_request_empty_handler(),其实,因为子请求并不直接关联客户端,所以在后续的处理过程中,该读回调基本也就是为空。代码第2451~2453行用于切换请求的先后排序情况,如果当前排在最前面的请求是父请求并且子请求是该父请求的第一个,那么就做切换。这个应该容易理解,子请求的优先级应该比父请求高,否则的话,也应该是父请求的相关数据已经产生,并且在子请求之前的数据已经发送到out chain 链内。这点是我们在实现Nginx模块时必须做好的前提保证,比如,对于 Nginx 本身提供的 ngx_http_addition_filter_module模块,如果只有 after_body(即它在父请求之后),此时父请求已经先通过 ngx_http_next_body_filter()函数(代码片段9.5-5 第178 行)把数据写到out chain 链内了,所以当前请求才能是 after_body 所对应的子请求对象。而对于同一父请求的所有子请求而言,因为我们在各种处理的过程中总是从前往后进行,所以在一般情况下,先创建的子请求也应该在前面,即它们的前后顺序就应该按照创建的先后顺序进行排列。函数ngx_http_subrequest()再接下来的代码如下。
-2458:代码片段9.5-8,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-2459: pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_postponed_request_t));
-2460: if (pr == NULL) {
-2461: return NGX_ERROR;
-2462: }
-2463:
-2464: pr->request = sr;
-2465: pr->out = NULL;
-2466: pr->next = NULL;
-2467:
-2468: if (r->postponed) {
-2469: for (p = r->postponed; p->next; p = p->next) { /* void */ }
-2470: p->next = pr;
-2471:
-2472: } else {
-2473: r->postponed = pr;
-2474: }
-2475:…
-2490: *psr = sr;
-2491:
-2492: return ngx_http_post_request(sr, NULL);
-2493:}
-代码第2459~2474行封装对应的ngx_http_postponed_request_t数据结构,并将其加入到父请求的postponed链表内。代码第2490行是把子请求通过传出参数psr导出。最后,调用函数 ngx_http_post_request()把子请求加入到主请求所对应的 ngx_http_request_t 结构体的posted_requests字段内。
-1892:代码片段9.5-9,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1893:ngx_int_t
-1894:ngx_http_post_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_posted_request_t *pr)
-1895:{
-1896: ngx_http_posted_request_t **p;
-1897:
-1898: if (pr == NULL) {
-1899: pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_posted_request_t));
-1900:…
-1905: pr->request = r;
-1906: pr->next = NULL;
-1907:
-1908: for (p = &r->main->posted_requests; *p; p = &(*p)->next) { /* void */ }
-1909:
-1910: *p = pr;
-1911:
-1912: return NGX_OK;
-1913:}
-调用函数ngx_http_subrequest()创建的子请求并没有马上执行,而是被加入到主请求的待处理链表posted_requests里。前面曾提到,在恰当的时机,Nginx就会遍历这个链表内的所有请求并逐个进行处理。
-1857:代码片段9.5-10,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1858:void
-1859:ngx_http_run_posted_requests(ngx_connection_t *c)
-1860:{
-1861: ngx_http_request_t *r;
-1862: ngx_http_log_ctx_t *ctx;
-1863: ngx_http_posted_request_t *pr;
-1864:
-1865: for ( ;; ) {
-1866:…
-1871: r = c->data;
-1872: pr = r->main->posted_requests;
-1873:…
-1878: r->main->posted_requests = pr->next;
-1879:
-1880: r = pr->request;
-1881:…
-1888: r->write_event_handler(r);
-1889: }
-1890:}
-主动执行函数ngx_http_run_posted_requests()的恰当时机并不多,整个Nginx内只有三处,分别在函数 ngx_http_process_request()、ngx_http_request_handler()和 ngx_http_upstream_handler()最末尾。这几个函数都处在 http 请求处理流程的关键路径里,在它们的最末尾调用ngx_http_run_posted_requests()函数,意味着当前请求(最开始时,也就是主请求)的主要流程已经启动并执行,此时在等待进一步事件的空档时机,因此看是否有待处理的子请求(注意:这包括当前请求的子请求、孙子请求等。因为posted_requests链表挂载的是所有需要进一步处理的子请求或数据)需要处理(或缓存数据是否可以开始发送),有的话则逐个触发它们。
-对于子请求而言,在初始情况下,代码第1888行执行的是函数ngx_http_handler(),执行它意味着开始对一个子请求的正式处理,除了必须的处理动作外,相关的读写事件、超时等也都已经设置,对于该子请求的后续处理就将以事件触发作为推动力向前推进执行。每一个被触发的子请求会立即从posted_requests链表里移除(代码第1872、1878行),但因最终的数据组合同步问题又有可能被迫停止而再一次被加入到posted_requests链表内。关于这点,在后面介绍具体的同步过程时会看到,这里先看看前面曾提到的 Filter 模块 ngx_http_ postpone_filter_module。该函数的核心函数为ngx_http_postpone_filter(),我们看几部分重要的相关逻辑。
-51: 代码片段9.5-11,文件名: ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c
-52: static ngx_int_t
-53: ngx_http_postpone_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
-54: {
-55: …
-63: if (r != c->data) {
-64:
-65: if (in) {
-66: ngx_http_postpone_filter_add(r, in);
-67: return NGX_OK;
-68: }
-69: …
-77: return NGX_OK;
-78: }
-对于上面代码流程的情况,此时当前请求对象并不是排在最前面的,因此不能向out chain链写入(如果有)数据,取而代之的是通过函数ngx_http_postpone_filter_add()将其加入到当前请求的postponed链内(图9-6中的B)。函数ngx_http_postpone_filter_add()的逻辑比较简单,其先判断postponed链最末尾(必定是在最末尾,前面曾解释过这个问题[13])的ngx_http_postponed_request_t 结构存放的是否就是数据(即pr->request ==NULL),如果是则把数据直接添加进去(具体也就是ngx_http_postponed_request_t结构体对象的out链)即可,否则的话,就需在postponed链表末尾新建一个对应的ngx_http_postponed_request_t结构来存放该数据。
-函数 ngx_http_postpone_filter()接下来的代码处理的逻辑是当前请求对象刚好排在最前面的情况。
-80: 代码片段9.5-12,文件名: ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c
-81: if (r->postponed == NULL) {
-82:
-83: if (in || c->buffered) {
-84: return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r->main, in);
-85: }
-86:
-87: return NGX_OK;
-88: }
-如果当前请求的postponed链表为空(没有子请求,也没有之前的缓存数据),那么非常简单,有数据就发(代码第83~84行,注意到后续filter不应再有对是否为子请求对象的判断,所以第一个参数直接为主请求 r->main,以便后续处理能够获取更多的信息),没有就直接返回NGX_OK。
-再接下来就是当前请求排在最前面但其postponed链表不为空的情况。为什么会出现这种情况?这是因为父请求的数据也被缓存到 postponed 链表的缘故,比如有如下这样的实际情况,客户端请求ssi.html页面时,父请求(此时也就是主请求)的postponed链表将有5个节点,如图9-8所示。
- -
-在继续处理的过程中,显然节点B所对应的子请求是排在最前面的,如果它被处理完后,排在最前面的请求就将是节点 M 所对应的主请求。为什么不是节点 test1 呢?这是因为,首先,它不是一个子请求,它只是对父请求M产生数据的封装,其次,由于它是数据,对应的ngx_chain_t结构体并没有相应的字段指向M,所以不能直接把c->data指向它。因此,在真正结束一个处于最前面的请求对象(此时,它必定没有子请求,代码第1995~2001行做了这点保证)时,新的排在最前面的请求对象就是其父请求。
-1915:代码片段9.5-13,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1916:void
-1917:ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
-1918:{
-1919:…
-1993: if (r != r->main) {
-1994:
-1995: if (r->buffered || r->postponed) {
-1996:…
-2001: return;
-2002: }
-2003:…
-2012: pr = r->parent;
-2013:
-2014: if (r == c->data) {
-2015:…
-2012: c->data = pr;
- -
-此时如果再进入到函数 ngx_http_postpone_filter(),出现的就是刚才提到的情形,而执行的也就是这一段逻辑。
-88: 代码片段9.5-14,文件名: ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c
-89: if (in) {
-90: ngx_http_postpone_filter_add(r, in);
-91: }
-92:
-93: do {
-94: pr = r->postponed;
-95:
-96: if (pr->request) {
-97: …
-102: r->postponed = pr->next;
-103:
-104: c->data = pr->request;
-105:
-106: return ngx_http_post_request(pr->request, NULL);
-107: }
-108:
-109: if (pr->out == NULL) {
-110: …
-114: } else {
-115: …
-119: if (ngx_http_next_body_filter(r->main, pr->out) == NGX_ERROR) {
-120: return NGX_ERROR;
-121: }
-122: }
-123:
-124: r->postponed = pr->next;
-125:
-126: } while (r->postponed);
-对照图示,这一段代码就很容易理解了。代码第89~90行判断当前请求是否有新数据产生,如果有的话需加到最后;接下来的大循环就是逐一判断postponed链表里的每一个节点,如果是数据(即pr->request字段为空,比如图9-9中的test1),那么就调用函数ngx_http_next_body_filter()走后续发送流程,将数据写入到outchain 链内;如果是子请求(即pr->request 字段不为空,比如图9-9中的节点I),此时先把该请求对象从父请求的postponed链表里移除,同时修改 c->data 的值,即把排列最前的请求对象改为该子请求,最后再调用函数ngx_http_post_request()把它加入到待处理链表r->main->posted_requests里并直接返回。Nginx在后面的执行中又会调用到ngx_http_run_posted_requests()函数触发子请求的执行。
-仅仅依靠函数ngx_http_postpone_filter()做数据同步还不够,因为组织子请求的postponed链表不能只增不减,所以在函数ngx_http_finalize_request()内对已经完成的子请求做删减操作,从而可以切换排序最前的请求对象。对于ngx_http_finalize_request()函数,在前面已经提到一部分实现,下面继续看另外的重点内容。
-2036:代码片段9.5-15,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2037: if (pr->postponed && pr->postponed->request == r) {
-2038: pr->postponed = pr->postponed->next;
-2039: }
-代码第2037行的判断是针对当前请求对象已经从postponed链表里移除的情况,此时当然无需再做移除。
-2051:代码片段9.5-16,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2052: if (ngx_http_post_request(pr, NULL) != NGX_OK) {
-2053: r->main->count++;
-2054: ngx_http_terminate_request(r, 0);
-2055: return;
-2056: }
-最后提到的这一段代码是把父请求再次加入到主请求的 posted_requests 链表内,以便主动触发对它的逻辑处理。我们知道,在一般情况下,Nginx 对请求的处理是通过触发事件来向前推进的,但是因为子请求对数据同步的需求,导致某些已经完成的请求却不能及时结束,而这些请求又基本不会再有事件触发,所以对于它们的向前推进,必须依靠Nginx主动去做,因此这里主动把父请求加入到 posted_requests 链表也就是这个原因,在后续执行函数ngx_http_run_posted_requests()时,该父请求的write_event_handler()回调函数就会被主动调用。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..23064abe7a81968d723fcb22617a77b4cf529d8e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + location / { + root html; + index index.html index.htm; + add_before_body /before.html; + add_after_body /after.html; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-10-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-10-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..20e53cb464b0f636197e3f0591bb74cd2cd6052f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-10-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +void +ngx_http_run_posted_requests(ngx_connection_t *c) +{ + ngx_http_request_t *r; + ngx_http_log_ctx_t *ctx; + ngx_http_posted_request_t *pr; + + for ( ;; ) { +… + r = c->data; + pr = r->main->posted_requests; +… + r->main->posted_requests = pr->next; + + r = pr->request; +… + r->write_event_handler(r); + } +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-11-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-11-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d748faa0df5280498dcd97e0fc2da4c322782179 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-11-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_postpone_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) + { + … + if (r != c->data) { + + if (in) { + ngx_http_postpone_filter_add(r, in); + return NGX_OK; + } + … + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-12-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-12-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ebc77efd855ab981d0fda712ea10916335eb2e39 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-12-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + if (r->postponed == NULL) { + + if (in || c->buffered) { + return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r->main, in); + } + + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-13-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-13-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3b878de21c8cbe4956684300d70d739a8fab34a5 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-13-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +void +ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc) +{ +… + if (r != r->main) { + + if (r->buffered || r->postponed) { +… + return; + } +… + pr = r->parent; + + if (r == c->data) { +… + c->data = pr; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-14-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-14-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9602590bed43e564af4b00a28c01a708058ec9e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-14-ngx_http_postpone_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ + if (in) { + ngx_http_postpone_filter_add(r, in); + } + + do { + pr = r->postponed; + + if (pr->request) { + … + r->postponed = pr->next; + + c->data = pr->request; + + return ngx_http_post_request(pr->request, NULL); + } + + if (pr->out == NULL) { +… + } else { +… + if (ngx_http_next_body_filter(r->main, pr->out) == NGX_ERROR) { + return NGX_ERROR; + } + } + + r->postponed = pr->next; + + } while (r->postponed); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-15-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-15-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..da67da2df2e1a8f72169cc29759b28b1af058a7f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-15-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + if (pr->postponed && pr->postponed->request == r) { + pr->postponed = pr->postponed->next; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-16-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-16-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ebdb496ee3930baecd5f47a0d6bed0018bc2458b --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-16-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + if (ngx_http_post_request(pr, NULL) != NGX_OK) { + r->main->count++; + ngx_http_terminate_request(r, 0); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-2-ngx_http_request.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-2-ngx_http_request.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cb58c41d2f6f6e630edc11a13519e633adfa63cb --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-2-ngx_http_request.h" @@ -0,0 +1,12 @@ +typedef struct ngx_http_postponed_request_s ngx_http_postponed_request_t; + +struct ngx_http_postponed_request_s { + ngx_http_request_t *request; + ngx_chain_t *out; + ngx_http_postponed_request_t *next; +}; +… +struct ngx_http_request_s { +… + ngx_http_request_t *parent; + ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-3-ngx_http_request.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-3-ngx_http_request.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9d6b11e3ade3d235b287fcc2c3854ebf5b9cdc87 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-3-ngx_http_request.h" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt)(ngx_http_request_t *r, + void *data, ngx_int_t rc); + +typedef struct { + ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt handler; + void *data; +} ngx_http_post_subrequest_t; +… +typedef struct ngx_http_posted_request_s ngx_http_posted_request_t; + +struct ngx_http_posted_request_s { + ngx_http_request_t *request; + ngx_http_posted_request_t *next; +}; +… +struct ngx_http_request_s { +… + ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest; + ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-4-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-4-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dac3127147ce9a088162067209564f9ed833adeb --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-4-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +void +ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc) +{ +… + if (r != r->main && r->post_subrequest) { + rc = r->post_subrequest->handler(r, r->post_subrequest->data, rc); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-5-ngx_http_addition_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-5-ngx_http_addition_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fab45788a30de69a9680bbf195a9ba013deee766 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-5-ngx_http_addition_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_addition_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) +{ +… + if (conf->before_body.len) { + if(ngx_http_subrequest(r, &conf->before_body, NULL, &sr, NULL, 0) + != NGX_OK) +… + rc = ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in); +… + if (ngx_http_subrequest(r, &conf->after_body, NULL, &sr, NULL, 0) + != NGX_OK) + { \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-6-ngx_http_core_module.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-6-ngx_http_core_module.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea951fded8aeb912690358e5ac35e13bdcbc2321 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-6-ngx_http_core_module.h" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ +ngx_int_t ngx_http_subrequest(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_str_t *uri, ngx_str_t *args, ngx_http_request_t **sr, + ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *psr, ngx_uint_t flags); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-7-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-7-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0947ceddcbdcc4cae930b1c6133abda8616959a1 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-7-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ + sr->method = NGX_HTTP_GET; +… + sr->uri = *uri; + + if (args) { + sr->args = *args; +… + sr->main = r->main; + sr->parent = r; + sr->post_subrequest = ps; + sr->read_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler; + sr->write_event_handler = ngx_http_handler; + + if (c->data == r && r->postponed == NULL) { + c->data = sr; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-8-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-8-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8e1cf7770f371afd54b8c6b401f5557d9815f33 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-8-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ + pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_postponed_request_t)); + if (pr == NULL) { + return NGX_ERROR; + } + + pr->request = sr; + pr->out = NULL; + pr->next = NULL; + + if (r->postponed) { + for (p = r->postponed; p->next; p = p->next) { /* void */ } + p->next = pr; + + } else { + r->postponed = pr; + } +… + *psr = sr; + + return ngx_http_post_request(sr, NULL); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-9-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-9-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b3617bbe445d00f46efe35028c7cfea84d4b68f0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.5 \345\255\220\350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.5-9-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +ngx_int_t +ngx_http_post_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_posted_request_t *pr) +{ + ngx_http_posted_request_t **p; + + if (pr == NULL) { + pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_posted_request_t)); +… + pr->request = r; + pr->next = NULL; + + for (p = &r->main->posted_requests; *p; p = &(*p)->next) { /* void */ } + + *p = pr; + + return NGX_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 1bcebcb77c67d0e92106e2f00ab029f1bab7dfd3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,358 +0,0 @@ - -虽然没明确描述,但我们肯定已经知道,得益于keepalive的帮助,在同一个http连接上可以连续承载多个http请求,而对于同一个http请求,又可能由于子请求或内部跳转等导致有多个request对象或请求处理状态机被执行多次,所以,http连接关闭的主要工作也就是关闭其上承载的每一个http请求的每一个request对象并释放其附带的所有相关资源。
-对某一个http请求进行正常关闭的操作实现在函数ngx_http_finalize_request()内,它带有两个参数。
-1915:代码片段9.6-1,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1916:void
-1917:ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
-1918:{
-1919:…
-1929: if (rc == NGX_DONE) {
-1930: ngx_http_finalize_connection(r);
-1931: return;
-1932: }
-1933:…
-1950: if (rc == NGX_ERROR
-1951: || rc == NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT
-1952: || rc == NGX_HTTP_CLIENT_CLOSED_REQUEST
-1953: || c->error)
-1954: {
-1955: if (ngx_http_post_action(r) == NGX_OK) {
-1956: return;
-1957: }
-1958:
-1959: if (r->main->blocked) {
-1960: r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_finalizer;
-1961: }
-1962:
-1963: ngx_http_terminate_request(r, rc);
-1964: return;
-1965: }
-1966:…
-2101: if (c->read->eof) {
-2102: ngx_http_close_request(r, 0);
-2103: return;
-2104: }
-2105:
-2106: ngx_http_finalize_connection(r);
-2107:}
-参数r是待关闭的request对象,而参数rc是关闭的程度状态值,如果其值为NGX_DONE则表示 http 请求已经明确正常结束,所以开始进入到 http 连接的结束流程上(代码第1930行)。否则表示当前http请求可能还有一些事情需要进一步处理,比如判错、删除定时器等,如果处理严重出错则将调用ngx_http_terminate_request()函数(代码第1950~1953行、第1963行,其内部也是调用ngx_http_close_request())或读结束则表示对端发送了FIN数据包,所以需要调用ngx_http_close_request()函数进行处理(代码第2101~2103行)。如果事情能够正常处理,那么函数可能会提前返回继续处理,关闭需等待下一次(代码第1950~1956 行)。如果所有事情都已经成功处理,那么最后也将调用 ngx_http_finalize_connection()函数(代码第2106行),而该函数也有可能会调用函数ngx_http_close_request()。
-虽然最终都(有可能)会进入到这个ngx_http_close_request()函数,但不同的进入路径所做的前期工作肯定不一样。ngx_http_terminate_request()函数会做一些清理工作,因为此时的request对象明显处于异常终止状态,不对这些资源进行主动释放的话,可能就会发生资源泄漏;而ngx_http_finalize_connection()函数走的是正常结束流程,此时如果连接是keepalive或是需要延迟关闭,那么就不会调用ngx_http_close_request()函数,换以更优雅的方式关闭http连接。
-先来看函数ngx_http_close_request(),它有一个重要判断。
-2960:代码片段9.6-2,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2961:static void
-2962:ngx_http_close_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
-2963:{
-2964: ngx_connection_t *c;
-2965:
-2966: r = r->main;
-2967:…
-2976: r->count--;
-2977:
-2978: if (r->count || r->blocked) {
-2979: return;
-2980: }
-2981:
-2982: ngx_http_free_request(r, rc);
-2983: ngx_http_close_connection(c);
-2984:}
-在代码第2966、2976~2978行,主请求对应的request对象有一个引用计数count,既然都说是引用计数,所以如果它的值不为 0,则表示其还在使用当中,所以就直接返回(代码第2979 行);否则的话,在代码第2982~2983 行调入到函数 ngx_http_free_request()和ngx_http_close_connection()内开始实际的资源释放操作。
-在开始新的子请求、内部跳转、命名location跳转、开始upstream请求等多种情况下,都可能导致主请求request对象的引用计数count自增1,这意味着在对应的操作完成(比如内部跳转处理结束)之前不能释放主请求对象和连接对象。之所以需要做这样的设计,原因仍然在于 Nginx 是通过事件触发来向前推进的,资源相互关联的各个请求对象在执行过程中谁先谁后不可预知,虽然在其他大部分地方不需要同步而各自自由前进,但在结束点上做资源释放时却需要同步,否则导致的结果就可想而知了。
-实现引用计数只需使用主请求对应的request对象的count字段即可,因为前面曾提到过,所有的子请求对象都有对主请求的引用,即r->main,因此随处都可以访问到该字段。主请求的另一个字段 blocked 也是做引用计数使用,它记录当前是否有读/写操作被阻塞(即对应事件未发生而导致读/写操作未能完成),如果有则也不能对请求做结束清理处理。字段blocked不能与count合二为一的原因是因为在某些地方,对于读/写操作被阻塞的情况需要特别处理,比如代码片段9.6-1的第1959~1961行。
-再来看在函数ngx_http_finalize_connection()内,也有对request对象引用计数count的判断。
-2169:代码片段9.6-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2170:static void
-2171:ngx_http_finalize_connection(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-2172:{
-2173:…
-2177: if (r->main->count != 1) {
-2178:…
-2189: ngx_http_close_request(r, 0);
-2190: return;
-2191: }
-这是必要的,如果引用计数count值不为1,则进入到函数ngx_http_close_request()做引用计数自减,然后一起返回。否则的话,表示这是对该request对象的最后一处引用,是暂作保留还是直接释放,就要看另外两个机制,即keepalive或延迟关闭是否启用。可以看到,一个请求最终是否释放的判断依据是引用计数,而一个连接最终是否释放的判断依据是该连接上是否还会有请求到来(即需做keepalive)或是否需要做延迟释放。
- -我们先来看 Nginx 对 keepalive 机制的实现。在 HTTP 1.0 协议里,客户端通过发送Connection:Keep-Alive的请求头来实现与服务器之间的keepalive;而在HTTP1.1 协议里,由于标准要求连接默认被保持,所以此时请求头Connection:Keep-Alive也不再有意义,但通过请求头Connection: Close可明确要求不进行keepalive 连接保持。在Nginx 内的具体判断,首先是获取Connection请求头并设置connection_type变量。
-1427:代码片段9.6.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1428: if (ngx_strcasestrn(h->value.data, "close", 5 - 1)) {
-1429: r->headers_in.connection_type = NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_CLOSE;
-1430:
-1431: } else if (ngx_strcasestrn(h->value.data, "keep-alive", 10 - 1)) {
-1432: r->headers_in.connection_type = NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_KEEP_ALIVE;
-1433: }
-然后将该字段赋值到request对象上去(r->keepalive在实际的处理过程中会发生变化,比如一条连接上处理的请求数达到一定的限制,默认是100,就会自动断开,即此时r->keepalive值为0,具体可以参考ngx_http_update_location_config()函数)。
-828: 代码片段9.6.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-829: if (!r->internal) {
-830: switch (r->headers_in.connection_type) {
-831: case 0:
-832: r->keepalive = (r->http_version > NGX_HTTP_VERSION_10);
-833: break;
-834:
-835: case NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_CLOSE:
-836: r->keepalive = 0;
-837: break;
-838:
-839: case NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_KEEP_ALIVE:
-840: r->keepalive = 1;
-841: break;
-842: }
-只有客户端与Nginx之间才有关注keepalive的必要,对于因Nginx内部流程(比如内部跳转、命名location跳转、子请求等)产生的request对象不会用到keepalive,自然就不用去关注(代码第829 行)。代码第830~842 的逻辑简单明了无需多说。回过头来接着看函数ngx_http_finalize_connection()里对keepalive机制的使用。
-2192:代码片段9.6.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2193: if (!ngx_terminate
-2194: && !ngx_exiting
-2195: && r->keepalive
-2196: && clcf->keepalive_timeout > 0)
-2197: {
-2198: ngx_http_set_keepalive(r);
-2199: return;
-2200: }
-几个判断条件很好懂,其中 clcf->keepalive_timeout 可由用户通过配置指令 keepalive_timeout设置,默认情况也就是75秒,函数ngx_http_set_keepalive()则是正式开始keepalive处理。该函数有点长,仍然只关注重点部分,首先是pipelining请求。
-2465:代码片段9.6.1-4,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2466: b = r->header_in;
-2467:
-2468: if (b->pos < b->last) {
-2469:
-2470: /* the pipelined request */
-2471:
-2472: if (b != c->buffer) {
-2473:…
-2501: hc->busy[0] = b;
-2502: hc->nbusy = 1;
-2503: }
-2504: }
-2508: ngx_http_free_request(r, 0);
-2509:...
-2522: if (b->pos < b->last) {
-2523:…
-2533: rev->handler = ngx_http_init_request;
-2534: ngx_post_event(rev, &ngx_posted_events);
-2535: return;
-2536: }
-核心的代码在第2522~2535行,前面的都是做资源释放。因为我们知道,一旦进入这个函数就意味着一个http请求已经处理并响应结束,所以能够释放的资源需尽量释放或重用,而代码第2468~2508行就是完成这工作中的一部分,第2468行的if判断为真则表示后续会进行pipelining处理,所以这里对大块内存做重用。具体代码未给出,但逻辑简单,就是将那些当前处理过程中(因接收请求头信息而)使用过的内存从busy状态移到free状态,从而在下一个请求处理过程中立即重用。注意下一个请求的请求头信息放在hc->busy[0]内(代码第2501~2502行),在后续调用函数ngx_http_init_request()时,对应的request对象可以重用这个大块内存和取出其内的已接收到的请求头数据。
-236: 代码片段9.6.1-5,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-237: static void
-238: ngx_http_init_request(ngx_event_t *rev)
-239: {
-240: …
-283: r = hc->request;
-284:
-285: if (r) {
-286: ngx_memzero(r, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t));
-287:
-288: r->pipeline = hc->pipeline;
-289:
-290: if (hc->nbusy) {
-291: r->header_in = hc->busy[0];
-292: }
-因为已经判断出是pipelining,所以下一个请求处理马上开始,这也就是第2533~2534行,即把读对象 rev 主动推送到 ngx_posted_events 链表里。注意它的事件处理回调函数为 ngx_ http_init_request(),在进程的下一次主循环里就会调用该函数,从而开始一个新的http请求处理过程。
-代码第2468~2522 行判断是否为pipelining请求的依据是什么?我们要知道pipelining请求的最大特征[14]是客户端在发出第n+1 个请求前不必等待是否已收到第n个请求的响应数据,这就意味着服务器端在刚结束客户端第n个请求的处理时,其存放请求头的缓存区里就已经有了客户端第n+1 个请求的请求头,这也就是如上代码中那样的判断。否则的话,最多也就只能算是持久连接,http请求响应依次进行。
-如果不是 pipelining 请求,那么接下来就是大量的资源释放动作,毕竟即使当前连接是keepalive 的,但其下一个请求什么时候来或者到底来不来都不清楚,所以相关资源尽量释放或重用,这不多说,只看我们所关心的超时定时器和可读事件设置。
-2511:代码片段9.6.1-6,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2512: ngx_add_timer(rev, clcf->keepalive_timeout);
-2513: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-2514:...
-2598: rev->handler = ngx_http_keepalive_handler;
-不管是超时亦或是客户端发出了一个新请求,都将执行回调函数 ngx_http_keepalive_handler(),而该函数的逻辑也比较简单。
-2662:代码片段9.6.1-7,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2663:static void
-2664:ngx_http_keepalive_handler(ngx_event_t *rev)
-2665:{
-2666:…
-2675: if (rev->timedout || c->close) {
-2676: ngx_http_close_connection(c);
-2677: return;
-2678: }
-2679:…
-2730: n = c->recv(c, b->last, size);
-2731: c->log_error = NGX_ERROR_INFO;
-2732:
-2733: if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
-2734: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-2735: ngx_http_close_connection(c);
-2736: }
-2737:
-2738: return;
-2739: }
-2740:…
-2767: ngx_http_init_request(rev);
-2768:}
-超时则关闭连接退出(代码第2675~2677行)或没有读到数据则继续监控读事件(如果出错也关闭连接退出,代码第2730~2739行),否则也就是客户端发送了新的请求,从而Nginx调用函数ngx_http_init_request()开始一轮新的请求处理。
- -Nginx通过依靠套接口选项SO_LINGER[15]和函数shutdown()、函数read()共同来实现延迟关闭机制。先来看看这几个额外的知识点。函数read()无需多说,而函数shutdown()的接口描述如下。
-#include
int shutdown(int sockfd, int how);
-其中参数how可取值SHUT_RD或SHUT_WR或SHUT_RDWR,分别表示关闭读、关闭写、关闭读/写,这也就比close()函数只能进行关闭读/写来得更灵活一点。该函数可能的返回值有0表示正常,−1表示出错,对应的errno被设置为EBADF(无效描述符)、ENOTSOCK (描述符不是套接口)或ENOTCONN(套接口未连接)。
-Linux 提供的套接口选项 SO_LINGER 可以改变在套接口上执行 close()函数时的默认行为。选项SO_LINGER用到的相关参数主要是一个linger结构体。
-50: 代码片段9.6.2-1,文件名: \linux-3.4.4\include\linux\socket.h
-51: struct linger {
-52: int l_onoff; /* Linger active */
-53: int l_linger;/* How long to linger for */
-54: };
-注释很清楚,字段l_onoff标记是否启用Linger特性,非0为启用,0为禁用(即内核对close()函数采取默认行为);字段l_onoff为非0的情况下,字段l_linger生效,如果它的值为0,那么在执行函数close()时,将丢弃缓存区内的所有数据并且立即终止连接(即发送RST数据包);如果字段l_linger的值为非0(假定为t秒),那么此时函数close()将被阻塞(假定为阻塞模式)直到[16]:
-1.待发送的数据全部得到了对端确认,返回值为0。
-2.发生信号中断或异常(比如意外收到对端发送过来的数据)或超时,返回值为0。
-下面,我们直接来看 Nginx 是如何利用这些套接口选项与系统函数实现延迟关闭的,首先是SO_LINGER选项的全部相关代码。
-2986:代码片段9.6.2-2,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2987:static void
-2988:ngx_http_free_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
-2989:{
-2990:…
-3033: if (r->connection->timedout) {
-3034: clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
-3035:
-3036: if (clcf->reset_timedout_connection) {
-3037: linger.l_onoff = 1;
-3038: linger.l_linger = 0;
-3039:
-3040: if (setsockopt(r->connection->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_LINGER,
-3041: (constvoid *)&linger,sizeof(structlinger))==-1)
-与SO_LINGER选项直接相关的代码的确就只有这些。注意两点:第一,进入设置SO_LINGER 选项的 if 判断,此时连接已经超时并且 Nginx 用户配置了超时重置;第二,linger结构体的字段l_onoff为1而l_linger为0,也就是close()套接口时直接发送RST数据包。
-可以看到在Nginx内部有很多代码处有对ngx_http_close_request()函数的调用,而这些都是在处理逻辑出现异常的情况下进行,比如
-934: 代码片段9.6.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-935: rv = ngx_http_alloc_large_header_buffer(r, 1);
-936:
-937: if (rv == NGX_ERROR) {
-938: ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
-939: return;
-940: }
-941: …
-976: if (rev->timedout) {
-977: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out");
-978: c->timedout = 1;
-979: ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT);
-980: return;
-981: }
-上面仅例举了两处:在第937行判断的是上一个ngx_http_alloc_large_header_buffer()函数执行出错的情况(返回值为NGX_ERROR),此时调用ngx_http_close_request()函数以结束对请求的继续处理;代码第976 行判断是当前客户端已超时,所以同样也调用 ngx_http_close_request()函数关闭请求。
-在函数ngx_http_close_request()末尾处依次调用了两个函数。
-ngx_http_close_request() ->1: ngx_http_free_request(r, rc)
-ngx_http_close_request() ->2: ngx_http_close_connection(c)
-前面已经看到在函数 ngx_http_free_request()内,会对已经超时的连接设置 SO_LINGER选项。而在函数ngx_http_close_connection()函数内最终将调用close()函数关闭连接套接口。
-ngx_http_close_connection() -> ngx_close_connection(c) -> close(fd)
-那么此时,已经超时的连接就直接发送RST包而强行中断。未超时的连接就调用close()函数进行常规的四次挥手流程,这里也没有使用 shutdown()函数,为什么?其实是因为对于这种本就异常结束的连接,Nginx不再多发心思而直接close()掉,否则的话,延迟关闭的异常连接过多反而影响其他正常请求处理的性能,Nginx把关注重点放在那些正常结束的连接上,只有它们才会走到延迟关闭的流程上来。
-在前面章节已经介绍过,函数 ngx_http_finalize_connection()是客户端请求被正常处理后的关闭函数,在资源真正释放之前需判断 keepalive 机制或延迟关闭机制是否启用。当然, keepalive 机制优先,因为它暂不关闭连接,而延迟关闭机制到底只是延迟一下,最终还是要关闭连接。如果走keepalive机制的流程,那么Nginx就和延迟关闭机制没有任何关系,从各自进入的条件判断以及先后顺序来看,一般情况下,Nginx的延迟关闭机制不会用得太多。
-2192:代码片段9.6.2-4,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2193: if (!ngx_terminate
-2194: && !ngx_exiting
-2195: && r->keepalive
-2196: && clcf->keepalive_timeout > 0)
-2197: {
-2198: ngx_http_set_keepalive(r);
-2199: return;
-2200: }
-2201:
-2202: if (clcf->lingering_close == NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_ALWAYS
-2203: || (clcf->lingering_close == NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_ON
-2204: && (r->lingering_close
-2205: || r->header_in->pos < r->header_in->last
-2206: || r->connection->read->ready)))
-2207: {
-2208: ngx_http_set_lingering_close(r);
-2209: return;
-2210: }
-进程退出的时机比较少,对于HTTP 1.1协议keepalive默认启用,而keepalive_timeout默认值为75秒,所以综合来看一般会调用第2198行的ngx_http_set_keepalive()函数走keepalive流程。
-如果不走keepalive流程,那么对于是否走延迟关闭流程仍需要做一些判断,因为延迟关闭就意味着资源不能及时释放,所以如要这么做则必需满足一定的条件。逐一来看,第2202行表示用户在配置文件里主动设置了 lingering_close 选项为 always,所以必须延迟关闭。第2203~2206行则是在用户设置lingering_close选项为on的情况下所做的判断,因为在某些情况下,即便用户做了这样的设置,但因为没有必要则也不进行延迟关闭。有哪些情况不必要体现在字段r->lingering_close内,我们看几处示例。
-819: 代码片段9.6.2-5,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-820: void
-821: ngx_http_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-822: {
-823: …
-844: r->lingering_close = (r->headers_in.content_length_n > 0);
-如果客户端发送的请求没有请求体,那么第844行就将设置r->lingering_close为0。另一处代码。
-437: 代码片段9.6.2-6,文件名: ngx_http_request_body.c
-438: ngx_int_t
-439: ngx_http_discard_request_body(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-440: {
-441: …
-484: if (ngx_http_read_discarded_request_body(r) == NGX_OK) {
-485: r->lingering_close = 0;
-代码第484行判断为真则表示成功全部丢弃客户端发送的请求体数据。再看一处代码。
-495: 代码片段9.6.2-7,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-496: void
-497: ngx_http_discarded_request_body_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-498: {
-499: …
-515: if (r->lingering_time) {
-516: timer = (ngx_msec_t) (r->lingering_time - ngx_time());
-517:
-518: if (timer <= 0) {
-519: r->discard_body = 0;
-520: r->lingering_close = 0;
-代码第518 行判断为真则表示已经延迟超时。所以,可以看到在某些情况下,即客户端明确不会发送数据过来或发送已经超时,就没有必要进行延迟关闭了。而与此相对,如果客户端有很大可能会发送数据过来,那么就需进行延迟关闭,前面的代码第2205~2206行就属于这种情况,此时缓存区里有数据(第2205行)或明确可读(第2206行)。总之,我们需知道延迟关闭所要避免的就是在close()掉套接口时或之后却由于接收缓冲区有客户端发送过来的数据或正收到客户端的数据包而导致发送RST包异常终止连接所带来的负面影响。因为根据RFC 2525[17]标准文档,当一个套接口正在或已经被关闭,如果在其接收队列有未读数据(不管是在关闭前就已收到的,或者还是在关闭后新到达的),那么此时就需给对端发送一个RST数据包,而这个RST数据包可能导致之前发送给对端并且尚在网络或在对端接收缓存区的正常响应数据丢失[18]。
-不管怎样,一旦对套接口进行延迟关闭,那就是调用函数ngx_http_set_lingering_close()。看一下这个函数的基本逻辑。
-2770:代码片段9.6.2-8,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2771:static void
-2772:ngx_http_set_lingering_close(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-2773:{
-2774:…
-2782: rev = c->read;
-2783: rev->handler = ngx_http_lingering_close_handler;
-2784:
-2785: r->lingering_time = ngx_time() + (time_t) (clcf->lingering_time / 1000);
-2786: ngx_add_timer(rev, clcf->lingering_timeout);
-2787:
-2788: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-2789:…
-2803: if (ngx_shutdown_socket(c->fd, NGX_WRITE_SHUTDOWN) == -1) {
-2804:…
-2810: if (rev->ready) {
-2811: ngx_http_lingering_close_handler(rev);
-2812: }
-2813:}
-代码第2782~2788行设置事件对象rev的超时定时器、监控其可读事件,这样后续不管超时还是发生可读事件,执行的都是回调函数ngx_http_lingering_close_handler();代码第2803行执行shutdown()函数关闭可写(宏ngx_shutdown_socket 为 shutdown ,宏NGX_WRITE_SHUTDOWN为SHUT_WR,这和直接调用close()函数是不一样的,这里表示如果接收缓存区有数据包或后续还收到对端的数据包,那么本端都是可以继续进行读取的,因此不会像前面描述的那样因为套接口已 close()而发送 RST 数据包),也就是向对端发送一个FIN包;代码第2810行,如果判断出此时已经是可读状态,那么直接执行函数ngx_http_lingering_close_handler()。下面就来看该函数。
-2815:代码片段9.6.2-9,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-2816:static void
-2817:ngx_http_lingering_close_handler(ngx_event_t *rev)
-2818:{
-2819:…
-2832: if (rev->timedout) {
-2833: ngx_http_close_request(r, 0);
-2834: return;
-2835: }
-2836:
-2837: timer = (ngx_msec_t) (r->lingering_time - ngx_time());
-2838: if (timer <= 0) {
-2839: ngx_http_close_request(r, 0);
-2840: return;
-2841: }
-2842:…
-2843: do {
-2844: n = c->recv(c, buffer, NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_BUFFER_SIZE);
-2845:…
-2848: if (n == NGX_ERROR || n == 0) {
-2849: ngx_http_close_request(r, 0);
-2850: return;
-2851: }
-2852:
-2853: } while (rev->ready);
-2854:…
-2862: timer *= 1000;
-2863:…
-2868: ngx_add_timer(rev, timer);
-2869:}
-代码第2832~2841 是判断超时,不管是读超时还是延迟关闭超时,此时都执行函数ngx_http_close_request()进行套接口关闭,受SO_LINGER选项影响将直接发送RST包。代码第2843~2853是进行读操作,如果读错(可能是网络断开等)或读的数据长度为0(表示收到对端发送的FIN包)则也调用函数ngx_http_close_request()进行套接口关闭,此时如果对端已经通过发送FIN包进行了关闭而断开了连接,那么这里close()调入到内核也就不会发送RST包,而只是简单地回收套接口。进入到最后的几行代码,表示需继续等待,所以重新启动定时器,当然,此时的超时时间timer已经变小了(代码第2837行)。
-综上所述,Nginx 对延迟关闭的整体实现与一般应用程序的标准延迟关闭方案类似,只是在具体的处理细节上有一点差别而已。
-1.设置SO_LINGER 选项参数l_onof 非0 而l_linger为0。
-2.调用函数shutdown(sock_fd, SHUT_WR)。
-3.设置超时定时器,假定为t 秒。
-4.调用函数read(sock_fd)阻塞等待,直到读到EOF 或被定时器超时中断。
-5.执行函数close(sock_fd)或者调用exit(0)退出进程。
-注 释
-[1].仅关注http模块:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#listen。
- -[3].http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9781565928626.do。
-[4].http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9781565925090.do。
-[5].http://www.amazon.com/HTTP-Developers-Handbook-Chris-Shiflett/dp/0672324547。
-[6].对应HTTP1.1:http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt。
-[7].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc822.txt。
-[8].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backus%E2%80%93Naur_Form。
-[9].在文件/etc/hosts内加入一行设置:192.168.1.2www.web_test2.com。
-[10].这需要在恰当的代码行下断点,捕获后才能执行打印命令显示这些客户端请求数据。具体哪行代码算是恰当,这里不多赘述。
-[11].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 页码:[Page 128]
- -[13].即:父请求的相关数据已经产生,并且在子请求之前的数据已经发送到out chain链内。
-[14].http://lenky.info/?p=2216
-[15].http://lenky.info/?p=2220
- -[17].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2525.txt 小节:2.17 Failureto RSTonclose withdata pending。
-[18].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc793.txt 页码:[Page 69]和http://lenky.info/?p=2220
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-1-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-1-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c549e34ebe0e78dc20d60847050833101d90efa0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-1-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,33 @@ +void +ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc) +{ +… + if (rc == NGX_DONE) { + ngx_http_finalize_connection(r); + return; + } +… + if (rc == NGX_ERROR + || rc == NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT + || rc == NGX_HTTP_CLIENT_CLOSED_REQUEST + || c->error) + { + if (ngx_http_post_action(r) == NGX_OK) { + return; + } + + if (r->main->blocked) { + r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_finalizer; + } + + ngx_http_terminate_request(r, rc); + return; + } +… + if (c->read->eof) { + ngx_http_close_request(r, 0); + return; + } + + ngx_http_finalize_connection(r); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-2-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-2-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4563d73f27827c1904800f5ff85e762adcb82fef --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-2-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +static void +ngx_http_close_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc) +{ + ngx_connection_t *c; + + r = r->main; +… + r->count--; + + if (r->count || r->blocked) { + return; + } + + ngx_http_free_request(r, rc); + ngx_http_close_connection(c); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d402c58135f84631137d56daae3a66b43f91dae4 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +static void +ngx_http_finalize_connection(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (r->main->count != 1) { +… + ngx_http_close_request(r, 0); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-1-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-1-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cbd0593995423527d5503754229e9269369eb29f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-1-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + if (ngx_strcasestrn(h->value.data, "close", 5 - 1)) { + r->headers_in.connection_type = NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_CLOSE; + + } else if (ngx_strcasestrn(h->value.data, "keep-alive", 10 - 1)) { + r->headers_in.connection_type = NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_KEEP_ALIVE; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fa82d55523d366665812aade5e94029e5202153a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ + if (!r->internal) { + switch (r->headers_in.connection_type) { + case 0: + r->keepalive = (r->http_version > NGX_HTTP_VERSION_10); + break; + + case NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_CLOSE: + r->keepalive = 0; + break; + + case NGX_HTTP_CONNECTION_KEEP_ALIVE: + r->keepalive = 1; + break; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4d873418acfaa27382bb94c578a4be0ff2c0bed9 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + if (!ngx_terminate + && !ngx_exiting + && r->keepalive + && clcf->keepalive_timeout > 0) + { + ngx_http_set_keepalive(r); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-4-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-4-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5c9ceeeaaad25a2962737a260e66826349cc70bf --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-4-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,20 @@ + b = r->header_in; + + if (b->pos < b->last) { + + /* the pipelined request */ + + if (b != c->buffer) { +… + hc->busy[0] = b; + hc->nbusy = 1; + } + } + ngx_http_free_request(r, 0); +... + if (b->pos < b->last) { +… + rev->handler = ngx_http_init_request; + ngx_post_event(rev, &ngx_posted_events); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-5-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-5-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dfd58d35d555a86daa45a3dc181074b8c74c6d8d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-5-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ +static void +ngx_http_init_request(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + r = hc->request; + + if (r) { + ngx_memzero(r, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t)); + + r->pipeline = hc->pipeline; + + if (hc->nbusy) { + r->header_in = hc->busy[0]; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-6-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-6-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5c02ec1d39e7659d579afeaddb67ce904f67bb12 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-6-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + ngx_add_timer(rev, clcf->keepalive_timeout); + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) { +... + rev->handler = ngx_http_keepalive_handler; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-7-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-7-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..211bb80e6421f1aebbc5e638015a9da9c73bb049 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.1-7-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ +static void +ngx_http_keepalive_handler(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + if (rev->timedout || c->close) { + ngx_http_close_connection(c); + return; + } +… + n = c->recv(c, b->last, size); + c->log_error = NGX_ERROR_INFO; + + if (n == NGX_AGAIN) { + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) { + ngx_http_close_connection(c); + } + + return; + } +… + ngx_http_init_request(rev); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-1-\\linux-3.4.4\\include\\linux\\socket.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-1-\\linux-3.4.4\\include\\linux\\socket.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bb299597204f02f14b75320dd8e4abb4762feaee --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-1-\\linux-3.4.4\\include\\linux\\socket.h" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + struct linger { + int l_onoff; /* Linger active */ + int l_linger;/* How long to linger for */ + }; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-2-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-2-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..65de2be94a2d94e875d9fbf4eb2112692f63252d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-2-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static void +ngx_http_free_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc) +{ +… + if (r->connection->timedout) { + clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); + + if (clcf->reset_timedout_connection) { + linger.l_onoff = 1; + linger.l_linger = 0; + + if (setsockopt(r->connection->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_LINGER, + (constvoid *)&linger,sizeof(structlinger))==-1) \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4eed89ababffd9ce31cc2f93c2aeae7797fc32ac --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + rv = ngx_http_alloc_large_header_buffer(r, 1); + + if (rv == NGX_ERROR) { + ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); + return; + } +… + if (rev->timedout) { + ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_INFO, c->log, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out"); + c->timedout = 1; + ngx_http_close_request(r, NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2d9724c2b43c359c7b8958ec5a6974e4ced65ea --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-4-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ + if (!ngx_terminate + && !ngx_exiting + && r->keepalive + && clcf->keepalive_timeout > 0) + { + ngx_http_set_keepalive(r); + return; + } + + if (clcf->lingering_close == NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_ALWAYS + || (clcf->lingering_close == NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_ON + && (r->lingering_close + || r->header_in->pos < r->header_in->last + || r->connection->read->ready))) + { + ngx_http_set_lingering_close(r); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-5-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-5-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8b0d127f6a43306dbeaad795388e48838e28a47d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-5-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ +void +ngx_http_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + r->lingering_close = (r->headers_in.content_length_n > 0); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-6-ngx_http_request_body.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-6-ngx_http_request_body.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dafdfd81122fec3a4ac2d6f1b4c7de3e83f2239e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-6-ngx_http_request_body.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ +ngx_int_t +ngx_http_discard_request_body(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (ngx_http_read_discarded_request_body(r) == NGX_OK) { + r->lingering_close = 0; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-7-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-7-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b5966dcce27e6e0ec34425acb6e1ed0c2cbe9ba4 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-7-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +void +ngx_http_discarded_request_body_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (r->lingering_time) { + timer = (ngx_msec_t) (r->lingering_time - ngx_time()); + + if (timer <= 0) { + r->discard_body = 0; + r->lingering_close = 0; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-8-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-8-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8901af9b99de3adc27369381df6a0ec9f4cd0041 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-8-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +static void +ngx_http_set_lingering_close(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + rev = c->read; + rev->handler = ngx_http_lingering_close_handler; + + r->lingering_time = ngx_time() + (time_t) (clcf->lingering_time / 1000); + ngx_add_timer(rev, clcf->lingering_timeout); + + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) { +… + if (ngx_shutdown_socket(c->fd, NGX_WRITE_SHUTDOWN) == -1) { +… + if (rev->ready) { + ngx_http_lingering_close_handler(rev); + } +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-9-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-9-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4563c7d8790e40a9347a128bb7ef39effcdcdc94 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/9.6 \350\277\236\346\216\245\345\205\263\351\227\255/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\2659.6.2-9-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,29 @@ +static void +ngx_http_lingering_close_handler(ngx_event_t *rev) +{ +… + if (rev->timedout) { + ngx_http_close_request(r, 0); + return; + } + + timer = (ngx_msec_t) (r->lingering_time - ngx_time()); + if (timer <= 0) { + ngx_http_close_request(r, 0); + return; + } +… + do { + n = c->recv(c, buffer, NGX_HTTP_LINGERING_BUFFER_SIZE); +… + if (n == NGX_ERROR || n == 0) { + ngx_http_close_request(r, 0); + return; + } + + } while (rev->ready); +… + timer *= 1000; +… + ngx_add_timer(rev, timer); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index de05d231a68229cd85c7838d6eb21b533e4fa671..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25409\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206\344\270\216\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -在前面章节曾断断续续地提到过 Nginx 对客户端请求的处理,但不甚连贯,所以本章将把这个请求处理响应过程完整地描述一遍。本章主要以图7-2所示的客户端请求Web服务器上静态文件为实例,因为这个是最简单、也是最基本的请求处理与响应流程。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.1 Location \347\232\204\347\224\237\346\210\220/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.1 Location \347\232\204\347\224\237\346\210\220/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index bcb2b4489d404e3b7060c71bd819aac728b0b12b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.1 Location \347\232\204\347\224\237\346\210\220/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,69 +0,0 @@ - -关于server的生成已经在前面章节解析过了,所以这里我们来看location的生成过程。即便是在同一个server里,Nginx的location一般也会有多个,以便灵活地处理客户端的各种请求。在Nginx配置文件中,除了直接的location指令以外,还有其他指令也会间接的导致生成location。先看最简单的情况,即由location指令直接生成。
-293: 代码片段10.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-294: { ngx_string("location"),
-295: NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF| NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_TAKE12,
-296: ngx_http_core_location,
-297: NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET,
-298: 0,
-299: NULL },
-根据我们对Nginx配置项的了解,由上面代码可以看到location指令只能用在server或location 上下文以内(NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF),它是一个复杂配置项(NGX_CONF_BLOCK)、并且可带1个或2个参数(NGX_CONF_TAKE12),对应的处理函数为ngx_http_core_location()。
-标准的location指令配置语法为
-location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ...}
-来看几个官方示例[1],先从感性上认识它。
-00: 代码片段10.1-2,文件名: nginx.conf
-01: location = / {
-02: # matches the query / only.
-03: [ configuration A ]
-04: }
-05: location / {
-06: # matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
-07: # expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
-08: # matched first.
-09: [ configuration B ]
-10: }
-11: location ^~ /images/ {
-12: # matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
-13: # so regular expressions will not be checked.
-14: [ configuration C ]
-15: }
-16: location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
-17: # matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg.However, all
-18: # requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
-19: # Configuration C.
-20: [ configuration D ]
-21: }
-可以看到,location 指令配置语法里被中括号包含的符号为可选,所以可以只有一个参数uri,这种location被称之为前缀匹配location或包含匹配location(请注意:这类命名只是我自己根据地址匹配的特点所起的名字),即以这个指定字符串为前缀的请求地址都能与它匹配上。比如请求地址"/document.html"以字符串"/"为前缀,所以它能与配置B匹配上(当然,最终的匹配结果是否就是配置B,还需看其他location配置,因为Nginx采用的是最佳匹配)。
-如果加上其他作为匹配限定符的可选符号,比如等号‘=’,则表示绝对匹配 location,在上面示例中,只有当前(客户端直接请求和内部跳转都包含在内)处理请求的 uri 完全匹配字符"/"(既不能多一个字符,也不能少一个字符)时,才被定位并使用对应的相关配置 A。正则匹配location是由限定符“~”(区分大小写)或“~*”(不区分大小写)指定的,此时给出的uri是一个正则表达式,请求地址满足该正则表达式的就能匹配上。
-由限定符“^~”指定的location也是前缀匹配location,不过它暗示了在实际进行location定位时不用搜索正则匹配location,这在后面小节会看到其具体实现。还有另外两种地址分别称之为命名location和未命名location(未命名location并不是由location指令来添加的,在后面会讲到),命名location仅用于server内部跳转,看如下实例[2]中的rewrite就是命名location(具体情况后面会讲到)。
-00: 代码片段10.1-3,文件名: nginx.conf
-01: location / {
-02: # This is cool because no php is touched for static content
-03: try_files $uri $uri/ @rewrite;
-04: }
-05:
-06: location @rewrite {
-07: rewrite ^/wiki/search(.*)$ /search.php?search=$1 last;
-08: …
-09: }
-回过头看函数 ngx_http_core_location()的具体实现,该函数虽然代码有点多,但涉及到location本身的相关逻辑并不复杂,需要重点注意的是那些旗标字段的设置,即exact_match、noregex、named以及后面会提到的noname。这些字段用于区分不同的location配置,比如exact_match标识这个location是绝对匹配,named标识这个location是命名location等。
-另外,特定location以及location之间的位置需要进行有效性判断,注意到这点对于理解后面的内容很重要。首先,虽然 location 可以有上下层次的嵌套,但是很明显,在一个绝对匹配location里不可能再包含其他location;其次,命名location里也不能包含其他location,并且命名location只能在server上下文里,也就是命名location不能包含在其他location里,这是因为命名location本身的特性,即用于server内部跳转所决定的。前缀匹配location之间的包含与被包含必须有一定的规则,比如"/ab"可以在"/a"之内,因为匹配"/a"的请求地址可能还可以匹配"/ab",但是"/ab"就不能在"/b"之内,因为如果请求地址匹配"/b",那么肯定就不会再匹配"/ab",这么明显的事情就不要再去降低针对每个客户端请求都要进行的地址匹配与查找的性能了,在location生成阶段就可以检测并识别出来。
-在对参数进行解析并区分出location 类型以及做出有效性判断后,重要的处理就是调用函数ngx_http_add_location()将这个location加入到一个队列里,然后调用函数ngx_conf_parse()开始解析这个新location里的相关配置。
-ngx_http_core_location() -> 1:ngx_http_add_location(cf, &pclcf->locations, clcf)
-ngx_http_core_location() -> 2:ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL)
-在配置解析一章的图示中曾提到过,一个server里的所有location会以队列的形式管理在locations字段下,具体实现在函数ngx_http_add_location()内,它会把location配置clcf加入到locations 字段下的队列里。从具体的代码来看,这种加入是间接的,也就是通过另外一个结构体 ngx_http_location_queue_t 来形成队列而并非 clcf 本身, clcf 会挂载到对应结构体ngx_http_location_queue_t的exact或inclusive字段下,具体来说就是:绝对匹配、正则匹配以及命名或未命名地址都挂载在exact字段下,其他的情况,比如前缀匹配(即匹配前面给定字符即可)则在inclusive字段下(图10-1中的实例显示了这些情况)。由于location本身可以存在于location上下文,所以一个location里的所有location也会以队列的形式管理在locations字段(即结构体ngx_http_core_loc_conf_s的locations字段)下,这样一层层下去就将形成一个树形结构。对于前面示例中给出的4个location,由于都存在于server之内而没有上下的层次嵌套,所以在配置文件解析后,组织结构比较简单,仅只是队列而没有形成树结构,如图10-1所示。
-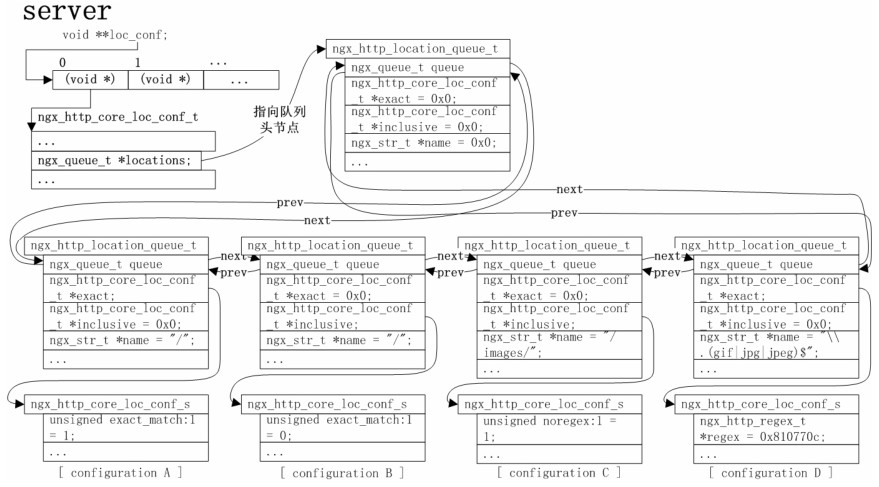 -
-如果整个配置里存在多个 location 的层次嵌套,那么对应的组织结构图就是这样的树型结构(已做大量简化,后面以locationtree 来代指它,此时,一个队列当作一个整体而被称之为一个节点)。
-在 Nginx 的所有源代码内搜索函数名 ngx_http_add_location ,会发现函数 ngx_http_core_limit_except()和 ngx_http_rewrite_if()也会直接调用到该函数,这也就是前面所提到的:除了location指令以外,还有指令limit_except和if也会间接的导致生成location,这些location即为前面曾提到的未命名location,它们对应的noname 字段会被设置为1(即clcf->noname =1;),记住这一点很重要,因为后面会介绍到这个字段的特殊使用。这些 location 同样也会加入到location tree,即便它们最终并没有用在一般的请求地址匹配查找过程里,但这样做仍然是必要的,因为在进行配置合并的时候,这样才能让它们也可以继承接受来之上层 location的相关设置值。
-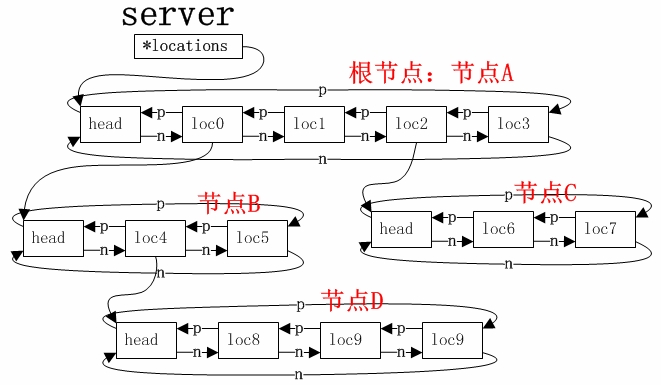 -
-在配置解析完后,所有的location都以tree的形式组织起来,但很明显的是,这棵根据用户配置而生成的tree树并不完善且需要进一步的修剪切并(比如把同类型的location放置在一起而便于查找等),才能在后续实际使用的过程中发挥最大效用。这部分逻辑的入口代码如下。
-117: 代码片段10.2-1,文件名: ngx_http.c
-118: static char *
-119: ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
-120: {
-121: …
-239: rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
-240: …
-279: for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
-280:
-281: clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
-282:
-283: if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != NGX_OK) {
-284: return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
-285: }
-286:
-287: if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
-288: return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
-289: }
-290: }
-在整个http配置块解析(第239行)完,也就是所有的location都成功收集并已根据各自所属server形成多棵不同的树(不同server的location不会相互干扰,因为对于请求的处理总是要先定位到具体server,然后在这个server之内去查找对应的location),在第279行,即遍历各个server的location tree,开始进行修剪切并。
-实现修剪切并逻辑的函数 ngx_http_init_locations()和 ngx_http_init_static_location_trees()一次只处理一个节点(也就是一个队列),然后根据tree树结构本身的伸展情况而进行递归调用。下面逐一来看。在函数ngx_http_init_locations()内,首先是对该节点上的location队列进行排序(第689行)。
-668: 代码片段10.2-2,文件名: ngx_http.c
-669: static ngx_int_t
-670: ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
-671: ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
-672: {
-673: …
-689: ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
-决定排序结果的因素也就是比较函数 ngx_http_cmp_locations(),它按照如下几条规则对队列里的任意两个location进行排序(规则优先级按序号由主到次,即如果使用第1条规则无法区分两个location的次序,那么就再使用第2条规则,直到确定先后次序或使用到最后一条规则为止)。
-1.两个比较location中的未命名location(即noname旗标为1)排到后面。
-2.如果比较的两个location都为未命名location,那么保持原定次序,即保持用户在配置文件里书写的先后顺序(按文件从头到尾)。
-3.两个比较location中的命名location(即named旗标为1)排到后面。
-4.如果比较的两个location都为命名location,那么按它们名称的字符序进行排序,即通过函数strcmp()比较它们的名称,名称字符序大的排到后面。
-5.两个比较location中的正则匹配location(即regex字段不为空)排到后面。
-6.如果比较的两个location都为正则匹配location,那么保持原定次序,即保持用户在配置文件里书写的先后顺序(按文件从头到尾)。
-7.其他情况,按名称的字符序进行排序。但是有一个特别处理,即对于出现比较的两个location名称相同的情况,如果存在有绝对匹配location,那么要把它放在前面。
-通过上面的这一系列规则,location队列将被合理排序,以如图10-3所示的初始队列为例(为了显示清晰,没有全部画在同一行,先后顺序为从左到右,从上到下;另外,队列头结点和各个location结点之间的前后链接也都被我省略掉了)。
- -
-排序之后的结果如图10-4所示。
- -
-回过头来继续看函数ngx_http_init_locations()内代码,接下来是对每个可能存在的节点进行递归调用。
-697: 代码片段10.2-3,文件名: ngx_http.c
-698: for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
-699: q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
-700: q = ngx_queue_next(q))
-701: {
-702: lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
-703:
-704: clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
-705:
-706: if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, NULL, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
-707: return NGX_ERROR;
-708: }
-再接下来的代码有点长,但并不复杂,讲清楚了就很容易理解,这些代码主要做了一件事情,即对前面排好序的队列做拆分,具体点讲就是把正则匹配location和命名location给拆出来。继续以前面的实例来看,经过正则匹配location和命名location的定位查找后,此时的相关局部变量指向如图10-5所示。
- -
-先对末尾的noname进行拆分,以便后面要拆分的处于队列中间的named和regex能正常进行。要注意的是,在拆分之前并没有对noname location进行转存,所以看似这些数据会全部“丢失”(即再也找不到对它们的引用),这种“丢失”当然是“假”的,在其他地方的其他字段,比如limit_except_loc_conf或脚本引擎里已经保存了对这些location数据的引用,所以无需担心。对应的代码和图示如图10-6所示。
-738: 代码片段10.2-4,文件名: ngx_http.c
-739: if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
-740: ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
-741: }
-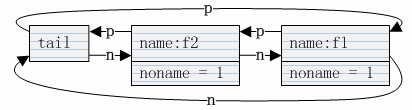 -
-再接着就是对队列末尾的named(因为noname已经被拆出队列,所以此时named处于队列尾部)进行拆分,在拆分之前,所有的named会被逐一保存到cscf->named_locations内(此时是一个数组,因为不论是遍历查找,还是访问性能,数组都要比队列更具优势)。理解这段代码的前提是要知道(在函数ngx_http_core_location()和ngx_http_add_location()里很容易找到这两个限定):named location 只会出现在 server 上下文里,并且 location 配置数据(即clcf)固定保存在exact字段下。
-同理,把named location 拆出队列后,剩在队列末尾的就是regex location,同样是先转储数据,把regex location 配置数据以数组的形式逐一保存到pclcf->regex_locations 字段下。把 regex location 拆出之后,原本的 pclcf->locations 就只剩下被称为静态(static)的 location配置,如图10-7所示。
-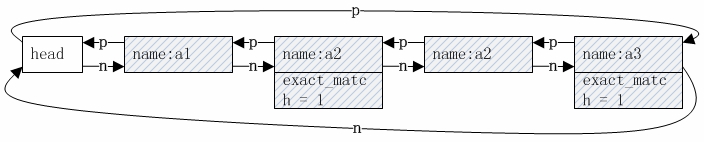 -
-函数 ngx_http_init_static_location_trees()就是继续对上面这个链表进行进一步的修剪切并操作。首先,同样是根据情况做递归调用,这无需多说。直接看该函数末尾处的几句重要代码。
-828: 代码片段10.2-5,文件名: ngx_http.c
-829: if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != NGX_OK) {
-830: return NGX_ERROR;
-831: }
-832:
-833: ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations));
-834:
-835: pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0);
-函数 ngx_http_join_exact_locations()做了一件事情,把同一层次里的名称相同的不同location 合并在一起。什么叫做“名称相同,但又是不同的 location”?这主要是因为 location有绝对匹配(对应 exact 字段)和包含匹配(也就是前缀匹配,以指定前缀开头的都匹配上,所以是包含匹配,对应 inclusive 字段),在前面的示例中,“[ configuration A]”属于绝对匹配,对应的 location 配置在 exact 字段下(对应的 inclusive 字段为 0x0),而“[ configuration B ]”属于包含匹配,对应的 location 配置在 inclusive 字段下(对应的 exact字段为0x0)。既然这两个location的名称相同(都为"/"),所以可以把它们共用在一个队列节点里。
-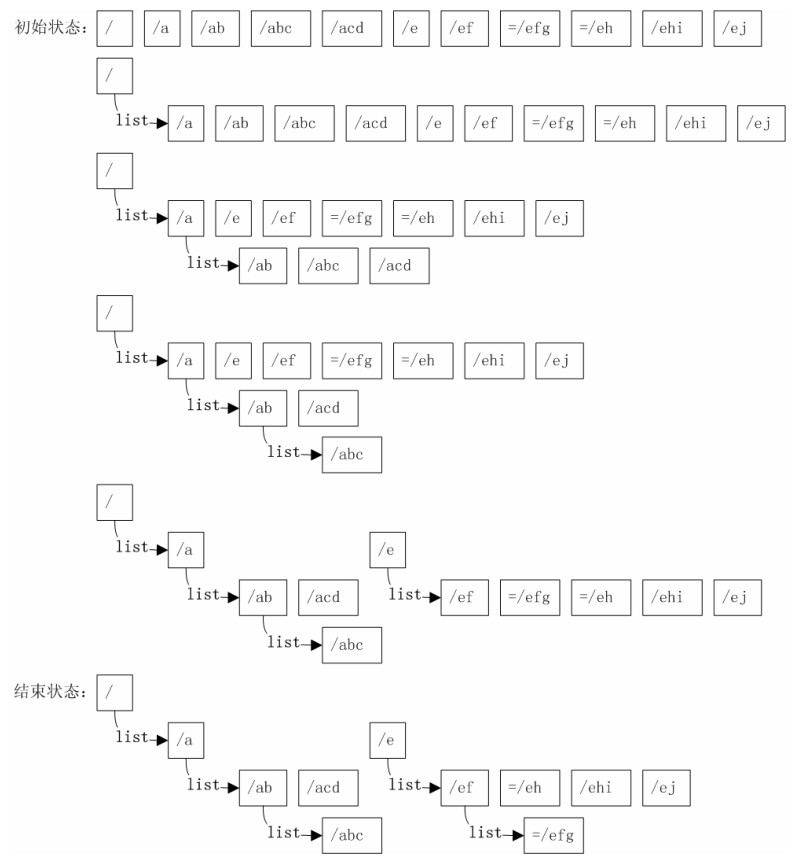 -
-962: 代码片段10.2-6,文件名: ngx_http.c
-963: static ngx_int_t
-964: ngx_http_join_exact_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations)
-965: {
-966: …
-978: if (ngx_strcmp(lq->name->data, lx->name->data) == 0) {
-979: …
-988: lq->inclusive = lx->inclusive;
-989:
-990: ngx_queue_remove(x);
-我们必须知道,Nginx 对包含匹配的查找采用的是最佳匹配原则,也就是说,如果有两个location A和B的包含匹配串分别为"/"和"/images/",那么对于uri地址"/images/top.jpg"在这两个location里的查找将匹配到location B。为了提高这种查找速度,所以有必要把队列转换成tree,而这就是函数ngx_http_create_locations_list()和ngx_http_create_locations_tree()所要实现的功能,所以单看函数ngx_http_create_locations_list()内部多次递归调用而略显复杂,但只要看清楚它的最终目的,那么也还是容易理解。
-函数 ngx_http_create_locations_list()已经初步把队列转换出树结构的雏形了,图10-8 显示了一些示例 location(需注意队列里的 location 已经按名称排序)经过函数 ngx_http_create_locations_list()处理的过程以及得到的最终结果。这个示例的最终结果虽然有点树结构的雏形,但是很明显,它离 Nginx 真正想要的 tree 还差一段距离,所以接着就由函数 ngx_http_create_locations_tree()来完成剩余的工作,而创建的这棵最终查找树被保存在字段 pclcf->static_locations 下。关于该函数的具体代码不过细讲解,因为对于每一句代码不存在难以理解的地方,继续前面的示例,看看最终的生成结果是如何之后,对于源代码本身的逻辑也就更容易理解了,如图10-9所示。
-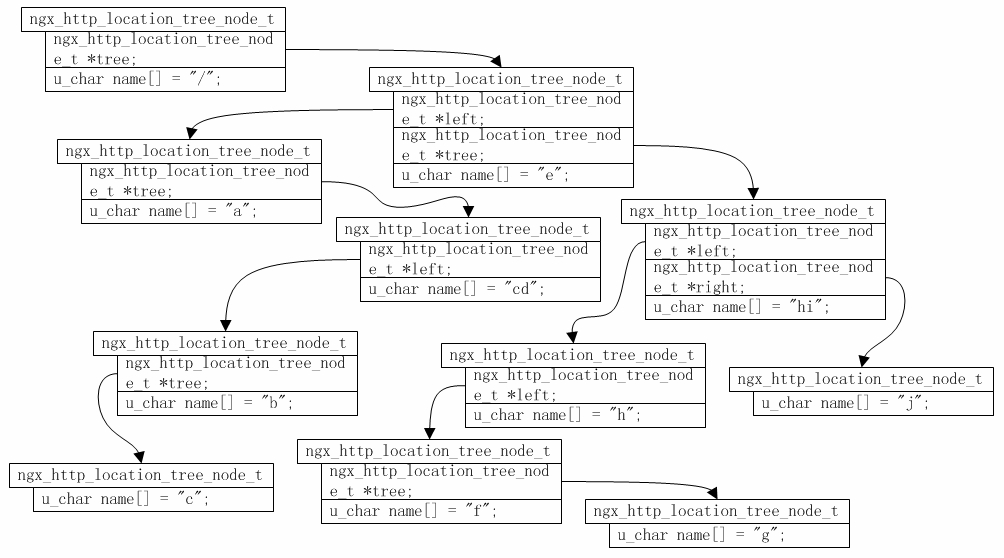 -
-毫无疑问,图10-9所示的是一棵树结构(为了指代,暂称之为小树或静态树),但是需注意的是,它仅仅对应一个上下文里的 location,这在前面也讲到了,它只是将一个 location队列转换成树,而对于location队列之间,由于上下层关系,本身也就是一棵树(相对可称之为大树),那么后面将讲到的location定位也就是在这棵大树与小树里进行反复查找。
-对于指定的uri,原本需在这个location队列里进行查找,现在可以在转换而成的树结构里进行查找,树深度当然要比队列长度小,因此需要比较的次数也就少,效率当然更高一些。进行实际匹配查找时,从树根往下进行即可,但并不是每移动一个树节点就需删剪对应的字符,比如左右节点的匹配移动就不用进行字符删剪。
-函数ngx_http_core_find_static_location()实现了具体的查找逻辑,这里根据前面的示例,举个在该树内的查找实例:对于uri地址"/abcdefg",先从树根开始查找,步骤如下。
-1.与根字符串"/"比较,结果匹配,但前面说过,Nginx对包含匹配的查找采用的是最佳匹配原则,既然 uri 地址字符串"/abcdefg"还有这么多字符未比较,并且根节点还有下级节点(即:tree 字段不为空),所以需继续。此时,要把 uri 地址字符串"/abcdefg"变成"abcdefg",即剪去了根字符串"/",才能继续往下移动。
-2.与节点"e"比较,结果小于,所以往左移动,继续匹配。注意:此时,不用对uri地址字符串进行删剪,即左右移动无需删剪字符。
-3.与节点"a"比较,结果匹配,删剪 uri 地址字符串"abcdefg"变成"bcdefg",即剪去本次节点比较字符串"a",继续往下移动。
-4.比较反复进行,直到uri地址字符串删减完或遇到树叶子节点(即空节点),查找结束。最近一次匹配成功的location会被记录到r->loc_conf,留待后续使用。
-总的下来,所有的 location 都被恰当地整理后放置在对应的字段下:未命名 location 被limit_except_loc_conf 或脚本引擎引用、命名 location 被放置在 server 配置的 cscf->named_locations字段下、正则匹配location被放置在server或location配置的pclcf->regex_locations字段下、静态匹配(包括绝对匹配和前缀匹配)location 被放置在 server 或 location 配置的pclcf->static_locations 字段下。在进行 location 定位时,实际用到的也就是静态匹配 location和正则匹配location,后面马上将讲到这一部分逻辑。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-1-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-1-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b5ca5ef140afcd5bfe0a0e6e8ad6b8b3e9340ef3 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-1-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) +{ +… + rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); +… + for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) { + + clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index]; + + if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != NGX_OK) { + return NGX_CONF_ERROR; + } + + if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) { + return NGX_CONF_ERROR; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-2-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-2-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2da8a16bffebe3804bfead18876feb0a52fdce8c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-2-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf, + ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf) +{ +… + ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-3-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-3-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d7a796e26238e495d051c358029aaf7482d357bb --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-3-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ + for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations); + q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations); + q = ngx_queue_next(q)) + { + lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q; + + clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive; + + if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, NULL, clcf) != NGX_OK) { + return NGX_ERROR; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-4-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-4-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3d827bca7e1c0277e3faff576f0aa2361062ca99 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-4-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) { + ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-5-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-5-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3b7d80ac5fcb06c9f39513ae79f442f9e1eda617 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-5-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ + if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != NGX_OK) { + return NGX_ERROR; + } + + ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations)); + + pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-6-ngx_http.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-6-ngx_http.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..66113ee04bc316adc74ad64573d67670dfbc511d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.2 Location \347\232\204\346\225\264\347\220\206/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.2-6-ngx_http.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_join_exact_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations) +{ +… + if (ngx_strcmp(lq->name->data, lx->name->data) == 0) { +… + lq->inclusive = lx->inclusive; + + ngx_queue_remove(x); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 24fb92cf22b18b40e99d079f49c3cbc198a205cb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,46 +0,0 @@ - -本章最开始提到,对于一个客户端请求,首先要把它定位到某个sever配置,这样才能做进一步的处理,否则就可能完全出错。比如,客户端明明请求的是A网站首页,却用B网站的相关配置进行处理,那么返回给客户端的也许就是 B 网站的首页内容,这当然是不容许的。为什么可能会出现这种情况,原因在于一个监听套接口描述符上可能会有多个网站,这可能是由于类似“listen*:80;”或“listen80;”这样的全局IP监听配置的影响,也可能是由于我们通常所说的配置多个“虚拟主机”的影响,但不管怎样,都必须识别并且区分出客户端真正想请求的那个server。
-对于有多个目的IP地址的监听套接口',那么需要先根据客户端实际请求的服务器IP把对应的目的IP配置找出来。具体是通过系统函数getsockname()来实现。
-ngx_connection_local_sockaddr() -> getsockname(c->fd, (struct sockaddr *) &sa, &len)
-函数getsockname()可从已建立连接的本地套接口描述符(c->fd)上获取到客户端请求的目的IP地址。然后,将该IP地址与全局IP监听套接口上的地址列表进行逐一比较,找到对应的IP配置。
-350: 代码片段10.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-351: sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) c->local_sockaddr;
-352:
-353: addr = port->addrs;
-354: …
-357: for (i = 0; i < port->naddrs - 1; i++) {
-358: if (addr[i].addr == sin->sin_addr.s_addr) {
-359: break;
-360: }
-361: }
-362:
-363: addr_conf = &addr[i].conf;
-如果监听套接口只有一个目的IP地址,那么就直接使用该IP配置即可。不管是多个目的IP地址还是单个目的IP地址,在找到其真正的server以前,客户端请求处理的相关初始值就以该IP配置上的default_server(即对应的listen指令后设置有default_server选项)配置为准,比如接收请求头的缓存区大小client_header_buffer_size等。
-387: 代码片段10.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-388: /* the default server configuration for the address:port */
-389: cscf = addr_conf->default_server;
-390:
-391: r->main_conf = cscf->ctx->main_conf;
-392: r->srv_conf = cscf->ctx->srv_conf;
-393: r->loc_conf = cscf->ctx->loc_conf;
-394: …
-440: if (c->buffer == NULL) {
-441: c->buffer = ngx_create_temp_buf(c->pool,
-442: cscf->client_header_buffer_size);
-有多个目的IP地址的监听套接口必定是带有任意IP监听,比如*:80配置而创建的,这在第9章9.3节也提到这个问题。
-这是没有办法的事情,因为要找到其真正的server,就必须分析客户端对应的请求头(即Host头)的具体内容,但要分析客户端的请求头,又必须先接收这些数据,而创建接收这些数据的缓存区的具体大小又依赖其 server 的配置,这是一个前后矛盾的事情,所以在找到其真正的server之前,只能使用默认server的配置值。从这点看来,如果我们在Nginx配置文件里所做的设置没有起作用,那可能需要检查一下,是不是应该设置在默认server里。
-在解析完(不考虑HTTP0.9 版本的情况)所有的客户端请求头数据后,就开始根据其Host头查找其真正的server配置,这部分相关逻辑也就是虚拟主机功能的实现。虚拟主机必须要有Host请求头的支持,对于支持HTTP1.1 的客户端,RFC标准文档[3]已经强制要求每一个请求都必须带有Host请求头。当然,对于 1.1 版本的http请求 ,Nginx也有实现这样的检查,如果客户端没有发送Host请求头,那么将获得“400BadRequest”的错误提示。对于HTTP1.0 的协议标准,客户端可以不带Host请求头,那么此时将无法使用虚拟主机的功能,每次访问的将都是默认主机。当然,如果带上Host请求头,那么即便是HTTP 1.0 协议,客户端也能够正确使用虚拟主机。根据Host请求头查找对应的虚拟主机,也就是查找其真正的server配置,相关逻辑代码都实现在函数ngx_http_find_virtual_server()内。
-ngx_http_process_request_header() -> ngx_http_find_virtual_server()
-第4章4.2节介绍的Hash数据结构是理解这部分查找代码的关键,在这里就不再对查找的具体代码进行讲解,不管怎样,在找到其真正的server配置后,修改对应的字段指向。
-1763:代码片段10.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_request.c
-1764:static ngx_int_t
-1765:ngx_http_find_virtual_server(ngx_http_request_t *r, u_char *host, size_t len)
-1766:{
-1767:…
-1815:found:
-1816:
-1817: r->srv_conf = cscf->ctx->srv_conf;
-1818: r->loc_conf = cscf->ctx->loc_conf;
-字段 r->main_conf 是不用修改的,因为全部指向同一处(配置解析一章有对此的详细描述),需要修改的只有r->srv_conf和r->loc_conf,把它们指向新的sever配置cscf对应的字段。如果没找到?那么继续使用前面设置的默认server配置。
-关于server的定位,上面的描述遗漏了很多特例处理和细节,不过没有关系,在后面章节,我们还会看到有对server定位相关内容的讲解,读者也可以参考这里[4]。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e63aea7a806908853b8ea95293e52ce5b3b08762 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-1-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ + sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) c->local_sockaddr; + + addr = port->addrs; +… + for (i = 0; i < port->naddrs - 1; i++) { + if (addr[i].addr == sin->sin_addr.s_addr) { + break; + } + } + + addr_conf = &addr[i].conf; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..14be91aaff7d83edb442459944c8a8636cea7800 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-2-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ + /* the default server configuration for the address:port */ + cscf = addr_conf->default_server; + + r->main_conf = cscf->ctx->main_conf; + r->srv_conf = cscf->ctx->srv_conf; + r->loc_conf = cscf->ctx->loc_conf; +… + if (c->buffer == NULL) { + c->buffer = ngx_create_temp_buf(c->pool, + cscf->client_header_buffer_size); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1968844b8c3cedf52b0ab350748c5e1136e76d7d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.3 Server \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.3-3-ngx_http_request.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_find_virtual_server(ngx_http_request_t *r, u_char *host, size_t len) +{ +… +found: + + r->srv_conf = cscf->ctx->srv_conf; + r->loc_conf = cscf->ctx->loc_conf; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index a34b25e87dabfc50fa4fc5546e22b7777fb62c04..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,28 +0,0 @@ - -如果还记得前面曾讲述过的Nginx对http请求处理所要经历的11个阶段,那么对于其中的第2(序号从0开始)个阶段,即NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE配置查找阶段的介绍肯定还有一点印象:该阶段是为了完成 Nginx 特定的功能而设置的,外部不能给它挂载其他回调函数(即便是挂载了其他回调函数,这些函数也永远不会被调用),而本节就将介绍该阶段的固定执行逻辑,即Location的定位与使用,也就是函数ngx_http_core_find_config_phase()。其最主要的实现是调用函数ngx_http_core_find_location()对当前请求uri进行location定位,以及在找到恰当的location后更新使用其相关配置值。
-ngx_http_core_find_config_phase() -> 1:ngx_http_core_find_location(r)
-ngx_http_core_find_config_phase() -> 2:ngx_http_update_location_config(r)
-对于函数ngx_http_core_find_location()的理解,可以逆向而行,我们先来看一下官方给出的location匹配原则。
-1.如果查找到绝对匹配location,那么定位成功,不用继续查找。这很容易理解,无需多说。
-2.查找前缀匹配 location,这个按最佳匹配查找,即如果同时存在前缀匹配"/a"和"/ab"两个location,那么对于uri地址"/abc"要匹配到"/ab"location。
-3.如果第2 步明确要求停止查找正则匹配 location,即第2 步最终查找到的前缀匹配location 被"^~"修饰,那么就算是定位成功,不用继续查找;否则就需继续查找正则匹配location,一旦查找到对应的正则匹配location,那么就使用这个正则匹配location,否则使用第2步中查找到的前缀匹配location。
-再来看代码实现就比较容易理解了,在函数 ngx_http_core_find_location()内首先对静态匹配,也就是绝对匹配和前缀匹配,进行查找。
-ngx_http_core_find_location() -> ngx_http_core_find_static_location(r, pclcf->static_ locations);
-前面讲过,静态匹配以树的形式挂载在 pclcf->static_locations 字段下,调入到函数 ngx_http_core_find_static_location()后,具体的查找过程,在前面的示例里已经说得很清楚了,但有一点需要注意的是这段代码。
-1676:代码片段10.4-1,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1677: if (len + 1 == (size_t) node->len && node->auto_redirect) {
-1678:
-1679: r->loc_conf = (node->exact) ? node->exact->loc_conf:
-1680: node->inclusive->loc_conf;
-1681: rv = NGX_DONE;
-1682: }
-这是对于 Nginx 充当中间代理情况的考虑,auto_redirect 也只有当 Nginx 启用 fastcgi、proxy、scgi或memcached等功能的情况下才为1,此时是直接跳转。也就是说,如果代理location名称末尾带有"/",比如location为"/proxy/",那么请求uri地址为"/proxy"就可以匹配上了。
-函数 ngx_http_core_find_static_location()的返回值代表了不同的查找结果,返回到函数ngx_http_core_find_location()后,会影响下一步逻辑,但整体都比较简单,为了达到最佳匹配,所以有一个递归查找的过程,如图10-10所示。
-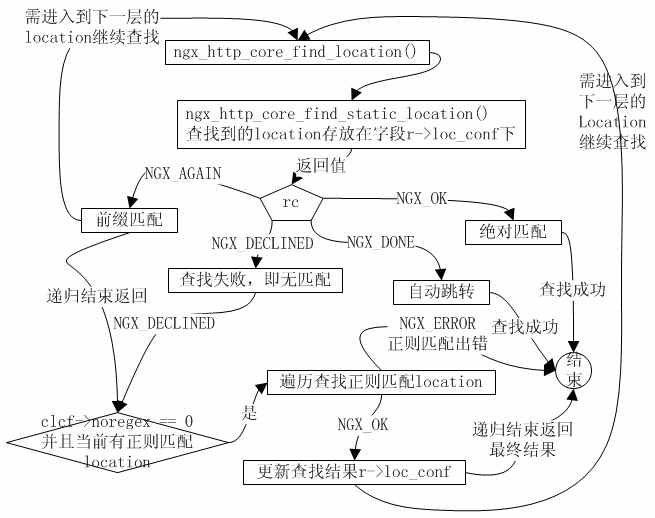 -
-对于location的查找,只要不是正则匹配出错(即函数ngx_http_core_find_location()返回值为 NGX_ERROR),那么都要使用我们查找到的结果,也就是调用函数 ngx_http_update_location_config()更新当前相关变量值,但并不会更新所有变量,只是一些全局变量(即必定会用到的)才会被更新到,而其他只是在某些执行逻辑里才会用到的变量,在后续对请求的处理过程中将逐步更新(查找到的location已经存放在字段r->loc_conf下),直到请求处理结束,比如内部跳转(此时,location将重新查找和定位)或最终响应数据发送到客户端。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.4-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.4-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..637628c308c4cb7eff11ace21c407630b27d5289 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.4 Location \347\232\204\345\256\232\344\275\215\344\270\216\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.4-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + if (len + 1 == (size_t) node->len && node->auto_redirect) { + + r->loc_conf = (node->exact) ? node->exact->loc_conf: + node->inclusive->loc_conf; + rv = NGX_DONE; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/-.txt" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/-.txt" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..25d641e0b833dc0b43b4885a1823732d10fbc146 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/-.txt" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ +… + if (conf->upstream.upstream || conf->proxy_lengths) { + clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); + if (clcf->handler == NULL && clcf->lmt_excpt) { + clcf->handler = ngx_http_proxy_handler; + conf->location = prev->location; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 9e35d82524f0a8eaf3b71a68e7aad9a1f10b66b8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,83 +0,0 @@ - -未命名location,也就是前面曾提到过的由指令limit_except和if所生成的location,这些location被额外独立开而不会被正常的location定位流程所查找,那么它们具体被使用在哪种场景下以及如何被使用呢?首先来看对指令 limit_except 生成的未命名 location 的使用,在Nginx源码树里搜索关键字limit_except_loc_conf(因为前面曾讲过指令limit_except生成的未命名location挂载在该字段下),这很容易找到对应的相关代码。
-1438:代码片段10.5-1,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1439:void
-1440:ngx_http_update_location_config(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-1441:{
-1442: ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
-1443:
-1444: clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
-1445:
-1446: if (r->method & clcf->limit_except) {
-1447: r->loc_conf = clcf->limit_except_loc_conf;
-1448: clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
-1449: }
-函数ngx_http_update_location_config()在上一小节刚讲到,也就是Nginx在针对当前请求成功定位到对应的location后调用的函数,该函数从该location(保存在字段r->loc_conf下)里取出相应的用户配置值(代码第1444 行),正准备在函数后面部分更新当前的相关变量,但是如果发现当前location下配置有指令limit_except(代码第1446行),判断r->method是否包含有指定的请求method是根据指令limit_except语法来的。
-Syntax: limit_except method ...{ ...}
-该指令只在 r->method 不为空的情况下才生效),那么意味着有一些特别限制(指令limit_except 表示对除了指定类型 method 以外的请求的限制),所以必须使用指令 limit_except所对应的location配置,也就是代码的第1447~1448行。
-对指令if生成的未命名location的使用就相对复杂一点,因为if指令既可以出现在server上下文,又可以出现在location上下文。而对于server上下文,if指令生成的location并不会被使用,而是直接丢弃。
-526: 代码片段10.5-2,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c
-527: static char *
-528: ngx_http_rewrite_if(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
-529: {
-530: …
-609: if (pclcf->name.len == 0) {
-610: if_code->loc_conf = NULL;
-611: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_SIF_CONF;
-612:
-613: } else {
-614: if_code->loc_conf = ctx->loc_conf;
-615: cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_LIF_CONF;
-616: }
-ctx->loc_conf是if指令生成的location,如果当前是server上下文(即第609行判断为真),那么ctx->loc_conf被直接丢弃,也就是if_code->loc_conf被设置为空(第610行)。如果当前是location上下文(即第613行的else里),那么ctx->loc_conf才被赋值给ctx->loc_conf等待后续使用。
-为什么可以这样做?原因有二:第一,对于server上下文里的if语句,其块内只能使用ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块的相关指令(可以在 Nginx 源码树里搜索关键字 NGX_HTTP_SIF_CONF),而这些指令无需关注当前的location,比如指令rewrite,不管当前是什么location,反正是跳转了;第二,前面讲过,NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE阶段后,马上就是NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE查找阶段。既然ngx_http_rewrite_module模块的相关指令不会关心当前是哪个location,而下一阶段马上就是location查找定位,所以保存当前的location是无意义的。
-对于if语句对应的脚本引擎的使用,其执行代码如下。
-1388:代码片段10.5-3,文件名: ngx_http_rewrite_module.c
-1389:void
-1390:ngx_http_script_if_code(ngx_http_script_engine_t *e)
-1391:{
-1392:…
-1402: if (code->loc_conf) {
-1403: e->request->loc_conf = code->loc_conf;
-1404: ngx_http_update_location_config(e->request);
-1405: }
-上面的第1402~1404行也就是对指令if生成的未命名location的使用,同样是先更新当前loc_conf,然后调用函数ngx_http_update_location_config()刷新相关变量值。
-对于if指令生成的未命名location的使用,看起来非常简单,但在Nginx官方网站,有一个专门的地址描述了if语句的负面作用[5],严格点也可以说是bug,但其根本原因在于对if脚本引擎以及Nginx内部分阶段处理的不理解,再加上不恰当的用户配置和滥用导致,这在变量机制一章例举过set指令的简单实例。这里再来看一个if指令的实例,相关Nginx配置如下。
-25: 代码片段10.5-4,文件名: nginx.conf
-26: # request will be sent to backend without uri changed
-27: # to '/' due to if
-28: location /proxy-pass-uri {
-29: proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
-30: set $true 1;
-31: if ($true) {
-32: # nothing
-33: }
-34: }
-如果上面的 Nginx 配置内容没有第30~33 行,那么客户端对代理地址“http://127.0.0.1/proxy-pass-uri”(假定监听套接口为80,以本地作为示例客户端)的请求访问将被转发到服务地址“http://127.0.0.1:8080/”,这是正确情况。如果存在第30~33 行的 if 相关语句,虽然可以看到这些语句什么实际功能也没起到,但是却实实在在地改变了 Nginx 代理的行为,即把请求“http://127.0.0.1/proxy-pass-uri”转发给服务地址“http://127.0.0.1:8080/proxy-pass-uri”,而这并不是我们所期望的。下面看看具体的原因。
-首先,请求URI地址“http://127.0.0.1/proxy-pass-uri”匹配location/proxy-pass-uri,这没问题,当 Nginx 执行流程执行到第3 阶段 NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE 时,就会执行当前location(也就是 location /proxy-pass-uri)上的脚本引擎,那么前面刚提到的函数 ngx_http_script_if_code()将被执行,当前location被切换到if location 里。
-接着,由于当前 location 切换到 if location 里,所以调用函数ngx_http_update_location_config(e->request)做变量更新。由于if location 里没有proxy_pass 指令(即没有对应的回调处理函数),所以做变量更新时不会更新到内容输出函数而继续延用上一层location /proxy-pass-uri的回调ngx_http_proxy_handler()函数。
-1438:代码片段10.5-5,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1439:void
-1440:ngx_http_update_location_config(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-1441:{
-1442:…
-1519: if (clcf->handler) {
-1520: r->content_handler = clcf->handler;
-1521: }
-然后,在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段执行ngx_http_proxy_handler()函数,开始中间代理处理,在组织发往真实服务器的URI地址时(具体实现在函数ngx_http_proxy_create_request()内),由于此时(在if location下)的plcf->location为空,导致变成了“http://127.0.0.1:8080/proxy-pass-uri”这种错误情况,而原本是要从请求uri里裁剪掉这个plcf->location来得到正确的转发URI地址[6]。
-那照此来看,配置在location上下文里的limit_except指令会不会有同样的问题呢?就上面这个示例情况而言不会,因为有专门的配置继承。
-2677:代码片段10.5-6,文件名: ngx_http_proxy_module.c
-2678: static char *
-2679: ngx_http_proxy_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
-2680 : {
-2681:…
-3024: if (conf->upstream.upstream || conf->proxy_lengths) {
-3025: clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
-3026: if (clcf->handler == NULL && clcf->lmt_excpt) {
-3027: clcf->handler = ngx_http_proxy_handler;
-3028: conf->location = prev->location;
-3029: }
-3030: }
-可以看到,它把location也继承了下来,所以转发URI地址可正确获得。如果让if location也做这种继承(即去掉第3026 行的后半句判断),貌似刚提到的那个问题也得到了解决,但是为什么 Nginx 源码一直没做这种改动?原因估计有几点:第一,这种改动的确局部修正了这个问题,但是否会影响到if语句的其他逻辑还不得而知;第二,从官网宣称来看,if语句的问题远远不止如此,if 语句存在的原本目的是为了条件跳转,所以如果要改,那么就要全面禁止在if语句内使用非ngx_http_rewrite_module模块的指令,而这无疑将使得现已在使用中的大量配置变得无效。
-总之,在Nginx配置文件里使用if语句时需特别小心,在实现同一配置功能时,我们也可以尽量使用其他的指令,比如下一节将介绍的try_files指令。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..97cfada771b3a0713029d83d6f3abd8e3f78a07c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ +void +ngx_http_update_location_config(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ + ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf; + + clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); + + if (r->method & clcf->limit_except) { + r->loc_conf = clcf->limit_except_loc_conf; + clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-2-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-2-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8c131feff77d47b2e929c74ec8c3bd7417d5ff8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-2-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,12 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_rewrite_if(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) +{ +… + if (pclcf->name.len == 0) { + if_code->loc_conf = NULL; + cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_SIF_CONF; + + } else { + if_code->loc_conf = ctx->loc_conf; + cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_LIF_CONF; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-3-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-3-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..210d2d38c0668bc786d3231309a9e1bf801c5519 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-3-ngx_http_rewrite_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ +void +ngx_http_script_if_code(ngx_http_script_engine_t *e) +{ +… + if (code->loc_conf) { + e->request->loc_conf = code->loc_conf; + ngx_http_update_location_config(e->request); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-4-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-4-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a8c749179cb7c6a0c572f917f72b1f141435b831 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-4-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ + # request will be sent to backend without uri changed + # to '/' due to if + location /proxy-pass-uri { + proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/; + set $true 1; + if ($true) { + # nothing + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0952c406af3c94538544e5cdf292f4eb644b6c5b --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +void +ngx_http_update_location_config(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (clcf->handler) { + r->content_handler = clcf->handler; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-6-ngx_http_proxy_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-6-ngx_http_proxy_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..771b547eb7e2f09c1401da9202e2c9e5d944fa29 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.5 \346\234\252\345\221\275\345\220\215location \347\232\204\344\275\277\347\224\250/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.5-6-ngx_http_proxy_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ + static char * + ngx_http_proxy_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child) \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/-.txt" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/-.txt" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b615c2a5b1f35edadac6e196b298ecde56724fb3 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/-.txt" @@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ + Filename : nginx.conf + try_files $uri @other @local; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 140e6ad46f06b171d5fe68c7c47ff3425c8dfe00..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,90 +0,0 @@ - -既然是单独分析指令,那么有必要先对该指令的语法、功能以及示例做一下介绍。try_files指令的语法如下。
-try_files file1 [file2 file3 ...fileN] fallback
-可使用在server和location两种上下文内,具体的作用就是依次判断file1file2file3...fileN这 n 文件是否存在并返回(返回意味着找到了对应的资源,具体含义后文再看)第一个存在的文件。如果都不存在,那么进行fallback处理。看一个实例。
-try_files $uri $uri/ /error.html =404;
-假定客户端请求的URI地址为:/test,那么上面这条指令将先判断文件/test是否存在(存在则立即返回,不再进行后面的判断;后面步骤类似处理),再判断文件夹/test/是否存在,然后判断/error.html是否存在,最后返回404错误。一般而言,给指令try_files设置的最后一个参数是必定可以处理的,这样才能称得上是fallback,比如上面示例里的返回404错误。
-可以看到try_files指令是连续的if判断,所以在某些场景下,它可以替换if语句的使用。比如这样一种需求,某一Web网站针对用户提供个性化皮肤设置,也就是对于皮肤图片文件的访问,优先使用个人目录(假定为/person目录)下的图片,但如果这个目录不存在(即用户未自定义个性化皮肤)则使用公共目录(假定为/目录)下的图片。如果用if语句实现这个需求,可以这样(只贴出了关键部分)。
-36: 代码片段10.6-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-37: if (-e "${document_root}/person") {
-38: rewrite ^/(.*)$ /person/$1 break;
-39: }
-但如果采用 try_files指令,那么简单如下即可。
-36: Filename : nginx.conf
-37: try_files /person$uri /$uri =400;
-关于 try_files 指令的内部细节以及其他值得注意的点,下面就从源码上来分析,具体讲解过程以“try_files $uri$uri//error.html =404;”为例。
-首先分析的就是其配置项回调处理函数ngx_http_core_try_files(),忽略相关细节看重点,非常简单,将try_files指令的具体配置内容提取出来存放到clcf->try_files数组字段下。不过,有另外两点处理。第一,如果 try_files 指令的具体配置内容包含有变量,那么就需要脚本引擎的帮助来针对每一个具体请求设置对应的变量值。比如变量$uri,这通过函数 ngx_http_script_compile()来组建对应的脚本引擎。
-4494:代码片段10.6-2,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-4495: static char *
-4496: ngx_http_core_try_files(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
-4497: {
-4498: …
-4534: n = ngx_http_script_variables_count(&tf[i].name);
-4535:
-4536: if (n) {
-4537: ngx_memzero(&sc, sizeof(ngx_http_script_compile_t));
-4538:
-4539: sc.cf = cf;
-4540: sc.source = &tf[i].name;
-4541: …
-4547: if (ngx_http_script_compile(&sc) != NGX_OK) {
-在第4534~4536行判断是否存在Nginx变量,如果存在才需要创建对应的脚本引擎sc,这只是一个局部过渡变量,真正用到的脚本引擎存放在sc->cf->pool内,所以无需为此担心。
-第二,如果 try_files 指令的最后一个参数以字符'='开头,那么表示这是一个状态码,所以调用函数ngx_atoi()做字符串到整型的转换,并设置状态码(注意:设置的是下一个数组元素,即tf[i]的code值,由于try_files指令可以有不定个参数,所以需要有这么一个元素来充当哨兵,标志结束)。
-4556:代码片段10.6-3,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-4557: if (tf[i - 1].name.data[0] == '=') {
-4558:
-4559: code = ngx_atoi(tf[i - 1].name.data + 1, tf[i - 1].name.len - 2);
-4560: …
-4568: tf[i].code = code;
-4569: }
-接着来看try_files指令的使用。我们已经知道Nginx为try_files指令单独提供了一个处理阶段 NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE ,紧跟着该阶段的就是内容产生阶段 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE,这也符合try_files指令的特定目的,即定位可实际输出的数据,如果找到了,那么在下一阶段就可以马上产生对应的输出数据。
-阶段NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE对应的函数为ngx_http_core_try_files_phase(),那么处理的主要逻辑也就是逐个文件去验证是否存在,由于 try_files 指令的参数不定,即需要验证的文件个数不定,所以外层是一个没有明确终止条件的无限for ( ;; )循环,每一次循环处理分三步。首先,根据当前请求的URI地址来组合实际的文件路径,如果当前待验证文件带有Nginx变量,那么需要先执行对应的脚本引擎,最终的文件绝对路径保存在变量path内;接着,通过调用 ngx_open_cached_file()函数尝试打开该文件来判断其是否存在,如果的确不存在,那么continue处理下一个;最后,如果当前待验证文件存在,那么就更新变量r->uri。如下所示(只给出了无alias的情况)。
-1347:代码片段10.6-4,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1348: path.len -= root;
-1349: path.data += root;
-1350:
-1351: if (!alias) {
-1352: r->uri = path;
-这是在前面文件找到的情况,即不是最后的fallback处理,可以看到对于这种情况,Nginx的处理很简单,仅仅只是设置内部变量 r->uri 的值。如果前面指定的所有文件都未找到,此时就进入到fallback处理。
-1285:代码片段10.6-5,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1286: tf++;
-1287:…
-1292: if (tf->lengths == NULL && tf->name.len == 0) {
-1293:
-1294: if (tf->code) {
-1295: ngx_http_finalize_request(r, tf->code);
-1296: return NGX_OK;
-1297: }
-第1292行是对哨兵结束的判断,如果判断为真则表示当前正在进行fallback处理。前面只介绍了try_files指令的一种fallback处理,即返回状态码(第1294~1297行)。另外两种处理就是命名location切换和内部redirect跳转。
-1301:代码片段10.6-6,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1302: if (path.data[0] == '@') {
-1303: (void) ngx_http_named_location(r, &path);
-1304:
-1305: } else {
-1306: ngx_http_split_args(r, &path, &args);
-1307:
-1308: (void) ngx_http_internal_redirect(r, &path, &args);
-1309: }
-切换到新的命名location重新开始处理(第1302~1303行),比如像下面这样的配置[7]。
-00: Filename : nginx.conf
-01: try_files /system/maintenance.html $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html @mongrel;
-02:
-03: location @mongrel {
-04: proxy_pass http://mongrel;
-05: }
-如果前面文件全部查找失败,那么fallback到另外一个服务器(或服务进程)http://mongrel去处理。
-对于内部redirect跳转的fallback处理(代码片段10.6-6的第1306~1308行),需要注意的是GET参数的传递问题,如果我们想要让这些GET参数向后传递,那么必须明确指定,比如下面这样。
-36: Filename : nginx.conf
-37: try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
-注意,只有fallback处理才需要明确加上$args,因为前面已经讲过,对于前n个文件的处理都只是简单查找,查找到后也只是简单地修改一下内部变量 r->uri 的值。也不要尝试在fallback处理前面使用命名location,比如
-38: Filename : nginx.conf
-39: try_files $uri @other @local;
-就与我们的预期不符,Nginx 会直接去磁盘上查找是否存在文件@other,而不是去查找是否存在名字为other的命名location。
-注 释
-[1].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#location。
-[2].http://wiki.nginx.org/BruisedFruit。
-[3].http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-14.23。
- -[5].http://wiki.nginx.org/IfIsEvil
-[6].需结合函数ngx_http_proxy_create_request()的源代码进行理解,此处代码比较多但不复杂,所以没有贴出来,请读者自行查阅。
-[7].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#try_files
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f24e9bcfc4d2c4e2c6047da7e5f9d3bb2407c5ed --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + if (-e "${document_root}/person") { + rewrite ^/(.*)$ /person/$1 break; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..66270ddc82e68acad136d4af5b4775bb1e418bdb --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-2-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + static char * + ngx_http_core_try_files(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) + { + … + n = ngx_http_script_variables_count(&tf[i].name); + + if (n) { + ngx_memzero(&sc, sizeof(ngx_http_script_compile_t)); + + sc.cf = cf; + sc.source = &tf[i].name; + … + if (ngx_http_script_compile(&sc) != NGX_OK) { \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f5687bbeeea27dc0722bc09fd794058e9be22efe --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + if (tf[i - 1].name.data[0] == '=') { + + code = ngx_atoi(tf[i - 1].name.data + 1, tf[i - 1].name.len - 2); + … + tf[i].code = code; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-4-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-4-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..311a3dc8f1fff9231f8de4a083eb65cc3223e5d8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-4-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + path.len -= root; + path.data += root; + + if (!alias) { + r->uri = path; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8c88b04f10a14c97511877a8bd39530b8c26a1a2 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-5-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + tf++; +… + if (tf->lengths == NULL && tf->name.len == 0) { + + if (tf->code) { + ngx_http_finalize_request(r, tf->code); + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f1477653634e747d6d7f9f985ec691b5fab0d78c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/10.6 try_files \346\214\207\344\273\244/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26510.6-6-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + if (path.data[0] == '@') { + (void) ngx_http_named_location(r, &path); + + } else { + ngx_http_split_args(r, &path, &args); + + (void) ngx_http_internal_redirect(r, &path, &args); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 77c38cd3e5312351dd139595eac1be881f6c85c3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25410\347\253\240 \350\257\267\346\261\202\345\256\232\344\275\215/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -我们知道,对于任何一个客户端请求,在Nginx内都必须有与之对应的server以及location来匹配,以提供处理该请求的上下文环境,否则 Nginx 将无法进行正常处理而返回错误。在一般的应用中,Nginx内的server和location会有多个,如何将客户端的请求正确定位到对应的server和location将是本章解析的主要内容。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.1 \346\265\213\350\257\225\347\216\257\345\242\203/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.1 \346\265\213\350\257\225\347\216\257\345\242\203/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 35259cd28f4954ef54737883dbba956df13e7aa5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.1 \346\265\213\350\257\225\347\216\257\345\242\203/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,76 +0,0 @@ - -在详解 Nginx+Fastcgi+PHP 整个流程之前,有必要先把对应的测试环境搭建起来,这样才能明确描述从客户端到 Nginx 再到 PHP 引擎过程中的每一步。搭建的环境是类似图11-1这样的情况,Nginx利用Fastcgi和Upstream模块转发客户端的PHP页面请求。
-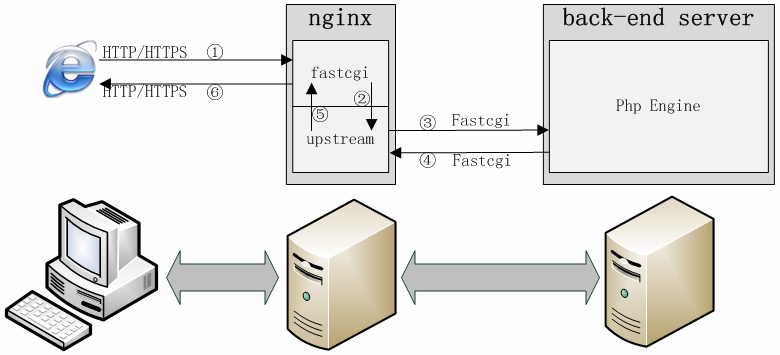 -
-客户端通过HTTP/HTTPS[1]协议对Web服务器端PHP资源的请求被Nginx的Fastcgi模块接手处理(图11-1中①),该模块将客户端请求数据的格式转换为FASTCGI协议[2]格式后(图11-1中②),通过Upstream模块与PHP引擎之间建立的连接,把它们转发送到Php引擎(图11-1中③)。PHP引擎根据转发请求进行处理后,通过同一条连接把数据再传回给Nginx(图11-1中④), Nginx通过Fastcgi模块将收到的响应数据转换回HTTP/HTTPS协议格式后(图11-1 中⑤),发回最终的客户端(图11-1中⑥)。
-在Linux系统上搭建这个简单的测试环境并不复杂,由于在装系统时,我把CentOS的相关开发包都附带上了,所以这里省去了大量的依赖库安装工作。如果PHP也安装了,那么下面这一步也可以省了,但由于我这里还没装,所以按习惯进行源码安装,直接从PHP官网[3]下载PHP源码后,执行Linux下软件源码安装的通用步骤。
-[root@localhost local]# tar xjf php-5.3.17.tar.bz2
-[root@localhost local]# cd php-5.3.17
-[root@localhost php-5.3.17]# ./configure
-[root@localhost php-5.3.17]# make
-[root@localhost php-5.3.17]# make install
-安装一切顺利,简单执行如下命令启动FastCGI管理器,从而可以接受Nginx的PHP解析请求。
-[root@localhost ~]# php-cgi -b 127.0.0.1:8000 &
-[1] 8955
-[root@localhost ~]# php-cgi -b 127.0.0.1:9000 &
-[2] 8956
-[root@localhost ~]# netstat -natp | grep php
-tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8955/php-cgi
-tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8956/php-cgi
-接着配置Nginx,相关配置信息如下。
-15: 代码片段11.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-16: upstream backend {
-17: server 127.0.0.1:8000;
-18: server 127.0.0.1:9000;
-19: }
-20: …
-30: location ~ \.php$ {
-31: root html;
-32: fastcgi_index index.php;
-33: fastcgi_pass backend;
-34:
-35: include fastcgi_params;
-36: fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
-37: }
-以该配置启动Nginx。
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]#./objs/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf.fastcgi
-[root@localhost nginx-1.2.0]# ps auxf | grep nginx | grep -v grep
-root 8240 0.0 0.1 5216 576 ? Ss 12:47 0:00 nginx: master process ./objs/nginx -c/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf.fastcgi
-nobody 8241 0.0 0.2 5404 900 ? S 12:47 0:00 \_ nginx: worker process
-在html目录下新增一个测试文件。
-[root@localhost html]# pwd
-/usr/local/nginx/html
-[root@localhost html]# cat > info.php << END
-> -
> phpinfo();
-> ?>
-> END
-利用wget请求127.0.0.1/info.php地址。
-[root@localhost ~]# wget 127.0.0.1/info.php
---2012-09-23 01:46:27-- http://127.0.0.1/info.php
-Connecting to 127.0.0.1:80...connected.
-HTTP request sent, awaiting response...200 OK
-Length: unspecified [text/html]
-OK,测试环境搭建成功,在本章接下来的几个小节,我们就一步步来看对PHP页面进行请求处理响应的整个流程。如果想要调试客户端请求有请求体的情况,那么可以使用如下这样一个带有上传功能的PHP页面。
-00: 代码片段11.1-2,文件名: fileupload.php
-01:
-02:
03:
-04:
-08:
-09:
-这样,具体的讲解内容就是在客户端打开 http://192.168.164.2/fileupload.php 页面,在文件域里选中一个文件并单击submit按钮进行请求提交后,Nginx对该请求的整个处理过程,如图11-2所示。
- -
-对于客户端发送的PHP资源请求,Nginx在前期的处理和对html资源请求的处理没什么两样,仍然还是创建request请求对象、解析请求头、定位location并开始转动请求处理状态机等,真正出现分叉的地方在状态机进入NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段后。我们已经知道,这个阶段是产生响应数据的阶段,对于PHP这种动态脚本而言,它的真实响应数据必须是通过PHP引擎对其进行解析后的结果,否则,客户端用户就能直接看到PHP源码,这明显是不允许的,如图11-3所示。
-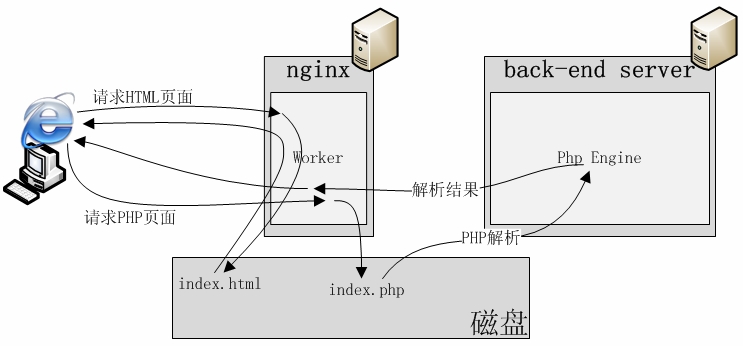 -
-由此可以看到,外部脚本引擎对访问资源有优先处理权限,当然这需要我们在配置文件里做设置,比如这里是把以.php结尾的文件访问都重定向到127.0.0.1:8000或127.0.0.1:9000地址去做解析。如果我们不做这个设置,那么客户端就能直接获取PHP源文件了。在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段的checker处理函数里会优先检查是否有类似的重定向回调函数,这在前面章节已经提到过。
-1385:代码片段11.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-1386:ngx_int_t
-1387:ngx_http_core_content_phase(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-1388: ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph)
-1389:{
-1390:…
-1394: if (r->content_handler) {
-1395: r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler;
-1396: ngx_http_finalize_request(r, r->content_handler(r));
-1397: return NGX_OK;
-1398: }
-回调函数r->content_handler()也就是函数ngx_http_fastcgi_handler(),代码第1396行将执行它,并把返回值当作 ngx_http_finalize_request()函数的第二个参数,在这里的处理就这么简单。
-在进入函数 ngx_http_fastcgi_handler()之前,我们需知道,到此时为止,Nginx 已经完整解析了http请求头并且根据需求已经做了一些是非判断,比如对客户端上传文件大小的限制(可通过指令client_max_body_size设置)判断就在函数ngx_http_core_find_config_phase()内。Nginx解析的http请求头存储在变量r内,通过ngx_http_fastcgi_handler()函数的唯一参数将这些信息传递了过去。而另一方面,请求体却不一定已完全接收完,可能有一部分已经跟随请求头信息一起被 Nginx 接收而存放在缓存区 r->header_in 内,但更多的请求体还在内核 tcp接收队列或网络上或客户端尚未发送,因此这一部分相关处理逻辑是在进入函数 ngx_http_fastcgi_handler()之后的事情。
-Nginx 判断出客户端请求需要转发到后端服务器进行解析,因此首先做的就是在函数ngx_http_fastcgi_handler()的最开始处调用函数ngx_http_upstream_create()创建upstream对象。创建的初始过程很简单,只是给upstream对象申请对应的内存空间并将它挂载在r->upstream字段下,这样也就和 request 对象关联起来了。接下来给 upstream 对象设置回调函数,fastcgi模块提出了5个核心功能函数,分别如下。
-572: 代码片段11.2-2,文件名: ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c
-573: static ngx_int_t
-574: ngx_http_fastcgi_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-575: {
-576: …
-588: if (ngx_http_upstream_create(r) != NGX_OK) {
-589: …
-617: u->create_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request;
-618: u->reinit_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_reinit_request;
-619: u->process_header = ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header;
-620: u->abort_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_abort_request;
-621: u->finalize_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_finalize_request;
-622: …
-635: rc = ngx_http_read_client_request_body(r, ngx_http_upstream_init);
-重要的是回调函数 create_request()和 process_header(),它们分别表示向后端服务器发起请求和从后端服务器接收数据,这一去一来无非是 Nginx 与后端服务器交互的核心。代码第635行正式开始着手处理,调用函数ngx_http_read_client_request_body()读取客户端请求体,注意它的参数为函数指针ngx_http_upstream_init(),Nginx会在读取全部客户端请求体后执行它,这意味着Nginx把读取客户端上传文件的压力放在了自己这一边,后端服务器(比如PHP引擎)是感知不到的。
-读取全部客户端请求体的相关逻辑,说起来非常的简单:循环读,直到读完本次请求的请求体为止。当然,在某一些情况下无需读取客户端的请求体,具体看实际代码。
-27: 代码片段11.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_request_body.c
-28: ngx_int_t
-29: ngx_http_read_client_request_body(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-30: ngx_http_client_body_handler_pt post_handler)
-31: {
-32: …
-42: if (r->request_body || r->discard_body) {
-43: post_handler(r);
-44: return NGX_OK;
-45: }
-46: …
-58: if (r->headers_in.content_length_n < 0) {
-59: post_handler(r);
-60: return NGX_OK;
-61: }
-62: …
-65: if (r->headers_in.content_length_n == 0) {
-66: …
-96: post_handler(r);
-97:
-98: return NGX_OK;
-99: }
-100: …
-111: preread = r->header_in->last - r->header_in->pos;
-112:
-113: if (preread) {
-114: …
-141: if ((off_t) preread >= r->headers_in.content_length_n) {
-142: …
-155: post_handler(r);
-156:
-157: return NGX_OK;
-158: }
-上面任意一个if判断成功都代表着无需再接收客户端的请求体:代码第42行表示请求体已经接收(比如当子请求进入该函数时,它已经从主请求那里继承了请求体)或者明确主动丢弃请求体;代码第58、65行表示客户端没有发送请求体或请求体已被丢弃;代码第113、141行则表示本次请求的请求体已经随着请求头一起被读到缓存区r->header_in内了,所以同样也无需再读;所有这些情况,Nginx都开始执行post_handler()函数,也就是函数ngx_http_upstream_init()着手本次请求从Nginx到后端服务器之间的转发处理。
-如果还需要继续读取客户端的请求体,那么涉及到的函数主要有三个:ngx_http_read_client_request_body()、ngx_http_do_read_client_request_body()和 ngx_http_read_client_request_body_handler()。对于第三个回调函数的出现是必然的,因为虽然刚才我们说循环读,但当然不是阻塞着循环读,而是通过读事件触发的,所以有这么一个handler函数来处理读事件,如果有数据可读就会回调它,而它的内部是调用 ngx_http_do_read_client_request_body()函数做真正的数据读取操作。整个流程如图11-4所示。
-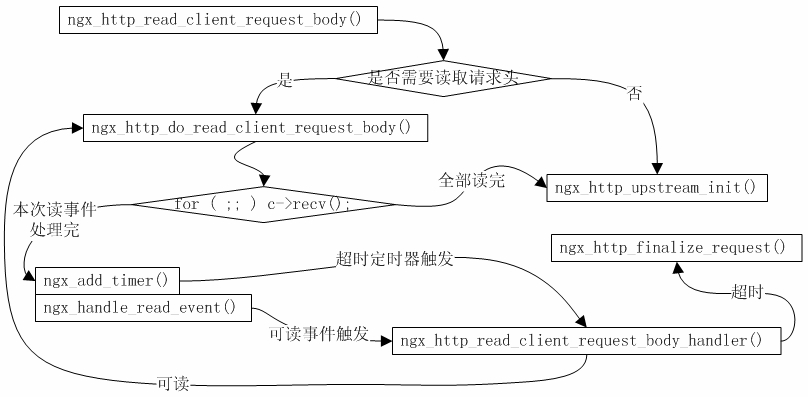 -
-从客户端读取的请求体存放在r->request_body内,受一些用户设置的影响,请求体数据可能放置在一块或多块内存缓存区,或者是某个临时文件内,但只要请求体大于一定的值(可通过指令client_body_buffer_size[4]设置,默认情况下是 2 页内存,一般也就是 8KB),则都会主动写到临时文件,这实现在函数ngx_http_write_request_body()内,注意它一次可以写入多个buf块。这些虽都属于具体的细节实现,但并不难以看懂,在此不做过多赘述。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..aef187c4e452c4f62b3045b1d38bff64e3e1613e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-1-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +ngx_int_t +ngx_http_core_content_phase(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph) +{ +… + if (r->content_handler) { + r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler; + ngx_http_finalize_request(r, r->content_handler(r)); + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-2-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-2-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..75a53bdd7f6ed14c622996225b2ec96d275cc1ce --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-2-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_fastcgi_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (ngx_http_upstream_create(r) != NGX_OK) { +… + u->create_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request; + u->reinit_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_reinit_request; + u->process_header = ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header; + u->abort_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_abort_request; + u->finalize_request = ngx_http_fastcgi_finalize_request; +… + rc = ngx_http_read_client_request_body(r, ngx_http_upstream_init); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-3-ngx_http_request_body.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-3-ngx_http_request_body.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..034914878997a8a05f95c2d08dd1b1ee8c2f13af --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.2 \345\256\242\346\210\267\347\253\257\345\217\221\350\265\267PHP \350\257\267\346\261\202/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.2-3-ngx_http_request_body.c" @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ + ngx_int_t + ngx_http_read_client_request_body(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_http_client_body_handler_pt post_handler) + { + … + if (r->request_body || r->discard_body) { + post_handler(r); + return NGX_OK; + } + … + if (r->headers_in.content_length_n < 0) { + post_handler(r); + return NGX_OK; + } + … + if (r->headers_in.content_length_n == 0) { + … + post_handler(r); + + return NGX_OK; + } +… + preread = r->header_in->last - r->header_in->pos; + + if (preread) { +… + if ((off_t) preread >= r->headers_in.content_length_n) { +… + post_handler(r); + + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ecb87fa90fe8a2f5ff2ba655ce82997b4bae2ba5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,244 +0,0 @@ - -从函数ngx_http_upstream_init()开始本节的内容,该函数应该重点关注的逻辑是在其最末尾处调用的ngx_http_upstream_init_request()函数。
-ngx_http_upstream_init() -> ngx_http_upstream_init_request()
-函数 ngx_http_upstream_init_request()首先做的是执行 create_request()回调函数,对于Fastcgi模块而言,也就是函数ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request()。整个函数代码有460行左右,比较繁琐而在其内处理的工作也比较多,一方面是配置文件里相关配置变量的解析、传递参数的设置,另一方面,还需从客户端与Nginx之间的HTTP通信协议转换为Nginx与后端服务器之间的Fastcgi通信协议。对这部分代码的理解,除了要了解前面第8章变量机制中介绍的脚本引擎以外,还涉及到具体的 Fastcgi 协议。这里不对 Fastcgi 协议做详细讲解,但是其最基本的组成概念为record记录,即所有来回传送的数据都是以记录的形式存在的。解析后的 Fastcgi 记录被放置在缓存区 u->request_bufs 内,我们可以简单验证一下(这是在执行完u->create_request()函数后所进行的内存查看)。
-(gdb) x/24db u->request_bufs->buf->pos
-0x930ab34: 1 1 0 1 0 8 0 0
-0x930ab3c: 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0x930ab44: 1 4 0 1 3 40 0 0
-这三行数据对应静态变量 ngx_http_fastcgi_request_start。
-504: 代码片段11.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c
-505: static ngx_http_fastcgi_request_start_t ngx_http_fastcgi_request_start = {
-506: { 1, /* version */
-507: NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_BEGIN_REQUEST, /* type */
-508: 0, /* request_id_hi */
-509: 1, /* request_id_lo */
-510: 0, /* content_length_hi */
-511: sizeof(ngx_http_fastcgi_begin_request_t),/* content_length_lo */
-512: 0, /* padding_length */
-513: 0 }, /* reserved */
-514:
-515: { 0, /* role_hi */
-516: NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_RESPONDER, /* role_lo */
-517: 0, /* NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_KEEP_CONN */ /* flags */
-518: { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } }, /* reserved[5] */
-519:
-520: { 1, /* version */
-521: NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_PARAMS, /* type */
-522: 0, /* request_id_hi */
-523: 1 }, /* request_id_lo */
-524:
-525: };
-而接下来的数据就是(名称,值)对(即Name-Value Pairs),它们以名称长度、值长度、名称、值的形式逐一排列,具体可以参考官方说明[5],这里还是看下面的实例。
-(gdb) x/88cb u->request_bufs->buf->pos+24
-0x930ab4c: 12 '\f' 0 '\000' 81 'Q' 85 'U' 69 'E' 82 'R' 89 'Y' 95 '_'
-0x930ab54: 83 'S' 84 'T' 82 'R' 73 'I' 78 'N' 71 'G' 14 '\016' 3 '\003'
-0x930ab5c: 82 'R' 69 'E' 81 'Q' 85 'U' 69 'E' 83 'S' 84 'T' 95 '_'
-0x930ab64: 77 'M' 69 'E' 84 'T' 72 'H' 79 'O' 68 'D' 71 'G' 69 'E'
-0x930ab6c: 84 'T' 12 '\f' 0 '\000' 67 'C' 79 'O' 78 'N' 84 'T' 69 'E'
-0x930ab74: 78 'N' 84 'T' 95 '_' 84 'T' 89 'Y' 80 'P' 69 'E' 14 '\016'
-0x930ab7c: 0 '\000' 67 'C' 79 'O' 78 'N' 84 'T' 69 'E' 78 'N' 84 'T'
-0x930ab84: 95 '_' 76 'L' 69 'E' 78 'N' 71 'G' 84 'T' 72 'H' 11 '\v'
-0x930ab8c: 6 '\006' 83 'S' 67 'C' 82 'R' 73 'I' 80 'P' 84 'T' 95 '_'
-0x930ab94: 78 'N' 65 'A' 77 'M' 69 'E' 47 '/' 116 't' 46 '.' 112 'p'
-0x930ab9c: 104 'h' 112 'p' 11 '\v' 6 '\006' 82 'R' 69 'E' 81 'Q' 85 'U'
-从上面数据可以看到前几个(名称,值)对分别如表11-1所示。
-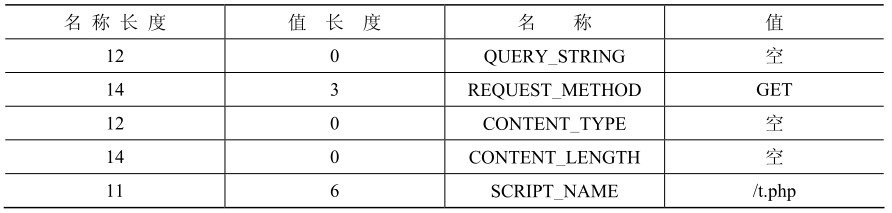 -
-针对协议转换的具体代码实现细节我们暂且略过,继续看函数 ngx_http_upstream_init_request()接下来的处理逻辑。
-449: 代码片段11.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-450: static void
-451: ngx_http_upstream_init_request(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-452: {
-453: …
-505: if (u->create_request(r) != NGX_OK) {
-506: …
-518: u->output.output_filter = ngx_chain_writer;
-519: u->output.filter_ctx = &u->writer;
-520: …
-523: if (r->upstream_states == NULL) {
-524:
-525: r->upstream_states = ngx_array_create(r->pool, 1,
-526: sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_state_t));
-527: …
-544: cln = ngx_http_cleanup_add(r, 0);
-545: …
-550: cln->handler = ngx_http_upstream_cleanup;
-551: cln->data = r;
-552: u->cleanup = &cln->handler;
-可以看到上面这部分代码是一些准备工作,记住代码第518~519 行的赋值,这很重要,因为在后面我们会看到对这两个字段的使用;代码第523~525行申请了一个数组,用于存在与PHP引擎之间的连接信息;代码第523~552行挂载了一个清理回调,以便最后做资源释放。
- -Nginx要把请求数据发送到PHP引擎,首先得建立起Nginx到PHP引擎之间的通信连接,如果用户在配置文件里设置的 PHP 引擎监听地址是很明确的,即没有带上配置变量,(暂称之为静态配置),那么此时可直接调用函数ngx_http_upstream_connect()发起连接建立请求。
-553: 代码片段11.3.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-554: if (u->resolved == NULL) {
-555:
-556: uscf = u->conf->upstream;
-557: …
-639: if (uscf->peer.init(r, uscf) != NGX_OK) {
-640: …
-641: }
-642:
-645: ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u);
-646: }
-代码第554~556、639行进行配置选定并执行对应的初始化,其中uscf->peer.init回调函数为当前选用的Load-balance模块的初始函数,比如我这里为ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin_peer()函数。
-如果用户在配置文件里设置的PHP引擎监听地址不明确,即里面包含有配置变量(暂称之为动态配置),因此对于每一个客户端请求都要做一次解析,比如下面这样的配置。
-18: 代码片段11.3.1-2,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-19: location ^~ /download {
-20: location ~ "^/download/(.*)/(.*)" {
-21: proxy_pass $1/$2;
-22: }
-23: }
-后端服务器地址不确定,被Nginx的脚本引擎解析后得到的值可能是IP地址,也可能是域名,如果是域名,Nginx则将执行域名解析逻辑以获得对应的后端服务器IP地址。在这里,Nginx当然不能[6]使用像gethostbyname()这样的阻塞系统调用,因此它自己实现了一个非阻塞的域名解析客户端。
-553: 代码片段11.3.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-554: if (u->resolved == NULL) {
-555: …
-558: } else {
-559:
-560: if (u->resolved->sockaddr) {
-561:
-562: if (ngx_http_upstream_create_round_robin_peer(r, u->resolved)
-563: …
-570: ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u);
-571:
-572: return;
-573: }
-574: …
-621: ctx->handler = ngx_http_upstream_resolve_handler;
-622: ctx->data = r;
-623: ctx->timeout = clcf->resolver_timeout;
-624: …
-627: if (ngx_resolve_name(ctx) != NGX_OK) {
-上面给出的代码主要在else分支里,也就是用在户配置文件里设置的后端服务器地址包含有配置变量,经过Nginx脚本引擎的执行后,最终的后端服务器地址明确起来,或IP地址或域名。如果是IP地址,那么执行的逻辑为代码562~573行;如果是域名,那么则开始域名解析的动作,域名解析成功或失败都将执行对应的回调函数 ngx_http_upstream_resolve_handler(),看它的内部代码。
-856: 代码片段11.3.1-4,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-857: static void
-858: ngx_http_upstream_resolve_handler(ngx_resolver_ctx_t *ctx)
-859: {
-860: …
-869: if (ctx->state) {
-870: …
-875: ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_HTTP_BAD_GATEWAY);
-876: return;
-877: }
-878: …
-898: if (ngx_http_upstream_create_round_robin_peer(r, ur) != NGX_OK) {
-899: …
-907: ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u);
-908: }
-截掉了很多其他逻辑,可以看到在域名解析成功的情况下,最后调用的也是函数ngx_http_upstream_connect()。整个过程如图11-5所示。
-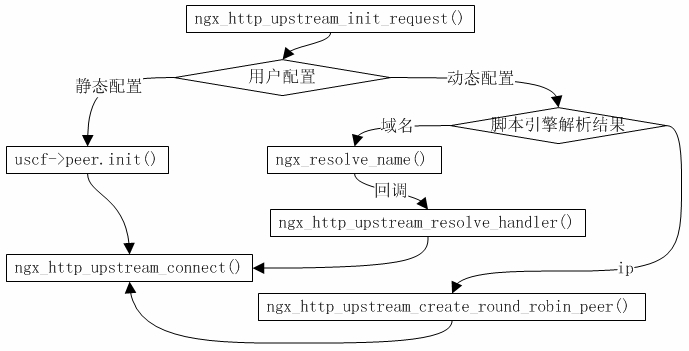 -
-在函数ngx_http_upstream_connect()内进而调用函数ngx_event_connect_peer()开始真正的请求建立连接操作。
-ngx_http_upstream_connect() -> ngx_event_connect_peer()
-函数ngx_event_connect_peer()首先通过Load-balance模块的get()接口选择一个后端服务器,比如如果是round_robin模块,那么就是函数ngx_http_upstream_get_round_robin_peer()。选定后端服务器后,执行一系列的系统调用,比如socket()、bind()、connect()进行连接。这里有一点值得注意:由于本地连接套接口被Nginx设置为非阻塞模式,所以connect()函数会立即返回,但当前连接可能还未建立起来,所以返回值将为−1,对于这种情况需要判断错误状态码 errno 是否为 NGX_EINPROGRESS(表示连接正在建立当中)。如果是这种情况,那么这属于正常,返回NGX_AGAIN即可。
-13: 代码片段11.3.1-5,文件名: ngx_event_connect.c
-14: ngx_int_t
-15: ngx_event_connect_peer(ngx_peer_connection_t *pc)
-16: {
-17: …
-118: if (ngx_add_conn) {
-119: if (ngx_add_conn(c) == NGX_ERROR) {
-120: …
-170: if (ngx_add_conn) {
-171: if (rc == -1) {
-172: …
-175: return NGX_AGAIN;
-176: }
-177: …
-180: wev->ready = 1;
-181:
-182: return NGX_OK;
-183: }
-代码第118行,将Nginx与后端服务器之间的连接对象(注意:这并不要求连接已经建立)加入到事件监控机制里,这其中当然也包括可写事件。代码第180 行的设置,此时表示连接已经建立起来,所以当前处于可写状态。再返回到函数ngx_http_upstream_connect()后,即开始准备向后端服务器发送请求数据,当然,这需要等待连接套接口可写。
-1090:代码片段11.3.1-6,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1091:static void
-1092:ngx_http_upstream_connect(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
-1093:{
-1094:…
-1151: c->write->handler = ngx_http_upstream_handler;
-1152: c->read->handler = ngx_http_upstream_handler;
-1153:
-1154: u->write_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler;
-1155: u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_header;
-1156:…
-1220: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1221: ngx_add_timer(c->write, u->conf->connect_timeout);
-1222: return;
-1223: }
-1224:…
-1234: ngx_http_upstream_send_request(r, u);
-1235:}
-代码第1220行处理的是连接当前正在建立的情况,这里设置了一个超时定时器,不论是可写事件到达(前面刚提到可写事件已经被加入到事件监控机制,可写事件到达表示连接建立完成)还是超时事件到达都将执行函数 ngx_http_upstream_handler() ,进而执行函数ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler()。在该函数内
-1461:代码片段11.3.1-7,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1462:static void
-1463:ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-1464: ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
-1465:{
-1466:…
-1473: if (c->write->timedout) {
-1474: ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u,
-1474: NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_TIMEOUT);
-1475: return;
-1476: }
-1477:…
-1495: ngx_http_upstream_send_request(r, u);
-1496:}
-代码第1473~1476行,如果是连接超时,那么调用函数ngx_http_upstream_next()选择其他后端服务器。否则,进入到函数ngx_http_upstream_send_request()内开始真正的发送请求数据操作。这整个流程如图11-6所示。
-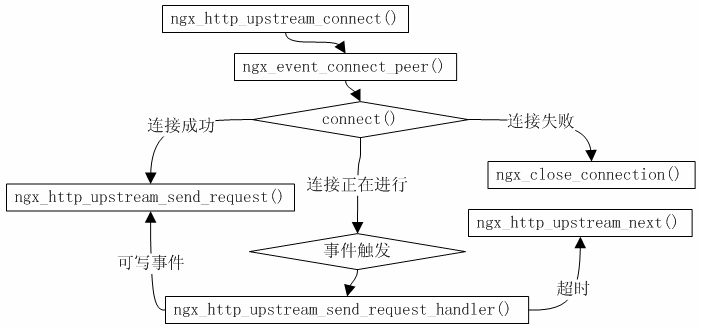 -
-Nginx发送请求数据到后端服务器的这部分逻辑比较简单,基本都实现在函数ngx_http_upstream_send_request()内。
-1375:代码片段11.3.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1376:static void
-1377:ngx_http_upstream_send_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
-1378:{
-1379:…
-1387: if (!u->request_sent && ngx_http_upstream_test_connect(c) != NGX_OK) {
-1388: ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR);
-1389: return;
-1390: }
-1391:…
-1395: rc=ngx_output_chain(&u->output, u->request_sent? NULL : u->request_bufs);
-1396:
-1397: u->request_sent = 1;
-1398:
-1399: if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
-1400: ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR);
-1401: return;
-1402: }
-1403:…
-1407: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1408: ngx_add_timer(c->write, u->conf->send_timeout);
-1409:…
-1416: return;
-1417: }
-1418:
-1419: /* rc == NGX_OK */
-1420:
-1421: if (c->tcp_nopush == NGX_TCP_NOPUSH_SET) {
-1422: if (ngx_tcp_push(c->fd) == NGX_ERROR) {
-1423:…
-1433: ngx_add_timer(c->read, u->conf->read_timeout);
-1434:…
-1436: if (c->read->ready) {
-1437:…
-1447: ngx_http_upstream_process_header(r, u);
-1448: return;
-1449: }
-在实际发送请求数据之前,Nginx先做了一下检查,u->request_sent是一个旗标,标记请求数据是否已经发送过,函数ngx_http_upstream_test_connect()利用套接口选项SO_ERROR[7]判断当前连接是否还正常。而请求数据的实际发送由函数ngx_output_chain()完成,第一个参数u->output的两个重要字段output_filter和filter_ctx在函数ngx_http_upstream_init_request()赋的值(从代码片段 11.3-2 里可以看到),这里正好用上。如果发送数据出错,那么调用函数ngx_http_upstream_next()选择其他后端服务器。如果数据未完全发送完,此时添加超时定时器,等待可写或超时事件,如果事件发生,重复进入到这个函数调用流程。
-ngx_http_upstream_handler() -> ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler() ->ngx_http_upstream_send_request()
-代码第1421~1422 行用于去掉套接口上可能存在的塞子(Linux下也就是TCP_CORK[8]选项),让内核TCP协议栈将发送缓存区里的请求数据立即发送出去。如果所有请求数据发送成功,那么Nginx就等待后端服务器的响应数据。当然,这需设置一个超时事件,以免无限等待,如果当前就已经可读,那么最好不过,执行函数ngx_http_upstream_process_header()开始处理。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ae266e6660a86d58371108663b3f51edbb78f57d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ +static ngx_http_fastcgi_request_start_t ngx_http_fastcgi_request_start = { + { 1, /* version */ + NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_BEGIN_REQUEST, /* type */ + 0, /* request_id_hi */ + 1, /* request_id_lo */ + 0, /* content_length_hi */ + sizeof(ngx_http_fastcgi_begin_request_t),/* content_length_lo */ + 0, /* padding_length */ + 0 }, /* reserved */ + + { 0, /* role_hi */ + NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_RESPONDER, /* role_lo */ + 0, /* NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_KEEP_CONN */ /* flags */ + { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } }, /* reserved[5] */ + + { 1, /* version */ + NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_PARAMS, /* type */ + 0, /* request_id_hi */ + 1 }, /* request_id_lo */ + +}; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0014cd49c40275fc85b4aa65cf03566564042b2f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_init_request(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (u->create_request(r) != NGX_OK) { +… + u->output.output_filter = ngx_chain_writer; + u->output.filter_ctx = &u->writer; +… + if (r->upstream_states == NULL) { + + r->upstream_states = ngx_array_create(r->pool, 1, + sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_state_t)); +… + cln = ngx_http_cleanup_add(r, 0); +… + cln->handler = ngx_http_upstream_cleanup; + cln->data = r; + u->cleanup = &cln->handler; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..558a9fe06428e7e054ba979f902559670ba2f918 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ + if (u->resolved == NULL) { + + uscf = u->conf->upstream; +… + if (uscf->peer.init(r, uscf) != NGX_OK) { +… + } + + ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-2-nginx.conf.fastcgi" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-2-nginx.conf.fastcgi" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1954ae702dff84a8c7523340019278db32da4a4f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-2-nginx.conf.fastcgi" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + location ^~ /download { + location ~ "^/download/(.*)/(.*)" { + proxy_pass $1/$2; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..54a3b130a86b435a80969c9bf92e76bc4c81c6ae --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ + if (u->resolved == NULL) { +… + } else { + + if (u->resolved->sockaddr) { + + if (ngx_http_upstream_create_round_robin_peer(r, u->resolved) +… + ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u); + + return; + } +… + ctx->handler = ngx_http_upstream_resolve_handler; + ctx->data = r; + ctx->timeout = clcf->resolver_timeout; +… + if (ngx_resolve_name(ctx) != NGX_OK) { \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8e881c426665705f8db1274787453c8b5d99c049 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_resolve_handler(ngx_resolver_ctx_t *ctx) +{ +… + if (ctx->state) { +… + ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_HTTP_BAD_GATEWAY); + return; + } +… + if (ngx_http_upstream_create_round_robin_peer(r, ur) != NGX_OK) { +… + ngx_http_upstream_connect(r, u); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-5-ngx_event_connect.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-5-ngx_event_connect.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ec4283c39d97c2a8865ba32366238938d385a5e0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-5-ngx_event_connect.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ + ngx_int_t + ngx_event_connect_peer(ngx_peer_connection_t *pc) + { + … + if (ngx_add_conn) { + if (ngx_add_conn(c) == NGX_ERROR) { +… + if (ngx_add_conn) { + if (rc == -1) { +… + return NGX_AGAIN; + } +… + wev->ready = 1; + + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3db92dc6d863ed160db1cc09b8f11f913883b932 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_connect(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u) +{ +… + c->write->handler = ngx_http_upstream_handler; + c->read->handler = ngx_http_upstream_handler; + + u->write_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler; + u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_header; +… + if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) { + ngx_add_timer(c->write, u->conf->connect_timeout); + return; + } +… + ngx_http_upstream_send_request(r, u); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-7-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-7-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c1ae6d0bf921e721ef11cd433cf9ae4d8145537d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.1-7-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_send_request_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_http_upstream_t *u) +{ +… + if (c->write->timedout) { + ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, + NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_TIMEOUT); + return; + } +… + ngx_http_upstream_send_request(r, u); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.2-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.2-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..60b346d9e7e592c7a3083a94b7d3b7e6bc12dfa8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.3 \350\257\267\346\261\202\350\275\254\345\217\221/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.3.2-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_send_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u) +{ +… + if (!u->request_sent && ngx_http_upstream_test_connect(c) != NGX_OK) { + ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR); + return; + } +… + rc=ngx_output_chain(&u->output, u->request_sent? NULL : u->request_bufs); + + u->request_sent = 1; + + if (rc == NGX_ERROR) { + ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR); + return; + } +… + if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) { + ngx_add_timer(c->write, u->conf->send_timeout); +… + return; + } + + /* rc == NGX_OK */ + + if (c->tcp_nopush == NGX_TCP_NOPUSH_SET) { + if (ngx_tcp_push(c->fd) == NGX_ERROR) { +… + ngx_add_timer(c->read, u->conf->read_timeout); +… + if (c->read->ready) { +… + ngx_http_upstream_process_header(r, u); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ca9a21935d68011ae1ab8beaddba9c8d32c3e912..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,465 +0,0 @@ - -不管是在函数ngx_http_upstream_send_request()末尾处直接调用
-ngx_http_upstream_send_request() -> ngx_http_upstream_process_header()
-还是可读事件发生或超时事件发生
-ngx_http_upstream_handler() -> ngx_http_upstream_process_header()
-Nginx 在向后端服务器发送完请求数据后,将会执行的都是函数 ngx_http_upstream_process_header(),即由该函数拉开后半部分,也就是数据响应处理流程的序幕。
- -函数ngx_http_upstream_process_header()用于读取后端服务器的响应数据,而在我们这里, Nginx读到的响应数据是FASTCGI协议格式的,所以需先做解析。逐一来看下面的代码。
-1498:代码片段11.4.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1499:static void
-1500:ngx_http_upstream_process_header(ngx_http_request_t*r,ngx_http_upstream_t*u)
-1501:{
-1502:…
-1513: if (c->read->timedout) {
-1514: ngx_http_upstream_next(r,u,NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_TIMEOUT);
-1515: return;
-1516: }
-1517:
-1518: if (!u->request_sent && ngx_http_upstream_test_connect(c) != NGX_OK) {
-1519: ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR);
-1520: return;
-1521: }
-这处理的是超时情况以及连接已断开的情况,对于这两种情况都将调用函数 ngx_http_upstream_next()重新选择后端服务器。在函数 ngx_http_upstream_process_header()后面还有一些情况会重新选择后端服务器,就不再一一列出,以免干扰了我们对主线流程的理解。
-1555:代码片段11.4.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1556: for ( ;; ) {
-1557:
-1558: n = c->recv(c, u->buffer.last, u->buffer.end - u->buffer.last);
-1559:
-1560: if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1561:…
-1565: if (ngx_handle_read_event(c->read, 0) != NGX_OK) {
-1566:…
-1571: return;
-1572: }
-1573:…
-1592: rc = u->process_header(r);
-1593:
-1594: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1595:…
-1605: continue;
-1606: }
-1607:
-1608: break;
-1609: }
-这是一个大循环,代码第1558行从后端服务器接收数据。代码第1560~1572行实现的是如果什么数据都没收到,那么重新注册可读事件的监控并返回,如果有收到数据,因为此时收到的是FASTCGI协议格式,所以要调用对应的回调函数u->process_header()进行处理,也就是函数 ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header() ,若处理的结果为 NGX_AGAIN ,则表示FASTCGI 响应头未完全接收完, continue 继续接收,否则的话break 跳出开始下面的处理。
-先看看函数ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header()里的处理逻辑,它循环处理每一条FASTCGI记录。
-1200:代码片段11.4.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c
-1201:static ngx_int_t
-1202:ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-1203:{
-1204:…
-1225: for ( ;; ) {
-1226:
-1227: if (f->state < ngx_http_fastcgi_st_data) {
-1228:…
-1232: rc = ngx_http_fastcgi_process_record(r, f);
-1233:…
-1237: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1238: return NGX_AGAIN;
-1239: }
-1240:…
-1263: if (f->state == ngx_http_fastcgi_st_padding) {
-1264:…
-1282: return NGX_AGAIN;
-1283: }
-1284:…
-1288: if (f->type == NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_STDERR) {
-1289:…
-1359: continue;
-1360: }
-1361:…
-1405: f->fastcgi_stdout = 1;
-1406:
-1407: start = u->buffer.pos;
-1408:…
-1423: for ( ;; ) {
-1424:…
-1428: rc = ngx_http_parse_header_line(r, &u->buffer, 1);
-1429:…
-1433: if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
-1434: break;
-1435: }
-1436:
-1437: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-1438:…
-1536: break;
-1537: }
-1538:
-1539: if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) {
-1540:…
-1575: break;
-1576: }
-1577:…
-1583: return NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER;
-1584: }
-1585:…
-1600: if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) {
-1601: return NGX_OK;
-1602: }
-1603:
-1604: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-1605: continue;
-1606: }
-1607:
-1608: /* rc == NGX_AGAIN */
-1609:….
-1630: return NGX_AGAIN;
-1631: }
-1632:}
-函数总代码比较多,400 多行,即便是在抽丝剥茧得到核心流程后,仍然有如此多的代码,但总体逻辑并不难以理解。有两个for ( ;; )循环,分别调用ngx_http_fastcgi_process_record()和ngx_http_parse_header_line()把Fastcgi记录和记录存放的Http响应头(这并不是发往客户端的最终 Http 响应头,Nginx 还要对它们做进一步的处理)解析出来做处理。分别简单验证一下,先看Fastcgi记录数据(这是在函数ngx_http_fastcgi_process_record()内进行的内存查看)。
-(gdb) x/88cb f->pos
-0x930b2d8: 1 '\001' 6 '\006' 0 '\000' 1 '\001' 0 '\000' 57 '9' 7 '\a' 0 '\000'
-0x930b2e0: 88 'X' 45 '-' 80 'P' 111 'o' 119 'w' 101 'e' 114 'r' 101 'e'
-0x930b2e8: 100 'd' 45 '-' 66 'B' 121 'y' 58 ':' 32 ' ' 80 'P' 72 'H'
-0x930b2f0: 80 'P' 47 '/' 53 '5' 46 '.' 51 '3' 46 '.' 49 '1' 55 '7'
-0x930b2f8: 13 '\r' 10 '\n' 67 'C' 111 'o' 110 'n' 116 't' 101 'e' 110 'n'
-0x930b300: 116 't' 45 '-' 116 't' 121 'y' 112 'p' 101 'e' 58 ':' 32 ' '
-0x930b308: 116 't' 101 'e' 120 'x' 116 't' 47 '/' 104 'h' 116 't' 109 'm'
-0x930b310: 108 'l' 13 '\r' 10 '\n' 13 '\r' 10 '\n' 116 't' 101 'e' 115 's'
-0x930b318: 116 't' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000'
-0x930b320: 1 '\001' 3 '\003' 0 '\000' 1 '\001' 0 '\000' 8 '\b' 0 '\000' 0 '\000'
-0x930b328: 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 0 '\000' 94 '^' 21 '\025' 29 '\035'
-上面显示的数据有两条Fastcgi记录,每一条Fastcgi记录在Nginx内对应的结构体为ngx_http_fastcgi_header_t,具体来看其数据分别表示如表11-2所示。
-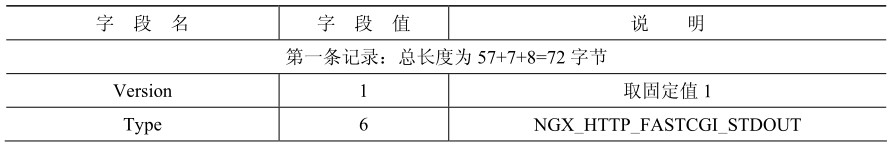 -
-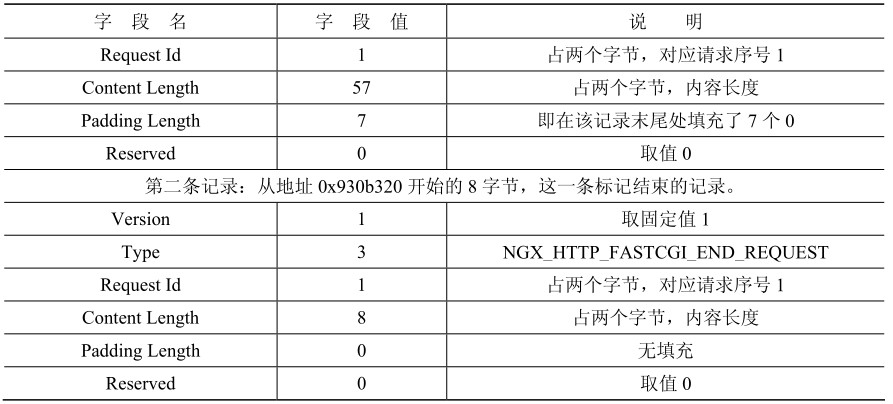 -
-再来看HTTP响应头数据(这是在函数ngx_http_parse_header_line()内进行的内存查看)。
-(gdb) x/sb b->pos
-0x930b2e0: "X-Powered-By: PHP/5.3.17\r\nContent-type: text/html\r\n\r\ntest"
-由于我的Php文件非常简单,就是
-[root@localhost html]# cat t.php
--
echo "test";
-?>
-所以把Http响应体数据也一次性地接收过来了,而Php引擎指定的Http响应头数据只有两个:版本申明和响应体数据类型。
-有了这些感性认识,再回过头来看函数ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header()的处理逻辑就简单了。如果一条 Fastcgi 记录未能处理完,比如数据未全部读到,那么返回 NGX_AGAIN 等待下一次收到数据时继续处理。否则进入到后面Http响应头数据的处理过程里,同样要判断每一个以及所有 Http 响应头数据的处理结果,如果全部解析完毕,即处理结果值为NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE,那么将返回 NGX_OK,这个函数的任务也就算圆满成功,否则继续反复处理。
-函数 ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header()里还有一大片代码尚未给出来,它们将在每一个 Http响应头被正确解析之后执行,所做的工作主要是将Php引擎发给Nginx 的Http 响应头存放在u->headers_in.headers内并做一些相关的可能处理,比如忽略Php引擎发过来的"Keep-Alive"等,关于这些,请各位读者直接参考全局变量ngx_http_upstream_headers_in的handler()回调字段。
-Fastcgi响应头的最后一点处理代码在函数ngx_http_upstream_process_header()内,所以得回到这个函数继续看。
-1498:代码片段11.4.1-4,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1499:static void
-1500:ngx_http_upstream_process_header(ngx_http_request_t*r,ngx_http_upstream_t*u)
-1501:{
-1502:…
-1622: /* rc == NGX_OK */
-1623:
-1624: if (u->headers_in.status_n > NGX_HTTP_SPECIAL_RESPONSE) {
-1625:…
-1637: }
-1638:
-1639: if (ngx_http_upstream_process_headers(r, u) != NGX_OK) {
-1640: return;
-1641: }
-1642:
-1643: if (!r->subrequest_in_memory) {
-1644: ngx_http_upstream_send_response(r, u);
-1645: return;
-1646: }
-上面给出的是前面处理一切OK的情况,也就是对应的返回值rc等于NGX_OK。代码第1624~1637行处理的是响应状态码大于300的情况,这表示Http处理异常,比如最常见的404错误。
-函数ngx_http_upstream_process_headers()所做的处理主要是将Fastcgi响应头数据从u->headers_in.headers拷贝到r->headers_out.headers,而我们知道r->headers_out.headers是Nginx发往客户端的最终HTTP响应头。不过,也有较为复杂一点的有针对性的拷贝,比如ngx_http_upstream_copy_content_type()等。关于这些,请各位读者直接参考全局变量ngx_http_upstream_headers_in的copy_handler()回调字段。另外值得注意的是,这里还包含了另外一个特别重要的功能实现,即Nginx支持的X-Accel-Redirect[9],如果走到这个逻辑里,这意味后端服务器已经告诉Nginx去哪里(由X-Accel-Redirect指定)获取资源,对当前客户端请求的处理不再需要后端服务器的参与,因此Nginx将执行ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request()函数断开连接,并进行ngx_http_internal_redirect()跳转处理,这无需多说。
-1858:代码片段11.4.1-5,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-1859: if (u->headers_in.x_accel_redirect
-1860: && !(u->conf->ignore_headers & NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_IGN_XA_REDIRECT))
-1861: {
-1862: ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_DECLINED);
-1863:…
-1904: ngx_http_internal_redirect(r, uri, &args);
-1905: ngx_http_finalize_request(r, NGX_DONE);
-1906: return NGX_DONE;
-Nginx 的 Fastcgi 模块明确不支持 Subrequest In Memory,这在函数 ngx_http_fastcgi_handler()内的开头就可以看到这点,所以代码第1643 行判断为真,进入到函数 ngx_http_upstream_send_response()内开始处理。
-发送Http响应头的代码非常的简单,因为在函数ngx_http_upstream_send_response()的入口处就能看到对应的函数调用。
-2045:代码片段11.4.1-6,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-2046:static void
-2047:ngx_http_upstream_send_response(ngx_http_request_t*r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
-2048:{
-2049:…
-2056: rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
-由函数ngx_http_send_header()进入到header过滤链,该过滤链上的处理并不会因为数据是来自Php引擎而有什么不同,这无需多述。
- -响应头数据被直接发送[10]出去了,但对于响应体数据而言,有个控制旗标u->buffering字段,表示Nginx作为后端服务器到最终客户端之间的中间人,对数据的传送是否要采取缓冲策略。如果开启缓冲,那么Nginx将尽可能多地读取后端服务器的响应数据,等达到一定量(比如buffer满)再传送给最终客户端。如果关闭,那么Nginx对数据的中转就是一个同步的过程,即从后端服务器接收到响应数据就立即将其发送给客户端。
-Nginx的Fastcgi模块默认强制开启缓冲并且无法关闭。
-572: 代码片段11.4.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c
-573: static ngx_int_t
-574: ngx_http_fastcgi_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-575: {
-576: …
-623: u->buffering = 1;
-Nginx为什么不能像Proxy模块那样针对Fastcgi模块提供类似于proxy_buffering[11]的配置指令,这仍然还是FASTCGI协议本身的原因。前面已经看到FASTCGI协议要求数据总是以记录的形式传输,所以当Nginx未能接收一个完整记录时,是无法进行解析和转送的,所以必须开启缓冲。如果有类似于Comet长连接这样的应用需求,由于缓冲会对它们产生负面影响,所以此时可能将无法很好地使用Fastcgi模块,而需换用Proxy或其他方式。
-针对 Fastcgi 模块,我们这里直接看缓冲开启的情况。在函数 ngx_http_upstream_send_response()内做了很多准备工作,其中最重要的就是给变量 u->pipe 做初始化处理。先看该变量所对应结构体ngx_event_pipe_t的具体定义。
-24: 代码片段11.4.2-2,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.h
-25: struct ngx_event_pipe_s {
-26: ngx_connection_t *upstream;
-27: ngx_connection_t *downstream;
-28:
-29: ngx_chain_t *free_raw_bufs;
-30: ngx_chain_t *in;
-31: ngx_chain_t **last_in;
-32:
-33: ngx_chain_t *out;
-34: ngx_chain_t *free;
-35: ngx_chain_t *busy;
-36: …
-42: ngx_event_pipe_input_filter_pt input_filter;
-43: void *input_ctx;
-44:
-45: ngx_event_pipe_output_filter_pt output_filter;
-46: void *output_ctx;
-看这几个字段就能大致了解到它封装了 Nginx 作为后端服务器与最终客户端之间的过渡人所需要的所有信息。比如:upstream表示Nginx与后端服务器之间的连接对象;downstream表示Nginx与客户端之间的连接对象;input_filter表示Nginx 接收到后端服务器的响应数据后所需执行的过滤回调,在这里也就是函数ngx_http_fastcgi_input_filter(),用于对Fastcgi记录做解析;output_filter 表示 Nginx 发送数据到客户端的过滤函数,这里直接指向 ngx_http_output_filter(),即走普通的HTTP响应体过滤链。其他的chain链就是对应的接收和发送缓存区,这无需多说。
-看函数ngx_http_upstream_send_response()内具体的初始化代码。
-2232:代码片段11.4.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-2233: p = u->pipe;
-2234:
-2235: p->output_filter = (ngx_event_pipe_output_filter_pt) ngx_http_output_filter;
-2236: p->output_ctx = r;
-2237:…
-2240: p->upstream = u->peer.connection;
-2241: p->downstream = c;
-2242:…
-2337: u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream;
-2338: r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream;
-2339:
-2340: ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream(r, u);
-2341:}
-注意代码第2337~2338行设置了对应的回调函数,这两个回调函数分别在后端服务器可读和最终客户端可写时被调用,而它们的内部实现又非常简单,除去超时判断等,主要就都是调用函数ngx_event_pipe()。函数ngx_event_pipe()的定义如下。
-88: 代码片段11.4.2-4,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.h
-89: ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write);
-其中第2个参数表示当前是否有数据可写,再结合函数ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream()与ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream()各自的功能,我们可以猜到情况应该如图11-7所示。
-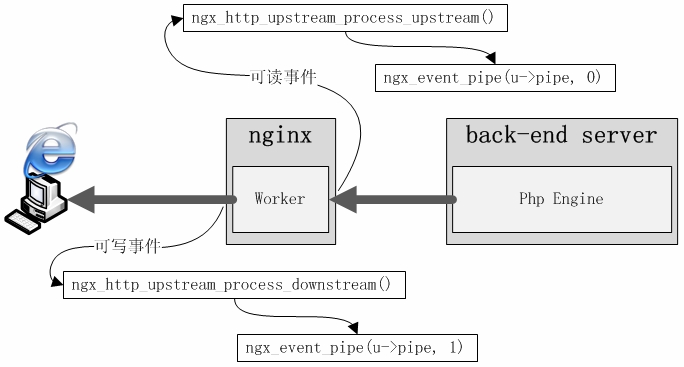 -
-看实际代码。
-2622:代码片段11.4.2-5,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-2623:static void
-2624:ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-2625: ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
-2626:{
-2627:…
-2641: if (ngx_event_pipe(u->pipe, 0) == NGX_ABORT) {
-2642:…
-2647: ngx_http_upstream_process_request(r);
-2648:}
-2552:代码片段11.4.2-6,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-2553:static void
-2554:ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-2555:{
-2556:…
-2563: p = u->pipe;
-2564:…
-2613: if (ngx_event_pipe(p, 1) == NGX_ABORT) {
-2614:…
-2619: ngx_http_upstream_process_request(r);
-2620:}
-末尾调用的函数 ngx_http_upstream_process_request()用于做一些检测,比如当前连接是否出错,请求是否处理完成等,这不多述,因此不管 Nginx 从哪条路径执行过来,我们的关注重点都将集中到函数ngx_event_pipe()上。
-函数ngx_event_pipe()的处理逻辑比较简明,具体代码如下。
-21: 代码片段11.4.2-7,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-22: ngx_int_t
-23: ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write)
-24: {
-25: …
-29: for ( ;; ) {
-30: if (do_write) {
-31: …
-33: rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(p);
-34: …
-42: }
-43: …
-49: if (ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(p) == NGX_ABORT) {
-50: …
-53: if (!p->read && !p->upstream_blocked) {
-54: break;
-55: }
-56:
-57: do_write = 1;
-58: }
-59: …
-65: if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, flags) != NGX_OK) {
-66: …
-79: if (ngx_handle_write_event(wev, p->send_lowat) != NGX_OK) {
-80: …
-93: return NGX_OK;
-94: }
-变量do_write控制是否需向客户端进行写数据的操作,这有可能参数do_write本来就是1,或者代码第49 行从后端服务器有读取到响应数据。如果从后端服务器没有读取到响应数据,那么p->read变量值为0且当前并非明确有数据可写,那么将break跳出。代码第65、79行继续关注对应的读/写事件,以便在事件发生时做再一次回调。
-函数ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream()与ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream()完成实际数据读/写操作,即一个从后端服务器读取响应数据,一个把响应数据发送给最终客户端。先来看实现接收Fastcgi响应体的ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream()函数,该函数虽然代码比较多,但分步骤来看也没那么复杂。
-首先,对preread数据的处理,在前面的示例中,我们看到过,在接收响应头数据时,部分或全部响应体数据也一起被接收过来了,所以先对这部分数据做处理。
-96: 代码片段11.4.2-8,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-97: static ngx_int_t
-98: ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
-99: {
-100: …
-112: for ( ;; ) {
-113: …
-122: if (p->preread_bufs) {
-123: …
-126: chain = p->preread_bufs;
-127: p->preread_bufs = NULL;
-128: n = p->preread_size;
-129: …
-133: if (n) {
-134: p->read = 1;
-135: }
-最外面是一个大的for ( ;; )循环,这无需多说,在前面我们已经看到过无数次这种处理方式。由于preread数据存放在p->preread_bufs缓存区内,所以如果p->preread_bufs不为NULL,则表示可能有 preread 数据,所以代码第122 行可以做这样的判断。注意代码第127 行,把p->preread_bufs赋值为NULL,以表示preread数据已被处理过了。如果preread数据的确存在,即n不为0,那么标记字段p->read被设置为1,在刚介绍过的函数ngx_event_pipe()内,我们看到过对该标记字段的使用。
-接下来就是从后端服务器读取响应体,但这需先准备对应的数据存储空间。
-169: 代码片段11.4.2-9,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-170: if (p->free_raw_bufs) {
-171: …
-174: chain = p->free_raw_bufs;
-175: …
-182: } else if (p->allocated < p->bufs.num) {
-183: …
-193: chain = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
-194: …
-201: } else if (!p->cacheable
-202: && p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx
-203: && p->downstream->write->ready
-204: && !p->downstream->write->delayed)
-205: {
-206: …
-211: p->upstream_blocked = 1;
-212: …
-216: break;
-217:
-218: } else if (p->cacheable
-219: || p->temp_file->offset < p->max_temp_file_size)
-220: {
-221: …
-227: rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
-228: …
-253: chain = p->free_raw_bufs;
-254: …
-261: } else {
-262: …
-268: break;
-269: }
-连续的 if-else 针对的是逐步在各种情况下获取可用缓存空间的途径:如果 p->free_raw_bufs 为真,表示还有可用缓存区,那么可直接使用;如果当前缓存区个数未超限,那么还可以申请使用;如果当前可以往客户端发送数据,即 Nginx 与客户端之间的套接口描述符处于可写状态,那么设置p->upstream_blocked 标记并break 跳出,回退到函数ngx_event_ pipe()内执行 ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream()写操作,从而空闲出一些缓存区来使用;调用ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file()函数把 p->in 链内数据写到临时文件并且把它们挂载在p->out链上,从而也可以空闲出一些缓存区来使用;最后,没有办法获得可用缓存空间,那么只能直接break跳出,等待Nginx把缓存数据写出给最终客户端以及下一次进入到该函数。如果数据存储空间已经准备妥善,那么即可开始接收Php引擎发过来的响应数据。
-270: 代码片段11.4.2-10,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-271: n = p->upstream->recv_chain(p->upstream, chain);
-272: …
-294: p->read = 1;
-295:
-296: if (n == 0) {
-297: p->upstream_eof = 1;
-298: break;
-299: }
-300: }
-执行 Nginx 与后端服务器连接对象 p->upstream 上的数据接收函数,这里也就是函数ngx_readv_chain(),如果读取无错,那么设置标记p->read。代码第296~299行用于判断本次请求的响应体数据是否已经全部读完,连接是否关闭。
-到这里,数据已经读取到了,虽然还不一定就是全部响应体数据,但可以做一些处理了,比如把数据移到Nginx与客户端之间的发送缓存区,从而让Nginx及时把数据发送出去,把缓存区释放出来(下面只给出了部分代码,完整逻辑需看全部代码,特别是对缓存区是否已经全满的判断以及未满缓存区的input_filter()过滤处理)。
-301: 代码片段11.4.2-11,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-302: p->read_length += n;
-303: cl = chain;
-304: …
-306: while (cl && n > 0) {
-307: …
-317: if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
-318: …
-330: }
-对于像Proxy等模块,它们的input_filter回调函数可能会比较简单,但是由于Fastcgi模块需对Fastcgi协议做解析,所以对应的回调函数ngx_http_fastcgi_input_filter()稍显复杂。在从Fastcgi记录里解析出实际的数据后,组建一个对应的缓存区链并且挂载在字段p->in下,同时p->last_in字段指向这个链上的最后一个缓存块。
-1649:代码片段11.4.2-12,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-1650:static ngx_int_t
-1651:ngx_http_fastcgi_input_filter(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_buf_t *buf)
-1652:{
-1653:…
-1821: if (p->in) {
-1822: *p->last_in = cl;
-1823: } else {
-1824: p->in = cl;
-1825: }
-1826: p->last_in = &cl->next;
-变量cl是缓存区链节点,因此我们待发送的响应体数据就在p->in这条链上。另外,字段p->last_in在这里辅助构建这条链,当然,如果只有一个节点,那么p->last_in将为NULL。在gdb里看下这个数据(这是在代码片段11.4.2-12的第1826行进行的查看)。
-(gdb) x/s p->in->buf->pos
-0x9120315: "test"
-从后端服务器接收响应数据的代码逻辑,分析到此就算是结束了,而把这些响应数据发送给最终客户端实现在函数ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream()内,下面就来看这个函数的具体情况。
-449: 代码片段11.4.2-13,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-450: static ngx_int_t
-451: ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
-452: {
-453: …
-467: for ( ;; ) {
-468: …
-472: if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
-473: …
-480: if (p->out) {
-481: …
-488: rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->out);
-489: …
-495: p->out = NULL;
-496: }
-497:
-498: if (p->in) {
-499: …
-506: rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->in);
-507: …
-513: p->in = NULL;
-514: }
-515: …
-533: p->downstream_done = 1;
-534: break;
-535: }
-536: …
-676: }
-677:
-678: return NGX_OK;
-679: }
-注意到代码第472 行的判断,可以看出上面给出的代码是在执行响应数据发送的最后环节,比如p->upstream_done标记,当然,也有可能是出错的情况,比如p->upstream_error。数据的发送通过回调函数 output_filter()来完成,在 Fastcgi 模块这里,该回调指向函数 ngx_http_output_filter(),这在之前介绍的函数ngx_http_upstream_send_response()内看到过。
-代码片段11.4.2-13里先发送p->out链内数据,然后再发送p->in链内数据。前面刚介绍到Nginx 在读取后端服务器的响应数据时,如果无可用缓存区则会调用ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file()函数把p->in链内数据写到临时文件并且把它们挂载在p->out链上,因此p->out链内存放的数据比p->in链内数据要早,所以必须先发送。
-数据发送完毕后,在代码第534 行break 跳出整个for ( ;; )循环,执行到底678 行退出函数。
-函数ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream()另外的发送逻辑是处理非最后一次的情况。
-563: 代码片段11.4.2-14,文件名: ngx_event_pipe.c
-564: out = NULL;
-565: …
-572: ll = NULL;
-573: …
-575: for ( ;; ) {
-576: if (p->out) {
-577: cl = p->out;
-578:
-579: …
-584: p->out = p->out->next;
-585:
-586: } else if (!p->cacheable && p->in) {
-587: cl = p->in;
-588: …
-606: p->in = p->in->next;
-607:
-608: } else {
-609: break;
-610: }
-611:
-612: cl->next = NULL;
-613:
-614: if (out) {
-615: *ll = cl;
-616: } else {
-617: out = cl;
-618: }
-619: ll = &cl->next;
-620: }
-621: …
-639: rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, out);
-组建了一个out链,同样也是先p->out,再p->in,然后通过回调函数output_filter()进行发送。
-至此,整个动态页面请求处理的核心流程就给抽取了出来并加以简单但较为连贯的解析,虽然忽略了很多其他细节上的处理,不过那些并没有特别难以理解的地方,所以倒也无碍本章内容的整体完整性。
-注 释
- -[2].http://www.fastcgi.com/drupal/node/6?q=node/22。
-[3].http://www.php.net/downloads.php。
-[4].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#client_body_buffer_size
-[5].http://www.fastcgi.com/devkit/doc/fcgi-spec.html#S3.4。
-[6].时刻记住Nginx的主要特性:非阻塞、事件驱动、异步。
-[7].http://lenky.info/?p=2234。
-[8].http://lenky.info/?p=2218。
-[9].http://wiki.nginx.org/X-accel。
-[10].“直接发送出去”是针对 Nginx 而言的,也就是这些数据已经到了发送链表out 里,但并不表示这些数据就已经发到了网络上,甚至可能都还没到Linux内核的TCP发送队列。
-[11].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpProxyModule#proxy_buffering
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b9600b3154c06df5dfe4533abc9086b603e9fb56 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-1-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_process_header(ngx_http_request_t*r,ngx_http_upstream_t*u) +{ +… + if (c->read->timedout) { + ngx_http_upstream_next(r,u,NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_TIMEOUT); + return; + } + + if (!u->request_sent && ngx_http_upstream_test_connect(c) != NGX_OK) { + ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c73a428d11b3a2c82a7ce7e7e56f87b11d97f855 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-2-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,20 @@ + for ( ;; ) { + + n = c->recv(c, u->buffer.last, u->buffer.end - u->buffer.last); + + if (n == NGX_AGAIN) { +… + if (ngx_handle_read_event(c->read, 0) != NGX_OK) { +… + return; + } +… + rc = u->process_header(r); + + if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) { +… + continue; + } + + break; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-3-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-3-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d31c0640bb8cd69b1576cfe19cb636e30aad3882 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-3-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + for ( ;; ) { + + if (f->state < ngx_http_fastcgi_st_data) { +… + rc = ngx_http_fastcgi_process_record(r, f); +… + if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) { + return NGX_AGAIN; + } +… + if (f->state == ngx_http_fastcgi_st_padding) { +… + return NGX_AGAIN; + } +… + if (f->type == NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_STDERR) { +… + continue; + } +… + f->fastcgi_stdout = 1; + + start = u->buffer.pos; +… + for ( ;; ) { +… + rc = ngx_http_parse_header_line(r, &u->buffer, 1); +… + if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) { + break; + } + + if (rc == NGX_OK) { +… + break; + } + + if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) { +… + break; + } +… + return NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER; + } +… + if (rc == NGX_HTTP_PARSE_HEADER_DONE) { + return NGX_OK; + } + + if (rc == NGX_OK) { + continue; + } + + /* rc == NGX_AGAIN */ +…. + return NGX_AGAIN; + } +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dad9177cdc28cd378fd7e4129cb690133dbc9bc0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-4-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_process_header(ngx_http_request_t*r,ngx_http_upstream_t*u) +{ +… + /* rc == NGX_OK */ + + if (u->headers_in.status_n > NGX_HTTP_SPECIAL_RESPONSE) { +… + } + + if (ngx_http_upstream_process_headers(r, u) != NGX_OK) { + return; + } + + if (!r->subrequest_in_memory) { + ngx_http_upstream_send_response(r, u); + return; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c73eb7d99757d0e67a7f9d6393eb4b28e81b0342 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + if (u->headers_in.x_accel_redirect + && !(u->conf->ignore_headers & NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_IGN_XA_REDIRECT)) + { + ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_DECLINED); +… + ngx_http_internal_redirect(r, uri, &args); + ngx_http_finalize_request(r, NGX_DONE); + return NGX_DONE; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dc374ea55f1a12cdb794720cbcb2f54c629465c9 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.1-6-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_send_response(ngx_http_request_t*r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u) +{ +… + rc = ngx_http_send_header(r); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fba2d38e0afebf94e6df177ff74ef63689c0ec9c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-1-ngx_http_fastcgi_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_fastcgi_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + u->buffering = 1; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-10-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-10-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..38a68110c759fe236263c5b265e8fc67c7e6a205 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-10-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ + n = p->upstream->recv_chain(p->upstream, chain); +… + p->read = 1; + + if (n == 0) { + p->upstream_eof = 1; + break; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-11-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-11-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..279ed3f7a7f5482f28e190917e8a1d7eb8a780b3 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-11-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + p->read_length += n; + cl = chain; +… + while (cl && n > 0) { +… + if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) { +… + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-12-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-12-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f08819523c9b457175880715e84f16115acaf8af --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-12-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_fastcgi_input_filter(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_buf_t *buf) +{ +… + if (p->in) { + *p->last_in = cl; + } else { + p->in = cl; + } + p->last_in = &cl->next; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-13-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-13-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..92a05617ba98d7bb4ea6b22bec583e9fc3252292 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-13-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p) +{ +… + for ( ;; ) { +… + if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) { +… + if (p->out) { +… + rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->out); +… + p->out = NULL; + } + + if (p->in) { +… + rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->in); +… + p->in = NULL; + } +… + p->downstream_done = 1; + break; + } +… + } + + return NGX_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-14-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-14-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1926bceb7360aa2395329e39032f924cfcd98dd0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-14-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,31 @@ + out = NULL; +… + ll = NULL; +… + for ( ;; ) { + if (p->out) { + cl = p->out; + +… + p->out = p->out->next; + + } else if (!p->cacheable && p->in) { + cl = p->in; +… + p->in = p->in->next; + + } else { + break; + } + + cl->next = NULL; + + if (out) { + *ll = cl; + } else { + out = cl; + } + ll = &cl->next; + } +… + rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, out); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-2-ngx_event_pipe.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-2-ngx_event_pipe.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f443d50867a1a437722349c3faf1159186394d60 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-2-ngx_event_pipe.h" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ + struct ngx_event_pipe_s { + ngx_connection_t *upstream; + ngx_connection_t *downstream; + + ngx_chain_t *free_raw_bufs; + ngx_chain_t *in; + ngx_chain_t **last_in; + + ngx_chain_t *out; + ngx_chain_t *free; + ngx_chain_t *busy; + … + ngx_event_pipe_input_filter_pt input_filter; + void *input_ctx; + + ngx_event_pipe_output_filter_pt output_filter; + void *output_ctx; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..be0671fe2ef736d3c702e08f5dc29c5718b33382 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + p = u->pipe; + + p->output_filter = (ngx_event_pipe_output_filter_pt) ngx_http_output_filter; + p->output_ctx = r; +… + p->upstream = u->peer.connection; + p->downstream = c; +… + u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream; + r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream; + + ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream(r, u); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-4-ngx_event_pipe.h" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-4-ngx_event_pipe.h" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..20f04418d252a9def72daf50153041801d90bc26 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-4-ngx_event_pipe.h" @@ -0,0 +1 @@ + ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write); \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a372425fe4d65db1cea729234d64af647b22c9fd --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-5-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +static void +ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_http_upstream_t *u) +{ +… + if (ngx_event_pipe(u->pipe, 0) == NGX_ABORT) { +… + ngx_http_upstream_process_request(r); +} +static void +ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + p = u->pipe; +… + if (ngx_event_pipe(p, 1) == NGX_ABORT) { +… + ngx_http_upstream_process_request(r); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-7-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-7-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3fe3d33417f2e434b4cf0652ec87c4752326ac1f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-7-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,26 @@ + ngx_int_t + ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write) + { + … + for ( ;; ) { + if (do_write) { + … + rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(p); + … + } + … + if (ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(p) == NGX_ABORT) { + … + if (!p->read && !p->upstream_blocked) { + break; + } + + do_write = 1; + } + … + if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, flags) != NGX_OK) { + … + if (ngx_handle_write_event(wev, p->send_lowat) != NGX_OK) { + … + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-8-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-8-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8495402eb782fcf31f2a78c4121977025a14e936 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-8-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p) + { +… + for ( ;; ) { +… + if (p->preread_bufs) { +… + chain = p->preread_bufs; + p->preread_bufs = NULL; + n = p->preread_size; +… + if (n) { + p->read = 1; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-9-ngx_event_pipe.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-9-ngx_event_pipe.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0aa518fc0dceb59195536347f03a29040a8c1a7a --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/11.4 \346\225\260\346\215\256\345\223\215\345\272\224/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26511.4.2-9-ngx_event_pipe.c" @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ + if (p->free_raw_bufs) { +… + chain = p->free_raw_bufs; +… + } else if (p->allocated < p->bufs.num) { +… + chain = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool); +… + } else if (!p->cacheable + && p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx + && p->downstream->write->ready + && !p->downstream->write->delayed) + { +… + p->upstream_blocked = 1; +… + break; + + } else if (p->cacheable + || p->temp_file->offset < p->max_temp_file_size) + { +… + rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p); +… + chain = p->free_raw_bufs; +… + } else { +… + break; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 05f1d0d54f4ac44d6e72edd17c4f5f6a23b9deed..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25411\347\253\240 \345\212\250\346\200\201\351\241\265\351\235\242\350\257\267\346\261\202\345\244\204\347\220\206/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -对于HTTP服务而言,Nginx自身能通过借助模块ngx_http_static_module处理简单的静态页面请求,而对于动态页面的请求,比如PHP等,Nginx只能把该请求转发给其他脚本引擎做处理,然后把获得的处理结果响应给客户端。Nginx+Fastcgi+PHP的配置模式是一种较为常见的使用场景,本章就将针对在这种环境下,对于客户端的一次请求,介绍 Nginx 所做的处理与响应过程的完整细节。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index c8b625c174814c2be6a3249d2e5c8606be945fb7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,103 +0,0 @@ - -not_modified_filter是放在头过滤链上第一位置的模块,即当响应数据经过这条过滤链时,第一个执行过滤检查的就是该模块,这是由not_modified_filter模块功能的特殊性所决定的,它主要实现的是对HTTP协议304状态码[1]的支持,而这个功能的最初目的也就是为了提高性能。如果该功能顺利实施,那么其他过滤模块也就无需再执行,另外该模块用到的相关变量值(比如r->headers_out.last_modified_time)不能受其他过滤模块的影响,所以把它放在第一位置是合理的。
- -下面通过一个实例来看看HTTP协议304状态码的具体功能。
-第一次请求。
-1.客户端向Nginx发起一个HTTPGET请求(假设请求一个文件A[2])。
-2.Nginx 处理该请求并返回响应头和文件内容,其中响应头里就包括有 Last-Modified(例如"Last-Modified:Sat,01 Sep201220:03:30GMT"),状态码200。
-3.客户端收到 Nginx 响应后,除了展示内容给最终用户外还会将文件内容、Date 等响应信息缓存起来。
-第二次请求。
-1.客户端第二次发起HTTPGET 请求(当然仍然请求的是文件A),此次客户端除了发送常规请求头外,还会发送一个If-Modified-Since 头(例如"If-Modified-Since:Sat, 01Sep 201220:03:30 GMT"),其内容就是第一次请求Nginx 时返回的Last-Modified 值。
-2.Nginx 判断客户端发送过来的请求头里的指定时间与当前站点里对应文件的最后修改时间,如果一致(或要晚)则表示自客户端第一次请求文件A之后,文件A未发生修改(或修改在前),于是直接返回304状态码,此时将不再有响应体。
-3.客户端收到 304 状态码后,知道服务器上站点内的文件 A 从上一次请求到现在未被修改过,于是继续使用本地缓存。
-从上面描述可以看到,对于客户端的第二次请求,Nginx只需返回一个304的状态码即可,而无需把文件A再次发给客户端,这在一定程度上减轻了Nginx的压力,也节约了网络带宽。这种带有条件判断请求头的GET请求,被称之为有条件的GET请求(conditional GET)。除了Last-Modified结合If-Modified-Since以外,另外两个请求头Etag[3]和If-None-Match也可以实现类似功能的条件GET请求[4]。两者在原理上是一样的,都是拿资源的一个特征值做标识,然后在后续做比较判断,只是Last-Modified依赖的资源特征值固定为时间戳,而Etag可依赖的资源特征值则比较灵活,也没有统一的标准规定必须使用哪个或哪几个特征值,任由Etag功能的具体实现者自己选择,比如可以是时间戳、文件大小或文件inode节点等。
-正是因为Etag的这种灵活性,使得它相对具有一定的优势。
-首先,Last-Modified 对文件的新旧检查只能到秒一级。如果文件修改非常频繁,比如在秒以下的时间内进行修改,这种修改Last-Modified无法判断。
-其次,如果文件的更改对用户的查阅影响并不大(比如一些文件周期性的更改,但是它的内容并不改变而仅仅改变修改时间),也没必要把文件重发给客户端,此时 Last-Modified无法做到判断,而使用ETag只需把修改时间不计算在标识值之内就能满足需求(像Apache,可由FileETag指令配置ETag值是由文件的inode(索引节点)、大小、最后修改时间之一或它们的组合来确定)。
-另外,有些服务器并不能精确地得到文件的最后修改时间,这就导致Last-Modified可能出现误判。
-当一个请求里ETag和Last-Modified都存在时,只有两者各自判断都满足返回 304 状态码的情况下,Web服务器才能返回304状态码,但Nginx-1.2.0尚未完全实现Etag机制[5],这也可能是因为Etag本身的计算与生成需要消耗服务器的计算资源,而对于追求高性能的Nginx而言,本地静态页面的处理使用Last-Modified就足够了。
-另一方面,有读者也许有这样的经验,对于需要强制刷新的页面以及不能缓存的请求,会在对应链接的后面加上伪随机数,比如javascript代码。
-"login.do?rnd=" + Math.random().toString();
-当客户端每次对 login.do 发起请求时,由于伪随机参数的存在,让浏览器认为它是一个完全不同的URL地址,所以在请求里就不会包含If-Modified-Since请求头,从而Nginx也就不会返回304状态码。
- -not_modified_filter模块支持的另外一个请求头为If-Unmodified-Since[6],该请求头要求Nginx检查对应的文件在指定的时间以来是否被修改过。如果没有,那么Nginx继续后面的处理,原本该怎么样做还是怎么样做,就好像请求头If-Unmodified-Since没有存在过一样如果有修改,那么Nginx必须停止继续处理,而立即返回一个412的状态码。
-另外,如果在客户端发起的一个请求里,请求头 If-Unmodified-Since 与上一小节提到的请求头If-Modified-Since同时存在,那么这种行为的结果是未定义的,不过对于Nginx而言,采取的措施是直接忽略If-Modified-Since请求头。
-有了上面介绍的这些基础知识,再看具体的代码实现就简单了。
-51: 代码片段12.1.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c
-52: static ngx_int_t
-53: ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-54: {
-55: if (r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_OK
-56: || r != r->main
-57: || r->headers_out.last_modified_time == -1)
-58: {
-59: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-60: }
-61:
-62: if (r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since) {
-63: return ngx_http_test_precondition(r);
-64: }
-65:
-66: if (r->headers_in.if_modified_since) {
-67: return ngx_http_test_not_modified(r);
-68: }
-69:
-70: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-71: }
-代码第55~60行是做前置判断与处理,如果当前处理结果不为200(只有被正常处理的请求才需关注本节提到的几个请求头)或者当前请求不是主请求(只有主请求才有资格直接修改与客户端交互的状态码)或没有获取到文件对应的最后修改时间(后面的比较需要这个时间),那么直接进入到过滤链上的下一个模块。
-接下来的两个if语句分别判断对应的请求头是否存在,如果存在则进入到对应的函数做进一步判断。可以看到对if_unmodified_since的判断在先,并且代码第51行直接return,所以如果If-Unmodified-Since请求头存在,那么后面的If-Modified-Since请求头被忽略。
-73: 代码片段12.1.2-2,文件名: ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c
-74: static ngx_int_t
-75: ngx_http_test_precondition(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-76: {
-77: time_t iums;
-78:
-79: iums = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since->value.data,
-80: r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since-> value.len);
-81: …
-85: if (iums >= r->headers_out.last_modified_time) {
-86: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-87: }
-88:
-89: return ngx_http_filter_finalize_request(r, NULL,
-90: NGX_HTTP_PRECONDITION_FAILED);
-91: }
-代码第85行,对两个时间做比较,如果为真,即修改时间在指定时间之前,也就是自指定时间以来,文件未被修改过,所以直接进入到滤链上的下一个模块,就像什么事情也没发生过一样,否则的话,执行函数ngx_http_filter_finalize_request()直接返回状态码NGX_HTTP_区性PRECONDITION_FAILED(该宏为412)。
-93: 代码片段12.1.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c
-94: static ngx_int_t
-95: ngx_http_test_not_modified(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-96: {
-97: …
-100: clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
-101:
-102: if (clcf->if_modified_since == NGX_HTTP_IMS_OFF) {
-103: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-104: }
-105:
-106: ims = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.data,
-107: r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.len);
-108: …
-112: if (ims != r->headers_out.last_modified_time) {
-113:
-114: if (clcf->if_modified_since == NGX_HTTP_IMS_EXACT
-115: || ims < r->headers_out.last_modified_time)
-116: {
-117: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-118: }
-119: }
-120:
-121: r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED;
-122: r->headers_out.status_line.len = 0;
-123: r->headers_out.content_type.len = 0;
-124: ngx_http_clear_content_length(r);
-125: ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(r);
-126: …
-132: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-133: }
-Nginx提供给用户一个配置选项
-if_modified_since off | exact | before
-如果是off,那么代码第102行if判断为真而进入到下一个过滤模块。代码第112行判断为真时,如果用户设置了精确匹配或者修改时间晚于请求头指定时间,这两种情况都表示不能直接返回 304 状态码,所以进入到下一个过滤模块,该怎么处理还是怎么处理。
-自代码第121行开始,表示可以返回304状态码(宏NGX_HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED)的情况,此时需清空响应体等,然后继续走下一个过滤模块。值得注意的是,这里不能像请求头If-Unmodified-Since判断失败那样,调用函数ngx_http_filter_finalize_request()直接返回。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-1-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-1-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a9d185ebe8211ad0c5f7d4ceb8acf924eff070f2 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-1-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,20 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) + { + if (r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_OK + || r != r->main + || r->headers_out.last_modified_time == -1) + { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } + + if (r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since) { + return ngx_http_test_precondition(r); + } + + if (r->headers_in.if_modified_since) { + return ngx_http_test_not_modified(r); + } + + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-2-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-2-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..01df59b2f9e4228cd9a225c3c49ba0326b636819 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-2-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_test_precondition(ngx_http_request_t *r) + { + time_t iums; + + iums = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since->value.data, + r->headers_in.if_unmodified_since-> value.len); + … + if (iums >= r->headers_out.last_modified_time) { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } + + return ngx_http_filter_finalize_request(r, NULL, + NGX_HTTP_PRECONDITION_FAILED); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-3-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-3-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d8d7e065105e0779e3159290e6851589df1a5181 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.1 ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.1.2-3-ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_test_not_modified(ngx_http_request_t *r) + { + … + clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); + + if (clcf->if_modified_since == NGX_HTTP_IMS_OFF) { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } + + ims = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.data, + r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.len); +… + if (ims != r->headers_out.last_modified_time) { + + if (clcf->if_modified_since == NGX_HTTP_IMS_EXACT + || ims < r->headers_out.last_modified_time) + { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } + } + + r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED; + r->headers_out.status_line.len = 0; + r->headers_out.content_type.len = 0; + ngx_http_clear_content_length(r); + ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(r); +… + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index c9423092241e63671128e6e672bad20c7588ba88..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,96 +0,0 @@ - -headers_filter模块实现对HTTP协议里缓存功能的扩展支持,而这涉及到两个响应头Expires[7]和Cache-Control[8]。Expires响应头的格式比较简单,示例如下。
-Expires: Sat, 07 Sep 2013 00:00:00 GMT
-这告诉客户端浏览器当前响应内容直到2013年9月7日才过期,因此允许客户端后续在这个时间之前,可以直接使用本地已缓存的这块响应内容而无需重新请求服务器。相比Expires而言,Cache-Control对缓存时间的控制更精准,它所对应的值也更多。
-cache-response-directive =
-"public" ; Section 14.9.1
-| "private" [ "=" <"> 1#field-name <"> ] ; Section 14.9.1
-| "no-cache" [ "=" <"> 1#field-name <"> ]; Section 14.9.1
-| "no-store" ; Section 14.9.2
-| "no-transform" ; Section 14.9.5
-| "must-revalidate" ; Section 14.9.4
-| "proxy-revalidate" ; Section 14.9.4
-| "max-age" "=" delta-seconds ; Section 14.9.3
-| "s-maxage" "=" delta-seconds ; Section 14.9.3
-| cache-extension ; Section 14.9.6
-限于篇幅,我们这里仅关注其中的两个值。no-cache表示禁止缓存,这在某些应用场合,比如利用Ajax动态请求获取数据时比较有用,禁止缓存可以让客户端每次都能正确获取到新的响应内容。max-age设置缓存的最长时间,比如
-Cache-Control: max-age=30
-表示当前响应内容将在30秒后才失效,也就是如果在这30秒内,客户端对同一资源进行访问,那么将直接使用本地缓存而无需重新访问服务器。Cache-Control的max-age和Expires响应头的功能一致,但如果这两者同时存在并且又不一致,那么一般的处理应该是以Cache-Control的max-age起主导作用,毕竟相比在HTTP 1.0[9]里就已存在的Expires响应头, Cache-Control属于更新的标准,即是在HTTP1.1里引入[10]的。
- -Nginx 对 HTTP 缓存功能的扩展在于它能让用户统一配置缓存的超时时间,而不管是Expires还是Cache-Control,Nginx提供给用户的都是通过配置指令expires,其使用有如下两种格式。
-expires epoch | max | off
-expires [ modified ] time
-第一种格式是很粗略的配置:epoch表示主动禁止缓存,也就是Expires响应头被设置为32位Unix纪元年的起点时间,即1970年1月1号,同时Cache-Control设置为no-cache;max表示最长时间缓存,Expires响应头被设置为32位Unix纪元年的终点时间,即2037年12月31号,同时Cache-Control设置为max-age=315360000,即此后10年;off表示不修改原本的缓存时间,即响应头里是如何就是如何,比如在Php文件里就可以通过header()函数设置Expires、Cache-Control响应头。
-第二种格式更为精确,modified 为可选参数,如果有此选项则表示基准时间为当前请求文件的最后修改时间,否则为当前请求处理时间,但这里有一处例外,如果时间以字符@开头,则是当天的绝对时间。来看这部分逻辑的代码。
-270: 代码片段12.2.1-1,文件名: ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c
-271: now = ngx_time();
-272:
-273: if (conf->expires == NGX_HTTP_EXPIRES_DAILY) {
-274: expires_time = ngx_next_time(conf->expires_time);
-275: max_age = expires_time - now;
-276:
-277: } else if (conf->expires == NGX_HTTP_EXPIRES_ACCESS
-278: || r->headers_out.last_modified_time == -1)
-279: {
-280: expires_time = now + conf->expires_time;
-281: max_age = conf->expires_time;
-282:
-283: } else {
-284: expires_time = r->headers_out.last_modified_time + conf->expires_time;
-285: max_age = expires_time - now;
-286: }
-代码第273~75行就是取当天绝对时间的情况,比如下面的配置。
-expires @12h00m00s;
-表示每天12点进行超时,比如今天13点对服务器某资源进行请求访问,那么获得的该资源到明天12点才过期。代码第274行的函数ngx_next_time()用于计算这个超时时间。
-代码第277~281行的基准时间为当前请求处理时间,也就是代码第271行的ngx_time()函数获得的当前时间。比如下面的配置。
-expires 12h;
-那么expires_time 的值就为now+43200,其中43200 也就是12小时的秒数。
-另外的情况是基准时间为当前请求文件的最后修改时间,也就是代码第284 行的r->headers_out.last_modified_time,比如下面的配置。
-expires modified 12h;
-时间还可以加上正/负修饰,当然,默认就是正,所以看负号修饰的情况。
-expires -12h;
-根据缓存的过期机制,这明显是强制不做缓存,所以在代码里的实现如下。
-289: 代码片段12.2.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c
-290: if (conf->expires_time < 0 || max_age < 0) {
-291: ngx_str_set(&cc->value, "no-cache");
-292: return NGX_OK;
-293: }
-将Cache-Control设置为no-cache。
- -headers_filter 模块提供的另外一个功能是可以让用户增加自定义响应头,配置语法简单如下。
-add_header name value
-通过这种方法配置的响应头都只是简单的加入,而不是修改,比如即便我做了这样的设置:
-add_header Server Apache/2;
-想伪装一下Nginx服务器,但是客户端获得的Server响应头的值却并非就是Apache/2,而是nginx/1.2.0,Apache/2。这部分实现在回调函数ngx_http_add_header()内,比较简单无需多说。
-但对于Last-Modified响应头是个例外,做如下配置。
-add_header Last-Modified "Sat, 01 Sep 2012 20:03:30 GMT";
-会修改Nginx原本(如果存在)的Last-Modified响应头,看其代码实现。
-366: 代码片段12.2.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c
-367: static ngx_int_t
-368: ngx_http_set_last_modified(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_header_val_t *hv,
-369: ngx_str_t *value)
-370: {
-371: …
-373: old = (ngx_table_elt_t **) ((char *) &r->headers_out + hv->offset);
-374: …
-377: if (*old == NULL) {
-378: …
-383: h = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_out.headers);
-384: …
-388: *old = h;
-389:
-390: } else {
-391: h = *old;
-392: …
-397: }
-398:
-399: h->hash = 1;
-400: h->key = hv->key;
-401: h->value = *value;
-402:
-403: return NGX_OK;
-404: }
-注意到变量old为二级指针,所以不管原本存在或不存在都会修改为指定的新value值。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..69613b28f93714e0541423990650f27456e24d6c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ + now = ngx_time(); + + if (conf->expires == NGX_HTTP_EXPIRES_DAILY) { + expires_time = ngx_next_time(conf->expires_time); + max_age = expires_time - now; + + } else if (conf->expires == NGX_HTTP_EXPIRES_ACCESS + || r->headers_out.last_modified_time == -1) + { + expires_time = now + conf->expires_time; + max_age = conf->expires_time; + + } else { + expires_time = r->headers_out.last_modified_time + conf->expires_time; + max_age = expires_time - now; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-2-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-2-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..161986befdd2a4cf30ed6d966d8d10a366790f72 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.1-2-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + if (conf->expires_time < 0 || max_age < 0) { + ngx_str_set(&cc->value, "no-cache"); + return NGX_OK; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.2-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.2-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a98be423d7a8d2c733f97246c9d7ac274f868e6e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.2 ngx_http_headers_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.2.2-1-ngx_http_headers_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,24 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_set_last_modified(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_header_val_t *hv, + ngx_str_t *value) +{ +… + old = (ngx_table_elt_t **) ((char *) &r->headers_out + hv->offset); +… + if (*old == NULL) { +… + h = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_out.headers); +… + *old = h; + + } else { + h = *old; +… + } + + h->hash = 1; + h->key = hv->key; + h->value = *value; + + return NGX_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 011ab9c2db6338c18b2dc9b5af205a5725b77bcd..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,63 +0,0 @@ - -gzip_filte模块用于对响应数据进行压缩,而除去gzip压缩方面的逻辑,gzip_filte模块本身是比较简单的,但是由于该模块既包含有头过滤链上的回调函数,又包含有体过滤链上的回调函数,所以来看下这两个回调函数之间是否有连动。当然,根据我们的猜想,肯定是有的,因为响应头和响应体需要一致。
-对于该模块,在头过滤链上的回调函数为ngx_http_gzip_header_filter(),主要是做一些检测工作,除去一看就懂的,下面重点关注几个地方。
-首先是gzip压缩所针对的内容类别(contenttype),在默认情况下,Nginx 仅压缩text/html内容,定义在全局变量ngx_http_html_default_types[0]内。可以通过配置指令gzip_types增加其他适用类型。
-gzip_types text/css text/xml text/plain;
-指定文本类型就好,对于图片、视频等已经是高压缩的文件再进行压缩,无非只是增加服务器的计算压力而已。
-236: 代码片段12.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c
-237: static ngx_int_t
-238: ngx_http_gzip_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-239: {
-240: …
-246: if (!conf->enable
-247: || (r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_OK
-248: && r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN
-249: && r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_NOT_FOUND)
-250: || (r->headers_out.content_encoding
-251: && r->headers_out.content_encoding->value.len)
-252: || (r->headers_out.content_length_n != -1
-253: && r->headers_out.content_length_n < conf->min_length)
-254: || ngx_http_test_content_type(r, &conf->types) == NULL
-255: || r->header_only)
-256: {
-257: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-258: }
-这有一大堆的判断,但都容易理解,其中代码第254行的函数ngx_http_test_content_type()调用就是判断响应内容是否是属于需要压缩的类别。
-接下来还有判断。
-273: 代码片段12.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c
-274: if (!r->gzip_tested) {
-275: if (ngx_http_gzip_ok(r) != NGX_OK) {
-276: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-277: }
-其主要是判断客户端是否支持解压缩,这在客户端发送请求时会根据自身情况附带对应的可接受的压缩数据类型,比如
-Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\n
-函数ngx_http_gzip_ok()判断出客户端支持gzip才会继续后面的动作,否则执行代码第276行进入到下一个头过滤模块。另外,函数ngx_http_gzip_ok()还有对代理请求的判断。
-经过层层验证后,已经允许对响应体进行压缩,所以开始准备工作。
-287: 代码片段12.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c
-288: ngx_http_set_ctx(r, ctx, ngx_http_gzip_filter_module);
-289: …
-301: ngx_str_set(&h->key, "Content-Encoding");
-302: ngx_str_set(&h->value, "gzip");
-303: …
-307: ngx_http_clear_content_length(r);
-308: ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(r);
-309:
-310: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-311: }
-重点记住代码第288行的设置,它将ctx保存起来,在响应体的处理里也就是通过它来判断是否要进行压缩。设置响应头、清空响应体长度等信息,进入下一个头过滤模块,这不多说。
-进入到体过滤回调函数后,首先做的就是判断是否要进行压缩处理。
-313: 代码片段12.3-4,文件名: ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c
-314: static ngx_int_t
-315: ngx_http_gzip_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
-316: {…
-317:
-321: ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_gzip_filter_module);
-322:
-323: if (ctx == NULL || ctx->done) {
-324: return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
-325: }
-63: 代码片段12.3-5,文件名: ngx_http.h
-64: #define ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, module) (r)->ctx[module.ctx_index]
-65: #define ngx_http_set_ctx(r, c, module) r->ctx[module.ctx_index] = c;
-代码片段12.3-3的第288行正是为此而设置,在其他模块中出现某个头过滤与某个体过滤一一匹配的情况也大多采用这种办法。另外,如果已经压缩过了,即变量ctx->done值为真,同样也将直接进入到下一个体过滤模块。如果需要对响应体做压缩,那么接下来就是利用zlib库里的函数进行处理,这部分代码略过不多讲。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-1-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-1-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bfadf345a463930ee5f016b8d48f3e1bceee774d --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-1-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_gzip_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (!conf->enable + || (r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_OK + && r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN + && r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_NOT_FOUND) + || (r->headers_out.content_encoding + && r->headers_out.content_encoding->value.len) + || (r->headers_out.content_length_n != -1 + && r->headers_out.content_length_n < conf->min_length) + || ngx_http_test_content_type(r, &conf->types) == NULL + || r->header_only) + { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-2-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-2-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..eca34170ff2dba615bb7e89baabf9a0514df17f5 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-2-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + if (!r->gzip_tested) { + if (ngx_http_gzip_ok(r) != NGX_OK) { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-3-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-3-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fa450232f5a42d1d2b394892aa5473e7e5001eed --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-3-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ + ngx_http_set_ctx(r, ctx, ngx_http_gzip_filter_module); +… + ngx_str_set(&h->key, "Content-Encoding"); + ngx_str_set(&h->value, "gzip"); +… + ngx_http_clear_content_length(r); + ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(r); + + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-4-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-4-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0a3d61319ee64f07d9127c90d99e72b2db9e4b65 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.3 ngx_http_gzip_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.3-4-ngx_http_gzip_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_gzip_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) +{… + + ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_gzip_filter_module); + + if (ctx == NULL || ctx->done) { + return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in); + } + #define ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, module) (r)->ctx[module.ctx_index] + #define ngx_http_set_ctx(r, c, module) r->ctx[module.ctx_index] = c; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index ed9157d300529821c7ff56a1b86161e0c71d51a6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,168 +0,0 @@ - -range_filter 被拆分为两个模块,仅仅只是因为它在头过滤链和体过滤链上的回调函数所在的相对位置不同,而过滤链上回调函数的位置又是通过模块的先后顺序来确定的。两个模块都实现在源文件 ngx_http_range_filter_module.c 内,分别为 ngx_http_range_header_filter_module与ngx_http_range_body_filter_module。
-搞清楚range_filter 相关两个模块的关键在于对分块请求(range requests)行为的理解,我们可以做如下实验来看看Nginx对分块请求的处理,这很简单,利用curl命令添加Range请求头即可。
-为了让测试结果可验证,在Nginx站点里有文件range.html,其内容如下(末尾有换行符未显示出来)。
-[root@localhost html]# cat range.html
-0123456789abcdef
-然后执行curl命令请求Nginx服务。
-[root@localhost html]# curl --header 'Range: bytes=1-3' -v http://127.0.0.1/range.html
-* About to connect() to 127.0.0.1 port 80 (#0)
-* Trying 127.0.0.1...connected
-* Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 80 (#0)
-> GET /range.html HTTP/1.1
-> User-Agent: curl/7.19.7 (i686-pc-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.12.7.0 zlib/1.2.3libidn/1.18 libssh2/1.2.2
-> Host: 127.0.0.1
-> Accept: */*
-> Range: bytes=1-3
->
-< HTTP/1.1 206 Partial Content
-< Server: nginx/1.2.0
-< Date: Fri, 05 Oct 2012 13:58:39 GMT
-< Content-Type: text/html
-< Content-Length: 3
-< Last-Modified: Fri, 05 Oct 2012 13:00:27 GMT
-< Connection: keep-alive
-< Content-Range: bytes 1-3/17
-<
-* Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intact
-* Closing connection #0
-123[root@localhost tmp]#
-可以看到Range请求的第1-3字节(字节序号从0开始),也就是文件range.html里的三个字符"123"被Nginx当作响应数据发回给客户端curl,由于后面没有换行符,所以终端的提示符[root@localhosttmp]#被直接跟在其后。
-上面显示的是single partformat 的情况,再看下mutlipartformat 的情形。
-[root@localhost tmp]# curl --header 'Range: bytes=0-1,-2' -v http://127.0.0.1/range.html
-* About to connect() to 127.0.0.1 port 80 (#0)
-* Trying 127.0.0.1...connected
-* Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 80 (#0)
-> GET /range.html HTTP/1.1
-> User-Agent: curl/7.19.7 (i686-pc-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.12.7.0 zlib/1.2.3libidn/1.18 libssh2/1.2.2
-> Host: 127.0.0.1
-> Accept: */*
-> Range: bytes=0-1,-2
->
-< HTTP/1.1 206 Partial Content
-< Server: nginx/1.2.0
-< Date: Fri, 05 Oct 2012 14:12:44 GMT
-< Content-Type: multipart/byteranges; boundary=00000000005
-< Content-Length: 171
-< Last-Modified: Fri, 05 Oct 2012 13:00:27 GMT
-< Connection: keep-alive
-<
---00000000005
-Content-Type: text/html
-Content-Range: bytes 0-1/17
-01
---00000000005
-Content-Type: text/html
-Content-Range: bytes 15-16/17
-f
---00000000005--
-* Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intact
-* Closing connection #0
-[root@localhost tmp]#
-这是2块数据,第一块内容为文件range.html的第0-1字节,也就是"01",第二块内容为文件range.html的倒数2 个字节,也就是"f\n"。在HTTP1.1 协议标准文档[11]里有对这种分块请求的具体描述,假设实体主体的总长度为10000字节,则利用Range请求部分数据的示例如下。
-Range: bytes=0-499 /* 第一个500字节,字节偏移是以0开始。*/
-Range: bytes=500-999 /* 第二个500字节。*/
-Range: bytes==-500 /* 最后500字节。*/
-Range: bytes=9500- /* 最后500字节的另一种表示方法。*/
-Range: bytes=0-0,-1 /* 仅仅第一个和最后一个字节。*/
-HTTP1.1 协议仅支持以bytes为单位[12]的请求块,所以在Nginx代码里设置的Accept-Ranges响应头也就为bytes。
-客户端可通过发送If-Range[13]请求头进行条件请求,这和前面介绍的If-Modified-Since请求头类似,同样是做一致性判断,可以通过比较实体标签(entitytag)或者实体最后修改时间,如果一致,那么Nginx返回请求指定的部分内容(此时状态码为 206),否则将返回全部内容(此时状态码为200)。
-有了上面介绍的这些基础知识,再来看代码就简单了,首先是头过滤链上回调函数ngx_http_range_header_filter()的实现。
-145: 代码片段12.4-1,文件名: ngx_http_range_filter_module.c
-146: static ngx_int_t
-147: ngx_http_range_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-148: {
-149: …
-153: if (r->http_version < NGX_HTTP_VERSION_10
-154: …
-157: || !r->allow_ranges)
-158: {
-159: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-160: }
-161: …
-164: if (clcf->max_ranges == 0) {
-165: return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
-166: }
-167:
-168: if (r->headers_in.range == NULL
-169: || r->headers_in.range->value.len < 7
-170: || ngx_strncasecmp(r->headers_in.range->value.data,
-171: (u_char *) "bytes=", 6)
-172: != 0)
-173: {
-174: goto next_filter;
-175: }
-一开始仍然是一些条件判断,注意代码第157行的allow_ranges变量,在前面的处理中,有些功能会执行ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges()宏设置allow_ranges变量为0,比如gzip功能[14]。
-变量 max_ranges 表示 Nginx 在一个请求里支持的最大分块数目,用户可通过配置指令max_ranges设置,如果设置为0,那么也就是禁止分块请求处理。默认情况下,变量max_ranges值非常大,为NGX_MAX_INT32_VALUE,即0x7fffffff。
-代码第168~174 行用于判断客户端是否在进行分块请求,并且分块请求的单位是否为bytes,如果不满足则goto跳到next_filter处,也就是要进入下一个过滤链继续处理。
-176: 代码片段12.4-2,文件名: ngx_http_range_filter_module.c
-177: if (r->headers_in.if_range && r->headers_out.last_modified_time != -1) {
-178:
-179: if_range = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_range->value.data,
-180: r->headers_in.if_range->value.len);
-181: …
-186: if (if_range != r->headers_out.last_modified_time) {
-187: goto next_filter;
-188: }
-189: }
-这是在做分块请求的条件请求判断,目前Nginx并不支持实体标签Etag,所以采用的是对最后修改时间进行比较。
-再接下来就是解析请求头里指定了哪些分块数据,函数ngx_http_range_parse()做这个工作。
-201: 代码片段12.4-3,文件名: ngx_http_range_filter_module.c
-202: switch (ngx_http_range_parse(r, ctx, clcf->max_ranges)) {
-203:
-204: case NGX_OK:
-205: ngx_http_set_ctx(r, ctx, ngx_http_range_body_filter_module);
-206:
-207: r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_PARTIAL_CONTENT;
-208: r->headers_out.status_line.len = 0;
-209:
-210: if (ctx->ranges.nelts == 1) {
-211: return ngx_http_range_singlepart_header(r, ctx);
-212: }
-213:
-214: return ngx_http_range_multipart_header(r, ctx);
-215:
-216: case NGX_HTTP_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE:
-217: return ngx_http_range_not_satisfiable(r);
-218:
-219: case NGX_ERROR:
-220: return NGX_ERROR;
-221:
-222: default: /* NGX_DECLINED */
-223: break;
-224: }
-解析成功的话,代码第205 行,在前面我们已经看到过这种情况,做这样的设置后,在对应的体过滤链上的回调函数就也会执行。设置状态码为 206 (即宏 NGX_HTTP_PARTIAL_CONTENT),并且根据客户端请求的分块数做不同的响应头设置,即“thesinglepartformat”与“the mutlipart format”,前面已经对它们做过演示了,这里不再赘述。
-体过滤链上的回调函数ngx_http_range_body_filter()如下。
-546: 代码片段12.4-3,文件名: ngx_http_range_filter_module.c
-547: static ngx_int_t
-548: ngx_http_range_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
-549: {
-550: …
-556: ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_range_body_filter_module);
-557:
-558: if (ctx == NULL) {
-559: return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
-560: }
-561:
-562: if (ctx->ranges.nelts == 1) {
-563: return ngx_http_range_singlepart_body(r, ctx, in);
-564: }
-565: …
-578: return ngx_http_range_multipart_body(r, ctx, in);
-579: }
-代码第556~559行,这与头过滤链上所做的设置一一对应。再接下来的代码是根据分块数切割不同的响应内容,这部分逻辑根据实例不难理解,也不多赘述。
-注 释
-[1].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:10.3.5 304 Not Modified。
-[2].后面描述也都以文件为例,而标准里有多种说法:resource资源、variant变量、entity实体等。
-[3].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt。
-[4].If-Range 结合If-Match等请求头也可以实现条件GET请求,具体请参考:http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt小节:9.3 GET。
-[5].有计划支持代理Etag:http://trac.nginx.org/nginx/ticket/101。
-[6].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:14.28 If-Unmodified-Since。
-[7].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:14.21Expires。
-[8].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:14.9Cache-Control,可以看到它也可作为请求头。
-[9].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1945.txt 小节:10.7Expires。
- -[11].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:14.35Range。
-[12].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:3.12Range Units。
-[13].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt 小节:14.27If-Range。
-[14].http://forum.nginx.org/read.php?2,209738,209738
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-1-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-1-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8bde8716d13bd46280d4ad31ceb13c870723cb89 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-1-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,23 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_range_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + if (r->http_version < NGX_HTTP_VERSION_10 +… + || !r->allow_ranges) + { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } +… + if (clcf->max_ranges == 0) { + return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r); + } + + if (r->headers_in.range == NULL + || r->headers_in.range->value.len < 7 + || ngx_strncasecmp(r->headers_in.range->value.data, + (u_char *) "bytes=", 6) + != 0) + { + goto next_filter; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-2-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-2-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a28b854082bf33f709df5db12a9f0b591a9dbeec --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-2-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ + if (r->headers_in.if_range && r->headers_out.last_modified_time != -1) { + + if_range = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_range->value.data, + r->headers_in.if_range->value.len); +… + if (if_range != r->headers_out.last_modified_time) { + goto next_filter; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-3-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-3-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..293eb783bfacf9aae4089af6574d59df43a05316 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/12.4 ngx_http_range_filter_module/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26512.4-3-ngx_http_range_filter_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_range_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) +{ +… + ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_range_body_filter_module); + + if (ctx == NULL) { + return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in); + } + + if (ctx->ranges.nelts == 1) { + return ngx_http_range_singlepart_body(r, ctx, in); + } +… + return ngx_http_range_multipart_body(r, ctx, in); +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index d2610c5160db7a1b422226392799e8793fff545b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25412\347\253\240 \350\277\207\346\273\244\346\250\241\345\235\227/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -关于过滤模块,我们已经在第6章 6.2 节看过其整体概要,而本章就将详细介绍几个有代表性的过滤模块的内部实现。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index d2ff37e1fff631a5ecb1da0074f76a747c88d93d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,35 +0,0 @@ - -如果不做任何多余的配置,那么Nginx默认是采用加权轮询策略,如果要采用IP哈希策略,那么必须在Nginx的配置文件里通过配置指令ip_hash明确指定(该配置项最好放在其他server指令等的前面,以便检查server的配置选项是否合理)。
-17: 代码片段13.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-18: upstream backend {
-19: ip_hash;
-20: server 127.0.0.1:8000;
-21: server 127.0.0.1:9000;
-22: }
-配置指令 ip_hash对应的回调处理函数为 ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash(),其实现如下。
-221: 代码片段13.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c
-222: static char *
-223: ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
-224: {
-225: …
-229: uscf->peer.init_upstream = ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash;
-230: …
-236: return NGX_CONF_OK;
-237: }
-当整个 http 配置块被 Nginx 解析完后,其会调用各个 http 模块对应的初始函数。对于模块ngx_http_upstream_module而言,对应的main配置初始函数为ngx_http_upstream_init_main_conf()。
-4649:代码片段13.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-4650:static char *
-4651:ngx_http_upstream_init_main_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *conf)
-4652:{
-4653:…
-4665: for (i = 0; i < umcf->upstreams.nelts; i++) {
-4666:
-4667: init = uscfp[i]->peer.init_upstream ? uscfp[i]->peer.init_upstream:
-4668: ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin;
-4669:
-4670: if (init(cf, uscfp[i]) != NGX_OK) {
-4671: return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
-4672: }
-4673: }
-默认是采用加权轮询策略的原因就在代码第4667~4668行。如果用户没有做任何策略选择,那么代码第4670行执行的策略初始函数为ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin(),也就是加权轮询策略。否则的话,执行的是 uscfp[i]->peer.init_upstream 指针函数,而如果有配置指令ip_hash,那么也就是函数ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash()。至此,通过执行不同的初始函数,在后续实际进行负载均衡时,所采取的策略也就不同了。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-1-nginx.conf.fastcgi" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-1-nginx.conf.fastcgi" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..529e7afec9ebbe65cb9b43bcca05741c15e18e67 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-1-nginx.conf.fastcgi" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + upstream backend { + ip_hash; + server 127.0.0.1:8000; + server 127.0.0.1:9000; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-2-ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-2-ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cb08fd738ebc93538a381bda62b6d71f0565a0ea --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-2-ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) +{ +… + uscf->peer.init_upstream = ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash; +… + return NGX_CONF_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ca7f2331f9fdbb4978a16cbafd7d80f978e1acb7 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.1 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241\347\255\226\347\225\245/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26513.1-3-ngx_http_upstream.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_upstream_init_main_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *conf) +{ +… + for (i = 0; i < umcf->upstreams.nelts; i++) { + + init = uscfp[i]->peer.init_upstream ? uscfp[i]->peer.init_upstream: + ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin; + + if (init(cf, uscfp[i]) != NGX_OK) { + return NGX_CONF_ERROR; + } + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.2 \345\212\240\346\235\203\350\275\256\350\257\242/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.2 \345\212\240\346\235\203\350\275\256\350\257\242/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 254a2e54ba497014f57ebbc9178196aeb078310a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/13.2 \345\212\240\346\235\203\350\275\256\350\257\242/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,214 +0,0 @@ - -加权轮询,直观上理解就是计算各个后端服务器的当前权值,然后选择得分最高的服务器处理当前请求,Nginx的处理大致如此,但是在具体实现时考虑很多其他细节,比如各个服务器可能具有不同的权重、某个服务器多次连接失败或处理出错后则在一定时间内不再参与被选择等。
- -使用加权轮询时,upstream上下文内server配置可带的参数有如下几个(ip_hash策略的参数也一起给出了),看下面的实例。
-17: 代码片段13.2.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-18: upstream backend {
-19: server backend1.example.com weight=5;
-20: server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
-21: server UNIX:/tmp/backend3 backup;
-22: # server 192.168.0.1:9000 down;
-23: }
-指定的server可以是域名、IP或UNIX域,它们代表不同的后端服务器,我们这里关心的是另外几个参数。
-1.weight:权重[4],默认值为1,与加权轮询策略配合使用。
-2.max_fails与fail_timeout:它们需配合使用,默认值分别为1和10s。具体含义是指,如果某台后端服务器在fail_timeout时间内发生了 max_fails次连接失败,那么该后端服务器在这 fail_timeout 时间内就不再参与被选择,直到 fail_timeout 时间后才重新加入而有机会被选择,其直白意思也就是请先休息一会,然后再来。
-3.backup:备机,平常不被选择,只有当其他所有非备机全部不可用(比如宕掉或繁忙)时才被使用。值得注意的是,backup选项不能用于ip_hash策略里[5],因为它会扰乱哈希的结果而违背ip_hash策略的初衷。
-4.down:即主动标识其为宕机状态,不参与被选择。
-需要注意,某些参数只能和某些策略配合使用,所以如果发现某参数没有生效,则应该检查一下这点。在配置解析的过程中,这些选项设置都被转换为 Nginx 内对应的变量值,对应的结构体如下。
-86: 代码片段13.2.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.h
-87: typedef struct {
-88: ngx_addr_t *addrs;
-89: ngx_uint_t naddrs;
-90: ngx_uint_t weight;
-91: ngx_uint_t max_fails;
-92: time_t fail_timeout;
-93:
-94: unsigned down:1;
-95: unsigned backup:1;
-96: } ngx_http_upstream_server_t;
-结构体的几个字段根据名称很容易理解,值得注意的是addrs地址事实上是个数组指针,这是因为一个域名可以对应多个IP地址,而数组的元素个数由字段naddrs指定。对于这里的域名解析,Nginx直接采用系统函数gethostbyname()阻塞获取,所以如果在Nginx的启动过程中发现卡住的情况,可以检查一下配置文件里是否有配置域名并且系统当前的DNS解析是否正常。
-在函数 ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin()内实现这部分相关逻辑,代码比较多,根据用户可能的配置分两种情况。
-第一种情况,用户使用类似于这样的配置。
-17: 代码片段13.2.1-3,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-18: upstream backend {
-19: server 127.0.0.1:9001 backup;
-20: server 127.0.0.1:9000 weight=5;
-21: server 127.0.0.1:8000 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
-22: server 127.0.0.1:7000 weight=3 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=10s;
-23: }
-24: …
-37: fastcgi_pass backend;
-为了方便说明,我这里全部用IP地址作为示例,如果配置有域名,因为在Nginx启动的过程中被解析成IP地址了,所以后续的处理也都与此类似。这种情况对应的逻辑在ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin()函数的前面。
-27: 代码片段13.2.1-4,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-28: ngx_int_t
-29: ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin(ngx_conf_t *cf,
-30: ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t *us)
-31: {
-32: …
-37: us->peer.init = ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin_peer;
-38:
-39: if (us->servers) {
-40: …
-148: return NGX_OK;
-149: }
-第二种情况,用户直接在 proxy_pass等指令后配置后端服务器地址,比如
-35: 代码片段13.2.1-5,文件名: nginx.conf.fastcgi
-36: fastcgi_pass localhost:9000;
-这种情况对应的处理逻辑在后面部分。不管哪种情况,函数ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin()所做的工作,除了把配置解析后的结果转存到对应的变量以外,主要还有以下几项。
-创建后端服务器列表,并且将非后备服务器与后备服务器分开进行各自单独的列表,每一个后端服务器用一个结构体 ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t 对应,列表最前面需带有一些 head信息,所以用 ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t 结构体对应。非后备服务器列表挂载在 us->peer.data字段下,而后备服务器列表挂载在非后备服务器列表head域里的next字段下。
-58: 代码片段13.2.1-6,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-59: peers = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t)
-60: +sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t) * (n - 1));
-61: …
-89: us->peer.data = peers;
-111: backup = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t)
-112: +sizeof(ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t) * (n - 1));
-113: …
-142: peers->next = backup;
-两个列表的服务器会按初始权重进行排序,高权重的在前面。另外,Nginx 会对(包括非后备服务器和后备服务器一共)只有一台后端服务器的情况做优化处理,即设置 peers->single字段为1,这样在后续针对客户端请求时就根本无需再做选择,只能直接用它如图13-2所示。
-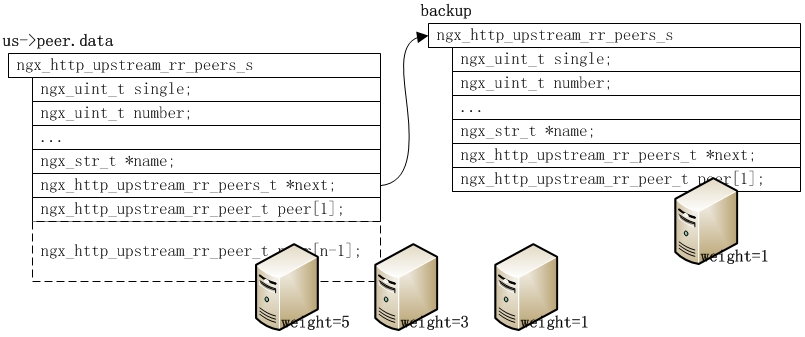 -
-全局初始准备工作做好以后,当一个客户端请求过来时,Nginx 就要选择合适的后端服务器来处理该请求。在正式开始选择前,Nginx还要单独为本轮选择(针对一个客户端请求, Nginx 会进行多次尝试选择,尝试全部失败才返回 502 错误,所以请注意一轮选择与一次选择的差别)做一些初始化,在代码片段13.2.1-4的第37行,我们能看到一句回调函数赋值语句,而这个回调函数在代码片段 11.3.1-1 的第639 行被执行,即在针对每个请求选择后端服务器前被调用。看下该函数的代码。
-217: 代码片段13.2.2-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-218: ngx_int_t
-219: ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin_peer(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-220: ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t *us)
-221: {
-222: …
-236: rrp->peers = us->peer.data;
-237: rrp->current = 0;
-238: …
-258: r->upstream->peer.get = ngx_http_upstream_get_round_robin_peer;
-259: r->upstream->peer.free = ngx_http_upstream_free_round_robin_peer;
-260: r->upstream->peer.tries = rrp->peers->number;
-261: …
-268: return NGX_OK;
-269: }
-设置回调函数是重点,另外中间还有一段代码未列出来,它建立一个 rrp->tried 位图来标识在一轮选择中,各个后端服务器是否已经被选择过。举个例子,假设有3台后端服务器,来了一个客户端请求,因此Nginx要针对该请求进行一轮选择,第一次选了第1台服务器,结果后续连接失败,因此需进行第二次选择,此时就不能再选择第1台服务器,因为它已经被选择并尝试过了,所以只能选择第2台或第3台服务器。这个位图只是针对本轮选择,也就是如果又来了一个客户端请求,那么针对它的一轮选择所对应的 rrp->tried 位图又是全新的。如果后端服务器个数(因为要同时让非后备服务器与后备服务器两个列表都能使用,所以取两个列表中个数较大的那个值)少于一个指针类型变量可以表示的范围(32位系统也就是32台),那么直接使用已有的指针类型的data变量做位图即可,否则使用ngx_pcalloc()函数申请对应的内存空间。
-对后端服务器进行一次选择的逻辑实现在ngx_http_upstream_get_round_robin_peer()函数内,该函数前面的last_cached相关代码是未实现的陈旧代码[6],当前并没有使用而不用管它。我们来看核心部分的执行流程(没有画出全部失败的情况),如图13-3所示。
-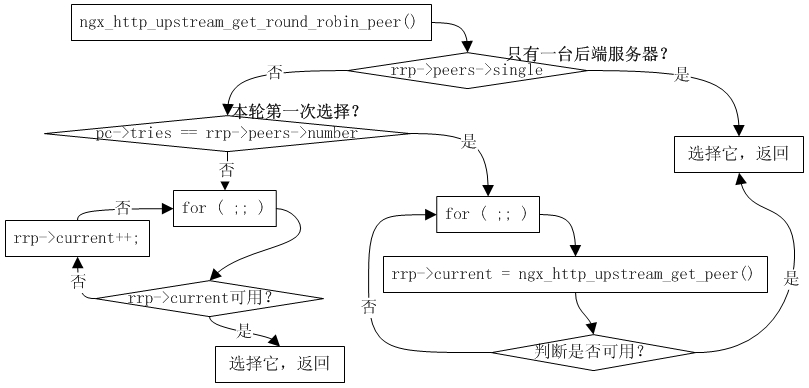 -
-对于只有一台后端服务器的情况,Nginx 直接选择它并返回。如果有多台后端服务器,对于第一次选择,Nginx会循环调用函数ngx_http_upstream_get_peer()按照各台服务器的当前权值进行选择。如果第一次选择的服务器因连接失败或其他情况导致需重新选择另外一台服务器,此时Nginx采用的是简单的遍历,起始节点为rrp->current,但这个值会在对第一次选择结果进行释放时自增 1,即起始节点和第一次选择节点并没有重复。为什么第二次及后续重选不再根据当前权值,原因暂不得而知,但我个人猜想其基于的大致原因是:首先,如果第二次仍按权值选择,那么函数ngx_http_upstream_get_peer()很有可能还会得到和第一次一样的结果;其次,既然第一次按权值选择的服务器连接失败,那么说明根据当前权值进行估算最优服务器的策略不稳定,所以干脆直接遍历也许反而会来得更简单有效。
-判断是否可用的方法主要是前面提到的那么几点,直接看代码很容易理解。
-442: 代码片段13.2.2-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-443: if (!(rrp->tried[n] & m)) {
-444: peer = &rrp->peers->peer[rrp->current];
-445:
-446: if (!peer->down) {
-447:
-448: if (peer->max_fails == 0
-449: || peer->fails < peer->max_fails)
-450: {
-451: break;
-452: }
-453:
-454: if (now - peer->checked > peer->fail_timeout) {
-455: peer->checked = now;
-456: break;
-457: }
-458:
-459: peer->current_weight = 0;
-460:
-461: } else {
-462: rrp->tried[n] |= m;
-463: }
-位图标记已尝试过的就不要再选择了;当前处于宕机状态的服务器也被排除;再有就是根据指定的一段时间内的最大失败次数做判断,这些无需多说。代码第459 行表示当前服务器要处于休息状态,所以设置其当前权重为0。
-如果有服务器被成功选择,那么将更新其权值并且修改已选择位图。
-534: 代码片段13.2.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-535: peer->current_weight--;
-536: …
-537: rrp->tried[n] |= m;
-图13-3没有给出对非后备服务器全部选择failed失败的情况,如果出现这种情况,此时将开始尝试后备服务器,这同样是对一个服务器列表进行选择,所以处理的情况和对非后备服务器进行选择的逻辑一致,只是把相关变量进行一下切换。
-如果后备服务器也选择失败,那么此时函数ngx_http_upstream_get_round_robin_peer()将返回NGX_BUSY,这意味着当前没有后端服务器来处理该请求,Nginx将获得 502 错误的状态码,此时Nginx可以直接将这个错误发送给客户端,或者对它做其他替换处理,以返回给客户端更优雅的响应(即这里[7]提到的fallback处理)。
- -假设有3台后端服务器A、B、C,它们的初始权值分别为5、3、1,在不考虑其他参数的影响下,那么当第一个客户端请求过来时,将被谁处理呢?按理论应该是服务器 A,但是Nginx并非如此,具体如何需看其对应函数ngx_http_upstream_get_peer()的内部逻辑。其核心是一个比较语句。
-597: 代码片段13.2.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-598: static ngx_uint_t
-599: ngx_http_upstream_get_peer(ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t *peers)
-600: {
-601: ...
-624: if (peer[n].current_weight * 1000 / peer[i].current_weight
-625: > peer[n].weight * 1000 / peer[i].weight)
-626: {
-627: return n;
-628: }
-629: …
-644: for (i = 0; i < peers->number; i++) {
-645: peer[i].current_weight = peer[i].weight;
-646: }
-在初始情况下,由于 peer[n].current_weight 等于 peer[n].weight 并且 peer[i].current_weight等于 peer[i].weight,所以实际的结果是,针对第一个客户端请求,Nginx 选择了服务器 C。不过,随着后续 current_weight 权重的改变,各个服务器的权值会发生变化,客户端的请求也就按5:3:1的分布形式分配到服务器A、B、C,并且相对较为空闲的服务器会有更多机被选中。代码第624行乘以1000是避免浮点处理,所以直接把被除数放大1000倍,也就是间接地把精度提升到小数点后三位,注意到这里是做权值比较,因此把两边权值都放大 1000 倍并不会影响到最终的比较结果。当所有权值全都小于等于0时,对它们进行重置,从而才能让客户端请求在整体上根据用户设定的服务器权重在各个服务器上按对应比例分布,代码在第644~646行。
- -连接后端服务器并且正常处理当前客户端请求后需释放后端服务器,如果是这种情况,那么所做的工作相对较少,而另外需要进行释放后端服务器操作的地方是在某一轮选择里,某次选择的服务器因连接失败或请求处理失败而需要重新进行选择,此时就需要做一些额外的处理,看下面的代码。
-650: 代码片段13.2.4-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c
-651: void
-652: ngx_http_upstream_free_round_robin_peer(ngx_peer_connection_t *pc, void *data,
-653: ngx_uint_t state)
-654: {
-655: …
-676: if (state & NGX_PEER_FAILED) {
-677: …
-681: peer->fails++;
-682: peer->accessed = now;
-683: peer->checked = now;
-684:
-685: if (peer->max_fails) {
-686: peer->current_weight -= peer->weight / peer->max_fails;
-687: }
-688: …
-699: } else {
-700:
-701: /* mark peer live if check passed */
-702:
-703: if (peer->accessed < peer->checked) {
-704: peer->fails = 0;
-705: }
-706: }
-707:
-708: rrp->current++;
-709:
-710: if (rrp->current >= rrp->peers->number) {
-711: rrp->current = 0;
-712: }
-713:
-714: if (pc->tries) {
-715: pc->tries--;
-716: }
-717:
-718: /* ngx_unlock_mutex(rrp->peers->mutex); */
-719: }
-如果是失败(不管是连接失败还是请求处理失败)的情况,此时需更新fails等变量;如果成功,那么需要判断一个fail_timeout时间段已过,才能重置fails变量,如果不这样做,那么将导致两个可能的错误,即要么当前fail_timeout时间段内的失败次数统计错误,要么把当前fail_timeout时间段内的失败次数错误的累加到下一个fail_timeout时间段。
-默认情况下,在一轮选择里,如果是连接错误或连接超时导致的失败,那么 Nginx 会尽量尝试每一台后端服务器进行请求处理,直到全部失败为止才返回 502 错误。当然,Nginx提供给用户有对应的配置选项来做修改,比如proxy_next_upstream或fastcgi_next_upstream,像下面这样的配置。
-fastcgi_next_upstream http_404;
-使得Nginx仅在上一台后端服务器返回404错误的情况下,才会尝试重新选择,否则直接返回对应的错误,或500或502等。这部分控制逻辑实现在函数ngx_http_upstream_next()内,注意代码第2883行的后半句判断。
-2813:代码片段13.2.4-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream.c
-2814:static void
-2815:ngx_http_upstream_next(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u,
-2816: ngx_uint_t ft_type)
-2817:{
-2818:…
-2883: if (u->peer.tries == 0 || !(u->conf->next_upstream & ft_type)) {
-2884:…
-2904: ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, status);
-2905: return;
-2906: }
-最后,看下整个加权轮询的大体流程图,如图13-4所示。
-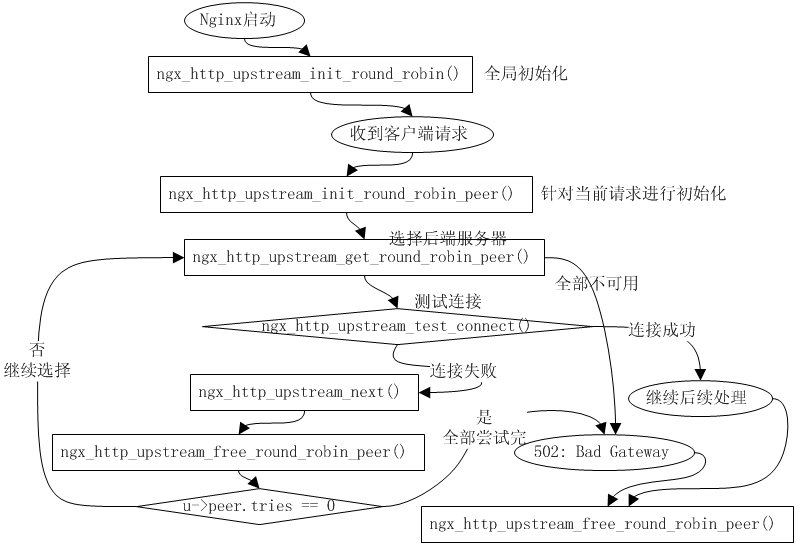 -
-根据IP哈希值来获取对应的后端服务器,这很好理解,Nginx-1.2.0仅支持IPv4,但在后续版本[8]已经支持对IPv6的哈希计算。
-有了前面对加权轮询的认识基础以及整个负载均衡的整体理解,对IP哈希策略就可以只关注几个地方了。加权轮询是 Nginx 负载均衡的基础策略,所以一些初始化的工作,比如配置值转存等,其他策略可以直接复用它,比如这里的代码第82行。
-78: 代码片段13.3-1,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c
-79: ngx_int_t
-80: ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t *us)
-81: {
-82: if (ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin(cf, us) != NGX_OK) {
-83: return NGX_ERROR;
-84: }
-85:
-86: us->peer.init = ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash_peer;
-87:
-88: return NGX_OK;
-89: }
-代码第86 行,修改了针对单个请求进行初始化的回调函数指针,这样当一个客户端请求过来时,Nginx将调用函数ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash_peer()做初始化。
- -客户端请求过来后,执行函数ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash_peer()进行初始化,它调用了加权轮询策略的初始函数ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin_peer()。之所以这样做是因为在多次哈希选择失败后,Nginx会将选择策略退化[9]为加权轮询。针对IP哈希所做的初始化工作主要是将对应的客户端IP转存出来。
-91: 代码片段13.3-2,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c
-92: static ngx_int_t
-93: ngx_http_upstream_init_ip_hash_peer(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-94: ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t *us)
-95: {
-96: …
-107: if (ngx_http_upstream_init_round_robin_peer(r, us) != NGX_OK) {
-108: return NGX_ERROR;
-109: }
-110:
-111: r->upstream->peer.get = ngx_http_upstream_get_ip_hash_peer;
-112:
-113: /* AF_INET only */
-114:
-115: if (r->connection->sockaddr->sa_family == AF_INET) {
-116:
-117: sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) r->connection->sockaddr;
-118: p = (u_char *) &sin->sin_addr.s_addr;
-119: iphp->addr[0] = p[0];
-120: iphp->addr[1] = p[1];
-121: iphp->addr[2] = p[2];
-122:
-123: } else {
-124: iphp->addr[0] = 0;
-125: iphp->addr[1] = 0;
-126: iphp->addr[2] = 0;
-127: }
-128:
-129: iphp->hash = 89;
-130: iphp->tries = 0;
-131: iphp->get_rr_peer = ngx_http_upstream_get_round_robin_peer;
-132:
-133: return NGX_OK;
-134: }
-注意几个回调指针的设置,比如r->upstream->peer.get与iphp->get_rr_peer。另外,从代码第119~121行可以看到转存的IPv4只保存了前3个字节的数据,这是因为后面在进行具体的哈希计算时只会用到3个字节。非AF_INET类协议族,比如AF_INET6就全部取0,这将导致后续的哈希值总是同一个。
-具体的选择就简单了,看下函数ngx_http_upstream_get_ip_hash_peer()实现。
-136: 代码片段13.3-3,文件名: ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c
-137: static ngx_int_t
-138: ngx_http_upstream_get_ip_hash_peer(ngx_peer_connection_t *pc, void *data)
-139: {
-140: …
-152: if (iphp->tries > 20 || iphp->rrp.peers->single) {
-153: return iphp->get_rr_peer(pc, &iphp->rrp);
-154: }
-155: …
-161: hash = iphp->hash;
-162:
-163: for ( ;; ) {
-164:
-165: for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
-166: hash = (hash * 113 + iphp->addr[i]) % 6271;
-167: }
-168:
-169: p = hash % iphp->rrp.peers->number;
-170:
-171: n = p / (8 * sizeof(uintptr_t));
-172: m = (uintptr_t) 1 << p % (8 * sizeof(uintptr_t));
-173:
-174: if (!(iphp->rrp.tried[n] & m)) {
-175: …
-200: }
-201:
-202: if (++iphp->tries >= 20) {
-203: return iphp->get_rr_peer(pc, &iphp->rrp);
-204: }
-205: }
-206: …
-209: pc->sockaddr = peer->sockaddr;
-210: pc->socklen = peer->socklen;
-211: pc->name = &peer->name;
-212: …
-218: return NGX_OK;
-219: }
-代码第152、202行,也就是哈希选择失败20以上或只有一台后端服务器,此时采用加权轮询策略。代码第165~167行,计算哈希值,这很简单,不过可以看到采用了通常的哈希规则,即相关数值,比如3、89、113、6271都是质数,这样能让哈希结果更散列。代码第169行,根据哈希值得到被选中的后端服务器,判断其是否可用,如果可用那么 break 跳出执行代码第209行等。否则,再在上次哈希结果hash的基础上再哈希,如此反复。整个过程的流程如图13-5所示。
-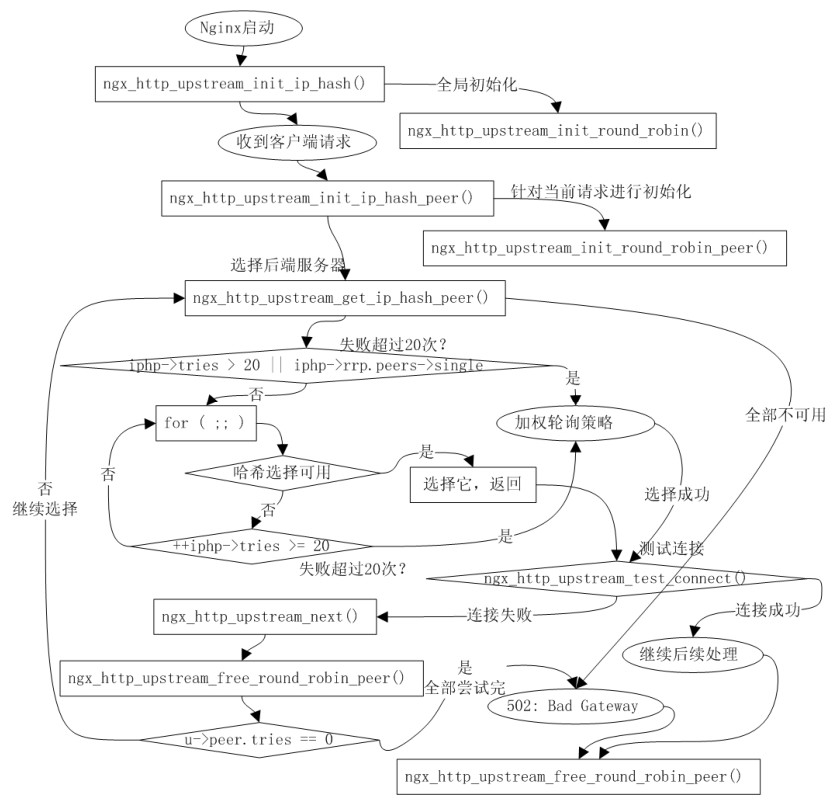 -
-显而易见,加权轮询策略的适用性更强,它不依赖于客户端的任何信息,而完全依靠后端服务器的情况来进行选择,优势就是能把客户端请求更合理更均匀地分配到各个后端服务器处理,但其劣势也很明显,同一个客户端的多次请求可能会被分配到不同的后端服务器进行处理,所以无法满足做会话保持的应用的需求。
-与此相对,IP哈希策略能较好地把同一个客户端的多次请求分配到同一台后端服务器处理,所以避免了加权轮询策略无法适用会话保持的需求。但是,因为IP哈希策略是根据客户端的IP地址来对后端服务器做选择,所以如果某个时刻,来自某个IP地址的请求特别多(比如大量用户通过同一个NAT代理发起请求),那么将导致某台后端服务器的压力可能非常大,而其他后端服务器却还很空闲的不均衡情况。
-注 释
-[1].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpUpstreamFairModule。
-[2].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpUpstreamConsistentHash。
-[3].http://wiki.nginx.org/3rdPartyModules。
-[4].权重与权值,在名词概念上意义相同,但为了方便说明,这里刻意称不变的初始设定权值为权重。
-[5].需要ip_hash 与backup共同使用的变通办法配置:http://forum.nginx.org/read.php?2,211408,211410。
-[6].http://forum.nginx.org/read.php?2,230366,230370。
-[7].http://forum.nginx.org/read.php?2,211408,211410
-[8].http://mailman.nginx.org/pipermail/nginx-devel/2012-June/002360.html。
-[9].并不是说ipIP 哈希策略比加权轮询策略好,但因为加权轮询策略是最基础的,所以暂用退化一词。
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 29dba9ec6c0976d8eb0d088a1f150a9ccc36a424..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25413\347\253\240 \350\264\237\350\275\275\345\235\207\350\241\241/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,11 +0,0 @@ -本章介绍的负载均衡与前面第7章7.4节的负载均衡内容完全不同,7.4节针对的是客户端请求在多个 Nginx 进程之间的均衡,而这里介绍的是客户端请求在多个后端服务器之间的均衡。它们各自不同的作用点如图13-1所示。
-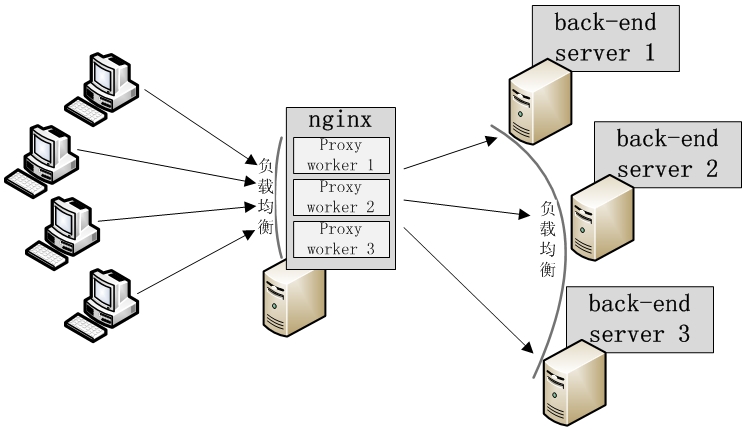 -
-Nginx 根据每个工作进程的当前压力调整它们获取监听套接口的机率,那些当前比较空闲的工作进程有更多机会获取到监听套接口,从而当客户端的请求到达后也就相应地被它捕获并处理。这就是第7章7.4节所描述的负载均衡。如果Nginx是以反向代理的形式配置运行,那么对请求的实际处理需转发到后端服务器进行,如果后端服务器有多台,如何选择一台合适的后端服务器来处理当前请求,也就是本节将介绍的内容,即通常所说的负载均衡。可以看到,这两种负载均衡不相互冲突而且能同时生效。
-负载均衡,顾名思义,是指将负载尽量均衡的分摊到多个不同的服务单元(比如这里的后端服务器),以保证服务的可用性和可靠性,提供给客户更好的用户体验。负载均衡的直接目标只有一个,即尽量发挥多个服务单元的整体效能,实现1+1等于2,甚至大于2的结果。要实现这个目标,也就要有好的选路策略,这也是负载均衡的重点。Nginx提供了较多的负载均衡策略,包括加权轮询、IP哈希、fair[1]、一致哈希[2]等。前两个是Nginx官方源码内置的策略,而后面几个都是第三方模块[3],所以下面我们重点来看前两个内置策略的具体实现。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index f1a833873ec29d8e08dd50632bf4665969d94d19..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,100 +0,0 @@ - -发现当前某用户在Web站点上进行恶意操作,比如对博客文章频繁发送垃圾评论,在论坛恶意灌水等,那么一种较为迅速的处理办法就是禁止他继续访问,这可通过模块ngx_http_access_module的deny[1]指令实现。
-17: 代码片段14.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: location / {
-19: root html;
-20: index index.html index.htm;
-21: deny 192.168.10.1;
-22: }
-以如上配置启动或重启Nginx让配置生效后,IP地址为192.168.10.1的客户端再访问站点根目录时就会收到 403 Forbidden 的错误信息。当然,这里只是一个测试,192.168.10.1 是局域网IP,不会用在正常的公网客户端上。可以把deny指令放在server上下文,从而对整个当前站点进行控制。
-下面来看其具体的实现,deny指令对应的回调解析函数为ngx_http_access_rule(),把配置的单个IP地址或CIDR[2]格式的IP段或关键词all(即表示所有)正确解析出来后存放在alcf->rules数组字段里。一个数组元素也就是一条规则,以ngx_http_access_rule_t结构体表示。如下配置所对应的规则如图14-1所示。
-17: 代码片段14.1-2,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: location / {
-19: root html;
-20: index index.html index.htm;
-21: deny 192.168.1.1;
-22: allow 192.168.1.0/24;
-23: allow 10.1.0.0/16;
-24: deny all;
-25: }
- -
-字段deny很好理解,1表示此规则为拒绝;0表示此规则为允许,显示的mask和addr为子网掩码和网络地址所对应[3]的 10 进制无符号表示。为什么有了deny all,还需要其他的,因为Nginx在执行规则匹配时是从上往下进行的,并且在匹配成功后就不再往下继续匹配,所以对于 192.168.1.2 的客户端将匹配到第二条规则,此时是允许访问的,而对于192.168.1.1的客户端将匹配到第一条规则,也就是禁止访问。
-看下面的实际代码。
-243: 代码片段14.1-2,文件名: ngx_http_access_module.c
-244: static char *
-245: ngx_http_access_rule(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
-246: {
-247: …
-262: all = (value[1].len == 3 && ngx_strcmp(value[1].data, "all") == 0);
-263:
-264: if (!all) {
-265:
-266: rc = ngx_ptocidr(&value[1], &cidr);
-267: …
-278: }
-279:
-280: switch (cidr.family) {
-281: …
-325: rule->mask = cidr.u.in.mask;
-326: rule->addr = cidr.u.in.addr;
-327: rule->deny = (value[0].data[0] == 'd') ? 1 : 0;
-328: }
-329:
-330: return NGX_CONF_OK;
-331: }
-代码第262 行,针对当前条目,先判断用户是否配置的 all,不是这种情况才有必要继续进行IP地址解析,也就是代码第266行的ngx_ptocidr()函数。最后把最终解析得到的规则保存起来,以便后续使用,所有这些配置条目形成最终判断客户端是否可访问的准入规则,这也就实现在函数 ngx_http_access_handler()内。该函数挂载在请求处理 11 阶段中的NGX_ HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE 阶段上,关于这在第6章已经讲述过,这里直接看函数的内部逻辑。
-106: 代码片段14.1-3,文件名: ngx_http_access_module.c
-107: static ngx_int_t
-108: ngx_http_access_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-109: {
-110: …
-118: alcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_access_module);
-119:
-120: switch (r->connection->sockaddr->sa_family) {
-121:
-122: case AF_INET:
-123: if (alcf->rules) {
-124: sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) r->connection->sockaddr;
-125: return ngx_http_access_inet(r, alcf, sin->sin_addr.s_addr);
-126: }
-127: break;
-128: …
-150: return NGX_DECLINED;
-151: }
-IPv6的处理类似,所以看IPv4的处理即可。代码第123行,判断出当前location下有准入规则才需做进一步的处理,否则返回NGX_DECLINED表示当前回调未做任何干涉处理,后续执行流程该怎么走继续怎么走。只有在有准入规则的情况下,执行并返回代码第125 行所示的函数ngx_http_access_inet()的结果。
-153: 代码片段14.1-4,文件名: ngx_http_access_module.c
-154: static ngx_int_t
-155: ngx_http_access_inet(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_access_loc_conf_t *alcf,
-156: in_addr_t addr)
-157: {
-158: …
-161: rule = alcf->rules->elts;
-162: for (i = 0; i < alcf->rules->nelts; i++) {
-163: …
-168: if ((addr & rule[i].mask) == rule[i].addr) {
-169: return ngx_http_access_found(r, rule[i].deny);
-170: }
-171: }
-172:
-173: return NGX_DECLINED;
-174: }
-175:
-224: static ngx_int_t
-225: ngx_http_access_found(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_uint_t deny)
-226: {
-227: ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
-228:
-229: if (deny) {
-230: …
-237: return NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN;
-238: }
-239:
-240: return NGX_OK;
-241: }
-根据每一条准入规则进行匹配,匹配成功后调用ngx_http_access_found()并且返回其执行结果,即不再继续往下匹配。如果当前匹配上的规则是拒绝,那么函数ngx_http_access_found()返回NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN;否则返回NGX_OK。根据这个返回值,在Nginx的请求处理状态机里就会做出相应的判断,也就是函数ngx_http_core_access_phase(),这在第6章6.1节提到过,这里不再赘述。把所有代码前后连贯起来,对禁止指定IP访问的整个流程也就理清楚了。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a8077d56743b810049dd8460718af7cde71397a9 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ + location / { + root html; + index index.html index.htm; + deny 192.168.10.1; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d40f9403aa00aa31725e3f75902c760d2a3cb118 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ + location / { + root html; + index index.html index.htm; + deny 192.168.1.1; + allow 192.168.1.0/24; + allow 10.1.0.0/16; + deny all; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-ngx_http_access_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-ngx_http_access_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bad24c6d36f9529bdb3a7850cdf96d681c07131c --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-2-ngx_http_access_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ +static char * +ngx_http_access_rule(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) +{ +… + all = (value[1].len == 3 && ngx_strcmp(value[1].data, "all") == 0); + + if (!all) { + + rc = ngx_ptocidr(&value[1], &cidr); +… + } + + switch (cidr.family) { +… + rule->mask = cidr.u.in.mask; + rule->addr = cidr.u.in.addr; + rule->deny = (value[0].data[0] == 'd') ? 1 : 0; + } + + return NGX_CONF_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-3-ngx_http_access_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-3-ngx_http_access_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f881f66aed963bda883cb8e690329254d0c659c8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-3-ngx_http_access_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_access_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + alcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_access_module); + + switch (r->connection->sockaddr->sa_family) { + + case AF_INET: + if (alcf->rules) { + sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) r->connection->sockaddr; + return ngx_http_access_inet(r, alcf, sin->sin_addr.s_addr); + } + break; +… + return NGX_DECLINED; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-4-ngx_http_access_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-4-ngx_http_access_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cf44aa6a80673bf79766937b4777364872a43f2f --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.1 \347\246\201\346\255\242\346\214\207\345\256\232IP \350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.1-4-ngx_http_access_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_access_inet(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_access_loc_conf_t *alcf, + in_addr_t addr) +{ +… + rule = alcf->rules->elts; + for (i = 0; i < alcf->rules->nelts; i++) { +… + if ((addr & rule[i].mask) == rule[i].addr) { + return ngx_http_access_found(r, rule[i].deny); + } + } + + return NGX_DECLINED; +} + +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_access_found(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_uint_t deny) +{ + ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf; + + if (deny) { +… + return NGX_HTTP_FORBIDDEN; + } + + return NGX_OK; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 9dad8df6e7e6257480173f20e8a79b12daaf95f5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,166 +0,0 @@ - -Nginx通过模块ngx_http_auth_basic_module提供对客户端进行密码认证访问的功能,该模块默认被加入编译,因此我们只要修改一下配置文件即可使用该功能。
-模块ngx_http_auth_basic_module使用的是HTTP协议的WWW-Authenticate[4]响应头来实现密码认证,在RFC 2617[5]文档里有对这方面的详细介绍,这里就不再从文字上去描述它的认证过程,我们直接根据Nginx的具体实例来进行理解。
-首先,需准备一个账号密码文件,Nginx默认使用的是以函数crypt()加密后的字符串,但在nginx-1.0.3 版本后也支持其他加密格式后的字符串,比如$apr1、SSHA,甚至是未加密的PLAIN明文,这里以默认情况为例。用命令htpasswd[6]生成如下面的文件实例(我在新密码提示符下输入的密码为1)。
-[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c /etc/ngx_passwd gqk
-New password:
-Re-type new password:
-Adding password for user gqk
-[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/ngx_passwd
-gqk:sPg7dCVzKivDI
-生成加密字符串的 crypt()函数的申明如下。
-char *crypt(const char *key, const char *salt);
-其中参数key为待加密字符串(即明文密码),参数salt为两个字符组成的字符串,用于决定crypt()函数推演演算过程的起点(类似于伪随机时的种子值),选择的salt不同,即起点不同,那么生成的加密后字符串也不相同。salt值会被包含在最终的加密后字符串内,比如上面得到的字符串"sPg7dCVzKivDI"的前两个字符"sP"即为本次生成加密密码时的salt值。另外,对于 key 字符串长度大于 8 的情况,crypt()函数只取前 8 个字符,也就是以"12345678"和"123456789"进行演算,得到的加密结果是一样的。
-每次执行htpasswd时随机选择的salt值不同,所以生成的加密字符串也不相同,但因为它会被包含在加密后字符串内(即前两个字符),所以在后续使用该密码时才能据此对用户输入的明文密码进行同样的推演演算并做出正确的对错判断。除了使用 htpasswd 命令生成对应的密码字符串以外,还可以借助其他命令来生成,只要同样是使用 crypt()函数即可。
-[root@localhost ~]# php -r "print(crypt('1','sP').\"\n\");"
-sPg7dCVzKivDI
-[root@localhost ~]# perl -e "print crypt('1','sP').\"\n\"";
-sPg7dCVzKivDI
-[root@localhost ~]# python -c 'import crypt; print crypt.crypt("1","sP")'
-sPg7dCVzKivDI
-[root@localhost ~]# php -r "print(crypt('123456789abcde','sP').\"\n\");"
-sPbmzdDmWzqfc
-[root@localhost ~]# php -r "print(crypt('12345678','sP').\"\n\");"
-sPbmzdDmWzqfc
-[root@localhost ~]# php -r "print(crypt('1234567','sP').\"\n\");"
-sPVtN55SHLeBs
-还有其他脚本语言,比如ruby、lua等都可以被利用来生成对应的加密字符串,使用的明文密码一样并且选择的 salt 值也一样,那么生成的加密字符串也就一样。注意,在上面示例命令中,密码会被以明文的形式记录在操作系统的命令历史里,所以如果这样生成加密字符串的话,需记得清空命令历史记录,以免密码泄露。
-Nginx 的账号密码文件格式为一行一个账号,如果有多个账号,那么就是多行,每一行的格式为(pass部分可能包含除了密码以外的字符,具体在后面会看到)
-user:pass
-可带comment注释信息:
-user2:pass2:comment
-修改Nginx配置如下。
-17: 代码片段14.2-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: location / {
-19: root html;
-20: index index.html index.htm;
-21: auth_basic Auth;
-22: auth_basic_user_file /etc/ngx_passwd;
-23: }
-auth_basic 指令后面的字符串为客户端弹窗时的提示字符;auth_basic_user_file 指令指定账号密码文件的路径,不要把这个文件放在 Web 站点下;否则很有可能会被客户端请求访问到。
-正常启动Nginx后,通过Firefox请求Web站点将得到如图14-2所示那样的认证提示。此时输入正确的账号,即gqk/1,那么将正常访问到首页,否则浏览器将继续弹出窗口提示输入账号,直到(Nginx 没有做会话记录,所以无法进行登录验证的次数限制)用户点取消按钮时,浏览器才显示401提示信息,如图14-3所示。
-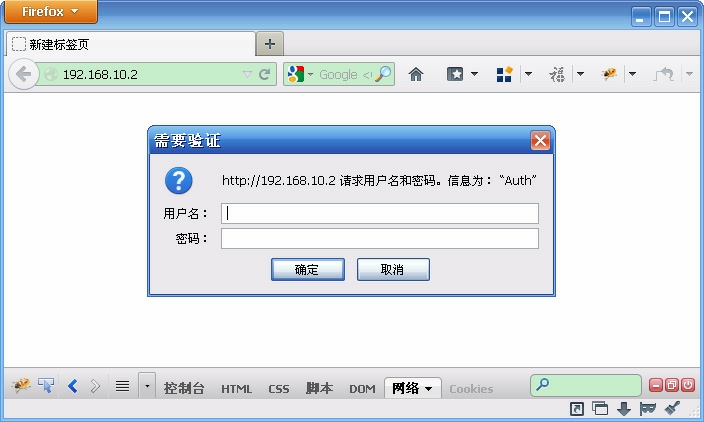 -
- -
-通过Firefox和Wireshark对整个过程进行抓包,结果如表14-1所示(仅列出重要的相关头部信息)。
- -
-如果每次都输入出错,那么第二次的步骤会一直循环进行,当输入正确(也就是上面第三次情况)时,Nginx 响应状态码 200 并且返回对应请求资源的内容。下面就根据这个流程来看Nginx代码的具体实现。
-模块 ngx_http_auth_basic_module 的回调函数为 ngx_http_auth_basic_handler(),也就是Nginx在处理客户端请求时,执行到NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE阶段就将执行该函数进行认证判断。如果Nginx用户使用auth_basic和auth_basic_user_file指令做了认证配置,那么就会继续处理,否则就直接返回NGX_DECLINED了。
-97: 代码片段14.2-2,文件名: ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c
-98: static ngx_int_t
-99: ngx_http_auth_basic_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-100: {
-101: …
-118: alcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_auth_basic_module);
-119:
-120: if (alcf->realm.len == 0 || alcf->user_file.value.len == 0) {
-121: return NGX_DECLINED;
-122: }
-其中两个变量 realm与 user_file 就是对应配置指令设置的字符串值。接下来要进行认证判断,首先就要获取客户端的输入并进行解码,在前面实例已经看到,客户端的输入是通过请求头Authorization进行传输的,所以实现这部分逻辑的函数ngx_http_auth_basic_user()也就是处理这个请求头。
-2000:代码片段14.2-3,文件名: ngx_http_core_module.c
-2001:ngx_http_auth_basic_user(ngx_http_request_t *r)
-2002:{
-2003: ngx_str_t auth, encoded;
-2004: ngx_uint_t len;
-2005:
-2006: if (r->headers_in.user.len == 0 && r->headers_in.user.data != NULL) {
-2007: return NGX_DECLINED;
-2008: }
-2009:
-2010: if (r->headers_in.authorization == NULL) {
-2011: r->headers_in.user.data = (u_char *) "";
-2012: return NGX_DECLINED;
-2013: }
-在客户端进行第一次请求时,肯定是不带Authorization请求头的,所以此时就走上面的逻辑,返回的 NGX_DECLINED 值到函数 ngx_http_auth_basic_handler()内就会设置响应头WWW-Authenticate并返回NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED。看下面的代码。
-130: 代码片段14.2-4,文件名: ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c
-131: rc = ngx_http_auth_basic_user(r);
-132:
-133: if (rc == NGX_DECLINED) {
-134: …
-139: return ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(r, &alcf->realm);
-140: }
-141: …
-344: static ngx_int_t
-345: ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_str_t *realm)
-346: {
-347: r->headers_out.www_authenticate = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_out.headers);
-348: …
-352: r->headers_out.www_authenticate->hash = 1;
-353: ngx_str_set(&r->headers_out.www_authenticate->key, "WWW-Authenticate");
-354: r->headers_out.www_authenticate->value = *realm;
-355:
-356: return NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED;
-357: }
-设置的设置响应头 WWW-Authenticate 发送给客户端,客户端浏览器解析后,从而对最终用户进行弹窗提示,此时相关的 401 响应体也会被发送到客户端,但是由于客户端浏览器(比如 IE、Firefox 等)进行模态弹窗进行了阻塞,所以响应体信息没有显示出来,但如果用wget–debug请求查看是可以确认有收到的,前面的列表也给出了这个结论。
-上面介绍的就是第一次请求流程,再来看第二次,假定此次最终用户输入了不正确的账号(以用户名正确但密码错误为例),这个账号信息经编码后通过Authorization请求头提交到Nginx。同样还是走函数 ngx_http_auth_basic_user()进行解码,并把结果分别存放到变量r->headers_in.user与r->headers_in.passwd内。
-(gdb) p r->headers_in.user
-$3 = {len = 3, data = 0x8bbe7e2 "gqk:2"}
-(gdb) p r->headers_in.passwd
-$4 = {len = 1, data = 0x8bbe7e6 "2"}
-所以,当回到函数 ngx_http_auth_basic_handler()后,剩下的工作就是将它与用户指定的账号密码文件里的各个账号进行逐个匹配。通过函数 ngx_http_complex_value()获得正确的账号密码文件的路径,这是为了支持用户指定路径时使用了 Nginx 变量的情况。使用ngx_open_file()函数打开文件以及相关处理,这无需多说。其他主要逻辑就是读取文件内容后进行匹配。根据文件内容的格式,采用了一个超简单的状态机,一般情况是先用户名,然后冒号后是秘密,如果此行还有冒号,那后面就是注释信息。另外,可以看到其还支持直接以#井号开头的注释。
-因为用户名是明文,所以在解析账号的过程中就逐个字符匹配了,如果账号一致,然后又把密码解析出来了,那么就调用函数ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler()进行密码匹配。整个这个过程不复杂,毕竟状态一共也就 3 个,但在最后有一处额外的判断需提示一下,这是处理当整个文件末尾不是回车或换行符的情况,也就是不能漏了最后一行的账号。
-265: 代码片段14.2-5,文件名: ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c
-266: if (state == sw_passwd) {
-267: …
-274: return ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler(r, NULL, &pwd, &alcf->realm);
-275: }
-函数 ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler()的主要处理在前面,即调用函数 ngx_crypt(), nginx-1.2.0已支持较多形式的加密密码,从该函数可以看出。
-32: 代码片段14.2-6,文件名: ngx_crypt.c
-33: ngx_int_t
-34: ngx_crypt(ngx_pool_t *pool, u_char *key, u_char *salt, u_char **encrypted)
-35: {
-36: if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "$apr1$", sizeof("$apr1$") - 1) == 0) {
-37: return ngx_crypt_apr1(pool, key, salt, encrypted);
-38:
-39: } else if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "{PLAIN}", sizeof("{PLAIN}") - 1) == 0) {
-40: return ngx_crypt_plain(pool, key, salt, encrypted);
-41:
-42: #if (NGX_HAVE_SHA1)
-43: } else if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "{SSHA}", sizeof("{SSHA}") - 1) == 0) {
-44: return ngx_crypt_ssha(pool, key, salt, encrypted);
-45: #endif
-46: }
-47:
-48: /* fallback to libc crypt() */
-49:
-50: return ngx_libc_crypt(pool, key, salt, encrypted);
-51: }
-使用哪种加密形式的密码是通过账号密码文件里密码的前面几个字符来判断的,并且各个账号可以有不同的加密形式(这也是为什么 Nginx 要先对客户端发过来的密码做解密,然后在这里又做加密的原因之一),比如我要再添加一个使用PLAIN明文密码的账号:lenky/9,那么我的账号密码文件的内容应该是像下面这样。
-[root@localhost html]# cat /etc/ngx_passwd
-gqk:sPg7dCVzKivDI
-lenky:{PLAIN}9
-注意第二行,它就表示账号 lenky/9,当最终用户输入 lenky/9 账号时,匹配流程将执行到代码第39~40行,而其他几种加密方法也是类似,当然,默认就是以函数crypt()为加密方式,这从代码可以看出来。
-函数 ngx_crypt()只是把用户输入的密码根据账号密码文件里指定的加密方式进行加密,得到对应的加密后字符串,真正的比较在函数ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler()内。
-284: 代码片段14.2-7,文件名: ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c
-285: static ngx_int_t
-286: ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r,
-287: ngx_http_auth_basic_ctx_t *ctx, ngx_str_t *passwd, ngx_str_t *realm)
-288: {
-289: …
-292: rc = ngx_crypt(r->pool, r->headers_in.passwd.data, passwd->data,
-293: &encrypted);
-294: …
-299: if (rc == NGX_OK) {
-300: if (ngx_strcmp(encrypted, passwd->data) == 0) {
-301: return NGX_OK;
-302: }
-303: …
-311: return ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(r, realm);
-312: }
-正常得到对应的加密后字符串,于是执行 ngx_strcmp()函数进行比较,一致返回NGX_OK,否则执行到函数ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm()内设置响应头WWW-Authenticate并返回NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED。
-整个过程描述完了,但是遗留了一个问题。通过前面的介绍,我们看到在阶段NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE上可以有多个访问控制措施,如何组合它们需一定的策略,据此Nginx提供了一个satisfy[7]的配置指令。如果其设置为all,则表示只有当所有控制条件都判断为可访问时才让客户端访问;如果其设置为any ,则表示有一个通过即可。这部分逻辑在函数ngx_http_core_access_phase()内,看一下也就明白了。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..197a0d4c7c0e045aacc794181aab90d3054366a2 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ + location / { + root html; + index index.html index.htm; + auth_basic Auth; + auth_basic_user_file /etc/ngx_passwd; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-2-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-2-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7065b441fb27949673ff695c3acc41e4301f886e --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-2-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ + static ngx_int_t + ngx_http_auth_basic_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ +… + alcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_auth_basic_module); + + if (alcf->realm.len == 0 || alcf->user_file.value.len == 0) { + return NGX_DECLINED; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e34c01aba9f0c0c99bd8e0dbeda56caeff4cdf30 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-3-ngx_http_core_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +ngx_http_auth_basic_user(ngx_http_request_t *r) +{ + ngx_str_t auth, encoded; + ngx_uint_t len; + + if (r->headers_in.user.len == 0 && r->headers_in.user.data != NULL) { + return NGX_DECLINED; + } + + if (r->headers_in.authorization == NULL) { + r->headers_in.user.data = (u_char *) ""; + return NGX_DECLINED; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-4-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-4-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..240752808106cce290479de902b076e982099779 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-4-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ + rc = ngx_http_auth_basic_user(r); + + if (rc == NGX_DECLINED) { +… + return ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(r, &alcf->realm); + } +… +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_str_t *realm) +{ + r->headers_out.www_authenticate = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_out.headers); +… + r->headers_out.www_authenticate->hash = 1; + ngx_str_set(&r->headers_out.www_authenticate->key, "WWW-Authenticate"); + r->headers_out.www_authenticate->value = *realm; + + return NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED; +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-5-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-5-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..369dfb9ffb71caf8e3040ab92e7f39dc0bac5b06 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-5-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + if (state == sw_passwd) { +… + return ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler(r, NULL, &pwd, &alcf->realm); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-6-ngx_crypt.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-6-ngx_crypt.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d355dabbc26a5a4fe777bdf065870ff266a83990 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-6-ngx_crypt.c" @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ + ngx_int_t + ngx_crypt(ngx_pool_t *pool, u_char *key, u_char *salt, u_char **encrypted) + { + if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "$apr1$", sizeof("$apr1$") - 1) == 0) { + return ngx_crypt_apr1(pool, key, salt, encrypted); + + } else if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "{PLAIN}", sizeof("{PLAIN}") - 1) == 0) { + return ngx_crypt_plain(pool, key, salt, encrypted); + + #if (NGX_HAVE_SHA1) + } else if (ngx_strncmp(salt, "{SSHA}", sizeof("{SSHA}") - 1) == 0) { + return ngx_crypt_ssha(pool, key, salt, encrypted); + #endif + } + + /* fallback to libc crypt() */ + + return ngx_libc_crypt(pool, key, salt, encrypted); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-7-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-7-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9a3ff1053dcd92cceb3188b403a789e465b254d0 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.2 \345\257\206\347\240\201\350\256\244\350\257\201\350\256\277\351\227\256/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.2-7-ngx_http_auth_basic_module.c" @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +static ngx_int_t +ngx_http_auth_basic_crypt_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r, + ngx_http_auth_basic_ctx_t *ctx, ngx_str_t *passwd, ngx_str_t *realm) +{ +… + rc = ngx_crypt(r->pool, r->headers_in.passwd.data, passwd->data, + &encrypted); +… + if (rc == NGX_OK) { + if (ngx_strcmp(encrypted, passwd->data) == 0) { + return NGX_OK; + } +… + return ngx_http_auth_basic_set_realm(r, realm); + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 16b788ff4f4bde36b2b173324c69cad5e583b533..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,33 +0,0 @@ - -还有一些对客户端进行访问控制的其他措施,它们主要是对Nginx现有功能的组合使用,如果我们掌握了前面章节介绍的内容,那么对于这些措施是很好理解的。下面从文字描述上逐一来分析下。
- -实现这个访问控制措施的可能Nginx配置如下。
-17: 代码片段14.3.1-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: server {
-19: listen 80 default;
-20: return 500;
-21: }
-这是一个超简单的server配置,因此它用到了很多默认配置,比如location(这在第5章5.5 节配置信息的继承有介绍)。虽然超简单,但是它却有两个重要的配置:第一,default 选项表示这个server是80 端口上的默认server;第二,return500;表示任何使用这个server配置的请求将会获得服务器内部错误的响应。
-当一个客户端请求通过80端口过来时,Nginx处理该请求首先做的事情就是把它定位到某个server配置(这在第10章10.3节Server的定位有介绍),而定位server配置是通过Host请求头进行的,当客户端通过服务器IP地址或其他Nginx里未配置的域名(假定这个域名是某用户恶意绑定的)来访问Nginx时,Nginx将查找不到对应的server配置,所以将使用上面代码片段14.3.1-1里指定的这个server配置,因为它是默认server,从而客户端获得500的错误。而如果客户端通过正常的域名访问 Nginx,那么请求将被定位到其他 server 配置,因此Nginx对请求的处理与响应也就是通常的情况,该怎么样就怎么样。
- -如下实例同样是利用了请求定位和其他功能的结合,只是此处是做location的定位。
-17: 代码片段14.3.2-1,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: location /private/ {
-19: return 404;
-20: }
-如果客户端访问了此私有目录,那么对应的 Location 将被定位过来,从而获得 404 的错误。
-17: 代码片段14.3.2-2,文件名: nginx.conf
-18: location /private/ {
-19: deny all;
-20: }
-以上配置将返回403错误。
-注 释
-[1].http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_access_module.html#deny。
-[2].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIDR
- -[4].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt 小节:3.2.1 The WWW-Authenticate Response Header。
-[5].http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt。
-[6].https://httpd.apache.org/docs/current/programs/htpasswd.html。
-[7].http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#satisfy。
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.1-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.1-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..379a77634419cdf0274579e13c85dd992f390a24 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.1-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ + server { + listen 80 default; + return 500; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-1-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-1-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d77fee90c039add7507951ccdd0401d3956f20e3 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-1-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + location /private/ { + return 404; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-2-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-2-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4c4e4727e3e9e8dfcc34ef3185c43c6f4decacdc --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/14.3 \345\205\266\344\273\226\350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266\346\216\252\346\226\275/\344\273\243\347\240\201\347\211\207\346\256\26514.3.2-2-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ + location /private/ { + deny all; + } \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 3acf3960d332f3833e81583ca4ec85d4ab80ad8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\347\254\25414\347\253\240 \350\256\277\351\227\256\346\216\247\345\210\266/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -与 Web 服务相关的另一个主题就是访问控制,这可能是受权限要求,比如禁止某些 IP地址访问或仅提供给通过密码认证的用户进行访问等。还可能是为了防止错误或恶意的客户端请求,比如禁止用户直接通过服务器IP地址进行访问、禁止对某个目录或某类文件的访问,等等,本章就来描述Nginx对这些功能的支持。
- diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/-objs-ngx_modules.c" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/-objs-ngx_modules.c" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dc05959902d73fb294c4833c164880efb68b5234 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/-objs-ngx_modules.c" @@ -0,0 +1,100 @@ + +#include +#include + + + +extern ngx_module_t ngx_core_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_errlog_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_conf_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_events_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_event_core_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_epoll_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_regex_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_core_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_log_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_static_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_autoindex_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_index_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_auth_basic_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_access_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_limit_conn_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_limit_req_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_geo_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_map_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_split_clients_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_referer_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_rewrite_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_proxy_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_fastcgi_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_uwsgi_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_scgi_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_memcached_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_empty_gif_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_browser_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_write_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_header_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_chunked_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_range_header_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_gzip_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_postpone_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_ssi_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_charset_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_userid_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_headers_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_copy_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_range_body_filter_module; +extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module; + +ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = { + &ngx_core_module, + &ngx_errlog_module, + &ngx_conf_module, + &ngx_events_module, + &ngx_event_core_module, + &ngx_epoll_module, + &ngx_regex_module, + &ngx_http_module, + &ngx_http_core_module, + &ngx_http_log_module, + &ngx_http_upstream_module, + &ngx_http_static_module, + &ngx_http_autoindex_module, + &ngx_http_index_module, + &ngx_http_auth_basic_module, + &ngx_http_access_module, + &ngx_http_limit_conn_module, + &ngx_http_limit_req_module, + &ngx_http_geo_module, + &ngx_http_map_module, + &ngx_http_split_clients_module, + &ngx_http_referer_module, + &ngx_http_rewrite_module, + &ngx_http_proxy_module, + &ngx_http_fastcgi_module, + &ngx_http_uwsgi_module, + &ngx_http_scgi_module, + &ngx_http_memcached_module, + &ngx_http_empty_gif_module, + &ngx_http_browser_module, + &ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module, + &ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module, + &ngx_http_write_filter_module, + &ngx_http_header_filter_module, + &ngx_http_chunked_filter_module, + &ngx_http_range_header_filter_module, + &ngx_http_gzip_filter_module, + &ngx_http_postpone_filter_module, + &ngx_http_ssi_filter_module, + &ngx_http_charset_filter_module, + &ngx_http_userid_filter_module, + &ngx_http_headers_filter_module, + &ngx_http_copy_filter_module, + &ngx_http_range_body_filter_module, + &ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module, + NULL +}; \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index 89a6579480c6daebb3c1db059e909fc9cb29de57..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225A/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,104 +0,0 @@ -下面给出的是在默认configure下,会被编译到Nginx可执行文件里的各个模块,因此,对于某些默认未加入编译的模块,必须在 configure 时主动指定,比如要加入 ngx_http_addition_module,则需执行:./configure --with-http_addition_module。关于这些具体帮助可以通过执行:./configure --help 查看。
-00: 文件名: objs/ngx_modules.c
-01:
-02: #include
03: #include
04:
-05:
-06:
-07: extern ngx_module_t ngx_core_module;
-08: extern ngx_module_t ngx_errlog_module;
-09: extern ngx_module_t ngx_conf_module;
-10: extern ngx_module_t ngx_events_module;
-11: extern ngx_module_t ngx_event_core_module;
-12: extern ngx_module_t ngx_epoll_module;
-13: extern ngx_module_t ngx_regex_module;
-14: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_module;
-15: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_core_module;
-16: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_log_module;
-17: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_module;
-18: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_static_module;
-19: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_autoindex_module;
-20: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_index_module;
-21: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_auth_basic_module;
-22: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_access_module;
-23: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_limit_conn_module;
-24: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_limit_req_module;
-25: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_geo_module;
-26: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_map_module;
-27: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_split_clients_module;
-28: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_referer_module;
-29: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_rewrite_module;
-30: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_proxy_module;
-31: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_fastcgi_module;
-32: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_uwsgi_module;
-33: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_scgi_module;
-34: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_memcached_module;
-35: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_empty_gif_module;
-36: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_browser_module;
-37: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module;
-38: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module;
-39: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_write_filter_module;
-40: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_header_filter_module;
-41: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_chunked_filter_module;
-42: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_range_header_filter_module;
-43: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_gzip_filter_module;
-44: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_postpone_filter_module;
-45: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_ssi_filter_module;
-46: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_charset_filter_module;
-47: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_userid_filter_module;
-48: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_headers_filter_module;
-49: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_copy_filter_module;
-50: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_range_body_filter_module;
-51: extern ngx_module_t ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module;
-52:
-53: ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = {
-54: &ngx_core_module,
-55: &ngx_errlog_module,
-56: &ngx_conf_module,
-57: &ngx_events_module,
-58: &ngx_event_core_module,
-59: &ngx_epoll_module,
-60: &ngx_regex_module,
-61: &ngx_http_module,
-62: &ngx_http_core_module,
-63: &ngx_http_log_module,
-64: &ngx_http_upstream_module,
-65: &ngx_http_static_module,
-66: &ngx_http_autoindex_module,
-67: &ngx_http_index_module,
-68: &ngx_http_auth_basic_module,
-69: &ngx_http_access_module,
-70: &ngx_http_limit_conn_module,
-71: &ngx_http_limit_req_module,
-72: &ngx_http_geo_module,
-73: &ngx_http_map_module,
-74: &ngx_http_split_clients_module,
-75: &ngx_http_referer_module,
-76: &ngx_http_rewrite_module,
-77: &ngx_http_proxy_module,
-78: &ngx_http_fastcgi_module,
-79: &ngx_http_uwsgi_module,
-80: &ngx_http_scgi_module,
-81: &ngx_http_memcached_module,
-82: &ngx_http_empty_gif_module,
-83: &ngx_http_browser_module,
-84: &ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module,
-85: &ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module,
-86: &ngx_http_write_filter_module,
-87: &ngx_http_header_filter_module,
-88: &ngx_http_chunked_filter_module,
-89: &ngx_http_range_header_filter_module,
-90: &ngx_http_gzip_filter_module,
-91: &ngx_http_postpone_filter_module,
-92: &ngx_http_ssi_filter_module,
-93: &ngx_http_charset_filter_module,
-94: &ngx_http_userid_filter_module,
-95: &ngx_http_headers_filter_module,
-96: &ngx_http_copy_filter_module,
-97: &ngx_http_range_body_filter_module,
-98: &ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module,
-99: NULL
-100:};
-101:
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/-nginx.conf" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/-nginx.conf" new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..478c94fe0dcc192b05b31705208ac5fbbcaee0d8 --- /dev/null +++ "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/-nginx.conf" @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ + +worker_processes 1; + +events { + worker_connections 1024; +} + +http { + include mime.types; + default_type application/octet-stream; + + sendfile on; + keepalive_timeout 65; + + server { + listen 80; + server_name localhost; + + location / { + root html; + index index.html index.htm; + } + + error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; + location = /50x.html { + root html; + } + } + +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index becb673308875555fa7569223db2028edf04b4d2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225B/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,34 +0,0 @@ -这里给出的是讨论本书时所默认使用的 Nginx 运行配置,以便读者能进行对照或做问题复现。
-00: 文件名: nginx.conf
-01:
-02: worker_processes 1;
-03:
-04: events {
-05: worker_connections 1024;
-06: }
-07:
-08: http {
-09: include mime.types;
-10: default_type application/octet-stream;
-11:
-12: sendfile on;
-13: keepalive_timeout 65;
-14:
-15: server {
-16: listen 80;
-17: server_name localhost;
-18:
-19: location / {
-20: root html;
-21: index index.html index.htm;
-22: }
-23:
-24: error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
-25: location = /50x.html {
-26: root html;
-27: }
-28: }
-29:
-30: }
-31:
\ No newline at end of file diff --git "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225C/text.html" "b/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225C/text.html" deleted file mode 100644 index a60bf400815d6a3646dd0c5fc67232dea80d58c1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --- "a/data/\346\267\261\345\205\245\345\211\226\346\236\220Nginx/\351\231\204\345\275\225C/text.html" +++ /dev/null @@ -1,14 +0,0 @@ -对于HTTP协议而言,最基本的是各个状态码的含义,下表给出一个HTTP状态码简单介绍的列表,以方便读者查阅。
- -
- -
-\d{1,5}\:.*? \n).*?)', + r'(?:(?:
\d{1,5}\:.*? \n).*?)*', section_content, flags=re.S) - print(html_save_path) - print(code_list) - print(len(code_list)) + + res_codelist = [] + for code in code_list: + if code != '': + res_codelist.append(code) + # print(res_codelist) # break + count = 0 + for code in res_codelist: + code = html.unescape(code) + soup = BeautifulSoup(code) + clean_code = soup.get_text() + print(clean_code) - # res_code_list = [] - # count = 0 - # for i in code_list: - # if len(i.split('\n')) < 2: - # continue - # count += 1 - # i = html.unescape(i) - # soup = BeautifulSoup(i) - # res_str = soup.get_text() + print('-------' * 10) + pianduan_name = re.findall(r'(代码片段.*),', clean_code) + if pianduan_name == []: + pianduan_name_str = '' + else: + pianduan_name_str = pianduan_name[0] + file_name_list = re.findall(r'文件名: (.*)\n', clean_code) + print(file_name_list) + if file_name_list == []: + file_name = '.txt' + else: + file_name = file_name_list[0] + file_name = file_name.replace('/', '-') + save_file_name = pianduan_name_str + '-' + file_name + # print(save_file_name) - # if idx == 0: - # code_save_dir = os.path.join( - # chapter_dir, 'code_0.java') - # else: - # code_save_dir = os.path.join( - # section_dir_list[idx - 1], - # 'code_{}.java'.format(count)) + if idx == 0: + code_save_path = os.path.join( + chapter_dir, save_file_name) + else: + count += 1 + code_save_path = os.path.join( + section_dir_list[idx - 1], save_file_name) + + res_code_list = [] + for line in clean_code.split('\n'): + if line.find('文件名') != -1 or line.find( + '代码片段') != -1 or line == '': + continue + clean_line = re.findall(r'^\d{1,5}\: *(.*)', + line)[0] + res_code_list.append(clean_line) + res_code = '\n'.join(res_code_list) - # print(code_save_dir) - # print(res_str) - # with open(code_save_dir, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: - # f.write(res_str) + with open(code_save_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: + f.write(res_code) # clean_text_list = [] # for line in res_str.split('\n'):