---
title: '二分查找高效判定子序列'
tags: ['二分查找', '字符串', '子序列']
---




**通知:[数据结构精品课](https://aep.h5.xeknow.com/s/1XJHEO) 已更新到 V2.1,[手把手刷二叉树系列课程](https://aep.xet.tech/s/3YGcq3) 上线。[第 18 期每日打卡](https://aep.xet.tech/s/2PLO1n) 开始报名。反馈或修正 chatGPT 翻译的多语言代码 [点击这里](https://github.com/labuladong/fucking-algorithm/issues/1113)。另外,建议你在我的 [网站](https://labuladong.github.io/algo/) 学习文章,体验更好。**
读完本文,你不仅学会了算法套路,还可以顺便解决如下题目:
| LeetCode | 力扣 | 难度 |
| :----: | :----: | :----: |
| [392. Is Subsequence](https://leetcode.com/problems/is-subsequence/) | [392. 判断子序列](https://leetcode.cn/problems/is-subsequence/) | 🟢
| [792. Number of Matching Subsequences](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-matching-subsequences/) | [792. 匹配子序列的单词数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-matching-subsequences/) | 🟠
**-----------**
二分查找本身不难理解,难在巧妙地运用二分查找技巧。
对于一个问题,你可能都很难想到它跟二分查找有关,比如前文 [最长递增子序列](https://labuladong.github.io/article/fname.html?fname=动态规划设计:最长递增子序列) 就借助一个纸牌游戏衍生出二分查找解法。
今天再讲一道巧用二分查找的算法问题,力扣第 392 题「判断子序列」:
请你判定字符串 `s` 是否是字符串 `t` 的子序列(可以假定 `s` 长度比较小,且 `t` 的长度非常大)。
举两个例子:
```
s = "abc", t = "**a**h**b**gd**c**", return true.
s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc", return false.
```
题目很容易理解,而且看起来很简单,但很难想到这个问题跟二分查找有关吧?
### 一、问题分析
首先,一个很简单的解法是这样的:
```java
boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length() && j < t.length()) {
if (s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(j)) {
i++;
}
j++;
}
return i == s.length();
}
```
其思路也非常简单,利用双指针 `i, j` 分别指向 `s, t`,一边前进一边匹配子序列:
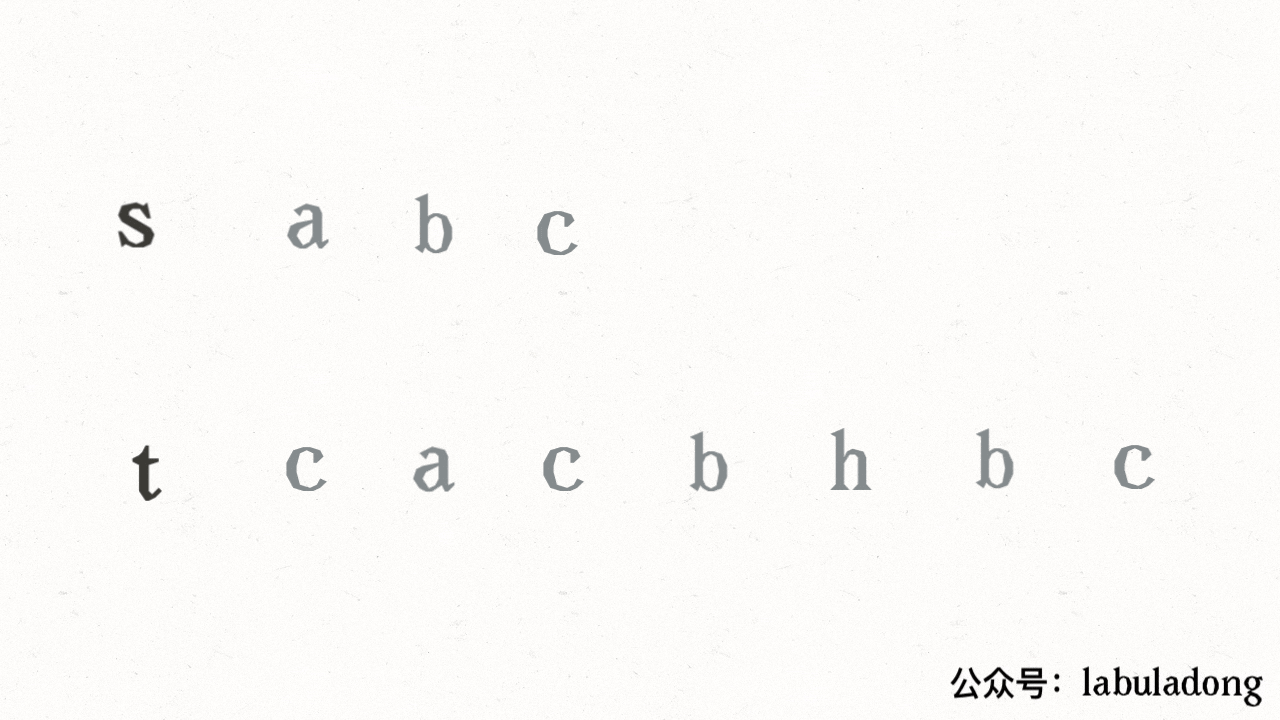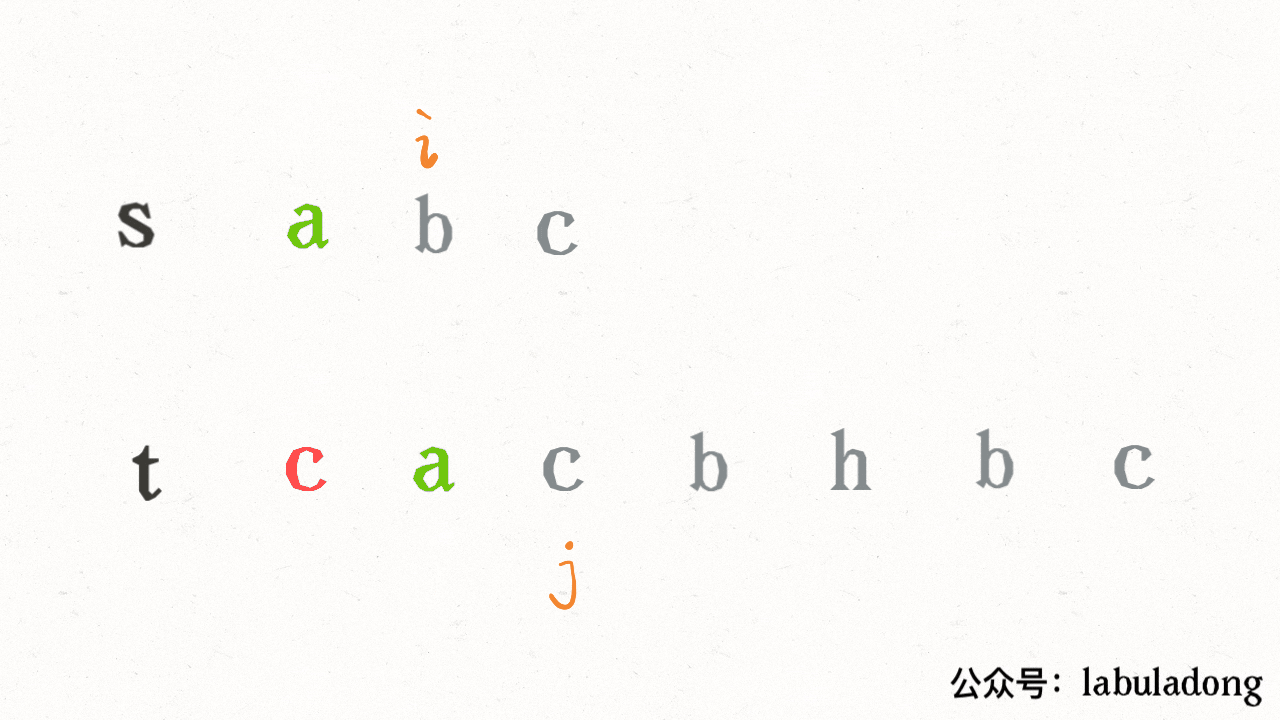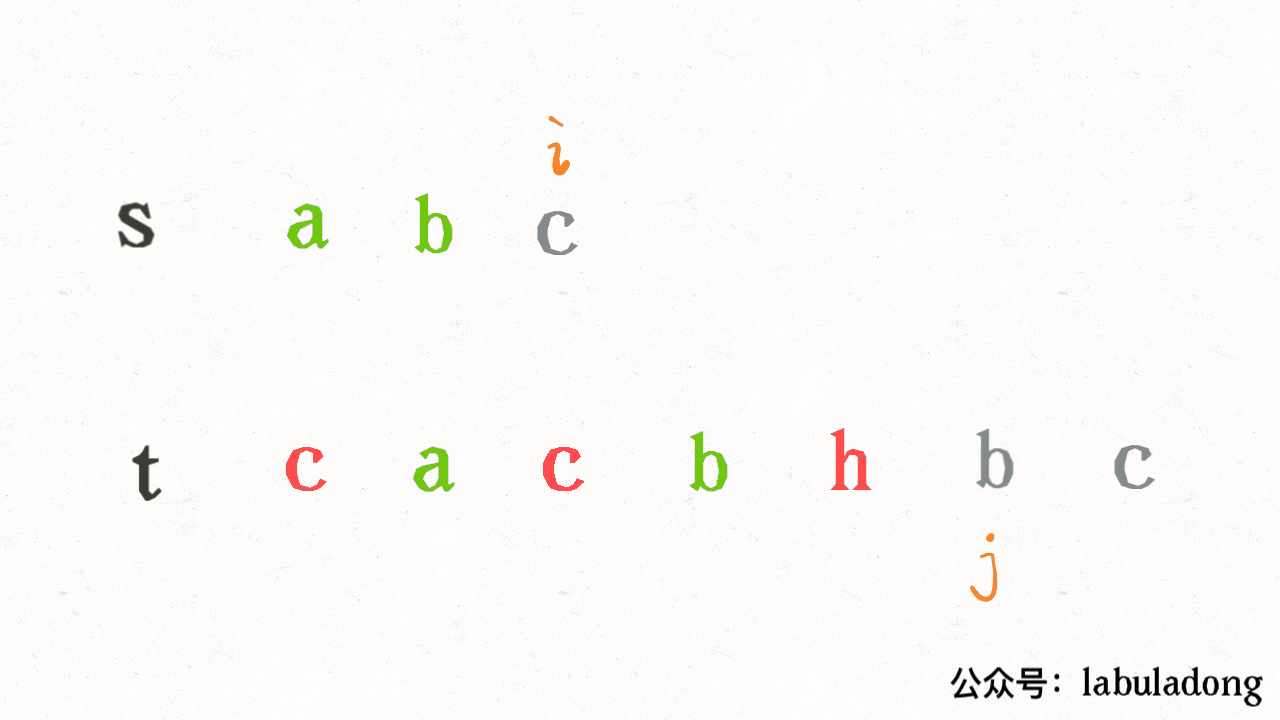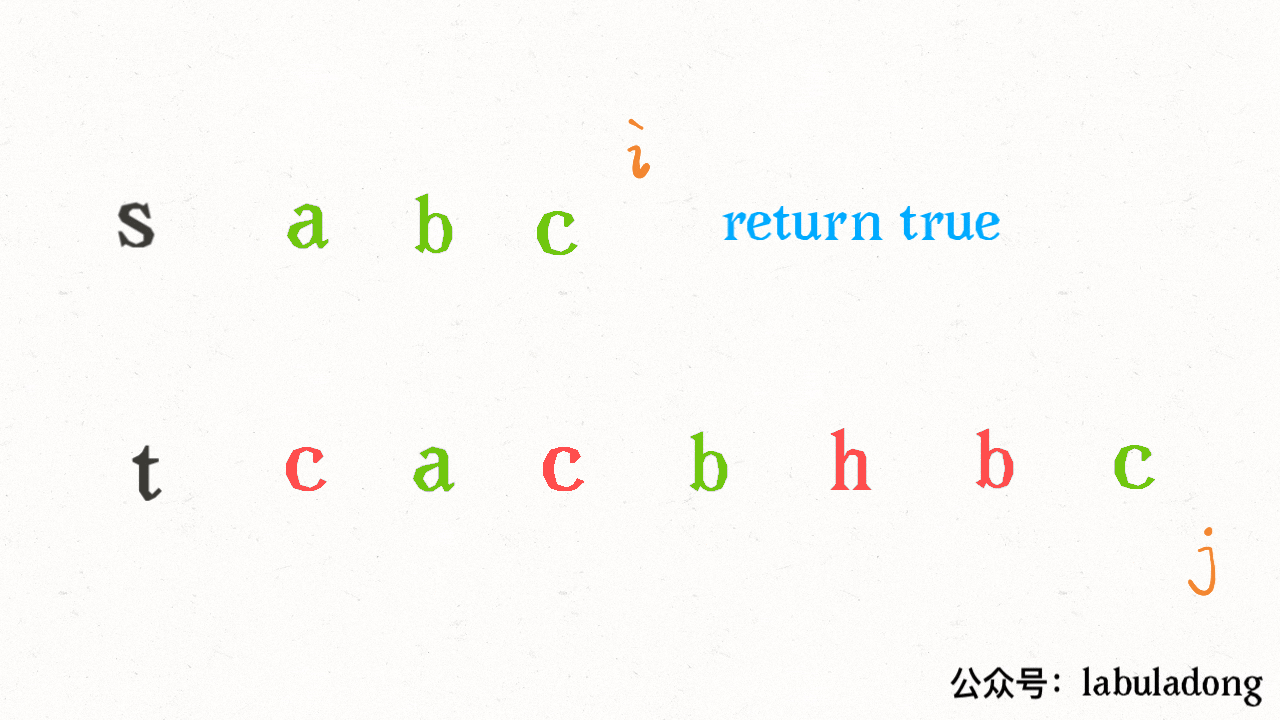
读者也许会问,这不就是最优解法了吗,时间复杂度只需 O(N),N 为 `t` 的长度。
是的,如果仅仅是这个问题,这个解法就够好了,**不过这个问题还有 follow up**:
如果给你一系列字符串 `s1,s2,...` 和字符串 `t`,你需要判定每个串 `s` 是否是 `t` 的子序列(可以假定 `s` 较短,`t` 很长)。
```java
boolean[] isSubsequence(String[] sn, String t);
```
你也许会问,这不是很简单吗,还是刚才的逻辑,加个 for 循环不就行了?
可以,但是此解法处理每个 `s` 时间复杂度仍然是 O(N),而如果巧妙运用二分查找,可以将时间复杂度降低,大约是 O(MlogN)。由于 N 相对 M 大很多,所以后者效率会更高。
### 二、二分思路
二分思路主要是对 `t` 进行预处理,用一个字典 `index` 将每个字符出现的索引位置按顺序存储下来:
```java
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
ArrayList[] index = new ArrayList[256];
// 先记下 t 中每个字符出现的位置
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = t.charAt(i);
if (index[c] == null)
index[c] = new ArrayList<>();
index[c].add(i);
}
```

比如对于这个情况,匹配了 "ab",应该匹配 "c" 了:

按照之前的解法,我们需要 `j` 线性前进扫描字符 "c",但借助 `index` 中记录的信息,**可以二分搜索 `index[c]` 中比 j 大的那个索引**,在上图的例子中,就是在 `[0,2,6]` 中搜索比 4 大的那个索引:
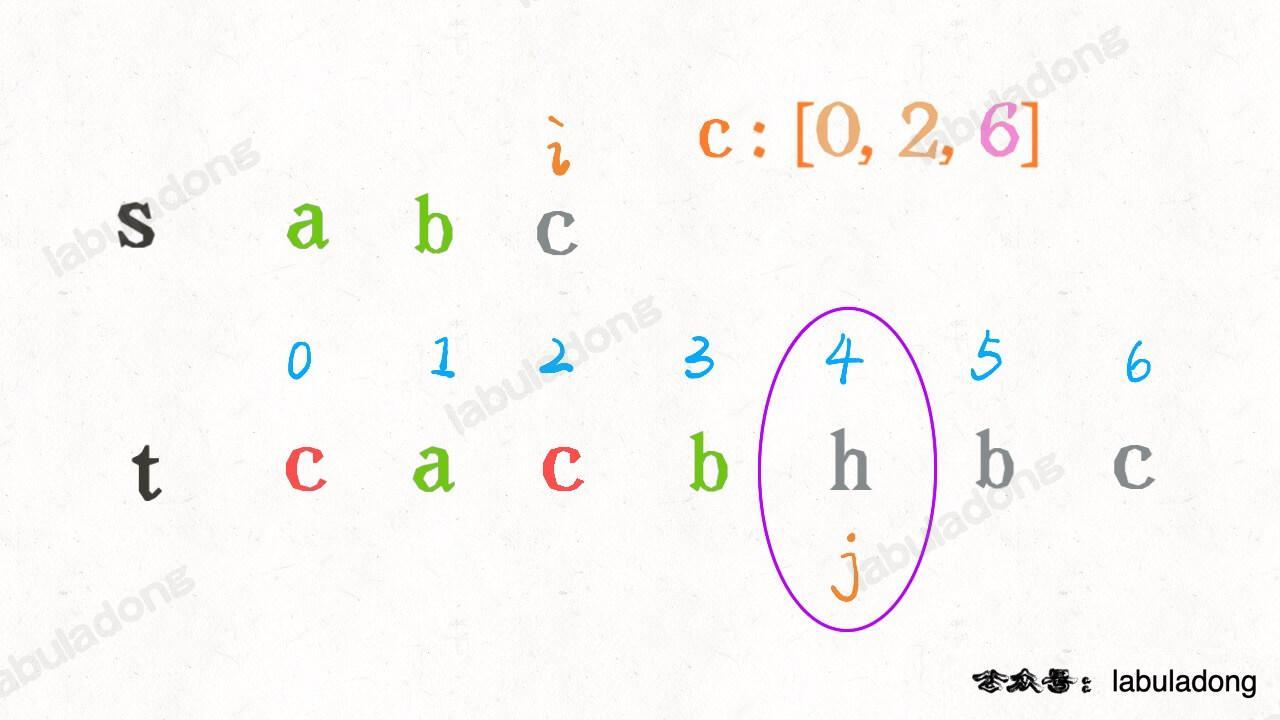
这样就可以直接得到下一个 "c" 的索引。现在的问题就是,如何用二分查找计算那个恰好比 4 大的索引呢?答案是,寻找左侧边界的二分搜索就可以做到。
### 三、再谈二分查找
在前文 [二分查找详解](https://labuladong.github.io/article/fname.html?fname=二分查找详解) 中,详解了如何正确写出三种二分查找算法的细节。二分查找返回目标值 `val` 的索引,对于搜索**左侧边界**的二分查找,有一个特殊性质:
**当 `val` 不存在时,得到的索引恰好是比 `val` 大的最小元素索引**。
什么意思呢,就是说如果在数组 `[0,1,3,4]` 中搜索元素 2,算法会返回索引 2,也就是元素 3 的位置,元素 3 是数组中大于 2 的最小元素。所以我们可以利用二分搜索避免线性扫描。
```java
// 查找左侧边界的二分查找
int left_bound(ArrayList arr, int target) {
int left = 0, right = arr.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target > arr.get(mid)) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
if (left == arr.size()) {
return -1;
}
return left;
}
```
以上就是搜索左侧边界的二分查找,等会儿会用到,其中的细节可以参见前文 [二分查找详解](https://labuladong.github.io/article/fname.html?fname=二分查找详解),这里不再赘述。
这里以单个字符串 `s` 为例,对于多个字符串 `s`,可以把预处理部分抽出来。
```java
boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
// 对 t 进行预处理
ArrayList[] index = new ArrayList[256];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = t.charAt(i);
if (index[c] == null)
index[c] = new ArrayList<>();
index[c].add(i);
}
// 串 t 上的指针
int j = 0;
// 借助 index 查找 s[i]
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
// 整个 t 压根儿没有字符 c
if (index[c] == null) return false;
int pos = left_bound(index[c], j);
// 二分搜索区间中没有找到字符 c
if (pos == -1) return false;
// 向前移动指针 j
j = index[c].get(pos) + 1;
}
return true;
}
```
算法执行的过程是这样的:
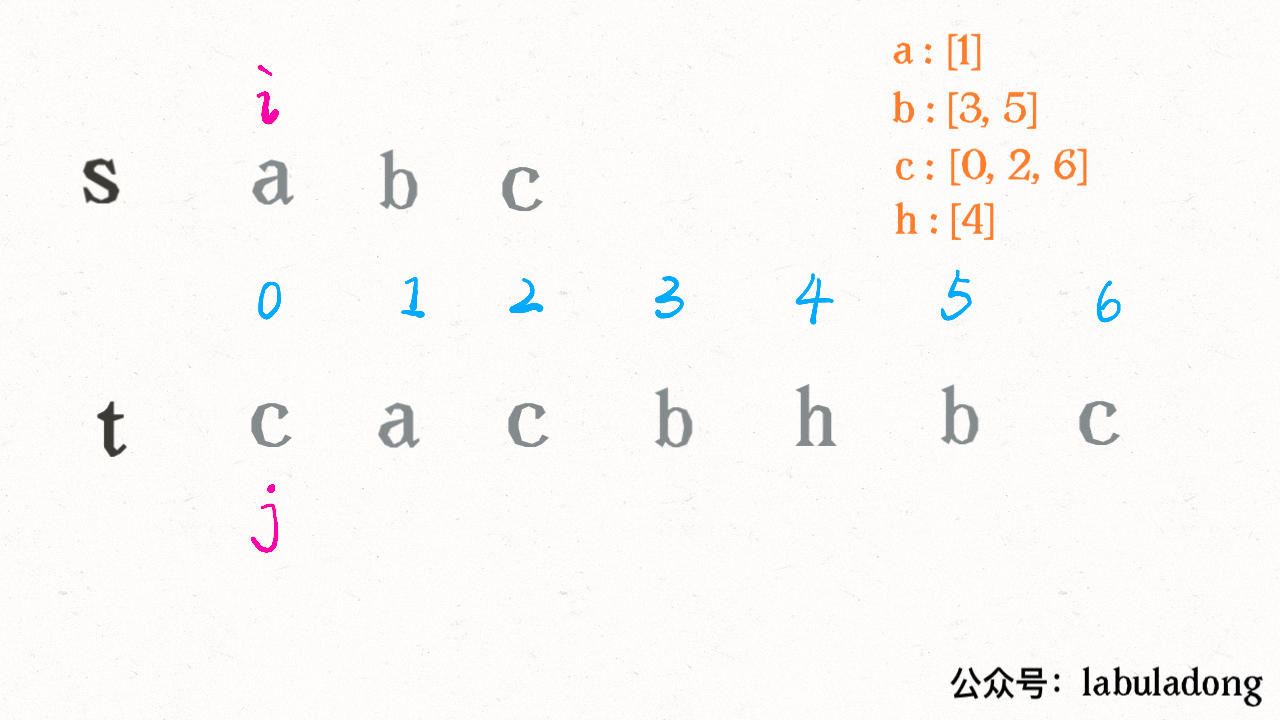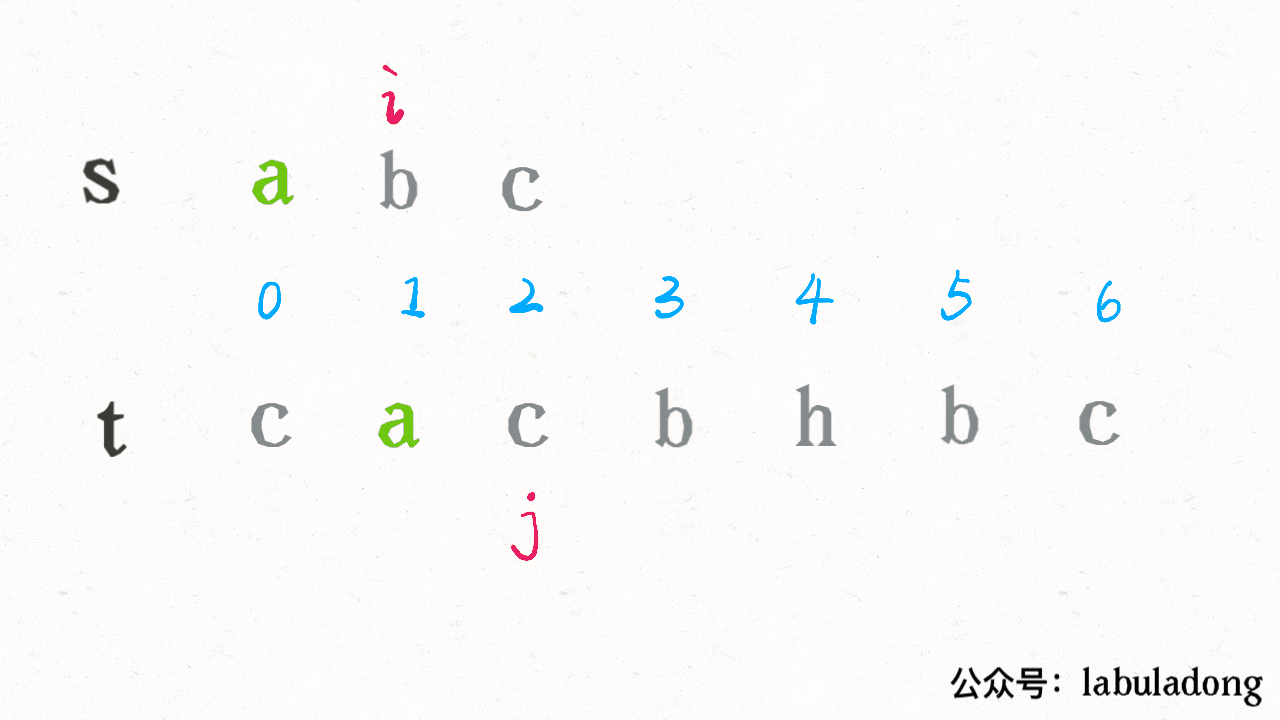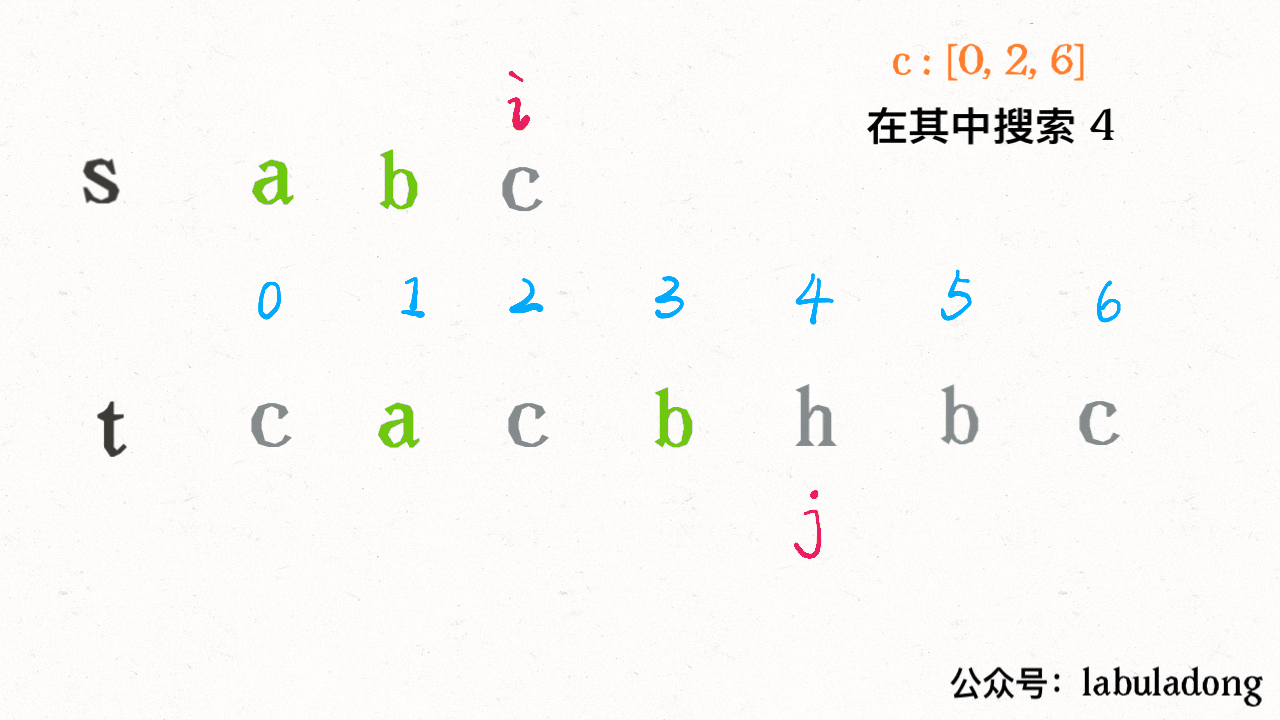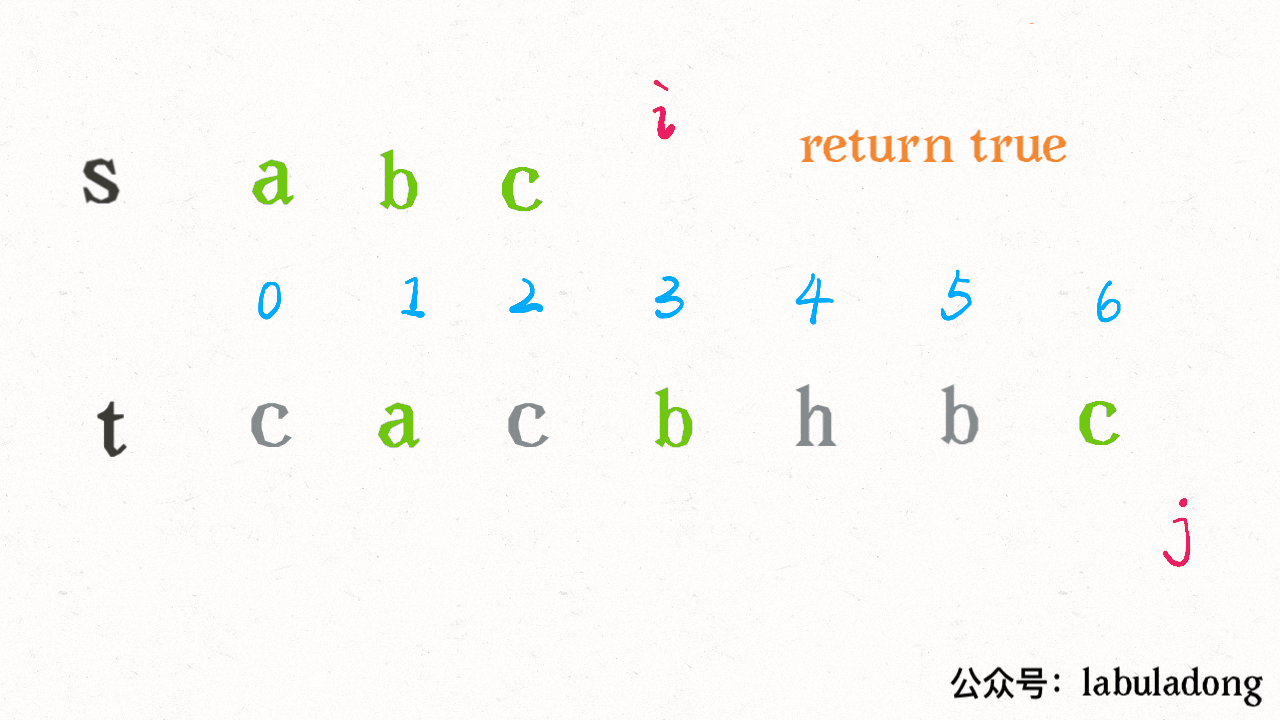
可见借助二分查找,算法的效率是可以大幅提升的。
明白了这个思路,我们可以直接拿下力扣第 792 题「匹配子序列的单词数」:给你输入一个字符串列表 `words` 和一个字符串 `s`,问你 `words` 中有多少字符串是 `s` 的子序列。
函数签名如下:
```java
int numMatchingSubseq(String s, String[] words)
```
我们直接把上一道题的代码稍微改改即可完成这道题:
```java
int numMatchingSubseq(String s, String[] words) {
// 对 s 进行预处理
// char -> 该 char 的索引列表
ArrayList[] index = new ArrayList[256];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (index[c] == null) {
index[c] = new ArrayList<>();
}
index[c].add(i);
}
int res = 0;
for (String word : words) {
// 字符串 word 上的指针
int i = 0;
// 串 s 上的指针
int j = 0;
// 借助 index 查找 word 中每个字符的索引
for (; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
// 整个 s 压根儿没有字符 c
if (index[c] == null) {
break;
}
int pos = left_bound(index[c], j);
// 二分搜索区间中没有找到字符 c
if (pos == -1) {
break;
}
// 向前移动指针 j
j = index[c].get(pos) + 1;
}
// 如果 word 完成匹配,则是子序列
if (i == word.length()) {
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
// 查找左侧边界的二分查找
int left_bound(ArrayList arr, int target) {
// 见上文
}
```
**_____________**
**《labuladong 的算法小抄》已经出版,关注公众号查看详情;后台回复关键词「**进群**」可加入算法群;回复「**全家桶**」可下载配套 PDF 和刷题全家桶**:

======其他语言代码======
[392.判断子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/is-subsequence)
### c++
[dekunma](https://www.linkedin.com/in/dekun-ma-036a9b198/) 提供C++代码
**解法一:遍历(也可以用双指针):**
```C++
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
// 遍历s
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
// 找到s[i]字符在t中的位置
size_t pos = t.find(s[i]);
// 如果s[i]字符不在t中,返回false
if(pos == std::string::npos) return false;
// 如果s[i]在t中,后面就只看pos以后的字串,防止重复查找
else t = t.substr(pos + 1);
}
return true;
}
};
```
**解法二:二分查找:**
```C++
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int m = s.size(), n = t.size();
// 对 t 进行预处理
vector index[256];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = t[i];
index[c].push_back(i);
}
// 串 t 上的指针
int j = 0;
// 借助 index 查找 s[i]
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
char c = s[i];
// 整个 t 压根儿没有字符 c
if (index[c].empty()) return false;
int pos = left_bound(index[c], j);
// 二分搜索区间中没有找到字符 c
if (pos == index[c].size()) return false;
// 向前移动指针 j
j = index[c][pos] + 1;
}
return true;
}
// 查找左侧边界的二分查找
int left_bound(vector arr, int tar) {
int lo = 0, hi = arr.size();
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (tar > arr[mid]) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
hi = mid;
}
}
return lo;
}
};
```
### javascript
双指针一遍扫描做法
```js
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string} t
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSubsequence = function (s, t) {
let i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length && j < t.length) {
if (s[i] === t[j]) i++;
j++;
}
return i === s.length;
};
```
**升级:二分法做法,可应对与多个s的情况**
```js
var isSubsequence = function (s, t) {
let m = s.length, n = t.length;
let index = new Array(256);
// 先记下 t 中每个字符出现的位置
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let c = t[i];
if (index[c] == null) {
index[c] = [];
}
index[c].push(i)
}
// 串t上的指针
let j = 0;
// 借助index查找s[i]
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
let c = s[i];
// 整个t压根没有字符c
if (index[c] == null) return false
let pos = left_bound(index[c], j);
// 二分搜索区间中没有找到字符c
if (pos == index[c].length) return false;
// 向前移动指针j
j = index[c][pos] + 1;
}
return true;
};
var left_bound = function (arr, tar) {
let lo = 0, hi = arr.length;
while (lo < hi) {
let mid = lo + Math.floor((hi - lo) / 2);
if (tar > arr[mid]) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
hi = mid;
}
}
return lo;
}
```



