Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into executor-design
Showing
doc/design/dcgan.png
0 → 100644
56.6 KB
doc/design/gan_api.md
0 → 100644
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


| W: | H:
| W: | H:


| W: | H:
| W: | H:


doc/design/optimizer.md
0 → 100644
doc/design/selected_rows.md
0 → 100644
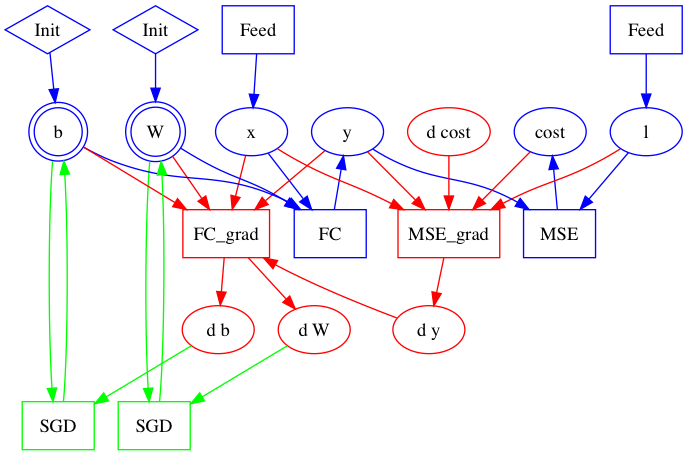
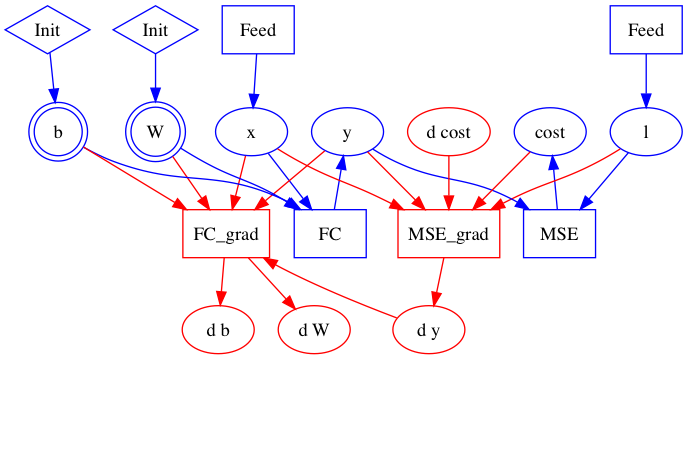
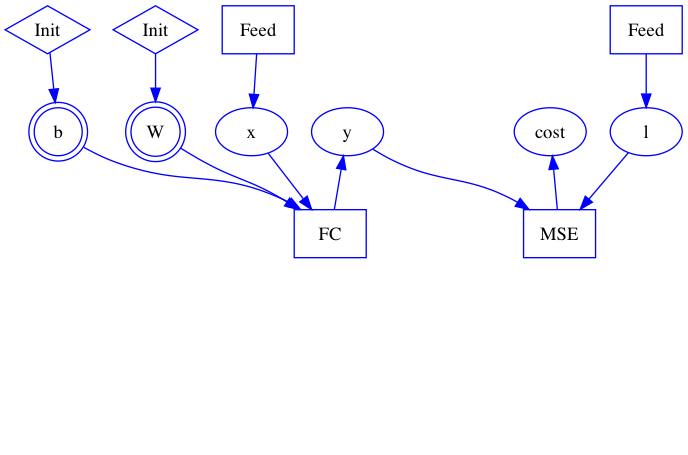
doc/design/test.dot
0 → 100644
doc/design/test.dot.png
0 → 100644
57.6 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动
455.6 KB
51.4 KB
48.7 KB
30.3 KB
455.6 KB
51.4 KB
48.7 KB
30.3 KB
doc/tutorials/index_cn.md
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/tutorials/index_en.md
已删除
100644 → 0
81.2 KB
30.5 KB
27.2 KB
52.0 KB
30.5 KB
27.2 KB
49.5 KB
34.8 KB
49.5 KB
30.3 KB
30.3 KB
doc/v1_api_tutorials/README.md
0 → 100644
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
paddle/framework/executor.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/executor.h
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/executor_test.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/selected_rows.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/framework/selected_rows.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/adam_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/adam_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/adam_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/conv_cudnn_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/conv_cudnn_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/feed_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/fetch_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/gru_unit_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/gru_unit_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/gru_unit_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/vol2col.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/vol2col.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/math/vol2col.h
0 → 100644