# torch.nn.functional
> 译者:[hijkzzz](https://github.com/hijkzzz)
## 卷积函数
### conv1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv1d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入信号进行一维卷积.
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见[`Conv1d`](#torch.nn.Conv1d "torch.nn.Conv1d").
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** – 可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: `None`
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组`(sW,)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组`(padW, )`. 默认值: 0
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组`(dW,)`. 默认值: 1
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 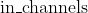 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> filters = torch.randn(33, 16, 3)
>>> inputs = torch.randn(20, 16, 50)
>>> F.conv1d(inputs, filters)
```
### conv2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入图像应用二维卷积.
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见[`Conv2d`](#torch.nn.Conv2d "torch.nn.Conv2d").
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** – 可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: `None`
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(sH, sW)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(padH, padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组 `(dH, dW)`. 默认值: 1
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 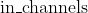 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> # With square kernels and equal stride
>>> filters = torch.randn(8,4,3,3)
>>> inputs = torch.randn(1,4,5,5)
>>> F.conv2d(inputs, filters, padding=1)
```
### conv3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv3d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入图像应用三维卷积.
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见 [`Conv3d`](#torch.nn.Conv3d "torch.nn.Conv3d").
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** – 可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: None
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(sT, sH, sW)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(padT, padH, padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组 `(dT, dH, dW)`. 默认值: 1
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 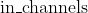 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> filters = torch.randn(33, 16, 3, 3, 3)
>>> inputs = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 10, 20)
>>> F.conv3d(inputs, filters)
```
### conv_transpose1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv_transpose1d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, dilation=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入信号应用一维转置卷积算子, 有时也称为反卷积.
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见 [`ConvTranspose1d`](#torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d "torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d")
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** – 可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: None
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(sW,)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 输入中的每个维度的两边都将添加零填充`kernel_size - 1 - padding`. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(padW,)`. 默认值: 0
* **output_padding** – 添加到输出形状中每个维度的一侧的额外大小. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(out_padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 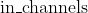 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组 `(dW,)`. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> inputs = torch.randn(20, 16, 50)
>>> weights = torch.randn(16, 33, 5)
>>> F.conv_transpose1d(inputs, weights)
```
### conv_transpose2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv_transpose2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, dilation=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入图像应用二维转置卷积算子, 有时也称为反卷积.
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见 [`ConvTranspose2d`](#torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d "torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d").
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** –可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: None
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(sH, sW)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 输入中的每个维度的两边都将添加零填充`kernel_size - 1 - padding`. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(padH, padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **output_padding** – 添加到输出形状中每个维度的一侧的额外大小. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(out_padH, out_padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 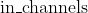 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组 `(dH, dW)`. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> # With square kernels and equal stride
>>> inputs = torch.randn(1, 4, 5, 5)
>>> weights = torch.randn(4, 8, 3, 3)
>>> F.conv_transpose2d(inputs, weights, padding=1)
```
### conv_transpose3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.conv_transpose3d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, dilation=1) → Tensor
```
对由多个输入平面组成的输入图像应用一个三维转置卷积算子,有时也称为反卷积
有关详细信息和输出形状, 请参见 [`ConvTranspose3d`](#torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d "torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d").
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **weight** – 卷积核, 形状为 )
* **bias** –可选的偏置, 形状为 ). 默认值: None
* **stride** – 卷积核的步幅, 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(sT, sH, sW)`. 默认值: 1
* **padding** – 输入中的每个维度的两边都将添加零填充`kernel_size - 1 - padding`. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(padT, padH, padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **output_padding** – 添加到输出形状中每个维度的一侧的额外大小. 可以是单个数字或元组 `(out_padT, out_padH, out_padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **groups** – 将输入分成组, 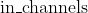 应该可以被组的数目整除. 默认值: 1
* **dilation** – 核元素之间的空洞. 可以是单个数字或单元素元组 `(dT, dH, dW)`. 默认值: 1
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> inputs = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 10, 20)
>>> weights = torch.randn(16, 33, 3, 3, 3)
>>> F.conv_transpose3d(inputs, weights)
```
### unfold
```py
torch.nn.functional.unfold(input, kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
```
Extracts sliding local blocks from an batched input tensor.
警告
Currently, only 4-D input tensors (batched image-like tensors) are supported.
见 [`torch.nn.Unfold`](#torch.nn.Unfold "torch.nn.Unfold") for details
### fold
```py
torch.nn.functional.fold(input, output_size, kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
```
Combines an array of sliding local blocks into a large containing tensor.
警告
Currently, only 4-D output tensors (batched image-like tensors) are supported.
见 [`torch.nn.Fold`](#torch.nn.Fold "torch.nn.Fold") for details
## Pooling functions
### avg_pool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.avg_pool1d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True) → Tensor
```
Applies a 1D average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AvgPool1d`](#torch.nn.AvgPool1d "torch.nn.AvgPool1d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 )
* **kernel_size** – the size of the window. Can be a single number or a tuple )
* **stride** – the stride of the window. Can be a single number or a tuple `(sW,)`. 默认值: `kernel_size`
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(padW,)`. 默认值: 0
* **ceil_mode** – when True, will use `ceil` instead of `floor` to compute the output shape. 默认值: `False`
* **count_include_pad** – when True, will include the zero-padding in the averaging calculation. 默认值: `True`
|
| --- | --- |
```py
例子::
```
```py
>>> # pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
>>> input = torch.tensor([[[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]]])
>>> F.avg_pool1d(input, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
tensor([[[ 2., 4., 6.]]])
```
### avg_pool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True) → Tensor
```
Applies 2D average-pooling operation in 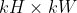 regions by step size 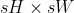 steps. The number of output features is equal to the number of input planes.
见 [`AvgPool2d`](#torch.nn.AvgPool2d "torch.nn.AvgPool2d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **input** – input tensor )
* **kernel_size** – size of the pooling region. Can be a single number or a tuple )
* **stride** – stride of the pooling operation. Can be a single number or a tuple `(sH, sW)`. 默认值: `kernel_size`
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(padH, padW)`. 默认值: 0
* **ceil_mode** – when True, will use `ceil` instead of `floor` in the formula to compute the output shape. 默认值: `False`
* **count_include_pad** – when True, will include the zero-padding in the averaging calculation. 默认值: `True`
|
| --- | --- |
### avg_pool3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.avg_pool3d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True) → Tensor
```
Applies 3D average-pooling operation in 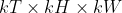 regions by step size 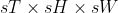 steps. The number of output features is equal to 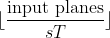.
见 [`AvgPool3d`](#torch.nn.AvgPool3d "torch.nn.AvgPool3d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **input** – input tensor )
* **kernel_size** – size of the pooling region. Can be a single number or a tuple )
* **stride** – stride of the pooling operation. Can be a single number or a tuple `(sT, sH, sW)`. 默认值: `kernel_size`
* **padding** – 在输入的两边隐式加零. 可以是单个数字或一个元素元组 `(padT, padH, padW)`, 默认值: 0
* **ceil_mode** – when True, will use `ceil` instead of `floor` in the formula to compute the output shape
* **count_include_pad** – when True, will include the zero-padding in the averaging calculation
|
| --- | --- |
### max_pool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_pool1d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 1D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`MaxPool1d`](#torch.nn.MaxPool1d "torch.nn.MaxPool1d") for details.
### max_pool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 2D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`MaxPool2d`](#torch.nn.MaxPool2d "torch.nn.MaxPool2d") for details.
### max_pool3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_pool3d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 3D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`MaxPool3d`](#torch.nn.MaxPool3d "torch.nn.MaxPool3d") for details.
### max_unpool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_unpool1d(input, indices, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, output_size=None)
```
Computes a partial inverse of `MaxPool1d`.
见 [`MaxUnpool1d`](#torch.nn.MaxUnpool1d "torch.nn.MaxUnpool1d") for details.
### max_unpool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_unpool2d(input, indices, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, output_size=None)
```
Computes a partial inverse of `MaxPool2d`.
见 [`MaxUnpool2d`](#torch.nn.MaxUnpool2d "torch.nn.MaxUnpool2d") for details.
### max_unpool3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.max_unpool3d(input, indices, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, output_size=None)
```
Computes a partial inverse of `MaxPool3d`.
见 [`MaxUnpool3d`](#torch.nn.MaxUnpool3d "torch.nn.MaxUnpool3d") for details.
### lp_pool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.lp_pool1d(input, norm_type, kernel_size, stride=None, ceil_mode=False)
```
Applies a 1D power-average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes. If the sum of all inputs to the power of `p` is zero, the gradient is set to zero as well.
见 [`LPPool1d`](#torch.nn.LPPool1d "torch.nn.LPPool1d") for details.
### lp_pool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.lp_pool2d(input, norm_type, kernel_size, stride=None, ceil_mode=False)
```
Applies a 2D power-average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes. If the sum of all inputs to the power of `p` is zero, the gradient is set to zero as well.
见 [`LPPool2d`](#torch.nn.LPPool2d "torch.nn.LPPool2d") for details.
### adaptive_max_pool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_max_pool1d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 1D adaptive max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveMaxPool1d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool1d "torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool1d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **output_size** – the target output size (single integer)
* **return_indices** – whether to return pooling indices. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
### adaptive_max_pool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_max_pool2d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 2D adaptive max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveMaxPool2d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d "torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **output_size** – the target output size (single integer or double-integer tuple)
* **return_indices** – whether to return pooling indices. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
### adaptive_max_pool3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_max_pool3d(*args, **kwargs)
```
Applies a 3D adaptive max pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveMaxPool3d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool3d "torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool3d") for details and output shape.
参数:
* **output_size** – the target output size (single integer or triple-integer tuple)
* **return_indices** – whether to return pooling indices. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
### adaptive_avg_pool1d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool1d(input, output_size) → Tensor
```
Applies a 1D adaptive average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveAvgPool1d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d "torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d") for details and output shape.
| 参数:| **output_size** – the target output size (single integer) |
| --- | --- |
### adaptive_avg_pool2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(input, output_size)
```
Applies a 2D adaptive average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveAvgPool2d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d "torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d") for details and output shape.
| 参数:| **output_size** – the target output size (single integer or double-integer tuple) |
| --- | --- |
### adaptive_avg_pool3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool3d(input, output_size)
```
Applies a 3D adaptive average pooling over an input signal composed of several input planes.
见 [`AdaptiveAvgPool3d`](#torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d "torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d") for details and output shape.
| 参数:| **output_size** – the target output size (single integer or triple-integer tuple) |
| --- | --- |
## Non-linear activation functions
### threshold
```py
torch.nn.functional.threshold(input, threshold, value, inplace=False)
```
Thresholds each element of the input Tensor.
见 [`Threshold`](#torch.nn.Threshold "torch.nn.Threshold") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.threshold_(input, threshold, value) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`threshold()`](#torch.nn.functional.threshold "torch.nn.functional.threshold").
### relu
```py
torch.nn.functional.relu(input, inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies the rectified linear unit function element-wise. 见 [`ReLU`](#torch.nn.ReLU "torch.nn.ReLU") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.relu_(input) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`relu()`](#torch.nn.functional.relu "torch.nn.functional.relu").
### hardtanh
```py
torch.nn.functional.hardtanh(input, min_val=-1., max_val=1., inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies the HardTanh function element-wise. 见 [`Hardtanh`](#torch.nn.Hardtanh "torch.nn.Hardtanh") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.hardtanh_(input, min_val=-1., max_val=1.) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`hardtanh()`](#torch.nn.functional.hardtanh "torch.nn.functional.hardtanh").
### relu6
```py
torch.nn.functional.relu6(input, inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies the element-wise function %20%3D%20%5Cmin(%5Cmax(0%2Cx)%2C%206)).
见 [`ReLU6`](#torch.nn.ReLU6 "torch.nn.ReLU6") for more details.
### elu
```py
torch.nn.functional.elu(input, alpha=1.0, inplace=False)
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20%5Cmax(0%2Cx)%20%2B%20%5Cmin(0%2C%20%5Calpha%20*%20(%5Cexp(x)%20-%201))).
见 [`ELU`](#torch.nn.ELU "torch.nn.ELU") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.elu_(input, alpha=1.) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`elu()`](#torch.nn.functional.elu "torch.nn.functional.elu").
### selu
```py
torch.nn.functional.selu(input, inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20scale%20*%20(%5Cmax(0%2Cx)%20%2B%20%5Cmin(0%2C%20%5Calpha%20*%20(%5Cexp(x)%20-%201)))), with 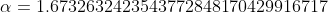 and 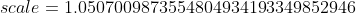.
见 [`SELU`](#torch.nn.SELU "torch.nn.SELU") for more details.
### celu
```py
torch.nn.functional.celu(input, alpha=1., inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20%5Cmax(0%2Cx)%20%2B%20%5Cmin(0%2C%20%5Calpha%20*%20(%5Cexp(x%2F%5Calpha)%20-%201))).
见 [`CELU`](#torch.nn.CELU "torch.nn.CELU") for more details.
### leaky_relu
```py
torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu(input, negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20%5Cmax(0%2C%20x)%20%2B%20%5Ctext%7Bnegative%5C_slope%7D%20*%20%5Cmin(0%2C%20x))
见 [`LeakyReLU`](#torch.nn.LeakyReLU "torch.nn.LeakyReLU") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu_(input, negative_slope=0.01) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`leaky_relu()`](#torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu "torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu").
### prelu
```py
torch.nn.functional.prelu(input, weight) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise the function %20%3D%20%5Cmax(0%2Cx)%20%2B%20%5Ctext%7Bweight%7D%20*%20%5Cmin(0%2Cx)) where weight is a learnable parameter.
见 [`PReLU`](#torch.nn.PReLU "torch.nn.PReLU") for more details.
### rrelu
```py
torch.nn.functional.rrelu(input, lower=1./8, upper=1./3, training=False, inplace=False) → Tensor
```
Randomized leaky ReLU.
见 [`RReLU`](#torch.nn.RReLU "torch.nn.RReLU") for more details.
```py
torch.nn.functional.rrelu_(input, lower=1./8, upper=1./3, training=False) → Tensor
```
In-place version of [`rrelu()`](#torch.nn.functional.rrelu "torch.nn.functional.rrelu").
### glu
```py
torch.nn.functional.glu(input, dim=-1) → Tensor
```
The gated linear unit. Computes:
)
where `input` is split in half along `dim` to form `A` and `B`.
See [Language Modeling with Gated Convolutional Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08083).
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input tensor
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – dimension on which to split the input
|
| --- | --- |
### logsigmoid
```py
torch.nn.functional.logsigmoid(input) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise %20%3D%20%5Clog%20%5Cleft(%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B1%20%2B%20%5Cexp(-x_i)%7D%5Cright))
见 [`LogSigmoid`](#torch.nn.LogSigmoid "torch.nn.LogSigmoid") for more details.
### hardshrink
```py
torch.nn.functional.hardshrink(input, lambd=0.5) → Tensor
```
Applies the hard shrinkage function element-wise
见 [`Hardshrink`](#torch.nn.Hardshrink "torch.nn.Hardshrink") for more details.
### tanhshrink
```py
torch.nn.functional.tanhshrink(input) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20x%20-%20%5Ctext%7BTanh%7D(x))
见 [`Tanhshrink`](#torch.nn.Tanhshrink "torch.nn.Tanhshrink") for more details.
### softsign
```py
torch.nn.functional.softsign(input) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, the function %20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7Bx%7D%7B1%20%2B%20%7Cx%7C%7D)
见 [`Softsign`](#torch.nn.Softsign "torch.nn.Softsign") for more details.
### softplus
```py
torch.nn.functional.softplus(input, beta=1, threshold=20) → Tensor
```
### softmin
```py
torch.nn.functional.softmin(input, dim=None, _stacklevel=3, dtype=None)
```
Applies a softmin function.
Note that %20%3D%20%5Ctext%7BSoftmax%7D(-x)). See softmax definition for mathematical formula.
见 [`Softmin`](#torch.nn.Softmin "torch.nn.Softmin") for more details.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – A dimension along which softmin will be computed (so every slice along dim will sum to 1).
* **dtype** (`torch.dtype`, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor.
|
| --- | --- |
:param If specified, the input tensor is casted to `dtype` before the operation: :param is performed. This is useful for preventing data type overflows. 默认值: None.
### softmax
```py
torch.nn.functional.softmax(input, dim=None, _stacklevel=3, dtype=None)
```
Applies a softmax function.
Softmax is defined as:
%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7Bexp(x_i)%7D%7B%5Csum_j%20exp(x_j)%7D)
It is applied to all slices along dim, and will re-scale them so that the elements lie in the range `(0, 1)` and sum to 1.
见 [`Softmax`](#torch.nn.Softmax "torch.nn.Softmax") for more details.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – A dimension along which softmax will be computed.
* **dtype** (`torch.dtype`, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor.
|
| --- | --- |
:param If specified, the input tensor is casted to `dtype` before the operation: :param is performed. This is useful for preventing data type overflows. 默认值: None.
注意
This function doesn’t work directly with NLLLoss, which expects the Log to be computed between the Softmax and itself. Use log_softmax instead (it’s faster and has better numerical properties).
### softshrink
```py
torch.nn.functional.softshrink(input, lambd=0.5) → Tensor
```
Applies the soft shrinkage function elementwise
见 [`Softshrink`](#torch.nn.Softshrink "torch.nn.Softshrink") for more details.
### gumbel_softmax
```py
torch.nn.functional.gumbel_softmax(logits, tau=1.0, hard=False, eps=1e-10)
```
Sample from the Gumbel-Softmax distribution and optionally discretize.
参数:
* **logits** – `[batch_size, num_features]` unnormalized log probabilities
* **tau** – non-negative scalar temperature
* **hard** – if `True`, the returned samples will be discretized as one-hot vectors, but will be differentiated as if it is the soft sample in autograd
|
| --- | --- |
| Returns: | Sampled tensor of shape `batch_size x num_features` from the Gumbel-Softmax distribution. If `hard=True`, the returned samples will be one-hot, otherwise they will be probability distributions that sum to 1 across features |
| --- | --- |
Constraints:
* Currently only work on 2D input `logits` tensor of shape `batch_size x num_features`
Based on [https://github.com/ericjang/gumbel-softmax/blob/3c8584924603869e90ca74ac20a6a03d99a91ef9/Categorical%20VAE.ipynb](https://github.com/ericjang/gumbel-softmax/blob/3c8584924603869e90ca74ac20a6a03d99a91ef9/Categorical%20VAE.ipynb) , (MIT license)
### log_softmax
```py
torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(input, dim=None, _stacklevel=3, dtype=None)
```
Applies a softmax followed by a logarithm.
While mathematically equivalent to log(softmax(x)), doing these two operations separately is slower, and numerically unstable. This function uses an alternative formulation to compute the output and gradient correctly.
见 [`LogSoftmax`](#torch.nn.LogSoftmax "torch.nn.LogSoftmax") for more details.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – A dimension along which log_softmax will be computed.
* **dtype** (`torch.dtype`, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor.
|
| --- | --- |
:param If specified, the input tensor is casted to `dtype` before the operation: :param is performed. This is useful for preventing data type overflows. 默认值: None.
### tanh
```py
torch.nn.functional.tanh(input) → Tensor
```
Applies element-wise, %20%3D%20%5Ctanh(x)%20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B%5Cexp(x)%20-%20%5Cexp(-x)%7D%7B%5Cexp(x)%20%2B%20%5Cexp(-x)%7D)
见 [`Tanh`](#torch.nn.Tanh "torch.nn.Tanh") for more details.
### sigmoid
```py
torch.nn.functional.sigmoid(input) → Tensor
```
Applies the element-wise function %20%3D%20%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B1%20%2B%20%5Cexp(-x)%7D)
见 [`Sigmoid`](#torch.nn.Sigmoid "torch.nn.Sigmoid") for more details.
## Normalization functions
### batch_norm
```py
torch.nn.functional.batch_norm(input, running_mean, running_var, weight=None, bias=None, training=False, momentum=0.1, eps=1e-05)
```
Applies Batch Normalization for each channel across a batch of data.
见 [`BatchNorm1d`](#torch.nn.BatchNorm1d "torch.nn.BatchNorm1d"), [`BatchNorm2d`](#torch.nn.BatchNorm2d "torch.nn.BatchNorm2d"), [`BatchNorm3d`](#torch.nn.BatchNorm3d "torch.nn.BatchNorm3d") for details.
### instance_norm
```py
torch.nn.functional.instance_norm(input, running_mean=None, running_var=None, weight=None, bias=None, use_input_stats=True, momentum=0.1, eps=1e-05)
```
Applies Instance Normalization for each channel in each data sample in a batch.
见 [`InstanceNorm1d`](#torch.nn.InstanceNorm1d "torch.nn.InstanceNorm1d"), [`InstanceNorm2d`](#torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d "torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d"), [`InstanceNorm3d`](#torch.nn.InstanceNorm3d "torch.nn.InstanceNorm3d") for details.
### layer_norm
```py
torch.nn.functional.layer_norm(input, normalized_shape, weight=None, bias=None, eps=1e-05)
```
Applies Layer Normalization for last certain number of dimensions.
见 [`LayerNorm`](#torch.nn.LayerNorm "torch.nn.LayerNorm") for details.
### local_response_norm
```py
torch.nn.functional.local_response_norm(input, size, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=1.0)
```
Applies local response normalization over an input signal composed of several input planes, where channels occupy the second dimension. Applies normalization across channels.
见 [`LocalResponseNorm`](#torch.nn.LocalResponseNorm "torch.nn.LocalResponseNorm") for details.
### normalize
```py
torch.nn.functional.normalize(input, p=2, dim=1, eps=1e-12, out=None)
```
Performs 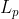 normalization of inputs over specified dimension.
For a tensor `input` of sizes ), each 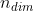 -element vector  along dimension `dim` is transformed as
%7D.%0D%0A%0D%0A)
With the default arguments it uses the Euclidean norm over vectors along dimension 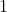 for normalization.
参数:
* **input** – input tensor of any shape
* **p** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")) – the exponent value in the norm formulation. 默认值: 2
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – the dimension to reduce. 默认值: 1
* **eps** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")) – small value to avoid division by zero. 默认值: 1e-12
* **out** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – the output tensor. If `out` is used, this operation won’t be differentiable.
|
| --- | --- |
## Linear functions
### linear
```py
torch.nn.functional.linear(input, weight, bias=None)
```
Applies a linear transformation to the incoming data: 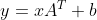.
Shape:
> * Input: ) where `*` means any number of additional dimensions
> * Weight: )
> * Bias: )
> * Output: )
### bilinear
```py
torch.nn.functional.bilinear(input1, input2, weight, bias=None)
```
## Dropout functions
### dropout
```py
torch.nn.functional.dropout(input, p=0.5, training=True, inplace=False)
```
During training, randomly zeroes some of the elements of the input tensor with probability `p` using samples from a Bernoulli distribution.
见 [`Dropout`](#torch.nn.Dropout "torch.nn.Dropout") for details.
参数:
* **p** – probability of an element to be zeroed. 默认值: 0.5
* **training** – apply dropout if is `True`. Defualt: `True`
* **inplace** – If set to `True`, will do this operation in-place. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
### alpha_dropout
```py
torch.nn.functional.alpha_dropout(input, p=0.5, training=False, inplace=False)
```
Applies alpha dropout to the input.
见 [`AlphaDropout`](#torch.nn.AlphaDropout "torch.nn.AlphaDropout") for details.
### dropout2d
```py
torch.nn.functional.dropout2d(input, p=0.5, training=True, inplace=False)
```
Randomly zero out entire channels (a channel is a 2D feature map, e.g., the 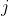-th channel of the 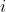-th sample in the batched input is a 2D tensor ) of the input tensor). Each channel will be zeroed out independently on every forward call. with probability `p` using samples from a Bernoulli distribution.
见 [`Dropout2d`](#torch.nn.Dropout2d "torch.nn.Dropout2d") for details.
参数:
* **p** – probability of a channel to be zeroed. 默认值: 0.5
* **training** – apply dropout if is `True`. Defualt: `True`
* **inplace** – If set to `True`, will do this operation in-place. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
### dropout3d
```py
torch.nn.functional.dropout3d(input, p=0.5, training=True, inplace=False)
```
Randomly zero out entire channels (a channel is a 3D feature map, e.g., the 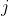-th channel of the 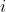-th sample in the batched input is a 3D tensor ) of the input tensor). Each channel will be zeroed out independently on every forward call. with probability `p` using samples from a Bernoulli distribution.
见 [`Dropout3d`](#torch.nn.Dropout3d "torch.nn.Dropout3d") for details.
参数:
* **p** – probability of a channel to be zeroed. 默认值: 0.5
* **training** – apply dropout if is `True`. Defualt: `True`
* **inplace** – If set to `True`, will do this operation in-place. 默认值: `False`
|
| --- | --- |
## Sparse functions
### embedding
```py
torch.nn.functional.embedding(input, weight, padding_idx=None, max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False, sparse=False)
```
A simple lookup table that looks up embeddings in a fixed dictionary and size.
This module is often used to retrieve word embeddings using indices. The input to the module is a list of indices, and the embedding matrix, and the output is the corresponding word embeddings.
见 [`torch.nn.Embedding`](#torch.nn.Embedding "torch.nn.Embedding") for more details.
参数:
* **input** (_LongTensor_) – Tensor containing indices into the embedding matrix
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – The embedding matrix with number of rows equal to the maximum possible index + 1, and number of columns equal to the embedding size
* **padding_idx** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – If given, pads the output with the embedding vector at `padding_idx` (initialized to zeros) whenever it encounters the index.
* **max_norm** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – If given, each embedding vector with norm larger than `max_norm` is renormalized to have norm `max_norm`. Note: this will modify `weight` in-place.
* **norm_type** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – The p of the p-norm to compute for the `max_norm` option. Default `2`.
* **scale_grad_by_freq** (_boolean__,_ _optional_) – If given, this will scale gradients by the inverse of frequency of the words in the mini-batch. Default `False`.
* **sparse** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – If `True`, gradient w.r.t. `weight` will be a sparse tensor. See Notes under [`torch.nn.Embedding`](#torch.nn.Embedding "torch.nn.Embedding") for more details regarding sparse gradients.
|
| --- | --- |
```py
Shape:
```
* Input: LongTensor of arbitrary shape containing the indices to extract
* ```py
Weight: Embedding matrix of floating point type with shape (V, embedding_dim),
```
where V = maximum index + 1 and embedding_dim = the embedding size
* Output: `(*, embedding_dim)`, where `*` is the input shape
例子:
```py
>>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each
>>> input = torch.tensor([[1,2,4,5],[4,3,2,9]])
>>> # an embedding matrix containing 10 tensors of size 3
>>> embedding_matrix = torch.rand(10, 3)
>>> F.embedding(input, embedding_matrix)
tensor([[[ 0.8490, 0.9625, 0.6753],
[ 0.9666, 0.7761, 0.6108],
[ 0.6246, 0.9751, 0.3618],
[ 0.4161, 0.2419, 0.7383]],
[[ 0.6246, 0.9751, 0.3618],
[ 0.0237, 0.7794, 0.0528],
[ 0.9666, 0.7761, 0.6108],
[ 0.3385, 0.8612, 0.1867]]])
>>> # example with padding_idx
>>> weights = torch.rand(10, 3)
>>> weights[0, :].zero_()
>>> embedding_matrix = weights
>>> input = torch.tensor([[0,2,0,5]])
>>> F.embedding(input, embedding_matrix, padding_idx=0)
tensor([[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.5609, 0.5384, 0.8720],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.6262, 0.2438, 0.7471]]])
```
### embedding_bag
```py
torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag(input, weight, offsets=None, max_norm=None, norm_type=2, scale_grad_by_freq=False, mode='mean', sparse=False)
```
Computes sums, means or maxes of ‘bags’ of embeddings, without instantiating the intermediate embeddings.
见 [`torch.nn.EmbeddingBag`](#torch.nn.EmbeddingBag "torch.nn.EmbeddingBag") for more details. .. include:: cuda_deterministic_backward.rst
参数:
* **input** (_LongTensor_) – Tensor containing bags of indices into the embedding matrix
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – The embedding matrix with number of rows equal to the maximum possible index + 1, and number of columns equal to the embedding size
* **offsets** (_LongTensor__,_ _optional_) – Only used when `input` is 1D. `offsets` determines the starting index position of each bag (sequence) in `input`.
* **max_norm** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – If given, each embedding vector with norm larger than `max_norm` is renormalized to have norm `max_norm`. Note: this will modify `weight` in-place.
* **norm_type** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – The `p` in the `p`-norm to compute for the `max_norm` option. Default `2`.
* **scale_grad_by_freq** (_boolean__,_ _optional_) – if given, this will scale gradients by the inverse of frequency of the words in the mini-batch. Default `False`. Note: this option is not supported when `mode="max"`.
* **mode** (_string__,_ _optional_) – `"sum"`, `"mean"` or `"max"`. Specifies the way to reduce the bag. 默认值: `"mean"`
* **sparse** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – if `True`, gradient w.r.t. `weight` will be a sparse tensor. See Notes under [`torch.nn.Embedding`](#torch.nn.Embedding "torch.nn.Embedding") for more details regarding sparse gradients. Note: this option is not supported when `mode="max"`.
|
| --- | --- |
Shape:
> * `input` (LongTensor) and `offsets` (LongTensor, optional)
>
>
> * If `input` is 2D of shape `B x N`,
>
>
>
> it will be treated as `B` bags (sequences) each of fixed length `N`, and this will return `B` values aggregated in a way depending on the `mode`. `offsets` is ignored and required to be `None` in this case.
>
>
> * If `input` is 1D of shape `N`,
>
>
>
> it will be treated as a concatenation of multiple bags (sequences). `offsets` is required to be a 1D tensor containing the starting index positions of each bag in `input`. Therefore, for `offsets` of shape `B`, `input` will be viewed as having `B` bags. Empty bags (i.e., having 0-length) will have returned vectors filled by zeros.
>
>
> * `weight` (Tensor): the learnable weights of the module of shape `(num_embeddings x embedding_dim)`
>
>
> * `output`: aggregated embedding values of shape `B x embedding_dim`
例子:
```py
>>> # an Embedding module containing 10 tensors of size 3
>>> embedding_matrix = torch.rand(10, 3)
>>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each
>>> input = torch.tensor([1,2,4,5,4,3,2,9])
>>> offsets = torch.tensor([0,4])
>>> F.embedding_bag(embedding_matrix, input, offsets)
tensor([[ 0.3397, 0.3552, 0.5545],
[ 0.5893, 0.4386, 0.5882]])
```
## Distance functions
### pairwise_distance
```py
torch.nn.functional.pairwise_distance(x1, x2, p=2.0, eps=1e-06, keepdim=False)
```
见 [`torch.nn.PairwiseDistance`](#torch.nn.PairwiseDistance "torch.nn.PairwiseDistance") for details
### cosine_similarity
```py
torch.nn.functional.cosine_similarity(x1, x2, dim=1, eps=1e-8) → Tensor
```
Returns cosine similarity between x1 and x2, computed along dim.
%7D%0D%0A%0D%0A)
参数:
* **x1** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – First input.
* **x2** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – Second input (of size matching x1).
* **dim** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Dimension of vectors. 默认值: 1
* **eps** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Small value to avoid division by zero. 默认值: 1e-8
|
| --- | --- |
```py
Shape:
```
* Input: ) where D is at position `dim`.
* Output: ) where 1 is at position `dim`.
Example:
```py
>>> input1 = torch.randn(100, 128)
>>> input2 = torch.randn(100, 128)
>>> output = F.cosine_similarity(input1, input2)
>>> print(output)
```
### pdist
```py
torch.nn.functional.pdist(input, p=2) → Tensor
```
Computes the p-norm distance between every pair of row vectors in the input. This is identical to the upper triangular portion, excluding the diagonal, of `torch.norm(input[:, None] - input, dim=2, p=p)`. This function will be faster if the rows are contiguous.
If input has shape 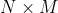 then the output will have shape ).
This function is equivalent to `scipy.spatial.distance.pdist(input, ‘minkowski’, p=p)` if ). When 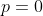 it is equivalent to `scipy.spatial.distance.pdist(input, ‘hamming’) * M`. When 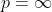, the closest scipy function is `scipy.spatial.distance.pdist(xn, lambda x, y: np.abs(x - y).max())`.
参数:
* **input** – 输入tensor, 形状为 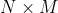.
* **p** – p value for the p-norm distance to calculate between each vector pair 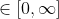.
|
| --- | --- |
## Loss functions
### binary_cross_entropy
```py
torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy(input, target, weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
Function that measures the Binary Cross Entropy between the target and the output.
见 [`BCELoss`](#torch.nn.BCELoss "torch.nn.BCELoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** – Tensor of arbitrary shape
* **target** – Tensor of the same shape as input
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – a manual rescaling weight if provided it’s repeated to match input tensor shape
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output, ‘sum’: the output will be summed. Note: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated, and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> input = torch.randn((3, 2), requires_grad=True)
>>> target = torch.rand((3, 2), requires_grad=False)
>>> loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(F.sigmoid(input), target)
>>> loss.backward()
```
### binary_cross_entropy_with_logits
```py
torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, target, weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)
```
Function that measures Binary Cross Entropy between target and output logits.
见 [`BCEWithLogitsLoss`](#torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss "torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** – Tensor of arbitrary shape
* **target** – Tensor of the same shape as input
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – a manual rescaling weight if provided it’s repeated to match input tensor shape
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output, ‘sum’: the output will be summed. Note: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated, and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. 默认值: ‘mean’
* **pos_weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – a weight of positive examples. Must be a vector with length equal to the number of classes.
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
>>> target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
>>> loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, target)
>>> loss.backward()
```
### poisson_nll_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.poisson_nll_loss(input, target, log_input=True, full=False, size_average=None, eps=1e-08, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
Poisson negative log likelihood loss.
见 [`PoissonNLLLoss`](#torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss "torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** – expectation of underlying Poisson distribution.
* **target** – random sample ).
* **log_input** – if `True` the loss is computed as %20-%20%5Ctext%7Btarget%7D%20*%20%5Ctext%7Binput%7D), if `False` then loss is ). 默认值: `True`
* **full** – whether to compute full loss, i. e. to add the Stirling approximation term. 默认值: `False` %20-%20%5Ctext%7Btarget%7D%20%2B%200.5%20*%20%5Clog(2%20*%20%5Cpi%20*%20%5Ctext%7Btarget%7D)).
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **eps** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Small value to avoid evaluation of ) when `log_input`=``False``. 默认值: 1e-8
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output, ‘sum’: the output will be summed. Note: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated, and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
### cosine_embedding_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.cosine_embedding_loss(input1, input2, target, margin=0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
见 [`CosineEmbeddingLoss`](#torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss "torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss") for details.
### cross_entropy
```py
torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(input, target, weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
This criterion combines `log_softmax` and `nll_loss` in a single function.
见 [`CrossEntropyLoss`](#torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss "torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – ) where `C = number of classes` or ) in case of 2D Loss, or ) where 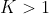 in the case of K-dimensional loss.
* **target** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – ) where each value is 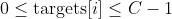, or ) where 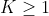 for K-dimensional loss.
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – a manual rescaling weight given to each class. If given, has to be a Tensor of size `C`
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **ignore_index** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the input gradient. When `size_average` is `True`, the loss is averaged over non-ignored targets. 默认值: -100
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output, ‘sum’: the output will be summed. Note: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated, and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
>>> target = torch.randint(5, (3,), dtype=torch.int64)
>>> loss = F.cross_entropy(input, target)
>>> loss.backward()
```
### ctc_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.ctc_loss(log_probs, targets, input_lengths, target_lengths, blank=0, reduction='mean')
```
The Connectionist Temporal Classification loss.
见 [`CTCLoss`](#torch.nn.CTCLoss "torch.nn.CTCLoss") for details.
注意
在某些情况下, 当使用CUDA后端与CuDNN时, 该操作符可能会选择不确定性算法来提高性能. 如果这不是您希望的, 您可以通过设置`torch.backends.cudn .deterministic = True`来尝试使操作具有确定性(可能会以性能为代价). 请参阅关于 [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) 了解背景.
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
参数:
* **log_probs** – ) where `C = number of characters in alphabet including blank`, `T = input length`, and `N = batch size`. The logarithmized probabilities of the outputs (e.g. obtained with [`torch.nn.functional.log_softmax()`](#torch.nn.functional.log_softmax "torch.nn.functional.log_softmax")).
* **targets** – ) or `(sum(target_lengths))`. Targets (cannot be blank). In the second form, the targets are assumed to be concatenated.
* **input_lengths** – ). Lengths of the inputs (must each be 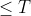)
* **target_lengths** – ). Lengths of the targets
* **blank** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Blank label. Default 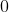.
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the output losses will be divided by the target lengths and then the mean over the batch is taken. 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
Example:
```py
>>> log_probs = torch.randn(50, 16, 20).log_softmax(2).detach().requires_grad_()
>>> targets = torch.randint(1, 20, (16, 30), dtype=torch.long)
>>> input_lengths = torch.full((16,), 50, dtype=torch.long)
>>> target_lengths = torch.randint(10,30,(16,), dtype=torch.long)
>>> loss = F.ctc_loss(log_probs, targets, input_lengths, target_lengths)
>>> loss.backward()
```
### hinge_embedding_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.hinge_embedding_loss(input, target, margin=1.0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
见 [`HingeEmbeddingLoss`](#torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss "torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss") for details.
### kl_div
```py
torch.nn.functional.kl_div(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
The [Kullback-Leibler divergence](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kullback-Leibler_divergence) Loss.
见 [`KLDivLoss`](#torch.nn.KLDivLoss "torch.nn.KLDivLoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** – Tensor of arbitrary shape
* **target** – Tensor of the same shape as input
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘batchmean’ | ‘sum’ | ‘mean’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied ‘batchmean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the batchsize ‘sum’: the output will be summed ‘mean’: the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
:param .. note:: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated,: and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. :param .. note:: `reduction=’mean’` doesn’t return the true kl divergence value, please use: `reduction=’batchmean’` which aligns with KL math definition.
> In the next major release, ‘mean’ will be changed to be the same as ‘batchmean’.
### l1_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.l1_loss(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
Function that takes the mean element-wise absolute value difference.
见 [`L1Loss`](#torch.nn.L1Loss "torch.nn.L1Loss") for details.
### mse_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
Measures the element-wise mean squared error.
见 [`MSELoss`](#torch.nn.MSELoss "torch.nn.MSELoss") for details.
### margin_ranking_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.margin_ranking_loss(input1, input2, target, margin=0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
见 [`MarginRankingLoss`](#torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss "torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss") for details.
### multilabel_margin_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.multilabel_margin_loss(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
见 [`MultiLabelMarginLoss`](#torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss "torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss") for details.
### multilabel_soft_margin_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.multilabel_soft_margin_loss(input, target, weight=None, size_average=None) → Tensor
```
见 [`MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss`](#torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss "torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss") for details.
### multi_margin_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.multi_margin_loss(input, target, p=1, margin=1.0, weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
```py
multi_margin_loss(input, target, p=1, margin=1, weight=None, size_average=None,
```
reduce=None, reduction=’mean’) -> Tensor
见 [`MultiMarginLoss`](#torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss "torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss") for details.
### nll_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.nll_loss(input, target, weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
The negative log likelihood loss.
见 [`NLLLoss`](#torch.nn.NLLLoss "torch.nn.NLLLoss") for details.
参数:
* **input** – ) where `C = number of classes` or ) in case of 2D Loss, or ) where 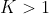 in the case of K-dimensional loss.
* **target** – ) where each value is 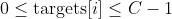, or ) where 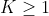 for K-dimensional loss.
* **weight** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")_,_ _optional_) – a manual rescaling weight given to each class. If given, has to be a Tensor of size `C`
* **size_average** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field `size_average` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is `False`. 默认值: `True`
* **ignore_index** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the input gradient. When `size_average` is `True`, the loss is averaged over non-ignored targets. 默认值: -100
* **reduce** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – Deprecated (see `reduction`). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on `size_average`. When `reduce` is `False`, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores `size_average`. 默认值: `True`
* **reduction** (_string__,_ _optional_) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: ‘none’ | ‘mean’ | ‘sum’. ‘none’: no reduction will be applied, ‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output, ‘sum’: the output will be summed. Note: `size_average` and `reduce` are in the process of being deprecated, and in the meantime, specifying either of those two args will override `reduction`. 默认值: ‘mean’
|
| --- | --- |
Example:
```py
>>> # input is of size N x C = 3 x 5
>>> input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
>>> # each element in target has to have 0 <= value < C
>>> target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 4])
>>> output = F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(input), target)
>>> output.backward()
```
### smooth_l1_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.smooth_l1_loss(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
Function that uses a squared term if the absolute element-wise error falls below 1 and an L1 term otherwise.
见 [`SmoothL1Loss`](#torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss "torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss") for details.
### soft_margin_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.soft_margin_loss(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') → Tensor
```
见 [`SoftMarginLoss`](#torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss "torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss") for details.
### triplet_margin_loss
```py
torch.nn.functional.triplet_margin_loss(anchor, positive, negative, margin=1.0, p=2, eps=1e-06, swap=False, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
```
见 [`TripletMarginLoss`](#torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss "torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss") for details
## Vision functions
### pixel_shuffle
```py
torch.nn.functional.pixel_shuffle()
```
Rearranges elements in a tensor of shape ) to a tensor of shape ).
见 [`PixelShuffle`](#torch.nn.PixelShuffle "torch.nn.PixelShuffle") for details.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – the input tensor
* **upscale_factor** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – factor to increase spatial resolution by
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> input = torch.randn(1, 9, 4, 4)
>>> output = torch.nn.functional.pixel_shuffle(input, 3)
>>> print(output.size())
torch.Size([1, 1, 12, 12])
```
### pad
```py
torch.nn.functional.pad(input, pad, mode='constant', value=0)
```
Pads tensor.
```py
Pading size:
```
The number of dimensions to pad is %7D%7D%7B2%7D%5Cright%5Crfloor) and the dimensions that get padded begins with the last dimension and moves forward. For example, to pad the last dimension of the input tensor, then pad has form (padLeft, padRight); to pad the last 2 dimensions of the input tensor, then use (padLeft, padRight, padTop, padBottom); to pad the last 3 dimensions, use (padLeft, padRight, padTop, padBottom, padFront, padBack).
```py
Padding mode:
```
见 [`torch.nn.ConstantPad2d`](#torch.nn.ConstantPad2d "torch.nn.ConstantPad2d"), [`torch.nn.ReflectionPad2d`](#torch.nn.ReflectionPad2d "torch.nn.ReflectionPad2d"), and [`torch.nn.ReplicationPad2d`](#torch.nn.ReplicationPad2d "torch.nn.ReplicationPad2d") for concrete examples on how each of the padding modes works. Constant padding is implemented for arbitrary dimensions. Replicate padding is implemented for padding the last 3 dimensions of 5D input tensor, or the last 2 dimensions of 4D input tensor, or the last dimension of 3D input tensor. Reflect padding is only implemented for padding the last 2 dimensions of 4D input tensor, or the last dimension of 3D input tensor.
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – `Nd` tensor
* **pad** ([_tuple_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#tuple "(in Python v3.7)")) – m-elem tuple, where 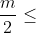 input dimensions and 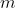 is even.
* **mode** – ‘constant’, ‘reflect’ or ‘replicate’. 默认值: ‘constant’
* **value** – fill value for ‘constant’ padding. 默认值: 0
|
| --- | --- |
例子:
```py
>>> t4d = torch.empty(3, 3, 4, 2)
>>> p1d = (1, 1) # pad last dim by 1 on each side
>>> out = F.pad(t4d, p1d, "constant", 0) # effectively zero padding
>>> print(out.data.size())
torch.Size([3, 3, 4, 4])
>>> p2d = (1, 1, 2, 2) # pad last dim by (1, 1) and 2nd to last by (2, 2)
>>> out = F.pad(t4d, p2d, "constant", 0)
>>> print(out.data.size())
torch.Size([3, 3, 8, 4])
>>> t4d = torch.empty(3, 3, 4, 2)
>>> p3d = (0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 3) # pad by (0, 1), (2, 1), and (3, 3)
>>> out = F.pad(t4d, p3d, "constant", 0)
>>> print(out.data.size())
torch.Size([3, 9, 7, 3])
```
### interpolate
```py
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None)
```
Down/up samples the input to either the given `size` or the given `scale_factor`
The algorithm used for interpolation is determined by `mode`.
Currently temporal, spatial and volumetric sampling are supported, i.e. expected inputs are 3-D, 4-D or 5-D in shape.
The input dimensions are interpreted in the form: `mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width`.
The modes available for resizing are: `nearest`, `linear` (3D-only), `bilinear` (4D-only), `trilinear` (5D-only), `area`
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – the input tensor
* **size** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_] or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_] or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – output spatial size.
* **scale_factor** ([_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_float_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#float "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – multiplier for spatial size. Has to match input size if it is a tuple.
* **mode** (_string_) – algorithm used for upsampling: ‘nearest’ | ‘linear’ | ‘bilinear’ | ‘trilinear’ | ‘area’. 默认值: ‘nearest’
* **align_corners** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – if True, the corner pixels of the input and output tensors are aligned, and thus preserving the values at those pixels. This only has effect when `mode` is `linear`, `bilinear`, or `trilinear`. 默认值: False
|
| --- | --- |
警告
With `align_corners = True`, the linearly interpolating modes (`linear`, `bilinear`, and `trilinear`) don’t proportionally align the output and input pixels, and thus the output values can depend on the input size. This was the default behavior for these modes up to version 0.3.1\. Since then, the default behavior is `align_corners = False`. 见 [`Upsample`](#torch.nn.Upsample "torch.nn.Upsample") for concrete examples on how this affects the outputs.
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
### upsample
```py
torch.nn.functional.upsample(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None)
```
Upsamples the input to either the given `size` or the given `scale_factor`
警告
This function is deprecated in favor of [`torch.nn.functional.interpolate()`](#torch.nn.functional.interpolate "torch.nn.functional.interpolate"). This is equivalent with `nn.functional.interpolate(...)`.
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
The algorithm used for upsampling is determined by `mode`.
Currently temporal, spatial and volumetric upsampling are supported, i.e. expected inputs are 3-D, 4-D or 5-D in shape.
The input dimensions are interpreted in the form: `mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width`.
The modes available for upsampling are: `nearest`, `linear` (3D-only), `bilinear` (4D-only), `trilinear` (5D-only)
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – the input tensor
* **size** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_] or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_] or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – output spatial size.
* **scale_factor** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – multiplier for spatial size. Has to be an integer.
* **mode** (_string_) – algorithm used for upsampling: ‘nearest’ | ‘linear’ | ‘bilinear’ | ‘trilinear’. 默认值: ‘nearest’
* **align_corners** ([_bool_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#bool "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ _optional_) – if True, the corner pixels of the input and output tensors are aligned, and thus preserving the values at those pixels. This only has effect when `mode` is `linear`, `bilinear`, or `trilinear`. 默认值: False
|
| --- | --- |
警告
With `align_corners = True`, the linearly interpolating modes (`linear`, `bilinear`, and `trilinear`) don’t proportionally align the output and input pixels, and thus the output values can depend on the input size. This was the default behavior for these modes up to version 0.3.1\. Since then, the default behavior is `align_corners = False`. 见 [`Upsample`](#torch.nn.Upsample "torch.nn.Upsample") for concrete examples on how this affects the outputs.
### upsample_nearest
```py
torch.nn.functional.upsample_nearest(input, size=None, scale_factor=None)
```
Upsamples the input, using nearest neighbours’ pixel values.
警告
This function is deprecated in favor of [`torch.nn.functional.interpolate()`](#torch.nn.functional.interpolate "torch.nn.functional.interpolate"). This is equivalent with `nn.functional.interpolate(..., mode='nearest')`.
Currently spatial and volumetric upsampling are supported (i.e. expected inputs are 4 or 5 dimensional).
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input
* **size** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_] or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – output spatia size.
* **scale_factor** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")) – multiplier for spatial size. Has to be an integer.
|
| --- | --- |
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
### upsample_bilinear
```py
torch.nn.functional.upsample_bilinear(input, size=None, scale_factor=None)
```
Upsamples the input, using bilinear upsampling.
警告
This function is deprecated in favor of [`torch.nn.functional.interpolate()`](#torch.nn.functional.interpolate "torch.nn.functional.interpolate"). This is equivalent with `nn.functional.interpolate(..., mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)`.
Expected inputs are spatial (4 dimensional). Use `upsample_trilinear` fo volumetric (5 dimensional) inputs.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input
* **size** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – output spatial size.
* **scale_factor** ([_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)") _or_ _Tuple__[_[_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_,_ [_int_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int "(in Python v3.7)")_]_) – multiplier for spatial size
|
| --- | --- |
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
### grid_sample
```py
torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(input, grid, mode='bilinear', padding_mode='zeros')
```
Given an `input` and a flow-field `grid`, computes the `output` using `input` values and pixel locations from `grid`.
Currently, only spatial (4-D) and volumetric (5-D) `input` are supported.
In the spatial (4-D) case, for `input` with shape ) and `grid` with shape ), the output will have shape ).
For each output location `output[n, :, h, w]`, the size-2 vector `grid[n, h, w]` specifies `input` pixel locations `x` and `y`, which are used to interpolate the output value `output[n, :, h, w]`. In the case of 5D inputs, `grid[n, d, h, w]` specifies the `x`, `y`, `z` pixel locations for interpolating `output[n, :, d, h, w]`. `mode` argument specifies `nearest` or `bilinear` interpolation method to sample the input pixels.
`grid` should have most values in the range of `[-1, 1]`. This is because the pixel locations are normalized by the `input` spatial dimensions. For example, values `x = -1, y = -1` is the left-top pixel of `input`, and values `x = 1, y = 1` is the right-bottom pixel of `input`.
If `grid` has values outside the range of `[-1, 1]`, those locations are handled as defined by `padding_mode`. Options are
> * `padding_mode="zeros"`: use `0` for out-of-bound values,
> * `padding_mode="border"`: use border values for out-of-bound values,
> * `padding_mode="reflection"`: use values at locations reflected by the border for out-of-bound values. For location far away from the border, it will keep being reflected until becoming in bound, e.g., (normalized) pixel location `x = -3.5` reflects by `-1` and becomes `x' = 2.5`, then reflects by border `1` and becomes `x'' = -0.5`.
注意
This function is often used in building Spatial Transformer Networks.
注意
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on [Reproducibility](notes/randomness.html) for background.
参数:
* **input** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input of shape ) (4-D case) or ) (5-D case)
* **grid** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – flow-field of shape ) (4-D case) or ) (5-D case)
* **mode** ([_str_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str "(in Python v3.7)")) – interpolation mode to calculate output values ‘bilinear’ | ‘nearest’. 默认值: ‘bilinear’
* **padding_mode** ([_str_](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str "(in Python v3.7)")) – padding mode for outside grid values ‘zeros’ | ‘border’ | ‘reflection’. 默认值: ‘zeros’
|
| --- | --- |
| Returns: | output Tensor |
| --- | --- |
| Return type: | output ([Tensor](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) |
| --- | --- |
### affine_grid
```py
torch.nn.functional.affine_grid(theta, size)
```
Generates a 2d flow field, given a batch of affine matrices `theta` Generally used in conjunction with [`grid_sample()`](#torch.nn.functional.grid_sample "torch.nn.functional.grid_sample") to implement Spatial Transformer Networks.
参数:
* **theta** ([_Tensor_](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) – input batch of affine matrices (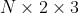)
* **size** (_torch.Size_) – the target output image size (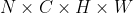) Example: torch.Size((32, 3, 24, 24))
|
| --- | --- |
| Returns: | output Tensor of size (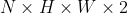) |
| --- | --- |
| Return type: | output ([Tensor](tensors.html#torch.Tensor "torch.Tensor")) |
| --- | --- |
## DataParallel functions (multi-GPU, distributed)
### data_parallel
```py
torch.nn.parallel.data_parallel(module, inputs, device_ids=None, output_device=None, dim=0, module_kwargs=None)
```
Evaluates module(input) in parallel across the GPUs given in device_ids.
This is the functional version of the DataParallel module.
参数:
* **module** ([_Module_](#torch.nn.Module "torch.nn.Module")) – the module to evaluate in parallel
* **inputs** (_tensor_) – inputs to the module
* **device_ids** (_list of python:int_ _or_ [_torch.device_](tensor_attributes.html#torch.torch.device "torch.torch.device")) – GPU ids on which to replicate module
* **output_device** (_list of python:int_ _or_ [_torch.device_](tensor_attributes.html#torch.torch.device "torch.torch.device")) – GPU location of the output Use -1 to indicate the CPU. (默认值: device_ids[0])
|
| --- | --- |
| Returns: | a Tensor containing the result of module(input) located on output_device |
| --- | --- |