# Building PaddlePaddle
## Goals
We want to make the building procedures:
1. Static, can reproduce easily.
1. Generate python `whl` packages that can be widely use cross many distributions.
1. Build different binaries per release to satisfy different environments:
- Binaries for different CUDA and CUDNN versions, like CUDA 7.5, 8.0, 9.0
- Binaries containing only capi
- Binaries for python with wide unicode support or not.
1. Build docker images with PaddlePaddle pre-installed, so that we can run
PaddlePaddle applications directly in docker or on Kubernetes clusters.
To achieve this, we maintain a dockerhub repo:https://hub.docker.com/r/paddlepaddle/paddle
which provides pre-built environment images to build PaddlePaddle and generate corresponding `whl`
binaries.(**We strongly recommend building paddlepaddle in our pre-specified Docker environment.**)
## Development Workflow
Here we describe how the workflow goes on. We start from considering our daily development environment.
Developers work on a computer, which is usually a laptop or desktop:
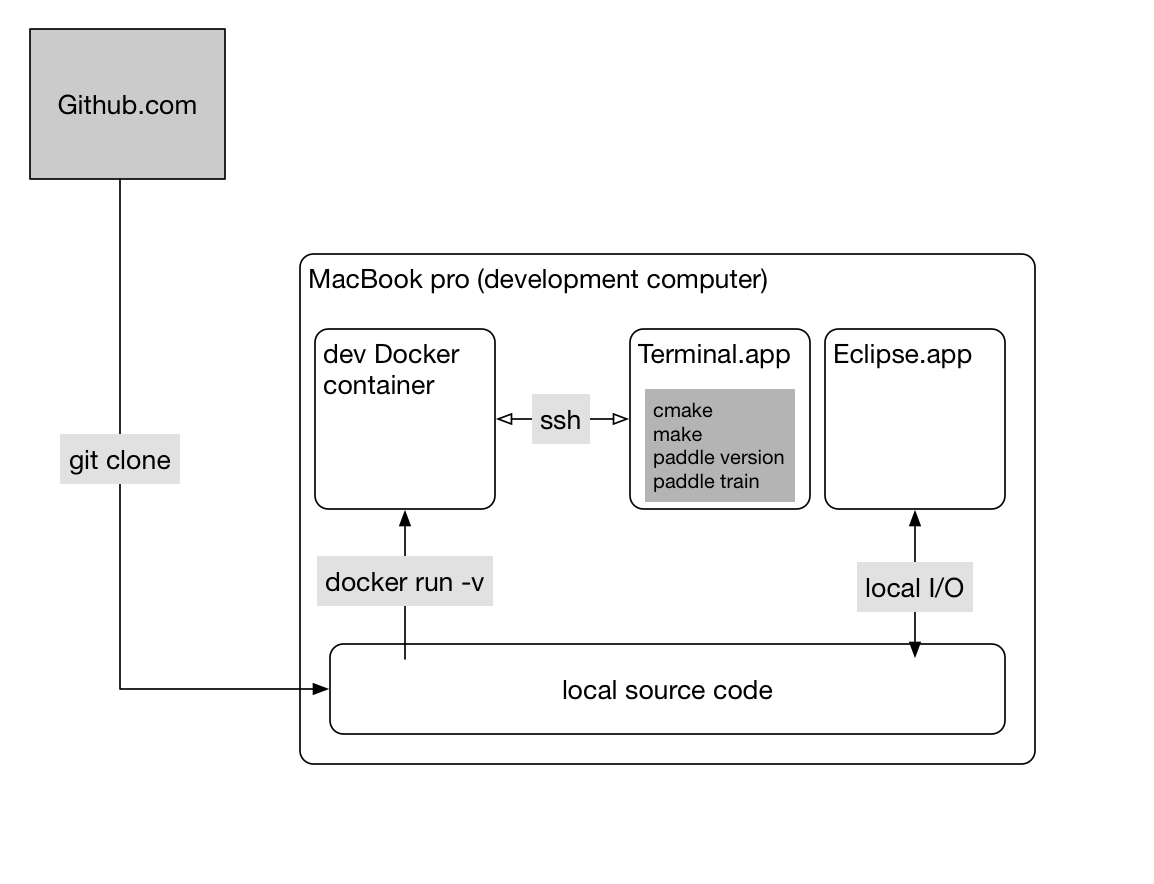 or, they might rely on a more sophisticated box (like with GPUs):
or, they might rely on a more sophisticated box (like with GPUs):
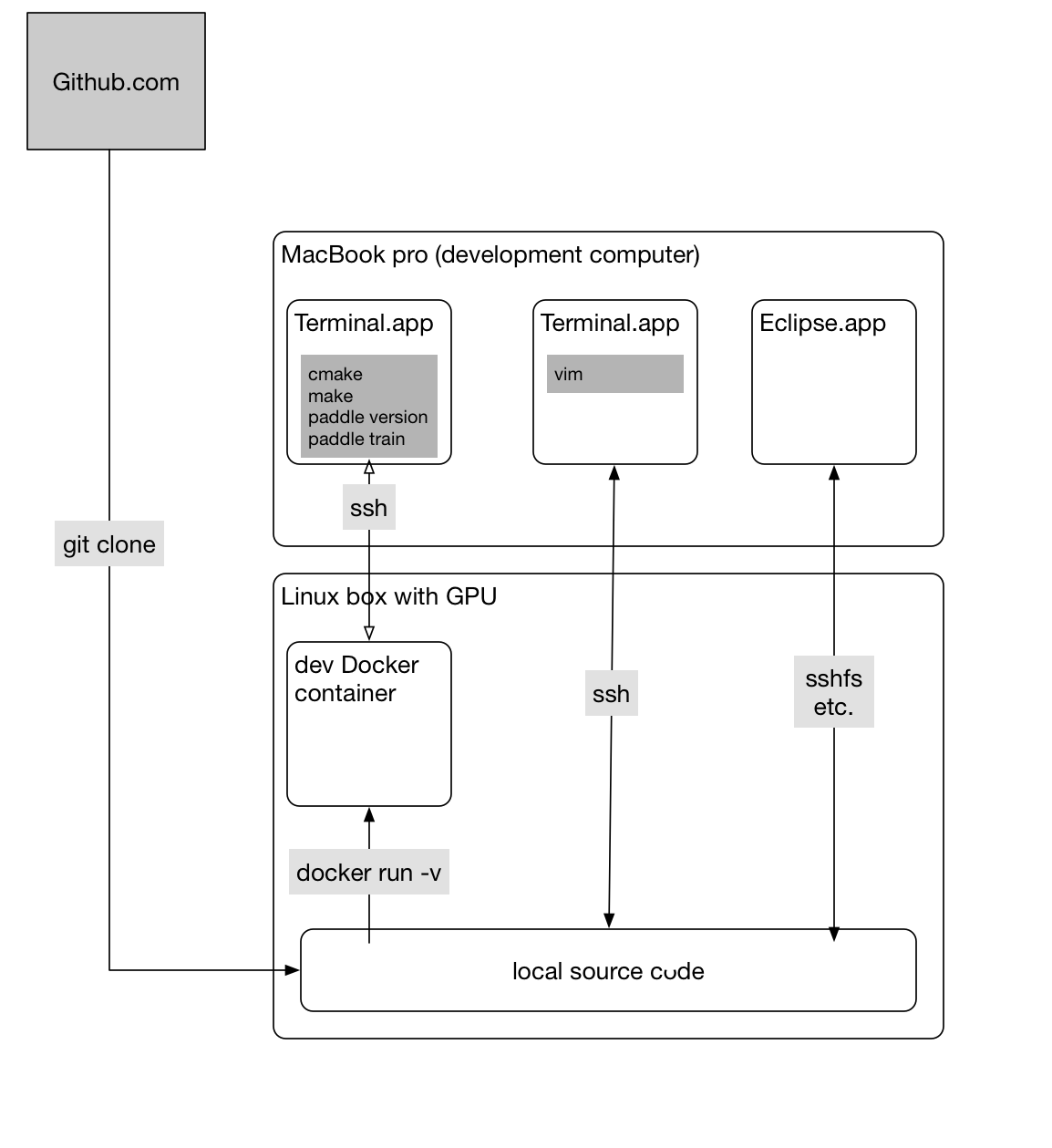 A principle here is that source code lies on the development computer (host) so that editors like Eclipse can parse the source code to support auto-completion.
## Build With Docker
### Build Environments
The lastest pre-built build environment images are:
| Image | Tag |
| ----- | --- |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev-android |
### Start Build
```bash
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
cd Paddle
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh build
```
After the build finishes, you can get output `whl` package under
`build/python/dist`.
This command will download the most recent dev image from docker hub, start a container in the backend and then run the build script `/paddle/paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build` in the container.
The container mounts the source directory on the host into `/paddle`.
When it writes to `/paddle/build` in the container, it writes to `$PWD/build` on the host indeed.
### Build Options
Users can specify the following Docker build arguments with either "ON" or "OFF" value:
| Option | Default | Description |
| ------ | -------- | ----------- |
| `WITH_GPU` | OFF | Generates NVIDIA CUDA GPU code and relies on CUDA libraries. |
| `WITH_AVX` | OFF | Set to "ON" to enable AVX support. |
| `WITH_TESTING` | OFF | Build unit tests binaries. |
| `WITH_MKL` | ON | Build with [Intel® MKL](https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl) and [Intel® MKL-DNN](https://github.com/01org/mkl-dnn) support. |
| `WITH_GOLANG` | OFF | Build fault-tolerant parameter server written in go. |
| `WITH_SWIG_PY` | ON | Build with SWIG python API support. |
| `WITH_C_API` | OFF | Build capi libraries for inference. |
| `WITH_PYTHON` | ON | Build with python support. Turn this off if build is only for capi. |
| `WITH_STYLE_CHECK` | ON | Check the code style when building. |
| `PYTHON_ABI` | "" | Build for different python ABI support, can be cp27-cp27m or cp27-cp27mu |
| `RUN_TEST` | OFF | Run unit test immediently after the build. |
| `WITH_DOC` | OFF | Build docs after build binaries. |
| `WOBOQ` | OFF | Generate WOBOQ code viewer under `build/woboq_out` |
## Docker Images
You can get the latest PaddlePaddle docker images by
`docker pull paddlepaddle/paddle:` or build one by yourself.
### Official Docker Releases
Official docker images at
[here](https://hub.docker.com/r/paddlepaddle/paddle/tags/),
you can choose either latest or images with a release tag like `0.10.0`,
Currently available tags are:
| Tag | Description |
| ------ | --------------------- |
| latest | latest CPU only image |
| latest-gpu | latest binary with GPU support |
| 0.10.0 | release 0.10.0 CPU only binary image |
| 0.10.0-gpu | release 0.10.0 with GPU support |
### Build Your Own Image
Build PaddlePaddle docker images are quite simple since PaddlePaddle can
be installed by just running `pip install`. A sample `Dockerfile` is:
```dockerfile
FROM nvidia/cuda:7.5-cudnn5-runtime-centos6
RUN yum install -y centos-release-SCL
RUN yum install -y python27
# This whl package is generated by previous build steps.
ADD python/dist/paddlepaddle-0.10.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whl /
RUN pip install /paddlepaddle-0.10.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whl && rm -f /*.whl
```
Then build the image by running `docker build -t [REPO]/paddle:[TAG] .` under
the directory containing your own `Dockerfile`.
- NOTE: note that you can choose different base images for your environment, you can find all the versions [here](https://hub.docker.com/r/nvidia/cuda/).
### Use Docker Images
Suppose that you have written an application program `train.py` using
PaddlePaddle, we can test and run it using docker:
```bash
docker run --rm -it -v $PWD:/work paddlepaddle/paddle /work/a.py
```
But this works only if all dependencies of `train.py` are in the production image. If this is not the case, we need to build a new Docker image from the production image and with more dependencies installs.
### Run PaddlePaddle Book In Docker
Our [book repo](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/book) also provide a docker
image to start a jupiter notebook inside docker so that you can run this book
using docker:
```bash
docker run -d -p 8888:8888 paddlepaddle/book
```
Please refer to https://github.com/paddlepaddle/book if you want to build this
docker image by your self.
### Run Distributed Applications
In our [API design doc](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/doc/design/api.md#distributed-training), we proposed an API that starts a distributed training job on a cluster. This API need to build a PaddlePaddle application into a Docker image as above and calls kubectl to run it on the cluster. This API might need to generate a Dockerfile look like above and call `docker build`.
Of course, we can manually build an application image and launch the job using the kubectl tool:
```bash
docker build -f some/Dockerfile -t myapp .
docker tag myapp me/myapp
docker push
kubectl ...
```
### Reading source code with woboq codebrowser
For developers who are interested in the C++ source code, you can build C++ source code into HTML pages using [Woboq codebrowser](https://github.com/woboq/woboq_codebrowser).
- The following command builds PaddlePaddle, generates HTML pages from C++ source code, and writes HTML pages into `$HOME/woboq_out` on the host:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh html
```
- You can open the generated HTML files in your Web browser. Or, if you want to run a Nginx container to serve them for a wider audience, you can run:
```
docker run -v $HOME/woboq_out:/usr/share/nginx/html -d -p 8080:80 nginx
```
## More Options
### Build Without Docker
Follow the *Dockerfile* in the paddlepaddle repo to set up your local dev environment and run:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build
```
### Additional Tasks
You can get the help menu for the build scripts by running with no options:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh
or ./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh
```
A principle here is that source code lies on the development computer (host) so that editors like Eclipse can parse the source code to support auto-completion.
## Build With Docker
### Build Environments
The lastest pre-built build environment images are:
| Image | Tag |
| ----- | --- |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev-android |
### Start Build
```bash
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
cd Paddle
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh build
```
After the build finishes, you can get output `whl` package under
`build/python/dist`.
This command will download the most recent dev image from docker hub, start a container in the backend and then run the build script `/paddle/paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build` in the container.
The container mounts the source directory on the host into `/paddle`.
When it writes to `/paddle/build` in the container, it writes to `$PWD/build` on the host indeed.
### Build Options
Users can specify the following Docker build arguments with either "ON" or "OFF" value:
| Option | Default | Description |
| ------ | -------- | ----------- |
| `WITH_GPU` | OFF | Generates NVIDIA CUDA GPU code and relies on CUDA libraries. |
| `WITH_AVX` | OFF | Set to "ON" to enable AVX support. |
| `WITH_TESTING` | OFF | Build unit tests binaries. |
| `WITH_MKL` | ON | Build with [Intel® MKL](https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl) and [Intel® MKL-DNN](https://github.com/01org/mkl-dnn) support. |
| `WITH_GOLANG` | OFF | Build fault-tolerant parameter server written in go. |
| `WITH_SWIG_PY` | ON | Build with SWIG python API support. |
| `WITH_C_API` | OFF | Build capi libraries for inference. |
| `WITH_PYTHON` | ON | Build with python support. Turn this off if build is only for capi. |
| `WITH_STYLE_CHECK` | ON | Check the code style when building. |
| `PYTHON_ABI` | "" | Build for different python ABI support, can be cp27-cp27m or cp27-cp27mu |
| `RUN_TEST` | OFF | Run unit test immediently after the build. |
| `WITH_DOC` | OFF | Build docs after build binaries. |
| `WOBOQ` | OFF | Generate WOBOQ code viewer under `build/woboq_out` |
## Docker Images
You can get the latest PaddlePaddle docker images by
`docker pull paddlepaddle/paddle:` or build one by yourself.
### Official Docker Releases
Official docker images at
[here](https://hub.docker.com/r/paddlepaddle/paddle/tags/),
you can choose either latest or images with a release tag like `0.10.0`,
Currently available tags are:
| Tag | Description |
| ------ | --------------------- |
| latest | latest CPU only image |
| latest-gpu | latest binary with GPU support |
| 0.10.0 | release 0.10.0 CPU only binary image |
| 0.10.0-gpu | release 0.10.0 with GPU support |
### Build Your Own Image
Build PaddlePaddle docker images are quite simple since PaddlePaddle can
be installed by just running `pip install`. A sample `Dockerfile` is:
```dockerfile
FROM nvidia/cuda:7.5-cudnn5-runtime-centos6
RUN yum install -y centos-release-SCL
RUN yum install -y python27
# This whl package is generated by previous build steps.
ADD python/dist/paddlepaddle-0.10.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whl /
RUN pip install /paddlepaddle-0.10.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whl && rm -f /*.whl
```
Then build the image by running `docker build -t [REPO]/paddle:[TAG] .` under
the directory containing your own `Dockerfile`.
- NOTE: note that you can choose different base images for your environment, you can find all the versions [here](https://hub.docker.com/r/nvidia/cuda/).
### Use Docker Images
Suppose that you have written an application program `train.py` using
PaddlePaddle, we can test and run it using docker:
```bash
docker run --rm -it -v $PWD:/work paddlepaddle/paddle /work/a.py
```
But this works only if all dependencies of `train.py` are in the production image. If this is not the case, we need to build a new Docker image from the production image and with more dependencies installs.
### Run PaddlePaddle Book In Docker
Our [book repo](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/book) also provide a docker
image to start a jupiter notebook inside docker so that you can run this book
using docker:
```bash
docker run -d -p 8888:8888 paddlepaddle/book
```
Please refer to https://github.com/paddlepaddle/book if you want to build this
docker image by your self.
### Run Distributed Applications
In our [API design doc](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/doc/design/api.md#distributed-training), we proposed an API that starts a distributed training job on a cluster. This API need to build a PaddlePaddle application into a Docker image as above and calls kubectl to run it on the cluster. This API might need to generate a Dockerfile look like above and call `docker build`.
Of course, we can manually build an application image and launch the job using the kubectl tool:
```bash
docker build -f some/Dockerfile -t myapp .
docker tag myapp me/myapp
docker push
kubectl ...
```
### Reading source code with woboq codebrowser
For developers who are interested in the C++ source code, you can build C++ source code into HTML pages using [Woboq codebrowser](https://github.com/woboq/woboq_codebrowser).
- The following command builds PaddlePaddle, generates HTML pages from C++ source code, and writes HTML pages into `$HOME/woboq_out` on the host:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh html
```
- You can open the generated HTML files in your Web browser. Or, if you want to run a Nginx container to serve them for a wider audience, you can run:
```
docker run -v $HOME/woboq_out:/usr/share/nginx/html -d -p 8080:80 nginx
```
## More Options
### Build Without Docker
Follow the *Dockerfile* in the paddlepaddle repo to set up your local dev environment and run:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build
```
### Additional Tasks
You can get the help menu for the build scripts by running with no options:
```bash
./paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh
or ./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh
```
 or, they might rely on a more sophisticated box (like with GPUs):
or, they might rely on a more sophisticated box (like with GPUs):
 A principle here is that source code lies on the development computer (host) so that editors like Eclipse can parse the source code to support auto-completion.
## Build With Docker
### Build Environments
The lastest pre-built build environment images are:
| Image | Tag |
| ----- | --- |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev-android |
### Start Build
```bash
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
cd Paddle
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh build
```
After the build finishes, you can get output `whl` package under
`build/python/dist`.
This command will download the most recent dev image from docker hub, start a container in the backend and then run the build script `/paddle/paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build` in the container.
The container mounts the source directory on the host into `/paddle`.
When it writes to `/paddle/build` in the container, it writes to `$PWD/build` on the host indeed.
### Build Options
Users can specify the following Docker build arguments with either "ON" or "OFF" value:
| Option | Default | Description |
| ------ | -------- | ----------- |
| `WITH_GPU` | OFF | Generates NVIDIA CUDA GPU code and relies on CUDA libraries. |
| `WITH_AVX` | OFF | Set to "ON" to enable AVX support. |
| `WITH_TESTING` | OFF | Build unit tests binaries. |
| `WITH_MKL` | ON | Build with [Intel® MKL](https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl) and [Intel® MKL-DNN](https://github.com/01org/mkl-dnn) support. |
| `WITH_GOLANG` | OFF | Build fault-tolerant parameter server written in go. |
| `WITH_SWIG_PY` | ON | Build with SWIG python API support. |
| `WITH_C_API` | OFF | Build capi libraries for inference. |
| `WITH_PYTHON` | ON | Build with python support. Turn this off if build is only for capi. |
| `WITH_STYLE_CHECK` | ON | Check the code style when building. |
| `PYTHON_ABI` | "" | Build for different python ABI support, can be cp27-cp27m or cp27-cp27mu |
| `RUN_TEST` | OFF | Run unit test immediently after the build. |
| `WITH_DOC` | OFF | Build docs after build binaries. |
| `WOBOQ` | OFF | Generate WOBOQ code viewer under `build/woboq_out` |
## Docker Images
You can get the latest PaddlePaddle docker images by
`docker pull paddlepaddle/paddle:
A principle here is that source code lies on the development computer (host) so that editors like Eclipse can parse the source code to support auto-completion.
## Build With Docker
### Build Environments
The lastest pre-built build environment images are:
| Image | Tag |
| ----- | --- |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev |
| paddlepaddle/paddle | latest-dev-android |
### Start Build
```bash
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
cd Paddle
./paddle/scripts/paddle_docker_build.sh build
```
After the build finishes, you can get output `whl` package under
`build/python/dist`.
This command will download the most recent dev image from docker hub, start a container in the backend and then run the build script `/paddle/paddle/scripts/paddle_build.sh build` in the container.
The container mounts the source directory on the host into `/paddle`.
When it writes to `/paddle/build` in the container, it writes to `$PWD/build` on the host indeed.
### Build Options
Users can specify the following Docker build arguments with either "ON" or "OFF" value:
| Option | Default | Description |
| ------ | -------- | ----------- |
| `WITH_GPU` | OFF | Generates NVIDIA CUDA GPU code and relies on CUDA libraries. |
| `WITH_AVX` | OFF | Set to "ON" to enable AVX support. |
| `WITH_TESTING` | OFF | Build unit tests binaries. |
| `WITH_MKL` | ON | Build with [Intel® MKL](https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl) and [Intel® MKL-DNN](https://github.com/01org/mkl-dnn) support. |
| `WITH_GOLANG` | OFF | Build fault-tolerant parameter server written in go. |
| `WITH_SWIG_PY` | ON | Build with SWIG python API support. |
| `WITH_C_API` | OFF | Build capi libraries for inference. |
| `WITH_PYTHON` | ON | Build with python support. Turn this off if build is only for capi. |
| `WITH_STYLE_CHECK` | ON | Check the code style when building. |
| `PYTHON_ABI` | "" | Build for different python ABI support, can be cp27-cp27m or cp27-cp27mu |
| `RUN_TEST` | OFF | Run unit test immediently after the build. |
| `WITH_DOC` | OFF | Build docs after build binaries. |
| `WOBOQ` | OFF | Generate WOBOQ code viewer under `build/woboq_out` |
## Docker Images
You can get the latest PaddlePaddle docker images by
`docker pull paddlepaddle/paddle: