# Design Doc: Asynchronous Update With Distributed Training
## Background
For the typical synchronous distributed training, some significant steps are as follows:
1. A trainer process will compute the gradients and **send** them to the parameter server (PS) nodes.
1. After the PS node received gradients came from all the Trainers, It will aggregate the
gradient variables for the same parameter into one gradient variable and then apply the aggregated
gradient to the respective parameter, finally using an optimize algorithms(SGD, Monument...)
to update the parameters.
1. The Trainer would wait for the PS finished the optimize stage, and GET the parameters from PS,
so all the Trainers would get the same parameters.
In Synchronous Distributed Training, there is a **barrier** on each PS to wait until all trainers processes
have completed running current mini-batch. After that, all trainers can continue to run the next
mini-batch. So, we can find that the overall performance of Synchronous Distributed Training depends
on the slowest node.
In Asynchronous Distributed Training, we don't need to wait for a global mini-bach, the optimizer on
the PS will run immediately when the gradient is uploaded to the PS from one trainer. This mode would
train such models that achieve scaling, better throughput. In this design doc, we will introduce how to
implement the Asynchronous Distributed Training base on PaddlePaddle Fluid.
## Design
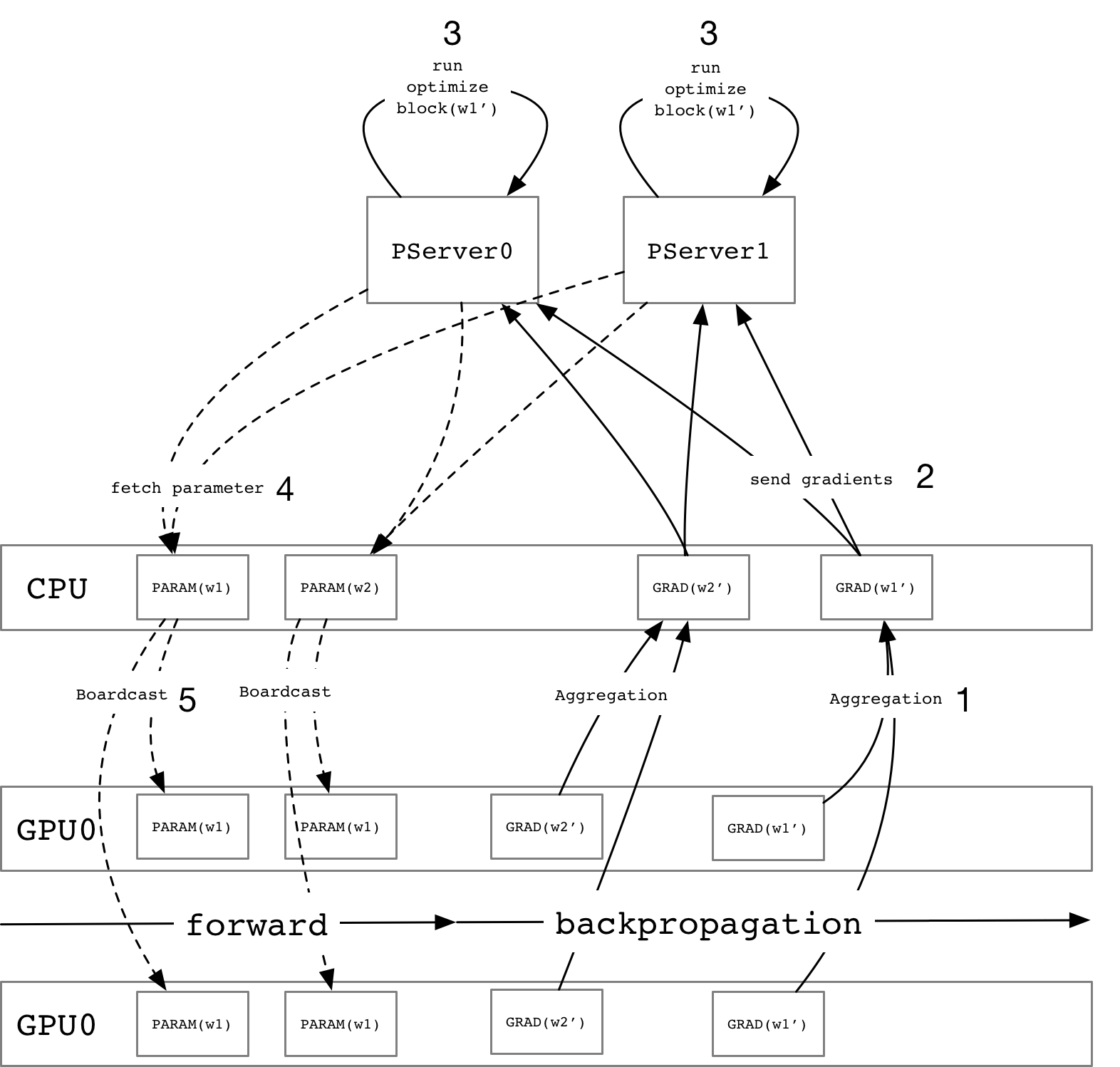 As the figure above, we describe a global view of the asynchronous update process and use
the parameter `w1` as an example to introduce the steps:
1. For each gradient variables, they may distribute on different GPU card and aggregate
them while they are all calculated.
1. Split the gradient variable into multiple blocks according to the number of PS
instances and then send them.
1. PS would run an `Optimize Block` using a specified optimize algorithm to update
the specified parameter.
1. The trainer will fetch the latest parameter from PS before running forward Op which depends
on the specified parameter.
1. Broadcast the received variable into multiple GPU cards and continue to run the next
mini-batch.
### Trainer
- For the multiple devices distributed training, we need to aggregate the gradient
variables which placed on different devices firstly and then schedule a `SendVars` Operator to
send the gradient variables to the multiple PS instances.
- Schedule `FetchVars` operator to fetch the latest parameter from PS before running
the forward ops.
- There could be a large number of gradient variables to be sent, so we need to use another
thread pool(IO Threadpool) whose a number of the schedulable threads is larger than the
computing thread pool to avoid competitive the thread resources with computing.
### Parameter Server
As the figure above, we describe a global view of the asynchronous update process and use
the parameter `w1` as an example to introduce the steps:
1. For each gradient variables, they may distribute on different GPU card and aggregate
them while they are all calculated.
1. Split the gradient variable into multiple blocks according to the number of PS
instances and then send them.
1. PS would run an `Optimize Block` using a specified optimize algorithm to update
the specified parameter.
1. The trainer will fetch the latest parameter from PS before running forward Op which depends
on the specified parameter.
1. Broadcast the received variable into multiple GPU cards and continue to run the next
mini-batch.
### Trainer
- For the multiple devices distributed training, we need to aggregate the gradient
variables which placed on different devices firstly and then schedule a `SendVars` Operator to
send the gradient variables to the multiple PS instances.
- Schedule `FetchVars` operator to fetch the latest parameter from PS before running
the forward ops.
- There could be a large number of gradient variables to be sent, so we need to use another
thread pool(IO Threadpool) whose a number of the schedulable threads is larger than the
computing thread pool to avoid competitive the thread resources with computing.
### Parameter Server
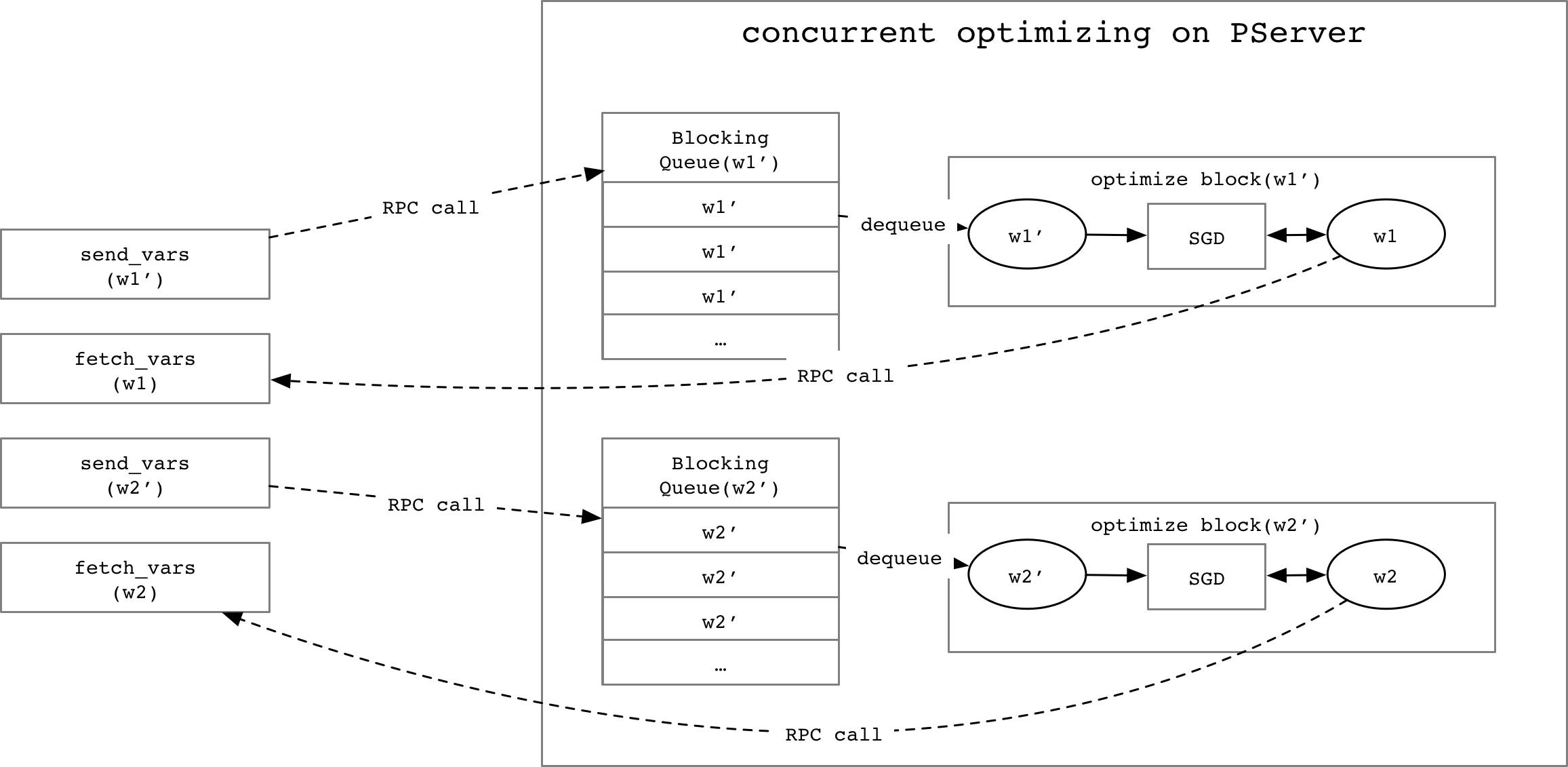 - There should be multiple trainer instances want to optimize the same parameter at
the same time, to avoid the racing, we need one `BlockingQueue` for each gradient
variable to process them one by one.
- We need a `Map` structure to map a gradient variable name to the `OptimizeBlock` which
can optimize the respective parameter.
- There should be multiple trainer instances want to optimize the same parameter at
the same time, to avoid the racing, we need one `BlockingQueue` for each gradient
variable to process them one by one.
- We need a `Map` structure to map a gradient variable name to the `OptimizeBlock` which
can optimize the respective parameter.
 As the figure above, we describe a global view of the asynchronous update process and use
the parameter `w1` as an example to introduce the steps:
1. For each gradient variables, they may distribute on different GPU card and aggregate
them while they are all calculated.
1. Split the gradient variable into multiple blocks according to the number of PS
instances and then send them.
1. PS would run an `Optimize Block` using a specified optimize algorithm to update
the specified parameter.
1. The trainer will fetch the latest parameter from PS before running forward Op which depends
on the specified parameter.
1. Broadcast the received variable into multiple GPU cards and continue to run the next
mini-batch.
### Trainer
- For the multiple devices distributed training, we need to aggregate the gradient
variables which placed on different devices firstly and then schedule a `SendVars` Operator to
send the gradient variables to the multiple PS instances.
- Schedule `FetchVars` operator to fetch the latest parameter from PS before running
the forward ops.
- There could be a large number of gradient variables to be sent, so we need to use another
thread pool(IO Threadpool) whose a number of the schedulable threads is larger than the
computing thread pool to avoid competitive the thread resources with computing.
### Parameter Server
As the figure above, we describe a global view of the asynchronous update process and use
the parameter `w1` as an example to introduce the steps:
1. For each gradient variables, they may distribute on different GPU card and aggregate
them while they are all calculated.
1. Split the gradient variable into multiple blocks according to the number of PS
instances and then send them.
1. PS would run an `Optimize Block` using a specified optimize algorithm to update
the specified parameter.
1. The trainer will fetch the latest parameter from PS before running forward Op which depends
on the specified parameter.
1. Broadcast the received variable into multiple GPU cards and continue to run the next
mini-batch.
### Trainer
- For the multiple devices distributed training, we need to aggregate the gradient
variables which placed on different devices firstly and then schedule a `SendVars` Operator to
send the gradient variables to the multiple PS instances.
- Schedule `FetchVars` operator to fetch the latest parameter from PS before running
the forward ops.
- There could be a large number of gradient variables to be sent, so we need to use another
thread pool(IO Threadpool) whose a number of the schedulable threads is larger than the
computing thread pool to avoid competitive the thread resources with computing.
### Parameter Server
 - There should be multiple trainer instances want to optimize the same parameter at
the same time, to avoid the racing, we need one `BlockingQueue` for each gradient
variable to process them one by one.
- We need a `Map` structure to map a gradient variable name to the `OptimizeBlock` which
can optimize the respective parameter.
- There should be multiple trainer instances want to optimize the same parameter at
the same time, to avoid the racing, we need one `BlockingQueue` for each gradient
variable to process them one by one.
- We need a `Map` structure to map a gradient variable name to the `OptimizeBlock` which
can optimize the respective parameter.