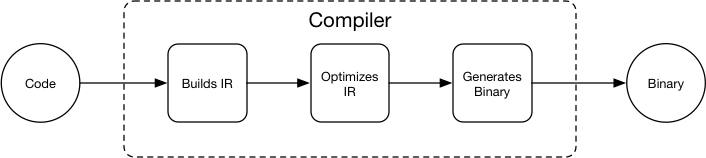
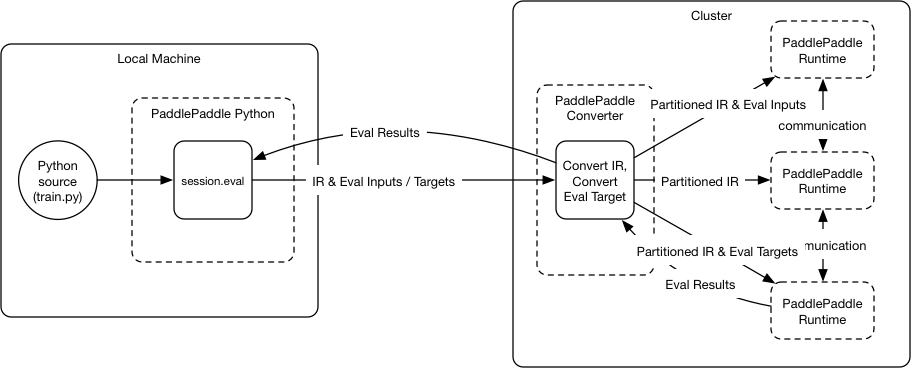
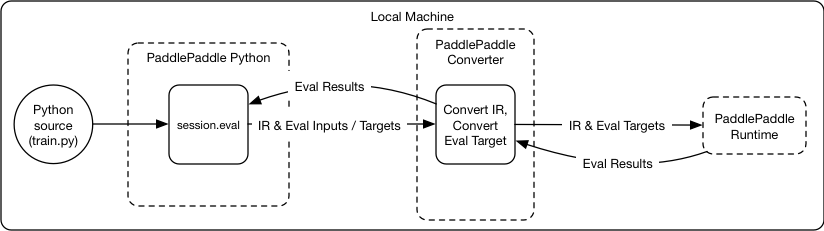
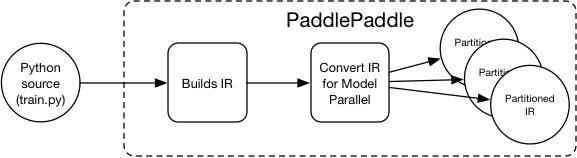
Merge branch 'develop' into softmax_with_cross_entropy_op
Showing
benchmark/paddle/image/vgg.py
0 → 100644
文件已添加
15.5 KB
文件已移动
文件已添加
46.5 KB
文件已移动
文件已添加
28.3 KB
文件已添加
19.7 KB
doc/howto/dev/new_op_en.md
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/lstm_unit_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/lstm_unit_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/lstm_unit_op.h
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/multiplex_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/multiplex_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/multiplex_op.h
0 → 100644